Study of Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study of Hydrophilic Nanofibrous Membranes
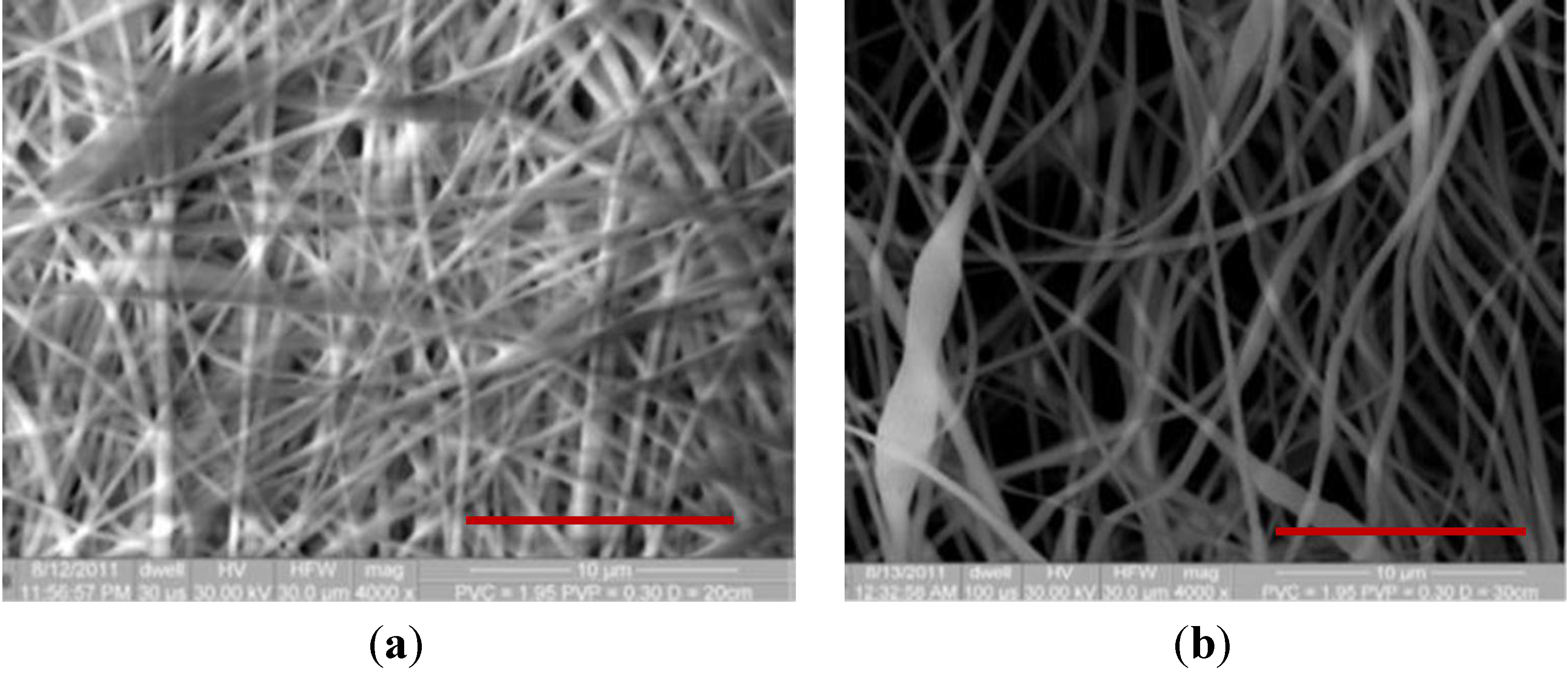
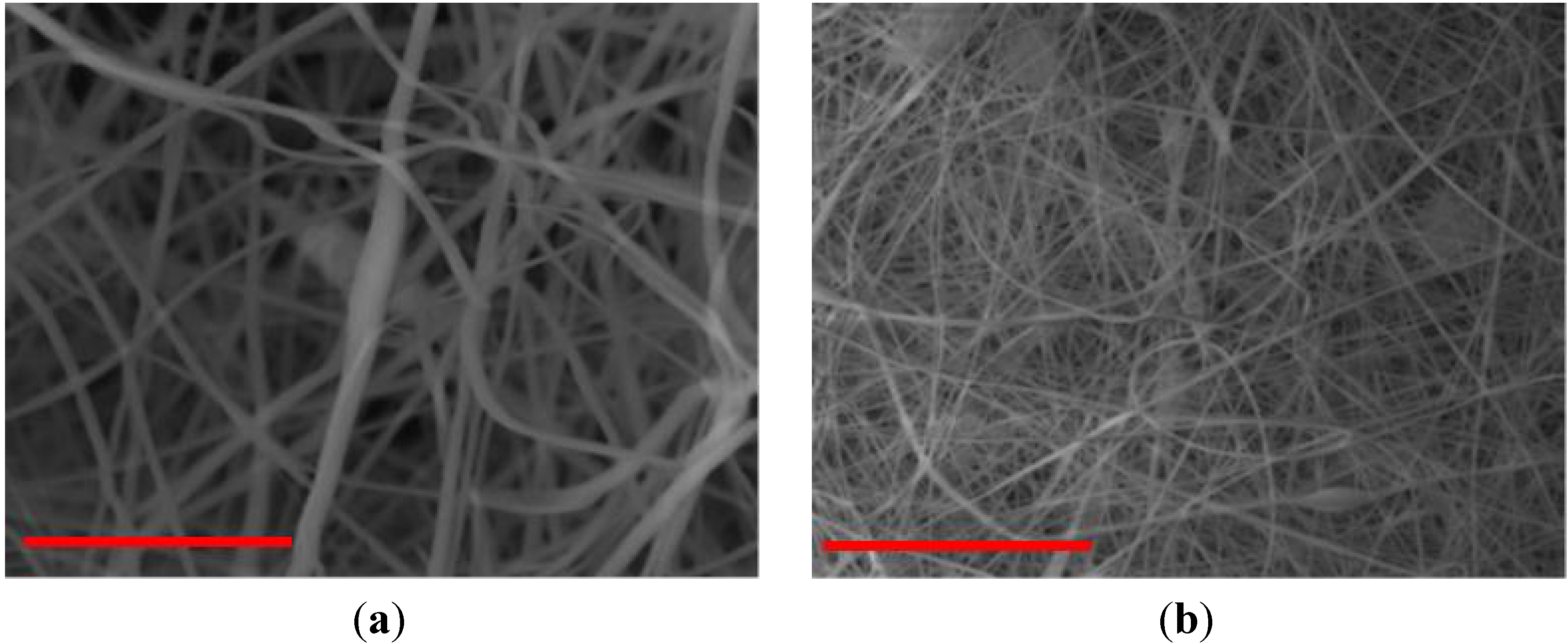
| PVC/PVP Fibers | Water Contact Angle (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| D = 20 cm | D = 25 cm | D = 30 cm | |
| Only PVC Fibers | 136.02 | 135.76 | 135.70 |
| Only PVP Fibers (water soluble) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| PVC + 2 wt % PVP Fibers | 127.14 | 125.26 | 124.23 |
| PVC + 3 wt % PVP Fibers | 118.35 | 116.08 | 105.85 |
| PVC + 4 wt % PVP Fibers | 103.03 | 70.95 | 58.51 |
| PVC + 5 wt % PVP Fibers | 21.30 | 20.30 | 16.12 |
| Electrospun Fibers | Water Contact Angle (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm | 25 cm | 30 cm | |
| PVC + 2 wt % PVP Fibers |  | 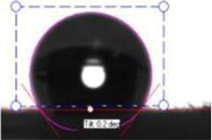 | 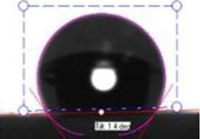 |
| PVC + 3 wt % PVP Fibers |  |  |  |
| PVC + 4 wt % PVP Fibers |  |  |  |
| PVC + 5 wt % PVP Fibers |  |  |  |
2.2. Coagulation-Filtration Experiments
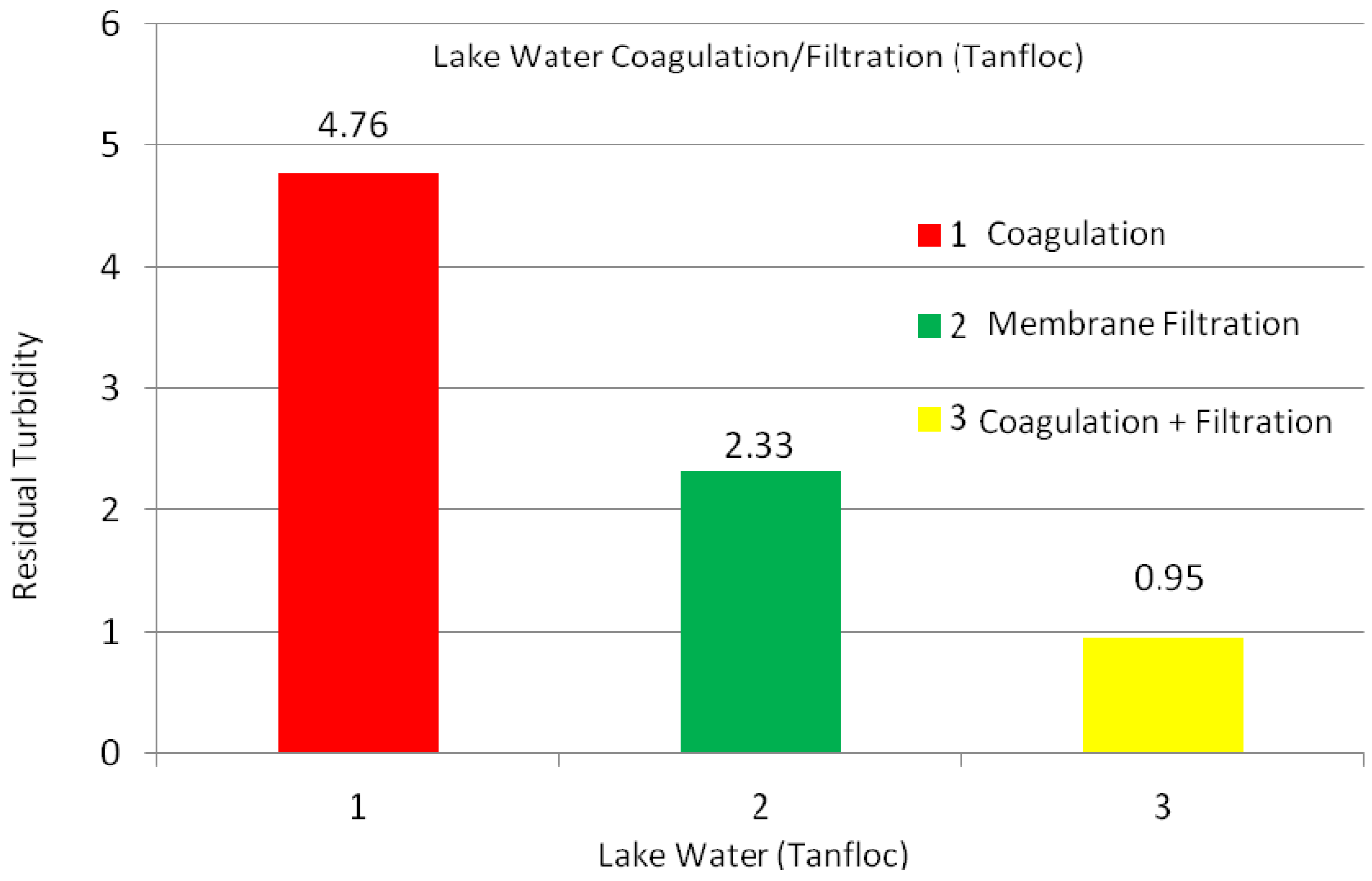
2.2.1. Lake Water
| Experiments | No Coagulation | Coagulation Dosage (mg/L) (1 h) | Coagulation Dosage (mg/L) (1 day) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 1 h | 24 h | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 21.0 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 6.4 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| pH | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | ||
| TDS (ppm) | 480 | 472 | 480 | 460 | 464 | 458 | 472 | 480 | 460 | 464 | 458 | ||
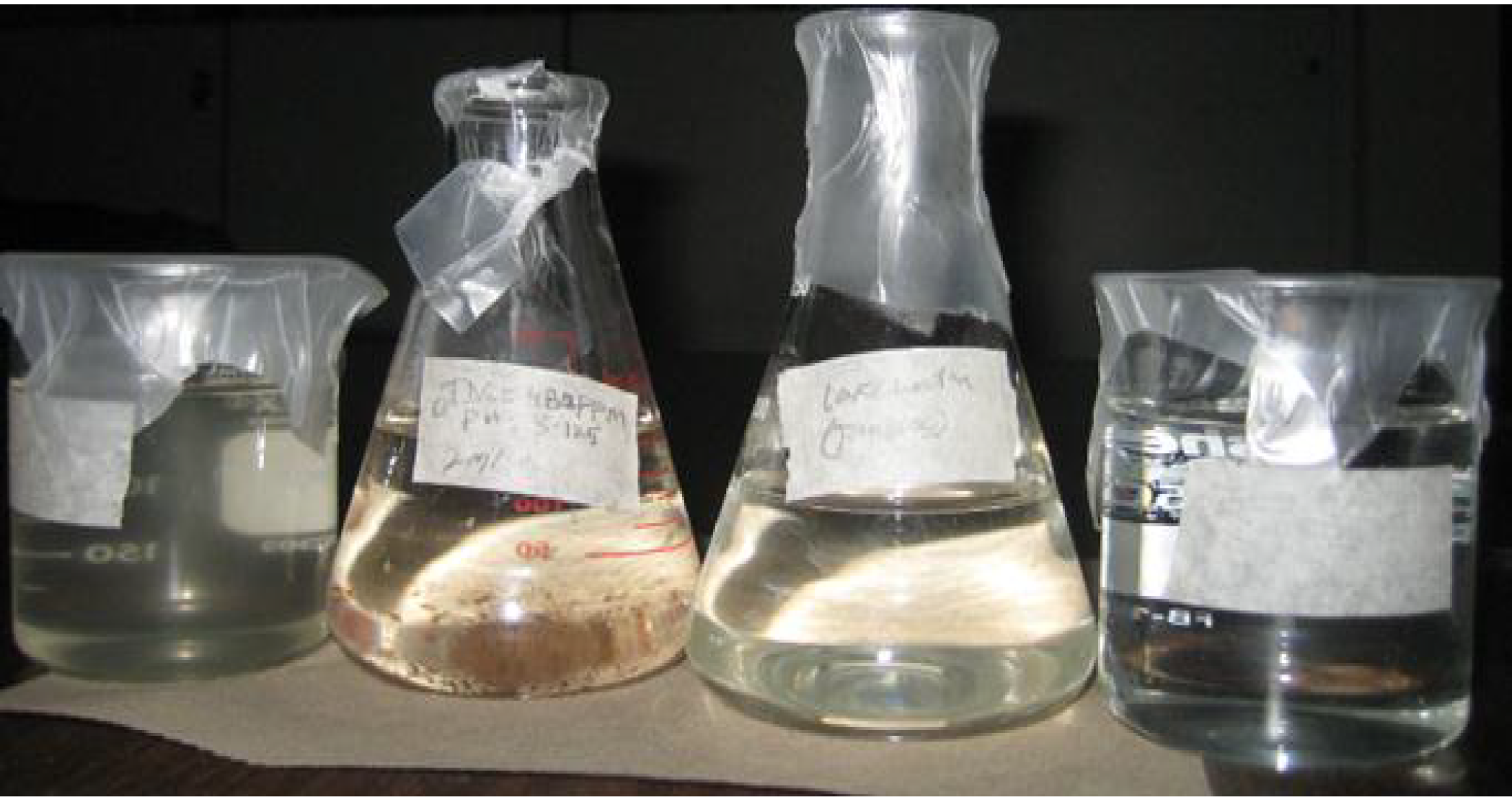

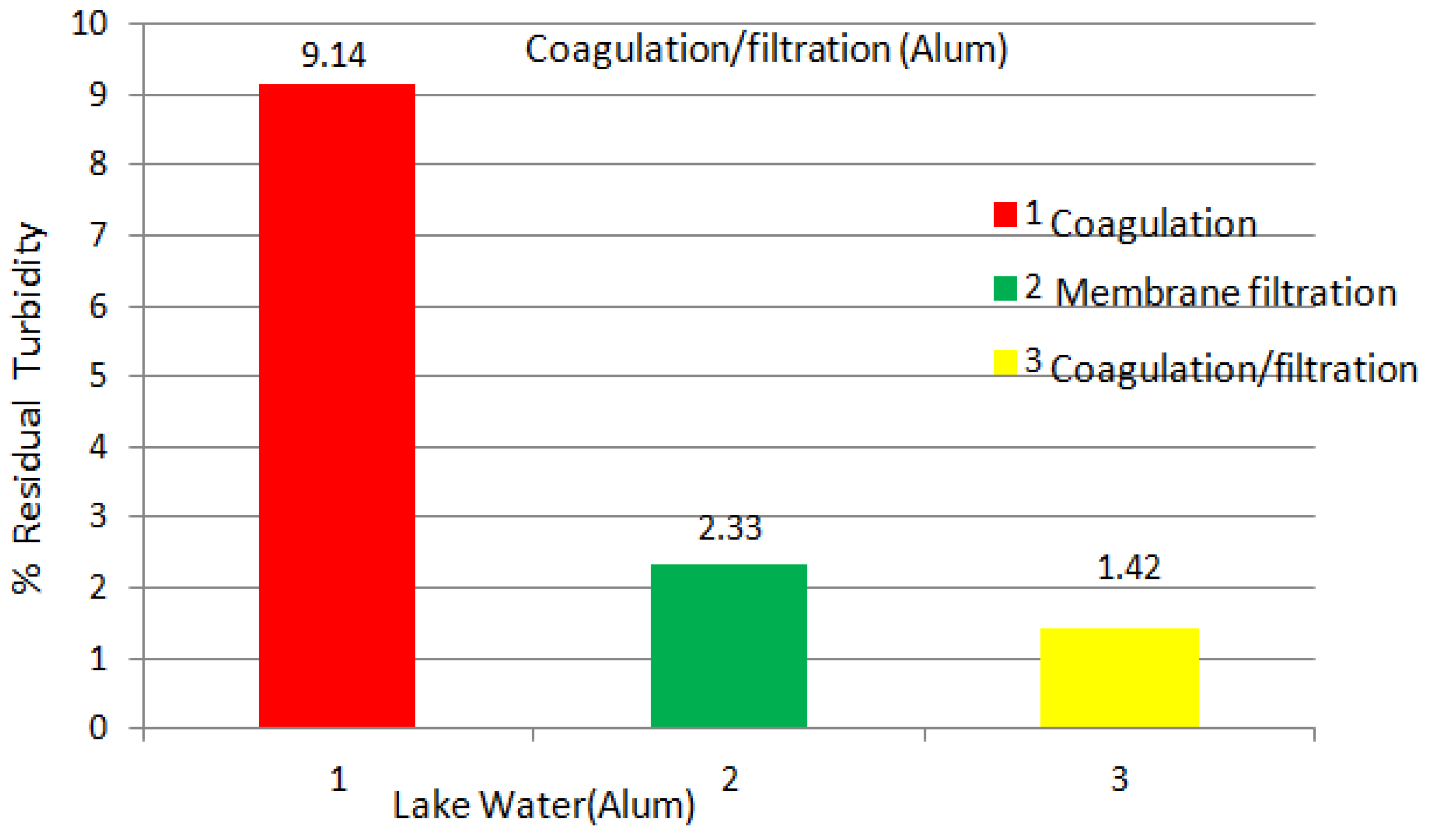
| Experiments | No Coagulation | Coagulation Dosage (mg/L) (1 h) | Coagulation Dosage (mg/L) (1 day) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 1 h | 24 h | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 21.0 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| pH | 8.1 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.5 | ||
| TDS (ppm) | 463 | 467 | 465 | 472 | 470 | 472 | 467 | 465 | 472 | 470 | 472 | ||
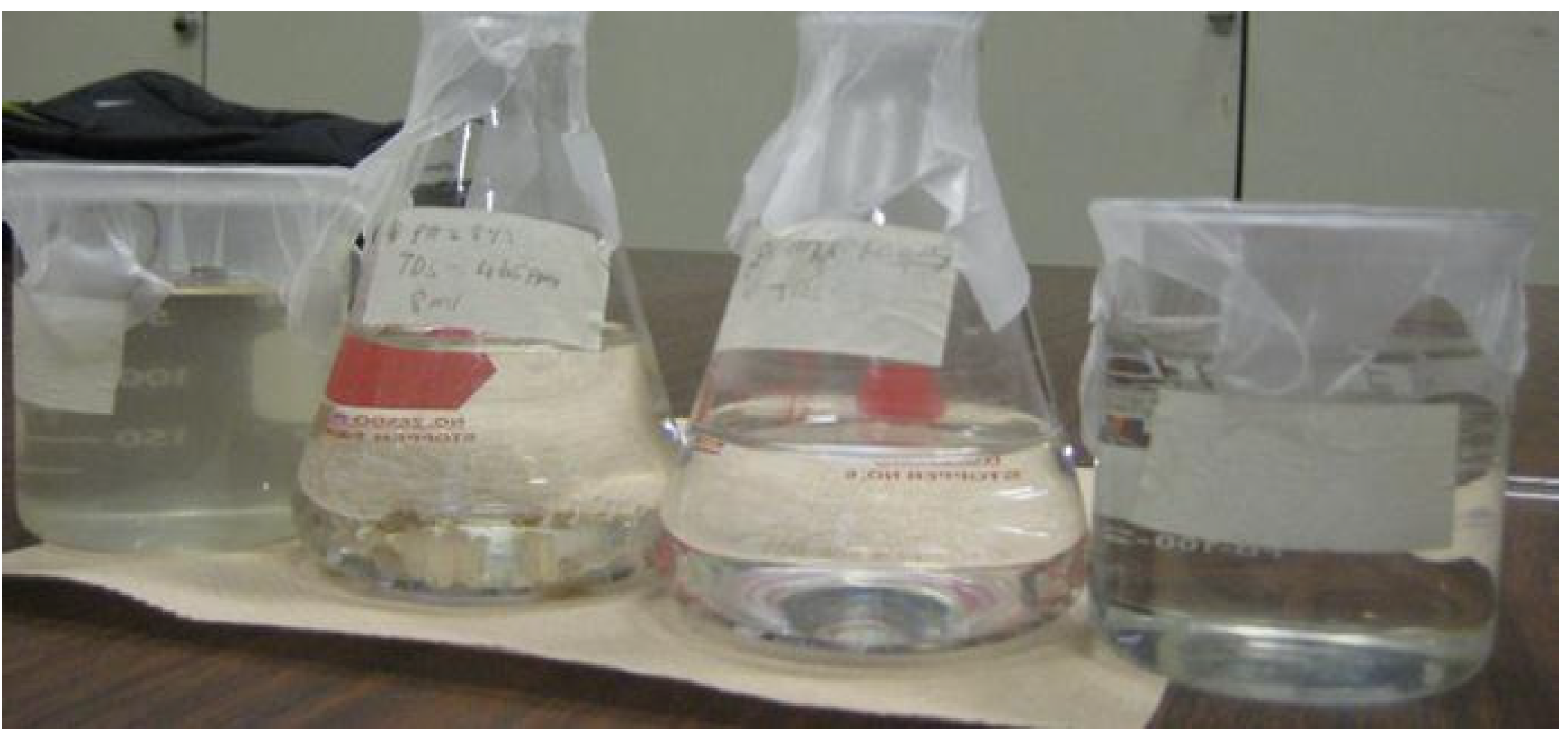

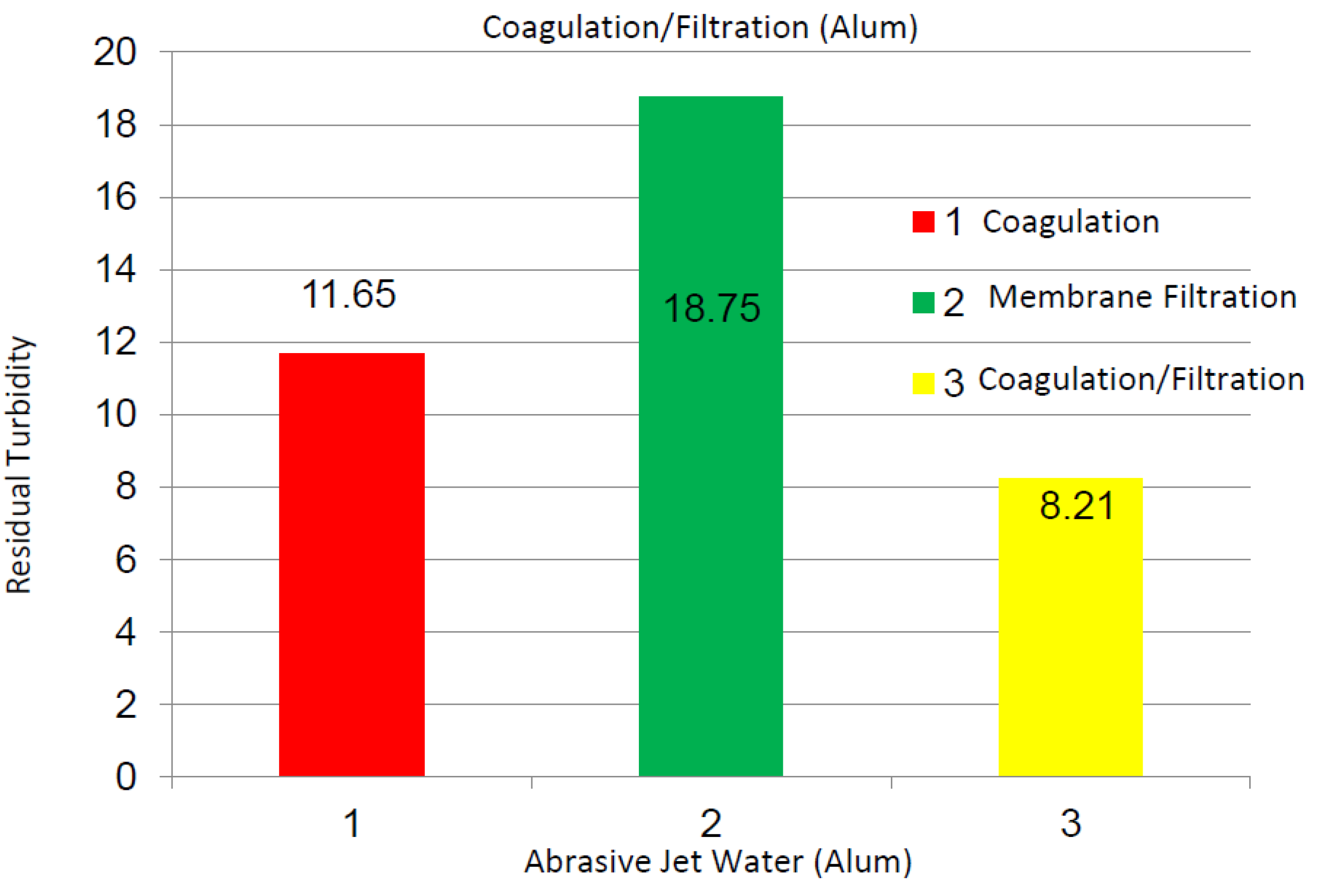
2.2.2. Abrasive Jet Water

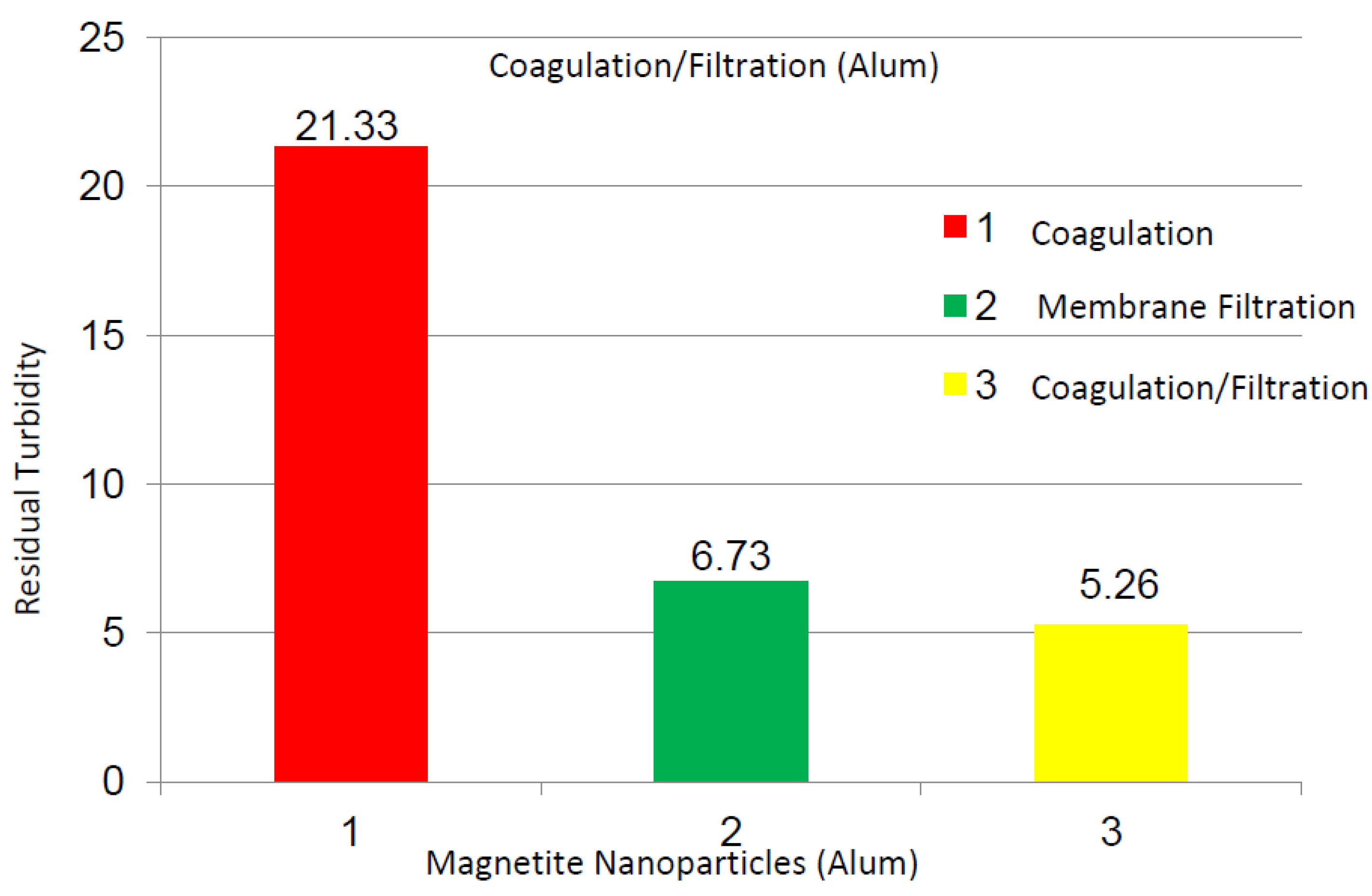
2.2.3. Magnetite Nanoparticles Suspensions
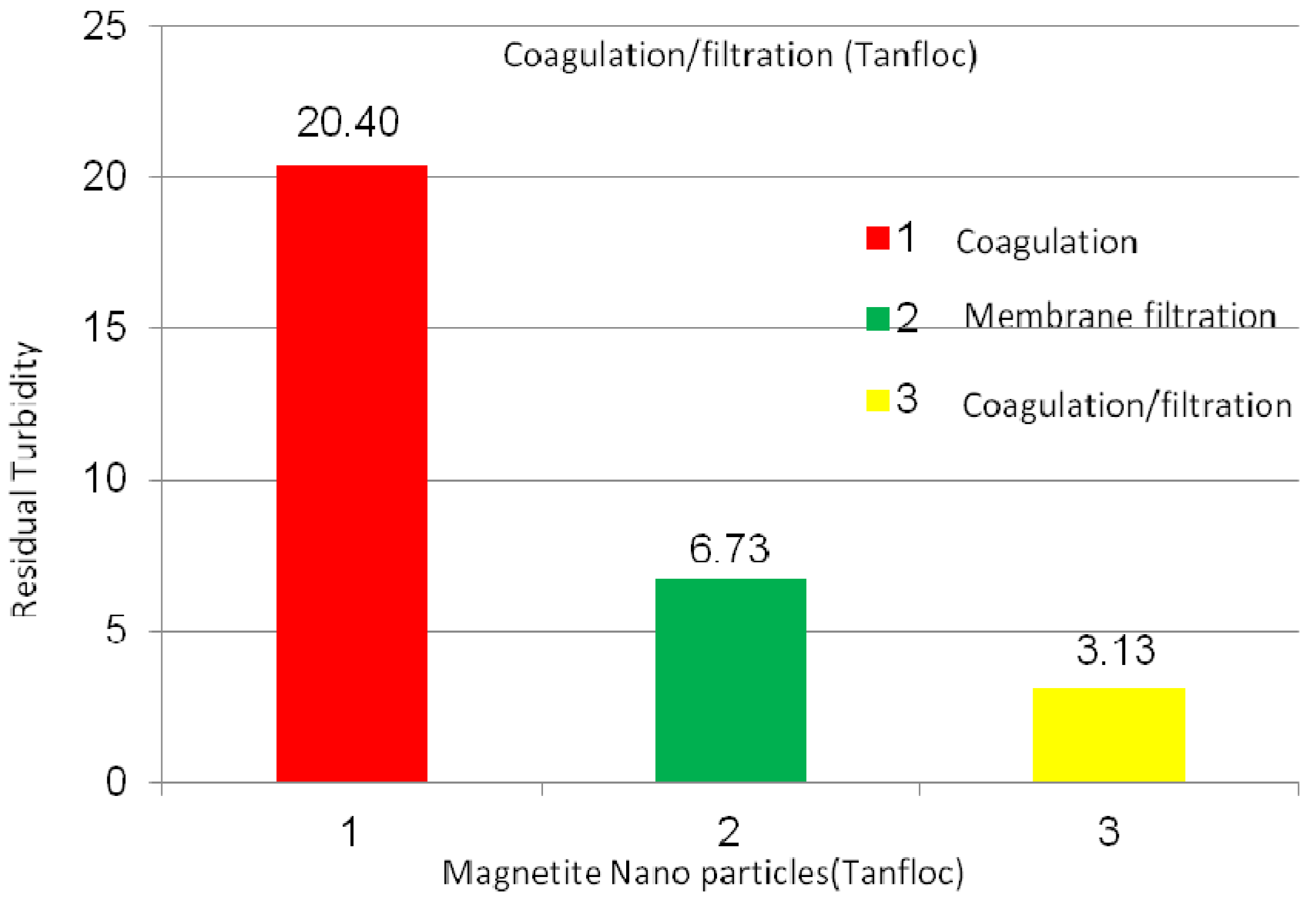
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
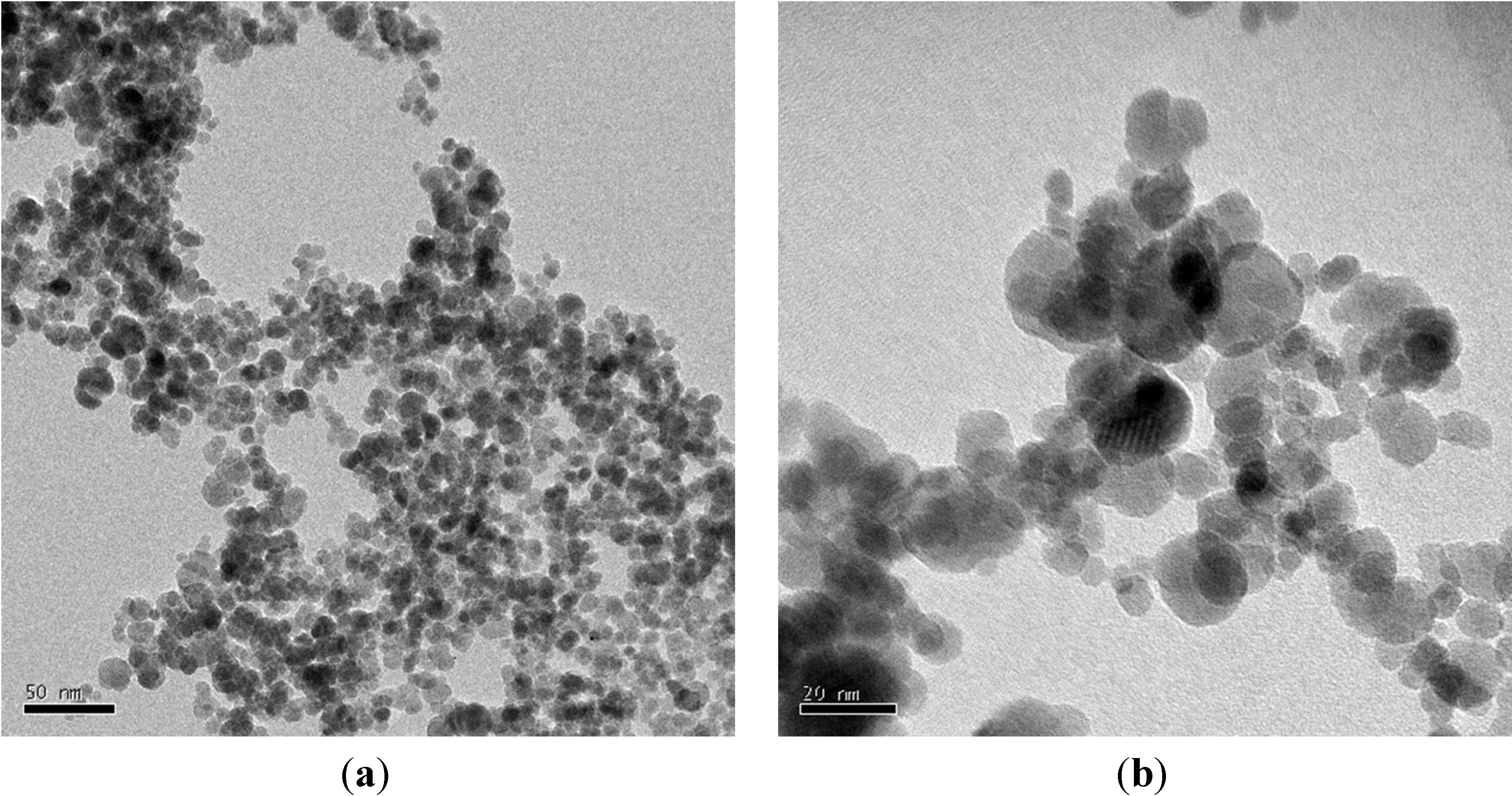
3.2. Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wendorff, J.H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Electrospinning: Materials, Processing, and Applications; Wiley: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Asmatulu, R.; Muppalla, H.; Veisi, Z.; Khan, W.S.; Ceyla, M.; Asaduzzaman, A.; Nuraje, N. Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles via Highly Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes. In Proceedings of the SAMPE Fall Technical Conference, Wichita, KS, USA, 21–24 October 2013; p. 14.
- Ayse, A.A. Improved Filtration Membranes through Self-Organizing Amphiphilic Comb Copolymers. Ph.D. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Muppalla, H. Highly Hydrophilic Electrospun Fibers for the Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Particles Treated with Coagulants. Master Thesis, Wichita State University, Wichita, KS, USA, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, K.L.; Lee, K.-W. Polymer Surfaces and Interfaces: Characterization, Modification and Application; VSP BV: Utrecht, the Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Abdala, A.A.; Macosko, C.W. Graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6515–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakur, S. Surface Modification of Electrospun Poly (Vinyldene Flouride) Nanofibrous Microfiltration Membrane. Master Thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.S.; El-Tabey, M.M.; Asmatulu, R. Electrical and thermal characterization of electrospun PVP nanocomposite fibers. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Department of the Army. Engineering and Design: Precipitation/Coagulation/Flocculation; Report No. EM 1110-1-4012; Department of the Army: Washington, DC, USA, 15 November 2001.
- Ghaly, A.E.; Snow, A.; Faber, B.E. Effective coagulation technology for treatment of grease filter washwater. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystyna, K.; Mariola, R.; Michal, B.; Anna, K. Water treatment using hybrid method of coagulation and low-pressure membrane filtration. Environ. Protect. Eng. 2009, 35, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Yueqi, Z. Study on Coagulation–Microfiltration Combination Process for Treating Luan River Water. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy and Environmental Technology, Guilin, Guangxi, China, 16–18 October 2009; Volume 2, pp. 767–770.
- Nuraje, N.; Khan, W.S.; Ceylan, M.; Lie, Y.; Asmatulu, R. Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Ceylan, M.; Nuraje, N. Study of superhydrophobic electrospun nanocomposite fibers for energy systems. Langmuir 2011, 27, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuraje, N.; Asmatulu, R.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F. Mechanically durable and permanent anti-fog films via layer-by-layer approach. Langmuir 2011, 27, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Yoon, R.H. Effects of Surface Forces on Dewatering of Fine Particles. In Separation Technologies for Minerals, Coal and Earth Resources; Young, C., Luttrell, G.H., Eds.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration (SME): Englewood, CO, USA, 2012; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Rushton, A.; Ward, A.S.; Holdich, R.G. Solid-Liquid Filtration and Separation Technology; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.S.; Asmatulu, R.; Ceylan, M.; Jabbarnia, A. Recent progress on conventional and non-conventional electrospinning processes. Fibers Polym. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ziabari, M.; Mottaghitalab, V.; Haghi, A.K. Application of direct tracking method for measuring electrospun nanofiber diameter. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R. Removal of moisture from the ultrafine particles using both high centrifugal force and air pressure. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R. Improving the dewetability characteristics of hydrophobic fine particles by air bubble entrapments. Powder Technol. 2008, 186, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Asmatulu, R.; Muppalla, H.; Veisi, Z.; Khan, W.S.; Asaduzzaman, A.; Nuraje, N. Study of Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles. Membranes 2013, 3, 375-388. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040375
Asmatulu R, Muppalla H, Veisi Z, Khan WS, Asaduzzaman A, Nuraje N. Study of Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles. Membranes. 2013; 3(4):375-388. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040375
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsmatulu, Ramazan, Harish Muppalla, Zeinab Veisi, Waseem S. Khan, Abu Asaduzzaman, and Nurxat Nuraje. 2013. "Study of Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles" Membranes 3, no. 4: 375-388. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040375
APA StyleAsmatulu, R., Muppalla, H., Veisi, Z., Khan, W. S., Asaduzzaman, A., & Nuraje, N. (2013). Study of Hydrophilic Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Filtration of Micro and Nanosize Suspended Particles. Membranes, 3(4), 375-388. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040375





