NMR and Electrochemical Investigation of the Transport Properties of Methanol and Water in Nafion and Clay-Nanocomposites Membranes for DMFCs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Uptake and Swelling Properties of the Nafion and Nanocomposites Membranes
| Membranes | Uptake (wt.%) 4M solution | Uptake (wt.%) 2M solution | Uptake (wt.%) pure H2O |
|---|---|---|---|
| filler-free Nafion | 34 | 28 | 24 |
| Lap/Nafion | 60 | 46 | 30 |
| Swy/Nafion | 60 | 56 | 45 |
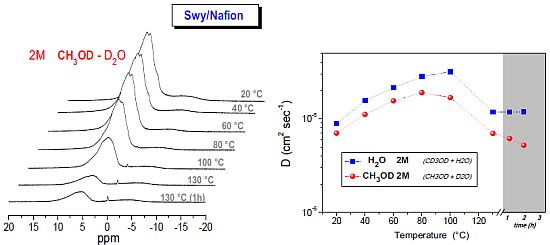
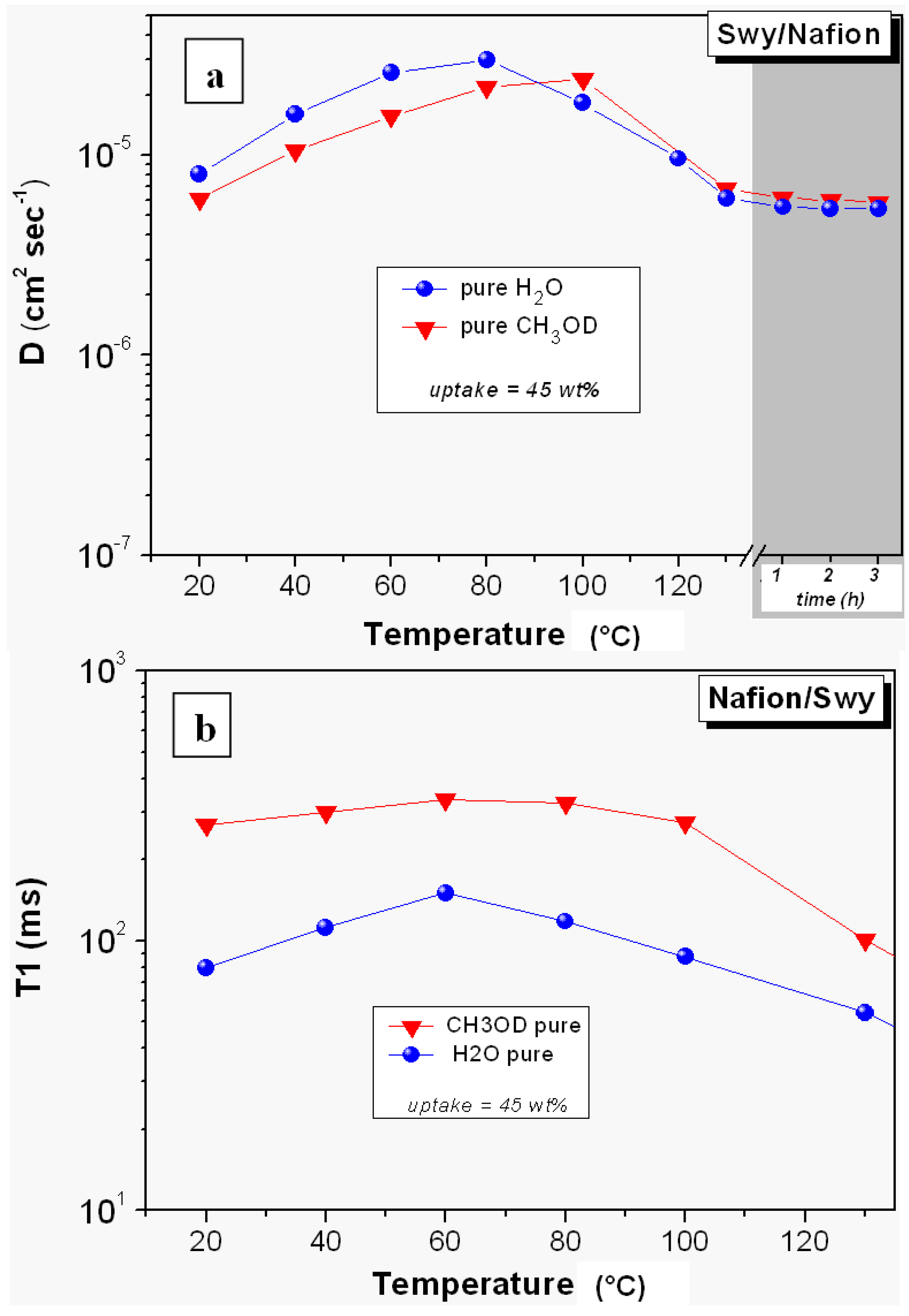
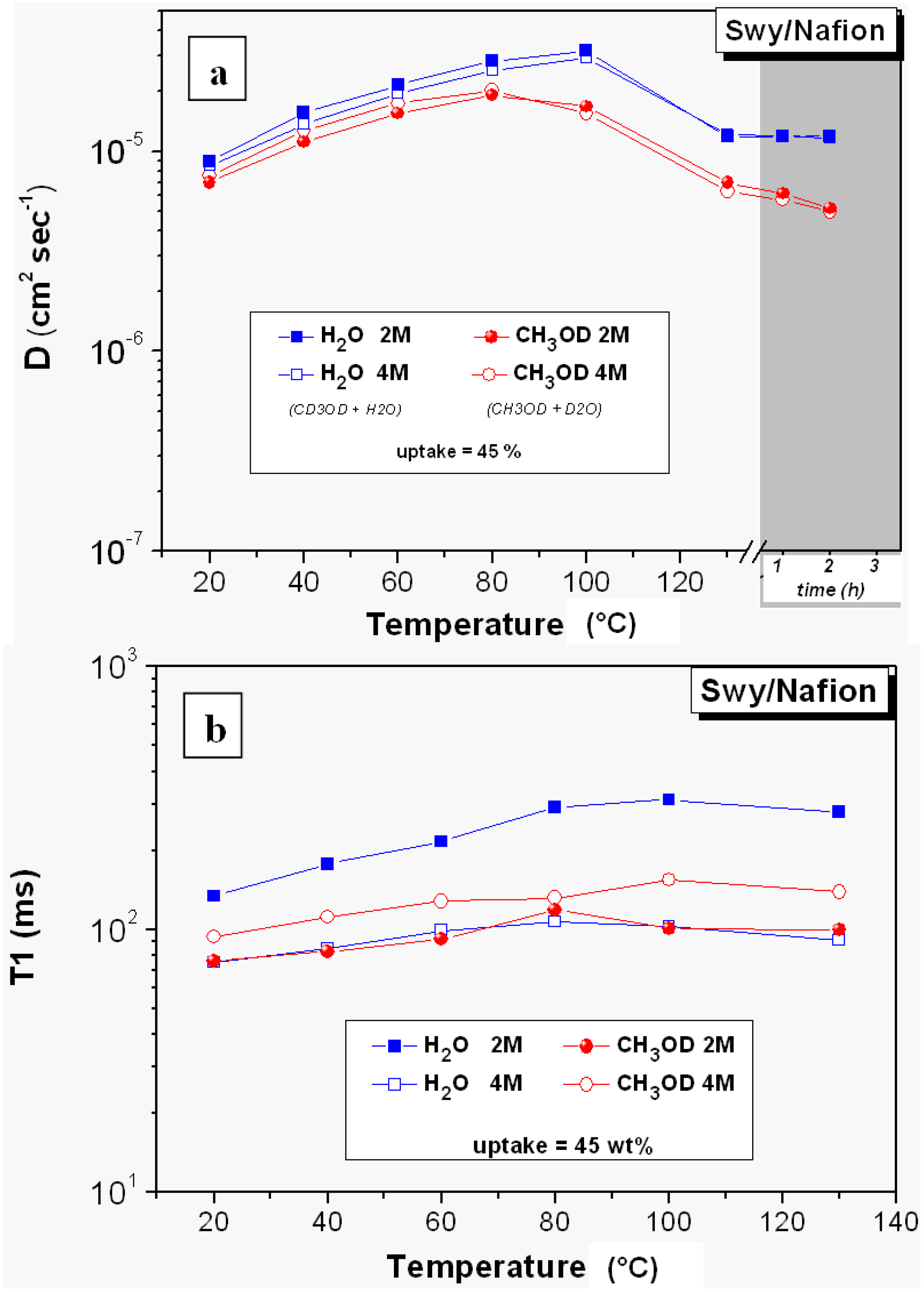
2.2. 1H-NMR Study: D, T1 and Spectra Lineshapes
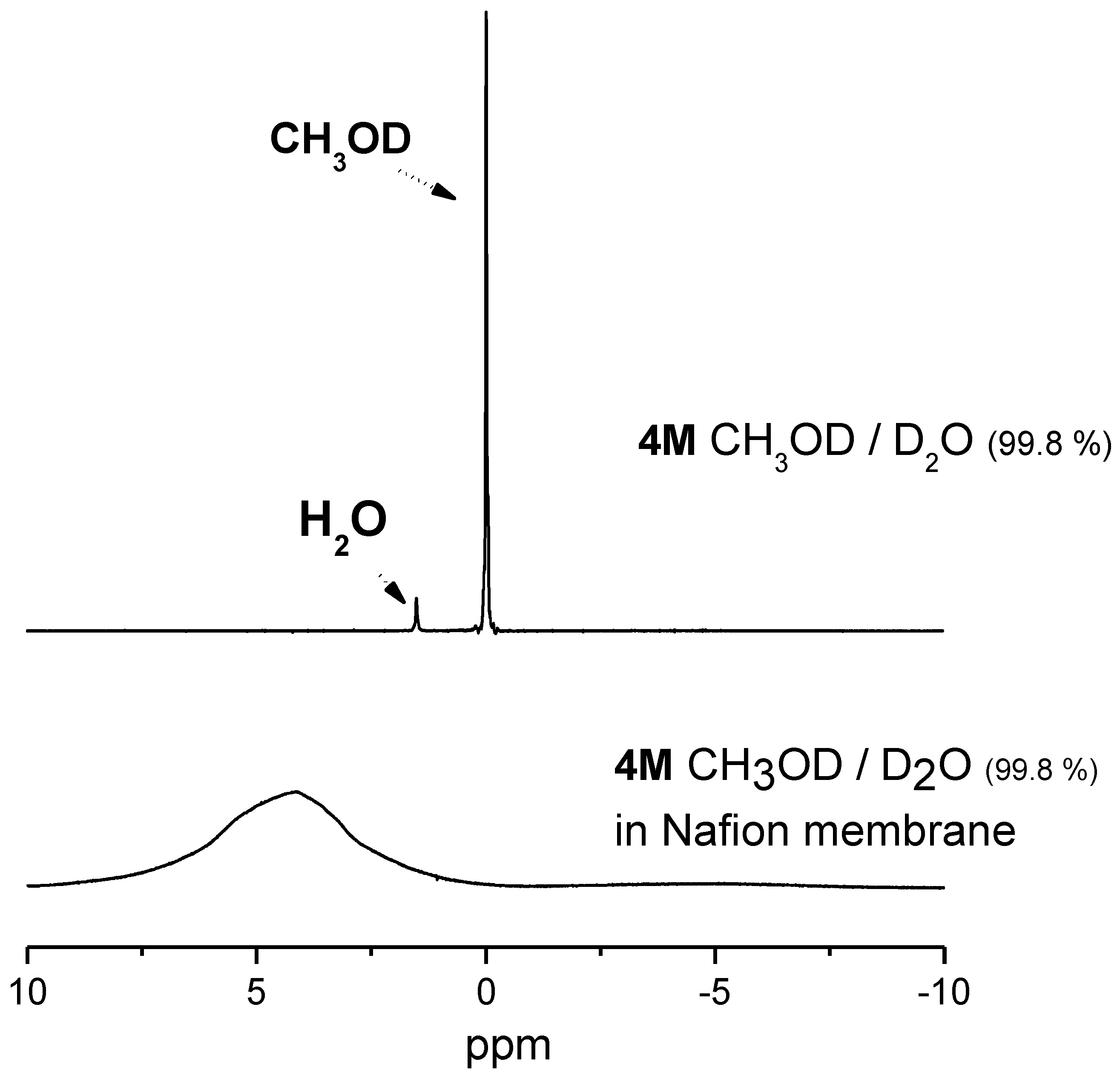
| solvents | concentration |
|---|---|
| CH3OD | pure |
| H2O | pure |
| CH3OD/D2O | 2M |
| CD 3OD/H2O | 2M |
| CH3OD/D2O | 4M |
| CD 3OD/H2O | 4M |

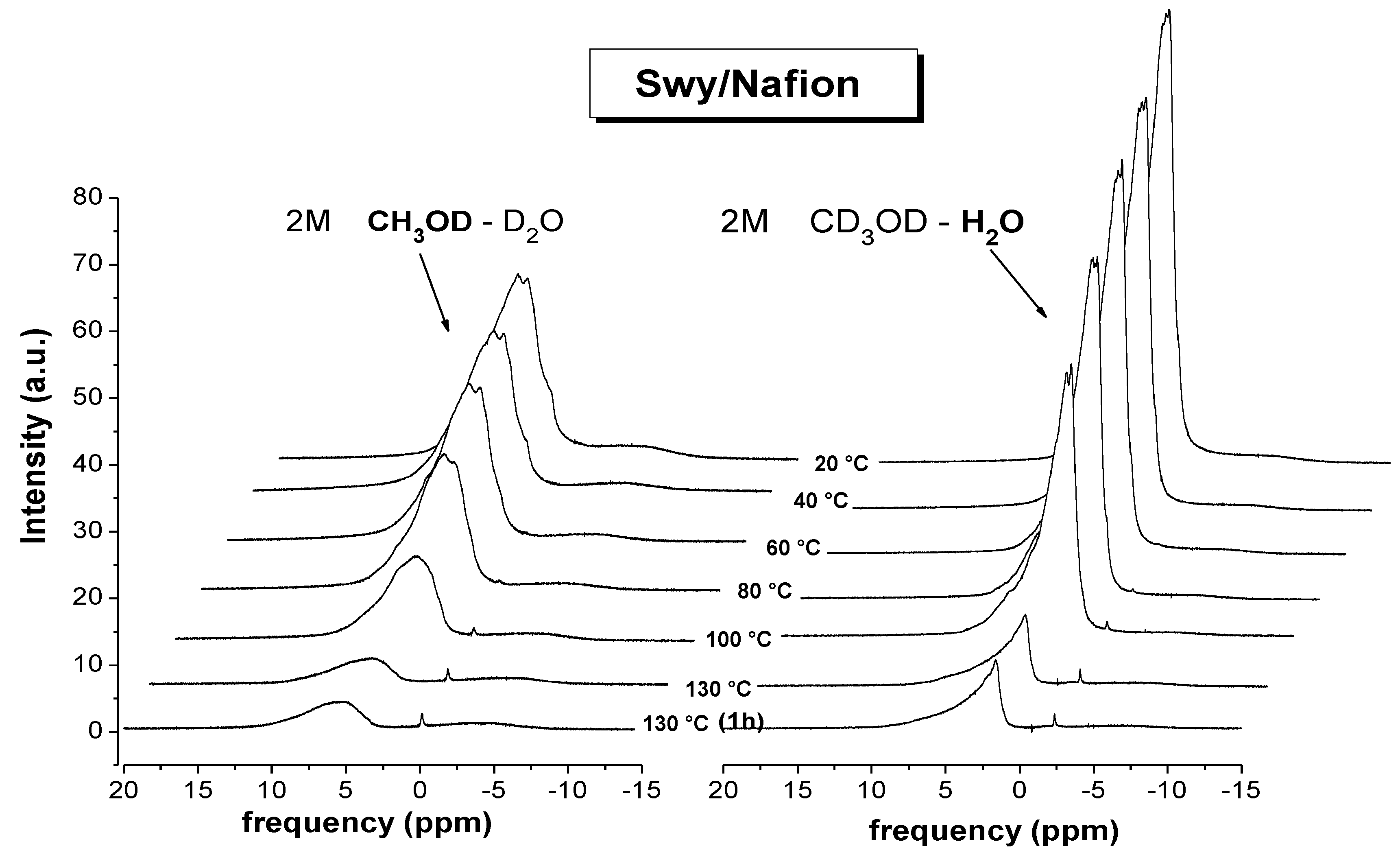
- (1)
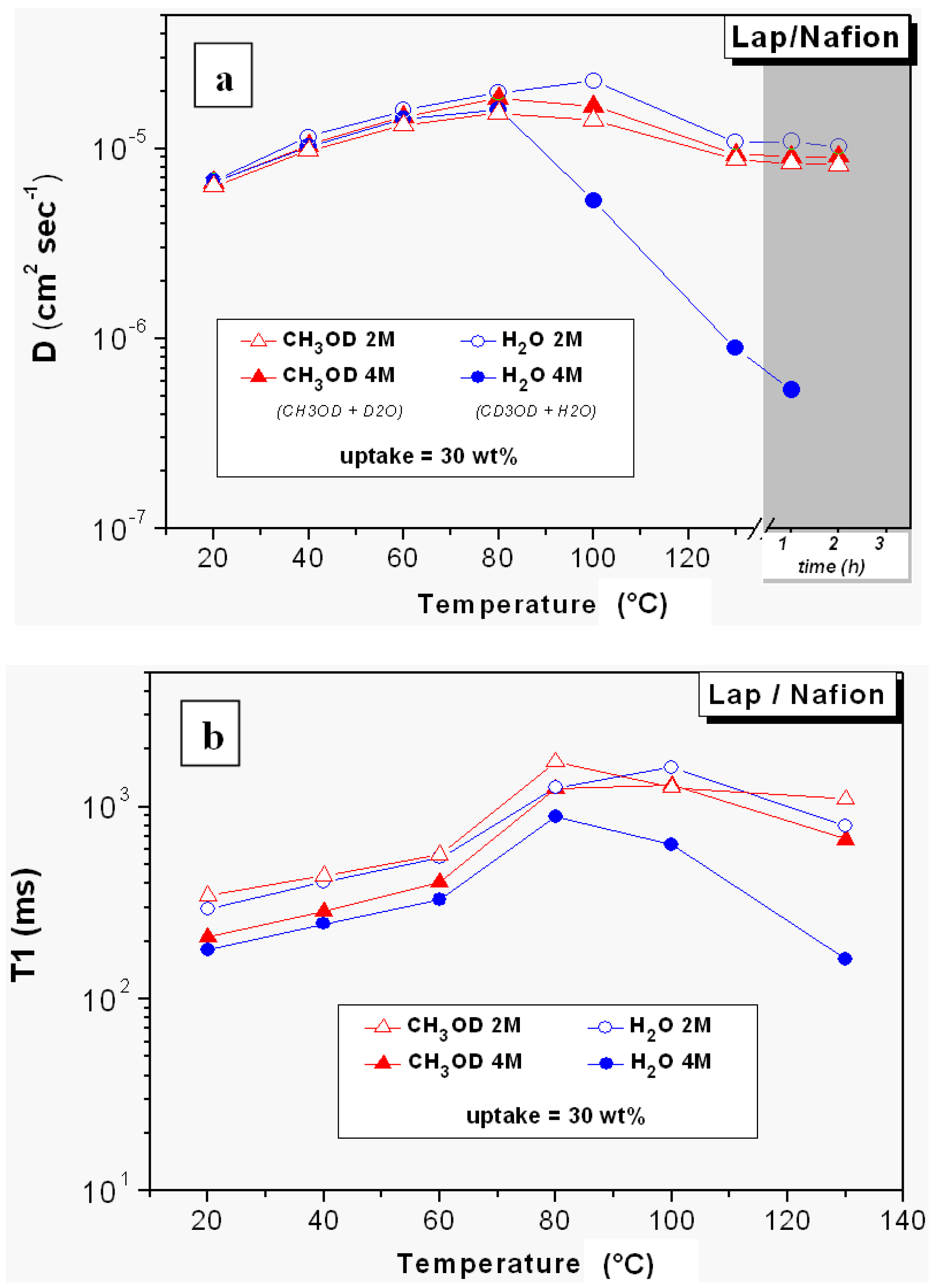
- The relaxation times of Lap-composite are higher over the whole temperature range, which implies higher local motions (rotations and translations) and therefore, weaker interactions with the filler;
- (2)
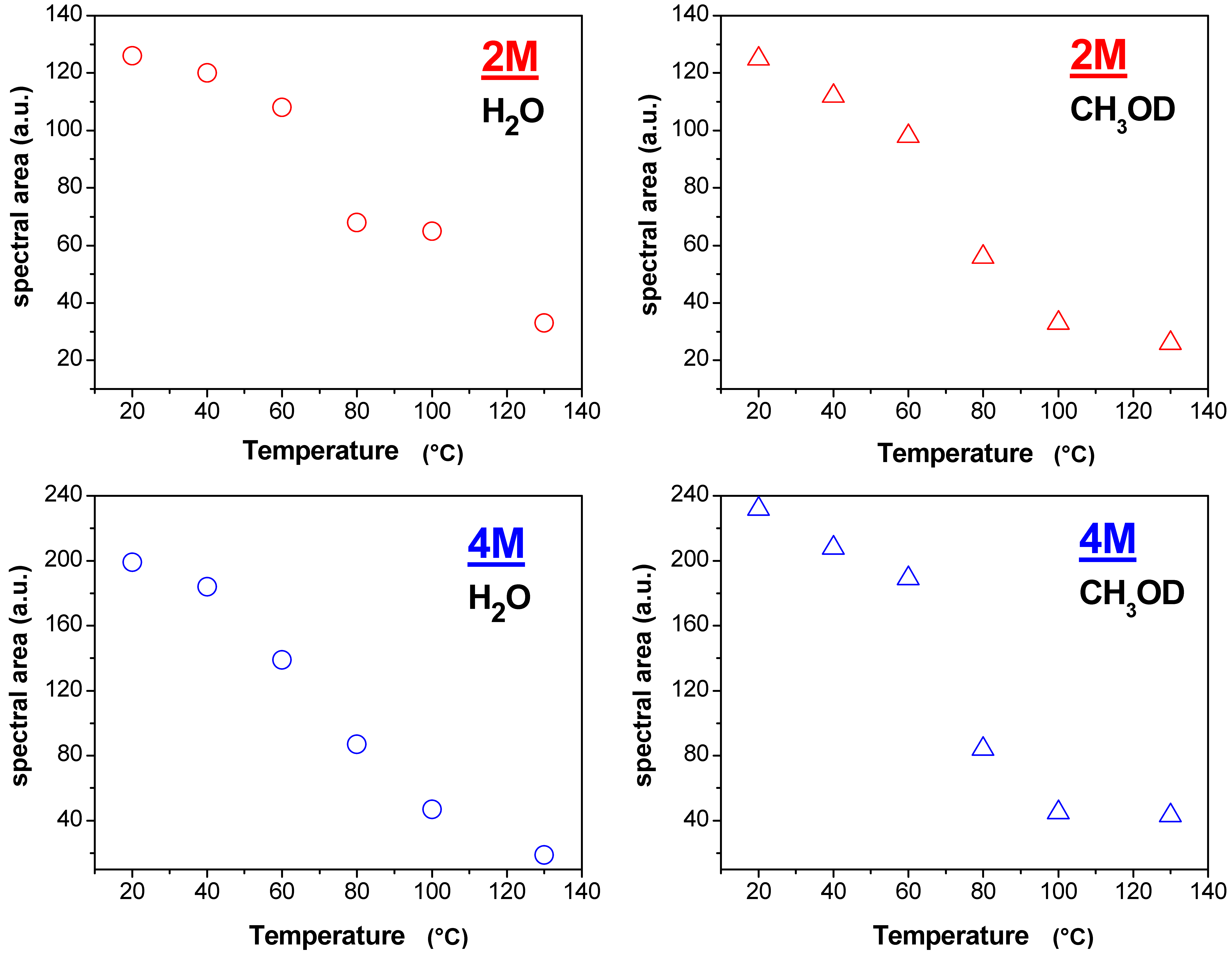
- significant evaporation on Lap-composite at 80 °C, evidenced by the strong reduction of the spectra integrals; in Swy-composite, this drop is found at 130 °C;
- (3)
- in Lap-composite, water for the 4 M solution shows a decrease of both diffusion and T1 after 80 °C, while for the 2 M solution, water and methanol diffusion is similar.
2.3. Electrochemical Investigation
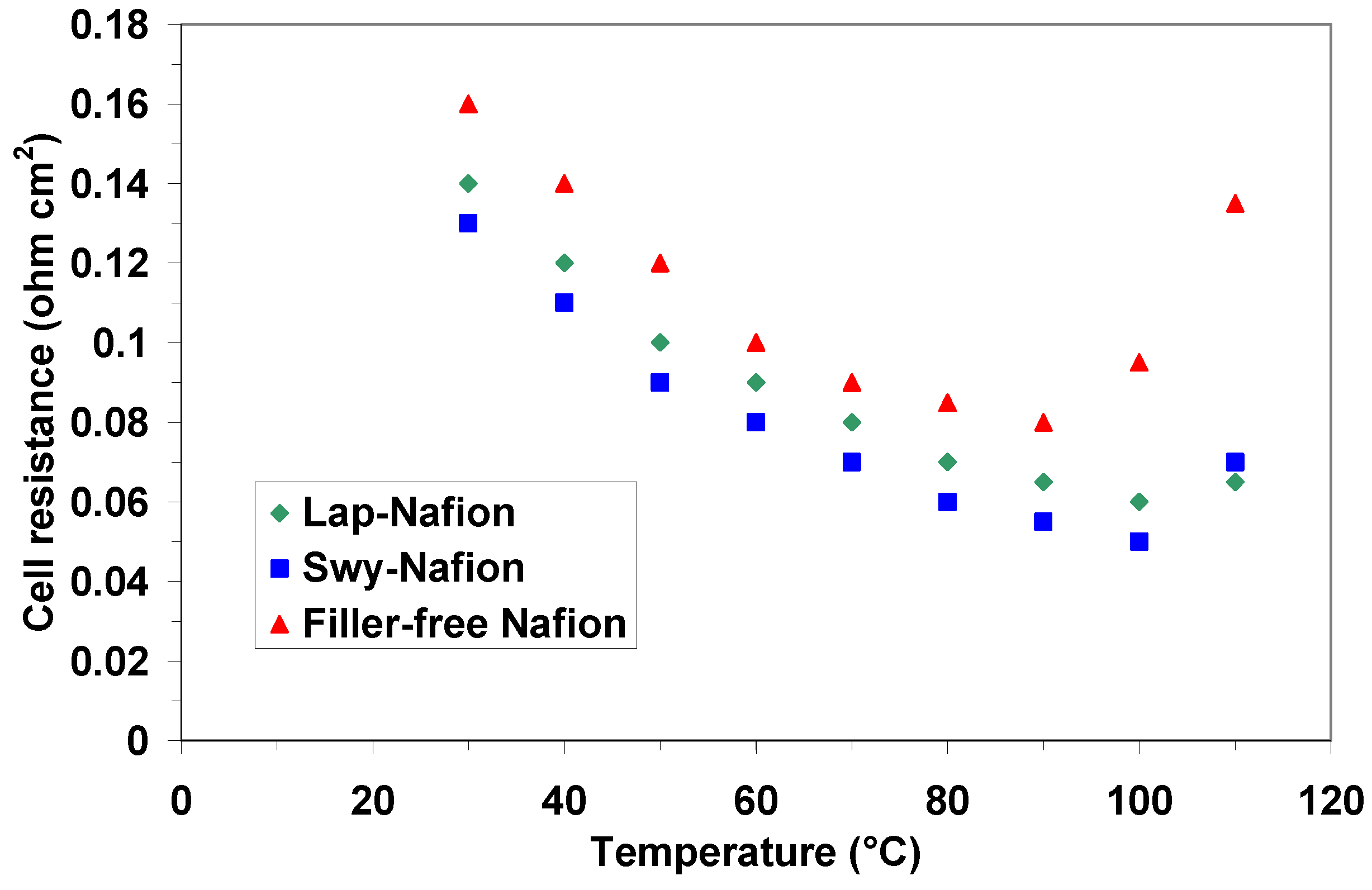
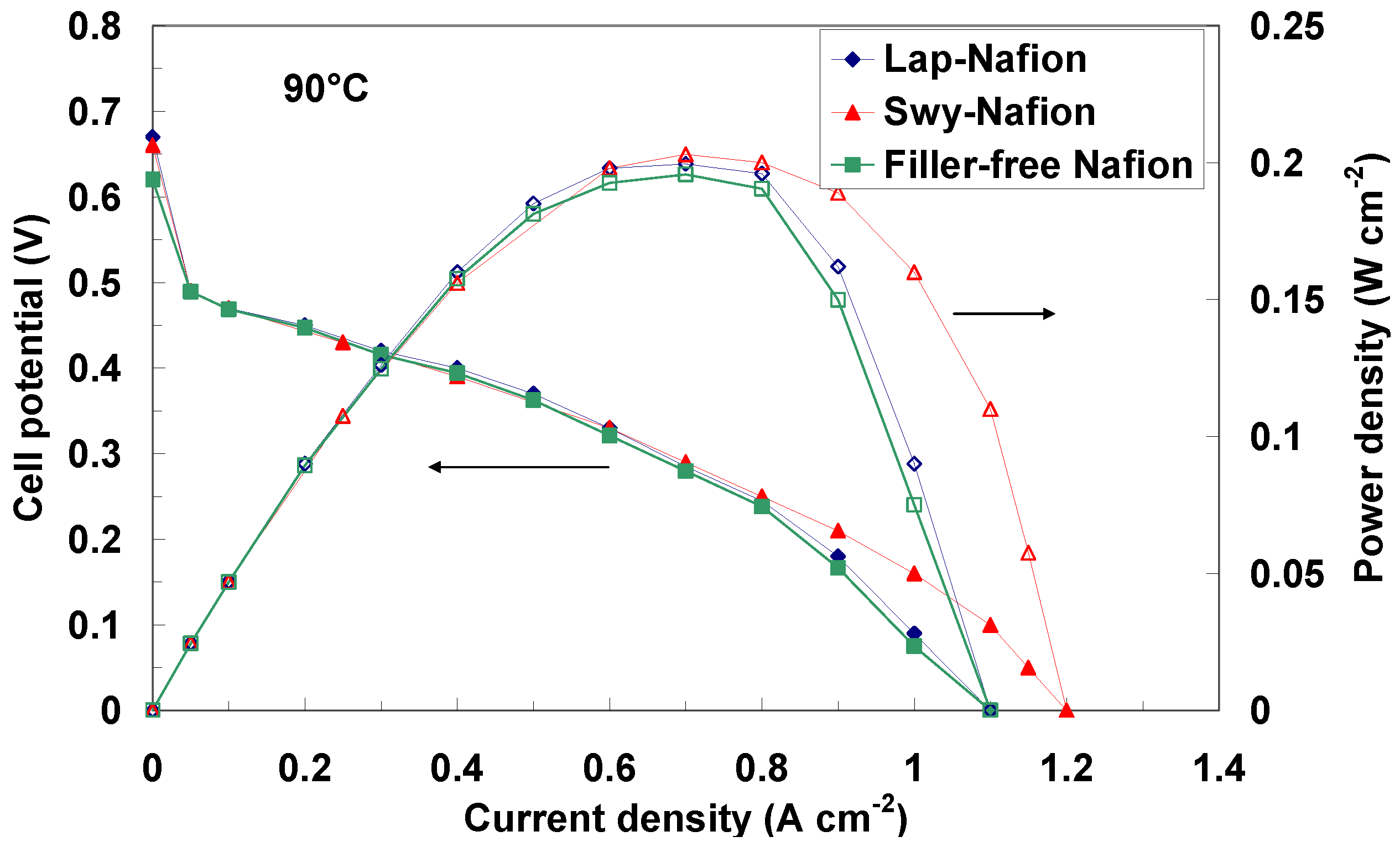
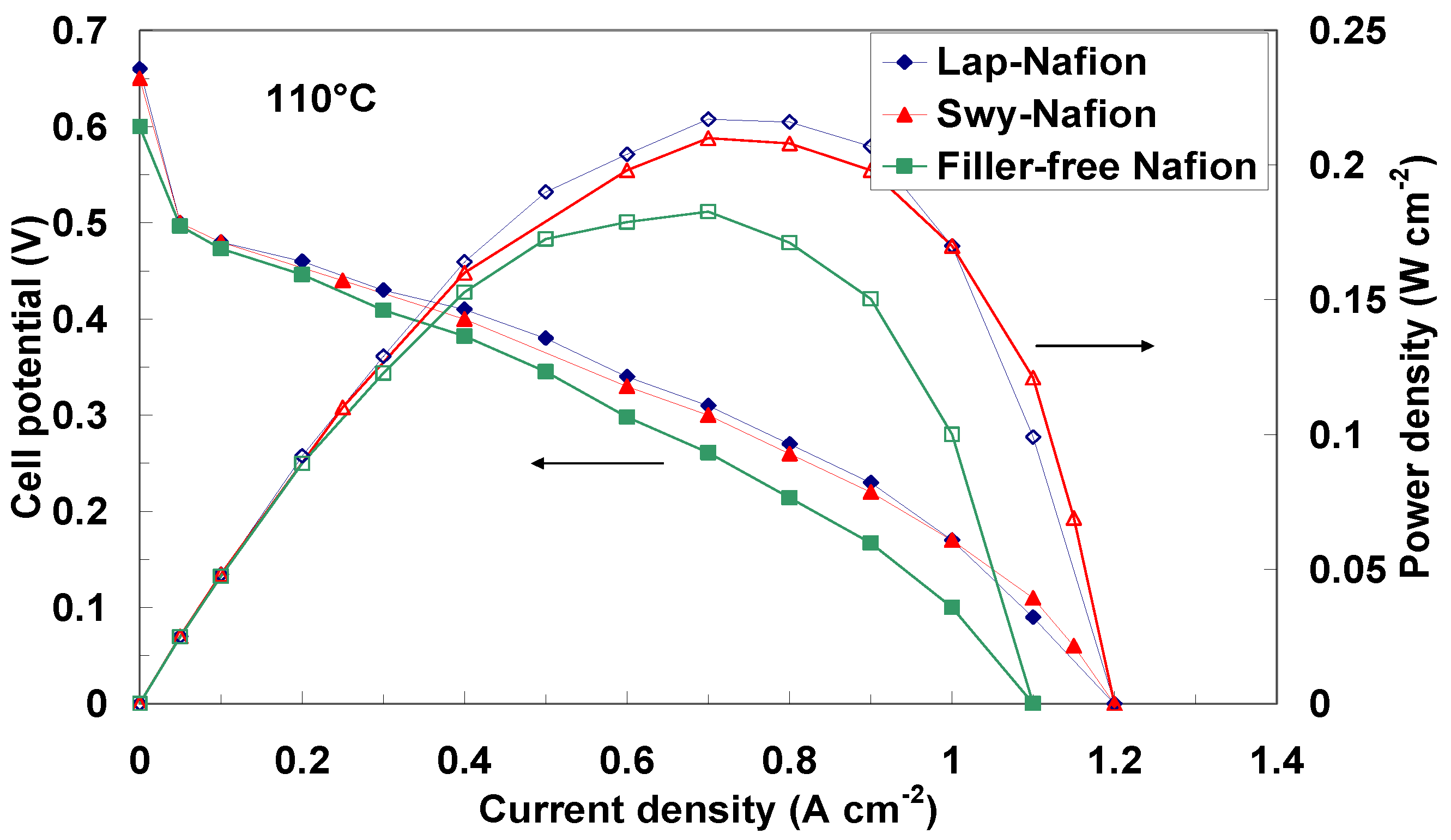
| Membranes | Open Circuit Potential (V) @ 90 °C | Open Circuit Potential (V) @ 100 °C | Open Circuit Potential (V) @ 110 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| filler-free Nafion | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.60 |
| Lap/Nafion | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Swy/Nafion | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.65 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Composites Membranes Preparation
3.3. Characterization Techniques
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Wasmus, S.; Kuver, A. Methanol oxidation and direct methanol fuel cells: A selective review. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 461, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Antonucci, V. DMFCs: From fundamental aspects to technology development. Fuel Cells 2001, 2, 133–161. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Liu, H. Real time measurements of methanol crossover in a DMFC. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Casciola, M. Composite membranes for medium-temperature PEM fuel cells. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2003, 33, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.L.; Fuller, T.F. A historical perspective of fuel cell technology in the 20th century. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, S59–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Costamagna, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Benziger, J.; Bocarsly, A.B. Approaches and technical challenges to high temperature operation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J.Power Sources 2001, 103, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, M.A.; Abbati, C.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. Temperature-dependent performances of a fuel cell using a superacid zirconia-doped Nafion polymer electrolyte. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Zhang, T.; Bocarsly, A.; Greenbaum, S. NMR characterization of composite polymer membranes for low-humidity PEM fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B466–B473. [Google Scholar]
- Baglio, V.; Aricò, A.S.; Antonucci, V.; Nicotera, I.; Oliviero, C.; Coppola, L.; Antonucci, P.L. An NMR spectroscopic study of water and methanol transport properties in DMFC composite membranes: Influence on the electrochemical behaviour. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Enotiadis, A.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Gournis, D. Evaluation of smectite clays as nanofillers for the synthesis of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 37, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar]
- Nicotera, I.; Enotiadis, A.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Ranieri, G.A.; Gournis, D. Effective improvement of water-retention in nanocomposite membranes using novel organo-modified clays as fillers for high temperature PEMFCs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9087–9097. [Google Scholar]
- Tazi, B.; Savadogo, O. Effect of various heteropolyacids (HPAs) on the characteristics of Nafion®-HPAS membranes and their H2/O2 polymer electrolyte fuel cell parameters. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2001, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, K.; Usuki, A.; Okada, A.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Synthesis and properties of polyimide-clay hybrid. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1993, 31, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelis, E.P. Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R.; Robeson, L.M. Polymer nanotechnology: Nanocomposites. Polymer 2008, 49, 3187–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Usuki, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Okada, A.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Synthesis of nylon-6-clay hybrid by montmorillonite intercalated with epsilon-caprolactam. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1993, 31, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gournis, D.; Floudas, G. Hairy” Plates: Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polyisoprene copolymers in the presence of laponite clay. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gournis, D.; Jankovic, L.; Maccallini, E.; Benne, D.; Rudolf, P.; Colomer, J.F.; Sooambar, C.; Georgakilas, V.; Prato, M.; Fanti, M.; Zerbetto, F.; Sarova, G.H.; Guldi, D.M. Clay-fulleropyrrolidine nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6154–6163. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Merino, J.; Aranda, P.; Galvan, J.C.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Reactive nanocomposites based on pillared clays. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 9, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Bébin, P.; Caravanier, M.; Galiano, H. Nafion®/clay-SO3H membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Huppert, D. Connection between proton abnormal conductivity in water and dielectric relaxation time. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 3598–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikerling, M.; Kornyshev, A.A.; Kuznetsov, A.M.; Ulstrup, J.; Walbran, S. Mechanisms of proton conductance in polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 3646–3662. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuer, K.D. Fast proton conductivity: A phenomenon between the solid and the liquid state? Solid State Ionics 1997, 94, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebel, G. Structural evolution of water swollen perfluorosulfonated ionomers from dry membrane to solution. Polymer 2000, 41, 5829–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddison, S.J.; Paul, R. The nature of proton transport in fully hydrated Nafion®. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, F.; Vernersson, T.; Pettersson, E.T.; Dvinskikh, S.V.; Lindbergh, G.; Furó, I. Electrokinetic transport of water and methanol in Nafion membranes as observed by NMR spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 2010, 55, 3542–3549. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Yan, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W. Methanol distribution and electroosmotic drag in hydrated poly(perfluorosulfonic) acid membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 15616–15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovic, I.; Gordon, M.S. Methanol−water mixtures: A microsolvation study using the effective fragment potential method. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slichter, C.P. Principles of Magnetic Resonance, 3rd ed; Springer Series in Solid State Science: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Baglio, V.; Tricoli, V.; Aricò, A.S.; Antonucci, V. PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer/Nafion blend as membrane material for intermediate temperature DMFCs. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Aricò, A.S.; Antonucci, V.; Antonucci, P.L.; Nannetti, F.; Tricoli, V. Investigation of the electrochemical behaviour in DMFCs of chabazite and clinoptilolite-based composite membranes. Electrochim Acta 2005, 50, 5181–5188. [Google Scholar]
- Baglio, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Aricò, A.S.; Antonucci, V.; Antonucci, P.L.; Trakanprapai, C.; Esposito, V.; Licoccia, S.; Traversa, E. Composite mesoporous titania Nafion-based membranes for direct methanol fuel cell operation at high temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1373–A1377. [Google Scholar]
- Staiti, P.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; Lufrano, F.; Passalacqua, E.; Antonucci, V. Hybrid Nafion-silica membranes doped with heteropolyacids for application in direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2001, 145, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Aricò, A.S.; Cretì, P.; Baglio, V.; Antonucci, V. Composite Nafion/zirconium phosphate membranes for direct methanol fuel cell operation at high temperature. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2001, 4, A31–A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Martina, F.; Ciccarella, G.; Zama, I.; Arriaga, L.G.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A.S. Solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyser based on Nafion-TiO2 composite membrane for high temperature operation. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Ledesma-Garcia, J.; Arriaga, L.G.; Aricò, A.S. High temperature operation of a composite membrane-based solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyser. Electrochim Acta 2008, 53, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar]
- Gournis, D.; Lappas, A.; Karakassides, M.A.; Tobbens, D.; Moukarika, A. A neutron diffraction study of alkali cation migration in montmorillonites. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2008, 35, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, B.; Sharp, A.R.; Armstrong, R.L. An n.m.r. investigation of the dynamical characteristics of water absorbed in Nafion. Polymer 1999, 40, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, E.O.; Tanner, J.E. Spin diffusion measurements: Spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicotera, I.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V. NMR and Electrochemical Investigation of the Transport Properties of Methanol and Water in Nafion and Clay-Nanocomposites Membranes for DMFCs. Membranes 2012, 2, 325-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020325
Nicotera I, Angjeli K, Coppola L, Aricò AS, Baglio V. NMR and Electrochemical Investigation of the Transport Properties of Methanol and Water in Nafion and Clay-Nanocomposites Membranes for DMFCs. Membranes. 2012; 2(2):325-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020325
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicotera, Isabella, Kristina Angjeli, Luigi Coppola, Antonino S. Aricò, and Vincenzo Baglio. 2012. "NMR and Electrochemical Investigation of the Transport Properties of Methanol and Water in Nafion and Clay-Nanocomposites Membranes for DMFCs" Membranes 2, no. 2: 325-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020325
APA StyleNicotera, I., Angjeli, K., Coppola, L., Aricò, A. S., & Baglio, V. (2012). NMR and Electrochemical Investigation of the Transport Properties of Methanol and Water in Nafion and Clay-Nanocomposites Membranes for DMFCs. Membranes, 2(2), 325-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020325