Effects of Surface Morphology on Mesoporous Silicon-Modified Nanofiltration Membranes for High Rejection Performances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Mesoporous Materials
2.3. Fabrication of Mesoporous Material-Modified PES Commercial NF Membranes
2.4. Membrane Characterization
2.4.1. Static Contact Angle Test (SCA)
2.4.2. Zeta Potential Tests
2.4.3. XPS Analysis
2.4.4. SEM Tests
2.4.5. Water Flux and Salt Rejection
2.4.6. Molecular Weight Cutoff (MWCO)
2.5. Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Mesoporous Silicon on the Hydrophilicity of PES Composite Membranes
3.2. Surface Charge of Mesoporous Silicon/PES Composite Membranes
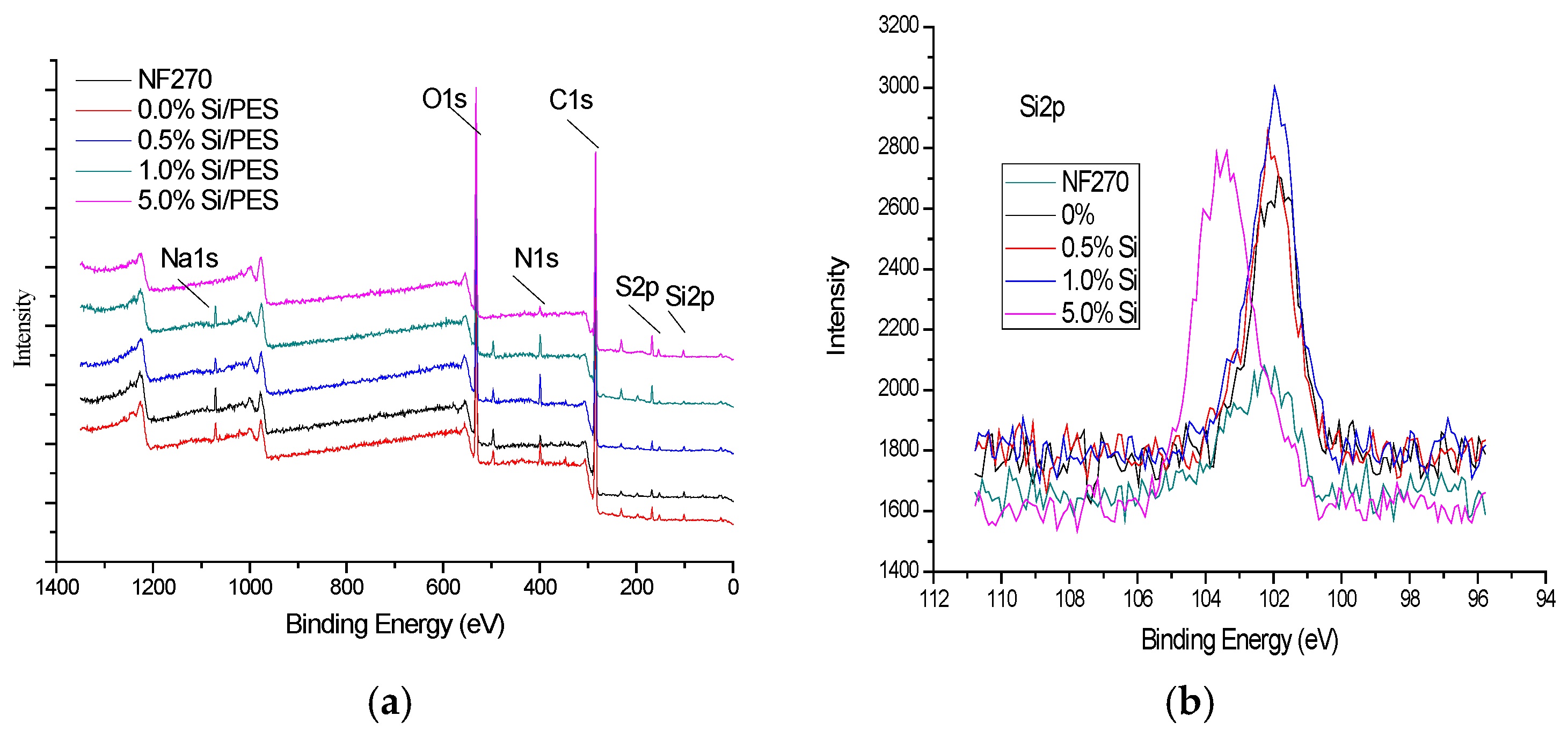
3.3. XPS Analysis of Mesoporous Silicon/PES Composite Membranes
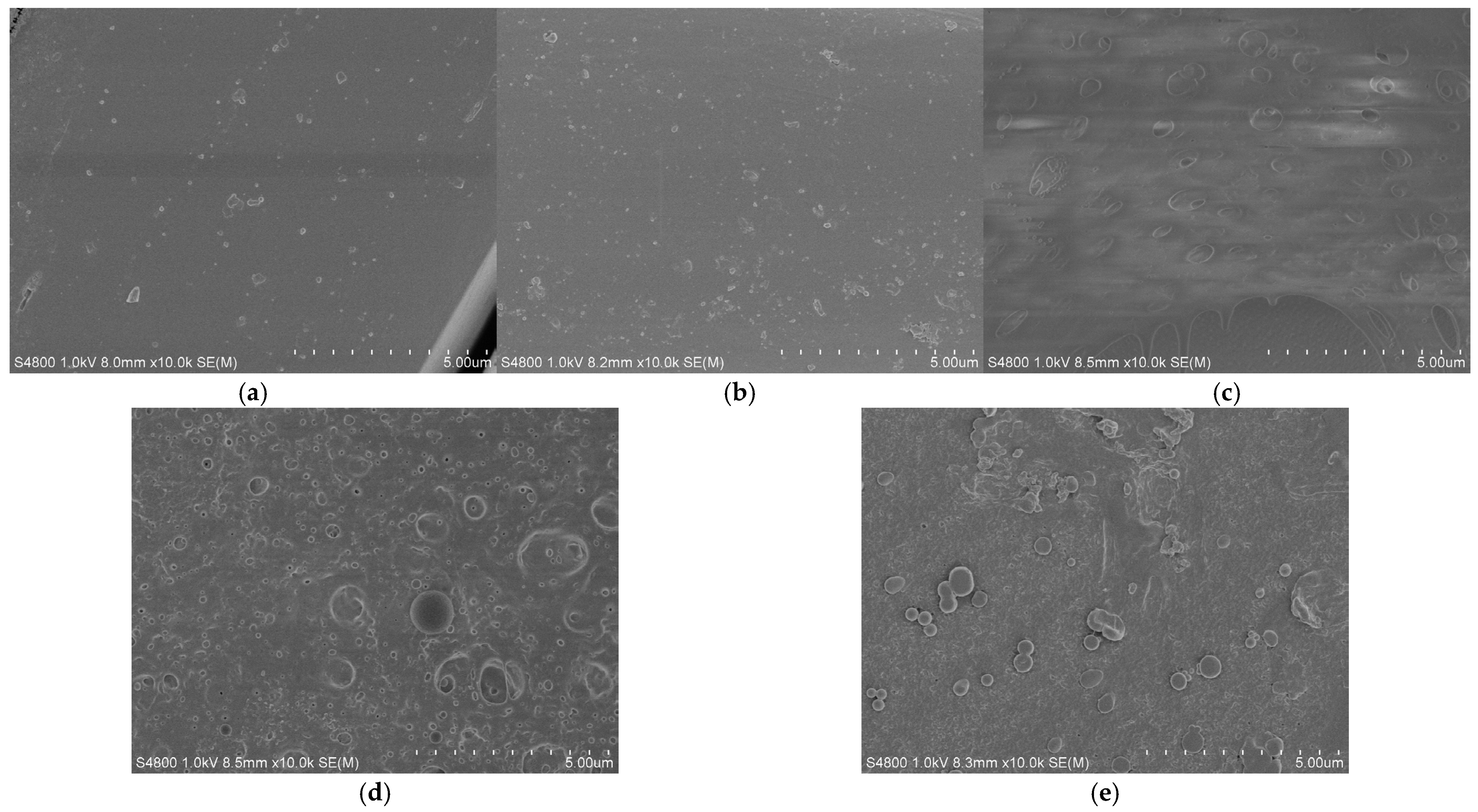
3.4. SEM Test of Mesoporous Silicon/PES Composite Membranes
3.5. Water Flux and Salt Rejection of Mesoporous Silicon/PES Composite Membranes
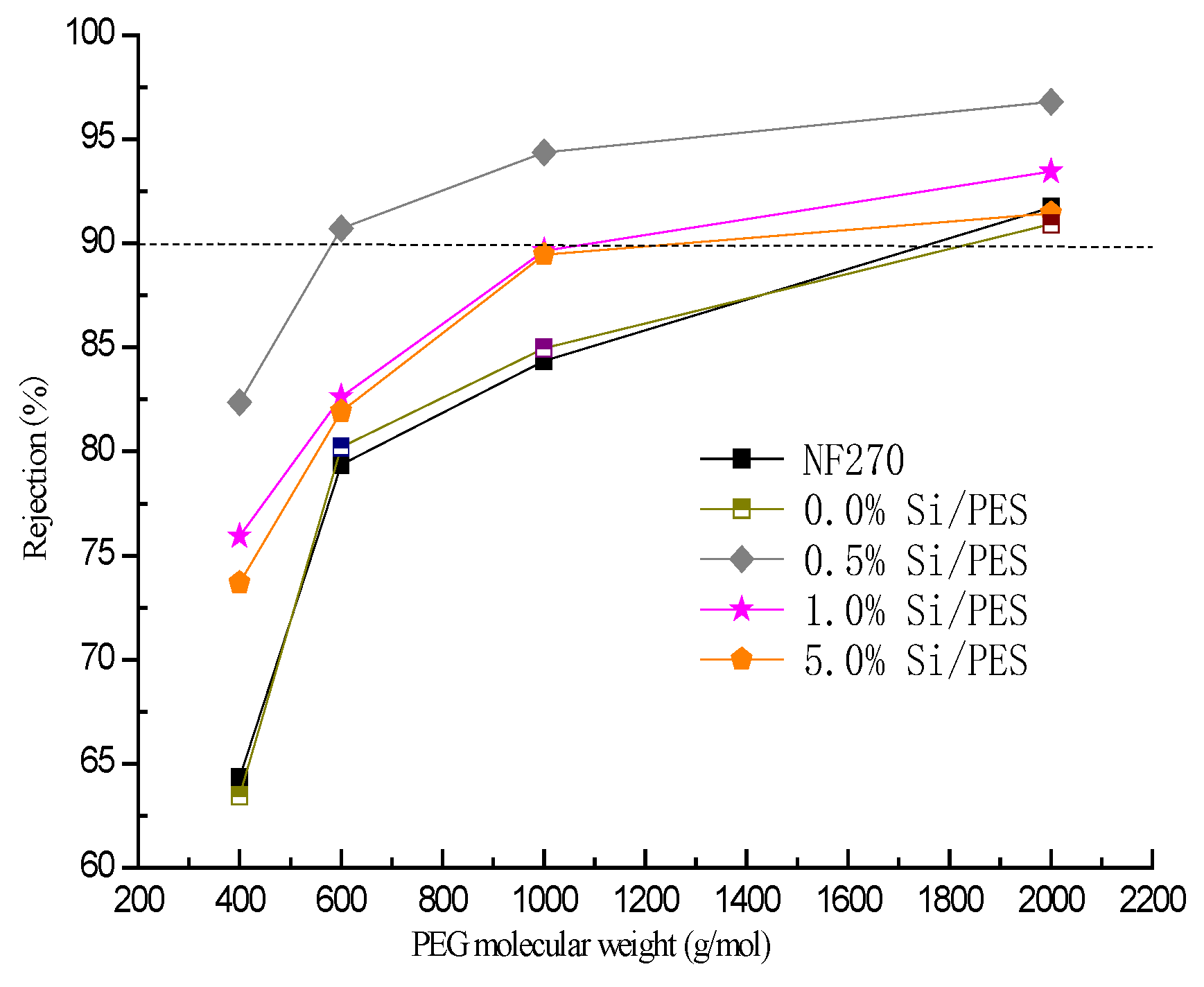
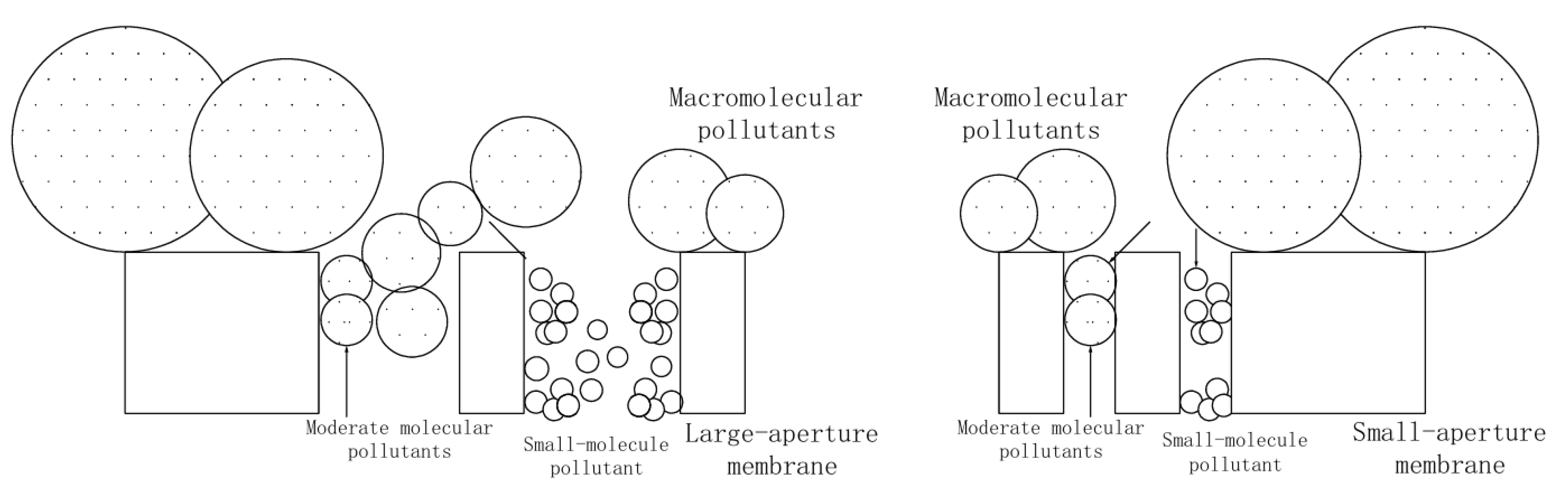
3.6. Pore Size Analysis of Mesoporous Silicon/PES Composite Membranes
3.7. Nanofiltration Performances of the PES Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination- Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, S.; Gorgojo, P.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Livingston, A.G. High Flux Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15201–15208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Teow, Y.; Ang, W.; Chung, Y.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes review: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2015, 363, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Gupta, V.K. Synthesis and characterization of alumina nano-particles polyamide membrane with enhanced flux rejection performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.F.J.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. High flux hydrophobic membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN)-Interfacial polymerization, surface modification and solvent activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Mi, B. Enabling Graphene Oxide Nanosheets as Water Separation Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.L.; Hill, A.J.; Caruso, F.; Kentish, S.E. Chlorine Resistant Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Membranes for Desalination. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, H.-C.; Liang, H.-Q.; Wan, L.-S.; Xu, Z.-K. Novel nanofiltration membrane with ultrathin zirconia film as selective layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 500, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgojo, P.; Karan, S.; Wong, H.C.; Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Cabral, J.T.; Livingston, A.G. Ultrathin Polymer Films with Intrinsic Microporosity: Anomalous Solvent Permeation and High Flux Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4729–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, C. High-Flux Graphene Oxide Nanofiltration Membrane Intercalated by Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8147–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, H.-C.; Liang, H.-Q.; Wan, L.-S.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes via co-deposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine followed by cross-linking. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Ali, M.E.; Abd Hamid, S.B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chowdhury, Z.Z. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: A bright future in water desalination. Desalination 2014, 336, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G. Sub-10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Unidirectional water-penetration composite fibrous film via electrospinning. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5996–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-N.; Yang, H.-C.; Huang, H.; Xu, Z.-K. Underwater superoleophobic coatings fabricated from tannic acid-decorated carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 16112–16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Nadzri, N.; Wang, R. Thin-film composite (TFC) membranes for sustainable desalination and water reuse: A perspective. Desalination 2025, 599, 118451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Tu, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Modelling of the separation performance and electrokinetic properties of nanofiltration membranes. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012, 31, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Chitosan-based membrane chromatography for protein adsorption and separation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2012, 32, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Lawler, J. Preparation and characterization of negatively charged organic–inorganic hybrid ultrafiltration membranes for protein separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Huang, X.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I. Physical–chemical properties, separation performance, and fouling resistance of mixed-matrix ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 283, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpurkar, L.P.; Shiwankar, N.B.; Zade, V.R.; Hese, S.V.; Kore, V.R.; Pangal, A.D. Modification, Blending, Characterization, and Investigation of Thermal Properties, pH Response of Chitosan-based Polymer Extracted from Labeo rohita Scales. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2024, 15, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Jia, Y.; Mu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Huang, P. Pyrolytic Modification of Heavy Coal Tar by Multi-Polymer Blending: Preparation of Ordered Carbonaceous Mesophase. Polymers 2024, 16, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, S.B.; Senaratne, W. Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Carbon-Silicon Nanocomposites. U.S. Patent 7910082 B2, 22 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tetala, K.K.; Skrzypek, K.; Levisson, M.; Stamatialis, D.F. A metal ion charged mixed matrix membrane for selective adsorption of hemoglobin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Hu, X. Mesoporous Materials as Catalyst support for Wastewater Treatment. Madridge J. Nanotechnol. Nanosci. 2019, 4, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Oatley, D.L.; Williams, P.M.; Wright, C.J. Positively charged nanofiltration membranes: Review of current fabrication methods and introduction of a novel approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Gung, C.-H.; Sun, J.-J.; Suen, S.-Y. Preparation of polyethersulfone/plant-waste-particles mixed matrix membranes for adsorptive removal of cationic dyes from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Abdulkarim, A.A.; Ismail, S.; Ooi, B.S. Preparation and characterisation of PES-ZnO mixed matrix membranes for humic acid removal. Desalin. Water Treat. Sci. Eng. 2015, 54, 3257–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S. Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of dichloroacetic acid from aqueous solution using mesoporous carbon. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ji, D.; Cao, Y.; Ling, X.; Chen, W. Enhancing adsorption efficiency of dichloroacetic acid onto mesoporous carbons: Procedure optimization, mechanism and characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 452, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, L.; Feng, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Y.; Stein, A.; et al. A Family of Highly Ordered Mesoporous Polymer Resin and Carbon Structures from OrganicOrganic Self-Assembly. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4447–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Madaeni, S.; Mehdipour-Ataei, S. Synthesis of a novel poly(amide-imide) (PAI) and preparation and characterization of PAI blended polyethersulfone (PES) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H. Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdulkarim, A.; Shafie, Z.M.; Ooi, B. Fouling evaluation of PES/ZnO mixed matrix hollow fiber membrane. Desalination 2017, 403, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Gholami, A.; Madaeni, S.; Moghadassi, A.; Hamidi, A. Fabrication of (polyvinyl chloride/cellulose acetate) electrodialysis heterogeneous cation exchange membrane: Characterization and performance in desalination process. Desalination 2012, 306, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Isloor, A.M.; Wanichapichart, P.; Ismail, A.F. Preparation and characterization of sulfonated polysulfone and N-phthloyl chitosan blend composite cation-exchange membrane for desalination. Desalination 2012, 298, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y. Polysulfone membranes decorated with Fe–Mn binary oxide nanoparticles and polydopamine for enhanced arsenate/arsenite adsorptive removal. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phao, N.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Mamba, B.B.; Mhlanga, S.D. A nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube enhanced polyethersulfone membrane system for water treatment. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2013, 66, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F.; Nxumalo, E.; Krause, R.; Hoek, E.; Mamba, B. Application of polysulfone/cyclodextrin mixed-matrix membranes in the removal of natural organic matter from water. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 67–69, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Membrane Type | PES (wt%) | Mesoporous Silicon Content (wt%) | DMAc |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF270 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 25 | 0.0 | 75 |
| 0.5% Si/PES | 25 | 0.5 | 75 |
| 1.0% Si/PES | 25 | 1.0 | 75 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 25 | 5.0 | 75 |
| Membrane Type | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| NF270 | 84.95 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 87.25 |
| 0.5% Si/PES | 67.65 |
| 1.0% Si/PES | 68.30 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 73.25 |
| Sample | IEP |
|---|---|
| NF270 | 2.59 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 2.53 |
| 0.5% Si/PES | 2.87 |
| 1.0% Si/PES | 3.25 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 3.22 |
| Samples | O1s | N1s | C1s | S2p | Si2p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE (eV) | % | BE (eV) | % | BE (eV) | % | BE (eV) | % | BE (eV) | % | |
| NF270 | 531.28 | 24.72 | 398.97 | 4.81 | 284.46 | 64.920 | 167.44 | 2.57 | 101.98 | 0.22 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 531.33 | 26.12 | 399.03 | 4.97 | 284.51 | 63.11 | 167.86 | 0.02 | 101.45 | 0.02 |
| 0.5% Si/PES | 531.46 | 22.06 | 398.92 | 2.61 | 284.24 | 71.45 | 167.91 | 1.01 | 101.34 | 1.41 |
| 1.0% Si/PES | 531.32 | 23.77 | 399.04 | 4.86 | 284.41 | 67.37 | 167.46 | 1.18 | 101.44 | 1.44 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 531.56 | 30.21 | 399.17 | 2.7 | 284.48 | 61.11 | 167.40 | 3.24 | 102.76 | 2.74 |
| Sample | Pure Water Flux (L/m2 h) | Salt Rejection % |
|---|---|---|
| NF270 | 16.73 | 58.28 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 9.09 | 34.13 |
| 0.5% Si/PES | 29.09 | 32.61 |
| 1.0% Si/PES | 26.46 | 39.34 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 8.71 | 38.52 |
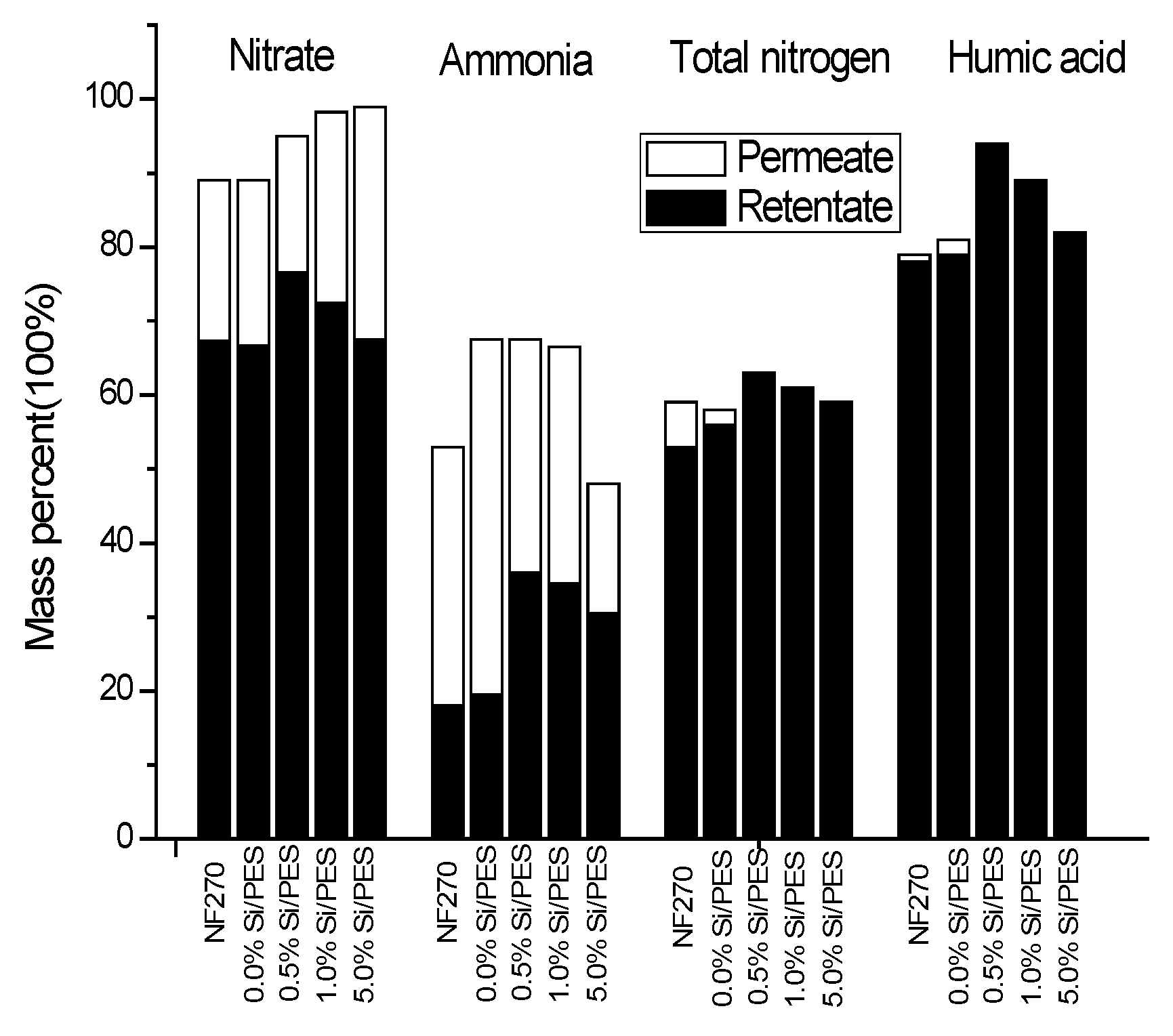
| Sample | NO3− % | NH4+ % | TN % | HA % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retentate | Permeate | Retentate | Permeate | Retentate | Permeate | Retentate | Permeate | |
| NF270 | 67.3 | 21.7 | 18.0 | 35.2 | 53.2 | 5.9 | 78.1 | 1.1 |
| 0.0%Si/PES | 66.7 | 22.3 | 19.5 | 48.3 | 56.1 | 2.0 | 78.9 | 2.1 |
| 0.5%Si/PES | 76.5 | 18.5 | 36.1 | 31.5 | 62.9 | 0 | 94.2 | 0 |
| 1.0%Si/PES | 72.4 | 25.8 | 34.5 | 32.0 | 61.0 | 0 | 88.7 | 0 |
| 5.0% Si/PES | 67.4 | 31.5 | 30.5 | 17.5 | 58.9 | 0 | 82.0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Ding, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D. Effects of Surface Morphology on Mesoporous Silicon-Modified Nanofiltration Membranes for High Rejection Performances. Membranes 2025, 15, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090274
Ding Y, Ding A, Liu Y, Liu D. Effects of Surface Morphology on Mesoporous Silicon-Modified Nanofiltration Membranes for High Rejection Performances. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090274
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ying, Aifang Ding, Yuqing Liu, and Dong Liu. 2025. "Effects of Surface Morphology on Mesoporous Silicon-Modified Nanofiltration Membranes for High Rejection Performances" Membranes 15, no. 9: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090274
APA StyleDing, Y., Ding, A., Liu, Y., & Liu, D. (2025). Effects of Surface Morphology on Mesoporous Silicon-Modified Nanofiltration Membranes for High Rejection Performances. Membranes, 15(9), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090274





