Separation Principles and Strategies for an Oil–Water Separation Membrane with Special Wettability
Abstract
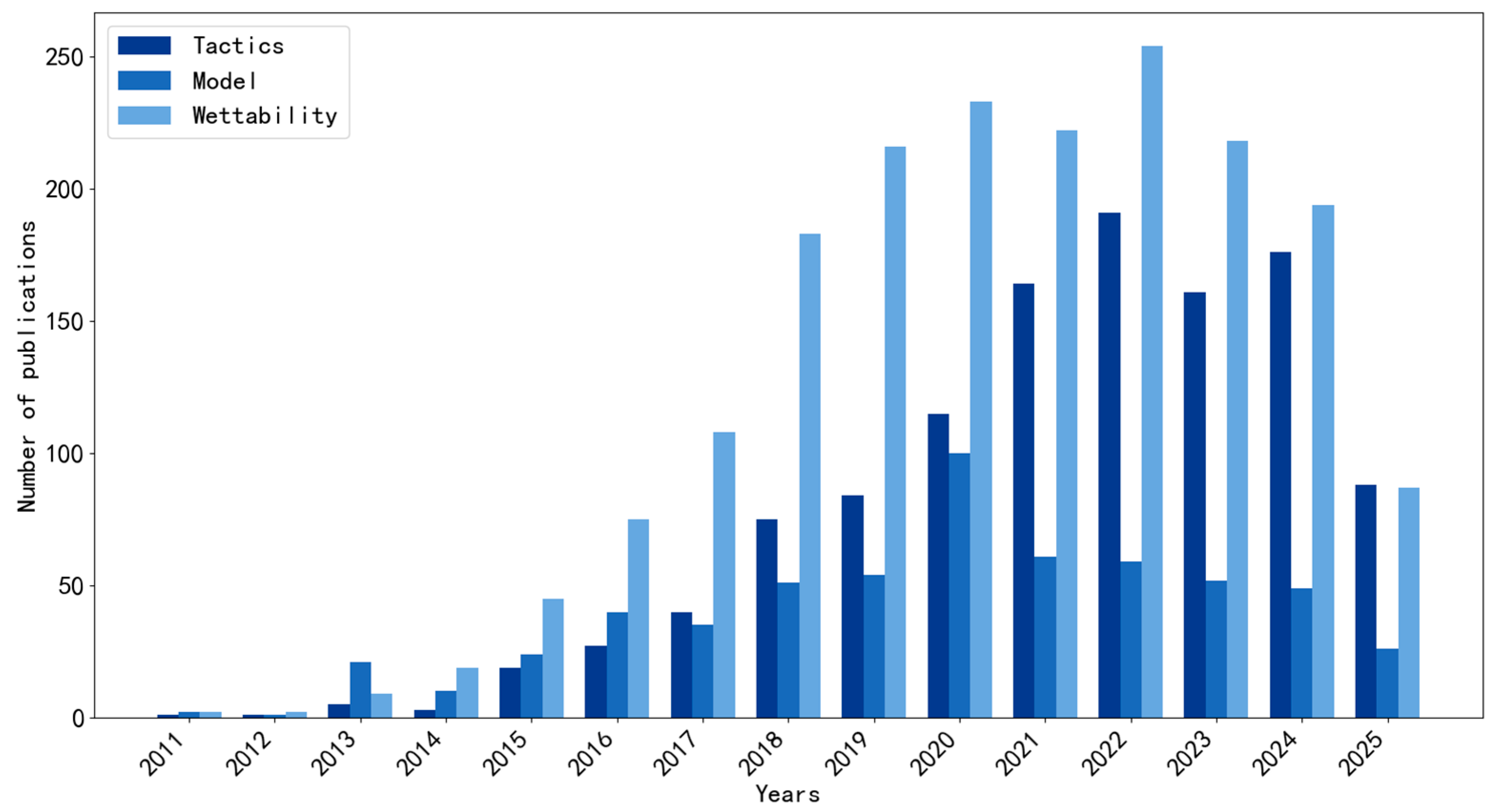
1. Introduction
2. Separation Principle
2.1. Droplet Modeling
2.2. Free Liquid Film Model
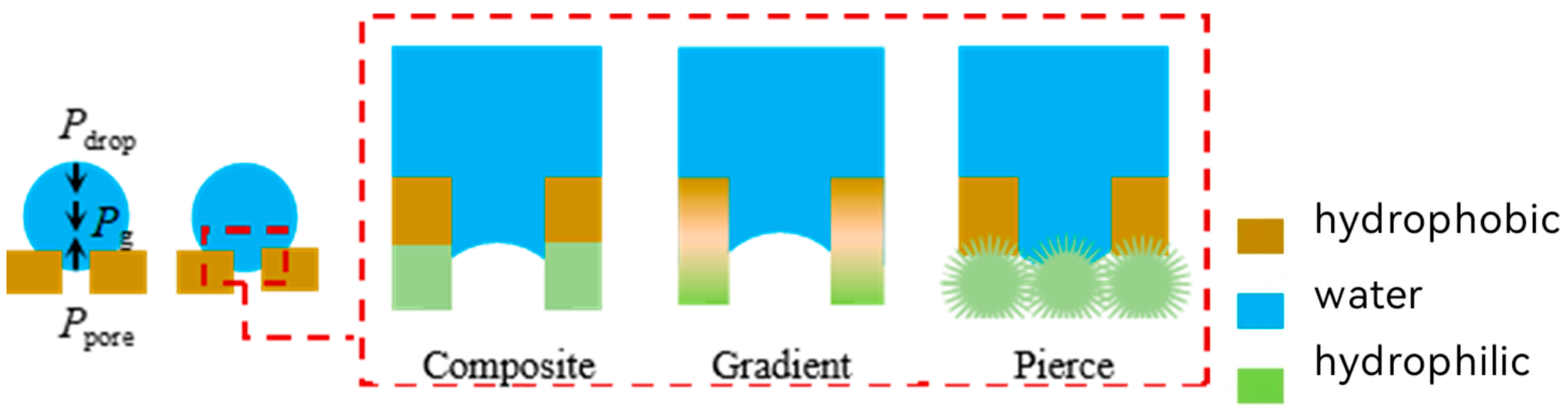
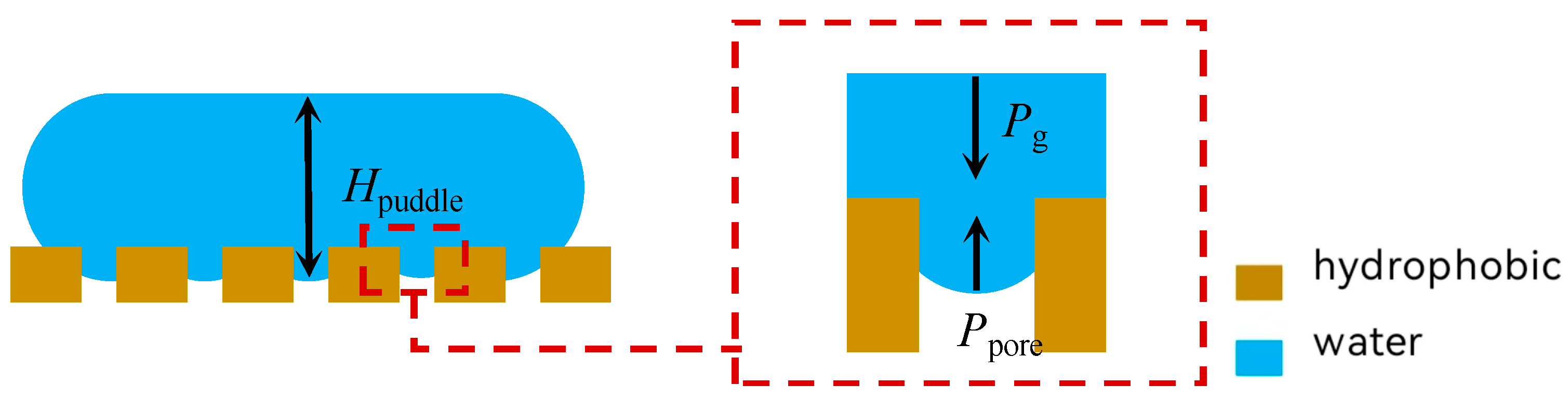
2.3. Modeling of Non-Free Liquid Surfaces
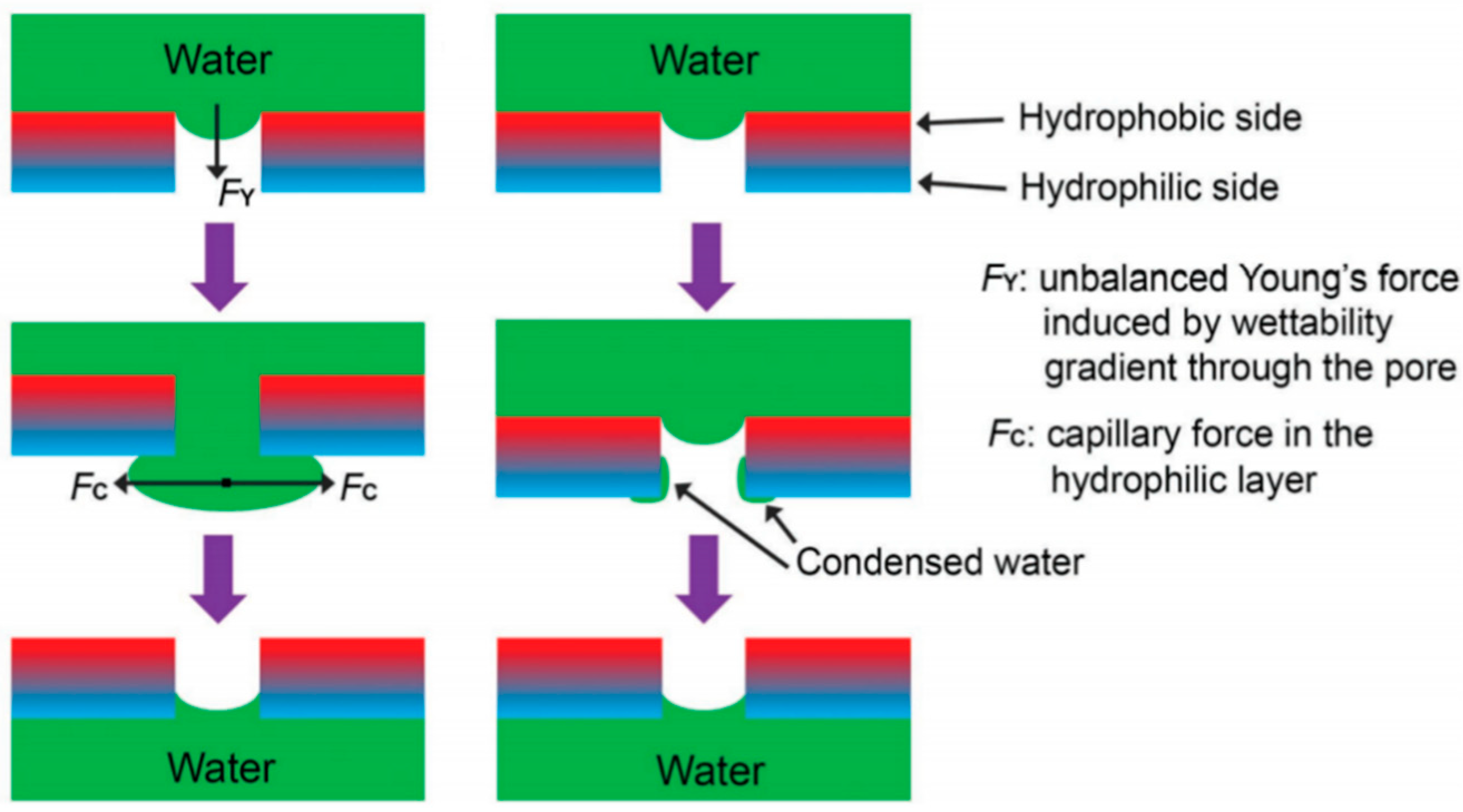
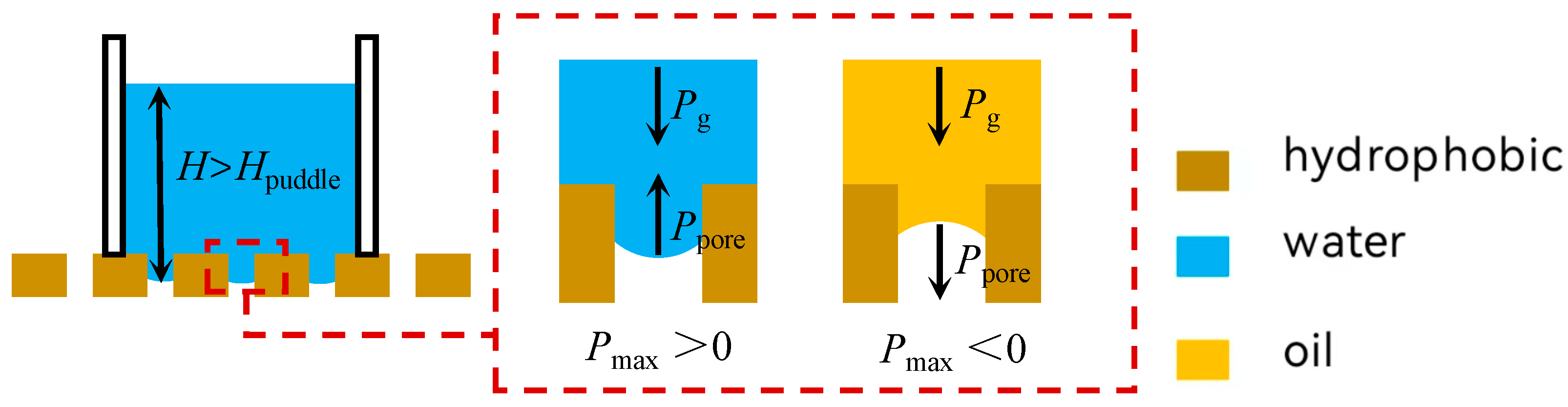
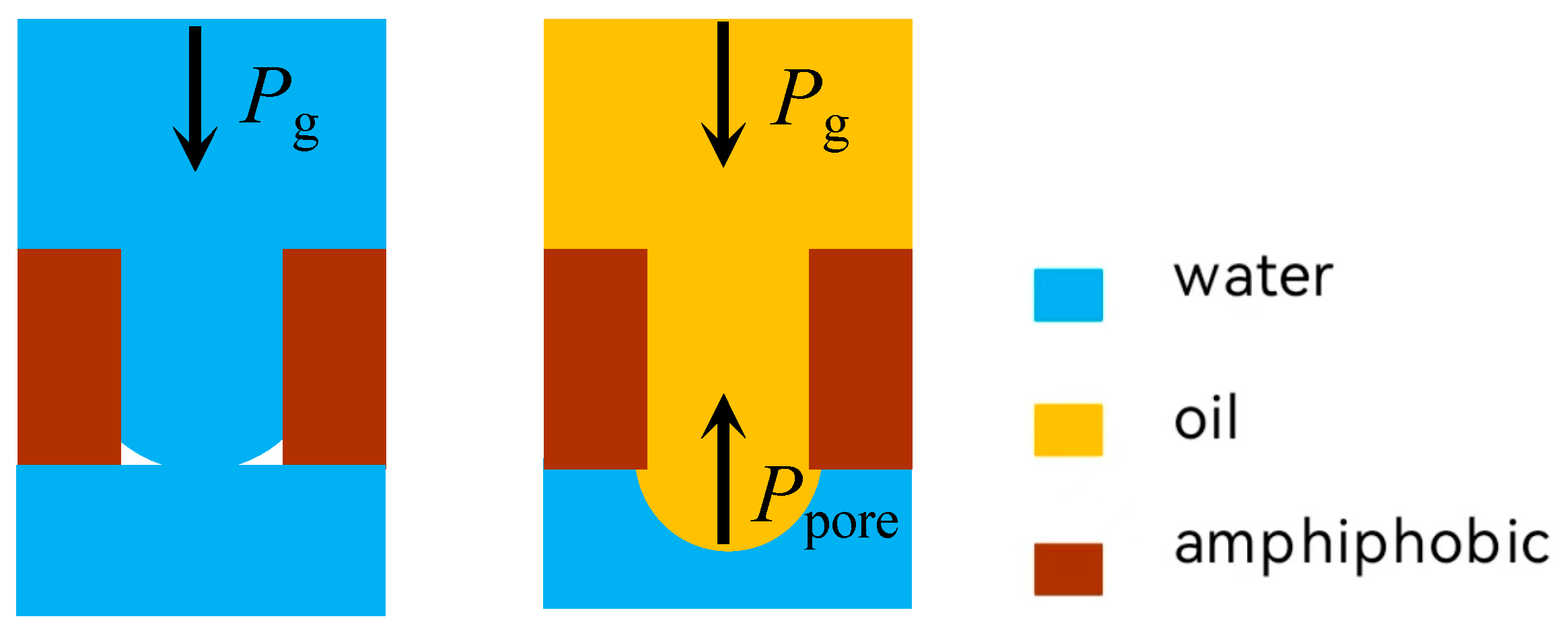
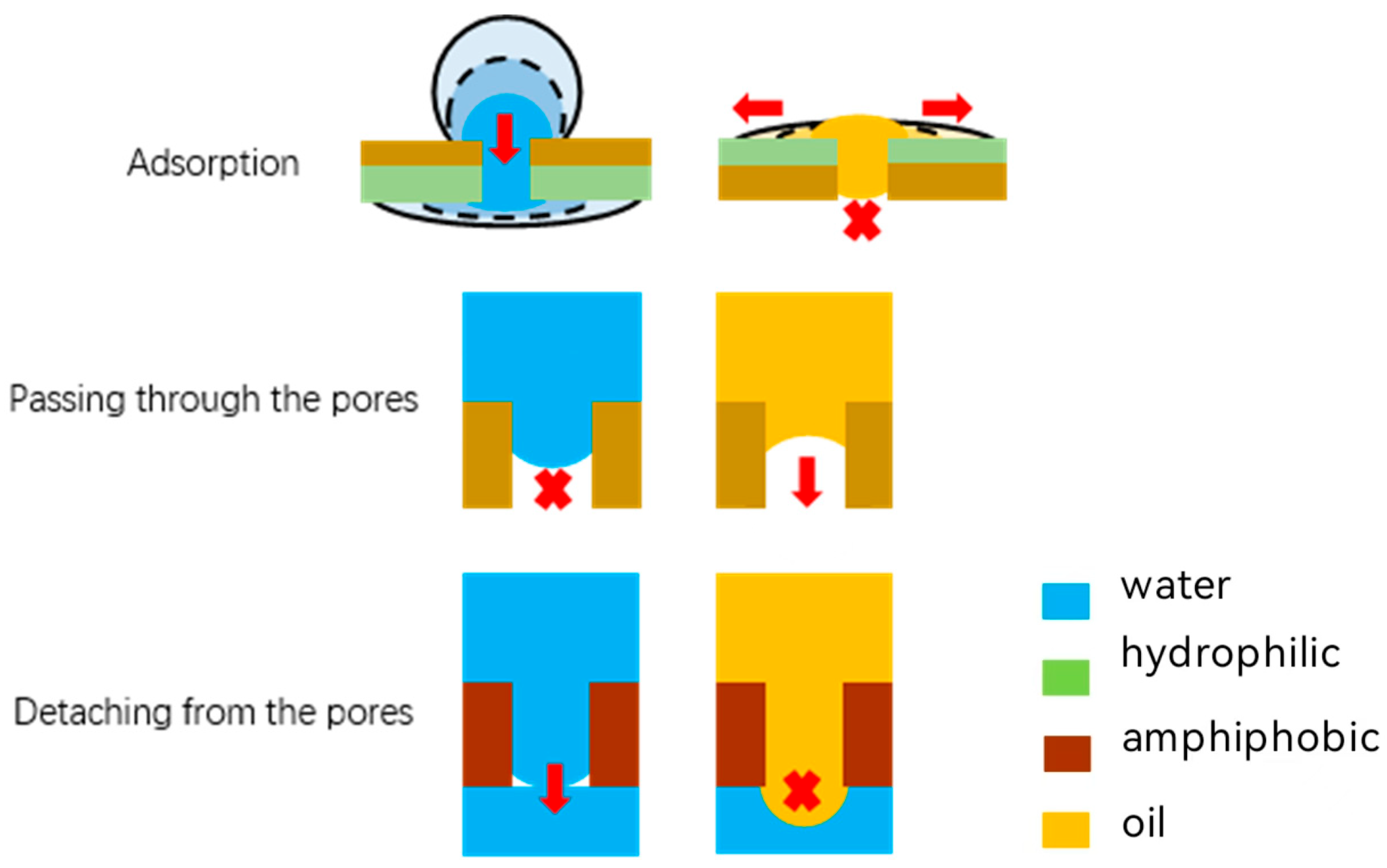
2.4. Separation Mechanisms
2.5. The Infiltration Law of Membrane
- (1)
- Young’s equation and static contact angle
- (2)
- Wenzel’s equation and rough surface correction
- (3)
- Cassie’s Equation and Non-Homogeneous Immersion
- (4)
- Dynamic contact angle and hysteresis effects
3. Separation Strategy
3.1. Superhydrophobic–Superoleophilic Strategy
3.2. Superhydrophilic–Superoleophobic Strategy
3.2.1. Superhydrophilic–Underwater Superoleophobic Strategy
3.2.2. Functional Group-Responsive Superhydrophilic–Superoleophobic Strategy
3.3. Superhydrophilic–Superoleophilic Strategy
3.4. Responsiveness
3.5. Janus Membrane
3.6. Oil–Water Super-Double Evacuation
3.7. Multifunctional Layered Structures and Hybrid Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Superwettability: New Insight on Theory, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Interfaces with Superwettability: From Materials to Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1727–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Verho, T.; Ras, R.H.A. Moving superhydrophobic surfaces toward real-world applications. Science 2016, 352, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milionis, A.; Loth, E.; Bayer, I.S. Recent advances in the mechanical durability of superhydrophobic materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Cui, P.; Jiang, W. A Review on Oil/Water Mixture Separation Material. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14546–14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hao, G.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, W. Facile preparation and characterization of modified magnetic silica nanocomposite particles for oil absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarathna, C.M.; Dewage, N.W.B.; Keeton, C.; Pennisson, J.; Henderson, R.; Lashley, B.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, E.B.; Perez, F.; Mohan, D.; et al. Biochar Adsorbents with Enhanced Hydrophobicity for Oil Spill Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9248–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churipard, S.R.; Kanakikodi, K.S.; Rambhia, D.A.; Raju, C.S.K.; Halgeri, A.B.; Choudary, N.V.; Ganesh, G.S.; Ravishankar, R.; Maradur, S.P. Porous polydivinylbenzene (PDVB) as an efficient adsorbent for hydrocarbons: Effect of porogens on adsorption capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Tao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yue, R.; Cui, Z. 3D superhydrophobic sponge with a novel compression strategy for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation and its separation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.; Hao, G.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. Design of Recyclable Superhydrophobic PU@Fe3O4@PS Sponge for Removing Oily Contaminants from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z. Designing novel superwetting surfaces for high-efficiency oil-water separation: Design principles, opportunities, trends and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16831–16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; Volume 658. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Ge, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, H.; Xing, G.; Lai, Y.; et al. Constructing Mechanochemical Durable and Self-Healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Directional Fluid Transport in Thin Porous Materials and its Functional Applications. Small 2017, 13, 1601070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xiao, J.; Yu, C.; Li, K.; Jiang, L. Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Cooperative Janus System for Enhancement of Fog Collection. Small 2015, 11, 4379–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Directional water-transfer through fabrics induced by asymmetric wettability. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G. Construction of Cellulose Based Super Wetting Material System and the Mechanism of Oil and Water Separation. Ph.D. Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Lin, T. Superphobicity/philicity Janus Fabrics with Switchable, Spontaneous, Directional Transport Ability to Water and Oil Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Cohen, R.E. Robust omniphobic surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18200–18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Guo, F.; Hou, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. A Robust Cu(OH)2 Nanoneedles Mesh with Tunable Wettability for Nonaqueous Multiphase Liquid Separation. Small 2016, 13, 1600499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.A.; Sadullah, M.S.; Qahtan, T.F.; Dastageer, M.A.; Baig, U.; McKinley, G.H. Fabrication and Wettability Study of WO3 Coated Photocatalytic Membrane for Oil-Water Separation: A Comparative Study with ZnO Coated Membrane. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Guo, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Separation of organic liquid mixture by flexible nanofibrous membranes with precisely tunable wettability. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Tuteja, A.; Chhatre, S.; Mabry, J.M.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H. Fabrics with Tunable Oleophobicity. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatre, S.S.; Choi, W.; Tuteja, A. Scale Dependence of Omniphobic Mesh Surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4027–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. The Establishment and Verification of Oil-Water Separation for Superamphiphobic Mesh Based on Low Surface Free Energy Theory. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extrand, C.W. Contact angles and hysteresis on surfaces with chemically heterogeneous islands. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3793–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Rational design of materials interface at nanoscale towards intelligent oil-water separation. Nanoscale Horiz. 2018, 3, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester Materials with Superwetting Silicone Nanofilaments for Oil/Water Separation and Selective Oil Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Rezaei, N.; Hamedi, H.; Zendehboudi, S.; Duan, X. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: A comprehensive review. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hou, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, B.; Liang, P. Hydrophilic surface coating on hydrophobic PTFE membrane for robust anti-oil-fouling membrane distillation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Mechanism and Application of Inorganic Porous Membranes in Liquid Separation. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, U.; Lynn, D.M. Synthetic Surfaces with Robust and Tunable Underwater Superoleophobicity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A Novel Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Hydrogel-Coated Mesh for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Fu, L.; Sun, X.; Zhong, J.; Dong, S.; Zhu, J. Preparation of superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic membranes for separating oil-in-water emulsion: Mechanism, progress, and perspective. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; He, F.; Cao, M.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. One-step transformation of highly hydrophobic membranes into superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic ones for high-efficiency separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3391–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Van der Bruggen, B. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic membranes—A review of synthesis methods. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 98, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Faizan, M.; Sajid, M. Multifunctional membranes with super-wetting characteristics for oil-water separation and removal of hazardous environmental pollutants from water: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Peng, C.; Dai, M.; Lin, D.; Ali, I.; Alhewairini, S.S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Naz, I. Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Men, X.; Zhou, X. Superhydrophilic–superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2834–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarter, J.A.; Genson, K.L.; Youngblood, J.P. Wetting behavior of oleophobic polymer coatings synthesized from fluorosurfactant-macromers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Kong, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Atomic-layer-deposition-enabled nonwoven membranes with hierarchical ZnO nanostructures for switchable water/oil separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L. An Intelligent Superwetting PVDF Membrane Showing Switchable Transport Performance for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z. Polymeric materials with switchable superwettability for controllable oil/water separation: A comprehensive review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 87, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Mu, P.; Li, J. Current research situation and future prospect of superwetting smart oil/water separation materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 20190–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Design and fabrication of superwetting fiber-based membranes for oil/water separation applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Kipper, M.J.; Tang, J. A review of superwetting membranes and nanofibers for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Janus porous membrane with conical nanoneedle channel for rapid unidirectional water transport. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10954–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Shi, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z. Janus membranes at the water-energy nexus: A critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 318, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Chen, V.; Darling, S.B. Janus Membranes: Creating Asymmetry for Energy Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, C.; Shui, X.; Yang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. Asymmetric Janus membranes based on in situ mussel-inspired chemistry for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Shao, L. Construction of oil-unidirectional membrane for integrated oil collection with lossless transportation and oil-in-water emulsion purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Qu, R.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Feng, L. Janus membrane decorated via a versatile immersion-spray route: Controllable stabilized oil/water emulsion separation satisfying industrial emission and purification criteria. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4941–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Mao, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Underwater superoleophobic-underoil superhydrophobic Janus ceramic membrane with its switchable separation in oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-P.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, M.-B.; Xu, Z.-K. Janus Membranes with Charged Carbon Nanotube Coatings for Deemulsification and Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9832–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Chen, M.; Shi, D. PDA controllably-modified Janus membranes with high-permeability for oil/water separation. Compos. Commun. 2023, 40, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. Flexible Janus wood membrane with asymmetric wettability for high-efficient switchable oil/water emulsion separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wen, X.; Tan, Y.; Yin, X. In-situ growth of robust and superhydrophilic nano-skin on electrospun Janus nanofibrous membrane for oil/water emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Mao, X.; Kipper, M.J.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. Janus Polyacrylonitrile/Carbon Nanotube Nanofiber Membranes for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Mechanically robust Janus nanofibrous membrane with asymmetric wettability for high efficiency emulsion separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Han, N.; Han, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Design of a Janus F-TiO2@PPS Porous Membrane with Asymmetric Wettability for Switchable Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 22408–22418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, S. In Situ Generated Janus Fabrics for the Rapid and Efficient Separation of Oil from Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14610–14613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Rapid and Efficient Separation of Oil from Oil-in-Water Emulsions Using a Janus Cotton Fabric. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lehtinen, M.; Liu, G. Universal Janus Filters for the Rapid Separation of Oil from Emulsions Stabilized by Ionic or Nonionic Surfactants. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13072–13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fang, W.; Jin, J.; Zhu, Y. Nanofibrous Janus membrane with improved self-cleaning property for efficient oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhu, L.; Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Ren, T.; Zhu, B.; Zeng, Z. Desert beetle-like microstructures bridged by magnetic Fe3O4 grains for enhancing oil-in-water emulsion separation performance and solar-assisted recyclability of graphene oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Chen, X.; Cai, S.; Yan, F.; Li, S.; Jin, S.; Zhu, H. A multifunctional heterogeneous superwettable coating for water collection, oil/water separation and oil absorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guan, M.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, J.; Shao, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Bioinspired Under-Liquid Dual Superlyophobic Surface for On-Demand Oil/Water Separation. Langmuir 2023, 39, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Mu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Inverse desert beetle-like ZIF-8/PAN composite nanofibrous membrane for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wei, P.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X. Liquid-assisted strategy for dual-purpose oil-water separation with super-omniphobic mesh. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Gammino, M. 3D wet-electrospun “branch leaf” graphene oxide polycaprolactone fibers structure for enhancing oil-water separation treatment performance in a multi-scale design. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2025, 43, e01200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mi, X.; Li, Y.; Zhan, S. 3D Graphene-Based Macrostructures for Water Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1806843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



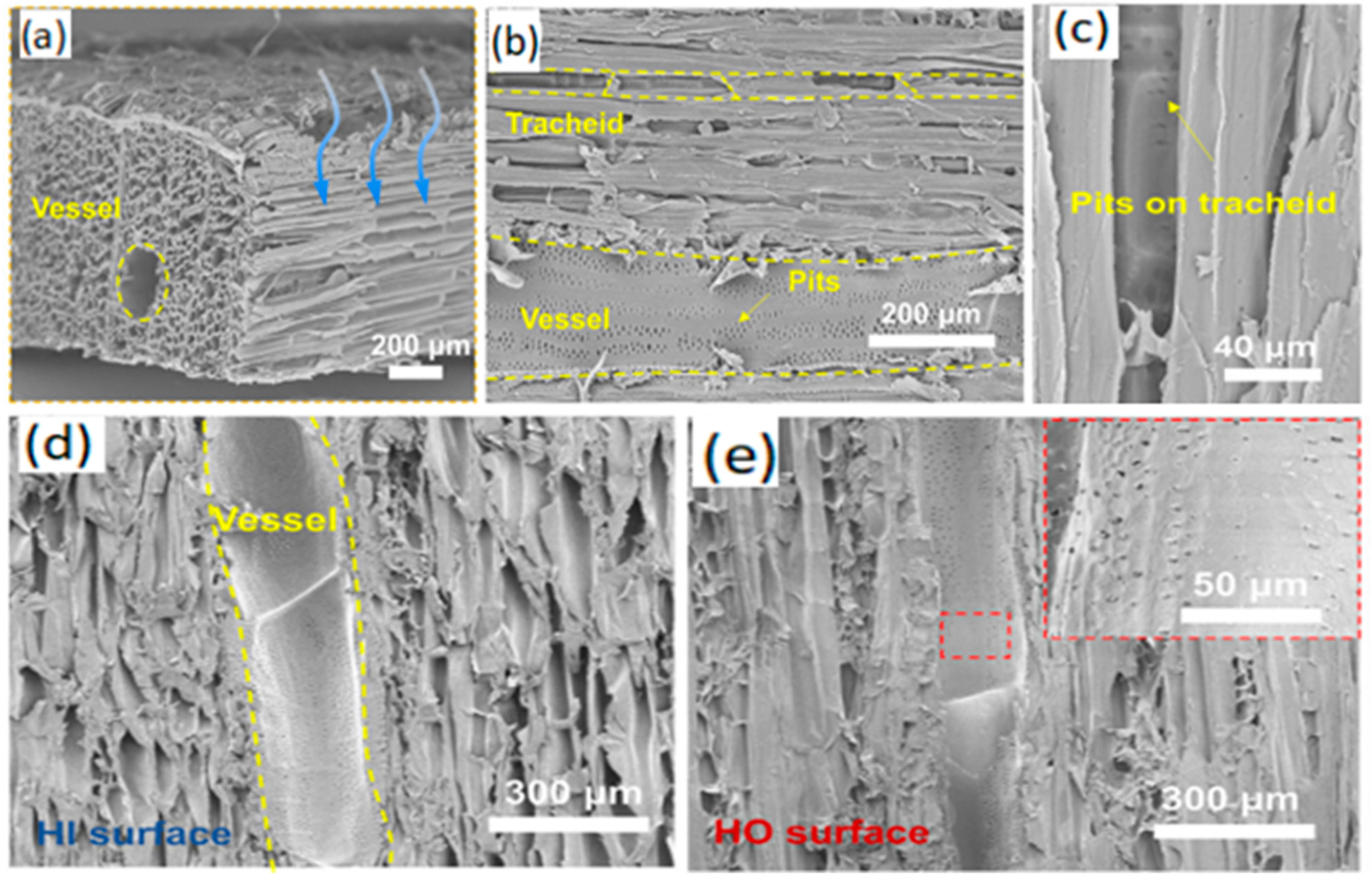
| References | Inadequateness |
|---|---|
| Jiang et al. [2,3,4] | Absence of dynamic wetting theory Limitations of the Wenzel/Cassie model |
| Tian et al. [5] | Lack of harmonized anti-wear test standards |
| Lack of data support for long-term durability | |
| Milionis et al. [6] | Limited adsorption capacity for high viscosity oils Poorly environmentally friendly |
| Zhang et al. [7] Liang et al. [8,9,10,11,12] | Unsummarized separation strategy for oil–water membrane separation |
| Separation Strategy | Reference | Contact Angle | Advantage | Disadvantage | Typical Substrate Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superhydrophobic–Superoleophilic | Feng [1]; Rasouli [36] | WCA > 150° (e.g., 156.2° ± 2.8°), OCA ≈ 0° | Initially, it was mainly used for light oil separation (density < water) | Easily clogged by oil contamination Requires additional energy consumption High maintenance costs | Metal mesh, ceramic, fabric |
| Superhydrophilic– Superoleophobic | [26,46,47] | Superoleophobic under water: WCA < 5°, OCA under water ≥ 150°; superoleophobic in air: WCA ≈ 0°, OCA ≥ 150° | Underwater oleophobic; anti-pollution; easy to clean Superoleophobic in the air Can block oil and permeability | Underwater superoleophobicity: amphiphilic surface (oil penetration when water-free) Slow response to infiltrative transitions | Metal mesh, polymer film, electrospun film |
| Superhydrophilic–underwater superoleophobic | Zarghami [43] | WCA < 5°, underwater OCA ≥ 150° | It is highly resistant to pollution and can be recycled | Failure in a waterless environment; can allow oil droplets to penetrate pores | Same as superhydrophilic–superolepophobic |
| Superhydrophilic–superoleophilic | Xiong [48] Tao [49] | Switchable wettability: hydrophobic (oil-pre-soaked)/oleophobic (water-pre-soaked). | High environmental adaptability Active filter phase selection | Dried state: reduced separation capacity (prewetted solution) | Metal mesh, composite film |
| Responsive | [36,44,45,50,51,52,53] | Switchable to “Water Block” or “Oil Block” | Flexibly adapt to different separation scenarios | Response speed, cycle stability and cost issues | Smart materials (e.g., temperature-sensitive/photopolymer-sensitive) |
| Researcher | Separation Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Zhang [60] | >99.8% |
| Cheng [65] | >99.5% |
| Yan [66] | >99.8% |
| Che [64] | >99% |
| 3D GBMs | PCLGO | |
|---|---|---|
| Flux | High | Extremely high |
| Rejection rate | >99% (adsorption-based) | 99.8% (emulsion separation) |
| Fouling resistance | Electrochemical regeneration (MB degradation) | Petroleum ether cleaning and regeneration |
| Suitability for stable emulsions | Requires assisted emulsion breaking (e.g., electrochemical or photocatalytic) | Designed for emulsions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Xing, T.; Wu, H.; Wei, K.; Souare, M.; Dong, C. Separation Principles and Strategies for an Oil–Water Separation Membrane with Special Wettability. Membranes 2025, 15, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080241
Hu X, Xing T, Wu H, Wei K, Souare M, Dong C. Separation Principles and Strategies for an Oil–Water Separation Membrane with Special Wettability. Membranes. 2025; 15(8):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080241
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaoying, Tong Xing, Huiyu Wu, Kunyu Wei, Mamadou Souare, and Changqing Dong. 2025. "Separation Principles and Strategies for an Oil–Water Separation Membrane with Special Wettability" Membranes 15, no. 8: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080241
APA StyleHu, X., Xing, T., Wu, H., Wei, K., Souare, M., & Dong, C. (2025). Separation Principles and Strategies for an Oil–Water Separation Membrane with Special Wettability. Membranes, 15(8), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080241





