Brackish Water Desalination Using Electrodialysis: Influence of Operating Parameters on Energy Consumption and Scalability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Field Sampling, and Chemical Analysis of Water Samples
2.2. Lab-Scale Electrodialysis Setup
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Characterization of the Brackish Water
3.2. Electrodialysis
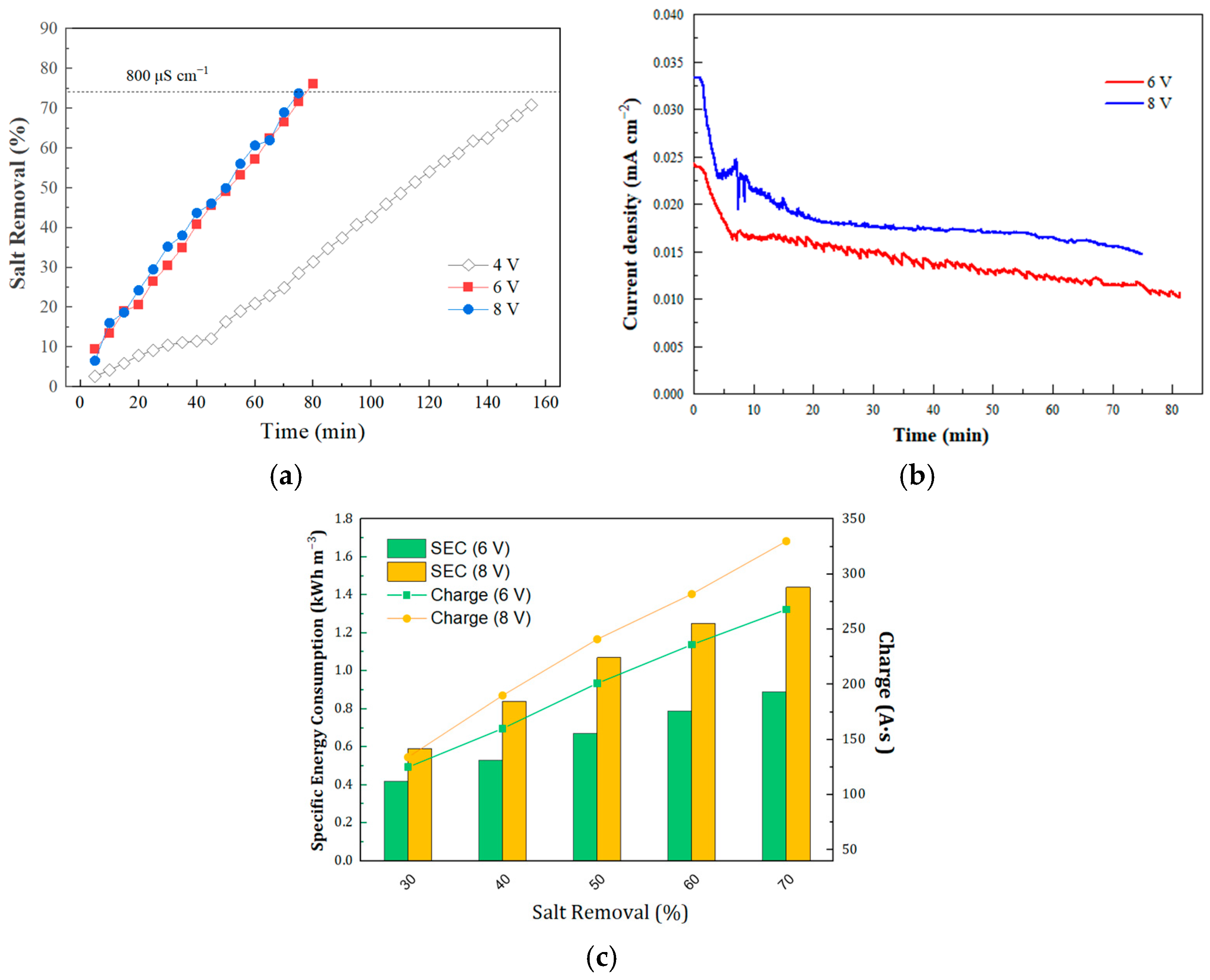
3.2.1. Effect of Voltage on Desalination Kinetics and Specific Energy Consumption
3.2.2. Impact of Water Recovery on Desalination Kinetics and Treatment Cost
| Membrane Pairs | Effective Membrane Area (m2) | Feed EC µS cm−1 | Water Sample | SEC kWh m−3 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.02 | 4800 | Synthetic | 1.24 | [21] |
| 10 | 0.02 | 3200–6250 | Synthetic | 1–2 | [21] |
| 14 | 0.18 | <4800 | Synthetic | 1.13 | [12] |
| 50 | 0.34 | 4800 | Synthetic | 0.50 | [21] |
| 50 | 0.34 | 7800 | Synthetic | 0.75 | [12] |
| 56 | 37.10 | <4800 | Synthetic | 0.73 | [56] |
| 6 | 0.08 | 3000 | Groundwater | 1.05 | This study |
3.2.3. Influence of Water Recovery and Ionic Composition on Specific Energy Consumption
3.2.4. Effect of the Diluted Volume and Cross-Flow Velocity
3.2.5. Concentrate Disposal and Reuse
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TWR | Theoretical Water Recovery |
| RWR | Real Water Recovery |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SEC | Specific Energy Consumption |
| RO | Reverse Osmosis |
| ED | Electrodialysis |
| CEM | Cation-Exchange Membranes |
| AEM | Anion-Exchange Membranes |
| IEM | Ion-Exchange Membrane |
| SEC | (Electrochemical) Specific Energy Consumption |
| SECp | Specific Energy Consumption of Pump |
| SECt | Total Specific Energy Consumption |
Appendix A

References
- Chatton, E.; Aquilina, L.; Pételet-Giraud, E.; Cary, L.; Bertrand, G.; Labasque, T.; Hirata, R.; Martins, V.; Montenegro, S.; Vergnaud, V.; et al. Glacial recharge, salinisation and anthropogenic contamination in the coastal aquifers of Recife (Brazil). Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Sudalaimuthu, K. Optimising groundwater recharge to counteract seawater intrusion through an inverse modelling approach and identifying efficient recharge structure locations. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Ruiz, J.I.; Barcia-Carreño, M.B.; Mejía-Bustamante, L.J.; Cornejo-Pozo, Á.K.; Salas-Vázquez, C.A.; Valverde-Armas, P.E. Assessment of the Performance of a Water Treatment Plant in Ecuador: Hydraulic Resizing of the Treatment Units. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Oyola, S.; Carrión Mero, P.; Romero Crespo, P. Ecuadorian Aquifer Studied for Marine Intrusion; IAEA—International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharikhina, L.V.; Lesnikova, P.S.; Kerimzade, V.V. Exploring secondary contamination in river and spring waters: A novel phenomenon arising from seawater intrusion into deep coastal aquifers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 211, 117364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, R.; Khan, K.M.; Dibaba, D.T.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Islam, M.Z. Health Implications of Drinking Water Salinity in Coastal Areas of Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vineis, P.; Chan, Q.; Khan, A. Climate change impacts on water salinity and health. J. Epidemiology Glob. Heal. 2011, 1, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UNICEF. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2017 Special Focus on Inequalities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Islam, M.S.; Sultana, A.; Saadat, A.H.M.; Islam, M.S.; Shammi, M.; Uddin, M.K. Desalination Technologies for Developing Countries: A Review. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filian, K.; Mendez-Ruiz, J.I.; Garces, D.; Reveychuk, K.; Ma, L.; Melendez, J.R.; Díaz-Mendoza, C.; Cornelissen, E.; Valverde-Armas, P.E.; Gutierrez, L. The Effect of pH on Aniline Removal from Water Using Hydrophobic and Ion-Exchange Membranes. Water 2025, 17, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyburo-Chávez, C.; Mendez-Ruiz, J.I.; Jiménez-Oyola, S.; Romero-Crespo, P.; Gutierrez, L.; Valverde-Armas, P.E. Pilot-scale reverse osmosis treatment of gold cyanidation effluent for the removal of cyanide, heavy metal(loid)s, and ionic species. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Elimelech, M. Energy Consumption of Brackish Water Desalination: Identifying the Sweet Spots for Electrodialysis and Reverse Osmosis. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.M.; Williams, M.; Paiva, M.; Demydov, D.; Do, T.D.; Fairey, J.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Hestekin, J.A. Potential of electrodialytic techniques in brackish desalination and recovery of industrial process water for reuse. Desalination 2017, 409, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walha, K.; Amar, R.B.; Firdaous, L.; Quéméneur, F.; Jaouen, P. Brackish groundwater treatment by nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis in Tunisia: Performance and cost comparison. Desalination 2007, 207, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariman, H.; Shafieian, A.; Khiadani, M. Small scale desalination technologies: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2023, 567, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.C.; Winter, A.G. Justification for community-scale photovoltaic-powered electrodialysis desalination systems for inland rural villages in India. Desalination 2014, 352, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilat, B. Practice of water desalination by electrodialysis. Desalination 2001, 139, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.G.; Barad, D.; Swaminathan, J. Desalination using pressure or electric field? A fundamental comparison of RO and electrodialysis. Desalination 2022, 530, 115620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Patel, S.K.; Elimelech, M. Correlation equation for evaluating energy consumption and process performance of brackish water desalination by electrodialysis. Desalination 2021, 510, 115089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.; Sotoca, J.; Expósito, E.; Gallud, F.; García-García, V.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Brackish water desalination by electrodialysis: Batch recirculation operation modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Qin, M.; Walker, W.S.; Elimelech, M. Energy Efficiency of Electro-Driven Brackish Water Desalination: Electrodialysis Significantly Outperforms Membrane Capacitive Deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3663–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Tufa, R.A.; Macedonio, F.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Membrane technology in renewable-energy-driven desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen QVan Nguyen, T.T.N.; Tran, T.S.; Doan, D.C.T.; Dang, T.M.D.; Dang, C.M. Designing, fabricating and testing at a laboratory scale a water desalination system using electrodialysis. J. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2022, 6, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, L.J.; Kruttschnitt, T.W.; Schäfer, A.I. Desalination using electrodialysis as a function of voltage and salt concentration. Desalination 2007, 205, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, T. Treatment of sea water using electrodialysis: Current efficiency evaluation. Desalination 2009, 249, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, T. Sea water desalination using electrodialysis. Desalination 2008, 221, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMadani, H.M.N. Water desalination by solar powered electrodialysis process. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, N. Solar photovoltaic desalination of brackish water in remote areas by electrodialysis. Desalination 1994, 98, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, E.; Elazhar, M.; Hafsi, M.; Elmidaoui, A. Performances of electrodialysis process in desalination of brackish waters at various salinities and voltage. Int. J. Adv. Chem. 2014, 2, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uche, J.; Círez, F.; Bayod, A.A.; Martínez, A. On-grid and off-grid batch-ED (electrodialysis) process: Simulation and experimental tests. Energy 2013, 57, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herawati, H.; Kartini Akbar, A.A.; Abdurrahman, T. Strategy for Realizing Regional Rural Water Security on Tropical Peatland. Water 2021, 13, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Ruiz, J.I.; Medina-Toala, A.N.; Gutierrez, L.; Valverde-Armas, P.E. Comparative evaluation of an advanced electrocoagulation treatment system versus a conventional lime softening treatment for removing Ca2+, SO42−, and Mn in groundwater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veolia América Latina & Iberia. Veolia Ecuador Realiza su Primera Planta Desalinizadora en la Isla de Puná; Veolia Ecudor: Guayaquil, Guayas, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, Fourth Edition, Incorporating The First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Enviromental Protection Agency (EPA). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Dietrich, A.M.; Burlingame, G.A. Critical Review and Rethinking of USEPA Secondary Standards for Maintaining Organoleptic Quality of Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioglu, M.; Kabay, N.; Kurucaovali, I.; Ersoz, E. Demineralization by electrodialysis (ED)—separation performance and cost comparison for monovalent salts. Desalination 2003, 153, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Ladshaw, A.; Bartholomew, T.V.; Atia, A.A.; Allu, S.; Dudchenko, A.V. Nonlinear programming optimization of a single-stack electrodialysis desalination system for cost efficiency. Desalination 2025, 601, 118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B.; Pourcelly, G. Ion Transfer in and Through Charged Membranes: Structure, Properties, and Theory. In Ionic Interactions in Natural and Synthetic Macromolecules; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 267–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledingham, J.; Sedransk Campbell, K.L.; In ’t Veen, B.; Keyzer, L.; Campbell, A.N. Barriers to electrodialysis implementation: Maldistribution and its impact on resistance and limiting current density. Desalination 2022, 531, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-B.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.-F.; Wang, J.; Dong, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. An emerging pilot-scale electrodialysis system for desalination of SWNF permeate: Evaluating the role of typical factors. Desalination 2022, 542, 116064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Káňavová, N.; Machuča, L.; Tvrzník, D. Determination of limiting current density for different electrodialysis modules. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Urtenov, M.K.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Han, J.; Sistat, P.; Pourcelly, G. Desalination at overlimiting currents: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Desalination 2014, 342, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belashova, E.D.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Sistat, P.; Pourcelly, G. Current-voltage characteristic of anion-exchange membrane in monosodium phosphate solution. Modelling and experiment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.; Urtenov, M.; Mareev, S.; Pourcelly, G. Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Water Splitting on Ion Transfer in the Depleted Diffusion Layer Near an Ion-Exchange Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, P.; Ortiz, J.M.; Richards, B.S.; Schäfer, A.I. Electrodialytic removal of NaCl from water: Impacts of using pulsed electric potential on ion transport and water dissociation phenomena. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 435, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, S.M.; Manukyan, G.; Staicu, A.; Rubinstein, I.; Zaltzman, B.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Mugele, F.; Wessling, M. Direct Observation of a Nonequilibrium Electro-Osmotic Instability. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 236101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, M.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Biesheuvel, P.M. Nernst-Planck transport theory for (reverse) electrodialysis: II. Effect of water transport through ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. Encyclopedia of Membranes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Shehzad, M.A.; Jiang, C.; Fu, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, T. Multistage-batch electrodialysis to concentrate high-salinity solutions: Process optimisation, water transport, and energy consumption. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, A.; Shi, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Cheng, S. Separation of NaCl and humic substances in anion exchange spent brine with electrodialysis. Desalination 2022, 523, 115442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Saakes, M.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Post, J.W. Seawater predesalination with electrodialysis. Desalination 2014, 342, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.C.; Shah, S.R.; Amrose, S.E.; Winter, A.G. A robust model of brackish water electrodialysis desalination with experimental comparison at different size scales. Desalination 2018, 443, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Haralambous, K.-J.; Loizidou, M. Desalination brine disposal methods and treatment technologies-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankoliya, D.; Mudgal, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Davies, P.; Licon, E.; Alegre, R.R.; Patel, V.; Patel, J. Design and optimization of electrodialysis process parameters for brackish water treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornbusch, G.J.; Tedesco, M.; Post, J.W.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Experimental investigation of multistage electrodialysis for seawater desalination. Desalination 2019, 464, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.; Kotoka, F.; Mendez, J.; Bossuyt, M.; Alhadidi, A.; Kourou, A.; Ouyang, Y.; Van Geem, K.M.; Valverde, P.; Cornelissen, E. Impact of Temperature, Membrane Type, and Process Parameters in Seawater Acidification Using Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. ACS Sustain. Resour. Manag. 2025, 2, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, E.; Sandeaux, J.; Persin, F.; Pourcelly, G.; Dornier, M.; Ruales, J. Deacidification of clarified tropical fruit juices by electrodialysis. Part, I. Influence of operating conditions on the process performances. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Abdu, S.; Wessling, M. Selectivity of ion exchange membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, S.; Cao, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X. Study on mass transfer performance and membrane resistance in concentration of high salinity solutions by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długołęcki, P.; Anet, B.; Metz, S.J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. Transport limitations in ion exchange membranes at low salt concentrations. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Le Henaff, A.-C.; Amrose, S.; Buonassisi, T.; Peters, I.M.; Winter, A.G. Voltage- and flow-controlled electrodialysis batch operation: Flexible and optimized brackish water desalination. Desalination 2021, 500, 114837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, L.; Ghassemi, A. Effects of operating conditions on ion removal from brackish water using a pilot-scale electrodialysis reversal system. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 8657–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Concentration polarization in ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis—The events arising in a flowing solution in a desalting cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, T.; Broeke, J.v.D.; Platteau, I.; Rijnaarts, T.; Alhadidi, A.; Gutierrez, L.; Cornelissen, E. Water reuse and resource recovery from greenhouse wastewater by capacitive electrodialysis at pilot scale. Desalination 2024, 583, 117669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, L.J.; Styan, C.A. The use of simulated whole effluents in toxicity assessments: A review of case studies from reverse osmosis desalination plants. Desalination 2015, 368, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, J.; Senanayake, P.S.; Lugo, A.; Xu, P.; Walker, W.S.; Wang, H.; Allu, S. Optimal design of power constrained bipolar membrane electrodialysis over a wide brine range. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 517, 163497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Item | Sample Type | Code | pH | EC (µS cm−1) | TDS (mg L−1) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Groundwater | P3 | 7.7 | 3070 | 1471 | 1.2 |
| 2 | Groundwater | P4 | 7.9 | 1219 | 564 | 0.4 |
| 3 | Groundwater | P5 | 7.5 | 2890 | 1410 | 0.6 |
| 4 | Groundwater | P6 | 8.5 | 1916 | 969 | 2.5 |
| 5 | Channel | P7 | 7.2 | 136 | 65 | 7.5 |
| 6 | Channel | P8 | 7.7 | 146 | 70 | 4.8 |
| 7 | Channel | P9 | 7.3 | 109 | 49 | 10.4 |
| 8 | Surface water | P1 | 7.7 | 3250 | 1709 | 4.1 |
| 9 | Surface water | P2 | 7.8 | 2010 | 1039 | 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina-Toala, A.N.; Valverde-Armas, P.E.; Mendez-Ruiz, J.I.; Franco-González, K.; Verdezoto-Intriago, S.; Vitvar, T.; Gutiérrez, L. Brackish Water Desalination Using Electrodialysis: Influence of Operating Parameters on Energy Consumption and Scalability. Membranes 2025, 15, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080227
Medina-Toala AN, Valverde-Armas PE, Mendez-Ruiz JI, Franco-González K, Verdezoto-Intriago S, Vitvar T, Gutiérrez L. Brackish Water Desalination Using Electrodialysis: Influence of Operating Parameters on Energy Consumption and Scalability. Membranes. 2025; 15(8):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080227
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina-Toala, Angie N., Priscila E. Valverde-Armas, Jonathan I. Mendez-Ruiz, Kevin Franco-González, Steeven Verdezoto-Intriago, Tomas Vitvar, and Leonardo Gutiérrez. 2025. "Brackish Water Desalination Using Electrodialysis: Influence of Operating Parameters on Energy Consumption and Scalability" Membranes 15, no. 8: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080227
APA StyleMedina-Toala, A. N., Valverde-Armas, P. E., Mendez-Ruiz, J. I., Franco-González, K., Verdezoto-Intriago, S., Vitvar, T., & Gutiérrez, L. (2025). Brackish Water Desalination Using Electrodialysis: Influence of Operating Parameters on Energy Consumption and Scalability. Membranes, 15(8), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080227









