Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Ion Separation: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Synthesis of COF Membranes
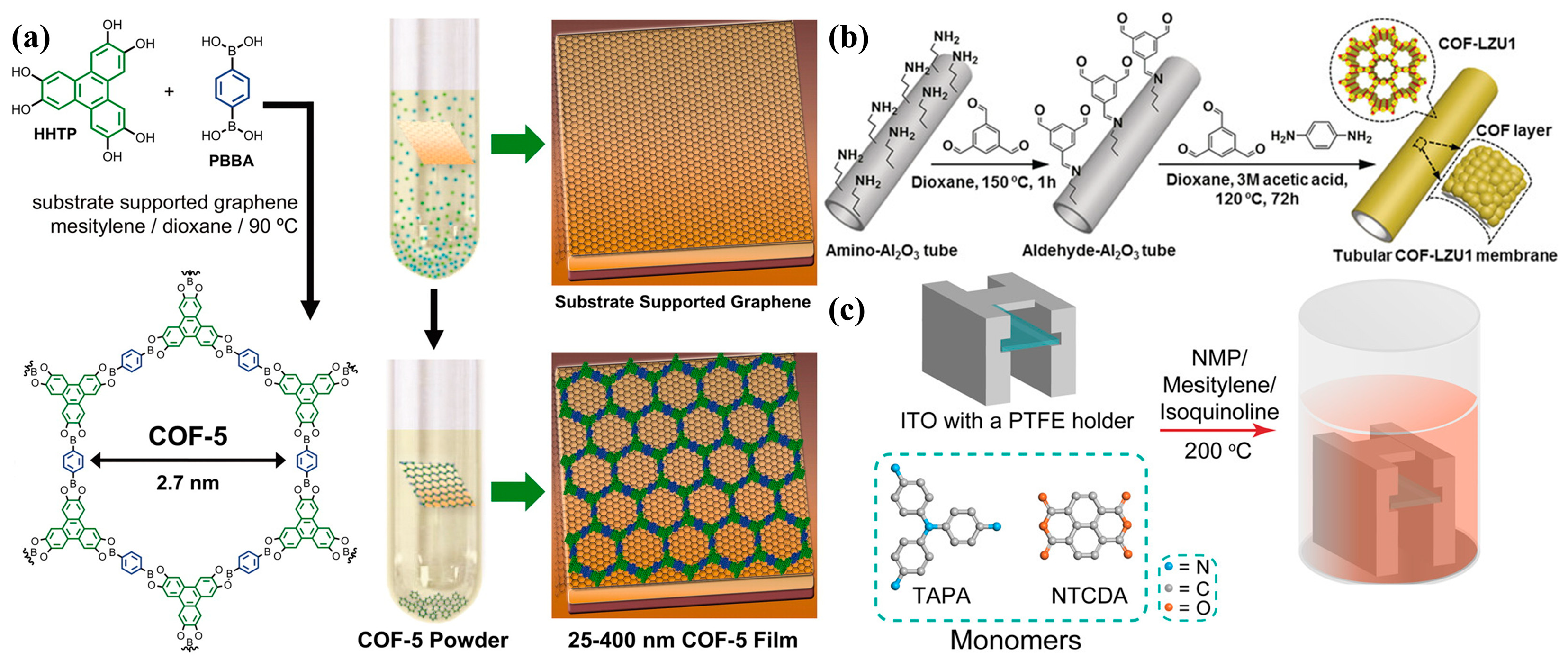
2.1. Solvothermal Synthesis
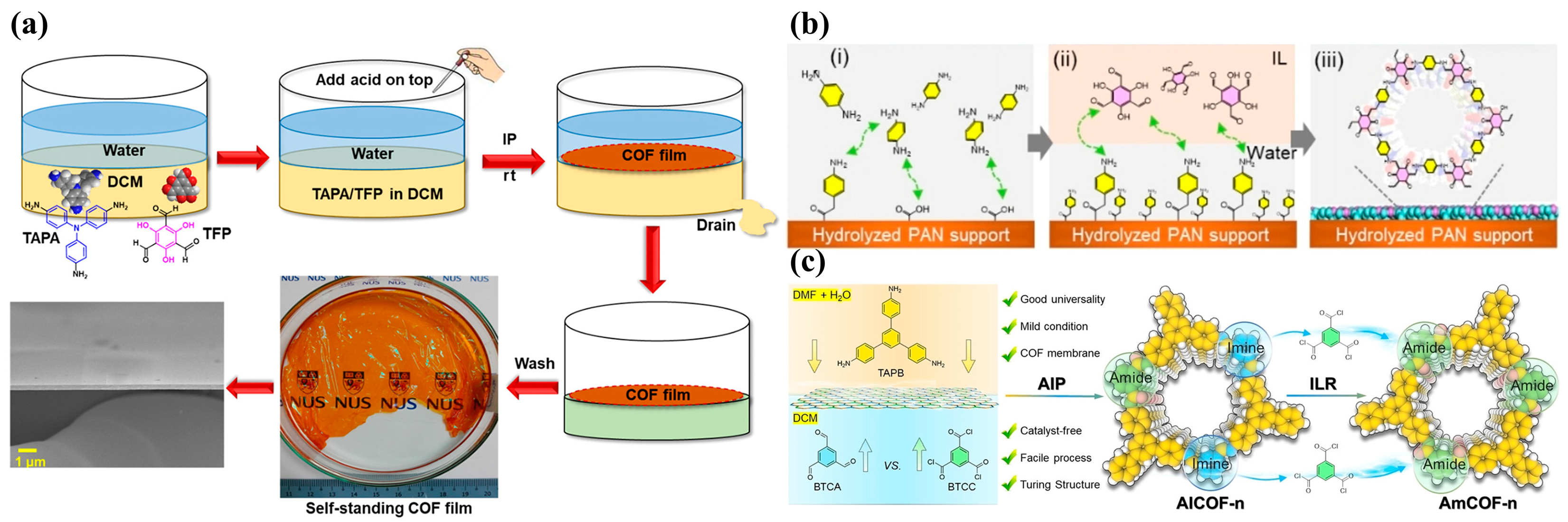
2.2. Interfacial Synthesis
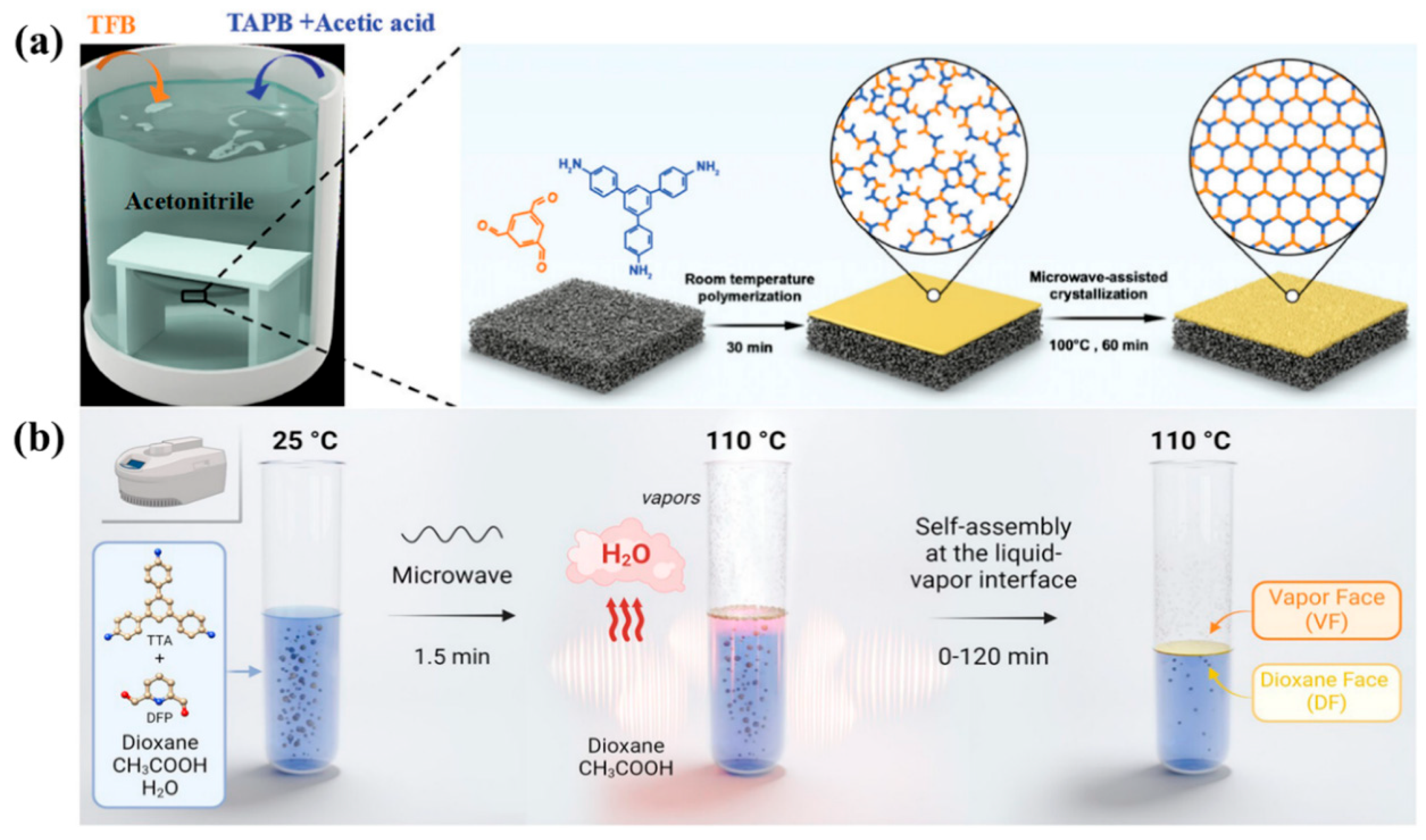
2.3. Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis
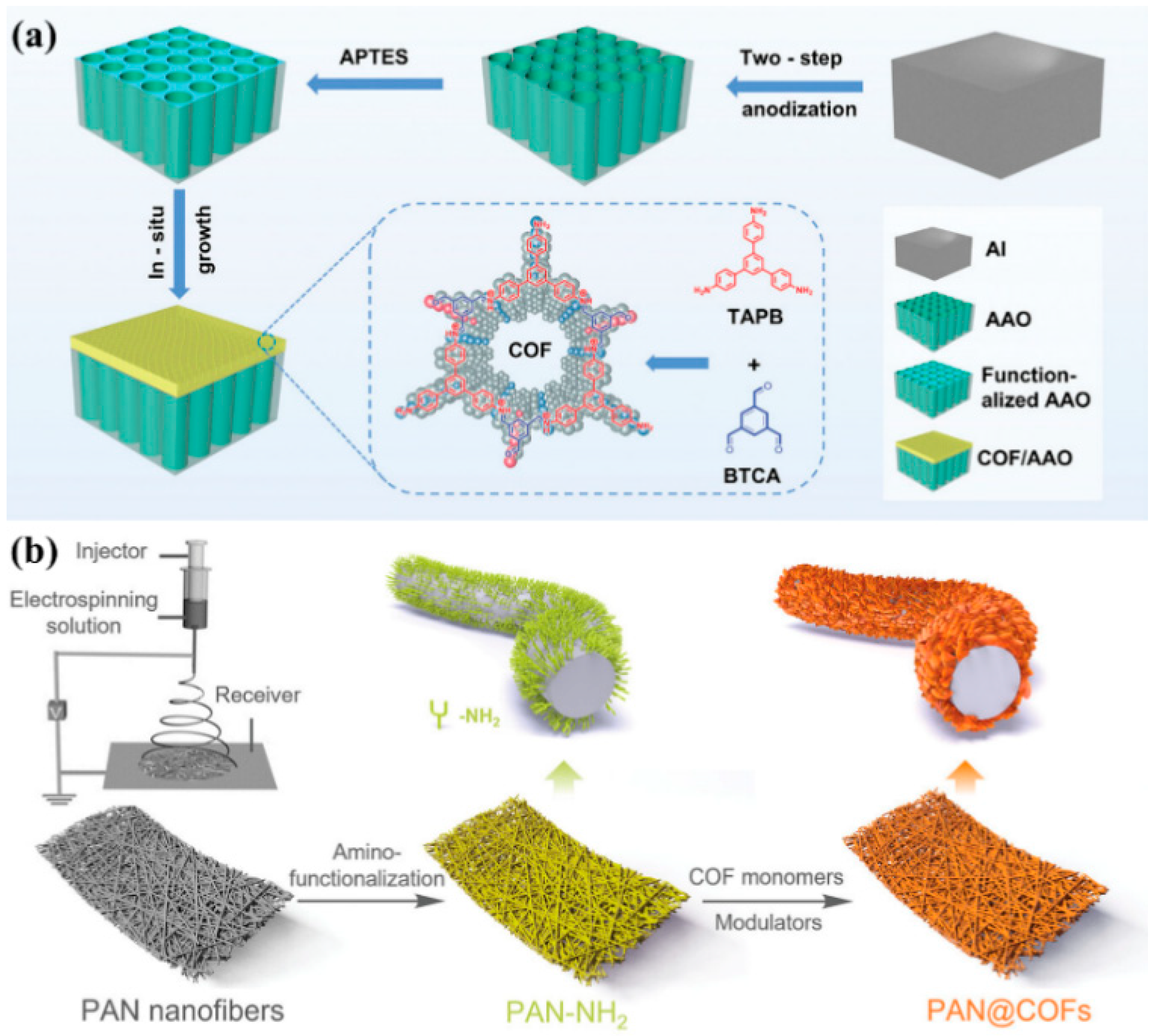
2.4. In Situ Growth
2.5. Comparison of the Synthesis Methods
3. Separation Mechanisms in COF Membranes
4. Ion Separation and Application
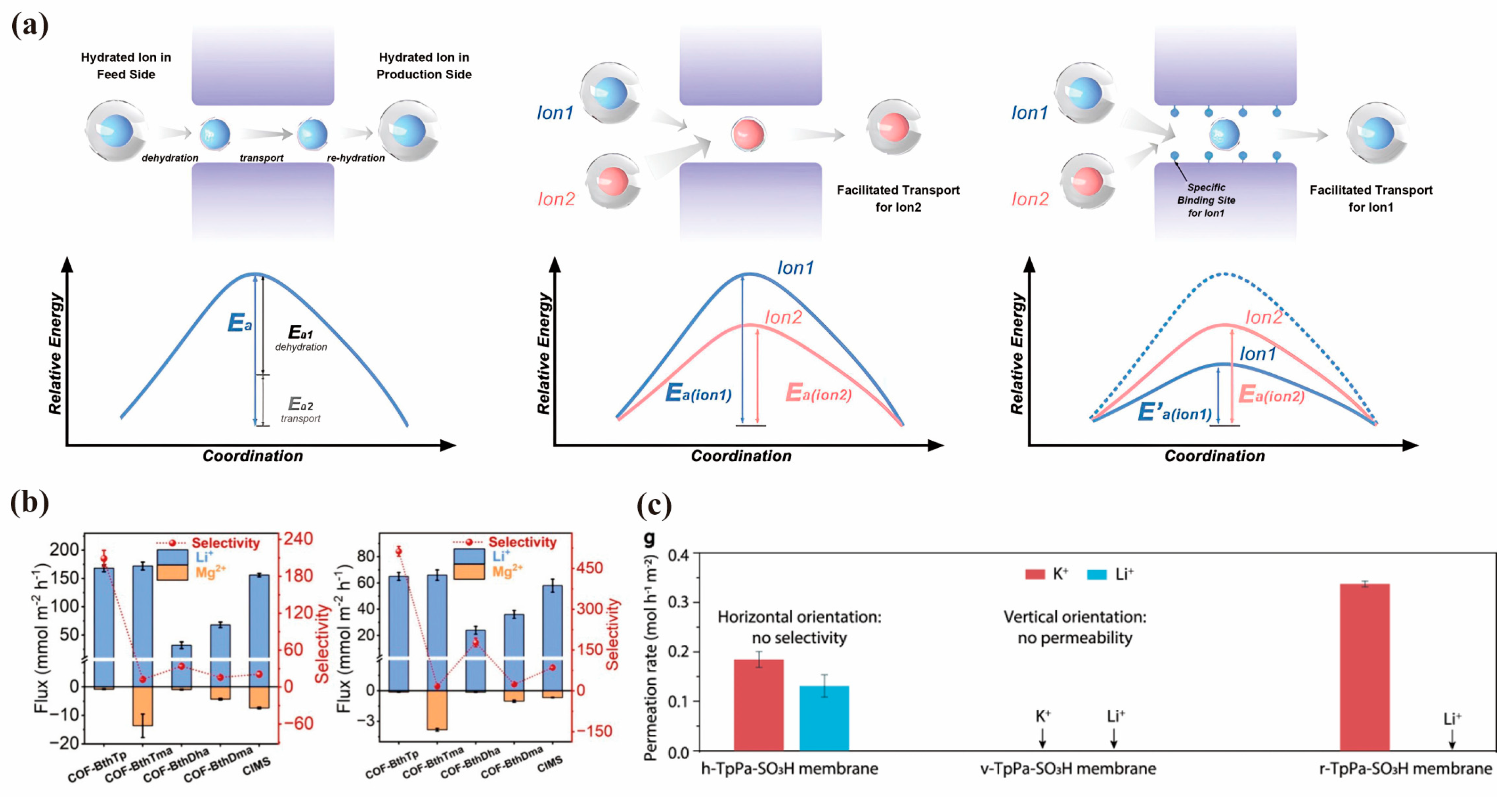
4.1. Separation Driven by Pressure
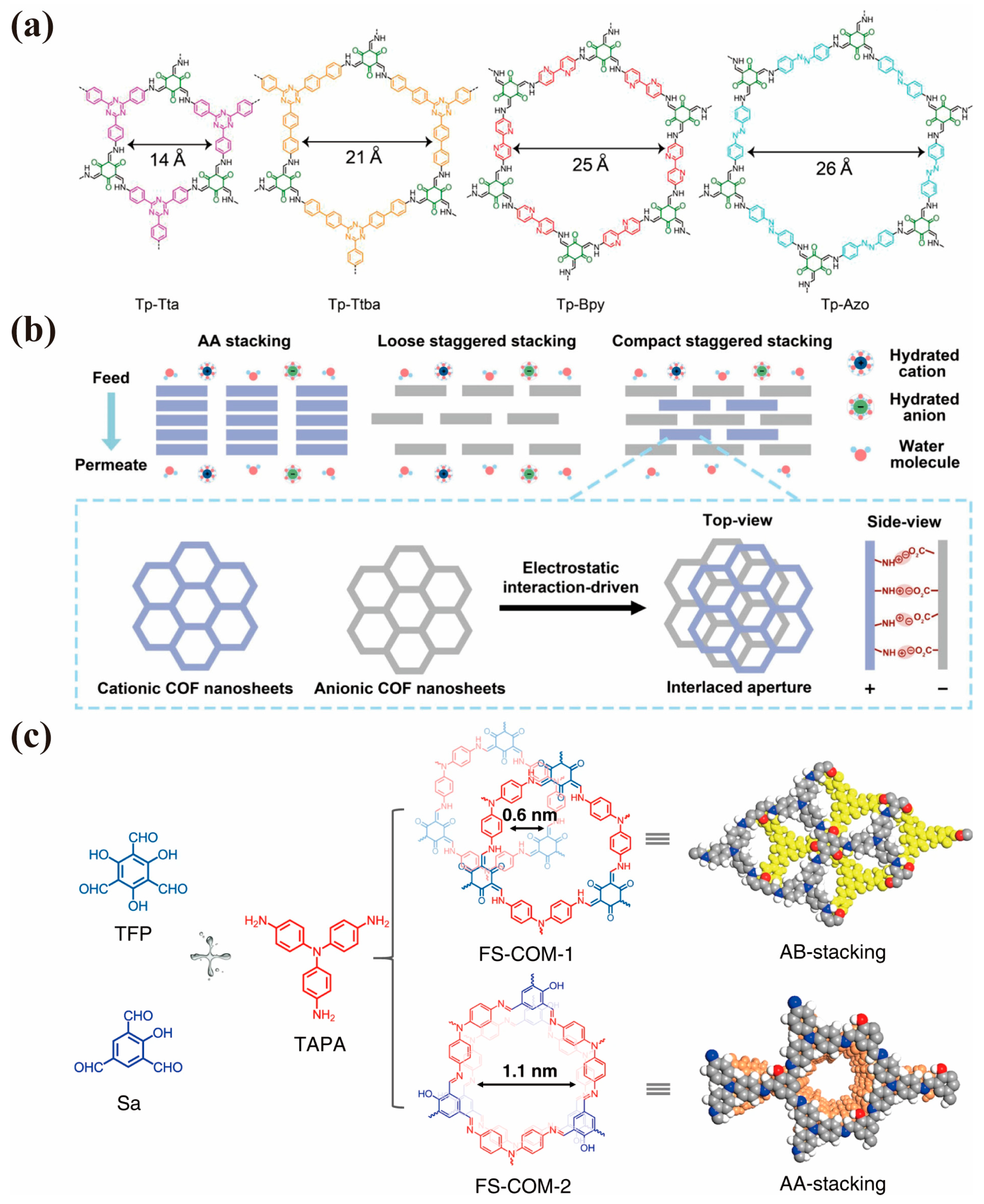
4.2. Separation Driven by Electric-Field
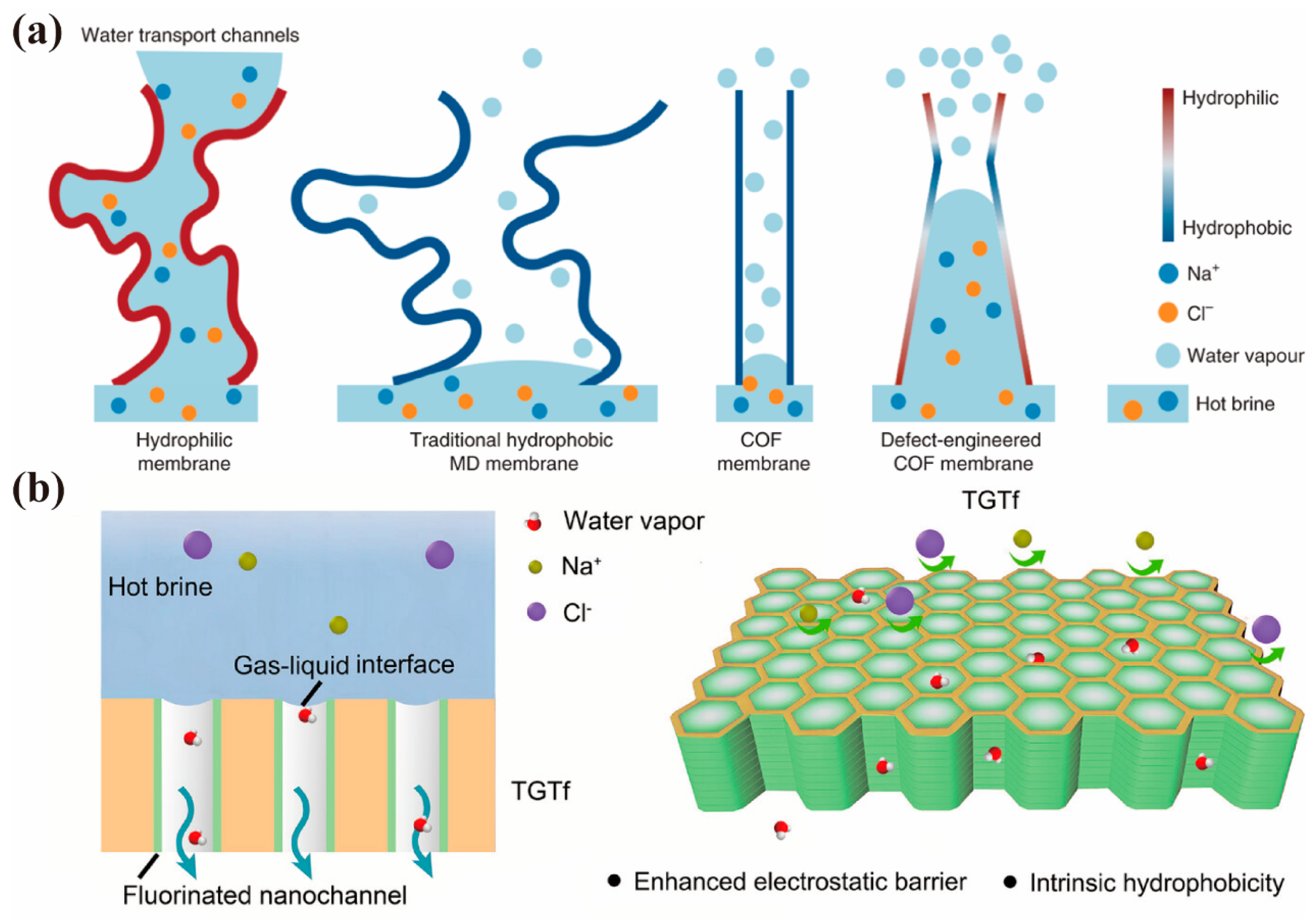
4.3. Separation Driven by Vapor-Pressure
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| COF | Covalent organic framework. |
| MF | Microfiltration. |
| UF | Ultrafiltration. |
| NF | Nanofiltration. |
| RO | Reverse osmosis. |
| ED | Electrodialysis. |
| CDI | Capacitive deionization. |
| MD | Membrane distillation. |
| PV | Pervaporation. |
| 1D | One-dimensional. |
| 2D | Two-dimensional. |
| 3D | Three-dimensional. |
| NiPc-PBBA-COF | Ni phthalocyanine 1,4-phenyl enebis(boronic acid) COF. |
| SLG | Single-layer graphene. |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. |
| TFB | 1,3,5-triformylbenzene. |
| D-A | Donor–acceptor. |
| ITO | Indium tin oxide. |
| PI-NT | Polyimide. |
| SAIP | Scraping-assisted interface aggregation. |
| AICOF | Amide and imine bilinker COF. |
| AmCOF | Amide-linked COF. |
| IL–H2O | Ionic liquid-H2O. |
| Tp | 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol. |
| Pa | P-phenylenediamine. |
| FPBA | 4-formylphenylboronic acid. |
| TTA-DFP-COF | 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl)trianiline 2,6-diformylpyridine COF. |
| TFB-TAPB | 1,3,5-triformylbenzene tris(4-aminophenyl)amine |
| AAO | Anodic aluminum oxide. |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile. |
| OFX | Ofloxacin. |
| LS | Liquid–solid interface. |
| LL | Liquid–liquid interface. |
| Bpy | 2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-diamine. |
| Azo | 4,4′-azodianiline. |
| Ttba | 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl) tris(1,1′-biphenyl) trianiline. |
| Tta | 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl) trianiline. |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds. |
| Tp-Bpy | 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol 2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-diamine. |
| Tp-Azo | 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol 4,4′-azodianiline. |
| Tp-Tta | 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl) trianiline. |
| Tp-Ttba | 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl) tris(1,1′-biphenyl) trianiline. |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride. |
| CPI | Crosslinked polyimide. |
| Dha | 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde. |
| TGcl | Triaminoguanidinium chloride. |
| LP-COF | Large-pore COF. |
| RhB | Rhodamine B. |
| TC | Tetracycline antibiotic. |
| CNFs | cellulose nanofibers |
| TGTf | Triaminoguanidinium hydrochloride-tetrafluoroterephthalaldehyde. |
| Pa-SO3H | 2,5-diaminobenzenesulfonic acid. |
| Bth | Benzene-1,3,5-tricarbohydrazide. |
| Tma | 2,4,6-trimethoxybenzene-1,3,5-tricarbaldehyde. |
| Dma | 2,5-dimethoxyterephthalaldehyde. |
| MMMs | Mixed matrix membranes. |
References
- Cheng, M.; Mi, K.; Han, S.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, S. A critical review on graphene-based membrane for ion separation: Mechanisms, research status, and development prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaed, M.A.; Saidur, R.; Saleque, A.M.; Tan, K.H.; Cherusseri, J.; Pandey, A.K.; Kabir, M.M. Unlocking desalination’s potential: Harnessing MXene composite for sustainable desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, A.; Alabaiadly, Y. Emerging technologies in water desalination: A review and future outlook. Energy Nexus 2025, 17, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Lv, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Huang, X. Recovery of heavy metal complexes from wastewaters: A critical review of mechanisms and technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Metal–organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werber, J.R.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.-X.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Pan, D.-W.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.-Y. Biomimetic Two-Dimensional Composited Membranes for Ion Separation and Desalination. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 14772–14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namla, D.; Oves, M.; Alshaeri, M.A.; Al-Maaqar, S.M.; Issa, H.N.Y.; Mangse, G. Nanofiltration as an advanced wastewater treatment technique: A comprehensive review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juve, J.-M.A.; Christensen, F.M.S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauk, M.; Bechelany, M.; Sistat, P.; Habchi, R.; Cretin, M.; Zaviska, F. Ion-selectivity advancements in capacitive deionization: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2024, 572, 117146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, R.; Kaur, D.P.; Raj, S. Membrane Distillation for Sustainable Water Desalination: A Review of Principles, Materials, and Applications. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 236, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, S. Membrane Design Principles for Ion-Selective Electrodialysis: An Analysis for Li/Mg Separation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3552–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Qin, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, J.; Gui, Y.; Guo, H.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The membrane-based desalination: Focus on MOFs and COFs. Desalination 2023, 557, 116598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ding, X.; Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6010–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Sun, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J. Smart Solvent-Responsive Covalent Organic Framework Membranes with Self-regulating Pore Size. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Lyu, B.; Wu, P.; Fang, C.; Wang, G.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. A Responsive 3D Covalent Organic Framework Membrane with Tunable Pore Sizes for Molecular Sieving. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2505907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, B.; Ma, H. A two-dimensional cationic covalent organic framework membrane for selective molecular sieving. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13331–13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duan, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the stability of β-ketoenamine-Type covalent organic framework membranes in organic solvent. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 726, 124052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-H.; Chu, J.-Q.; Wang, W.-Z.; Qi, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X. A two-step solvothermal procedure to improve crystallinity of covalent organic frameworks and achieve scale-up preparation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Aramesh, N.; Sher, F.; Bilal, M. Covalent organic frameworks as robust materials for mitigation of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, M.; Liu, K.; Cao, H.; Yan, H. Covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 276, 119174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wu, H.; Guan, J.; You, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Shi, B.; Peng, Q.; Kong, Y.; et al. Scalable Fabrication of Crystalline COF Membranes from Amorphous Polymeric Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 18051–18058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandambeth, S.; Jia, J.; Wu, H.; Kale, V.S.; Parvatkar, P.T.; Czaban-Jóźwiak, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, X.; Ameur, Z.O.; Abou-Hamad, E.; et al. Covalent Organic Frameworks as Negative Electrodes for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Qi, Q.-Y.; Jiang, G.-F.; Cui, F.-Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X. Toward Covalent Organic Frameworks Bearing Three Different Kinds of Pores: The Strategy for Construction and COF-to-COF Transformation via Heterogeneous Linker Exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6736–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemont, A.; Matthys, G.; Lavendomme, R.; Van Der Voort, P. Mild and Scalable Conditions for the Solvothermal Synthesis of Imine-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202412420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, J.W.; Woll, A.R.; Mukherjee, A.; Levendorf, M.P.; Spitler, E.L.; Shields, V.B.; Spencer, M.G.; Park, J.; Dichtel, W.R. Oriented 2D Covalent Organic Framework Thin Films on Single-Layer Graphene. Science 2011, 332, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Knebel, A.; Caro, J. High-Flux Membranes Based on the Covalent Organic Framework COF-LZU1 for Selective Dye Separation by Nanofiltration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Li, X.; Feng, T.; Cai, S.; Chen, T.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y. Resistive Switching Memory Performance of Two-Dimensional Polyimide Covalent Organic Framework Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51837–51845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ding, L.; Xue, J.; Fan, H.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. Green and large-scale production of covalent organic framework nanofiltration membranes. Commun. Mater. 2025, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tsuchida, K.; Iwase, K.; Harada, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Kamiya, K. Metal-doped bipyridine linked covalent organic framework films as a platform for photoelectrocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 11073–11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Valentino, L.; Stiehl, G.M.; Balch, H.B.; Corcos, A.R.; Wang, F.; Ralph, D.C.; Mariñas, B.J.; Dichtel, W.R. Lewis-Acid-Catalyzed Interfacial Polymerization of Covalent Organic Framework Films. Chem 2018, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Tripathi, B.P. Flexible covalent organic framework membranes with linear aliphatic amines for enhanced organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 16321–16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Ouyang, D.; Cai, Z.; Lin, Z. Dual-activation interfacial polymerization based anionic covalent organic framework nanofiltration membrane for high-flux dye separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ren, L.-F.; Ying, D.; Jia, J.; Shao, J. Electrospray interface-less polymerization to fabricate high-performance thin film composite polyamide membranes with controllable skin layer growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 632, 119369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Sheng, G.; Li, X.; Ostwal, M.; Emwas, A.-H.; Huang, K.-W.; Lai, Z. Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for High-Flux Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14342–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, K.; Pal, M.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu H, S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; Banerjee, R. Selective Molecular Separation by Interfacially Crystallized Covalent Organic Framework Thin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13083–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Zhao, C.; Sun, B.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Wan, L.-J.; Wang, D. Confined Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework Thin Films within Superspreading Water Layer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12152–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Gai, Y.N.; Gai, X.T.; Qin, J.; Wang, Z.G.; Cui, L.S.; Guo, H.; Jiang, M.Y.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, T.; et al. Interfacial synthesized covalent organic framework nanofiltration membranes for precisely ultrafast sieving. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, G.; Zhao, D.; Lu, K.; Gao, J.; Chung, T.-S. Self-standing and flexible covalent organic framework (COF) membranes for molecular separation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Liang, L.; Dong, L.; Meng, H. Membranes based on Covalent Organic Frameworks through Green and Scalable Interfacial Polymerization using Ionic Liquids for Antibiotic Desalination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202316315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Xu, H.; Qiu, S.; Ye, T.; Wang, T.; Shang, J.; Gu, C.; Kitagawa, S.; Li, L. Autocatalytic Interfacial Synthesis of Self-Standing Amide-Linked Covalent Organic Framework Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202423220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Guo, Y.-S.; Xie, H.-M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Guo, D.-S. Rapid microwave synthesis of dioxin-linked covalent organic framework for efficient micro-extraction of perfluorinated alkyl substances from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.L.; Clowes, R.; Ritchie, L.K.; Cooper, A.I. Rapid Microwave Synthesis and Purification of Porous Covalent Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Leng, W.; Ge, R.; Dai, X.; Gao, Y. Fabrication of a COF-5 membrane on a functionalized α-Al2O3 ceramic support using a microwave irradiation method. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Z. Microwave-Assisted Fabrication of Highly Crystalline, Robust COF Membrane for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyettou, F.; Jrad, A.; Matouk, Z.; Prakasam, T.; Hamoud, H.I.; Clet, G.; Varghese, S.; Das, G.; Khair, M.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Tunable Wettability of a Dual-Faced Covalent Organic Framework Membrane for Enhanced Water Filtration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 23537–23554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Guo, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, H. Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Efficient Chemicals Separation. Small Struct. 2021, 2, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, T.S.; Mahmood, J.; Yavuz, C.T. Covalent Organic Framework Membranes and Water Treatment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 3567–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, P.; Sasikumar, B.; Krishnan, S.A.G.; Arthanareeswaran, G. Covalent-organic porous framework (COF) integrated hybrid membranes for energy and environmental applications: Current and future perspectives. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 166, 105067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Xia, X.-H.; Wang, C. In Situ Growth of Imine-Bridged Anion-Selective COF/AAO Membrane for Ion Current Rectification and Nanofluidic Osmotic Energy Conversion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Pachfule, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Wu, M.; Thomas, A. Construction of Covalent Organic Framework Nanofiber Membranes for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics. Small 2023, 19, 2301200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Song, Z.; Du, J.; Yao, A.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Hassan, S.U.; Guan, J.; Liu, J. Covalent Organic Framework Membranes with Regulated Orientation for Monovalent Cation Sieving. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 27065–27076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwandin, D.D.; Page, K.A.; Tran, L.D.; Yao, Y.; Reidell, A.; Muratore, C.; Fang, Q.; Ruditskiy, A.; Hampton, C.M.; Kennedy, W.J.; et al. Orientation and morphology control in acid-catalyzed covalent organic framework thin films. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 8369–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Ding, D.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Tian, Z.; Tang, Z. Surface growth of highly oriented covalent organic framework thin film with enhanced photoresponse speed. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92573–92576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Xu, T.; Shehzad, M.A.; Wang, X.; Ge, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, T. Efficient Ion Sieving in Covalent Organic Framework Membranes with Sub-2-Nanometer Channels. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; You, X.; Khan, N.A.; Li, R.; Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Cao, L.; Long, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Photo-tailored heterocrystalline covalent organic framework membranes for organics separation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, C.; Long, J.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y. Covalent organic framework membranes with vertically aligned nanorods for efficient separation of rare metal ions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Shao, L.; Zhang, S. Membrane-Ion Interactions Creating Dual-Nanoconfined Channels for Superior Mixed Ion Separations. Adv. Mater. 2025, 2414898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, J.; Fang, C.; Zhu, L. Highly crystalline and robust covalent organic framework membranes for predictable solvent transport and molecular separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 19374–19383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z. Recent advances in the synthesis of covalent organic framework-based membranes and their applications for liquid-based separation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 185, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yuan, K.; Liu, Y.; Luo, B.; Wu, Q.; Bao, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, J. Recent advances in covalent organic framework-based membranes for water purification: Insights into separation mechanisms and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, J.; Uliana, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, M.; Van der Bruggen, B. The rapid emergence of two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-performance separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3773–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, S.; Jing, X.; Niu, Z.; Feng, X. Covalent organic framework-based membranes for liquid separation. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 3943–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Polyelectrolyte-modified covalent organic framework membranes for multivalent cation removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.-W.; Zhu, X.; Xian, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Dai, Z.; Yin, H.; Ma, S.; Sun, Q. Enhancing ion selectivity by tuning solvation abilities of covalent-organic-framework membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2316716121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, S.; Xian, W.; Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Hou, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L. Bio-inspired construction of ion conductive pathway in covalent organic framework membranes for efficient lithium extraction. Matter 2021, 4, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizumi, T.; Kim, K.; Li, H.; Govorunova, E.G.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Bertalan, É.; Bondar, A.-N.; Askari, A.; et al. Structures of channelrhodopsin paralogs in peptidiscs explain their contrasting K+ and Na+ selectivities. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebesskaya, A.P.; Balynin, A.V.; Yushkin, A.A.; Markelov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V. Ultrafiltration Separation of Crude Oil and Waste Oil. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2024, 6, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.E. Dielectric exclusion of ions from membranes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 193–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadaei, F.; Hoshyargar, V.; Shirazian, S.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Mass transfer simulation of ion separation by nanofiltration considering electrical and dielectrical effects. Desalination 2012, 284, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ju, T.; Xiong, S.; Wang, Y. Large-pore covalent organic frameworks for ultra-fast tight ultrafiltration (TUF). J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; Lin, G.; Ding, H.; Gao, C.; Mal, A.; Wang, C. Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks: From Topology Design to Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zheng, H.; Yusran, Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, S.; Fang, Q. Exploring high-connectivity three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks: Topologies, structures, and emerging applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 484–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Chen, F.; Fang, Q.; Qiu, S. Design and applications of three dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1357–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.-L.; Wei, L.; Zhou, B.; Tan, J.; Zhou, H.-L.; Zhang, Y.-B. Guest-Dependent Dynamics in a 3D Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Flexible and Robust Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Precise Separations under Extreme Conditions. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8355–8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Usadi, A.K.; Calabro, D.C.; Baugh, L.S.; Yu, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Aggregated Structures of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3192–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukose, B.; Kuc, A.; Heine, T. The Structure of Layered Covalent-Organic Frameworks. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, W.; Lang, X.; Zheng, L.; Cao, Q. Modulating the Stacking Model of Covalent Organic Framework Isomers with Different Generation Efficiencies of Reactive Oxygen Species. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29471–29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Control Interlayer Stacking and Chemical Stability of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks via Steric Tuning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16124–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Usadi, A.K.; Calabro, D.C.; Baugh, L.S.; Chai, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Tunable Interlayer Shifting in Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks Triggered by CO2 Sorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20363–20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, R.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, Y. Staggered-Stacking Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Molecular and Ionic Sieving. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 34698–34707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Nasir, N.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; et al. Covalent organic framework membranes through a mixed-dimensional assembly for molecular separations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B.; Wei, G.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Ma, L. Laminated self-standing covalent organic framework membrane with uniformly distributed subnanopores for ionic and molecular sieving. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wee, V.; Usadi, A.K.; Calabro, D.C.; Baugh, L.S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Interlayer Shifting in Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12995–13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rager, S.; Jakowetz, A.C.; Gole, B.; Beuerle, F.; Medina, D.D.; Bein, T. Scaffold-Induced Diketopyrrolopyrrole Molecular Stacks in a Covalent Organic Framework. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 2707–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.; Bessinger, D.; Reuter, S.; Calik, M.; Ascherl, L.; Hanusch, F.C.; Auras, F.; Bein, T. Oligothiophene-Bridged Conjugated Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8194–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Yang, B.; Tian, W.; Yang, X.; Zou, B. Boosting Multicolor Emission Enhancement in Two-Dimensional Covalent–Organic Frameworks via the Pressure-Tuned π–π Stacking Mode. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.d.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Metal Recovery from Wastewater Using Electrodialysis Separation. Metals 2024, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, R.; Qin, B.; Zhang, F.; Ren, L.; Yang, H.; Yuan, M. Selective Ion Separation by Capacitive Deionization: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2025, 18, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, E. Application of capacitive deionization technology in water treatment and coupling technology: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2024, 10, 2313–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Liang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, F.; et al. Ultrafast seawater desalination with covalent organic framework membranes. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Wang, M.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, Z. Molecular design of covalent−organic framework membranes for Li+/Mg2+ separation: Significant charge effect. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 662, 120976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, L.; Tang, Z. An efficient lithium extraction pathway in covalent organic framework membranes. Matter 2021, 4, 2666–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdardottir, S.B.; DuChanois, R.M.; Epsztein, R.; Pinelo, M.; Elimelech, M. Energy barriers to anion transport in polyelectrolyte multilayer nanofiltration membranes: Role of intra-pore diffusion. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, L.-L.; Liu, Z. Covalent organic framework membranes for lithium extraction: Facilitated ion transport strategies to enhance selectivity. Mater. Horiz. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Epsztein, R.; Zhan, C.; Li, W.; Fortner, J.D.; Pham, T.A.; Kim, J.-H.; Elimelech, M. Intrapore energy barriers govern ion transport and selectivity of desalination membranes. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, M.; Tang, M.; Sun, L.; Xiong, F.; Xie, L.; Zeng, G.; Ren, X.; Wang, K.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Sustainable lithium extraction and magnesium hydroxide co-production from salt-lake brines. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violet, C.; Ball, A.; Heiranian, M.; Villalobos, L.F.; Zhang, J.; Uralcan, B.; Kulik, H.; Haji-Akbari, A.; Elimelech, M. Designing membranes with specific binding sites for selective ion separations. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Shao, P.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Fast Ion Transport Pathway Provided by Polyethylene Glycol Confined in Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.-W.; Li, J.; Xing, Z.; Xian, W.; Lai, Z.; Dai, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yin, H.; Ma, S.; et al. Regulation of Ion Binding Sites in Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Enhanced Selectivity under High Ionic Competition. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 12080–12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Ma, Z.; Yu, L.; Li, Q.; Xia, J.; Song, S.; Sui, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, J. Randomly oriented covalent organic framework membrane for selective Li+ sieving from other ions. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, C.R.S.; Gómez, A.O.C.; Cotta, C.P.N.; Cotta, R.M. Comparison of Different Polymeric Membranes in Direct Contact Membrane Distillation and Air Gap Membrane Distillation Configurations. Membranes 2025, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Luo, T.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, R.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Recent Advances in Membrane Synthesis by Interfacial Polymerization for Pervaporation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2500708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nikolaeva, D.; Hartanto, Y.; Luis, P. MOF-based membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Alibakhshi, M.A.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, C. Exploring Ultimate Water Capillary Evaporation in Nanoscale Conduits. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 4813–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Jiang, C.; Fan, J.; Hong, S.; Mei, P.; Yao, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Hydrophilicity gradient in covalent organic frameworks for membrane distillation. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S.; Alibakhshi, M.A.; Lo, C.-W.; Lu, M.-C.; Duan, C. Ultrafast Diameter-Dependent Water Evaporation from Nanopores. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3363–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.J.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, L.-F.; Zhang, B.; Shao, J. Facile preparation of COF-LZU1 modified membrane via electrostatic spraying for emerging contaminants treatment in direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gui, L.; Qiao, D.; Tao, M.; Huang, S.; Tian, X. Fluorinated Covalent Organic Framework Membranes with Robust Wetting Resistance for Durable Membrane Distillation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202507913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, M.; Roy, S.; Bhowmick, K.; Majumdar, S.; Prihatiningtyas, I.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Mondal, P. Development of high performance pervaporation desalination membranes: A brief review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (COF-LZU1) based mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Synthesis Method | Orientation | Crystallinity | Substrate | Thickness | Defect | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvothermal synthesis |
| High |
|
| Relatively low | [26,27] |
| Interfacial synthesis |
| Moderate |
|
| Considerable | [52,53] |
| Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis |
| High |
|
| Low | [44,45] |
| In situ growth |
| Moderate |
|
| Low | [50,51,54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Lang, S.; Fan, J.; Ke, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xue, J. Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Ion Separation: A Review. Membranes 2025, 15, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070211
Lou Y, Wang Z, Yang W, Lang S, Fan J, Ke Q, Wang R, Zhang Z, Chen W, Xue J. Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Ion Separation: A Review. Membranes. 2025; 15(7):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070211
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Yutong, Zhanyong Wang, Wanbei Yang, Shuchen Lang, Jiaxing Fan, Qiaomei Ke, Rui Wang, Zhen Zhang, Wentao Chen, and Jian Xue. 2025. "Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Ion Separation: A Review" Membranes 15, no. 7: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070211
APA StyleLou, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, W., Lang, S., Fan, J., Ke, Q., Wang, R., Zhang, Z., Chen, W., & Xue, J. (2025). Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Ion Separation: A Review. Membranes, 15(7), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070211




