X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure Analysis Unravels How the Unique Thylakoid Lipid Composition Is Utilized by Cytochrome b6f for Driving Reversible Proteins’ Reorganization During State Transitions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-EM Structures of Cytochrome b6f
3.1.1. Characteristic Distances for the Conformational Dynamics of Cytb6f
3.1.2. The Cytochrome b6f Cryo-EM Structures Are More Swollen at the n-Side than the Cytbc1 Cryo-EM Structures
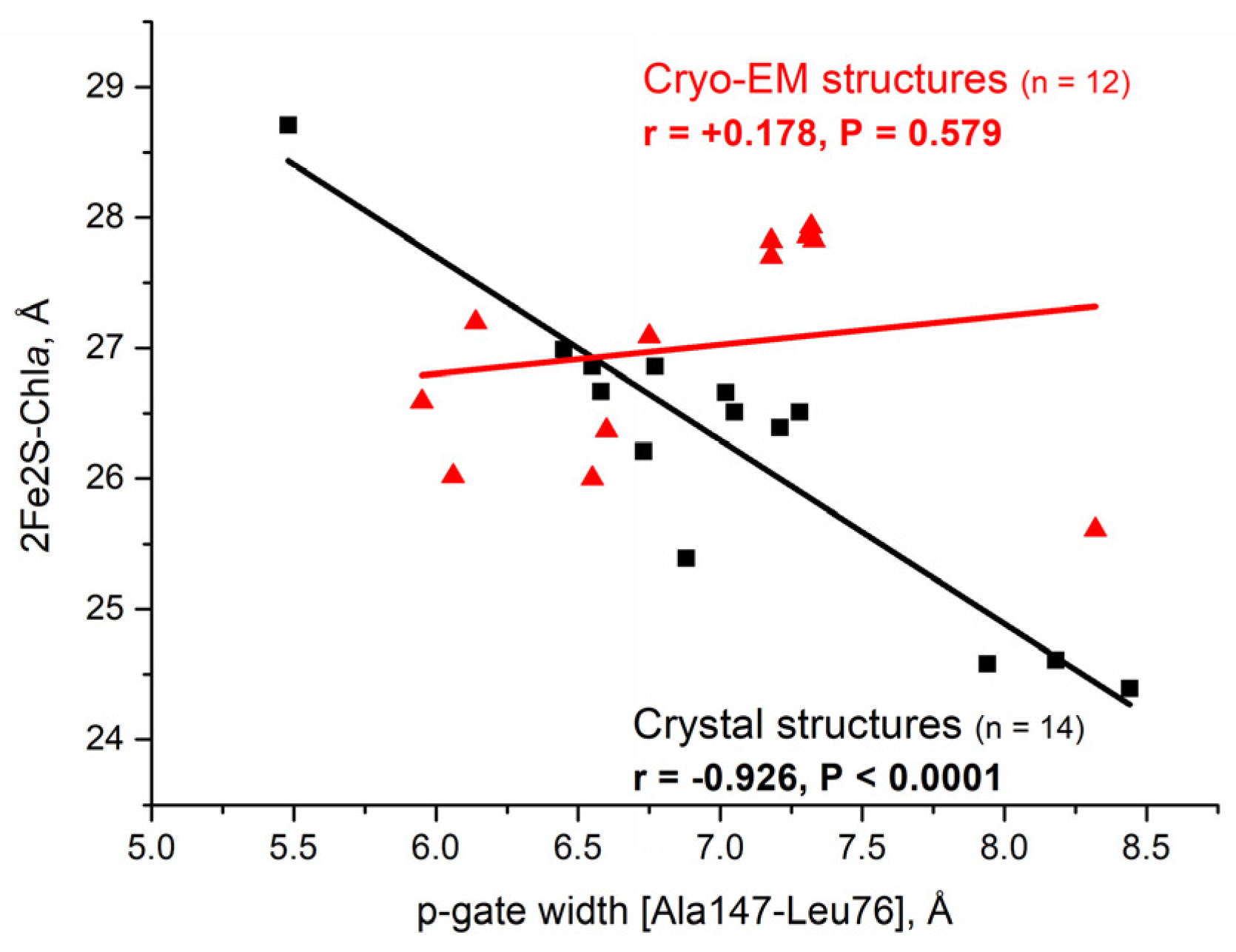
3.1.3. The Chlorophyll a Redox Sensor and Transmembrane Signal Transmission Role Is Not Active During the Q-Cycle
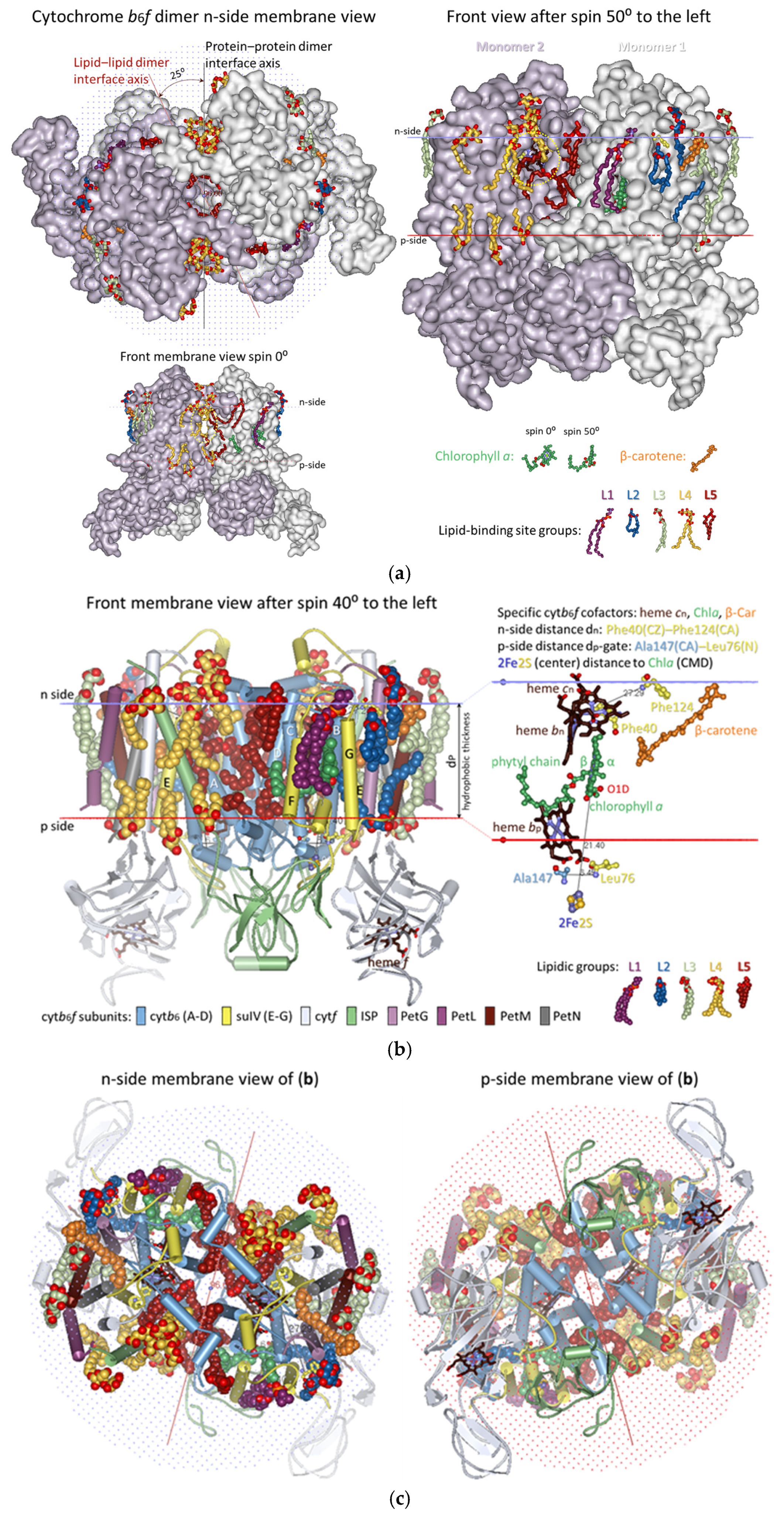
3.2. Lipid-Binding Sites of Cytb6f Under Optimal Conditions Under Low-Intensity Light
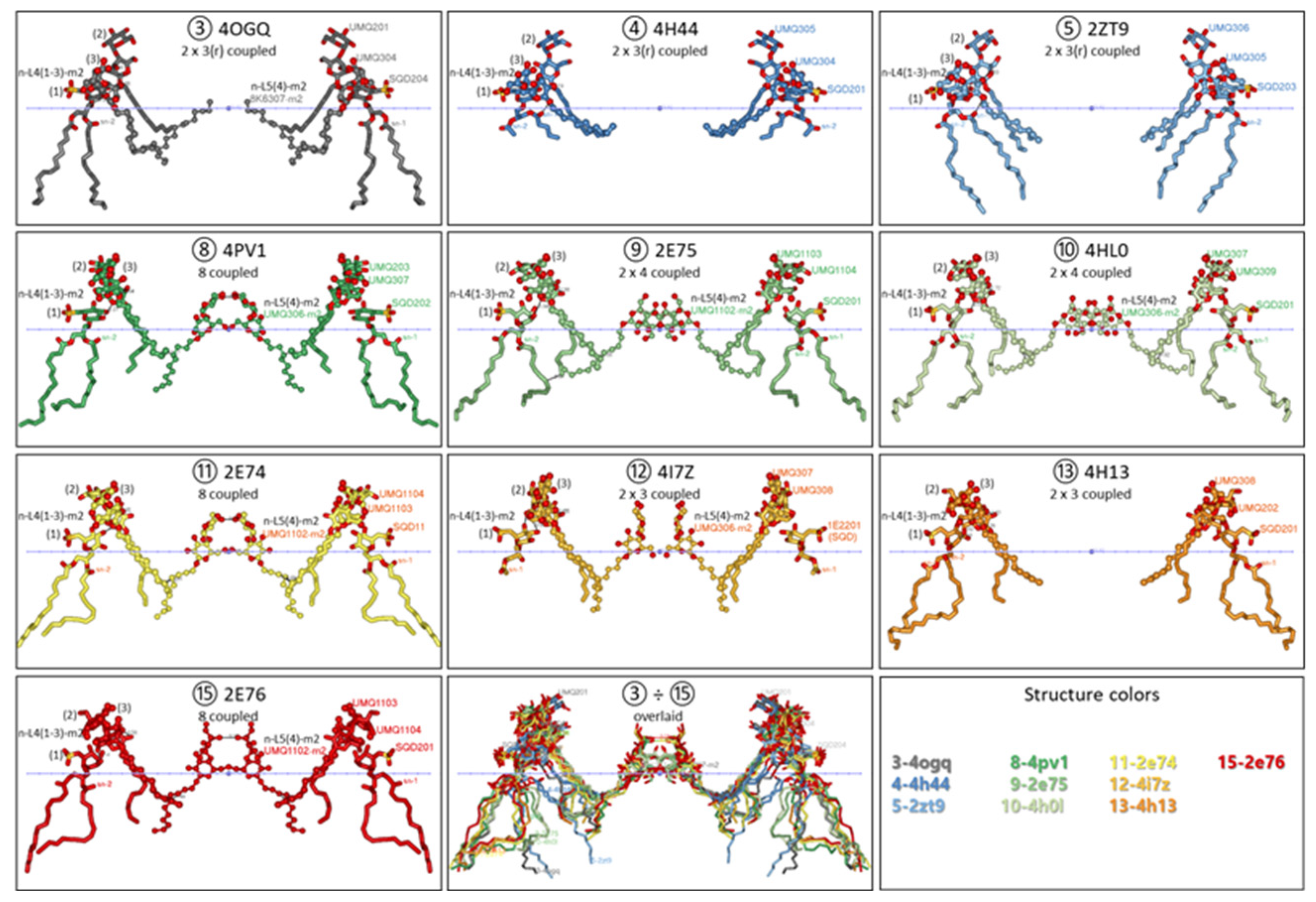
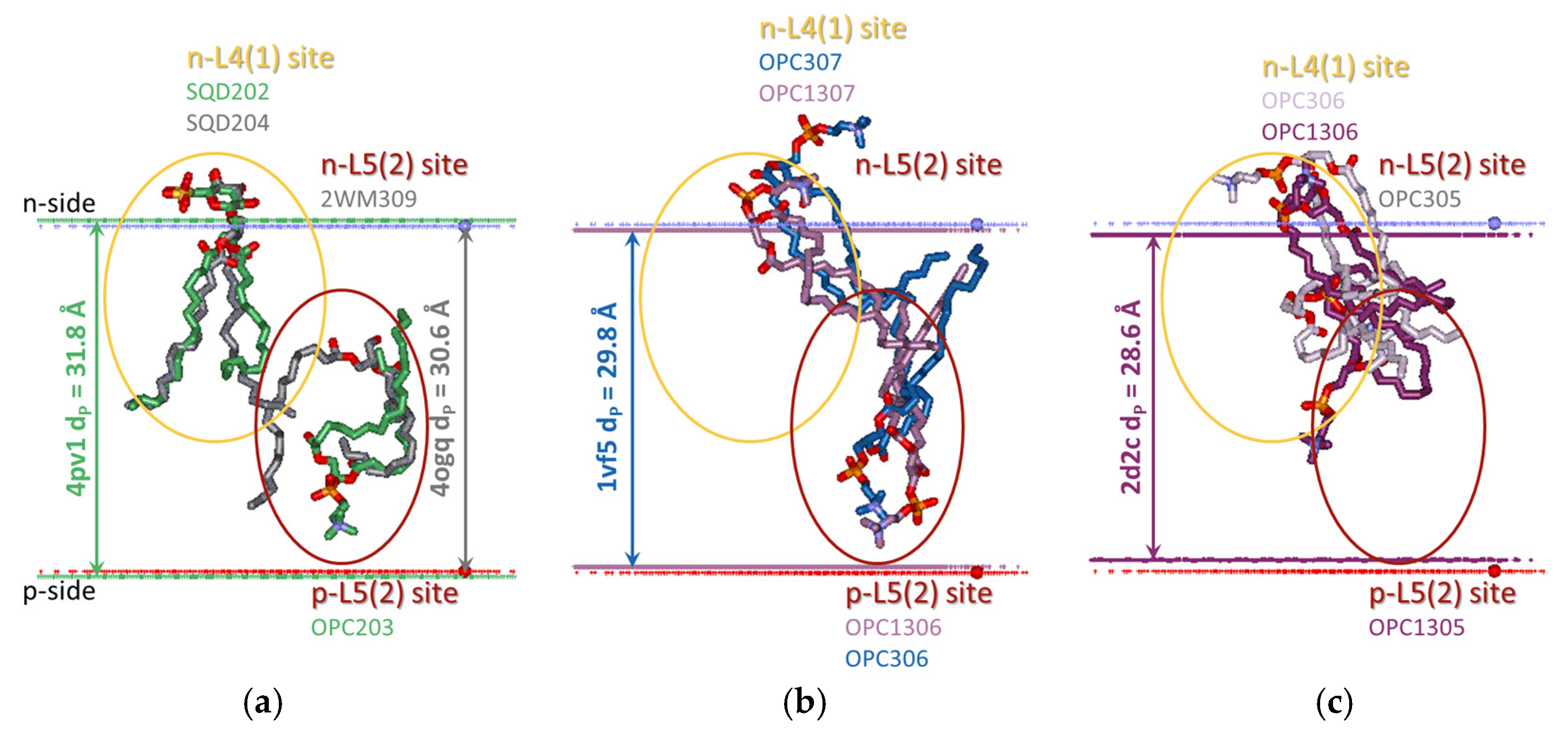
3.2.1. Five Groups of Lipid-Binding Sites
3.2.2. All Lipid-Binding Sites of Cytochrome b6f Contact the Bulk Lipid Phase
3.3. Variable Occupation of the Lipid-Binding Sites in the Diverse Cytochrome b6f Crystal Structures During Induction of the Transition to State 2 and State 1
3.3.1. Lipid-Binding Changes During the Induction of Transition to State 2
3.3.2. Lipid-Binding Changes During the Induction of Transition to State 1
3.4. Comparison of the Lipid-Binding Sites in Cryo-EM and X-Ray Crystal Structures
3.4.1. Lipid-Binding Sites in X-Ray Crystal Structures Are Not Affected by Crystal Packing
3.4.2. Cytoplasmic/Stromal Surface-Bound Peripheral Proteins Do Not Affect the Hydrophobic Thickness of Cytochrome b6f
3.4.3. The Emptying of the SQDG n-L4(1) Site and PC p-L3(1) Site Is the First Lipid Response to the Decreased Hydrophobic Thickness of Cryo-EM Cytochrome b6f Structures
3.4.4. SQDG Translocation Escape Pathway to the Bulk Lipid Phase: Scramblase Function of Cytochrome b6f?
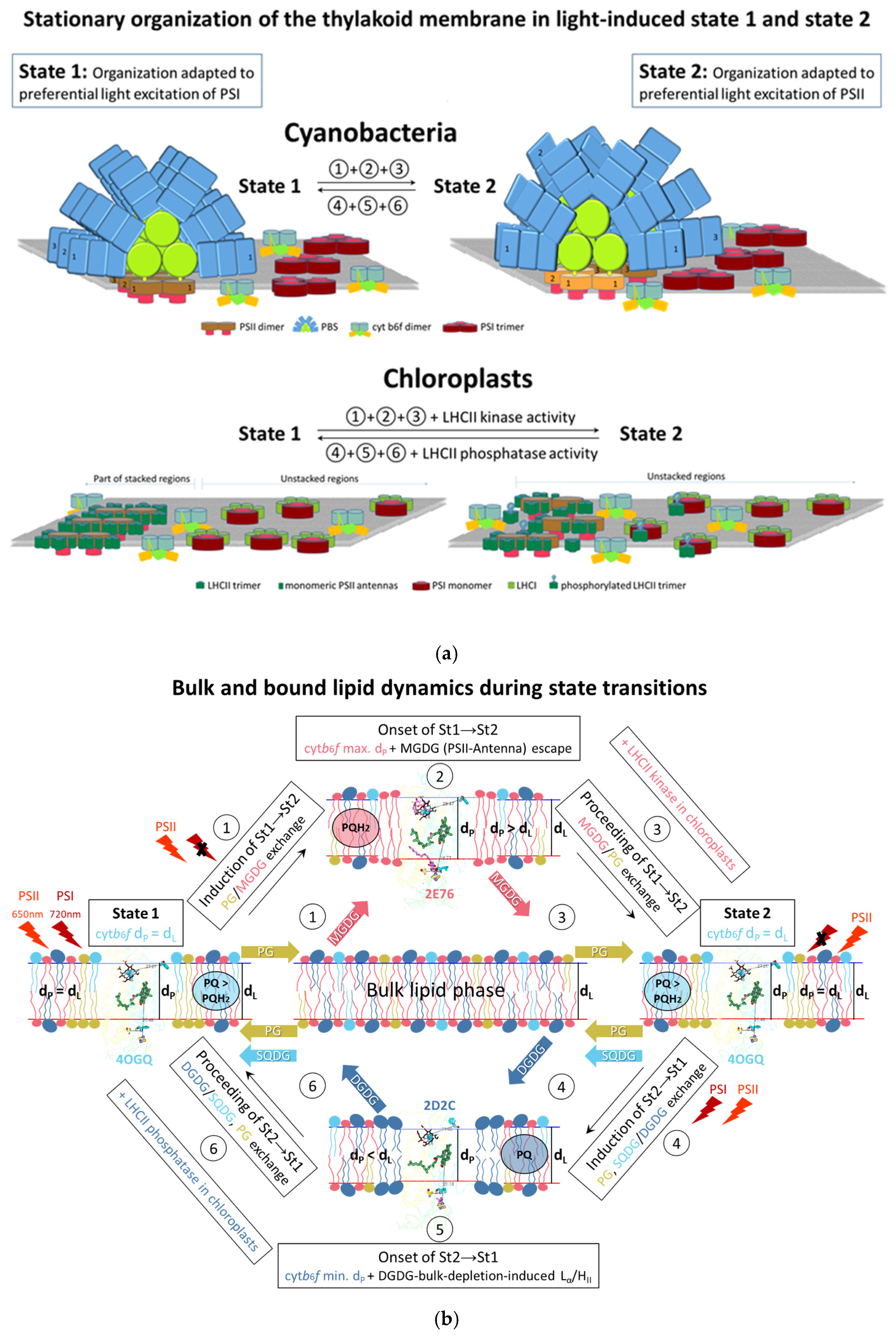
3.5. Predicted Native Lipid Exchange at/Escape from Cytochrome b6f Complex upon Induction of State Transitions
3.6. Continuous Chlorophyll a Movement and Membrane Normal Alignment upon Increasing the Reduction Level of the Plastoquinone Pool
3.7. Communications and Signaling Between the Three Main Players in State Transitions
3.7.1. Chla Signaling to Phe/Tyr124fg-loop-suIV Under Optimal and Reducing Conditions: Role for β-Car
3.7.2. Under Low-Light and Optimal Stationary Conditions for Photosynthesis—Two Thylakoid Lipid Raft-like Nanodomains Around Cytochrome b6f Dimer
3.7.3. Communication Under Reducing Conditions: The n-Side Monolayer Thylakoid Lipid Raft-Like Nanodomain
4. Discussion
4.1. Cytochrome b6f-Induced Positive and Negative Hydrophobic Mismatch Operates in a Time Range of a Few Seconds
4.2. An Idea of How the Volume of the Chlorophyllide Part of Chlorophyll a Could Sense the Position of the [2Fe-2S] Cluster Relative to the Mg of Chlorophyll a
4.3. Lipid- and Carotenoid-Mediated Signaling Pathways from Chla to the Center of Flexibility Phe/Tyr124fg-loop-suIV Residue
4.4. Raft-like Nanodomains and Different Timescales of Cytb6f Lipid Nanoenvironment Dynamics
4.5. Strong Lipid Selectivity of the Different Conformational States of Cytochrome b6f
4.6. State Transitions Are the Regulatory Mechanism That Relies on the Evolutionarily Conserved Thylakoid Lipid Composition
4.7. The Hydrophobic Mismatch Model for Cytochrome b6f-Driven State Transitions—Bulk and Bound Lipid Dynamics
4.8. Testable Predictions of the Hydrophobic Mismatch Model for Cytochrome b6f-Driven State Transitions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| DGDG | Digalactosyldiacylglycerol |
| HMM | Hydrophobic mismatch |
| ISP | Iron–Sulfur protein |
| LHC | Light-harvesting complex |
| MGDG | Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol |
| PAM | Pulse-Amplitude-Modulated |
| PBS | Phycobilisome |
| PG | Phosphatidylglycerol |
| PQ | Plastoquinone |
| PQH2 | Plastoquinol |
| PSI | Photosystem I |
| PSII | Photosystem II |
| SQDG | Sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol |
References
- Harayama, T.; Riezman, H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huster, D.; Maiti, S.; Herrmann, A. Phospholipid membranes as chemically and functionally tunable materials. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2312898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, N.; Siegenthaler, P.A. Lipids in Photosynthesis: An Overview. In Lipids in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function and Genetics. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Paul-André, S., Norio, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yoshihara, A.; Kubota-Kawai, H. Evolutionary implications from lipids in membrane bilayers and photosynthetic complexes in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. J. Biochem. 2023, 174, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.J. Lipid Phase Behaviour and Lipid-Protein Interactions in the Chloroplast Photosynthetic Membrane. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1987, 15, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Murata, N. Membrane lipids in cyanobacteria. In Lipids in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function and Genetics. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Siegenthaler, P.-A., Murata, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 6, pp. 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demé, B.; Cataye, C.; Block, M.A.; Maréchal, E.; Jouhet, J. Contribution of galactoglycerolipids to the 3-dimensional architecture of thylakoids. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3373–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroutsos, D.; Amiar, S.; Abida, H.; Dolch, L.J.; Bastien, O.; Rébeillé, F.; Jouhet, J.; Falconet, D.; Block, M.A.; McFadden, G.I.; et al. Evolution of galactoglycerolipid biosynthetic pathways: From cyanobacteria to primary plastids and from primary to secondary plastids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 54, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, R.E. Origin and early evolution of photosynthesis. Photosynth. Res. 1992, 33, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. Photosystems and global effects of oxygenic photosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, D.; Stirbet, A.; Björn, L.O.; Govindjee, G. Light quality, oxygenic photosynthesis and more. Photosynthetica 2022, 60, 25–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, H. Molecular crowding and order in photosynthetic membranes. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevela, D.; Kern, J.F.; Govindjee, G.; Messinger, J. Solar energy conversion by photosystem II: Principles and structures. Photosynth. Res. 2023, 156, 279–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippler, M.; Nelson, N. The Plasticity of Photosystem I. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhoff, H.; Horstmann, S.; Weis, E. Control of the photosynthetic electron transport by PQ diffusion microdomains in thylakoids of higher plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2000, 1459, 148–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.F.; de Paula, W.B.; Puthiyaveetil, S.; Nield, J. A structural phylogenetic map for chloroplast photosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saer, R.G.; Blankenship, R.E. Light harvesting in phototrophic bacteria: Structure and function. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 2107–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, M.; Patel-Tupper, D.; Niyogi, K.K. Structural Diversity in Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Light Harvesting. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2024, 75, 119–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.A.; Canniffe, D.P. How nature designs light harvesting antenna systems: Design principles and functional realization in chlorophototrophic prokaryotes. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adir, N.; Bar-Zvi, S.; Harris, D. The amazing phycobilisome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, R.; van Amerongen, H. Light harvesting in oxygenic photosynthesis: Structural biology meets spectroscopy. Science 2020, 369, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.S.; Green, B.R. Biochemical and Biophysical Properties of Thylakoid Acyl Lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1991, 1060, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuks, B.; Homble, F. Permeability and Electrical Properties of Planar Lipid Membranes from Thylakoid Lipids. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dlouhý, O.; Karlický, V.; Javornik, U.; Kurasová, I.; Zsiros, O.; Šket, P.; Kanna, S.D.; Böde, K.; Večeřová, K.; Urban, O.; et al. Structural Entities Associated with Different Lipid Phases of Plant Thylakoid Membranes—Selective Susceptibilities to Different Lipases and Proteases. Cells 2022, 11, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchêne, S.; Siegenthaler, P. Do glycerolipids display lateral heterogeneity in the thylakoid membrane? Lipids 2000, 35, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, D.; Geier, B.; Pabst, G. Asymmetric lipid membranes: Towards more realistic model systems. Membranes 2015, 5, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; London, E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17221–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.L.; Orjuela, J.D.; de Groot, B.L.; Aponte Santamaría, C.; Walz, T. Structure and dynamics of cholesterol-mediated aquaporin-0 arrays and implications for lipid rafts. eLife 2024, 12, RP90851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.F. Lipid rafts: Contentious only from simplistic standpoints. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Sampaion, J.L. Membrane Organization and Lipid Rafts. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, D.R.; Staehelin, L.A. Lateral Distribution of the Cytochrome b(6)/f and Coupling Factor ATP Synthetase Complexes of Chloroplast Thylakoid Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1985, 78, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, W.H.J.; Johnson, M.P. Modeling the Role of LHCII-LHCII, PSII-LHCII, and PSI-LHCII Interactions in State Transitions. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koochak, H.; Puthiyaveetil, S.; Mullendore, D.L.; Li, M.; Kirchhoff, H. The structural and functional domains of plant thylakoid membranes. Plant J. 2019, 97, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strašková, A.; Steinbach, G.; Konert, G.; Kotabová, E.; Komenda, J.; Tichý, M.; Kaňa, R. Pigment-protein complexes are organized into stable microdomains in cyanobacterial thylakoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2019, 1860, 148053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, B.; Anderson, J.M. Lateral heterogeneity in the distribution of chlorophyll-protein complexes of the thylakoid membranes of spinach chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1980, 593, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, M.; Rantala, S.; Aro, E.M. Composition, phosphorylation and dynamic organization of photosynthetic protein complexes in plant thylakoid membrane. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, A.; Neofotis, P.; Davis, G.A.; Fisher, N.; Kramer, D.M. Diversity in photoprotection and energy balancing in terrestrial and aquatic phototrophs. In Photosynthesis in Algae: Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms; Larkum, A., Grossman, A., Raven, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 45, pp. 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Külheim, C.; Agren, J.; Jansson, S. Rapid regulation of light harvesting and plant fitness in the field. Science 2002, 297, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, J. Dynamic reorganization of photosynthetic supercomplexes during environmental acclimation of photosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, N.; Periole, X.; Marrink, S.J.; Croce, R. From light-harvesting to photoprotection: Structural basis of the dynamic switch of the major antenna complex of plants (LHCII). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P.; Wientjes, E. The relevance of dynamic thylakoid organisation to photosynthetic regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messant, M.; Krieger-Liszkay, A.; Shimakawa, G. Dynamic Changes in Protein-Membrane Association for Regulating Photosynthetic Electron Transport. Cells 2021, 10, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzi, J.A.; Steinkühler, J.; Vu, T.Q.; Gunnels, T.F.; Hu, V.T.; Lu, P.; Baker, D.; Kamat, N.P. Hydrophobic mismatch drives self-organization of designer proteins into synthetic membranes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, D.; Honigmann, A.; Koike, S.; Göttfert, F.; Pähler, G.; Junius, M.; Müllar, S.; Diederichsen, U.; Janshoff, A.; Grubmüller, H.; et al. Hydrophobic mismatch sorts SNARE proteins into distinct membrane domains. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, P.; Mavelli, F.; Altamura, E. Light energy transduction in liposome-based artificial cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1161730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Wang, W.; Min, S.H.; Ren, Y.; Shin, K.; Han, X. Artificial organelles for sustainable chemical energy conversion and production in artificial cells: Artificial mitochondrion and chloroplasts. Biophys. Rev. 2023, 4, 011311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Yu, F.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Xia, K.; Jiang, D.; Kong, H. Nature-Inspired Thylakoid-Based Photosynthetic Nanoarchitectures for Biomedical Applications. Small Methods 2024, 8, e2301143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Hancock, A.M.; Kuwabara, H.; Adams, P.G.; Dewa, T. Photocurrent Generation by Plant Light-Harvesting Complexes is Enhanced by Lipid-Linked Chromophores in a Self-Assembled Lipid Membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2025; Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, N. Control of excitation transfer in photosynthesis. I. Light-induced change of chlorophyll a fluorescence in Porphyridium cruentum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1969, 172, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, C.; Myers, J. Fluorescence and Oxygen Evolution from Chlorella Pyrenoidosa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1969, 189, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, R. Chlorophyll a is the crucial redox sensor and transmembrane signal transmitter in the cytochrome b6f complex. Components and mechanisms of state transitions from the hydrophobic mismatch viewpoint. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, R. The Cytochrome b6f Complex as a Perpetual Mobile for Adaptive Structural Reorganizations of the Photosynthetic Membranes in Chloroplasts and Cyanobacteria. In Proceedings of the 3rd National Congress on Physical Sciences, Section: Physics of Living and Soft Matter, Physics in Medicine, Sofia, Bulgaria, 29 September–2 October 2016; S0814. Available online: https://phys.uni-sofia.bg/upb/conference/3kongres/disk/html/pdf/S0814.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Magdaong, N.C.M.; Blankenship, R.E. Photoprotective, excited-state quenching mechanisms in diverse photosynthetic organisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5018–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Procházka, V.; Vítězová, M.; Dordević, D.; Abd El-Salam, M.; Rittmann, S.K.R. Anoxygenic photosynthesis with emphasis on green sulfur bacteria and a perspective for hydrogen sulfide detoxification of anoxic environments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1417714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benning, C. Membrane Lipids in Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria. In Lipids in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function and Genetics; Paul-André, S., Norio, M., Eds.; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullineaux, C.W.; Emlyn-Jones, D. State transitions: An example of acclimation to low-light stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.F.; Bennett, J.; Steinback, K.E.; Arntzen, C.J. Chloroplast protein-phosphorylation couples plastoquinone redox state to distribution of excitation-energy between photosystems. Nature 1981, 291, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.V.; Johnson, M.P. Dynamics of higher plant photosystem cross-section associated with state transitions. Photosynth. Res. 2009, 99, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.; Khorobrykh, S.; Hakala-Yatkin, M.; Havurinne, V.; Kuusisto, I.; Antal, T.; Tyystjärvi, T.; Tyystjärvi, E. Action spectrum of the redox state of the plastoquinone pool defines its function in plant acclimation. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1088–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollman, F.A. State transitions reveal the dynamics and flexibility of the photosynthetic apparatus. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3623–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont, M.; Bassi, R. Sharing light between two photosystems: Mechanism of state transitions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, S.; Barneche, F.; Peltier, G.; Rochaix, J.D. State transitions and light adaptation require chloroplast thylakoid protein kinase STN7. Nature 2005, 433, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depège, N.; Bellafiore, S.; Rochaix, J.D. Role of chloroplast protein kinase Stt7 in LHCII phosphorylation and state transition in Chlamydomonas. Science 2003, 299, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Tokutsu, R.; Li, A.; Takizawa, K.; Song, C.; Murata, K.; Yamasaki, T.; Liu, Z.; Minagawa, J.; Li, M. Structural basis of LhcbM5-mediated state transitions in green algae. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribil, M.; Pesaresi, P.; Hertle, A.; Barbato, R.; Leister, D. Role of plastid protein phosphatase TAP38 in LHCII dephosphorylation and thylakoid electron flow. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiguzov, A.; Ingelsson, B.; Samol, I.; Andres, C.; Kessler, F.; Rochaix, J.D.; Vener, A.V.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, M. The PPH1 phosphatase is specifically involved in LHCII dephosphorylation and state transitions in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4782–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallas, T. Cytochrome b6f complex at the heart of energy transduction and redox signaling. In Photosynthesis. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration, 1st ed.; Eaton-Rye, J., Tripathy, B., Sharkey, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 34, pp. 501–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, P.I.; Zhan, J.; Sétif, P.; Lemaire, C.; Solymosi, D.; Battchikova, N.; Wang, Q.; Kirilovsky, D. The Cytochrome b6f Complex Is Not Involved in Cyanobacterial State Transitions. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 911–931, Erratum in: Plant Cell 2020, 32, 525. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzadilla, P.I.; Kirilovsky, D. Revisiting cyanobacterial state transitions. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.W.; Sui, S.F. In situ structure of the red algal phycobilisome-PSII-PSI-LHC megacomplex. Nature 2023, 616, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochaix, J.-D. The Dynamics of the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Algae. In Photosynthesis in Algae: Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms; Larkum, A.W.D., Grossmann, A.R., Raven, J.A., Eds.; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 45, pp. 57–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, J.; M’Bina, I.; Vernotte, C.; Astier, C.; Wollman, F. Randomization of the EF particles in thylakoid membranes of synechocystis 6714 upon transition from state I to state II. FEBS Lett. 1986, 208, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, J.; Ajlani, G.; Astier, C.; Recouvreur, M.; Vernotte, C. Ultrastructure and light adaptation of phycobilisome mutants of Synechocystis PCC 6803. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1997, 1319, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vener, A.V.; van Kan, P.J.; Rich, P.R.; Ohad, I.; Andersson, B. Plastoquinol at the quinol oxidation site of reduced cytochrome bf mediates signal transduction between light and protein phosphorylation: Thylakoid protein kinase deactivation by a single-turnover flash. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, F.; Finazzi, G.; Delosme, R.; Nitschke, W.; Picot, D.; Wollman, F.A. The Qo site of cytochrome b6f complexes controls the activation of the LHCII kinase. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullineaux, C.W.; Allen, J.F. State 1-State 2 transitions in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6301 are controlled by the redox state of electron carriers between Photosystems I and II. Photosynth. Res. 1990, 23, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.B.; Li, G.F.; Ruan, X.; Wu, Q.Y.; Gong, Y.D.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhao, N.M. The redox state of plastoquinone pool regulates state transitions via cytochrome b6f complex in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. FEBS Lett. 2002, 519, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Bryant, D.A. Kinetic analyses of state transitions of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 and its mutant strains impaired in electron transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2003, 1607, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, L.A.; Proctor, M.S.; Hitchcock, A.; Hunter, C.N.; Johnson, M.P. Cytochrome b6f—Orchestrator of photosynthetic electron transfer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2021, 1862, 148380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, A.N. The cytochrome b6f complex at the crossroad of photosynthetic electron transport pathways. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 81, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroebel, D.; Choquet, Y.; Popot, J.L.; Picot, D. An atypical haem in the cytochrome b6f complex. Nature 2003, 426, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisu, G.; Zhang, H.; Smith, J.L.; Cramer, W.A. Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis: Tuning the cavity. Science 2003, 302, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.N. The Cytochrome b6f Complex: Biophysical Aspects of Its Functioning in Chloroplasts. Subcell. Biochem. 2018, 87, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchert, F.; Zito, F. Chloroplast ATP synthase and the cytochrome b6f complex. In The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Li, M.; Pan, X. Dynamic Regulation of the Light-Harvesting System through State Transitions in Land Plants and Green Algae. Plants 2023, 12, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemeille, S.; Willig, A.; Depège-Fargeix, N.; Delessert, C.; Bassi, R.; Rochaix, J.D. Analysis of the chloroplast protein kinase Stt7 during state transitions. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiguzov, A.; Chai, X.; Fucile, G.; Longoni, P.; Zhang, L.; Rochaix, J.D. Activation of the Stt7/STN7 Kinase through Dynamic Interactions with the Cytochrome b6f Complex. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder, T.; Xu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wanner, G.; Leister, D.; Pribil, M. The major thylakoid protein kinases STN7 and STN8 revisited: Effects of altered STN8 levels and regulatory specificities of the STN kinases. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Lee, J.H.; Weaver, S.; Kwizera, R.; Lohman, J.R.; Puthiyaveetil, S. Cysteine residues contribute to the regulation of Arabidopsis state transition 7 kinase. FEBS Lett. 2024, 599, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Hasan, S.S.; Zakharov, S.D.; Naurin, S.; Cohn, W.; Ma, J.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Cramer, W.A. Trans-membrane Signaling in Photosynthetic State Transitions: REDOX-AND STRUCTURE-DEPENDENT INTERACTION IN VITRO BETWEEN STT7 KINASE AND THE CYTOCHROME b6f COMPLEX. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21740–21750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, L.; Zito, F.; Blangy, S.; Auroy, P.; Johnson, X.; Peltier, G.; Alric, J. A stromal region of cytochrome b6f subunit IV is involved in the activation of the Stt7 kinase in Chlamydomonas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12063–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riché, A.; Dumas, L.; Malesinski, S.; Bossan, G.; Madigou, C.; Zito, F.; Alric, J. The stromal side of the cytochrome b6f complex regulates state transitions. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 4234–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintscher, S.; Pietras, R.; Mielecki, B.; Szwalec, M.; Wójcik-Augustyn, A.; Indyka, P.; Rawski, M.; Koziej, Ł.; Jaciuk, M.; Ważny, G.; et al. Molecular basis of plastoquinone reduction in plant cytochrome b6f. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 1814–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Cramer, W.A. Internal Lipid Architecture of the Hetero-Oligomeric Cytochrome b6f Complex. Structure 2014, 22, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, M.; Węgrzyn, A.; Kowalewska, Ł.; Kulik, A.; Ostaszewska-Bugajska, M.; Mazur, J.; Garstka, M.; Mazur, R. Light-independent pathway of STN7 kinase activation under low temperature stress in runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, F.; Vinh, J.; Popot, J.L.; Finazzi, G. Chimeric fusions of subunit IV and PetL in the b6f complex of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Structural implications and consequences on state transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 12446–12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Zhao, J. Loss of the cytochrome b6f subunit PetN destabilizes the complex and severely impairs state transitions in Anabaena variabilis. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiaf094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bissati, K.; Delphin, E.; Murata, N.; Etienne, A.; Kirilovsky, D. Photosystem II fluorescence quenching in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803: Involvement of two different mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2000, 1457, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarcina, M.; Tobin, M.J.; Mullineaux, C.W. Diffusion of phycobilisomes on the thylakoid membranes of the Cyanobacterium synechococcus 7942: Effects of phycobilisome size, temperature, and membrane lipid composition. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46830–46834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarcina, M.; Murata, N.; Tobin, M.J.; Mullineaux, C.W. Lipid diffusion in the thylakoid membranes of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp.: Effect of fatty acid desaturation. FEBS Lett. 2003, 553, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncel, M.; Yruela, I.; Kirilovsky, D.; Guerrero, F.; Alfonso, M.; Picorel, R.; Ortega, J.M. Changes in photosynthetic electron transfer and state transitions in an herbicide-resistant D1 mutant from soybean cell cultures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullineaux, C.W. Phycobilisome-reaction centre interaction in cyanobacteria. Photosynth. Res. 2008, 95, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetoshkina, D.V.; Kozuleva, M.A.; Proskuryakov, I.I.; Terentyev, V.V.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Naydov, I.A.; Ivanov, B.N.; Klenina, I.B.; Borisova-Mubarakshina, M.M. Dependence of state transitions on illumination time in Arabidopsis and barley plants. Protoplasma 2024, 261, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, M.F.; Ernst, R. Membrane homeostasis beyond fluidity: Control of membrane compressibility. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, A.; Kobayashi, K. Lipids in photosynthetic protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 2735–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kurisu, G.; Cramer, W.A. Intraprotein transfer of the quinone analogue inhibitor 2,5-dibromo-3-methyl-6-isopropyl-p-benzoquinone in the cytochrome b6f complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, E.; Zhang, H.; Cramer, W.A. Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex: Quinone analogue inhibitors as ligands of heme cn. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniulis, D.; Yamashita, E.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Zatsman, A.I.; Hendrich, M.P.; Hasan, S.S.; Ryan, C.M.; Cramer, W.A. Structure-Function, Stability, and Chemical Modification of the Cyanobacterial Cytochrome b6f Complex from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9861–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Yamashita, E.; Baniulis, D.; Cramer, W.A. Quinone-dependent proton transfer pathways in the photosynthetic cytochrome b6f complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4297–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Stofleth, J.T.; Yamashita, E.; Cramer, W.A. Lipid-induced conformational changes within the cytochrome b6f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2649–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Proctor, E.A.; Yamashita, E.; Dokholyan, N.V.; Cramer, W.A. Traffic within the Cytochrome b6f Lipoprotein Complex: Gating of the Quinone Portal. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, L.A.; Qian, P.; Mayneord, G.E.; Hitchcock, A.; Farmer, D.A.; Thompson, R.F.; Swainsbury, D.J.K.; Ranson, N.A.; Hunter, C.N.; Johnson, M.P. Cryo-EM structure of the spinach cytochrome b6f complex at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature 2019, 575, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, M.S.; Malone, L.A.; Farmer, D.A.; Swainsbury, D.J.K.; Hawkings, F.R.; Pastorelli, F.; Emrich-Mills, T.Z.; Siebert, C.A.; Hunter, C.N.; Johnson, M.P.; et al. Cryo-EM structures of the Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 cytochrome b6f complex with and without the regulatory PetP subunit. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarewicz, M.; Szwalec, M.; Pintscher, S.; Indyka, P.; Rawski, M.; Pietras, R.; Mielecki, B.; Koziej, Ł.; Jaciuk, M.; Glatt, S.; et al. High-resolution cryo-EM structures of plant cytochrome b6f at work. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, S.R.; Hunte, C. Structure of complex III with bound cytochrome c in reduced state and definition of a minimal core interface for electron transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17542–17549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Yamashita, E.; Ryan, C.M.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Cramer, W.A. Conservation of lipid functions in cytochrome bc complexes. J. Mol. Boil. 2011, 414, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Cramer, W.A. Lipid functions in cytochrome bc complexes: An odd evolutionary transition in a membrane protein structure. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2012, 367, 3406–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Yamashita, E.; Cramer, W.A. Transmembrane signaling and assembly of the cytochrome b6f-lipidic charge transfer complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2013, 1827, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, N.; Croce, R.; Marrink, S.J.; Thallmair, S. Molecular dynamics simulations in photosynthesis. Photosynth. Res. 2020, 144, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Lomize, M.A.; Mosberg, H.I. Positioning of proteins in membranes: A computational approach. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1318–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Mosberg, H.I. Anisotropic solvent model of the lipid bilayer. 2. Energetics of insertion of small molecules, peptides, and proteins in membranes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Tol’s Color Schemes. Technical Note SRON/EPS/TN/09-002 3.2. SRON. 2021. Available online: https://sronpersonalpages.nl/~pault/data/colourschemes.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Vladkova, R.; Koynova, R.; Teuchner, K.; Tenchov, B. Bilayer structural destabilization by low amounts of chlorophyll a. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, R. Ordering of the numerous cytochrome bc1 x-ray crystal structures in a sequence of events during substrate processing in the Qo-site of the complex. In Proceedings of the 12th National Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering Conference-NMPEC-2016 with International Participation, Sofia, Bulgaria, 3–5 November 2016; Bulgarian Society of Biomedical Physics and Engineering: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2018. Part 2. pp. 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, L.; Quinn, B.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, M.; Elberry, M.; Yu, L.; Yu, C.A.; Xia, D. Crystallographic studies of quinol oxidation site inhibitors: A modified classification of inhibitors for the cytochrome bc(1) complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacroix de Lavalette, A.; Finazzi, G.; Zito, F. b6f-Associated chlorophyll: Structural and dynamic contribution to the different cytochrome functions. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5259–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniulis, D.; Hasan, S.S.; Stofleth, J.T.; Cramer, W.A. Mechanism of enhanced superoxide production in the cytochrome b(6)f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 8975–8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.D.; Heberle, F.A.; Waxham, M.N. Visualizing lipid membrane structure with cryo-EM: Past, present, and future. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2023, 7, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D. Straightforward Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Brooks/Cole Publishing, Co.: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1996; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- Pogozheva, I.D.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. Structural adaptations of proteins to different biological membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2592–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulke, M.; Weraduwage, S.M.; Sharkey, T.D.; Vermaas, J.V. Nanoscale simulation of the thylakoid membrane response to extreme temperatures. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, H. An Overview of Chlorophylls and Bacteriochlorophylls: Biochemistry, Biophysics, Functions and Applications. In Chlorophylls and Bacteriochlorophylls. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Grimm, B., Porra, R.J., Rüdiger, W., Scheer, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 25, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.G. Lipid-protein interactions in biological membranes: A structural perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2003, 1612, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Endo, K.; Wada, H. Specific Distribution of Phosphatidylglycerol to Photosystem Complexes in the Thylakoid Membrane. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsdottir, H.; Hunte, C. Lipids in membrane protein structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Essex, J.W.; Lee, A.G. G protein coupled receptor interactions with cholesterol deep in the membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.—Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T.; Cheng, Y.; Sliz, P.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Harrison, S.C.; Walz, T. Lipid-protein interactions in double-layered two-dimensional AQP0 crystals. Nature 2005, 438, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, R.K.; Li, Z.; Walz, T. Principles of membrane protein interactions with annular lipids deduced from aquaporin-02D crystals. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.F. Modulation of rhodopsin function by properties of the membrane bilayer. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1994, 73, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsila, F.; Bikádi, Z.; Deli, J.; Simonyi, M. Configuration of a single centre determines chirality of supramolecular carotenoid self-assembly. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2561–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Fujiwara, T.K.; Tsunoyama, T.A.; Kasai, R.S.; Liu, A.A.; Hirosawa, K.M.; Kinoshita, M.; Matsumori, N.; Komura, N.; Ando, H.; et al. Defining raft domains in the plasma membrane. Traffic 2020, 21, 106–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolmatov, D.; Kinnun, J.J.; Katsaras, J.; Lavrentovich, M.O. Phonon-mediated lipid raft formation in biological membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2020, 232, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.J.; Yano, K.; Cha, M.; Colombari, M.F.; Kim, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Sun, K.; Kruger, J.M.; de Moura, A.F.; et al. Chiral phonons in microcrystals and nanofibrils of biomolecules. Nat. Photon. 2022, 16, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, R.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis, Chapter 5. In Antenna Complexes and Energy Transfer Processes, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 61–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, X.B.; Sang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, L.B.; Kuang, T.Y. Singlet oxygen formation and chlorophyll a triplet excited state deactivation in the cytochrome b6f complex from Bryopsis corticulans. Photosynth. Res. 2009, 100, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosumi, D.; Nishiguchi, T.; Amao, Y.; Cogdell, R.J.; Hashimoto, H. Singlet and Triplet Excited States Dynamics of Photosynthetic Pigment Chlorophyll a Investigated by Sub-nanosecond Pump-probe Spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2018, 358, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazibt, S.; Bouarab, S.; Ziane, A.; Parlebas, J.C.; Demangeat, C. Electronic, magnetic and structural properties of neutral, cationic and anionic Fe2S2, Fe3S4 and Fe4S4 clusters. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 43, 165101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braslavsky, S.E. Volume changes on triplet production and quenching: Time-resolved optoacoustic studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1996, 102, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, F.N.; Laursen, I.; Bohr, H.; Nielsen, C.H. Protein-induced bilayer perturbations: Lipid ordering and hydrophobic coupling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klusch, N.; Dreimann, M.; Senkler, J.; Rugen, N.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Braun, H.P. Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory I + III2 supercomplex from Arabidopsis thaliana at 2 Å resolution. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, E. Ordered Domain (Raft) Formation in Asymmetric Vesicles and Its Induction upon Loss of Lipid Asymmetry in Artificial and Natural Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, F.; Lebrun, M.C.; Tocanne, J.F. Is the protein/lipid hydrophobic matching principle relevant to membrane organization and functions? FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Kindt, J.T. Hydrophobic mismatch and lipid sorting near OmpA in mixed bilayers: Atomistic and coarse-grained simulations. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van den Brink-van der Laan, E.; Killian, J.A.; de Kruijff, B. Nonbilayer lipids affect peripheral and integral membrane proteins via changes in the lateral pressure profile. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.P.; Brain, A.P.; Ruban, A.V. Changes in thylakoid membrane thickness associated with the reorganization of photosystem II light harvesting complexes during photoprotective energy dissipation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.V.; Wilson, S. The Mechanism of Non-Photochemical Quenching in Plants: Localization and Driving Forces. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Clarke, C.D.; Carbajal, M.A.; Buccafusca, R.; Fleck, R.A.; Daskalakis, V.; Ruban, A.V. Hydrophobic Mismatch in the Thylakoid Membrane Regulates Photosynthetic Light Harvesting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14905–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.J. The effect of cholesterol on the structure of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 1978, 513, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerka, N.; Pencer, J.; Nieh, M.P.; Katsaras, J. Influence of cholesterol on the bilayer properties of monounsaturated phosphatidylcholine unilamellar vesicles. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter Biol. Phys. 2007, 23, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, S.; Zhang, H.; Erramilli, S.; Cramer, W.A. Structural and functional contributions of lipids to the stability and activity of the photosynthetic cytochrome b6f lipoprotein complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17758–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, A.V.; Gibson, N.J.; Thurmond, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Brown, M.F. Conformational energetics of rhodopsin modulated by nonlamellar-forming lipids. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6354–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.D.E.; Lewis, J.W.; Szundi, I.; Martinez-Mayorga, K.; Mahalingam, M.; Vogel, R.; Kliger, D.S.; Brown, M.F. Membrane Curvature Revisited-the Archetype of Rhodopsin Studied by Time-Resolved Electronic Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenbach, C.; Kusnetzow, A.K.; Ernst, O.P.; Hofmann, K.P.; Hubbell, W.L. High-resolution distance mapping in rhodopsin reveals the pattern of helix movement due to activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7439–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavi, O.; Vossoughi, M.; Naghdabadi, R.; Jamali, Y. The Combined Effect of Hydrophobic Mismatch and Bilayer Local Bending on the Regulation of Mechanosensitive Ion Channels. PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0150578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eerden, F.J.; Melo, M.N.; Frederix, P.W.J.M.; Marrink, S.J. Prediction of Thylakoid Lipid Binding Sites on Photosystem II. Biophys. J 2017, 113, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, S.; Hu, Z.; Kuang, T.; Paulsen, H.; Yang, C. Effect of monogalactosyldiacylglycerol on the interaction between photosystem II core complex and its antenna complexes in liposomes of thylakoid lipids. Photosynth. Res. 2009, 99, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thallmair, S.; Vainikka, P.A.; Marrink, S.J. Lipid Fingerprints and Cofactor Dynamics of Light-Harvesting Complex II in Different Membranes. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, J.; Bommer, M.; Burkhardt, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Kern, J.; Meents, A.; Müh, F.; Dobbek, H.; Zouni, A. Native-like photosystem II superstructure at 2.44 Å resolution through detergent extraction from the protein crystal. Structure 2014, 22, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rast, A.; Schaffer, M.; Albert, S.; Wan, W.; Pfeffer, S.; Beck, F.; Plitzko, J.M.; Nickelsen, J.; Engel, B.D. Biogenic regions of cyanobacterial thylakoids form contact sites with the plasma membrane. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayermann, S.P.; Rayermann, G.E.; Cornell, C.E.; Merz, A.J.; Keller, S.L. Hallmarks of Reversible Separation of Living, Unperturbed Cell Membranes into Two Liquid Phases. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuartzman, S.G.; Nevo, R.; Shimoni, E.; Charuvi, D.; Kiss, V.; Ohad, I.; Brumfeld, V.; Reich, Z. Thylakoid membrane remodeling during state transitions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumova, S.B.; Laptenok, S.P.; Kovács, L.; Tóth, T.; van Hoek, A.; Garab, G.; van Amerongen, H. Digalactosyl-diacylglycerol-deficiency lowers the thermal stability of thylakoid membranes. Photosynth. Res. 2010, 105, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronsson, H.; Schöttler, M.A.; Kelly, A.A.; Sundqvist, C.; Dörmann, P.; Karim, S.; Jarvis, P. Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol deficiency in Arabidopsis affects pigment composition in the prolamellar body and impairs thylakoid membrane energization and photoprotection in leaves. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.G.; Hendrickson, L.; Krol, M.; Selstam, E.; Oquist, G.; Hurry, V.; Huner, N.P. Digalactosyl-diacylglycerol deficiency impairs the capacity for photosynthetic intersystem electron transport and state transitions in Arabidopsis thaliana due to photosystem I acceptor-side limitations. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.G.; Krol, M.; Savitch, L.V.; Szyszka-Mroz, B.; Roche, J.; Sprott, D.P.; Selstam, E.; Wilson, K.W.; Gardiner, R.; Öquist, G.; et al. The decreased PG content of pgp1 inhibits PSI photochemistry and limits reaction center and light-harvesting polypeptide accumulation in response to cold acclimation. Planta 2022, 255, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, T.; Szalontai, B.; Kłodawska, K.; Vladkova, R.; Malec, P.; Gombos, Z.; Laczko-Dobos, H. Photosystem I oligomerization affects lipid composition in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłodawska, K.; Kovács, L.; Vladkova, R.; Rzaska, A.; Gombos, Z.; Laczkó-Dobos, H.; Malec, P. Trimeric organization of photosystem I is required to maintain the balanced photosynthetic electron flow in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Photosynth. Res. 2020, 143, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, P.; Biswas, A.; Balog-Vig, F.; Domonkos, I.; Kovács, L.; Lambrev, P.H. Trimeric photosystem I facilitates energy transfer from phycobilisomes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


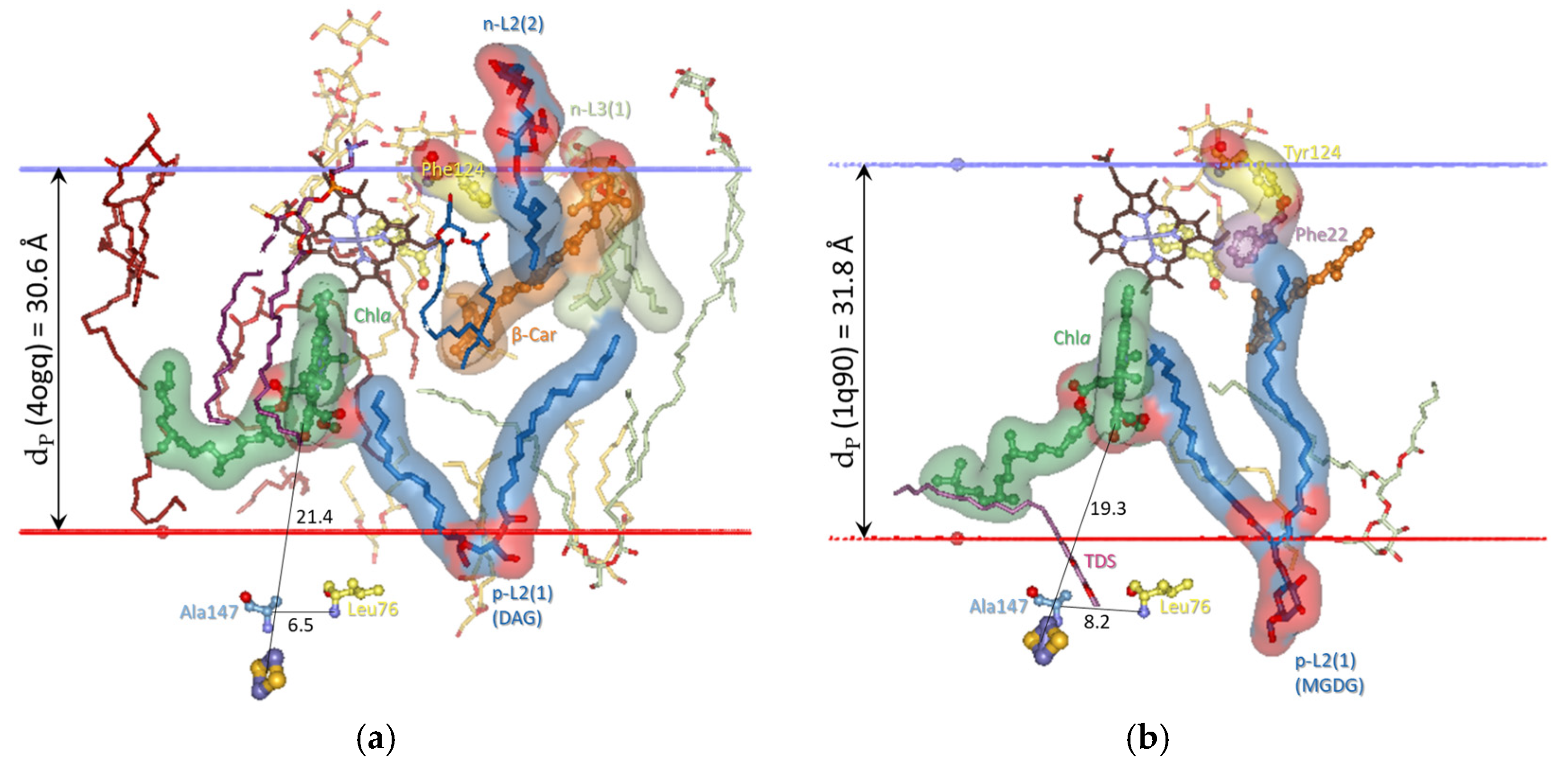

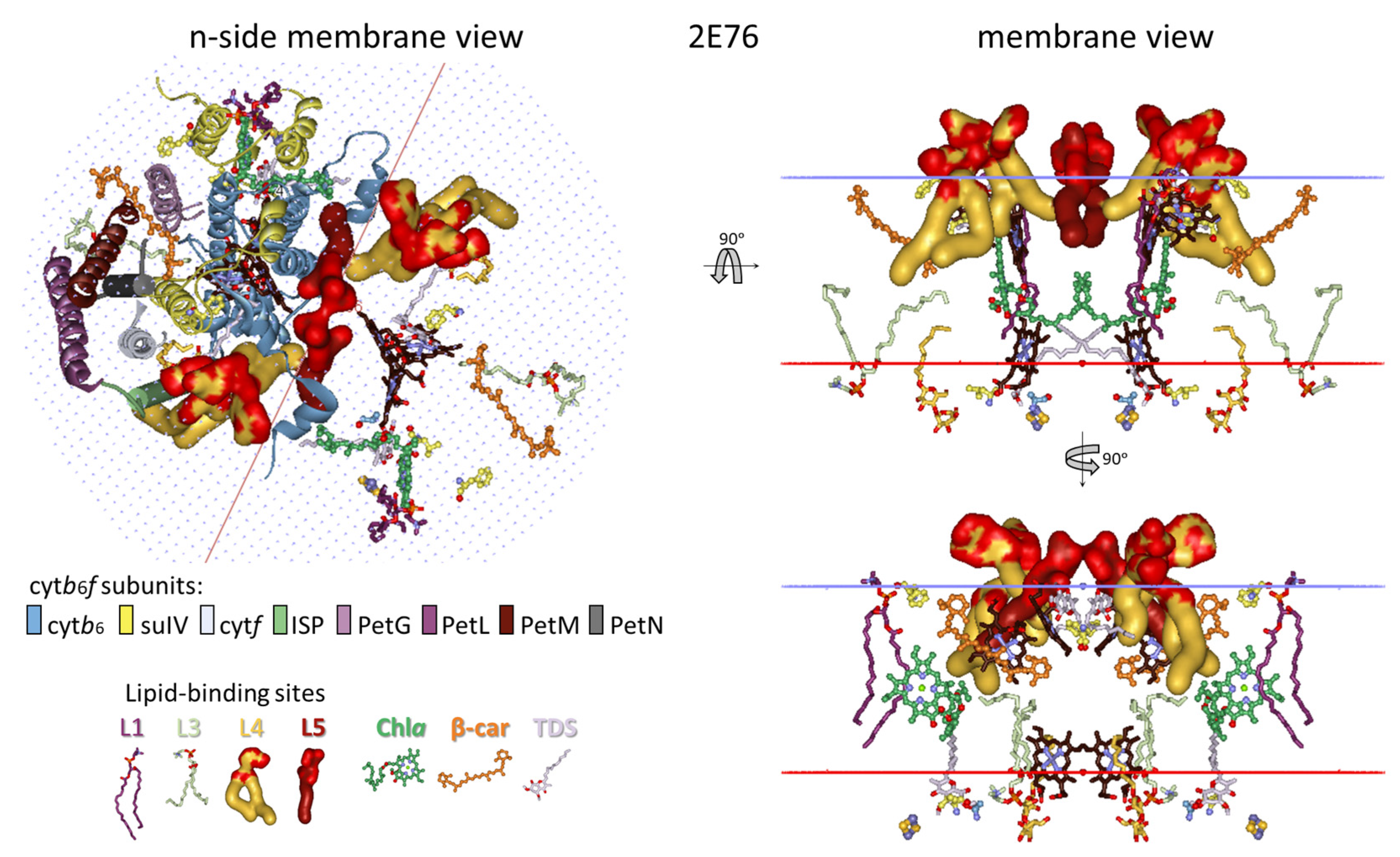
| Specific Lipid-Binding Sites | Optimal (Oxidized) Stationary Conditions (p-Gate = 6.5 Å; dP = 30.6 Å) | From Optimal to Over-Reduced (Induction Phase for State 2) (p-Gate > 7.2 Å, dP > 31.2Å) | From Optimal to Over-Oxidized (Induction Phase for State 1) (p-Gate < 6.5 Å; dP < 30.6 Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-L1(1) | PG c | PG c,d | Escape of PG to bulk |
| n-L2(1) | PG c | Escape of PG to bulk | Escape of PG to bulk |
| p-L2(1) a | PG c | Exchange of PG with MGDG | Escape of PG to bulk |
| p-L3(1) a | PG d | Exchange of PG with MGDG | Escape of PG to bulk |
| n-L4(1) | SQDG | SQDG | Exchange of SQDG with DGDG e |
| n-L4(3) | n.i. (detergent) | MGDG c | Empty |
| p-L4(1) | PG c | PG | Escape of PG to bulk |
| n/p-L5(2) b | DAG/PQ | PQ | Exchange of DAG/PQ with DGDG e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vladkova, R. X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure Analysis Unravels How the Unique Thylakoid Lipid Composition Is Utilized by Cytochrome b6f for Driving Reversible Proteins’ Reorganization During State Transitions. Membranes 2025, 15, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050143
Vladkova R. X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure Analysis Unravels How the Unique Thylakoid Lipid Composition Is Utilized by Cytochrome b6f for Driving Reversible Proteins’ Reorganization During State Transitions. Membranes. 2025; 15(5):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050143
Chicago/Turabian StyleVladkova, Radka. 2025. "X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure Analysis Unravels How the Unique Thylakoid Lipid Composition Is Utilized by Cytochrome b6f for Driving Reversible Proteins’ Reorganization During State Transitions" Membranes 15, no. 5: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050143
APA StyleVladkova, R. (2025). X-Ray Crystal and Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure Analysis Unravels How the Unique Thylakoid Lipid Composition Is Utilized by Cytochrome b6f for Driving Reversible Proteins’ Reorganization During State Transitions. Membranes, 15(5), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050143






