Characterization, Performance, and Toxicological Assessment of Polysulfone-Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Membranes for Water Separation Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Sulfonated PEEK (SPEEK) and Membrane Fabrication
2.2. Membrane Characterization
2.3. Toxicity Assays
2.4. Membrane Performance
3. Results and Discussion
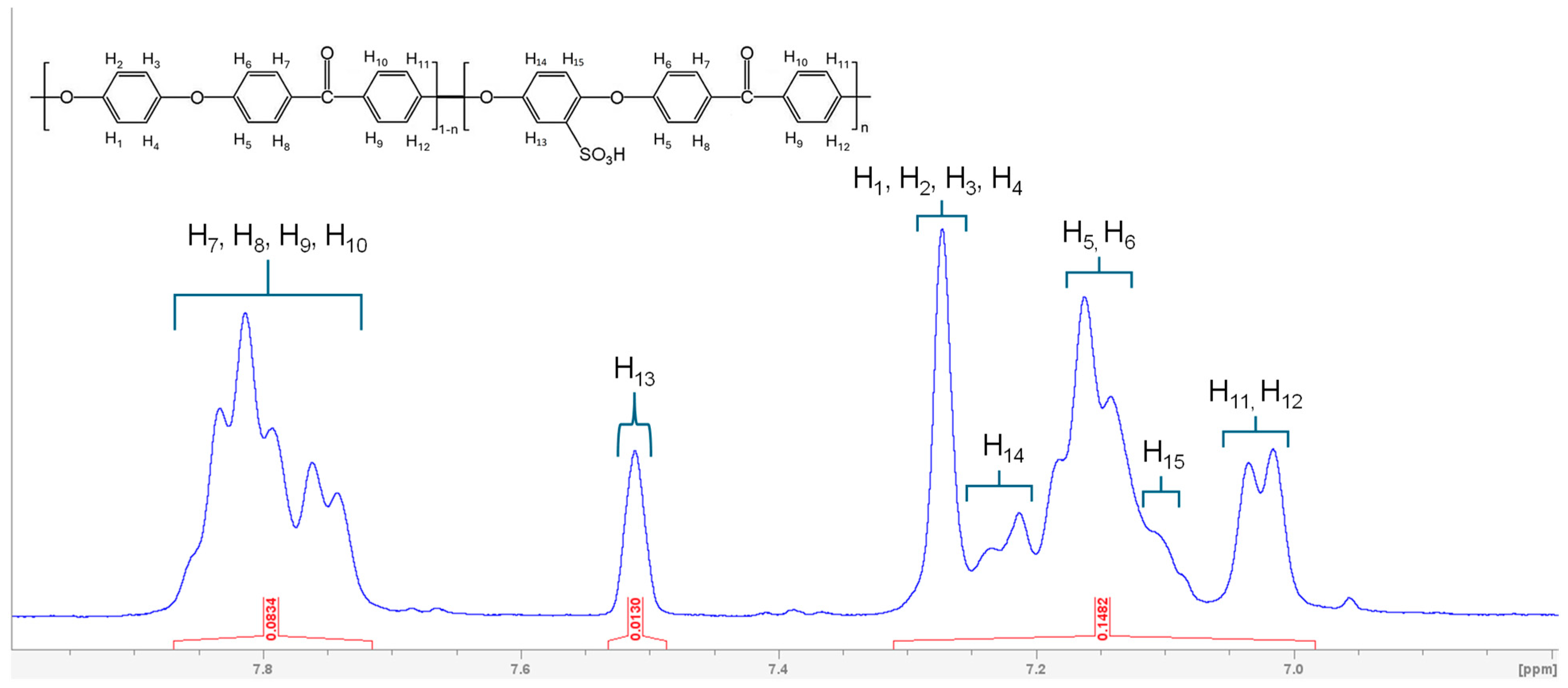
3.1. Characterizations of Synthesized SPEEK
3.2. Dope Solution Behavior: Cloud Point and Viscosity
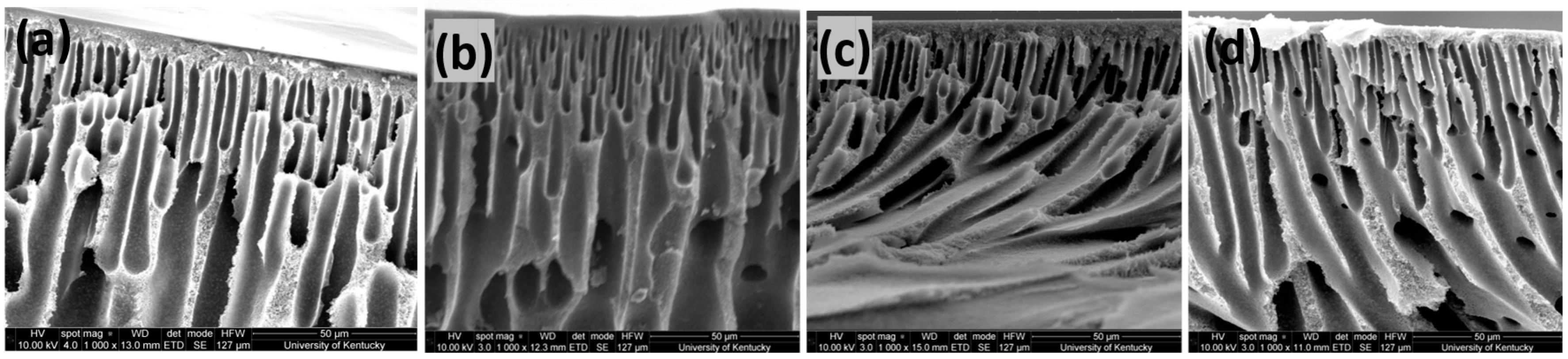
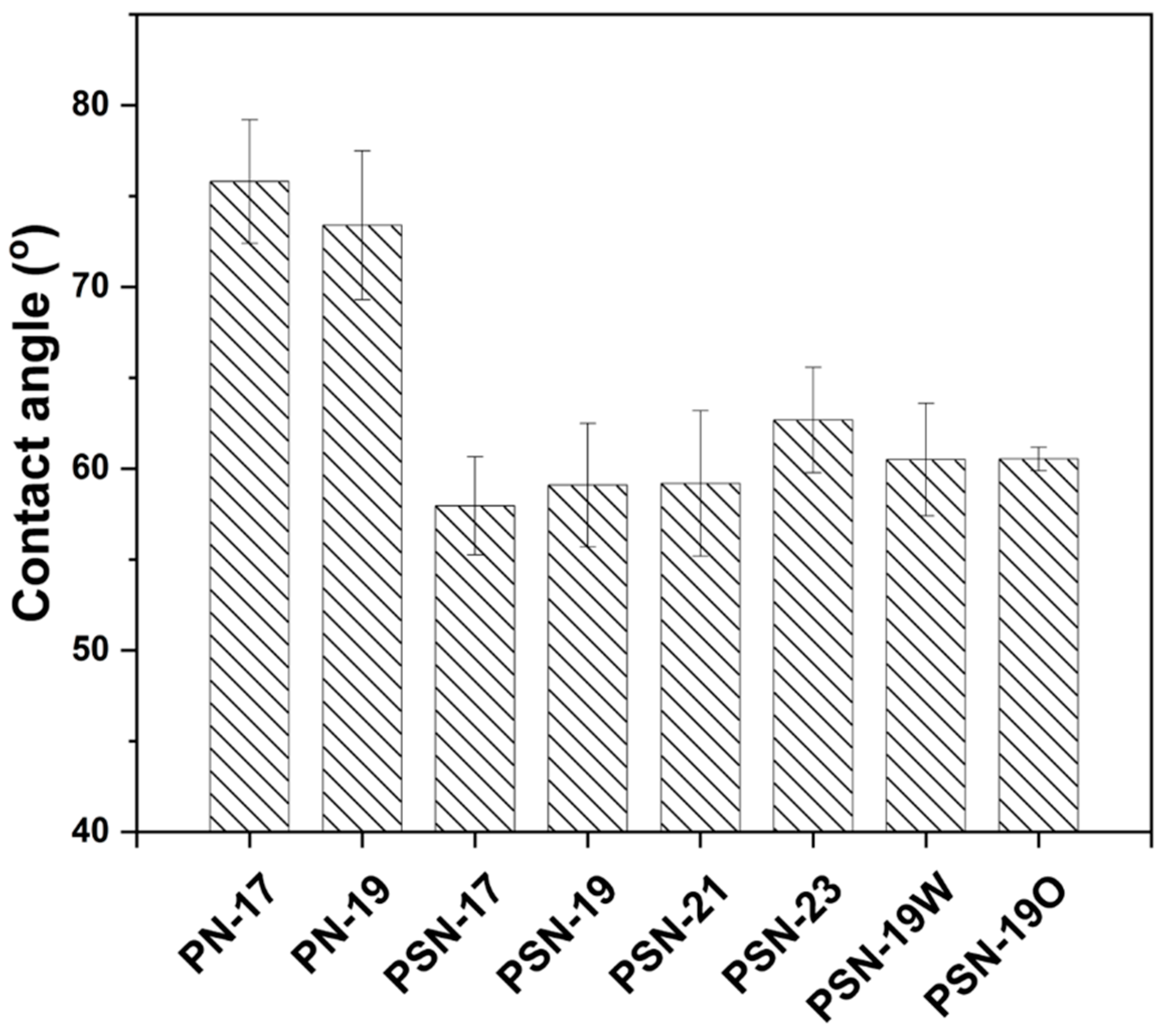
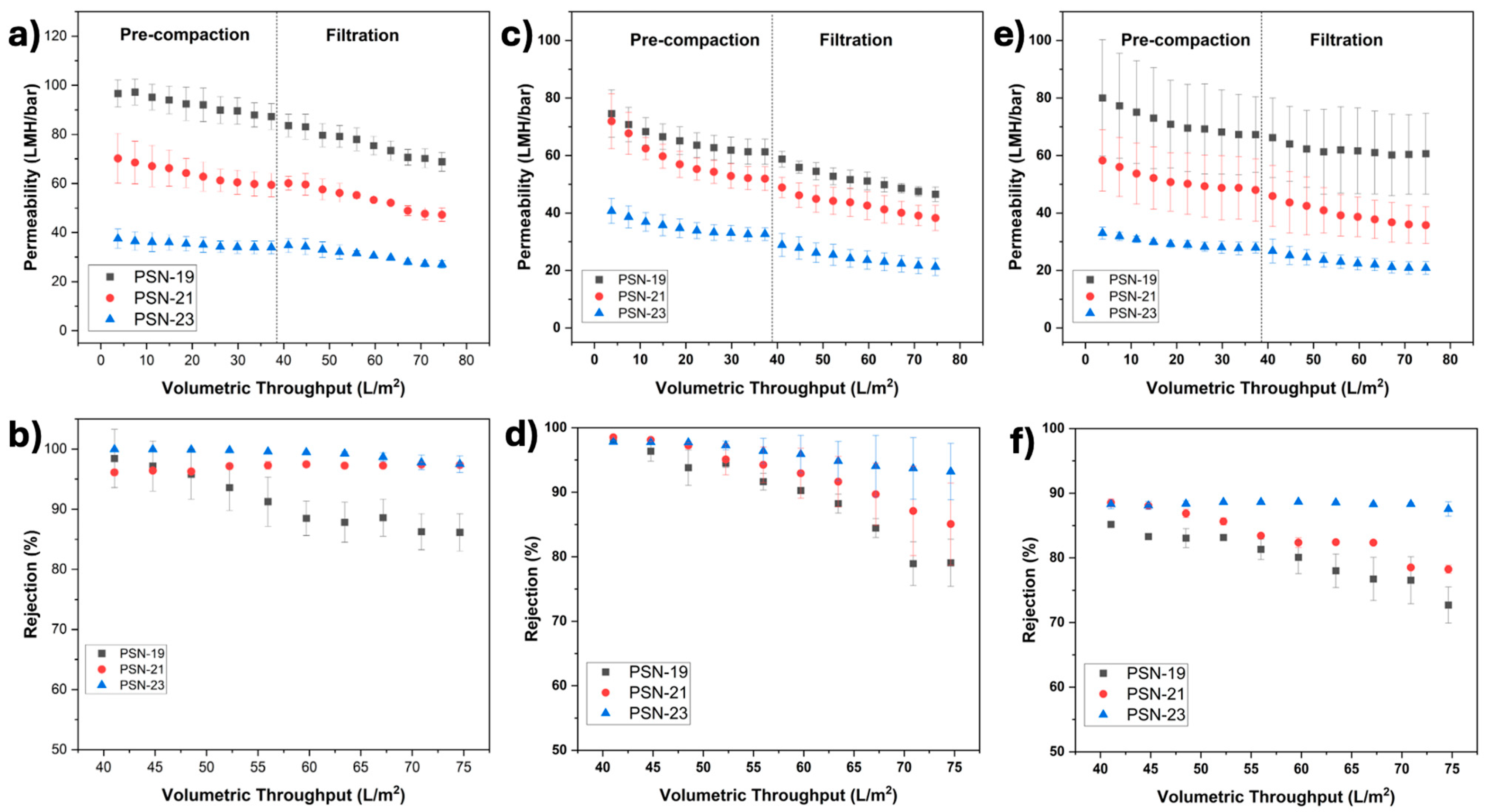
3.3. Characterization of Fabricated Membranes
3.4. Toxicity Assessments
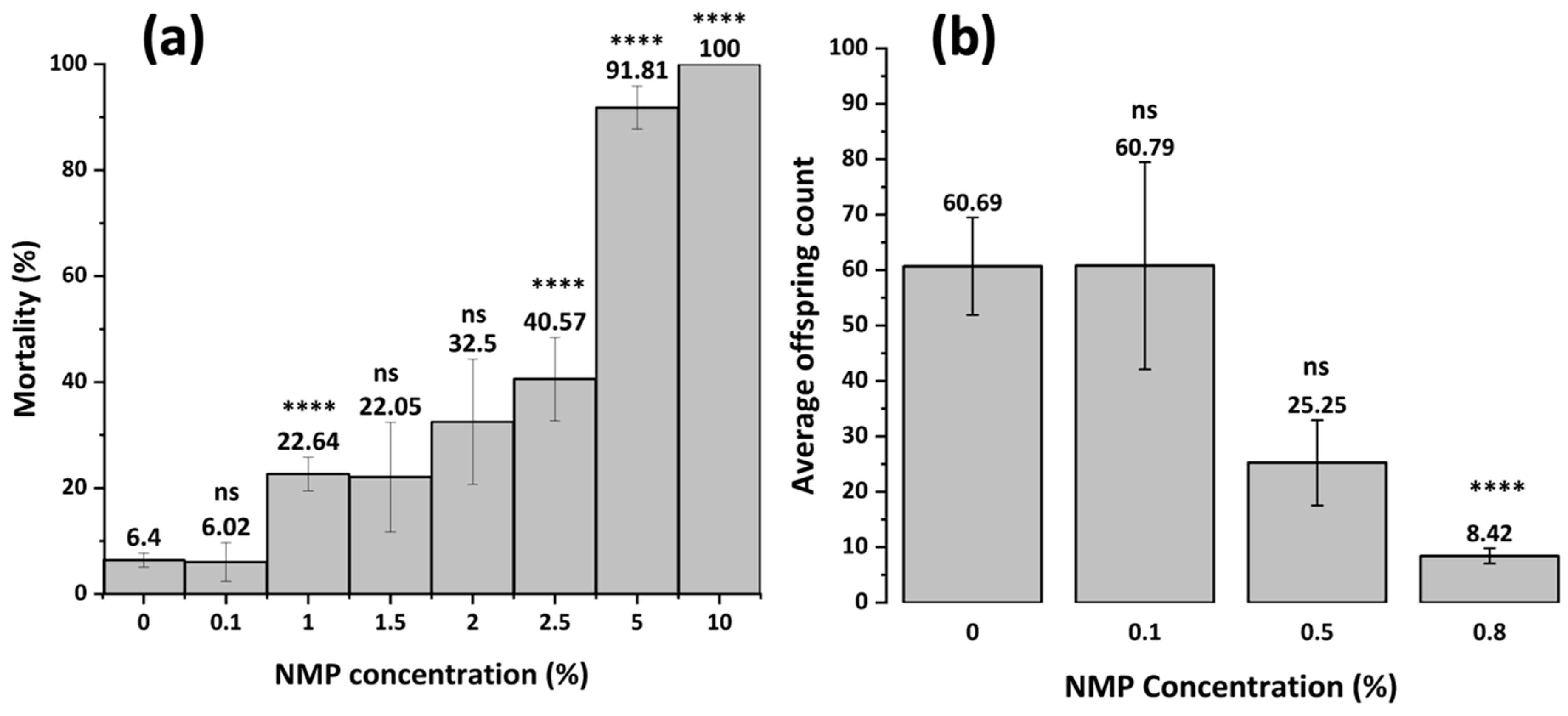
3.4.1. NMP Toxicity (Mortality and Reproduction)
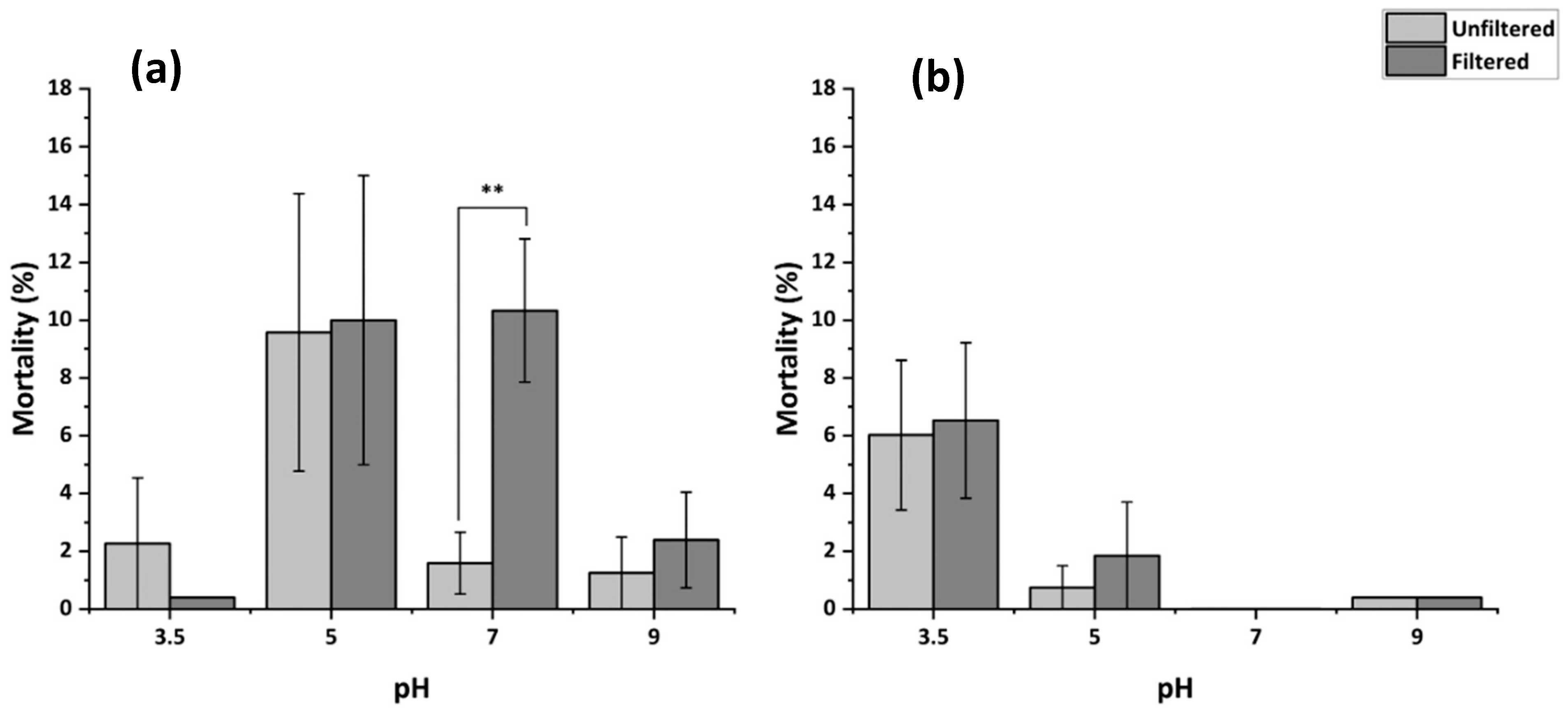
3.4.2. Mortality Following Filtration of MHRW at Varying pH
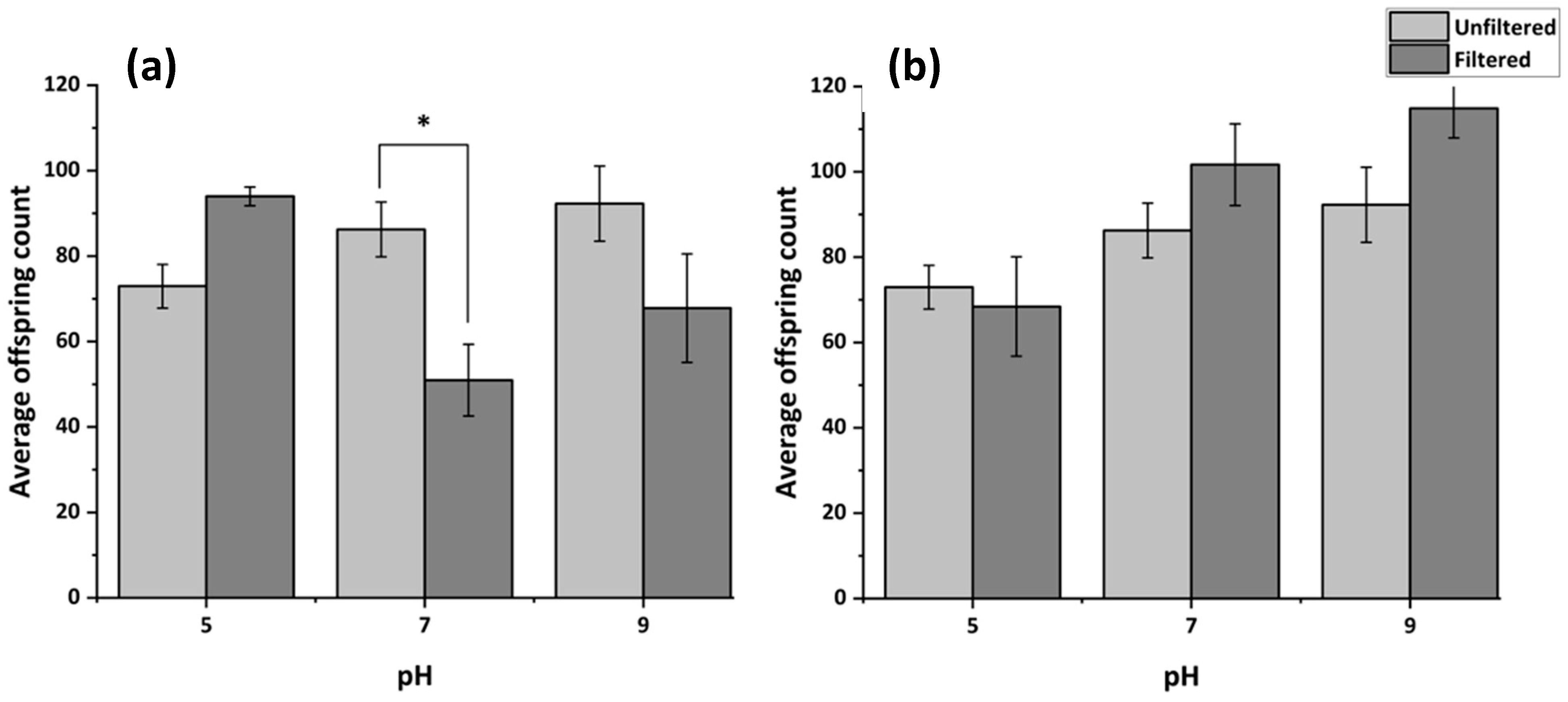
3.4.3. Reproduction Following Filtration of MHRW at Varying pH
3.4.4. Total Nitrogen (TN) Concentrations After Filtration
4. Investigation of Membrane Performance
4.1. Selective Filtration Using Binary Dye Mixtures
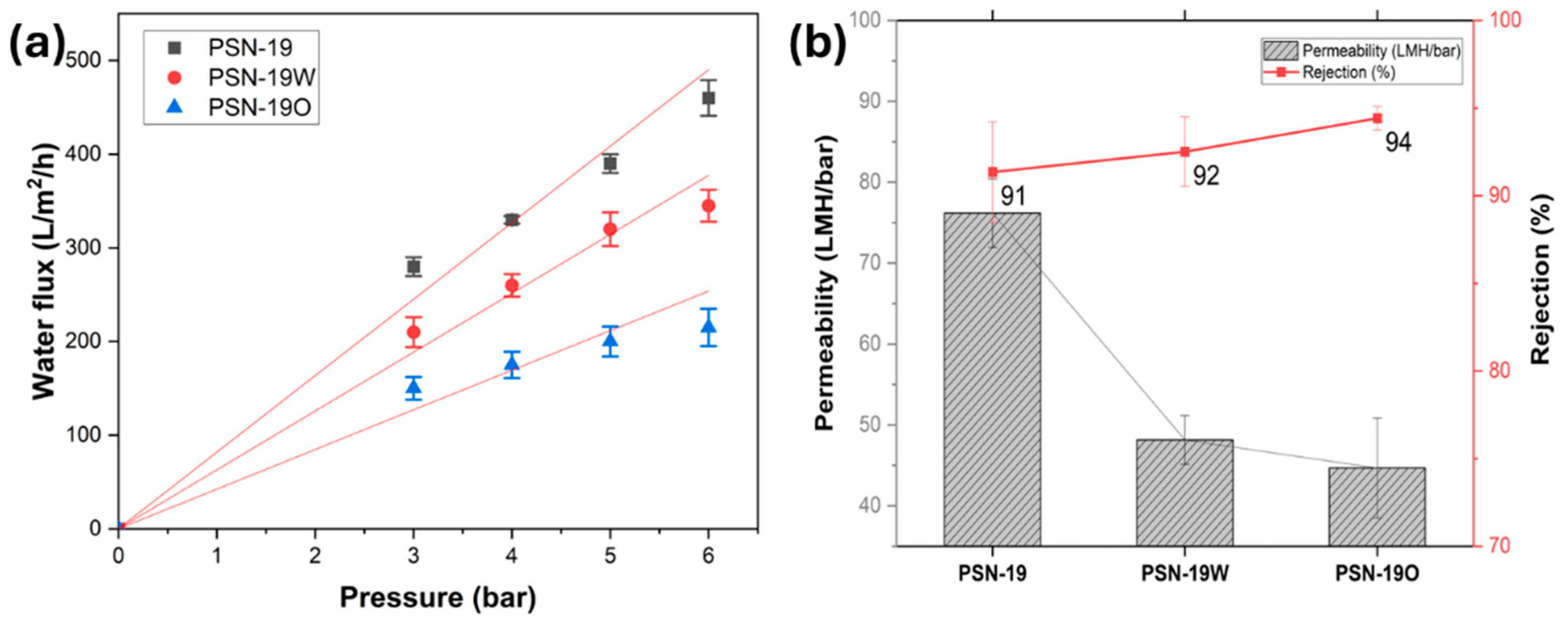
4.2. Annealed Membrane Performance
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aristizábal, S.L.; Lively, R.P.; Nunes, S.P. Solvent and thermally stable polymeric membranes for liquid molecular separations: Recent advances, challenges, and perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 685, 121972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Hazarika, G.; Yadav, D.; Ingole, P.G. Polymeric membranes for industrial applications: Recent progress, challenges and perspectives. Desalination 2023, 573, 117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian Chaleshtari, Z.; Foudazi, R. A review on per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) remediation: Separation mechanisms and molecular interactions. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 2258–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jung, K.; Shim, J.Y.; Harris, T.A.; Escobar, I.C. Manufacturing supported loose-nanofiltration polymeric membranes with eco-friendly solvents on an R2R System. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrs, C.; Schwellenbach, J. Membrane formation via non-solvent induced phase separation using sustainable solvents: A comparative study. Polymer 2020, 186, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Tuning pore size and surface charge of poly (piperazinamide) nanofiltration membrane by enhanced chemical cleaning treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 643, 120054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Raveshiyan, S.; Amini, Y.; Zadhoush, A. A critical review with emphasis on the rheological behavior and properties of polymer solutions and their role in membrane formation, morphology, and performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 319, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamah, S.C.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Suzaimi, N.D.; Yogarathinam, L.T.; Raji, Y.O.; El-badawy, T.H. Recent development in modification of polysulfone membrane for water treatment application. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wavhal, D.S.; Fisher, E.R. Modification of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by CO2 plasma treatment. Desalination 2005, 172, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, N.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.Z.; Yu, G.; An, Z.; Lin, X.; Tang, L. Anti-fouling ultrafiltration membrane prepared from polysulfone-graft-methyl acrylate copolymers by UV-induced grafting method. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Konruang, S.; Chittrakarn, T.; Sirijarukul, S. Surface modification of asymmetric polysulfone membrane by UV irradiation. J. Teknol. Sci. Eng. 2014, 70, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, S.; McDonald, J.A.; Kuchel, R.P.; Khan, S.J.; Leslie, G.; Tang, C.Y.; Mansouri, J.; Fane, A.G. Surface modification of nanofiltration membranes to improve the removal of organic micropollutants: Linking membrane characteristics to solute transmission. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.; Fayomi, O.S.I.; Sadiku, R.; Popoola, P.; Alaba, P.A.; Adegbola, A.T. Polymers blends for the improvement of nanofiltration membranes in wastewater treatment: A short review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 3365–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Bi, W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, J. High-strength corrosion resistant membranes for the separation of oil/water mixtures and immiscible oil mixtures based on PEEK. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahimai, B.M.; Sivasubramanian, G.; Sekar, K.; Kannaiyan, D.; Deivanayagam, P. Sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone): Efficient ion-exchange polymer electrolytes for fuel cell applications—A versatile review. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 6085–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaheem, Y.; Alomair, A.; Alhendi, A.; Alkandari, S.; Tanoli, N.; Alnajdi, N.; Quesada-Peréz, A. Preparation of polyetherimide membrane from non-toxic solvents for the separation of hydrogen from methane. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, J.; Farmer, T.J.; Clark, J.H. Catalyst: Possible Consequences of the N-Methyl Pyrrolidone REACH Restriction. Chem 2018, 4, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyulin, A.V.; Sengupta, S.; Varughese, A.; Komarov, P.; Venkatnathan, A. Effect of annealing on structure and diffusion in hydrated Nafion membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5058–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vona, M.L. Annealing of Polymer Membranes. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Di Vona, M.L.; Sgreccia, E.; Licoccia, S.; Alberti, G.; Tortet, L.; Knauth, P. Analysis of temperature-promoted and solvent-assisted cross-linking in sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone)(SPEEK) proton-conducting membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 7505–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, L.P.; Luke, C.J.; Perlmutter, D.H.; Silverman, G.A.; Pak, S.C. C. elegans in high-throughput drug discovery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69–70, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.R. The C. elegans model in toxicity testing. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuthner, T.C.; Zhang, S.; Kohrn, B.F.; Stapleton, H.M.; Baugh, L.R. Structure-specific variation in per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances toxicity among genetically diverse Caenorhabditis elegans strains. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, J.P.; Unrine, J.M.; Coyne, M.; Tsyusko, O.V. Multiple stressor effects on a model soil nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans: Combined effects of the pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms; US Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Eke, J.; Mills, P.A.; Page, J.R.; Wright, G.P.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Escobar, I.C. Nanohybrid membrane synthesis with phosphorene nanoparticles: A study of the addition, stability and toxicity. Polymers 2020, 12, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnian, M.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Gashoul, F. Comprehensive investigation of physicochemical and electrochemical properties of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes with different degrees of sulfonation for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Energy 2017, 125, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Raj, S.K.; Sharma, J.; Rathod, N.H.; Maru, P.; Kulshrestha, V. Sulfonated poly ether ether ketone (SPEEK) based composite cation exchange membranes for salt removal from brackish water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 614, 126157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Nie, S.; Liu, H.; Gong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liao, G. Design and development of nucleobase modified sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes for high-performance direct methanol fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 19914–19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fionah, A.; McLarney, K.; Judd, A.; Escobar, I.C. Effects of the Applied Potential on the Performance of Polysulfone Membranes Functionalized with Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Polymers. Membranes 2023, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.-J.; Ismail, A. Effect of SPEEK content on the morphological and electrical properties of PES/SPEEK blend nanofiltration membranes. Desalination 2009, 249, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-C.; Su, J.F.; Cheng, L.-P. Fabrication of high-flux asymmetric polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membranes by nonsolvent induced phase separation process: Effects of H2O contents in the dope. Polymer 2021, 217, 123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-J.; Nam, S.-T. Thermodynamic and rheological variation in polysulfone solution by PVP and its effect in the preparation of phase inversion membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Aernouts, B.; Saeys, W.; Vankelecom, I.F. Study of polymer concentration and evaporation time as phase inversion parameters for polysulfone-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirzadi, M.A.A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Ruan, G.; Tan, N. Tailoring PES nanofiltration membranes through systematic investigations of prominent design, fabrication and operational parameters. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49080–49097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, D.S.; Matindi, C.; Vilakati, G.D.; Tesha, J.M.; Motsa, M.M.; Thwala, J.M.; Mamba, B.B.; Hoek, E.; Li, J. Fine-tuning the architecture of loose nanofiltration membrane for improved water flux, dye rejection and dye/salt selective separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 621, 118930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, Y.; Yue, Z.; Economy, J. Preparation of polyelectrolyte multilayer films consisting of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) alternating with selected anionic layers. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.F.; Islam, M.A.; Khorshidi, B.; Tehrani-Bagha, A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Surface characterization of thin-film composite membranes using contact angle technique: Review of quantification strategies and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Kumoro, A.C.; Aryanti, N.; Utomo, D.P.; Hasbullah, H.; Alexandro, S.R. Effects of crosslinking and thermal annealing modifications on the performance of nanohybrid PSf-ZnO membranes for the treatment of raw and ozonated petroleum refinery wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basma, N.S.; Headen, T.F.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Skipper, N.T.; Howard, C.A. Local Structure and Polar Order in Liquid N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 8963–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, H.L.; Striebig, B.A. Evaluation of N-Methylpyrrolidone and Its Oxidative Products Toxicity Utilizing the Microtox Assay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, J.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Zhang, P.; Song, B.; Cao, W.-C.; Fang, S.-Y.; Huan, S.-Y.; Ye, J. The performance of UiO-66-NH2/graphene oxide (GO) composite membrane for removal of differently charged mixed dyes. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.-l. High efficient dye removal with hydrolyzed ethanolamine-Polyacrylonitrile UF membrane: Rejection of anionic dye and selective adsorption of cationic dye. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Su, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. A metal-nano GO frameworks/PPS membrane with super water flux and high dyes interception. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verliefde, A.; Cornelissen, E.; Heijman, S.; Verberk, J.; Amy, G.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Van Dijk, J. The role of electrostatic interactions on the rejection of organic solutes in aqueous solutions with nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Wong, G.K.W.; Ting, Y.-P. Electrostatic interaction governed solute transport in forward osmosis. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Gao, A.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhan, X.; Yan, Y. Bio-inspired underwater superoleophobic PVDF membranes for highly-efficient simultaneous removal of insoluble emulsified oils and soluble anionic dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.R.; Isloor, A.M.; Bhat, U.K.; Ismail, A.; Obaid, A.; Fun, H.-K. Preparation and performance studies of polysulfone-sulfated nano-titania (S-TiO2) nanofiltration membranes for dye removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53874–53885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahazadeh, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A.; Khanlari, S.; Karimi, H.; Emrooz, H.B.M. Development of cellulose acetate/metal-organic framework derived porous carbon adsorptive membrane for dye removal applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 638, 119692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ni, C.; Xiao, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. Ionic liquid grafted polyethersulfone nanofibrous membrane as recyclable adsorbent with simultaneous dye, heavy metal removal and antibacterial property. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shen, X.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Polythyleneimine-modified original positive charged nanofiltration membrane: Removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriem, O.A.; Kamel, A.M.; Shaaban, W.; Elkady, M.F. Enhancement of dye separation performance of eco-friendly cellulose acetate-based membranes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, S.; Shahbazi, A. High–performance nanofiltration membrane blended by Fe3O4@ SiO2–CS bionanocomposite for efficient simultaneous rejection of salts/heavy metals ions/dyes with high permeability, retention increase and fouling decline. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 127930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H.-X.; Zhang, B.-X.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, T.-L.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Preparation of three dimensional hydroxyapatite nanoparticles/poly (vinylidene fluoride) blend membranes with excellent dye removal efficiency and investigation of adsorption mechanism. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, T.T.; Kumar, S.R.; Lue, S.J. Separation mechanisms of binary dye mixtures using a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane: Donnan effect and intermolecular interaction. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-J.; Bhattacharyya, D. Thermal annealing effect on cellulose acetate reverse osmosis membrane structure. Desalination 1995, 101, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ren, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.; Sheng, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Deng, M. Effect of thermal annealing on gas separation performance and aggregation structures of block polyimide membranes. Polymer 2021, 219, 123538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-J.; Park, H.-D. Effect of transmembrane pressure, linear velocity, and temperature on permeate water flux of high-density vertically aligned carbon nanotube membranes. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26706–26717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavania, J.; Rastogi, N.K.; Balaraman, M.; Rangaswamy, S. Nonlinear Flux–Pressure Behavior of Solvent Permeation through a Hydrophobic Nanofiltration Membrane. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27052–27061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Jean, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Effects of annealing on the microstructure and performance of cellulose acetate membranes for pressure-retarded osmosis processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Membrane | Porosity (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| PN-17 | 63.1 ± 3.43 | 4.40 ± 0.14 |
| PN-19 | 64.9 ± 3.75 | 5.28 ± 0.19 |
| PSN-17 | 86.4 ± 3.6 | 3.65 ± 0.14 |
| PSN-19 | 82.1 ± 1.56 | 3.86 ± 0.45 |
| PSN-21 | 80.13 ± 1.79 | 5.27 ± 0.12 |
| PSN-23 | 78.5 ± 2.14 | 5.71 ± 0.21 |
| PSN-19W | 79.4 ± 3.21 | 4.84 ± 0.25 |
| PSN-19O | 78.9 ± 0.89 | 4.17 ± 0.60 |
| Model Dye | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Ionic Nature | Observed Rejection | Observed Behavior Based on Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 319.85 | Cationic | 99% | High rejection due to size exclusion and strong electrostatic attraction between the cationic MB and the negatively charged membrane surface, combined with moderate molecular size. |
| CR | 696.7 | Anionic | 86% | Good rejection since CR is a large, anionic dye. The electrostatic interactions, and size exclusion helped achieve relatively high rejection. |
| CV | 407.99 | Cationic | 95% | High rejection due to electrostatic attraction between the cationic nature and the membrane’s negative charge. CV’s moderate size contributed to efficient rejection. |
| AO2 | 350.22 | Anionic | 38% | Low rejection due to both smaller molecular size and electrostatic repulsion between the anionic AO2 and the negatively charged membrane surface. The smaller size of AO2 resulted in low retention. |
| Membrane | Process | Flux (LMH) | Pressure (Bar) | Feed | % Removal | Suggested Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinylidene fluoride/chitosan/dopamine membranes | UF | 116–201 | 1 | OG | 96.8% (MB) 92.7% (OG) | Electrostatic attraction | [50] |
| PSf/sulfonated-TiO2 | NF | 6.50 | 6 | MB | 90.4% | Electrostatic attraction/adsorption | [51] |
| UiO-66-NH2/(GO) on polyurethane composite membranes | MF | - | - | MB, CR | 95% (MB), 90% (CR) | Electrostatic attraction and hydrogen bonding | [45] |
| Cellulose acetate/metal-organic framework adsorptive membrane | UF | 76.03 | 1 | MB | 98.2% | Electrostatic attraction | [52] |
| Hydrolyzed PAN-ETA | UF | 50–53 | 2 | MB, CV | 96% | Electrostatic interaction and adsorption | [46] |
| Polyethersulfone nanofibrous membrane | MF | - | - | CR, and Cd | - | Electrostatic attraction and adsorption | [53] |
| Polythyleneimine-modified positive charged TFC NF membrane | NF | 34–38 | 10 | TO (+), VB (−), SO (−), NR (+) | >98% | Pore size, electrostatic interactions | [54] |
| Cellulose acetate (CA)-based membranes by phase inversion and electrospinning | MF | - | - | MB and CR | 31 to 70% (MB) and <10% (CR) | Electrostatic attraction | [55] |
| PES/Fe3O4@SiO2 | NF | 70.6 | 4 | MB | 98 | Donnan exclusion and adsorption | [56] |
| PVDF/Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles UF Membrane | MF | 400 | 1 | CR | 88% | Electrostatic attraction, Lewis interaction | [57] |
| PSf/SPEEK | UF | 90 | 4.13 | MB CV CV MB + AO2 | 99% (MB) 97% (CV) 87% (CR) MB (99%) | Electrostatic interactions, Size exclusion | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousaf, M.U.; Madeo Cortarelli, L.; Jebet, N.I.; Unrine, J.M.; Aich, N.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Escobar, I.C. Characterization, Performance, and Toxicological Assessment of Polysulfone-Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Membranes for Water Separation Applications. Membranes 2025, 15, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030087
Yousaf MU, Madeo Cortarelli L, Jebet NI, Unrine JM, Aich N, Tsyusko OV, Escobar IC. Characterization, Performance, and Toxicological Assessment of Polysulfone-Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Membranes for Water Separation Applications. Membranes. 2025; 15(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousaf, Muhammad Usman, Lucca Madeo Cortarelli, Nerissa I. Jebet, Jason M. Unrine, Nirupam Aich, Olga V. Tsyusko, and Isabel C. Escobar. 2025. "Characterization, Performance, and Toxicological Assessment of Polysulfone-Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Membranes for Water Separation Applications" Membranes 15, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030087
APA StyleYousaf, M. U., Madeo Cortarelli, L., Jebet, N. I., Unrine, J. M., Aich, N., Tsyusko, O. V., & Escobar, I. C. (2025). Characterization, Performance, and Toxicological Assessment of Polysulfone-Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Membranes for Water Separation Applications. Membranes, 15(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030087









