Conformation and Membrane Topology of the N-Terminal Ectodomain of Influenza A M2 Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
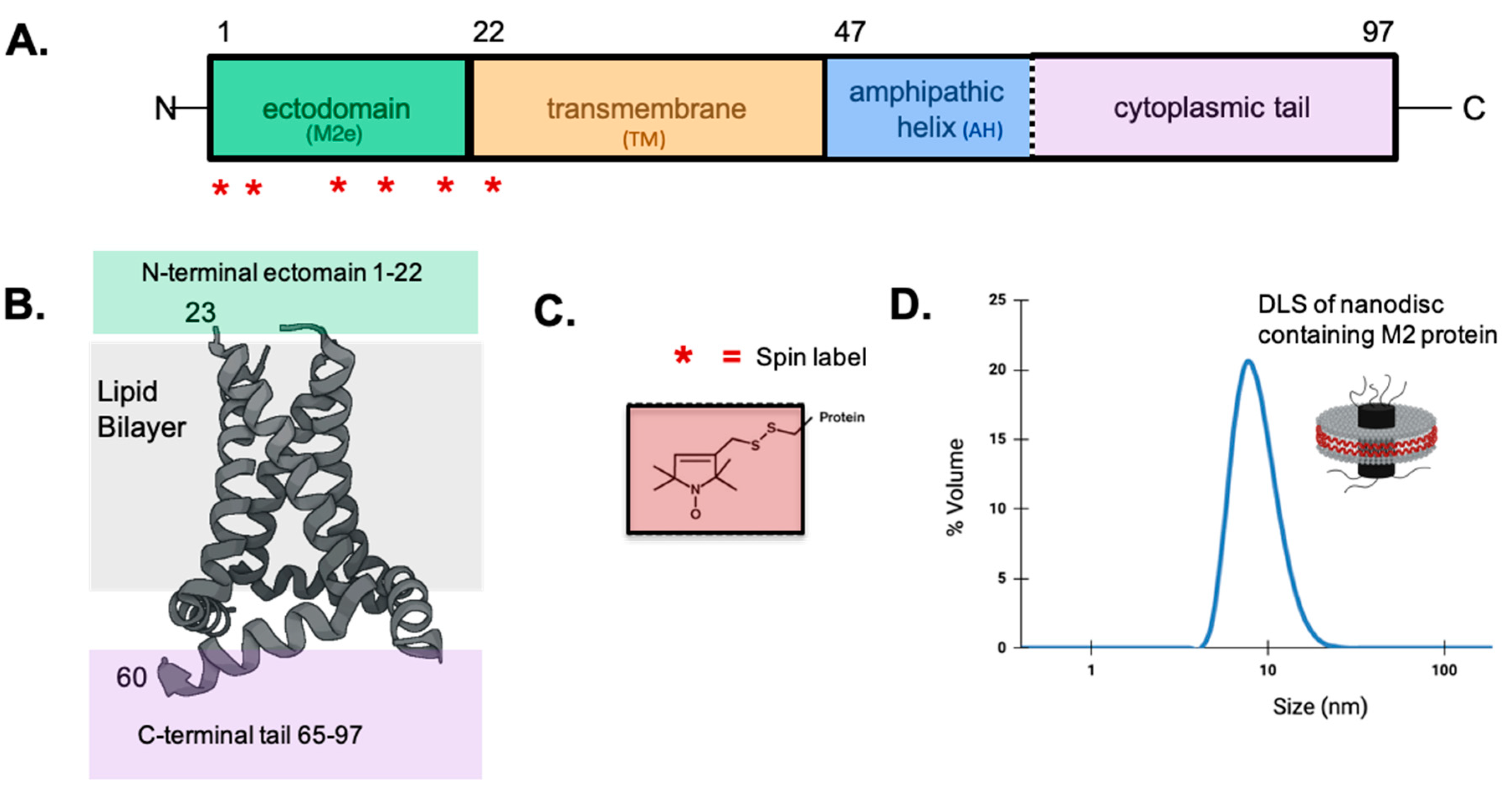
2.1. Expression, Spin Labeling, and Purification of Spin-Labeled Full-Length M2 Protein
2.2. Reconstitution of Spin-Labeled M2 Protein into Nanodiscs
2.3. Composition of Cholesterol and Drug Samples
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.5. EPR Spectroscopy and Data Analysis
3. Results
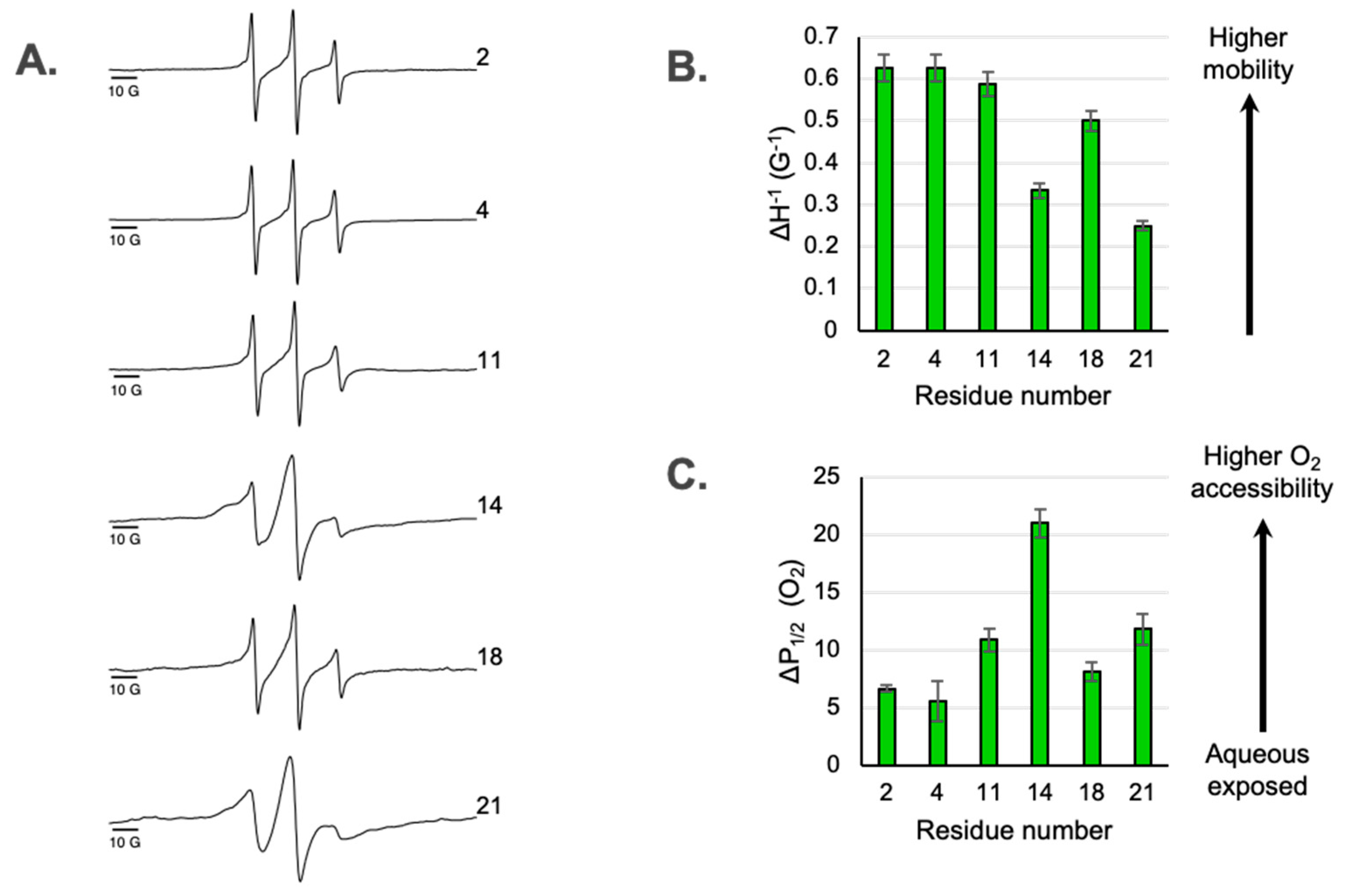
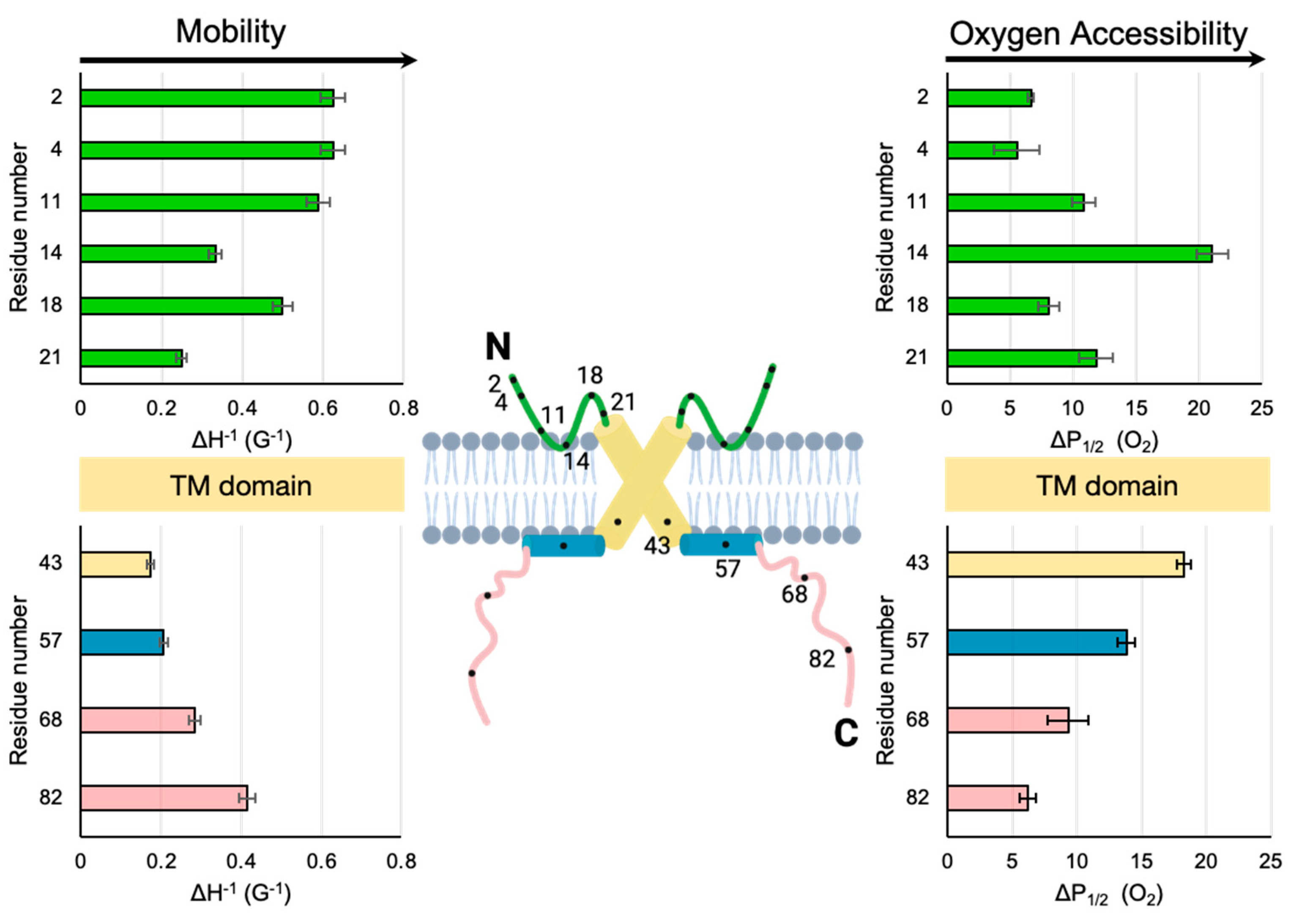
3.1. Dynamic Properties of Sites Along the Ectodomain
3.2. Access to Paramagnetic Relaxation Agents Along the Ectodomain
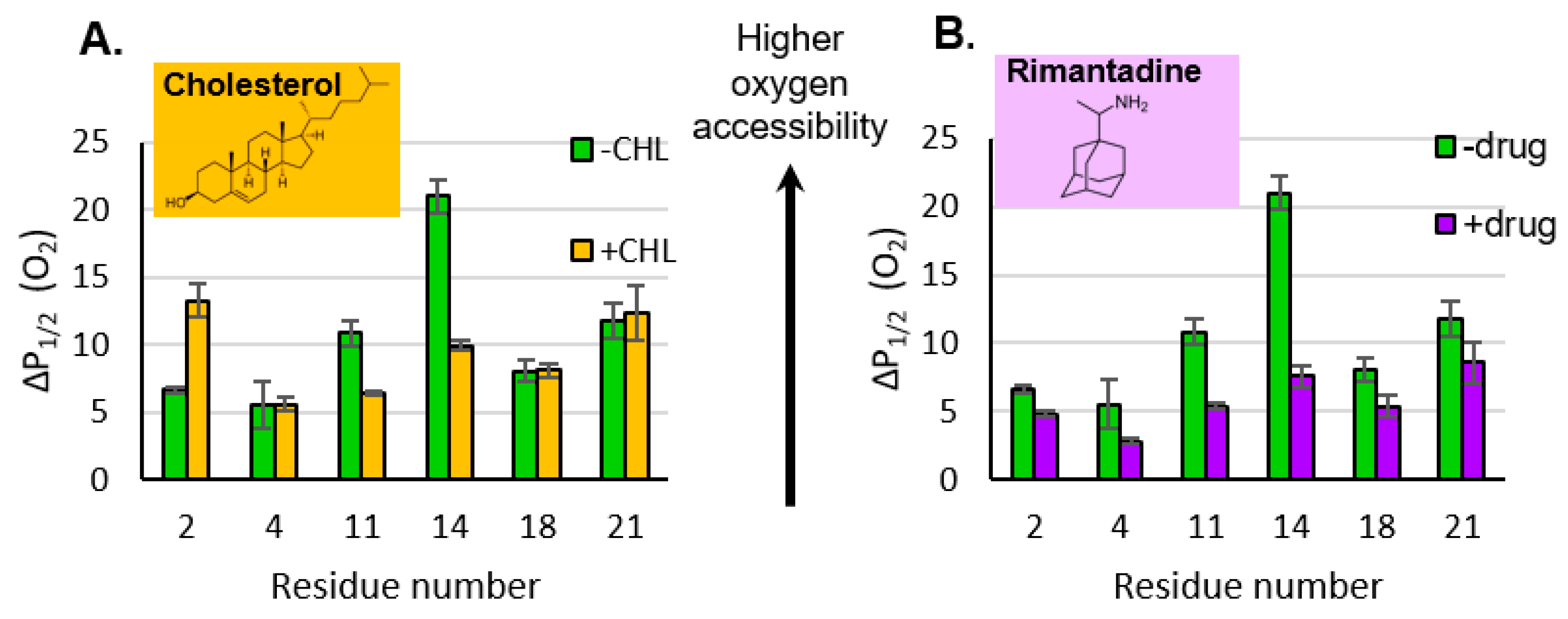
3.3. Impact of Cholesterol and Drug on Properties of M2e
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Two Extramembranous Domains of M2
4.2. Putative Membrane Insertion Motif Within the Ectodomain
4.3. Cholesterol and the Ectodomain
4.4. Drug Binding Impacts Ectodomain Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paules, C.; Subbarao, K. Influenza. Lancet 2017, 390, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.X.; De Jong, S.P.J.; Russell, C.A. Co-evolution of immunity and seasonal influenza viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeil, A.; Patton, C.; Jones, J.C.; Jeevan, T.; Harrington, W.N.; Trifkovic, S.; Seiler, J.P.; Fabrizio, T.; Woodard, K.; Turner, J.C.; et al. Rapid evolution of A(H5N1) influenza viruses after intercontinental spread to North America. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, F.G.; Asher, J.; Cowling, B.J.; Hurt, A.C.; Ikematsu, H.; Kuhlbusch, K.; Lemenuel-Diot, A.; Du, Z.; Meyers, L.A.; A Piedra, P.; et al. Reducing Influenza Virus Transmission: The Potential Value of Antiviral Treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Jiang, N.; Shi, W.; Chi, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.-L.; Wang, S. Development and Effects of Influenza Antiviral Drugs. Molecules 2021, 26, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.-X.; Liu, L.A.; Wei, D.-Q. Structural and energetic analysis of drug inhibition of the influenza A M2 proton channel. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.K.; Castrucci, M.R.; Portner, A.; Kawaoka, Y. The M2 Ectodomain Is Important for Its Incorporation into Influenza A Virions. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepens, B.; De Vlieger, D.; Saelens, X. Vaccine options for influenza: Thinking small. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthys, A.; Saelens, X. Promises and challenges of single-domain antibodies to control influenza. Antivir. Res. 2024, 222, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Ding, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; et al. Screening and characterization of inhibitory vNAR targeting nanodisc-assembled influenza M2 proteins. iScience 2023, 26, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.A.; Soto, C.S.; Polishchuk, A.; Caputo, G.A.; Tatko, C.D.; Ma, C.; Ohigashi, Y.; Pinto, L.H.; DeGrado, W.F.; Howard, K.P. pH-Induced Conformational Change of the Influenza M2 Protein C-Terminal Domain. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9934–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhenskaya, D.; Isakova-Sivak, I.; Rudenko, L. M2e-based universal influenza vaccines: A historical overview and new approaches to development. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, C.S.; Feix, J.B. Methods and Applications of Site-Directed Spin Labeling EPR Spectroscopy. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 84, pp. 617–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, A.; Roepke, K.; Arthur, T.; Howard, K.P. Conformation of influenza AM2 membrane protein in nanodiscs and liposomes. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2023, 1865, 184152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Raymond, H.E.; Herneisen, A.L.; Wong-Rolle, A.; Howard, K.P. The distal cytoplasmic tail of the influenza A M2 protein dynamically extends from the membrane. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herneisen, A.L.; Sahu, I.D.; McCarrick, R.M.; Feix, J.B.; Lorigan, G.A.; Howard, K.P. A Budding-Defective M2 Mutant Exhibits Reduced Membrane Interaction, Insensitivity to Cholesterol, and Perturbed Interdomain Coupling. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5955–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Green, B.; Thompson, M.; Chen, R.; Thomaston, J.; DeGrado, W.F.; Howard, K.P. C-terminal juxtamembrane region of full-length M2 protein forms a membrane surface associated amphipathic helix. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Schepens, B.; Seok, J.H.; Kim, S.; Roose, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Gallardo, R.; Van Hamme, E.; Schymkowitz, J.; Rousseau, F.; et al. Structure of the Extracellular Domain of Matrix Protein 2 of Influenza A Virus in Complex with a Protective Monoclonal Antibody. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.J.; Schepens, B.; Moonens, K.; Deng, L.; Fiers, W.; Remaut, H.; Saelens, X. Crystal Structure of the Conserved Amino Terminus of the Extracellular Domain of Matrix Protein 2 of Influenza A Virus Gripped by an Antibody. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.Y.; Fritzsching, K.J.; Hong, M. Conformational analysis of the full-length M2 protein of the influenza A virus using solid-state NMR. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 1623–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.; Hong, M. The Influenza M2 Ectodomain Regulates the Conformational Equilibria of the Transmembrane Proton Channel: Insights from Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5387–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiding, T.; Wang, J.; Martinsson, J.; DeGrado, W.F.; Årsköld, S.P. Proton and cation transport activity of the M2 proton channel from influenza A virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15409–15414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.H.; Dieckmann, G.R.; Gandhi, C.S.; Papworth, C.G.; Braman, J.; Shaughnessy, M.A.; Lear, J.D.; Lamb, R.A.; DeGrado, W.F. A functionally defined model for the M 2 proton channel of influenza A virus suggests a mechanism for its ion selectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11301–11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuck, K.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Analysis of the Pore Structure of the Influenza A Virus M 2 Ion Channel by the Substituted-Cysteine Accessibility Method. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7755–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, J.S.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus assembly and budding. Virology 2011, 411, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, J.A.; Sanders, H.M.; Rolland, A.D.; Park, C.K.; Horton, N.C.; Prell, J.S.; Wang, J.; Marty, M.T. Influenza AM2 Channel Oligomerization Is Sensitive to Its Chemical Environment. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16273–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagn, F.; Nasr, M.L.; Wagner, G. Assembly of phospholipid nanodiscs of controlled size for structural studies of membrane proteins by NMR. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaston, J.L.; Nguyen, P.A.; Brown, E.C.; Upshur, M.A.; Wang, J.; DeGrado, W.F.; Howard, K.P. Detection of drug-induced conformational change of a transmembrane protein in lipid bilayers using site-directed spin labeling. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Widomska, J.; Feix, J.B. Physical properties of lipid bilayers from EPR spin labeling and their influence on chemical reactions in a membrane environment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.A.; Wisner, M.A.; Malmberg, N.J.; Victor, K.G.; Fanucci, G.E.; Nalefski, E.A.; Falke, J.J.; Cafiso, D.S. Membrane Orientation and Position of the C2 Domain from cPLA2 by Site-Directed Spin Labeling. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6282–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Oxygen Permeability of Phosphatidylcholine--Cholesterol Membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4474–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Sakharam, K.A. Tackling Influenza A virus by M2 ion channel blockers: Latest progress and limitations. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 267, 116172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Cross, T.A.; Zhou, H.-X. Conformational heterogeneity of the M2 proton channel and a structural model for channel activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13311–13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Luo, W.; Cady, S.D.; Hong, M. Conformational plasticity of the influenza A M2 transmembrane helix in lipid bilayers under varying pH, drug binding, and membrane thickness. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, L.H.; Lamb, R.A. The M2 Proton Channels of Influenza A and B Viruses. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8997–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.I.; Prenner, E.J.; Vogel, H.J. Tryptophan- and arginine-rich antimicrobial peptides: Structures and mechanisms of action. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1184–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Östbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A Virus Cell Entry, Replication, Virion Assembly and Movement. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, J.; Pang, X.; Hung, I.; Zhou, H.-X.; Cross, T.A. Influenza A M2 Channel Clustering at High Protein/Lipid Ratios: Viral Budding Implications. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyna, A.; Bahsoun, B.; Madsen, J.J.; Jackson, F.S.J.S.; Badham, M.D.; Voth, G.A.; Rossman, J.S. Cholesterol Alters the Orientation and Activity of the Influenza Virus M2 Amphipathic Helix in the Membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6738–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekanayake, E.V.; Fu, R.; Cross, T.A. Structural Influences: Cholesterol, Drug, and Proton Binding to Full-Length Influenza A M2 Protein. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalily, P.H.; Duncan, M.C.; Fedida, D.; Wang, J.; Tietjen, I. Put a cork in it: Plugging the M2 viral ion channel to sink influenza. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohigashi, Y.; Ma, C.; Jing, X.; Balannick, V.; Pinto, L.H.; Lamb, R.A. An amantadine-sensitive chimeric BM2 ion channel of influenza B virus has implications for the mechanism of drug inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18775–18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roepke, K.C.; Howard, K.P. Conformation and Membrane Topology of the N-Terminal Ectodomain of Influenza A M2 Protein. Membranes 2025, 15, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020040
Roepke KC, Howard KP. Conformation and Membrane Topology of the N-Terminal Ectodomain of Influenza A M2 Protein. Membranes. 2025; 15(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoepke, Kyra C., and Kathleen P. Howard. 2025. "Conformation and Membrane Topology of the N-Terminal Ectodomain of Influenza A M2 Protein" Membranes 15, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020040
APA StyleRoepke, K. C., & Howard, K. P. (2025). Conformation and Membrane Topology of the N-Terminal Ectodomain of Influenza A M2 Protein. Membranes, 15(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020040




