Numerical Assessment of Elliptical Pore Orientation and Eccentricity Effects on Charge Transport in Anisotropic Functional Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
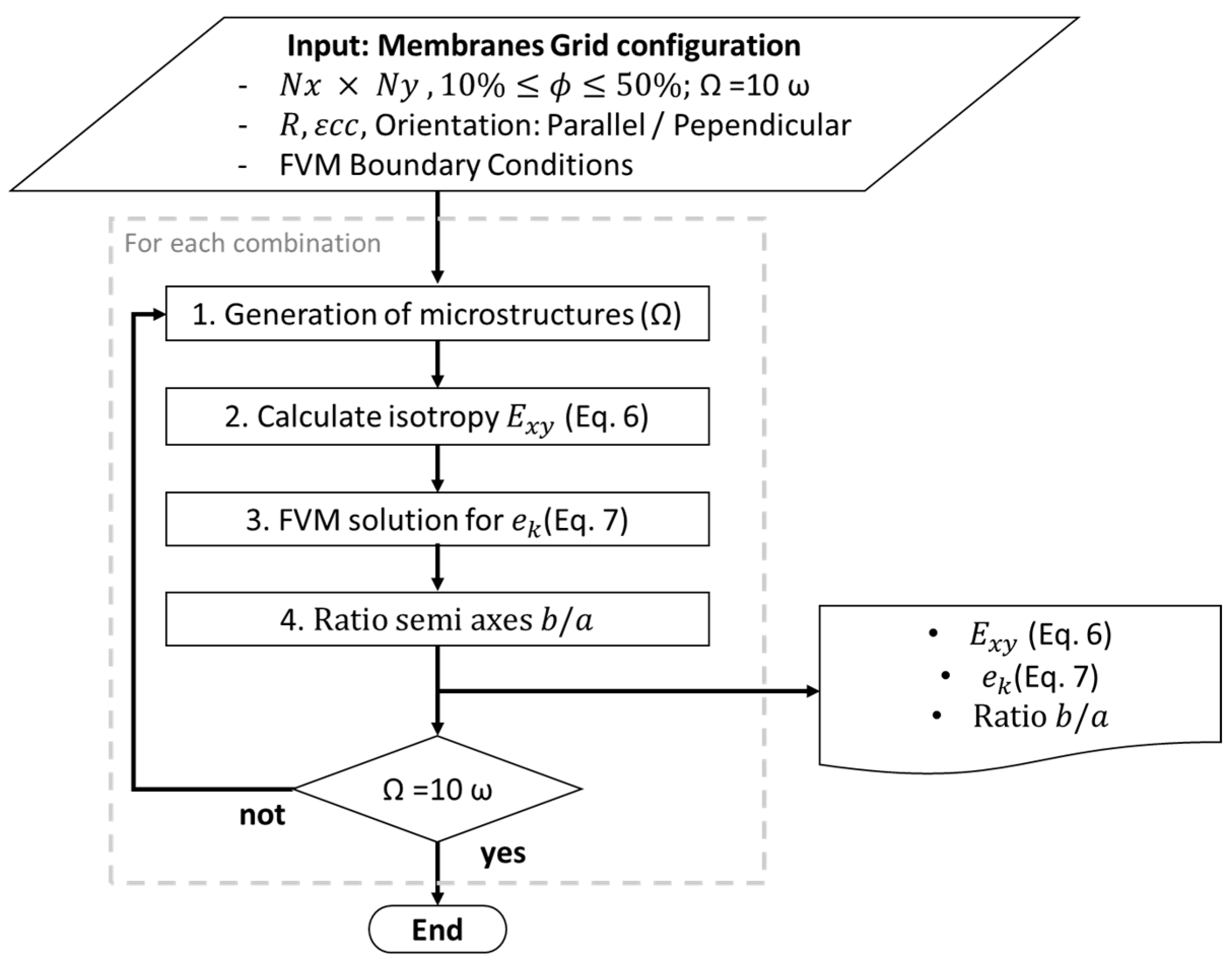
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of the Mesh of Canonical Microstructures
2.2. Isotropy Evaluation
2.3. Charge Transport Efficiency ()
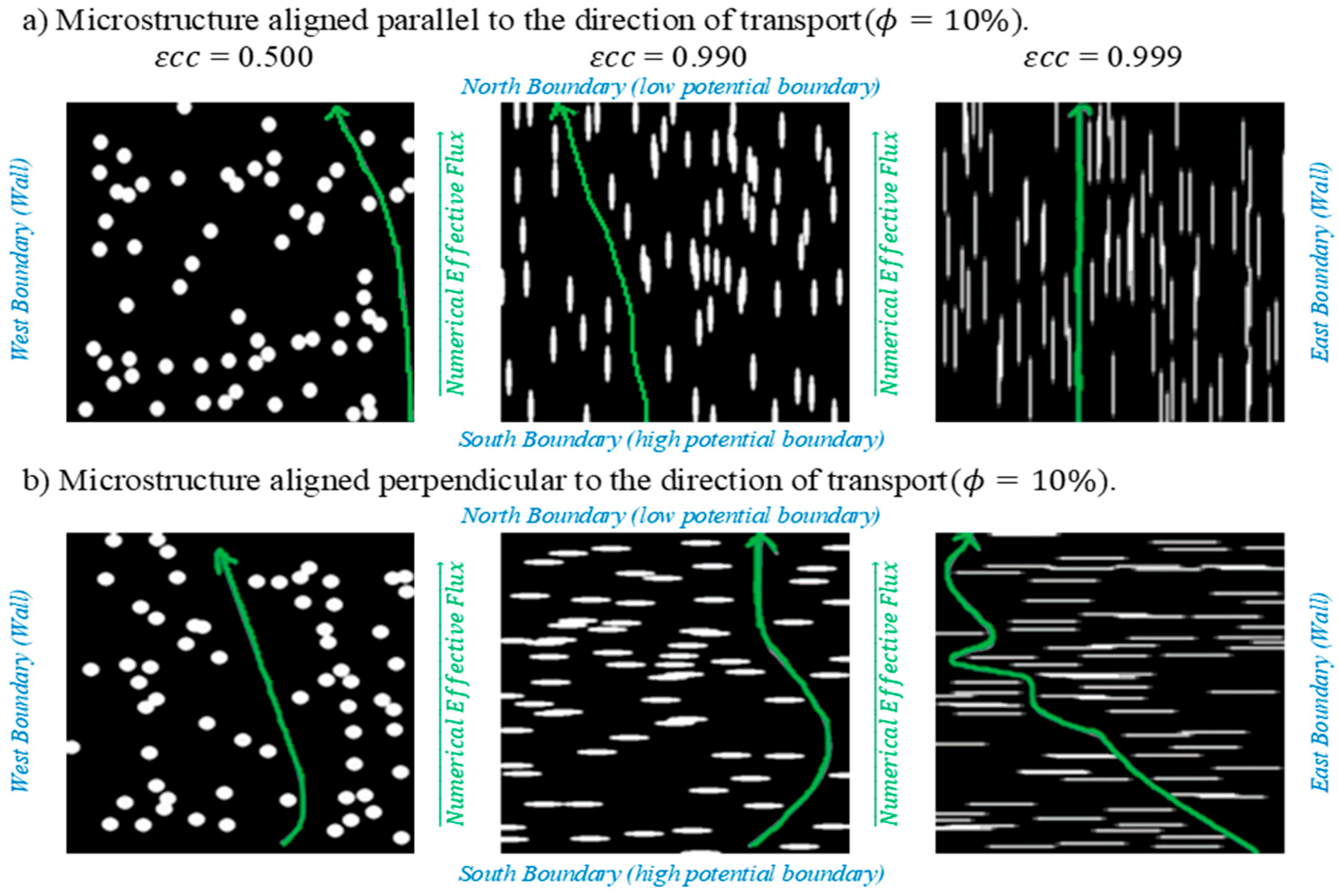
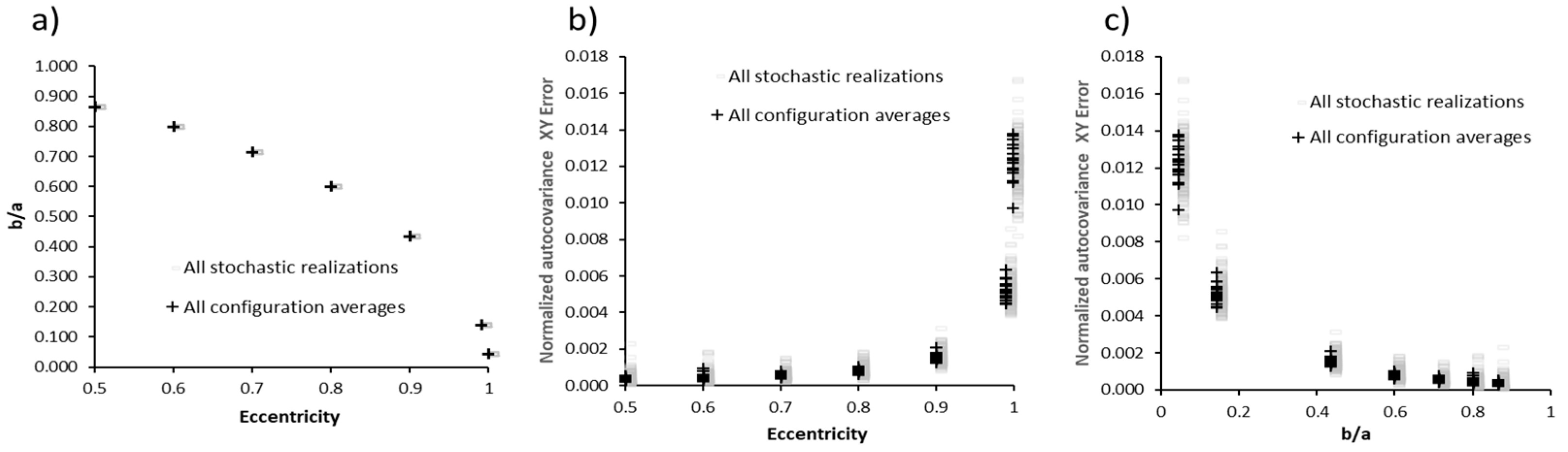
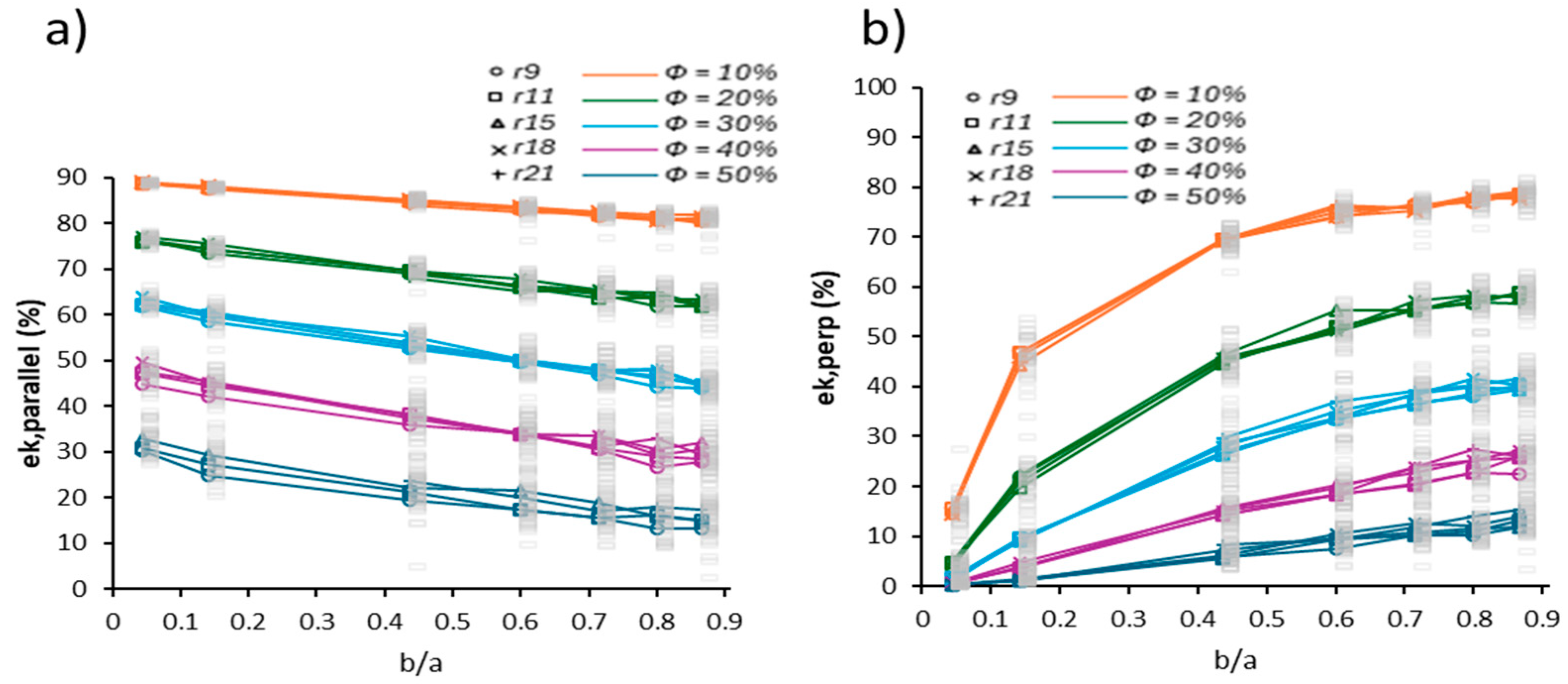
3. Results
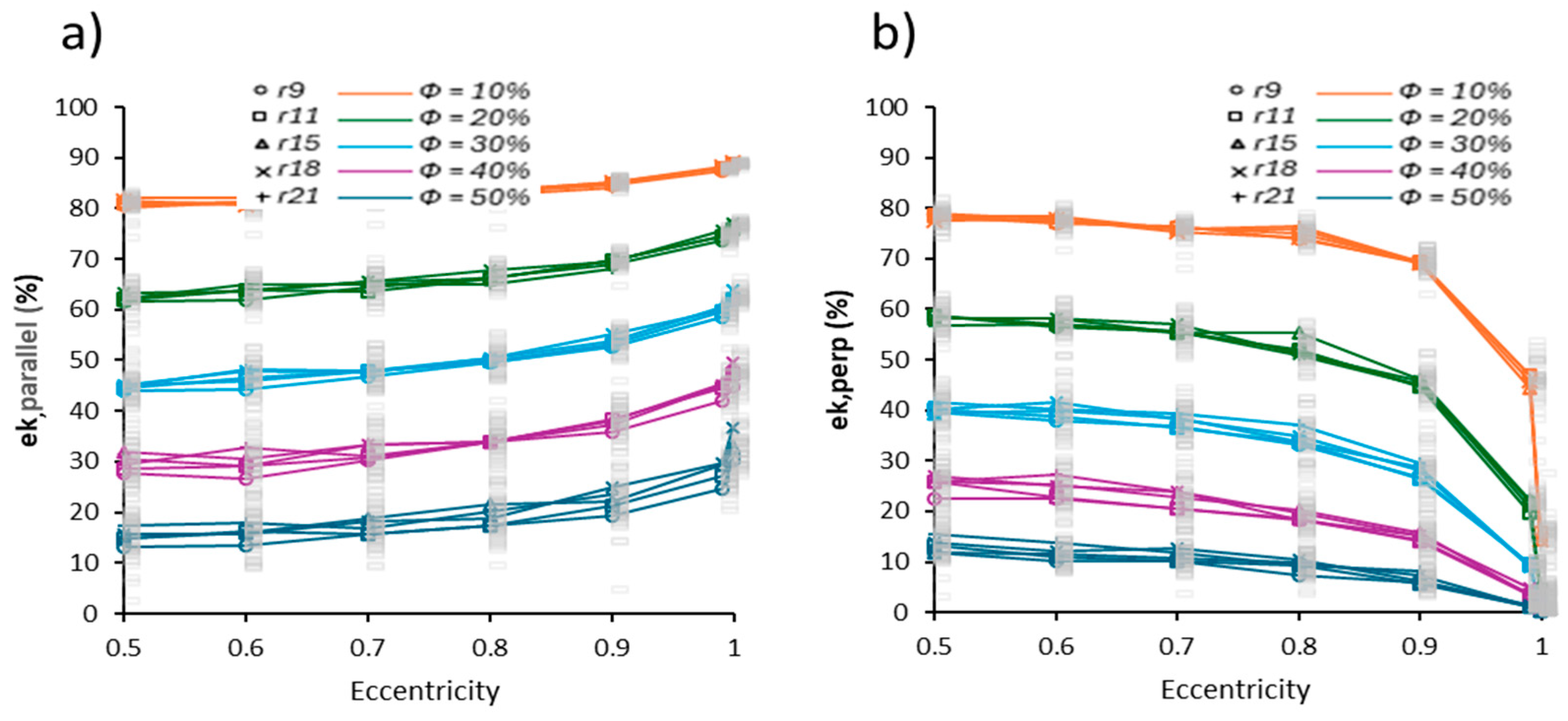
- In the parallel configuration, grows linearly and moderately with increasing eccentricity from de to , with average values ranging from to , for Φ = 10%. The difference between , and is increasingly larger as the porosity increases. This trend suggests that pore elongation aligned with the charge gradient favors more direct and less tortuous conductive paths, which reduces the effective resistance of the medium. Similar results have been reported by Li et al. [37], who demonstrated that anisotropic functional membranes with pores aligned parallel to the flow maintain high relative conductivities, even under compressive conditions.
- In contrast, in the perpendicular orientation (Figure 4b), the efficiency decreases progressively with increasing eccentricity and the difference between and becomes smaller and smaller (as porosity increases). This reduction responds to the increase in tortuosity and loss of transverse connectivity generated by elongated pores in the direction perpendicular to the charge transport flow. The charge-transport flow is forced to go around the pores, which increases the effective length of conductive paths and creates dead zones. Kang et al. [32] showed that such misalignment can cut effective transport coefficients by 40–70%, corroborating reductions in conductivity of up to 60% in anisotropic PEM membranes.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.-D.; Ohira, A. Water Electrolysis Using a Porous IrO2/Ti/IrO2 Catalyst Electrode and Nafion Membranes at Elevated Temperatures. Membranes 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Du, S. Optimizing Porous Transport Layers in PEM Water Electrolyzers: A 1D Two-Phase Model. Batteries 2025, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, N.; Mladenova, B.; Borisov, G.; Slavcheva, E. Catalytic Activity of Pt/Pd Mono- and Bimetallic Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Pump/Compressor. Inorganics 2025, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, A.; Han, C. Study on Purging Strategy of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell under Different Operation Conditions. Processes 2023, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrova, L.; Eremeev, N.; Vernikovskaya, N.; Sadykov, V.; Smorygo, O. Effect of Asymmetric Membrane Structure on Hydrogen Transport Resistance and Performance of a Catalytic Membrane Reactor for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Membranes 2021, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Escobar, B.; Cano, U.; Ortegon, J.; Sanchez, V.M. Multiscale Relationship of Electronic and Ionic Conduction Efficiency in a PEMFC Catalyst Layer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 19399–19407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, B.; Ortegón, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Oskam, G.; Pacheco, C.; Hernández, J.; Barbosa, R. Simulated Annealing and Finite Volume Method to Study the Microstructure Isotropy Effect on the Effective Transport Coefficient of a 2D Unidirectional Composite. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, W.; Ning, T.; Meng, L.; Yin, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, C. Effect of GDL Compression on PEMFC Performance: A Comprehensive Cross-Scale Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jin, Z.; Xiao, M.; Liu, C.; Xing, W. Influence of Compression Effect on the MEA Structure and Performance Based on M−N–C Electrocatalysts for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 86, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetabi, E.M.; Bouziane, K.; François, X.; Lachat, R.; Meyer, Y.; Candusso, D. Analysis of Local Current Density, Temperature, and Mechanical Pressure Distributions in an Operating PEMFC under Variable Compression. Appl. Energy 2025, 394, 126187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Kong, D.; He, L. Mechanical Response and Failure Analysis of Similar Materials Considering Moisture Conditions and Pore Structure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 491, 142778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Pool, R.; Ortegon, J.; Escobar, B.; Barbosa, R. Effect of the Agglomerate Geometry on the Effective Electrical Conductivity of a Porous Electrode. Membranes 2021, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; El Kaddouri, A.; Perrin, J.-C.; Mozet, K.; Dillet, J.; Morel, J.-Y.; Lottin, O. The Impact of Chemical-Mechanical Ex Situ Aging on PFSA Membranes for Fuel Cells. Membranes 2021, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godini, H.R.; Prahlad, A.V.; Middelkoop, V.; Görke, O.; Li, S.; Gallucci, F. Electrochemical Surface Treatment for Tailored Porous Structures. Processes 2023, 11, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Barbosa, R.; Rios, A.; Ortegon, J.; Escobar, B.; Gayosso, B.; Couder, C. Effect of an Image Resolution Change on the Effective Transport Coefficient of Heterogeneous Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, S. Recent Development and Progress of Structural Energy Devices. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Qu, Z.G.; Zhou, L.; Tao, W.Q. A Microscopic Investigation of Ion and Electron Transport in Lithium-Ion Battery Porous Electrodes Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, I.-C.; Rehman, L.M.; Aboalsaud, A.M.; Shinde, D.B.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, Z. Conjugated Microporous Polymer Membranes for Light-Gated Ion Transport. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Niksiar, P.; Meng, Z. Identifying Structure-Property Relationships of Micro-Architectured Porous Scaffolds through 3D Printing and Finite Element Analysis. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 202, 110987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, F.; Zhao, W.; Cai, J.; Wei, Y. Multi-Phase Field Lattice Boltzmann Model of Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Entire Welding Molten Pool. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 204, 111182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-B.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Perrot, C.; de Anda, A.R.; Renard, E.; Naili, S. Multiscale Approach to Characterize Effective Mechanical, Hydraulic and Acoustic Properties of a New Bio-Based Porous Material. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tonks, M.R.; Millett, P.C.; Zhang, Y.; Chockalingam, K.; Biner, B. Phase-Field Modeling of Temperature Gradient Driven Pore Migration Coupling with Thermal Conduction. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 56, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, F.; Kunz, W.; Altschuh, P.; Lu, T.; Laqua, M.; August, A.; Löffler, F.; Selzer, M.; Nestler, B. A 3D Computational Method for Determination of Pores per Inch (PPI) of Porous Structures. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Andaverde, J.; Escobar, B.; Cano, U. Stochastic Reconstruction and a Scaling Method to Determine Effective Transport Coefficients of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Catalyst Layer. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, S.; Haslach, H.W., Jr. Random Heterogeneous Materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, B62–B63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.J. The Geometry of Random Fields; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; ISBN 0898716934. [Google Scholar]
- Chiles, J.-P.; Delfiner, P. Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 0470183152. [Google Scholar]
- Patankar, S. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2018; ISBN 1482234211. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, E.; Djilali, N.; Bahrami, M. Effective Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Contact Resistance of Gas Diffusion Layers in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Part 1: Effect of Compressive Load. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.; Nebavsky, A.; Mareev, S.; Kovalenko, A.; Urtenov, M.; Pourcelly, G. Modelling of Ion Transport in Electromembrane Systems: Impacts of Membrane Bulk and Surface Heterogeneity. Appl. Sci. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Alonso, R.; Barbosa, R.; Ortegón, J. Effect of the Image Resolution on the Statistical Descriptors of Heterogeneous Media. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 23304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.K.; De Anna, P.; Nunes, J.P.; Bijeljic, B.; Blunt, M.J.; Juanes, R. Pore-scale Intermittent Velocity Structure Underpinning Anomalous Transport through 3-D Porous Media. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6184–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Escobar, B.; Rodriguez, A.; Andaverde, J. A study on the conduction efficiency of solid materials that evolves from a particulate system to an overlapping discs agglomerate. Powder Technol. 2021, 391, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Stanley, R.; Kumari, N. A Computational Modeling Approach for Prediction of Polarization Losses inside Porous Micro-Structured Cathode Used for CO2 Reduction in SOEC. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S. Effects of Porosity and Pore Microstructure on the Mechanical Behavior of Nanoporous Silver. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Minelli, M.; De Angelis, M.G. Modelling Sorption and Transport of Gases in Polymeric Membranes across Different Scales: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Cai, S.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Tu, Z. Pore-Scale Study of Water and Mass Transport Characteristic in Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells with Anisotropic Gas Diffusion Layer. Energy 2024, 293, 130599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvidchenko, A.V.; Odinokov, A.S.; Primachenko, O.N.; Gofman, I.V.; Yevlampieva, N.P.; Marinenko, E.A.; Lebedev, V.T.; Kuklin, A.I.; Kulvelis, Y.V. Improving PFSA Membranes Using Sulfonated Nanodiamonds. Membranes 2023, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, W.; Jin, A.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z. Research and Analysis of the Impact of the Pore Structure on the Mechanical Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Sandstone. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Diankai, Q.; Xu, Z.; Yi, P.; Peng, L. Comprehensive Analysis of the Gradient Porous Transport Layer for the Proton-Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 47357–47367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacheco, C.; Navarro, A.; Escobedo, E.; Barbosa, R. Numerical Assessment of Elliptical Pore Orientation and Eccentricity Effects on Charge Transport in Anisotropic Functional Membranes. Membranes 2025, 15, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120370
Pacheco C, Navarro A, Escobedo E, Barbosa R. Numerical Assessment of Elliptical Pore Orientation and Eccentricity Effects on Charge Transport in Anisotropic Functional Membranes. Membranes. 2025; 15(12):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120370
Chicago/Turabian StylePacheco, Carlos, Alfonso Navarro, Enrique Escobedo, and Romeli Barbosa. 2025. "Numerical Assessment of Elliptical Pore Orientation and Eccentricity Effects on Charge Transport in Anisotropic Functional Membranes" Membranes 15, no. 12: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120370
APA StylePacheco, C., Navarro, A., Escobedo, E., & Barbosa, R. (2025). Numerical Assessment of Elliptical Pore Orientation and Eccentricity Effects on Charge Transport in Anisotropic Functional Membranes. Membranes, 15(12), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120370




