Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides, and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Surface Water Occurrence Levels—Impact of Compound Specific Physicochemical Properties on Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. NF and RO Experiments
2.3. Sample Preparation and Instrumental Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
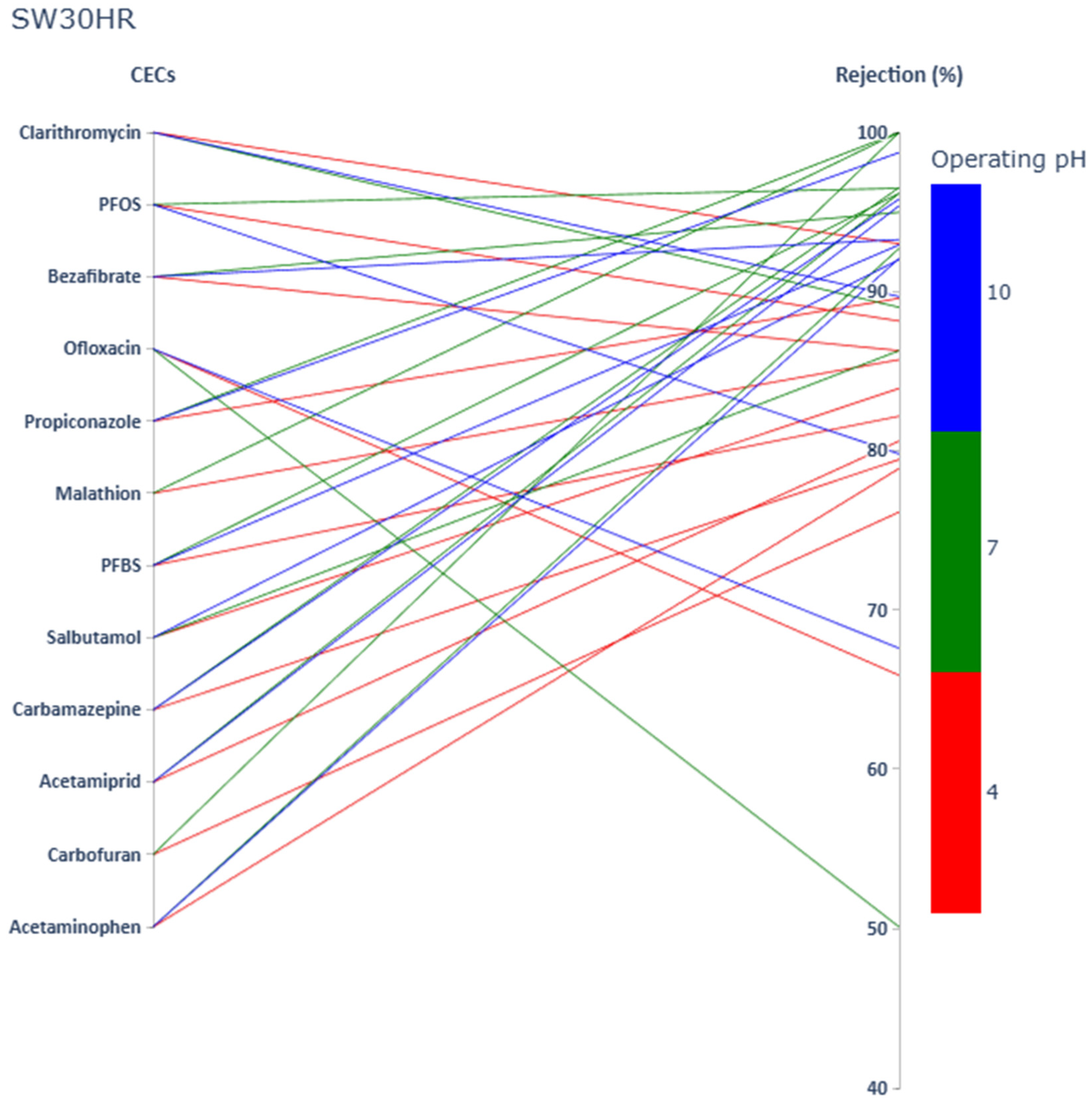
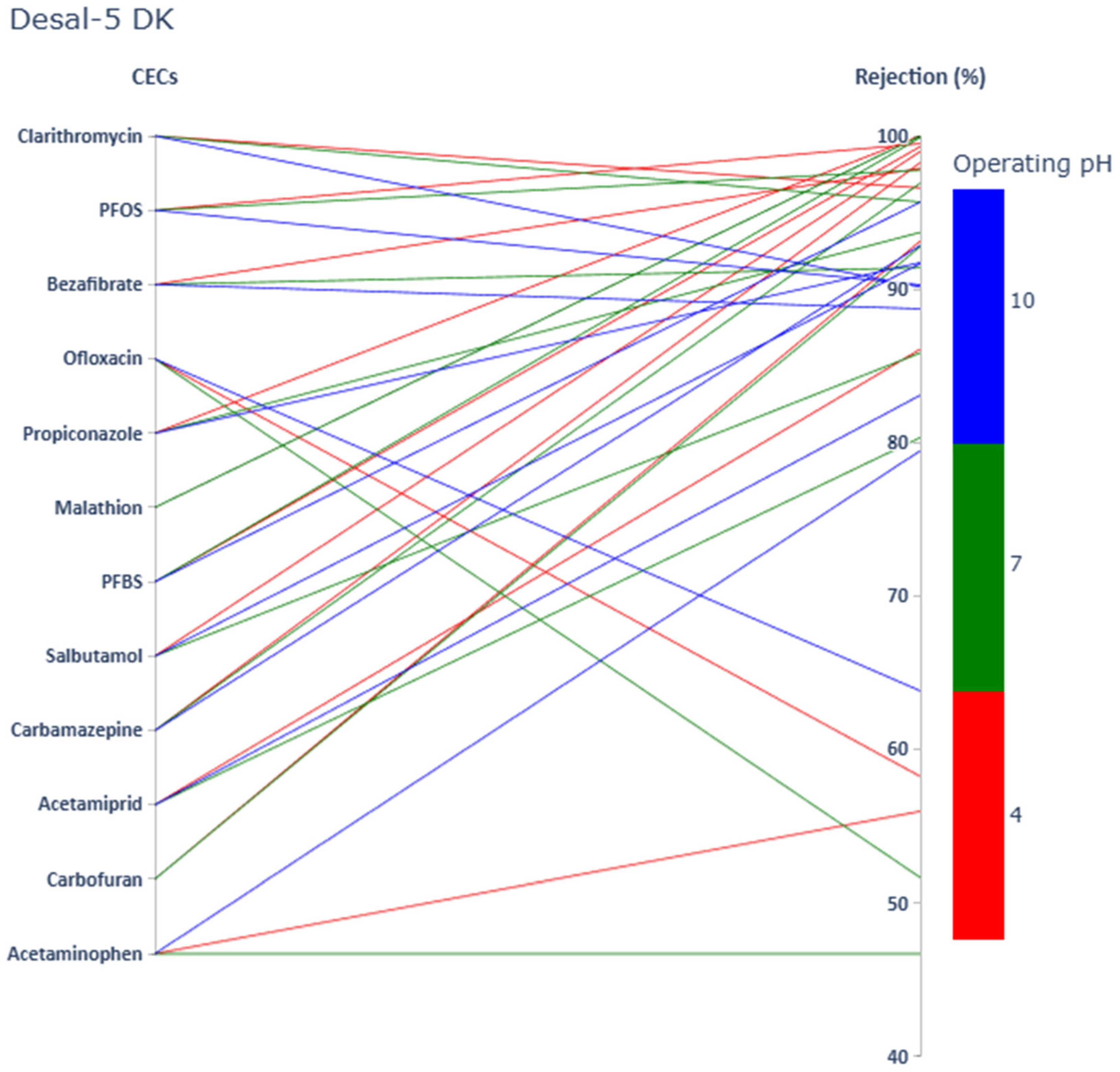
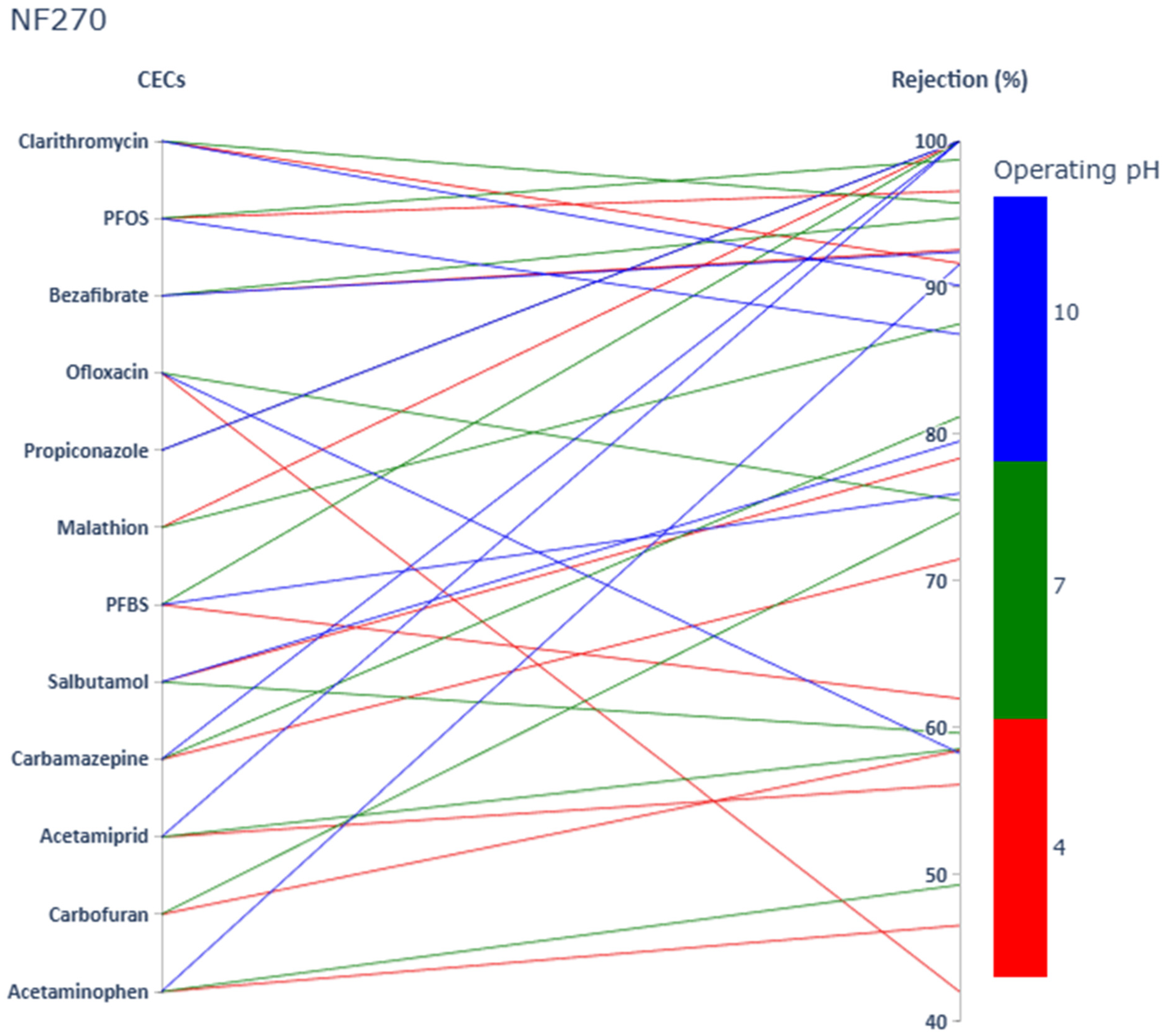
3.1. Impact of CECs’ Physicochemical Properties and Operating pH on CECs Rejection
3.1.1. Acetaminophen
3.1.2. Carbamazepine
3.1.3. Salbutamol
3.1.4. Ofloxacin
3.1.5. Bezafibrate
3.1.6. Clarithromycin
3.1.7. Carbofuran
3.1.8. Acetamiprid
3.1.9. Malathion
3.1.10. Propiconazole
3.1.11. PFBS
3.1.12. PFOS
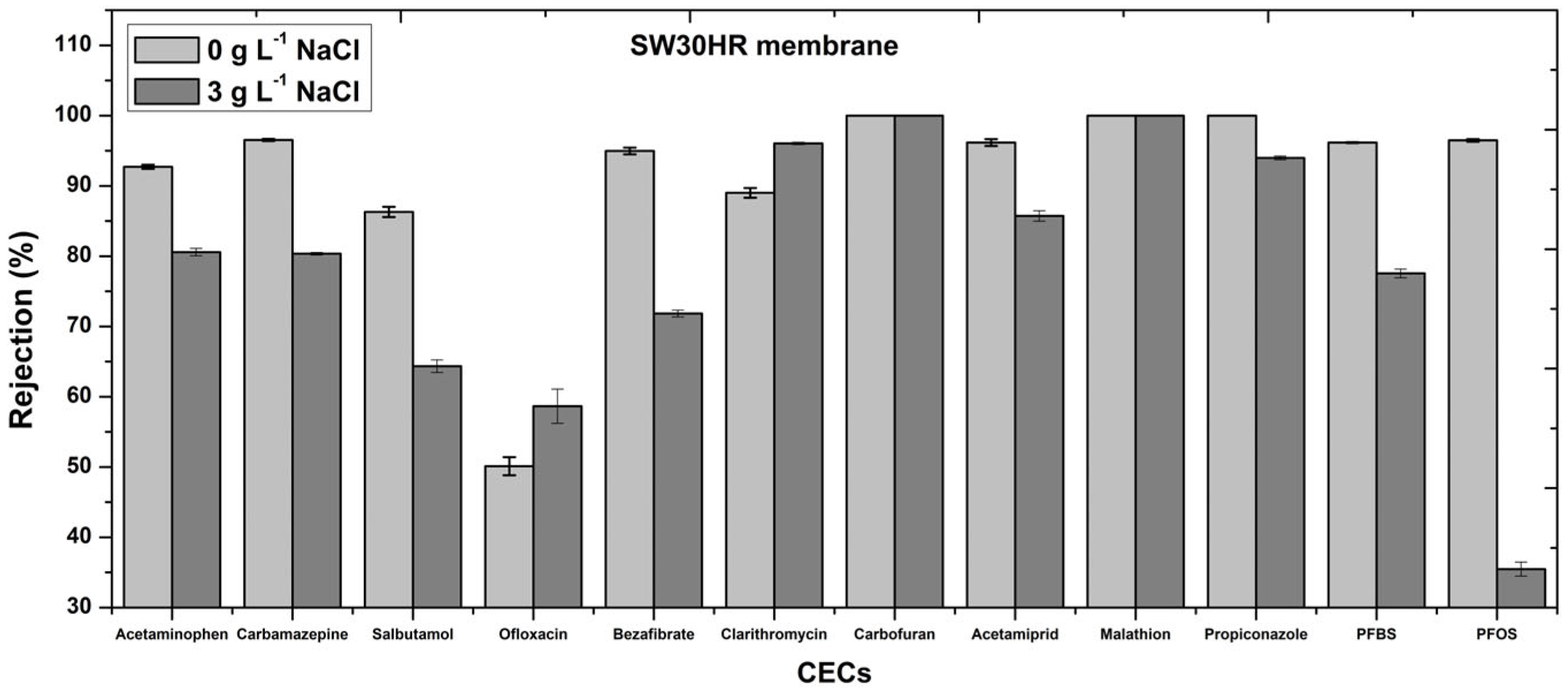
3.2. Influence of Sodium Chloride Addition on the Rejection of PhACs, Pesticides, and PFAS with the RO Membrane
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CECs | Contaminants of emerging concern |
| HLB | Hydrophilic–lipophilic balance |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MM | Molecular mass |
| MWCO | Molecular weight cut off |
| NF | Nanofiltration |
| PFAS | Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFBA | Perfluorobutanoic acid |
| PFBS | Perfluorobutane sulfonic acid |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoate |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid |
| PFOSA | Perfluorooctane sulfonamide |
| PhACs | Pharmaceutically active compounds |
| RO | Reverse osmosis |
| SPE | Solid phase extraction |
| TFC | Thin-film composite |
| UHPLC-MS/MS | High performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry |
References
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 546–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, M.; Esrafili, A.; Gholami, M.; Jonidi Jafari, A.; Rezaei Kalantary, R.; Farzadkia, M.; Kermani, M.; Sobhi, H.R. Contaminants of emerging concern: A review of new approach in AOP technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đurišić-Mladenović, N.; Živančev, J.; Antić, I.; Rakić, D.; Buljovčić, M.; Pajin, B.; Llorca, M.; Farre, M. Occurrence of contaminants of emerging concern in different water samples from the lower part of the Danube River Middle Basin—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benotti, M.J.; Stanford, B.D.; Wert, E.C.; Snyder, S.A. Evaluation of a photocatalytic reactor membrane pilot system for the removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds from water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.A.; Adham, S.; Redding, A.M.; Cannon, F.S.; DeCarolis, J.; Oppenheimer, J.; Wert, E.C.; Yoon, Y. Role of membranes and activated carbon in the removal of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals. Desalination 2007, 202, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Akanyeti, I.; Semião, A.J. Micropollutant sorption to membrane polymers: A review of mechanisms for estrogens. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Yoon, Y.; Snyder, S.; Wert, E. Fate of Endocrine-Disruptor, and Personal Care Product Chemicals During Simulated Drinking Water Treatment Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6649–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Nadzri, N.; Wang, R. Thin-film composite (TFC) membranes for sustainable desalination and water reuse: A perspective. Desalination 2024, 599, 118451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.J.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Baig, U.; Ihsanullah, I.; Alhooshani, K. Removal of pharmaceutically active compounds from water sources using nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Comparison of removal efficiencies and in-depth analysis of rejection mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, T.I.A.; Cristóvão, M.B.; Pereira, V.J.; Crespo, J.G.; Alves, A.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Silva, A.; Santos, M.S.F. Antineoplastic drugs in urban wastewater: Occurrence, nanofiltration treatment and toxicity screening. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 332, 121944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Darling, S.B. Sharpening Nanofiltration: Strategies for Enhanced Membrane Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39948–39966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, F.; Shang, W.; Zhang, X.; Dong, W.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, S. Removal mechanisms of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) by nanofiltration: Roles of membrane-contaminant interactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, B.; Buscio, V.; Odabasi, S.U.; Buyukgungor, H. A study on behavior, interaction and rejection of Paracetamol, Diclofenac and Ibuprofen (PhACs) from wastewater by nanofiltration membranes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, M.B.; Bernardo, J.; Bento-Silva, A.; Ressureição, M.; Bronze, M.R.; Crespo, J.G.; Pereira, V.J. Treatment of anticancer drugs in a real wastewater effluent using nanofiltration: A pilot scale study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, R.; Chen, J.; Lv, B. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and environmental estrogens (EEs) from water using positively charged hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8486–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater: Chemical, physical and biological treatment approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, S.; Penetra, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Ferreira, E.; Cardoso, V.V.; Benoliel, M.J.; Crespo, J.G. Nanofiltration of hormones and pesticides in different real drinking water sources. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 94, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, M.Q.; Ng, Z.C.; Lai, G.S.; Lau, W.J.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Alias, N.H.; Ismail, A.F. Removal of multiple pesticides from water by different types of membranes. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Meier, A.; Neale, P.A. Impact of organic matrix compounds on the retention of steroid hormone estrone by a ‘loose’ nanofiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.; Rahimpour, A.; Shirzad Kebria, M.R. Pesticides removal from water using modified piperazine-based nanofiltration (NF) membranes. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24844–24854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Schaep, J.; Maes, W.; Wilms, D.; Vandecasteele, C. Nanofiltration as a treatment method for the removal of pesticides from ground waters. Desalination 1998, 117, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Chen, G.X.; Braeken, L.; Vandecasteele, C. Removal of pesticides by nanofiltration: Effect of the water matrix. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. The rejection of perfluoroalkyl substances by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis: Influencing factors and combination processes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1928–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, Q. A comparative study of suitability on different molecular size descriptors with the consideration of molecular geometry in nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 332, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Barceló, D.; Diaz, A.; Ventura, F. Low nanogram per liter determination of halogenated nonylphenols, nonylphenol, and bisphenol A in water by solid-phase extraction and LC-MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 444–453. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, S.R.; Kay, P.; Brown, L.E. Global synthesis and critical evaluation of pharmaceutical data sets collected from river systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wu, W.; Ma, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, R. Occurrence and distribution of emerging contaminants in wastewater treatment plants: A global review over the past two decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.J.; Chang, E.E.; Chiang, P.C. Effects of concentrations and types of natural organic matters on rejection of compounds of emerging concern by nanofiltration. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6929–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mänttäri, M.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Nyström, M. Effect of pH on hydrophilicity and charge and their effect on the filtration efficiency of NF membranes at different pH. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil Mouhoumed, E.; Szymczyk, A.; Schäfer, A.; Paugam, L.; La, Y.H. Physico-chemical characterization of polyamide NF/RO membranes: Insight from streaming current measurements. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanninen, J.; Mänttäri, M.; Nyström, M. Effect of salt mixture concentration on fractionation with NF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Škrbić, B.; Živančev, J.; Ferrando-Climent, L.; Barcelo, D. Determination of 81 pharmaceutical drugs by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with hybrid triple quadrupole-linear ion trap in different types of water in Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, D.; Antić, I.; Živančev, J.; Buljovčić, M.; Šereš, Z.; Đurišić-Mladenović, N. Solid-phase extraction as promising sample preparation method for compound of emerging concerns analysis. Analecta Tech. Szeged. 2023, 17, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Wei, S.; Dai, J. Analysis of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Progress and current issues. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, S.G.; Hawker, D.W.; Mackie, R.; Higgins, C.P.; Bowles, K.; Li, Y.; Kaserzon, S. Sorption affinity and mechanisms of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) with commercial sorbents: Implications for passive sampling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Higgins, C.P.; Alarif, W.M.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Ghandourah, M.; Kallenborn, R. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in contaminated coastal marine waters of the Saudi Arabian Red Sea: A baseline study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyasu, S.; Kannan, K.; So, M.K.; Gulkowska, A.; Sinclair, E.; Okazawa, T.; Yamashita, N. Analysis of fluorotelomer alcohols, fluorotelomer acids, and short-and long-chain perfluorinated acids in water and biota. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1093, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumovský, M.; Bečanová, J.; Karásková, P.; Nizzetto, L. Retention performance of three widely used SPE sorbents for the extraction of perfluoroalkyl substances from seawater. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Fast and comprehensive multi-residue analysis of a broad range of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals and some of their metabolites in surface and treated waters by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1248, 104–121. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, O.K.; Cakmakci, M.; Zengin, I.H.; Karadag, D.; Yuksel, E. Improving PFAS Rejection by Ultrafiltration Membranes via Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Coating. Membranes 2025, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Nong, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S. Advanced Materials-Based Nanofiltration Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Micropollutants in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2025, 15, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazouli, M.A.; Susanto, H.; Nasseri, S.; Ulbricht, M. Influences of solution chemistry and polymeric natural organic matter on the removal of aquatic pharmaceutical residuals by nanofiltration. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3270–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cocquyt, J.; Van der Meeren, P.; Volodin, A.; Van Haesendonck, C.; Martens, J.A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Characterization of polymeric nanofiltration membranes for systematic analysis of membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.-F.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Ying, D.; Jia, J.; Shao, J.; He, Y. Antibiotics separation from saline wastewater by nanofiltration membrane based on tannic acid-ferric ions coordination complexes. Desalination 2022, 541, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Raghavan, D.S.; Qiu, G.; Ting, Y.-P. Fate and removal of selected antibiotics in an osmotic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, X. Performance of nanofiltration membrane in rejecting trace organic compounds: Experiment and model prediction. Desalination 2015, 370, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiber, J.N.; Catahan, M.P.; Barril, C.R. Loss of carbofuran from rice paddy water: Chemical and physical factors. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 1978, 13, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhart, K. Environmental fate of malathion. Calif. Environ. Prot. Agency 2006, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, X.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Cao, W.; Wan, Y. Removal and recovery of perfluorooctanoate from wastewater by nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 145, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Enhanced the swelling resistance of polyamide membranes with reinforced concrete structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CECs | Structure | MM (Da) a | pKa a | logKo/w a | Hydrophobicity b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutically active compounds | |||||
| Clarithromycin | 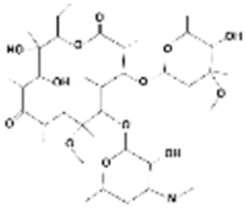 | 748.0 | 8.99 | 3.16 | Hydrophobic |
| Ofloxacin | 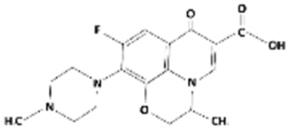 | 361.4 | 5.97–8.22 | –0.39 | Hydrophilic |
| Carbamazepine | 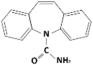 | 236.3 | 2.3 | 2.45 | Hydrophobic |
| Acetaminophen | 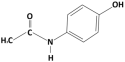 | 151.2 | 9.38/9.7 | 0.46 | Hydrophilic |
| Salbutamol |  | 239.3 | 9.1–10.4 | 1.4 –0.64 | Hydrophilic |
| Bezafibrate | 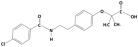 | 361.8 | 3.6 | 4.3 | Hydrophobic |
| Pesticides | |||||
| Carbofuran | 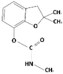 | 221.3 | 11.9 | 2.32 | Hydrophobic |
| Acetamiprid | 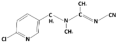 | 222.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | Hydrophilic |
| Malathion |  | 330.4 | 6.8 | 2.36 | Hydrophobic |
| Propiconazole |  | 342.2 | 1.09 | 3.7 | Hydrophobic |
| PFAS | |||||
| Perfluorooctane sulfonamide (PFOSA) | 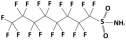 | 499.1 | 6.2 | 5.8 | Hydrophobic |
| Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) | 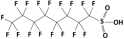 | 500.1 | 0.14 | 4.49 | Hydrophobic |
| Perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) | 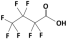 | 214.0 | 0.08 | 2.2 | Hydrophobic |
| Perfluorobutane sulfonic acid (PFBS) | 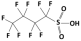 | 300.1 | –3.31 | 1.82 | Hydrophilic |
| Commercial Name | SW30HR | Desal-5 DK | NF270 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | RO | NF | NF |
| Manufacturer | FilmTec™ | SUEZ | FilmTec™ |
| Material a | TFC polyamide | TFC polyamide | TFC polyamide |
| MWCO (Da) a | 100 | 150–300 | 400 |
| pH range a | 2–11 | 2–10 | 2–11 |
| pKa | 4.0 d | 4.1 c | 3.3/5.0 b |
| Surface charge at pH 4 e | neutral | neutral | neutral |
| Surface charge at pH 7 e | negative | negative | negative |
| Surface charge at pH 10 e | negative | negative | negative |
| pH | 4 | 7 | 10 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal Mechanisms | Size Exclusion | Electrostatic Interactions | Hydrophobicity | Size Exclusion | Electrostatic Interactions | Hydrophobicity | Size Exclusion | Electrostatic Interactions | Hydrophobicity |
| Acetaminophen | + | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| Carbamazepine | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| Salbutamol | + | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | − |
| Ofloxacin | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | − |
| Bezafibrate | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| Clarithromycin | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − |
| Carbofuran | + | − | + | + | − | − | X | X | X |
| Acetamiprid | + | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| Malathion | + | − | + | + | − | − | X | X | X |
| Propiconazole | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| PFBS | + | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| PFOS | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šurlan, J.; Galinha, C.F.; Maravić, N.; Brazinha, C.; Antić, I.; Živančev, J.; Đurišić-Mladenović, N.; Šereš, Z.; Crespo, J.G. Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides, and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Surface Water Occurrence Levels—Impact of Compound Specific Physicochemical Properties on Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes. Membranes 2025, 15, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120358
Šurlan J, Galinha CF, Maravić N, Brazinha C, Antić I, Živančev J, Đurišić-Mladenović N, Šereš Z, Crespo JG. Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides, and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Surface Water Occurrence Levels—Impact of Compound Specific Physicochemical Properties on Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes. Membranes. 2025; 15(12):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120358
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠurlan, Jelena, Claudia F. Galinha, Nikola Maravić, Carla Brazinha, Igor Antić, Jelena Živančev, Nataša Đurišić-Mladenović, Zita Šereš, and João G. Crespo. 2025. "Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides, and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Surface Water Occurrence Levels—Impact of Compound Specific Physicochemical Properties on Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes" Membranes 15, no. 12: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120358
APA StyleŠurlan, J., Galinha, C. F., Maravić, N., Brazinha, C., Antić, I., Živančev, J., Đurišić-Mladenović, N., Šereš, Z., & Crespo, J. G. (2025). Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides, and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Surface Water Occurrence Levels—Impact of Compound Specific Physicochemical Properties on Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes. Membranes, 15(12), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120358





