Microwave-Assisted Syntheses of 1-Acetyl 2-Methylbenzimidazole Sodium Bisulfate pH-Responsive Ionic Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.2. Membranes
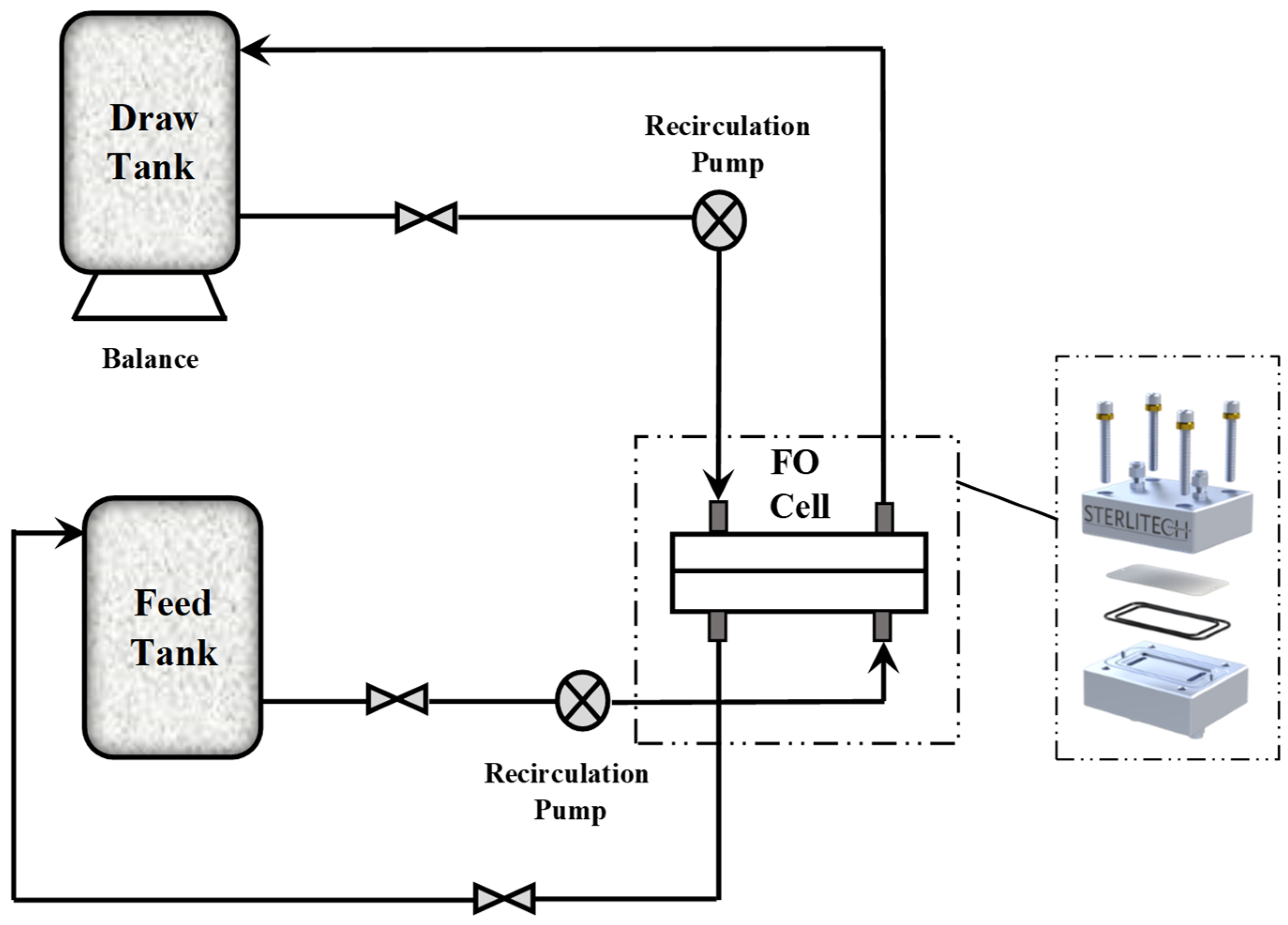
2.2. Methods
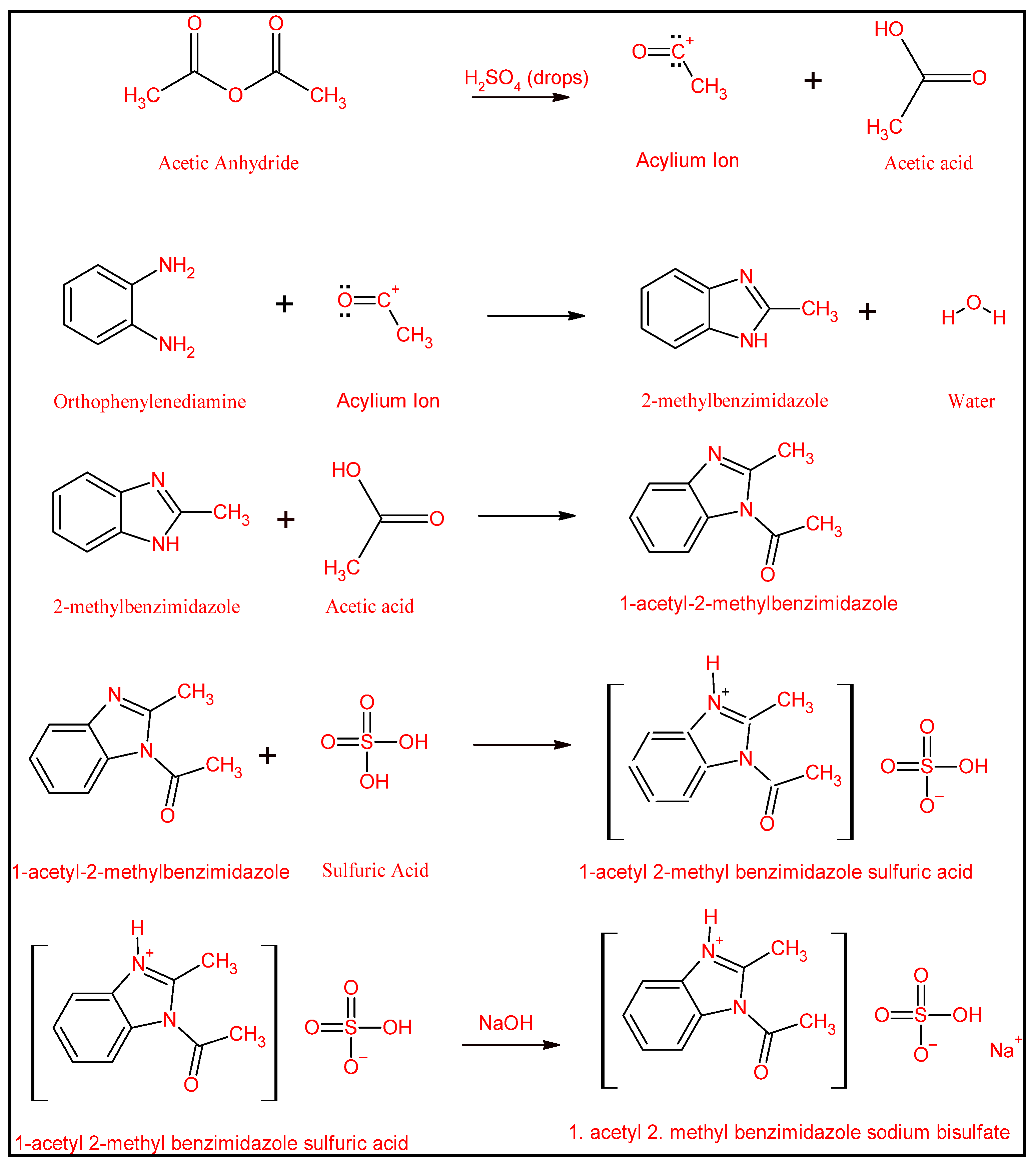
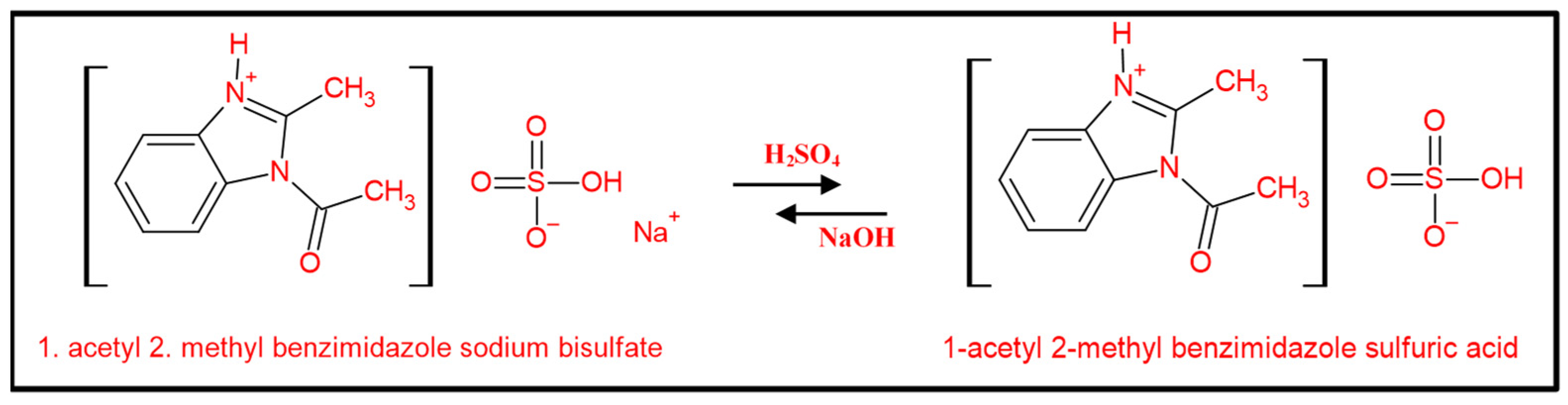
2.2.1. Preparation of the pH-Sensitive DS
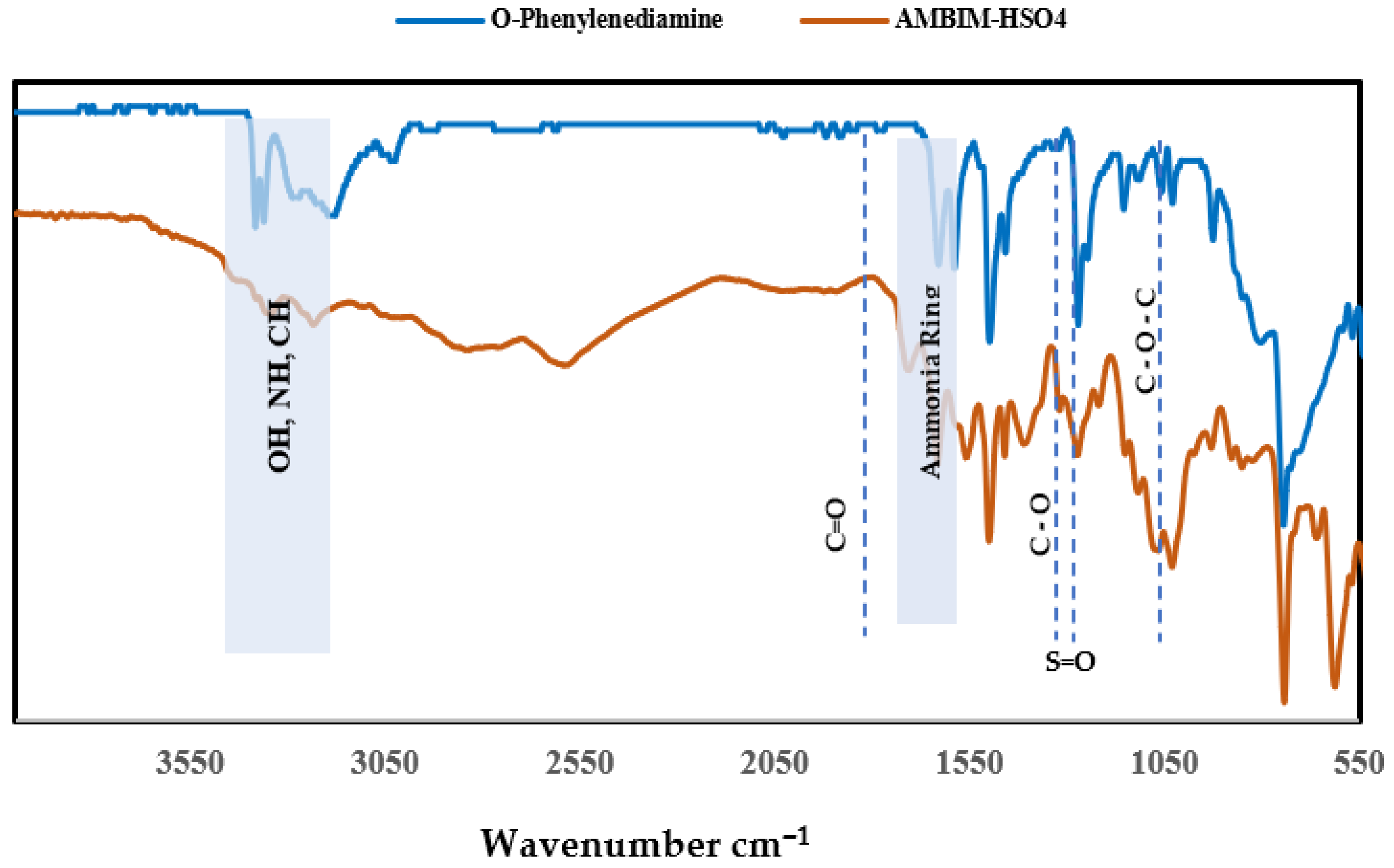
2.2.2. Characterizations of AMBIM-HSO4
2.2.3. Determination of Osmotic Pressure, π
2.2.4. Draw Solute Performance
2.2.5. Application for Brackish Water Desalination
2.2.6. DS Regeneration
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Syntheses and Characterizations of AMBIM-HSO4
3.2. AMBIM-Na OP
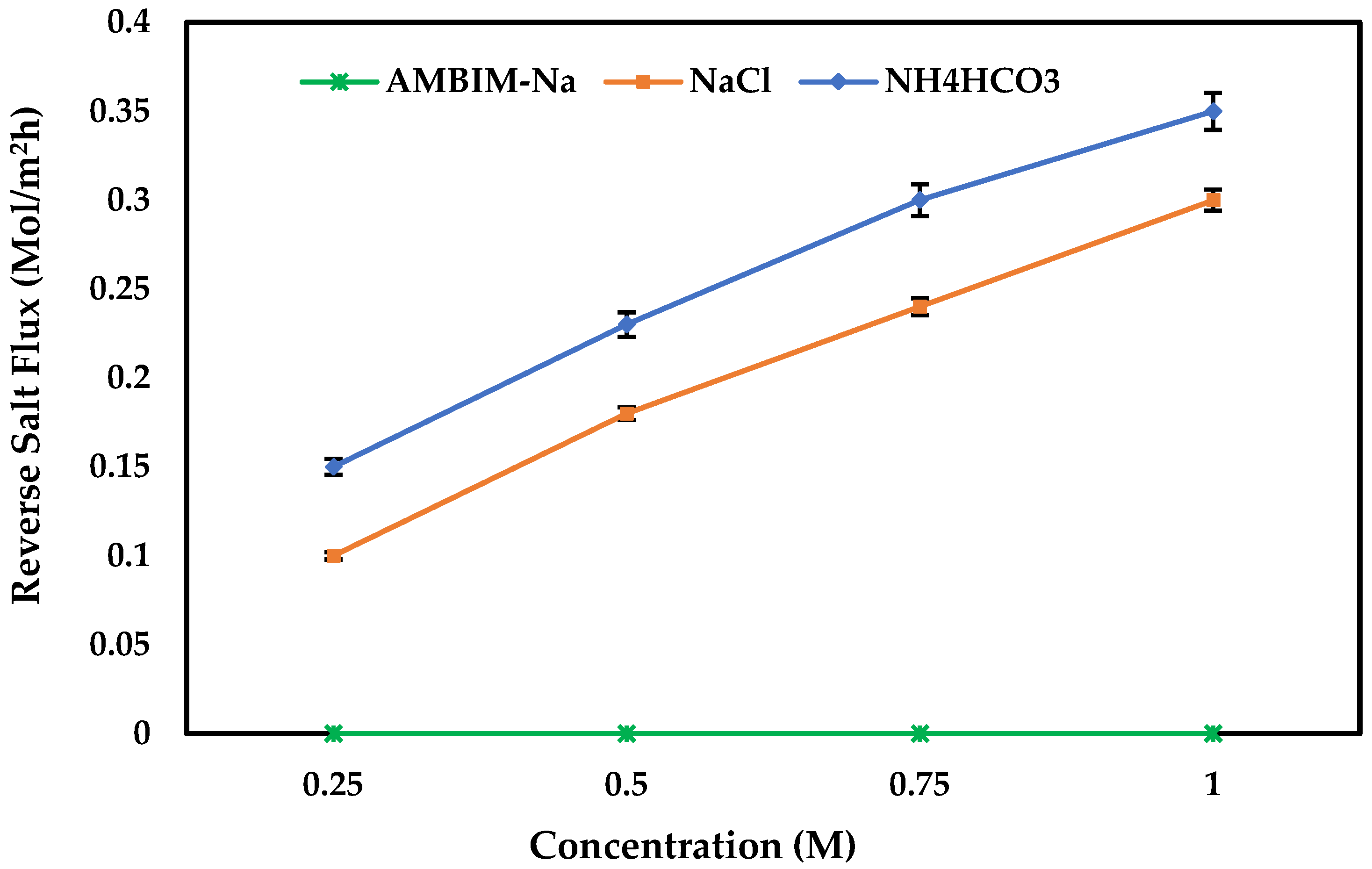
3.3. FO Performance
3.4. AMBIM-Na Application
3.5. The Long-Term FO Performance
3.6. Regeneration of DS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Liu, X. Forward osmosis technology for water treatment: Recent advances and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth.Org. Global Water Crisis: Why the World Urgently Needs Water-Wise Solutions. Available online: https://earth.org/global-water-crisis-why-the-world-urgently-needs-water-wise-solutions/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Aende, A.; Gardy, J.; Hassanpour, A. Seawater desalination: A review of forward osmosis technique, its challenges, and prospects. Processes 2020, 8, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, R. The World Water Development Report 2014: Water and Energy; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Yoshikawa, S.; Iseri, Y.; Fujimori, S.; Kanae, S. An economic assessment of the global potential for seawater desalination to 2050. Water 2017, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.C.; Tao, T.; Zhou, A.; Chen, L.; Bie, X. A review on the recovery methods of draw solutes in forward osmosis. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaileh, W.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Advances in forward osmosis membranes: Altering the sub-layer structure via recent fabrication and chemical modification approaches. Desalination 2018, 436, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Goh, K.; Li, X.; Setiawan, L.; Wang, R. Membranes and processes for forward osmosis-based desalination: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2018, 434, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes: Fouling reversibility and cleaning without chemical reagents. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, S.E.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Elimelech, M. Biofouling in forward osmosis and reverse osmosis: Measurements and mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lee, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Role of pressure in organic fouling in forward osmosis and reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard, S.A.; Ghanavatyan, M.A.; Jangizehi, A.; Salehi, H.; Shakeri, A.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Al-Timimi, D.; Bantz, C.; Maskos, M.; Seiffert, S. Challenges of forward osmosis desalination processes using hydrogels as draw agents. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 714, 123408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, X.M. A critical review on draw solutes development for forward osmosis. Desalination 2016, 391, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.C.; Nguyen, H.T.; Chen, S.-S.; Bui, X.T. Application of an innovative draw solute in forward osmosis (FO) processes. Phys. Sci. Eng. 2021, 63, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of flat-sheet thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, L.; Wang, R.; Li, K.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of novel poly(amide–imide) forward osmosis hollow fiber membranes with a positively charged nanofiltration-like selective layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, T.; Arruebo, M.; Carcelen, V.; Monsalvo, V.M.; Sebastian, V. Advances in draw solutes for forward osmosis: Hybrid organic-inorganic nanoparticles and conventional solutes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, F.; Zheng, J.; Yu, B. Recent advance on draw solutes development in forward osmosis. Processes 2018, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.J.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Functional materials in desalination: A review. Desalination 2019, 468, 114077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Wu, S. A comprehensive review of responsive draw solutes in forward osmosis: Categories, characteristics, mechanisms and modifications. Desalination 2024, 583, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Q. A bifunctional zwitterion that serves as both a membrane modifier and a draw solute for forward osmosis wastewater treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 36118–36129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.H.; Ge, Q. A pH-responsive supramolecular draw solute that achieves high-performance in arsenic removal via forward osmosis. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, R.; Ge, Q. pH-responsive polyoxometalates that achieve efficient wastewater reclamation and source recovery via forward osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12664–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zou, S.; Yang, X.; Long, T.E.; He, Z. Efficient recovery of polyelectrolyte draw solutes in forward osmosis towards sustainable water treatment. Desalination 2017, 422, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, M.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Sustainable operation of osmotic microbial fuel cells through effective reproduction of polyelectrolyte draw solutes facilitated by cathodic pH increase. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, S.K.; Haja, F.M.N.; Su, M.; Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.-S. Study of draw solutes using 2-methylimidazole-based compounds in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiu, F.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Q. Value-added resource recovery through forward osmosis promoted by pH-responsive biscarboxyimidazolium materials. Desalination 2024, 587, 117926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.S.; Kumar, K.; Redhu, S.; Bhardwaj, S. Microwave assisted synthesis: A green chemistry approach. Int. Res. J. Pharm. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Karthikeyan, E. Microwave synthesis—A potential tool for green chemistry. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2011, 3, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, M.; Dhingra, N. Microwave chemistry: General features and applications. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2011, 5, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Willert-Porada, M. Advances in Microwave and Radio Frequency Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Chemat-Djenni, Z.; Hamada, B.; Chemat, F. Atmospheric pressure microwave assisted heterogeneous catalytic reactions. Molecules 2007, 12, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairmode, S.; Khade, R.; Tamboli, F.; More, H.; Patil, D.; Dhuri, K.; Kanse, N.; Mohite, S. Comparative studies on conventional and microwave assisted synthesis of N-(phenylcarbamothioyl) benzamide derivatives and its anti-inflammatory activity. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2021, 5, 1–3. Available online: https://www.chemicaljournals.com/assets/archives/2021/vol5issue3/5-2-16-532.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- El-Nahas, S.; El-sadek, M.S.A.; Salman, H.M.; Elkady, M.M. Controlled morphological and physical properties of ZnO nanostructures synthesized by domestic microwave route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, J.K.; Kumara, M.; Geetika. Growth of ZnO nanostructures: Cones, rods and hollow-rods, by microwave assisted wet chemical growth and their characterization. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5300–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.C.; Su, J.C.; Amy, G.L.; Chung, T.S. Exploration of polyelectrolytes as draw solutes in forward osmosis processes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, M.; Remon, E.; Gadallah, H.; Azab, A.A.; Ali, H.M. Comparative study for the preparation of superparamagnetic-citric coated magnetic nanoparticle and FO desalination application. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Mounir, M.; Gadallah, H.; Ali, H.M.; Souaya, E.R.; Azab, A.A. Ferric hydroacid & diamine complex as draw solute for forward osmosis (FO) desalination processes. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslah, S.S.; Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Jazani, O.M.; Samimi, A. Forward osmosis water desalination: Fabrication of graphene oxide-polyamide/polysulfone thin-film nanocomposite membrane with high water flux and low reverse salt diffusion. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Hou, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Fabrication and performance of PET mesh enhanced cellulose acetate membranes for forward osmosis. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 45, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Maity, S.; Jana, T. Polybenzimidazole gel membrane for the use in fuel cell. Polymer 2011, 52, 4319–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.; Zaidi, H.; Thakur, A.; Agarwal, T.; Alam, S. Synthesis of polypyrrole/polythiophene copolymers in supercritical carbon dioxide. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhangelsky, E.; Wicaksana, F.; Chou, S.; Al-Rabiah, A.A.; Al-Zahrani, S.M.; Wang, R. Effects of scaling and cleaning on the performance of forward osmosis hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.; McCutcheon, J.; Elimelech, M. Internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis: Role of membrane orientation. Desalination 2006, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ge, Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Chung, T.S. Novel forward osmosis process to effectively remove heavy metal ions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; An, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, Q.; He, Z. EDTA-Na2 as a recoverable draw solute for water extraction in forward osmosis. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



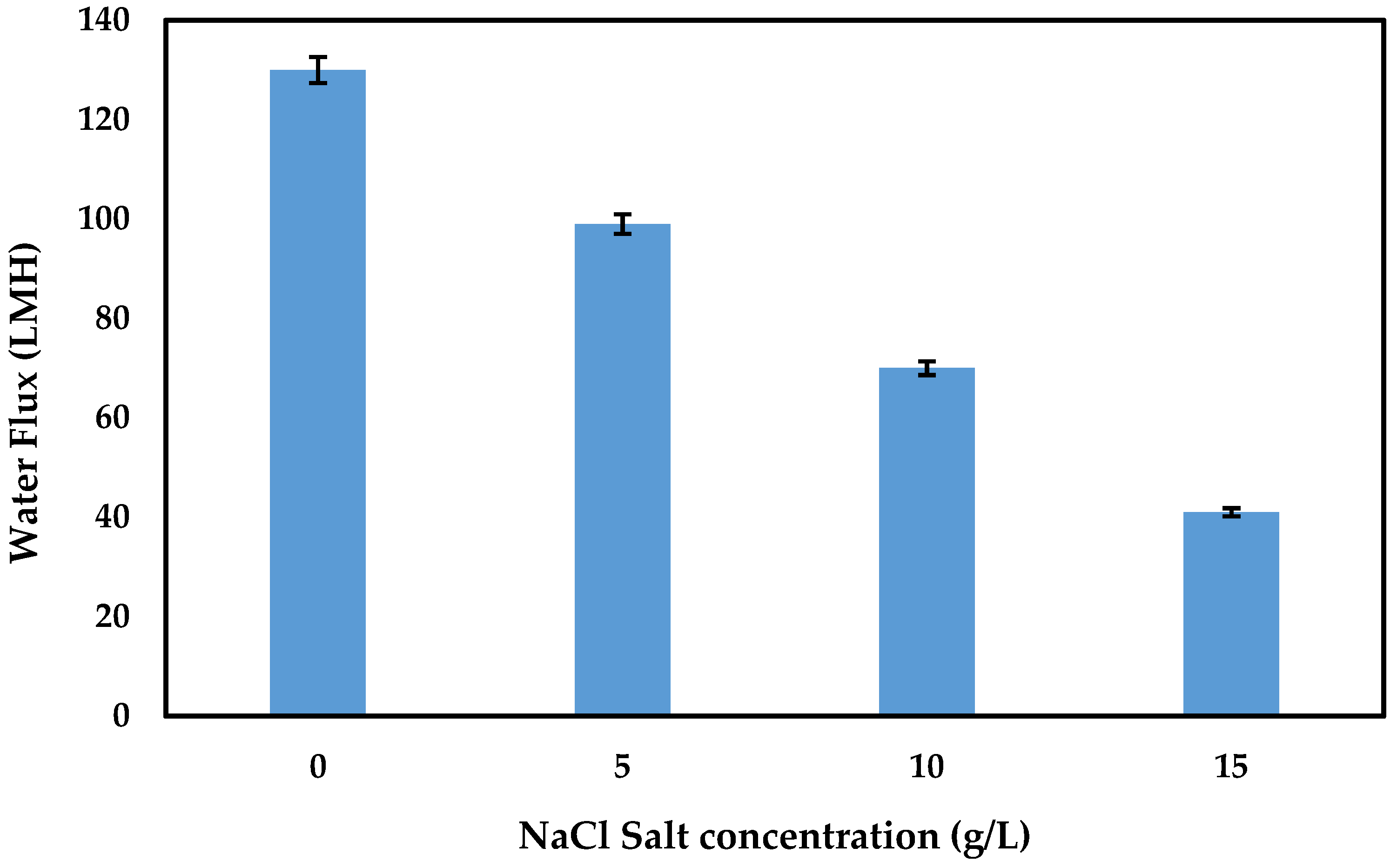
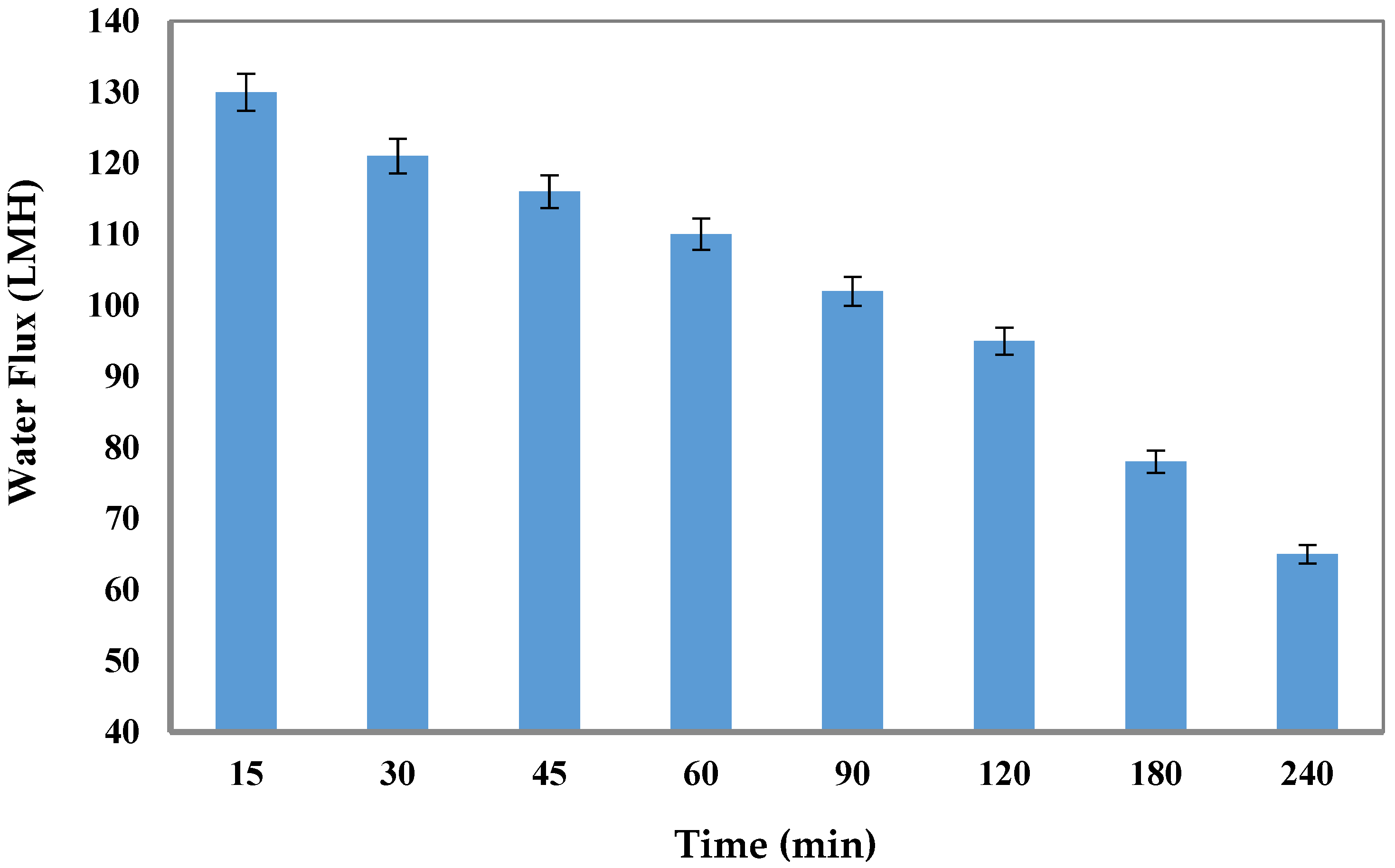
| “Draw Solute” | Operating Conditions | Feed Solution | Water Flux (LMH)/Reverse Salt Flux (gMH) | pH | % Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | 1 M | DIW | 130/0 | 2 | 100 |
| 0.25 M | DIW | 59/0 | |||
| 1 M | (5–15) g/L NaCL | 99–41/0 | |||
| Polyoxometalates [24] | (NH4)6Mo7O24 (0.4 M) | DIW | 16.4/0 | <2 | 100 |
| Na6Mo7O24 (0.4 M) | DIW | 14.2/0 | |||
| (NH4)6Mo7O24 (0.4 M) | 2 g/L glutathione | 10.0/0 | |||
| Na6Mo7O24 (0.4 M) | 2 g/L glutathione | 9.6/0 | |||
| 1,4-bis (3-propane-sulphonate sodium)-piperazinediethanesulfonic acid disodium-sulfate [23] | 0.24 M | DIW | 58.4/0 | <7 | 100 |
| Polyacrylic acid sodium salts (Mw, 2000) [25] | 20 wt% | DIW | 17.26/0.110 | 7.78 | 99.90 |
| (1-(3-aminopropyl)-imidazole) propane-sulfonate (APIS) [22] | 1 M | DIW | 20–25/0 | 2 | 100 |
| EDTA-2Na [51] | 0.25 M | DIW | 4/0.2 | 2 | 98.56 |
| sodium salts of imidazole-based ionic solid, im-IS-Na and im-IS-2Na [28] | 1 M im-IS-Na 1 M im-IS-2Na | DIW | 32/0 27.5/0 | 2 | 98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhran, A.A.; Gadallah, A.G.; Ali, H.M.; Ali, S.S.; Gadallah, H.; Sabry, R. Microwave-Assisted Syntheses of 1-Acetyl 2-Methylbenzimidazole Sodium Bisulfate pH-Responsive Ionic Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Applications. Membranes 2025, 15, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15110325
Bhran AA, Gadallah AG, Ali HM, Ali SS, Gadallah H, Sabry R. Microwave-Assisted Syntheses of 1-Acetyl 2-Methylbenzimidazole Sodium Bisulfate pH-Responsive Ionic Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Applications. Membranes. 2025; 15(11):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15110325
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhran, Ahmed A., Abdelrahman G. Gadallah, Hanaa M. Ali, Sahar S. Ali, Hanaa Gadallah, and Rania Sabry. 2025. "Microwave-Assisted Syntheses of 1-Acetyl 2-Methylbenzimidazole Sodium Bisulfate pH-Responsive Ionic Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Applications" Membranes 15, no. 11: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15110325
APA StyleBhran, A. A., Gadallah, A. G., Ali, H. M., Ali, S. S., Gadallah, H., & Sabry, R. (2025). Microwave-Assisted Syntheses of 1-Acetyl 2-Methylbenzimidazole Sodium Bisulfate pH-Responsive Ionic Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Applications. Membranes, 15(11), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15110325







