PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane with Confined Mass Transfer Structure: The Effect of COFs with Different Porous Structures and Chemical Properties in the Pervaperation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
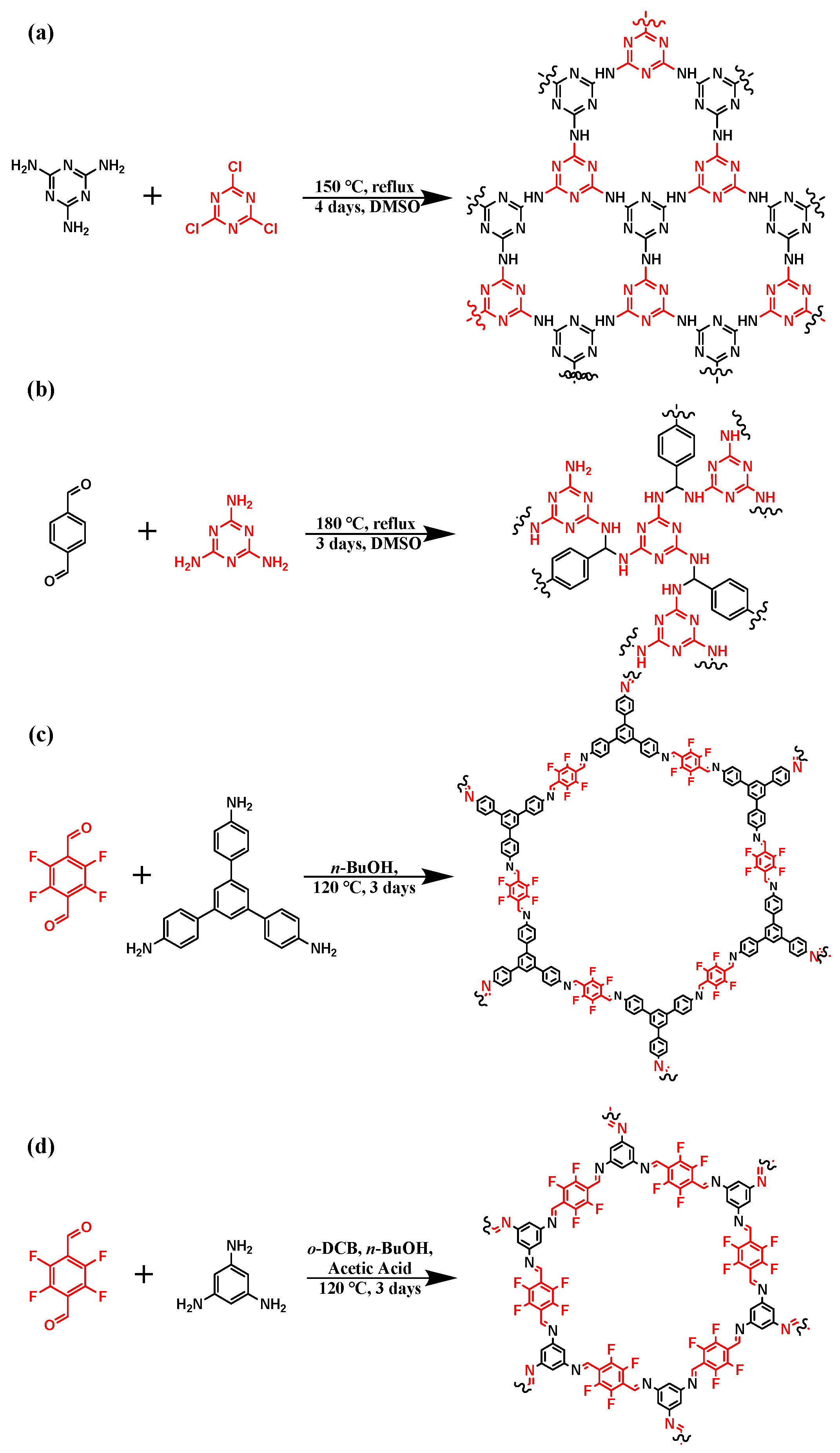
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Part
2.3. Vapor Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Establishment of COFs Crystal Model
2.5. Mass Transfer Process Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vapor Adsorption Properties of Hydrophilic COFs and Hydrophobic COFs
3.2. Simulation of Mass Transfer of Water and Ethanol Molecules in Four Different COFs
3.3. Optimization of Alcohol Mass Transfer Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Jin, W. Pervaporation Membrane Materials: Recent Trends and Perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, G.; Zhang, G. How to Transform Microporous Organic Polymers for Membrane-Based Separation: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.F.; Zhang, H. Recent Advances in Polymer Blend Membranes for Gas Separation and Pervaporation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 116, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.M.; Feng, Y.; Li, B.; Tham, H.M.; Lai, J.-Y.; Chun, T.-S. Recent Progress of Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 123, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C. Confined Mass Transfer Mechanism and Preparation Strategies of Separation Membranes: A Review. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Ren, H.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, D. Research Progress on Simulation of Multiscale Mass Transfer Processes in Gas-Solid System by Computational Mass Transfer. Particuology 2024, 90, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, K.; Feng, X. Mass Transfer Fundamentals in Pervaporation, Perstraction and Sorption: A Unified Approach. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 204, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Ren, S.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Recent Developments of Organic Solvent Resistant Materials for Membrane Separations. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Cheng, D.C.; Yi, M.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Karnik, R.; et al. Highly Porous Nanofiber-Supported Monolayer Graphene Membranes for Ultrafast Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, P.R.; Mace, A.; Thomas, S.N.; Jeon, J.-W. Nanostructured Porous Graphene and Its Composites for Energy Storage Applications. Nano Converg. 2017, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.; Dobner, C.; Zahl, P.; Fiankor, C.; Zhang, J.; Saxena, A.; Aluru, N.; Enders, A.; Sinitskii, A. Porous Nanographenes, Graphene Nanoribbons, and Nanoporous Graphene Selectively Synthesized from the Same Molecular Precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14453–14467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, T. Multiphase Nanoconfined Fluid Flow Mechanisms in Nanopores, Insights Derived from Molecular Dynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Neek-Amal, M.; Peeters, F.M.; Bai, B.; Sun, C. Interlink between Abnormal Water Imbibition in Hydrophilic and Rapid Flow in Hydrophobic Nanochannels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 132, 184001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, A.; Gao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X. Progress in Molecular-Simulation-Based Research on the Effects of Interface-Induced Fluid Microstructures on Flow Resistance. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirannahalage, S.P.K.; Meftahi, N.; Elbourne, A.; Weiss, A.C.G.; McConville, C.F.; Padua, A.; Winkler, D.A.; Gomes, M.C.; Greaves, T.L.; Le, T.C.; et al. Systematic Comparison of the Structural and Dynamic Properties of Commonly Used Water Models for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 4521–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.I.; Rao, S.; Sansom, M.S.P. Water in Nanopores and Biological Channels: A Molecular Simulation Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10298–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Francisco, J.S.; Zeng, X.C.; Meng, S. Water Transport through Subnanopores in the Ultimate Size Limit: Mechanism from Molecular Dynamics. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisbey, R.P.; Dichtel, W.R. Covalent Organic Frameworks as a Platform for Multidimensional Polymerization. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, P.T.; Ta, Q.T.H.; Nguyen, P.K.T. Designed Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Mini Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, A.; Ma, D. Editorial: Novel Design, Synthesis, and Environmental Applications of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1434454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, D.D.; Sick, T.; Bein, T. Photoactive and Conducting Covalent Organic Frameworks. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Shao, Z.; Hong, J.; Bi, K.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C. Structural Survey of Metal-Covalent Organic Frameworks and Covalent Metal-Organic Frameworks. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, S.; Altintas, C.; Erucar, I.; Keskin, S. Computational Investigation of Dual Filler-Incorporated Polymer Membranes for Efficient CO2 and H2 Separation: MOF/COF/Polymer Mixed Matrix Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, H.; Dong, S.; Xu, J.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Preparation of High-Performance and Pressure-Resistant Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2/H2 Separation by Modifying COF Surfaces with the Groups or Segments of the Polymer Matrix. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, N.; Pang, X.; Meng, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Kong, Y.; Ding, C.; Wu, H.; et al. Incorporating Graphene Oxide into COF Membranes Enables Ultrahigh Proton Conductivity and Ultralow H2 Crossover. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 688, 122103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, R.; Zaremba, O.; Dinca, M.; Arnauts, G.; Ameloot, R.; Skorupskii, G.; Bavykina, A.; Gascon, J.; Ejsmont, A.; Goscianska, J.; et al. The Current Status of MOF and COF Applications. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23975–24001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Karimi, M.; Gong, Y.-N.; Dai, N.; Safarifard, V.; Jiang, H.-L. Integration of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Covalent Organic Frameworks: Design, Synthesis, and Applications. Matter 2021, 4, 2230–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; Dai, M.; Peng, C. Metal-Organic Framework Membranes: Recent Development in the Synthesis Strategies and Their Application in Oil-Water Separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127004. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Van der Bruggen, B. Regulating Composition and Structure of Nanofillers in Thin Film Nanocomposite (TFN) Membranes for Enhanced Separation Performance: A Critical Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoranjan, N.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. A Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Covalent Organic Framework Nanocomposite Ultrathin Membrane with High Organic Solvent Resistance for Molecule Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53096–53103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, S.; Ren, J.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Cyclodextrin Functionalized Graphene Nanosheets with High Supramolecular Recognition Capability: Synthesis and Host−Guest Inclusion for Enhanced Electrochemical Performance. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, S.; Fan, L.; Pang, J.; Fan, W.; Kong, G.; Kang, Z.; Sun, D. Covalent Organic Frameworks Combined with Graphene Oxide to Fabricate Membranes for H2/CO2 Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Engineering Fast Water-Selective Pathways in Graphene Oxide Membranes by Porous Vermiculite for Efficient Alcohol Dehydration. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 677, 121587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, J.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Nasir, N.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z. 110th Anniversary: Mixed Matrix Membranes with Fillers of Intrinsic Nanopores for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7706–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, A.R.; Patel, C.M.; Murthy, Z.V.P. A Review on the Recent Advances in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation Processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pan, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Walker, S.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Construction of Molecule-Selective Mixed Matrix Membranes with Confined Mass Transfer Structure. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1563–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Guan, X.; Meng, Q.; Gao, M.-L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, H.-L. Tailoring Catalysis of Encapsulated Platinum Nanoparticles by Pore Wall Engineering of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2024, 136, e202410097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sheng, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework with Ceq Topology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Huang, N. Pore Partition in Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the Right Stuff: The Trade-off between Membrane Permeability and Selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Lin, E.; Wang, T.; Geng, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, P.; et al. Bottom-Up Synthesis of 8-Connected Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Efficient Ethylene/Ethane Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5643–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, H.S.; Mahato, A.K.; Majumder, P.; Banerjee, R. Landscaping Covalent Organic Framework Nanomorphologies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11482–11498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Hu, W. 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks: From Synthetic Strategies to Advanced Optical-Electrical-Magnetic Functionalities. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Jiang, H.; Douglin, J.C.C.; Chen, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Wu, H.; Yin, Y.; Dekel, D.R.R.; et al. Single Solution-Phase Synthesis of Charged Covalent Organic Framework Nanosheets with High Volume Yield. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202209306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jing, X.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Bulk COFs and COF Nanosheets for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3565–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Lim, Y.J.; Zhang, K. Engineering Multi-Channel Water Transport in Surface-Porous MXene Nanosheets for High-Performance Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 728, 124151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
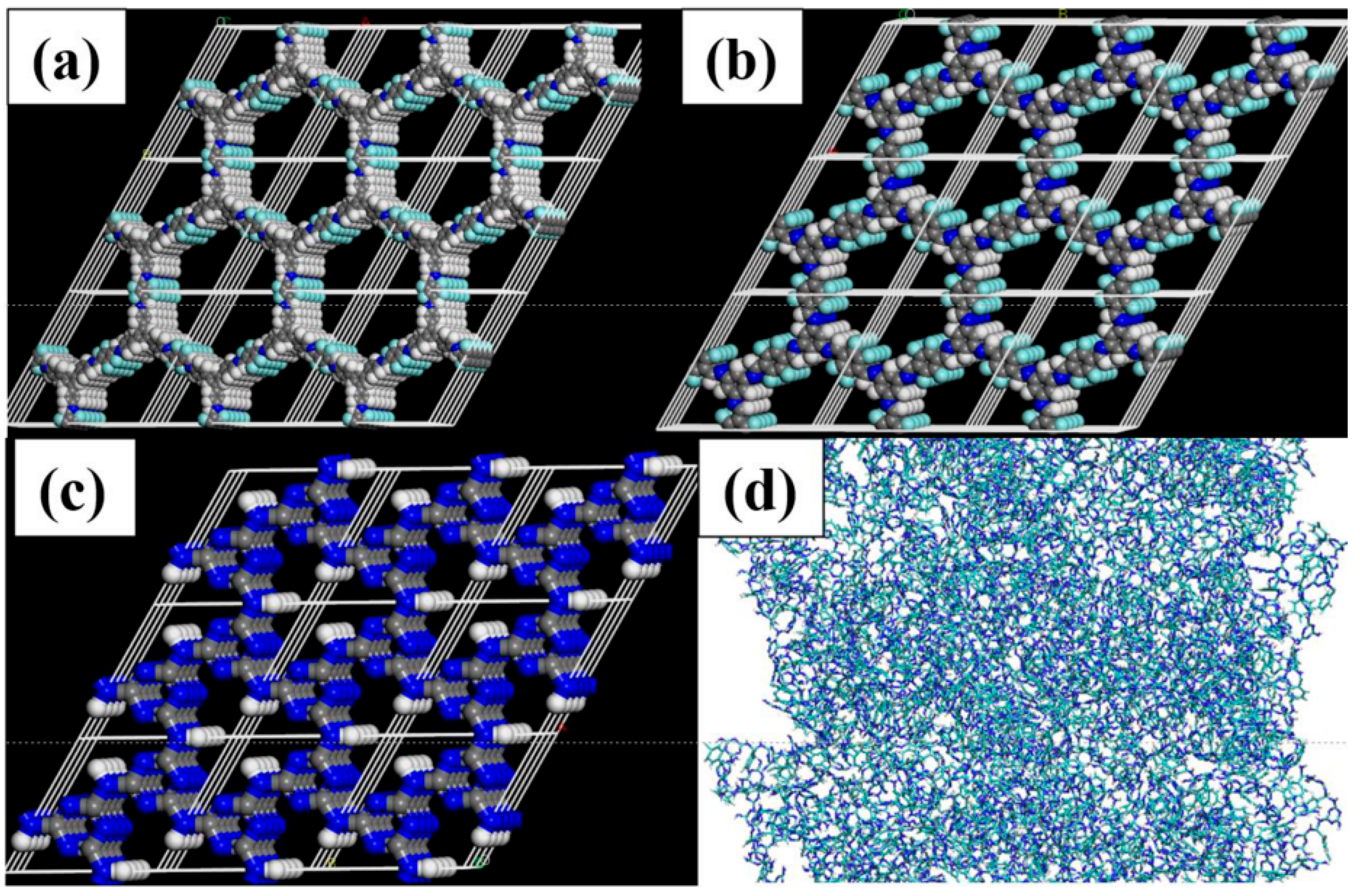


| Classification | Length (nm) | Width (nm) | Height (nm) | Volume (nm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCF-FCOF-2 | 15.12 | 13.09 | 13.09 | 2590.93 |
| SCF-FCOF-2x | 6.83 | 5.91 | 8.26 | 333.57 |
| NENP-1 | 6.9 | 5.97 | 6.77 | 278.76 |
| SNW-1 | 7.79 | 7.79 | 3.46 | 209.88 |
| P/P0 | NENP-1 | SNW-1 | SCF-FCOF-2 | SCF-FCOF-2x | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (cm3g−1) | Ethanol (cm3g−1) | Water (cm3g−1) | Ethanol (cm3g−1) | Water (cm3g−1) | Ethanol (cm3g−1) | Water (cm3g−1) | Ethanol (cm3g−1) | |
| 0.1 | 20.3 | 27.5 | 28.6 | 75.4 | 4.7 | 20.0 | 23.6 | 32.7 |
| 0.2 | 37.8 | 36.9 | 49.4 | 100.6 | 6.6 | 34.8 | 39.6 | 46.2 |
| 0.3 | 56.9 | 44.3 | 70.9 | 122.3 | 8.6 | 46.6 | 56.3 | 55.7 |
| 0.5 | 89.8 | 59.1 | 132.9 | 163.5 | 15.4 | 61.3 | 87.3 | 74.9 |
| 0.7 | 123.5 | 76.7 | 173.8 | 209.7 | 31.4 | 76.2 | 114.7 | 94.5 |
| 0.9 | 189.6 | 117.3 | 247.9 | 296.0 | 96.5 | 91.4 | 159.5 | 130.4 |
| Model | Electrostatic Force (nm−3) | Electrostatic Force Ratio (Water/Ethanol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Ethanol | ||
| NENP-1 | −120.1 | −12.1 | 992.6% |
| SNW-1 | −1054.6 | −305.5 | 345.2% |
| SCF-FCOF-2 | −48.7 | −33.2 | 146.7% |
| SCF-FCOF-2x | −103.0 | −57.7 | 178.5% |
| Media | Diffusion Coefficient (1 × 10−5 cm2s−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Ethanol | |
| NENP-1 | 0.004026 (±0.00295) | 3.4610 (±0.1017) |
| SNW-1 | 0.2158 (±0.0404) | 0.4879 (±0.2050) |
| SCF-FCOF-2 | 3.1769 (±0.0258) | 0.8553 (±0.2917) |
| SCF-FCOF-2x | 2.7561 (±0.7002) | 0.5128 (±0.3604) |
| Media | Dissolution Selectivity | Diffusion Selectivity | Total Flux of MMMs (g∙m−2h−1) | Separation Factor of MMMs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NENP-1 | Excellent | Excellent | 596 | 17.1 |
| SNW-1 | Medium | Medium | 422 | 14.7 |
| SCF-FCOF-2 | Excellent | Excellent | 605 | 16.8 |
| SCF-FCOF-2x | Bad | Bad | 223 | 8.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Cui, X.; Jiang, K.; Sheng, A.; Wang, H. PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane with Confined Mass Transfer Structure: The Effect of COFs with Different Porous Structures and Chemical Properties in the Pervaperation Process. Membranes 2025, 15, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100316
Zhai Y, Zheng Z, Cui X, Jiang K, Sheng A, Wang H. PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane with Confined Mass Transfer Structure: The Effect of COFs with Different Porous Structures and Chemical Properties in the Pervaperation Process. Membranes. 2025; 15(10):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100316
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yuan, Zimeng Zheng, Xinhao Cui, Kun Jiang, Ao Sheng, and Heyun Wang. 2025. "PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane with Confined Mass Transfer Structure: The Effect of COFs with Different Porous Structures and Chemical Properties in the Pervaperation Process" Membranes 15, no. 10: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100316
APA StyleZhai, Y., Zheng, Z., Cui, X., Jiang, K., Sheng, A., & Wang, H. (2025). PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane with Confined Mass Transfer Structure: The Effect of COFs with Different Porous Structures and Chemical Properties in the Pervaperation Process. Membranes, 15(10), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100316






