Assessing the Stability of Polymer Inclusion Membranes: The Case of Aliquat 336-Based Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. PIM Leaching Studies
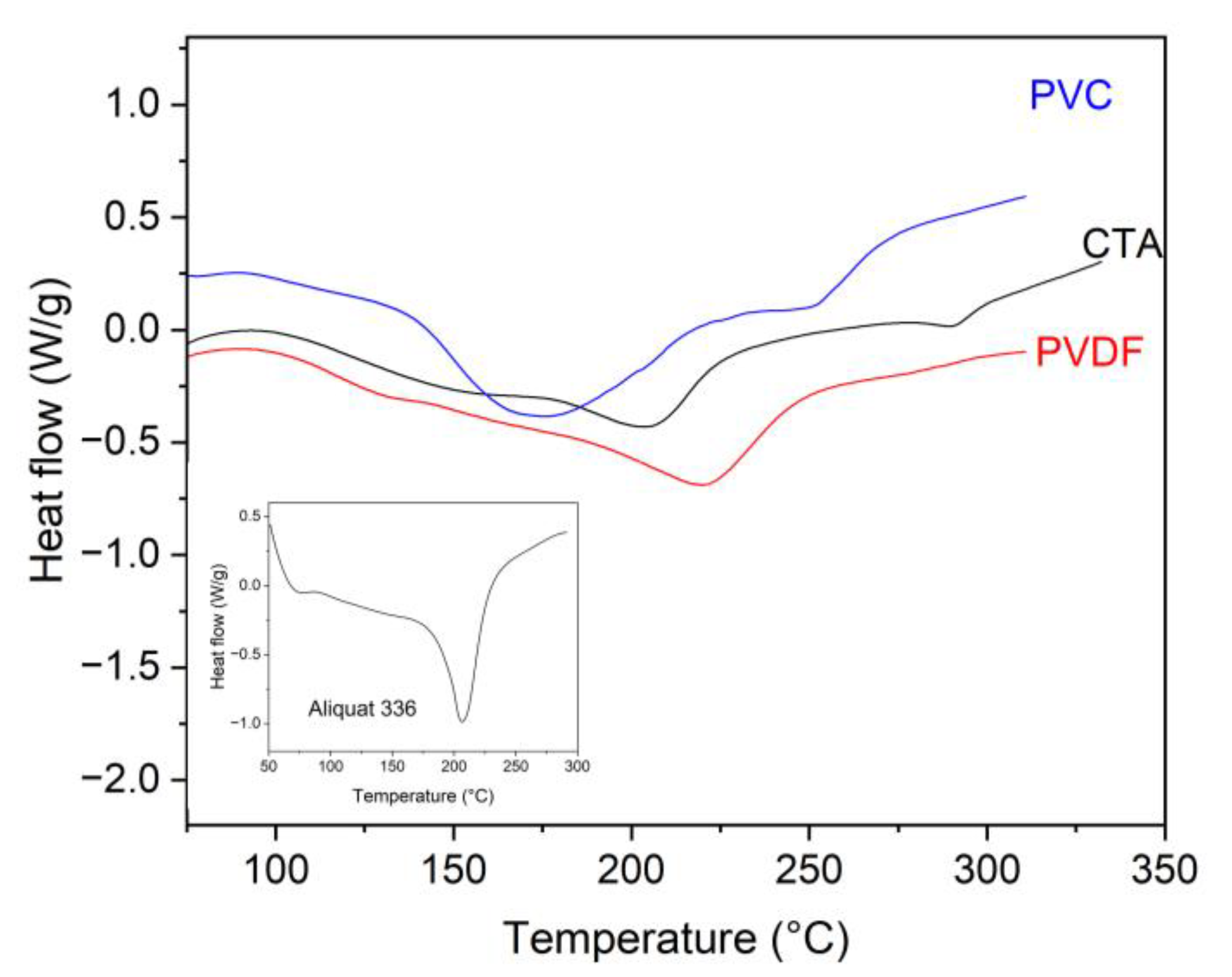
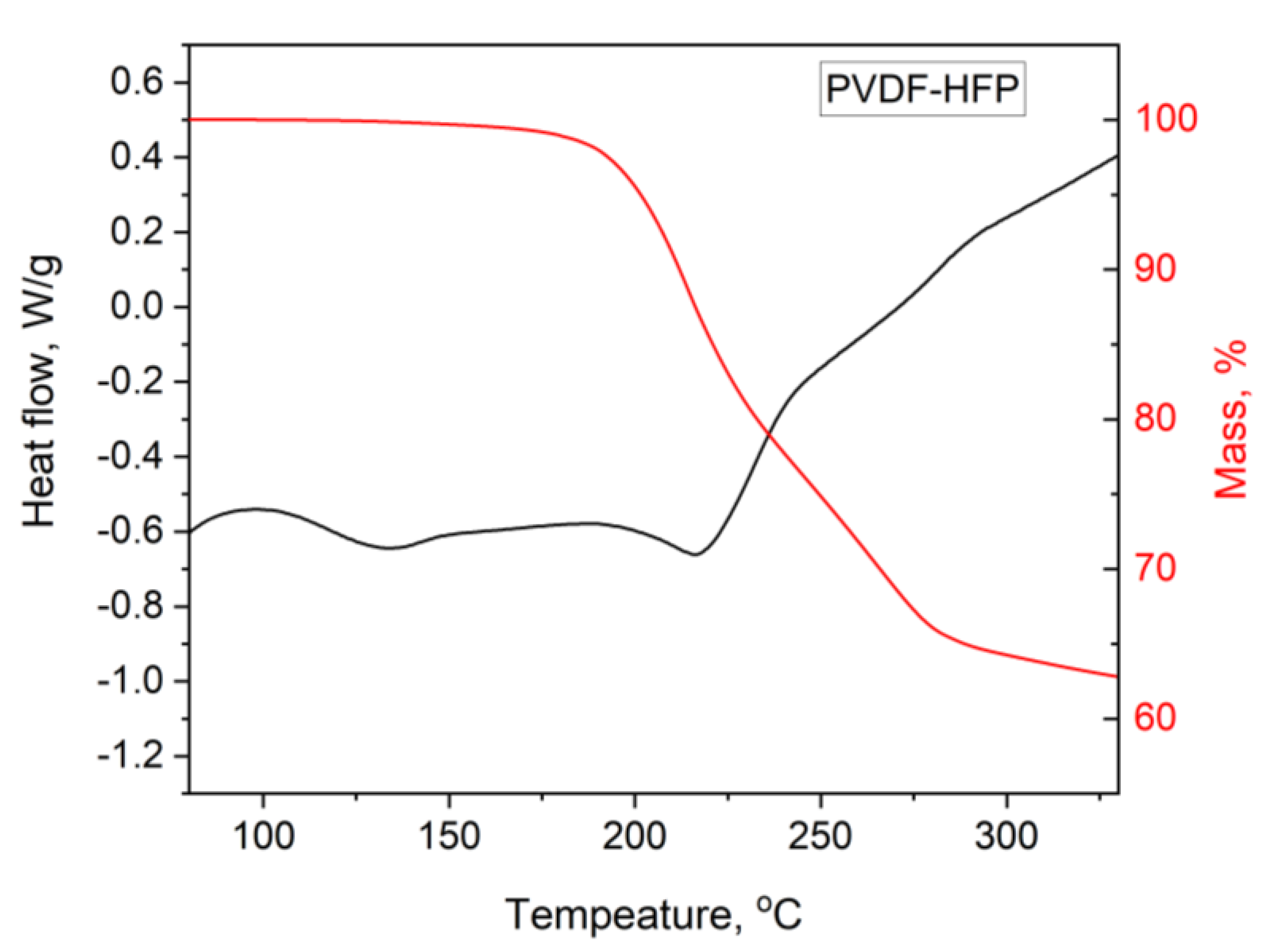
2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.5. Computational Methods
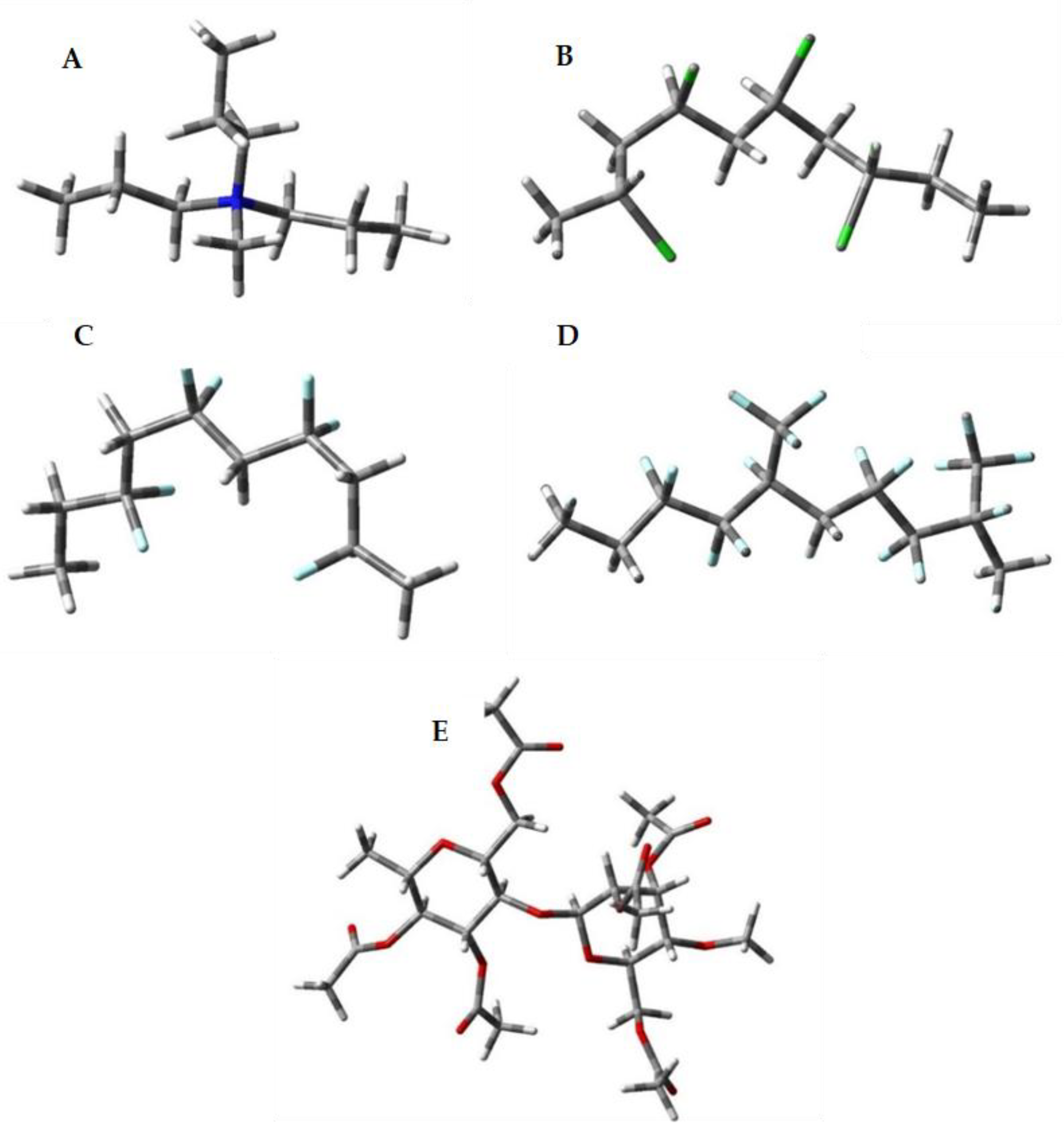
2.5.1. Models Used
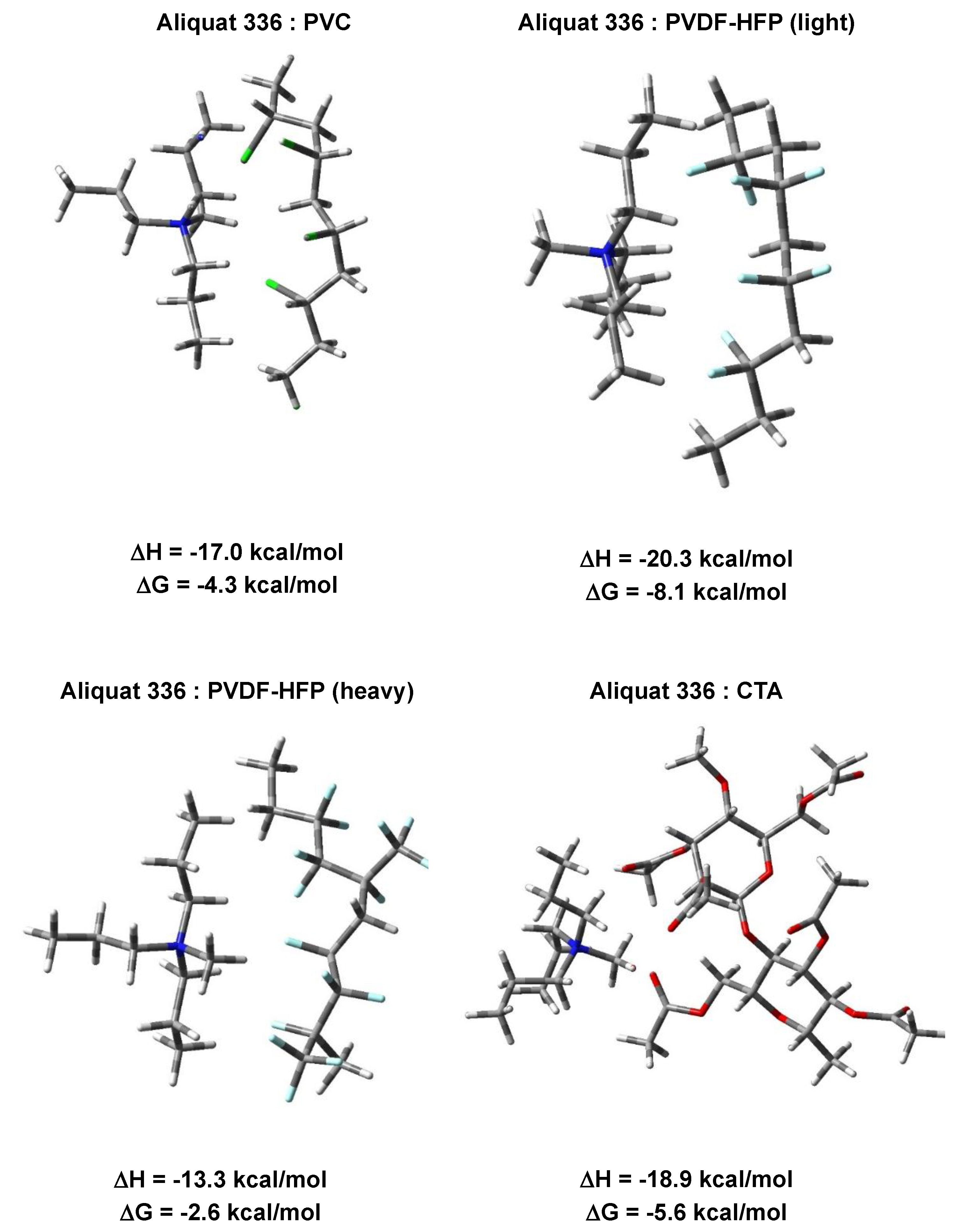
2.5.2. DFT Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DTA/TG PIM Stability Study
3.2. Quantum Chemical Calculations
3.3. Aliquat 336 Leaching and TGA of the PIMs Post-Leaching
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.; Samadi, A.; Wang, Z.; Pringle, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kolev, S.D. Ionic liquid-based polymer inclusion membranes for metal ions extraction and recovery: Fundamentals, considerations, and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowik-Zając, A.; Sabadash, V. Recent Developments in Polymer Inclusion Membranes: Advances in Selectivity, Structural Integrity, Environmental Applications and Sustainable Fabrication. Membranes 2025, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, K.; Czajka, J. Novel advances in the modification of polymer inclusion membranes: Design and applications—A short review. Express Polym. Lett. 2025, 19, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, Y.; Cattrall, R.W.; Truong, Y.B.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Kolev, S.D. The use of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) for the preparation of polymer inclusion membranes. Application to the extraction of thiocyanate. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Abdollahy, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Mohseni, M. Investigating the mechanism of Au(III) transport using a polymer inclusion membrane with dibutyl carbitol as a carrier. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 227, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, W.; Goto, M. Ternary extractant system consisting of PC-88A, TOPO, and Versatic 10 for recovery of scandium(III) from nickel laterite processing liquors. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 217, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiphetlho, K.; Chimuka, L.; Tutu, H.; Richards, H. Technical design and optimisation of polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) for sample pre-treatment and passive sampling—A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 799, 149483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. A novel polymer inclusion membrane based method for continuous clean-up of thiocyanate from gold mine tailings water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswandi, B.; Nitti, F.; Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Kolev, S.D. Water monitoring using polymer inclusion membranes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 18, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagul, E.A.; Croft, C.F.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Nanostructural characterisation of polymer inclusion membranes using X-ray scattering. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, W. Chemical and morphological stability of Aliquat 336/PVC membranes in membrane extraction: A preliminary study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 46, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; John, A.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Perera, J.M.; Kolev, S.D. Influence of the composition of polymer inclusion membranes on their homogeneity and flexibility. Desalination 2009, 236, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.S.A.; Whitten, P.G.; Nghiem, L.D. The effect of aging on thermomechanical and metal extraction properties of poly (vinyl chloride)/Aliquat 336 polymer inclusion membranes. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.S.A.; Idris, N.S.U.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Chee, T.M. The Removal of Methyl Orange Using CTA-Aliquat 336 Electrospun Fibers From Aqueous Solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 549, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, F.; Kebiche-Senhadji, O.; Marais, S.; Colasse, L.; Fatyeyeva, K. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) by polymer inclusion membrane based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Aliquat 336. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, Y.; Truong, Y.B.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Kolev, S.D. A new generation of highly stable and permeable polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) with their carrier immobilized in a crosslinked semi-interpenetrating polymer network. Application to the transport of thiocyanate. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader-Trejo, F.E.; Miguel, E.R.d.S.; de Gyves, J. Mercury(II) removal using polymer inclusion membranes containing Cyanex 471X. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Recent Advances in the Selective Transport and Recovery of Metal Ions using Polymer Inclusion Membranes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zeng, X.; He, Q.; Deng, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Stable ionic liquid-based polymer inclusion membranes for lithium and magnesium separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchn, R.; Chaouqi, Y.; Louafy, R.; Avci, A.H.; Curcio, E.; Santoro, S.; Cherkaoui, O.; Hlaibi, M. Polymer Inclusion membranes with long term-stability in desalination via membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2023, 191, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebiche-Senhadji, O.; Tingry, S.; Seta, P.; Benamor, M. Selective extraction of Cr(VI) over metallic species by polymer inclusion membrane (PIM) using anion (Aliquat 336) as carrier. Desalination 2010, 258, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.; Romero, V.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E.; Benavente, J. Polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) with the ionic liquid (IL) Aliquat 336 as extractant: Effect of base polymer and IL concentration on their physical–chemical and elastic characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisawi, H.A.O. Performance of wastewater treatment during variable temperature. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian 09, Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013.
- Pereva, S.; Nikolova, V.; Angelova, S.; Spassov, T.; Dudev, T. Water inside β-cyclodextrin cavity: Amount, stability and mechanism of binding. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafska, T.P.; Spassova, M.I.; Dudev, T.M.; Pereva, S.M.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Spassov, T.G. Easy and Effective Method for α-CD:N(2)O Host-Guest Complex Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Ma, C.; Qiao, Y.; Yao, H. Thermal degradation of PVC: A review. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, C.F.; Almeida, M.I.G.; Kolev, S.D. Characterisation of micro polymer inclusion beads by thermogravimetric analysis. Polymer 2023, 283, 126203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PIM Base Polymer | PVC | CTA | PVDF-HFP |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS ± SD [%] at 0.05 M NaCl | 6.37 ± 0.35 | 5.85 ± 0.30 | 4.76 ± 0.30 |
| MS ± SD [%] at 0.1 M NaCl | 5.03 ± 0.30 | 4.02 ± 0.25 | 3.75 ± 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velikova, K.; Dudev, T.; Sarafska, T.; Kukoc-Modun, L.; Kolev, S.D.; Spassov, T. Assessing the Stability of Polymer Inclusion Membranes: The Case of Aliquat 336-Based Membranes. Membranes 2025, 15, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100309
Velikova K, Dudev T, Sarafska T, Kukoc-Modun L, Kolev SD, Spassov T. Assessing the Stability of Polymer Inclusion Membranes: The Case of Aliquat 336-Based Membranes. Membranes. 2025; 15(10):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100309
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelikova, Kalina, Todor Dudev, Tsveta Sarafska, Lea Kukoc-Modun, Spas D. Kolev, and Tony Spassov. 2025. "Assessing the Stability of Polymer Inclusion Membranes: The Case of Aliquat 336-Based Membranes" Membranes 15, no. 10: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100309
APA StyleVelikova, K., Dudev, T., Sarafska, T., Kukoc-Modun, L., Kolev, S. D., & Spassov, T. (2025). Assessing the Stability of Polymer Inclusion Membranes: The Case of Aliquat 336-Based Membranes. Membranes, 15(10), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100309










