Removal of Aggregates During Bispecific Antibody Purification Using Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibody and Its Properties
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Protein A Chromatography
2.4. AEX
2.5. CEX
2.6. HIMC
2.7. Analytical Techniques
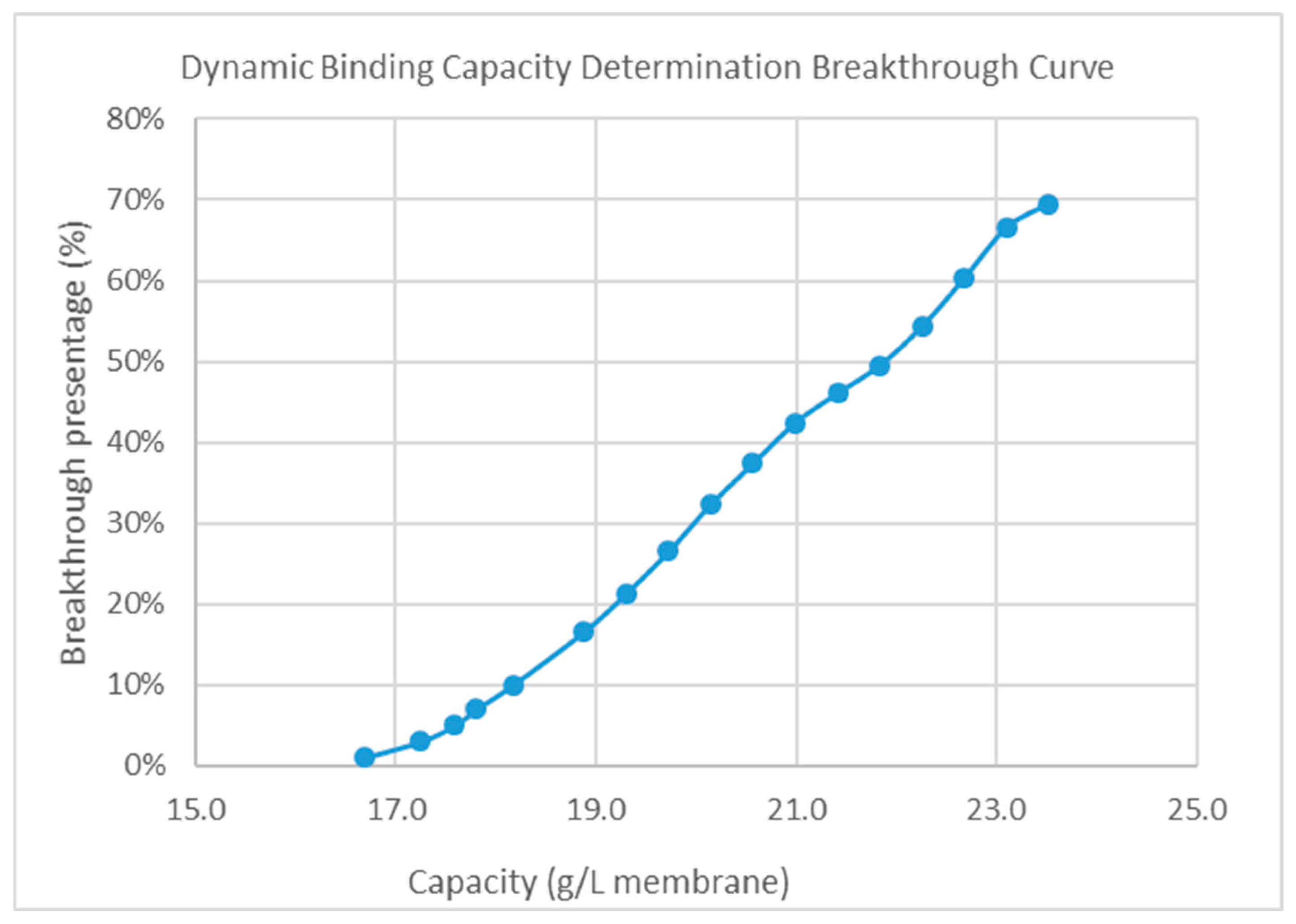
2.7.1. Determination of DBC
2.7.2. Design of Experiment (DoE) Screening Study Design and Data Analysis
2.7.3. Recovery
2.7.4. Size Exclusion Chromatography-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (SEC-HPLC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The HMWs Removal Ability Evaluation of the CEX Column
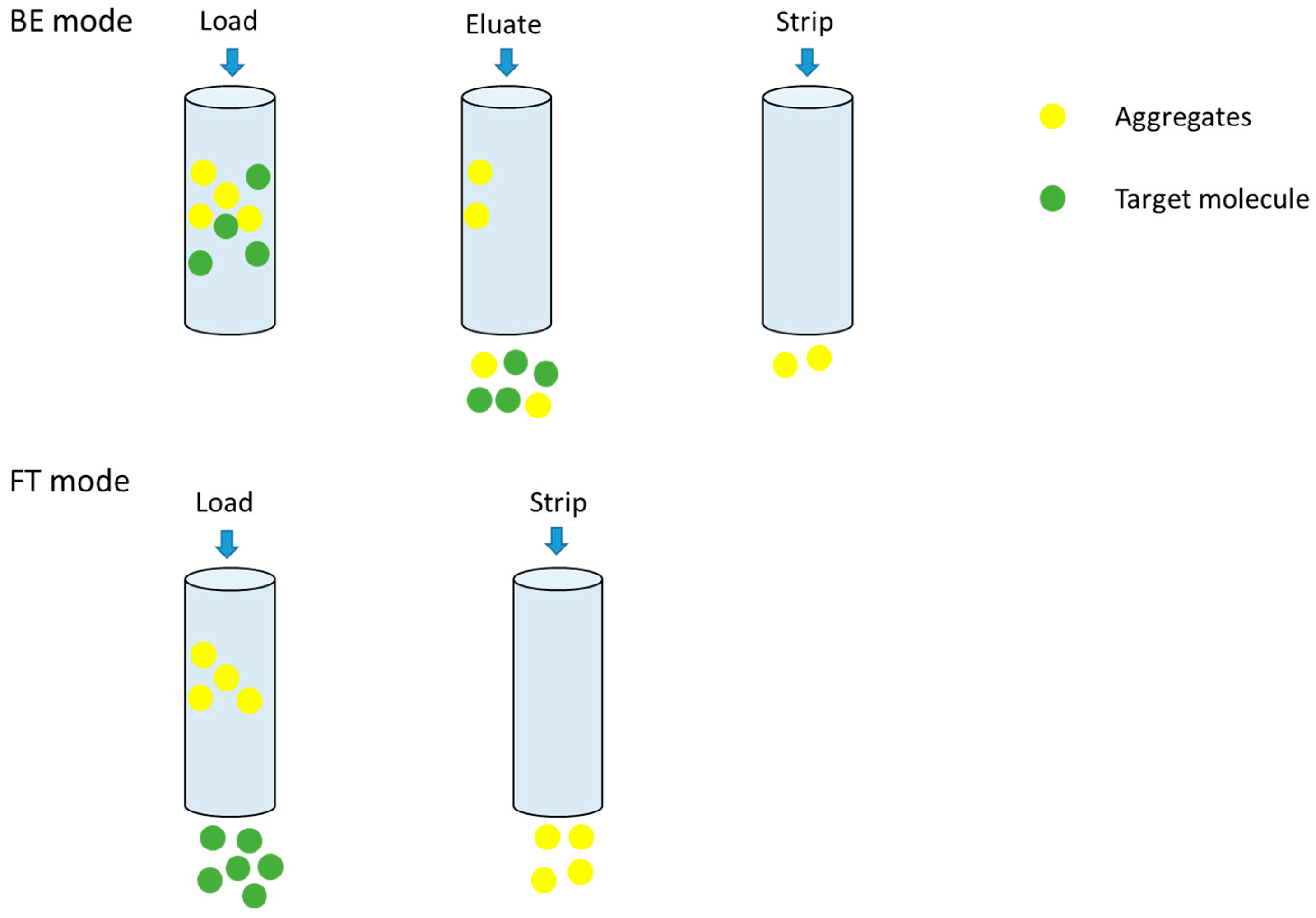
3.2. The Evaluation of FT and BE Mode of HIMC
3.2.1. The Dynamic Binding Capacity of HIMC for BE Mode
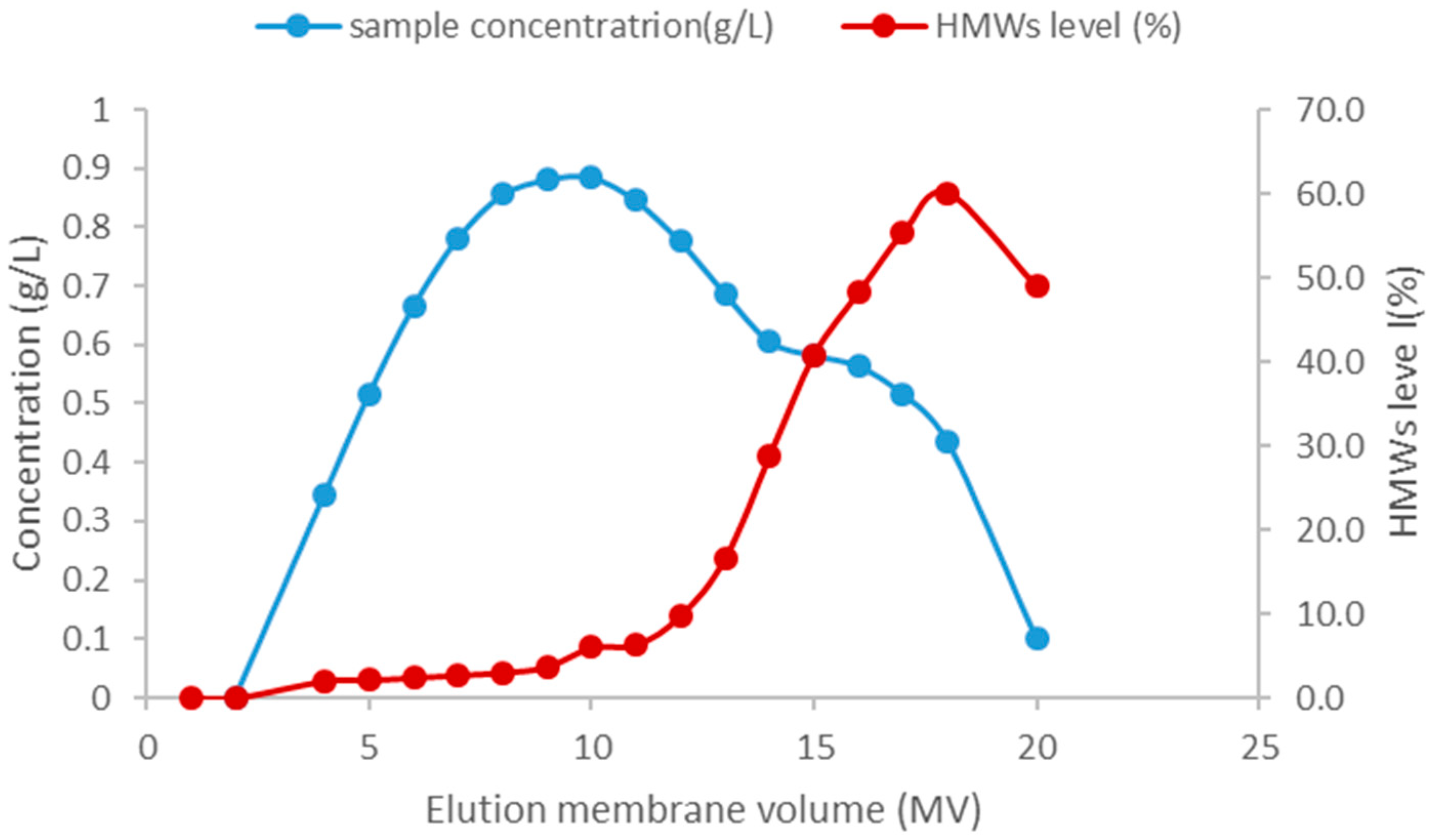
3.2.2. The Aggregate Removal Ability of HIMC for BE Mode and FT Mode
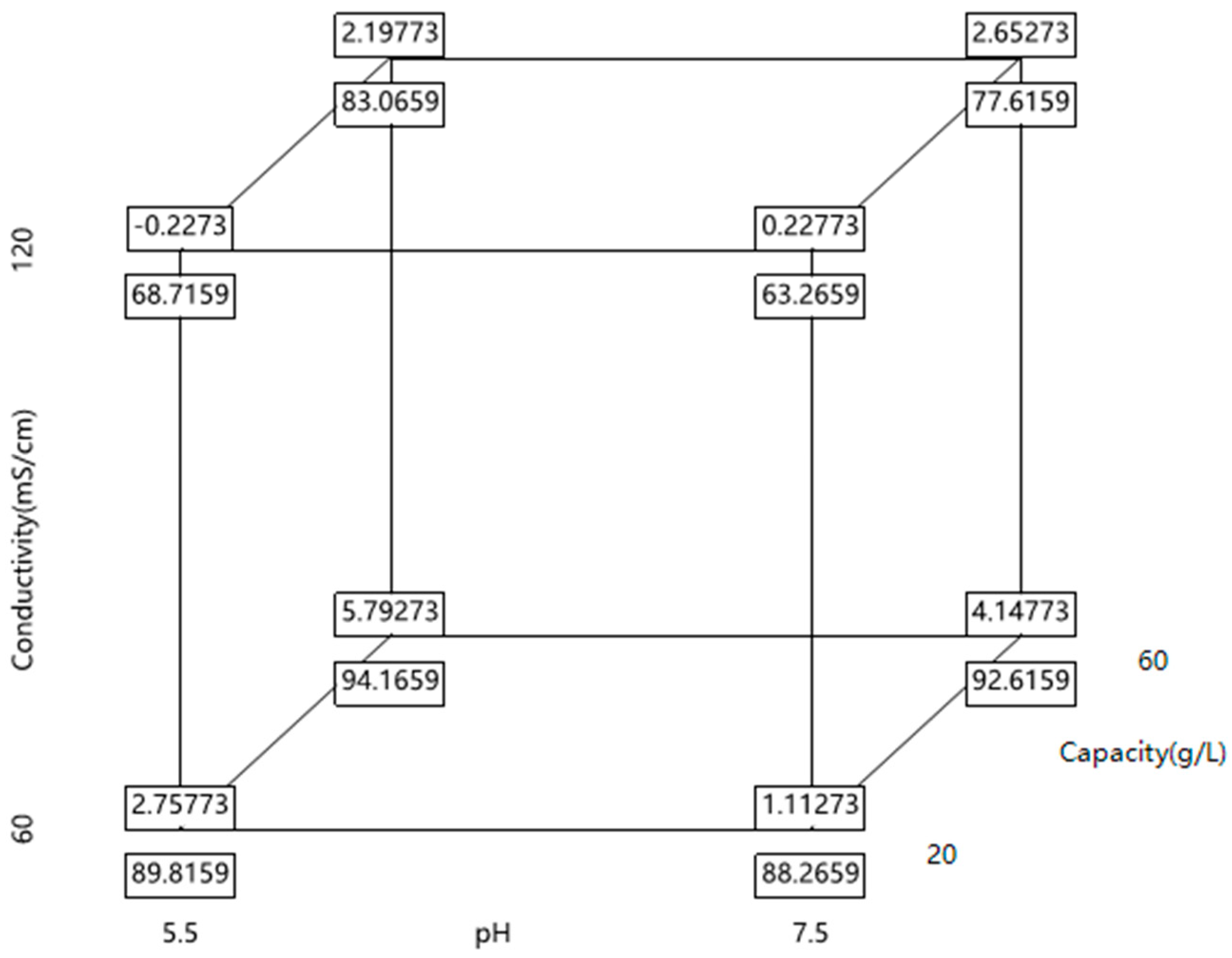
3.3. The Optimization of HIMC FT Mode by DoE Study and Analysis
3.3.1. Experimental Strategy, Results, and Statistical Analysis of DoE
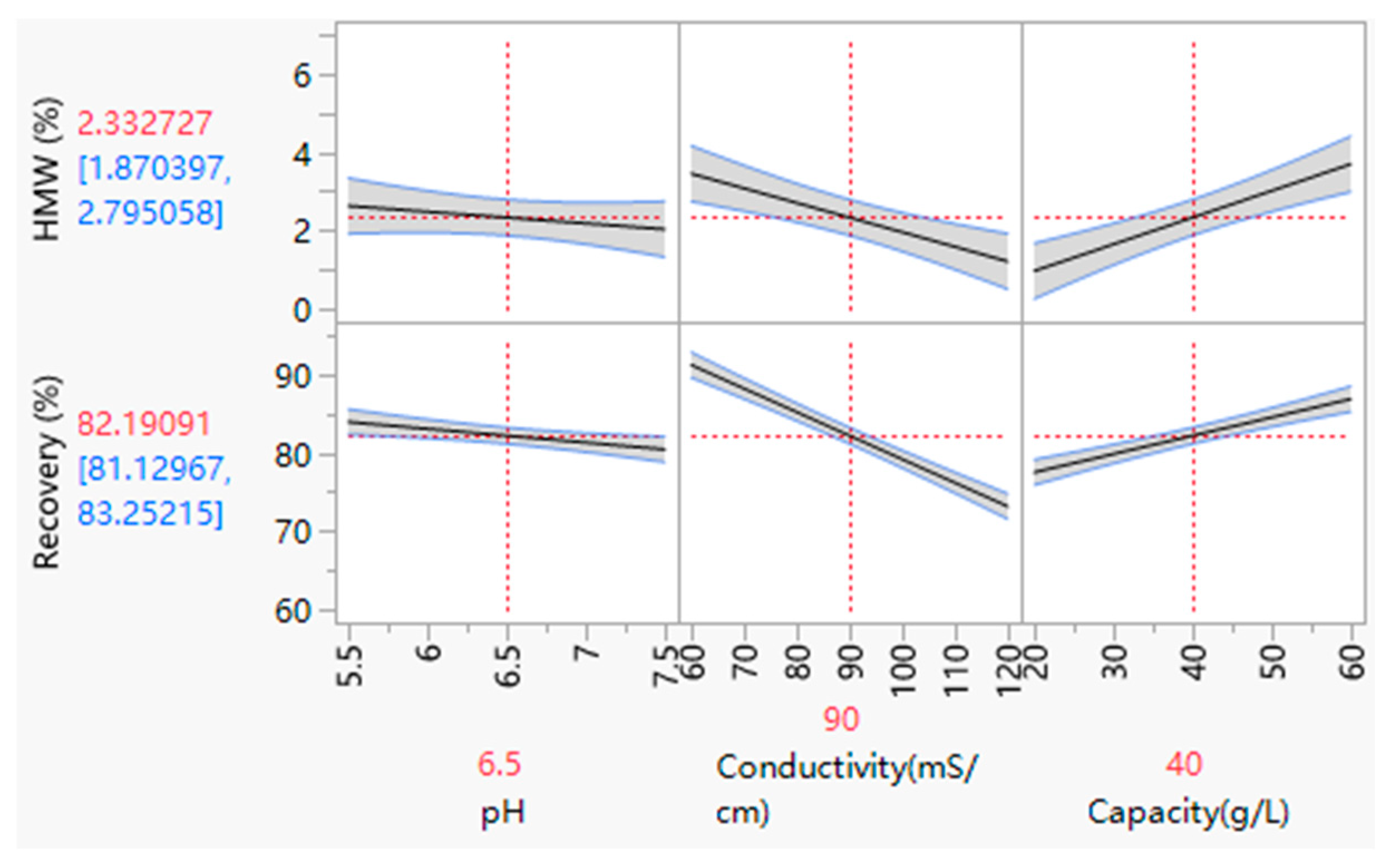
3.3.2. The Load pH and Conductivity for HIMC FT Mode
3.3.3. The Capacity for HIMC FT Mode
3.3.4. The Design Space of HIMC FT Mode
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BsAbs | Bispecific antibodies |
| ProA | Protein A |
| DAF | Dual Action Fab |
| CHO | Chinese Hamster Ovary |
| AEX | Anion exchange chromatography |
| CEX | Cation exchange chromatography |
| HIMC | Hydrophobic interaction membrane chromatography |
| HCs | Heavy chains |
| LCs | Light chains |
| IEX | Ion exchange chromatography |
| PI | Isoelectric point |
| HIC | Hydrophobic interaction chromatography |
| mAbs | Monoclonal antibodies |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| BT | Binding–elution |
| FT | Flow-through |
| CV | Column volume |
| MV | Membrane volume |
| HPW | High-purity water |
| HMWs | High molecular weights |
| C0 | Protein concentration in the sample (mg/mL) |
| VL | Accumulated volume per fraction (mL) |
| V0 | System void volume (mL) |
| VM | Membrane volume (mL) |
| DoE | Design of experiment |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HCD | Host cell DNA |
| HCP | Host cell protein |
| RT | Retention time |
References
- Guo, G.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. A potential downstream platform approach for WuXiBody-based IgG-like bispecific antibodies. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 173, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, P.; Zhou, W. A roadmap for IgG-like bispecific antibody purification. In Approaches to the Purification, Analysis and Characterization of Antibody-Based Therapeutics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.; Wang, Z.; Moscoso-Castro, M.; D’Souza, P.; Lei, C.; Xu, J.; Gu, J. Biology drives the discovery of bispecific antibodies as innovative therapeutics. Antib. Ther. 2020, 3, 18–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Pretelli, G.; Desai, J.; Garralda, E.; Siu, L.L.; Steiner, T.M.; Au, L. Bispecific antibodies: Advancing precision oncology. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 893–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, C. Bispecific antibodies in cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 65, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, C.; Arnold, L.; Motabar, D.; Aspelund, M.; Tang, A.; Hunter, A.; Chung, W.K. An Integrated Approach to Aggregate Control for Therapeutic Bispecific Antibodies Using an Improved Three Column Mab Platform-Like Purification Process. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 35, e2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Han, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Monitoring removal of hole-hole homodimer by analytical hydrophobic interaction chromatography in purifying a bispecific antibody. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 164, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prabakaran, P.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S. Antibody Aggregation: Insights from Sequence and Structure. Antibodies 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, R.; Rawat, P.; Thangakani, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Gromiha, M.M. Protein aggregation: In silico algorithms and applications. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Shahzadi, S.; Li, M.S.; Kloczkowski, A. Prediction and Evaluation of Protein Aggregation with Computational Methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2867, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandel, T.I.; Zaman, M.; Khan, M.V.; Ali, M.; Rabbani, G.; Ishtikhar, M.; Khan, R.H. A mechanistic insight into protein-ligand interaction, folding, misfolding, aggregation and inhibition of protein aggregates: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekharzadeh, B.; Hyman, B.T.; Wegmann, S. Structural studies on the mechanism of protein aggregation in age related neurodegenerative diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2016, 156, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, E.M.; Samant, R.S.; Frydman, J. Mechanisms and Functions of Spatial Protein Quality Control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Hoi, K.M.; Mahfut, F.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Effective flow-through polishing strategies for knob-into-hole bispecific antibodies. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.; Kelly, G.M.; Emery, W.R. Use of mobile phase additives for the elution of bispecific and monoclonal antibodies from phenyl based hydrophobic interaction chromatography resins. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1096, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.; Kruse, T.; Minceva, M.; Kampmann, M. Integrated double flow-through purification of monoclonal antibodies using membrane adsorbers and single-pass tangential flow filtration. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 195, 108913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Wang, L. Purification of humanized monoclonal antibody by hydrophobic interaction membrane chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1107, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuofa, J.; Husson, S.M. Comparative Evaluation of Commercial Protein A Membranes for the Rapid Purification of Antibodies. Membranes 2023, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünberg, M.; Kuchemüller, K.B.; Töppner, K.; Busse, R.A. Scalable, Robust and Highly Productive Novel Convecdiff Membrane Platform for mAb Capture. Membranes 2022, 12, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steegmüller, T.; Kratky, T.; Gollwitzer, L.; Schwaminger, S.P.; Berensmeier, S. Development of a New Affinity Gold Polymer Membrane with Immobilized Protein A. Membranes 2024, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Braczkowski, R.; Chen, S.-H.; Busse, R.; Li, Y.; Fabri, L.; Bekard, I.B. Scalability of Sartobind® Rapid A Membrane for High Productivity Monoclonal Antibody Capture. Membranes 2023, 13, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. Recent development and application of membrane chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 415, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boi, C.; Malavasi, A.; Carbonell, R.G.; Gilleskie, G. A direct comparison between membrane adsorber and packed column chromatography performance. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1612, 460629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraud, N.; Faber, R.; Kiss, C.; Demmer, W.; Hoerl, H.H.; Fischer-Fruehholz, S. Hydrophobic-interaction membrane chromatography for large-scale purification of biopharmaceuticals. BioProcess Int. 2009, 7, 30–35. Available online: https://www.bioprocessintl.com/chromatography/hydrophobic-interaction-membrane-chromatography-for-large-scale-purification-of-biopharmaceuticals (accessed on 1 June 2009).
- Wang, Y.; Bhaskar, U.; Chennamsetty, N.; Noyes, S.; Guo, J.; Song, Y.; Lewandowski, A.; Ghose, S. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography in continuous flow-through mode for product-related variant removal. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1736, 465356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Bekard, I.; Hunt, B.; Black, J.; Fabri, L.; Gras, S.L.; Kentish, S.E. The Transition from Resin Chromatography to Membrane Adsorbers for Protein Separations at Industrial Scale. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2023, 53, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorek, J.K.; Karkov, H.S.; Matthiesen, F.; Dainiak, M. High throughput screening for rapid and reliable prediction of monovalent antibody binding behavior in flowthrough mode. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2024, 121, 2332–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Qian, X. Electrospun Weak Anion-exchange Fibrous Membranes for Protein Purification. Membranes 2020, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Beck, A.; Guillarme, D. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography for the characterization of monoclonal antibodies and related products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbauer, A.; Machold, C.; Hahn, R. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography of proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1079, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, D.; Damjanovic, L.; Kaisermayer, C.; Sommeregger, W.; Gili, A.; Gasselhuber, B.; Castan, A.; Mayrhofer, P.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Kunert, R. Bioprocessing of Recombinant CHO-K1, CHO-DG44, and CHO-S: CHO Expression Hosts Favor Either mAb Production or Biomass Synthesis. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, e1700686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüttimann, B.; Wegener, K. The Power of DOE: How to Increase Experimental Design Success and Avoid Pitfalls. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 2015, 8, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, W.; Muca, R.; Woś, S.; Piątkowski, W.; Antos, D. Isolation of monoclonal antibody from a Chinese hamster ovary supernatant. II: Dynamics of the integrated separation on ion exchange and hydrophobic interaction chromatography media. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, S.; Tao, Y.; Conley, L.; Cecchini, D. Purification of monoclonal antibodies by hydrophobic interaction chromatography under no-salt conditions. mAbs 2013, 5, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tetrault, J.; Ley, A. Comparison of standard and new generation hydrophobic interaction chromatography resins in the monoclonal antibody purification process. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1177, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Molecule Class | pI | MW (kDa) |
|---|---|---|
| BsAb | 8.15 | 150.52 |
| Procedure | Buffer | RT (min) | Volume (CV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanitization | 1 M NaOH | 5 | 3 |
| Equilibration | 50 mM Tris-HAc, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4 | 3 | |
| Elution | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, pH 3.6 | 3 | |
| Regeneration | 120 mM HAc | 3 |
| Procedure | Buffer | RT (min) | Volume (CV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanitization | 1 M NaOH | 5 | 3 |
| Equilibration | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, pH 5.5 | 3 | |
| Strip | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, 500 mM NaCl, pH 5.5 | 3 |
| Procedure | Buffer | RT (min) | Volume (CV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanitization | 1 M NaOH | 5 | 3 |
| Equilibration | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, pH 5.5 | 3 | |
| Elution | A:50 mM NaAc-HAc, pH 5.5 B:50 mM NaAc-HAc, 500 mM NaCl, pH 5.5 | 0–100%B, 20 CV | |
| Regeneration | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, 500 mM NaCl, pH 5.5 | 3 |
| Procedure | Buffer | RT (min) | Volume (MV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanitization | 1 M NaOH | 0.3 | 15 |
| Equilibration | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, 900 mM (NH4)2SO4, pH 5.5 | 15 | |
| Elution | A: 50 mM NaAc-HAc, 1.05 M (NH4)2SO4, pH 5.5 B: 50 mM NaAc-HAc, pH 5.5 | 0–100%B, 20 MV | |
| Regeneration | HPW | 15 |
| Procedure | Buffer | RT (min) | Volume (MV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanitization | 1 M NaOH | 0.3 | 15 |
| Equilibration | 50 mM NaAc-HAc, 450–900 mM(NH4)2SO4, pH 5.5 | 15 | |
| Regeneration | HPW | 15 |
| Mode | pH | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Capacity (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 |
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 |
| − + − | 5.5 | 120 | 20 |
| − − + | 5.5 | 60 | 60 |
| + − − | 7.5 | 60 | 20 |
| − − − | 5.5 | 60 | 20 |
| + + − | 7.5 | 120 | 20 |
| + + + | 7.5 | 120 | 60 |
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 |
| + − + | 7.5 | 60 | 60 |
| − + + | 5.5 | 120 | 60 |
| Sample | Recovery (%) | SEC-HPLC | CE-NR | HCP (ppm) | HCD (ppb) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMWs (%) | Monomers (%) | LMWs (%) | Purity (%) | LMWs (%) | ||||
| CEX load | N/A | 20.9 | 79.1 | ND | 96.1 | 3.9 | 36.9 | <0.3 |
| CEX eluate 4–7 | 90.1 | 18.7 | 81.3 | ND | 96.2 | 3.8 | 3.6 | <0.2 |
| Mode | Capacity (g/L Membrane Volume) | Loading pH/Conductivity (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Binding–elution | 14.5 | 5.5/140.0 |
| Flow-through | 30.0 | 5.5/70.0 |
| Sample | Recovery (%) | SEC-HPLC | CE-NR | HCP (ppm) | HCD (ppb) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMWs (%) | Monomers (%) | LMWs (%) | Purity (%) | LMWs (%) | ||||
| HIMC load | N/A | 20.9 | 79.1 | ND | 96.1 | 3.9 | 36.9 | <0.3 |
| HIMC eluate 4–17 | 74.2 | 4.1 | 95.9 | ND | 96.1 | 3.9 | 3.1 | <0.3 |
| HIMC flow-through | 80.2 | 3.0 | 97.0 | ND | 96.3 | 3.7 | 3.4 | <0.3 |
| Mode | pH | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Capacity (g/L) | HMW (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 | 1.81 | 83.5 |
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 | 1.79 | 83.1 |
| − + − | 5.5 | 120 | 20 | 0.31 | 67.3 |
| − − + | 5.5 | 60 | 60 | 6.16 | 94.1 |
| + − − | 7.5 | 60 | 20 | 1.48 | 88.2 |
| − − − | 5.5 | 60 | 20 | 2.80 | 89.5 |
| + + − | 7.5 | 120 | 20 | 0.10 | 64.3 |
| + + + | 7.5 | 120 | 60 | 3.19 | 76.2 |
| 0 0 0 | 6.5 | 90 | 40 | 1.76 | 81.5 |
| + − + | 7.5 | 60 | 60 | 4.19 | 92.3 |
| − + + | 5.5 | 120 | 60 | 2.07 | 84.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Qi, Y.; Gao, K. Removal of Aggregates During Bispecific Antibody Purification Using Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography. Membranes 2025, 15, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100299
Zhao P, Qi Y, Gao K. Removal of Aggregates During Bispecific Antibody Purification Using Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography. Membranes. 2025; 15(10):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100299
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Puya, Yue Qi, and Kai Gao. 2025. "Removal of Aggregates During Bispecific Antibody Purification Using Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography" Membranes 15, no. 10: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100299
APA StyleZhao, P., Qi, Y., & Gao, K. (2025). Removal of Aggregates During Bispecific Antibody Purification Using Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography. Membranes, 15(10), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100299








