Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Carbon Black Support for Enhancing the Durability of Catalysts Used in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Against Carbon Corrosion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Fuel Cell Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
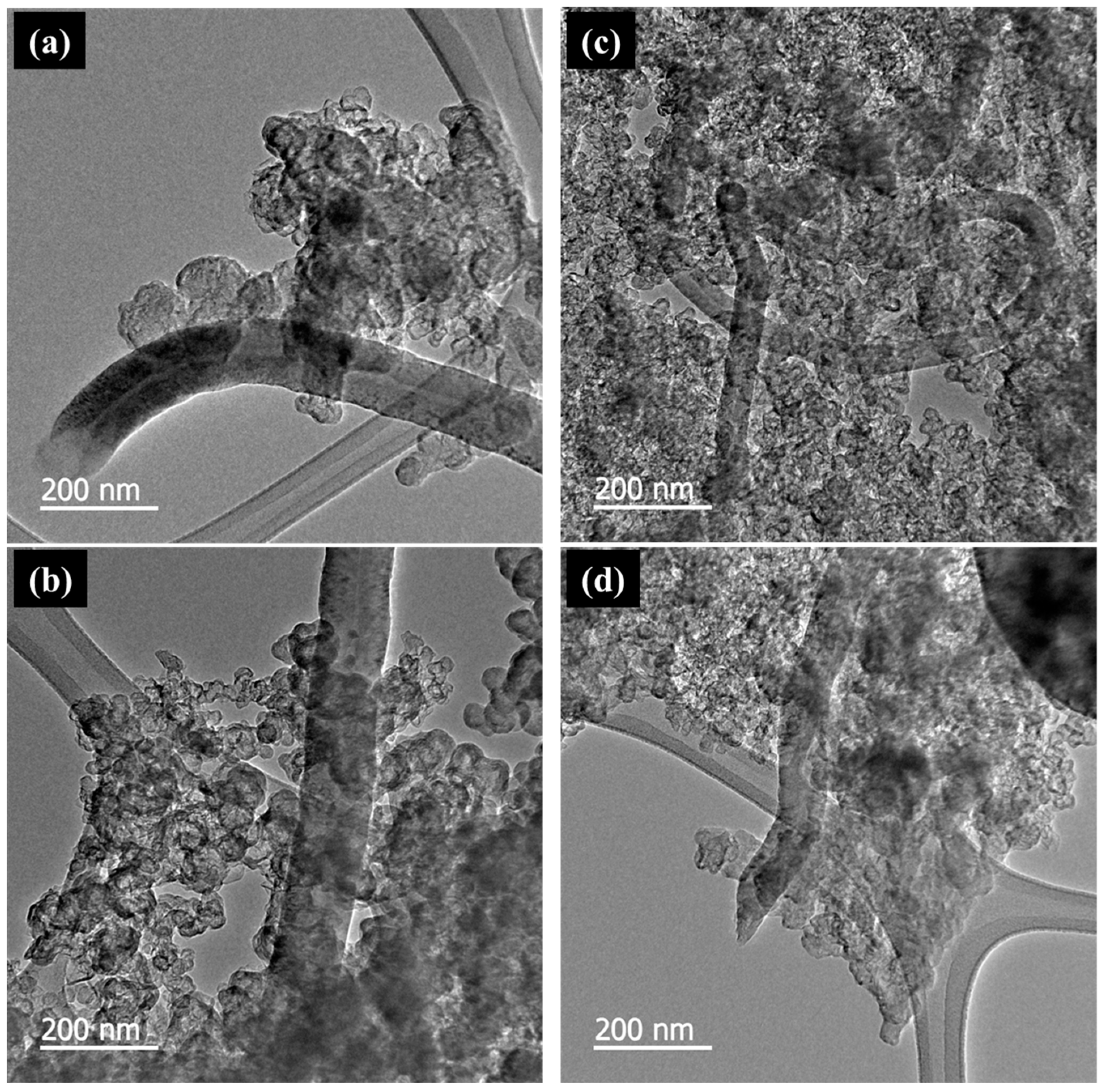
3.1. Properties and Selection of CNFs
3.2. Properties of the CNF–CB Hybrid Supports
3.3. Fuel Cell Evaluation Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steele, B.C.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, B.C. The enabling technology for the commercialisation of fuel cell systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2001, 36, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Niguyen, Q.M. Solid oxide fuel cell technology—Features and applications. Solid. State Ion. 2004, 174, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y. Fundamental Models for Fuel Cell Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4727–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P. Reviews on the effects of contaminations and research methodologies for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 23174–23200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, L.; Kang, J.-G.; Baik, K.D.; Kim, K.; Ahn, C. Advancement and applications of PEMFC energy systems for large-class unmanned underwater vehicles: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 79, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, W.; Ken, S.C.; Jeffrey, M.; Sung, C.C.; Xavier, C.A. A Review of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Technology, Applications, and Needs on Fundamental Research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, E.C.; Robert, D.L.; Timothy, J.H.; Paul, C.T.; Monica, E.T. Advanced materials for improved PEMFC performance and life. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lee, C.; Qiao, X.; Siddharth, K.B.; Ulises, M.; Jacob, S.S. Advanced Electrode Structures for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Current Status and Path Forward. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2024, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, N.A.; Battal, D.; Murat, K.Y. Investigation of the performance parameters for a PEMFC by thermodynamic analyses: Effects of operating temperature and pressure. Energy J. 2023, 282, 128907. [Google Scholar]
- Shintaro, T.; Kenji, N.; Masakuni, Y.; Hiroto, C.; Keiko, Y.; Ryu, O. Fuel cell system for Honda CLARITY fuel cell. eTransportation 2020, 3, 100046. [Google Scholar]
- Carton, J.G.; Olabi, A.G. Wind/hydrogen hybrid systems: Opportunity for Ireland’s wind resource to provide consistent sustainable energy supply. Energy J. 2010, 35, 4536–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, D.; Osman, K. Comparative evaluation of different power management strategies of a stand-alone PV/Wind/PEMFC hybrid power system. Int. J. Elec Power 2012, 34, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bizon, N.; Mihai, O.; Mircea, R. Efficient energy control strategies for a standalone Renewable/Fuel Cell Hybrid Power Source. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.G.; Kim, L.; Sung, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Chung, J.S. Degradation mechanism of electrocatalyst during long-term operation of PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 8974–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Cai, S.; Tu, Z. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) operation in high current density (HCD): Problem, progress and perspective. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 307, 118348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Jonathan, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Wu, S.; Walter, M. A review of PEM fuel cell durability: Degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.O.; Oladeji, O.I.; El, M.B.; Paul, C.U.; Wilfred, E.; Abdelbaki, B.; Aboubakr, M.A. Platinum degradation mechanisms in proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) system: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 15850–15865. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Tu, Z. Comparison of the performance and degradation mechanism of PEMFC with Pt/C and Pt black catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 5418–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanny, C.; Stephane, R.; Frederic, J.; Dodelet, J.P. Increasing the activity of Fe/N/C catalysts in PEM fuel cell cathodes using carbon blacks with a high-disordered carbon content. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6881–6889. [Google Scholar]
- Dionysios, S.K.; Kostantinos, I.D.; Petros, M.S.; Georgia, S.; Bruno, G.P.; Christos, A. Sonoelectrochemical one-pot synthesis of Pt–Carbon black nanocomposite PEMFC electrocatalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem 2017, 35, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Carbon corrosion mechanism and mitigation strategies in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC): A review. J. Power Sources 2021, 488, 229434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexey, L.; Andrey, K.; Andrey, S.; Ivan, L.; Rustam, B. Investigation of PEM Fuel Cell Characteristics in Steady and Dynamic Operation Modes. Energies 2022, 15, 6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, K.M.; Praveenkumar, T.; Ram, K.; Mohanraj, T.; Arulmozhivarman, J.C.; Ilhami, C. Carbon-based materials in proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A critical review on performance and application. Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 885. [Google Scholar]
- Kregar, A.; Kravos, A.; Katrasnik, T. Methodology for Evaluation of Contributions of Ostwald Ripening and Particle Agglomeration to Growth of Catalyst Particles in PEM Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2020, 20, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, L.; Zeng, G.; Li, M.; Huang, H. Stabilizing Pt-Based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: Fundamental Understanding and Design Strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Shao, Y.; Sun, J.; Yin, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Advanced Catalyst Supports for PEM Fuel Cell Cathodes. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbhi, S.; Bruno, G.P. Support Materials for PEMFC and DMFC Electrocatalysts—A Review. J. Power Sources 2012, 208, 96–119. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Choi, S.R.; Jang, J.; Park, G.-G.; Yu, S.H.; Park, J.-Y. Tolerance to carbon corrosion of various carbon structures as catalyst supports for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 12781–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hwang, S.-M.; Park, G.-G.; Park, S.-H.; Park, E.-D.; Yim, S.-D. Variations in performance-degradation behavior of Pt/CNF and Pt/C MEAs for the same degree of carbon corrosion. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Lim, S.; Hong, S.-H.; Qiao, W.; Darrell, D.W.; Mochida, I.; An, B.; Yokogawa, K. A Conceptual Model for the Structure of Catalytically Grown Carbon Nanofibers. Carbon 2005, 43, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Lim, S.; Hong, S.-H.; Qiao, W.; Mochida, I.; An, B.; Yokogawa, K. Carbon Nano-Rod as a Structural Unit of Carbon Nanofibers. Carbon 2004, 42, 3087–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.M.; Borghei, M.; Lund, P.; Yli-Rantala, E.; Pasanen, A.; Kauppinen, E.; Ruiz, V.; Kauranen, P.; Skou, E.M. Durability of carbon nanofiber (CNF) & carbon nanotube (CNT) as catalyst support for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Solid State Ionics 2013, 231, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-S.; Wang, X.-Z.; Fu, R.; Yang, D.-J.; Li, P.; Lv, H.; Ma, J.-X. Microstructure effect of carbon nanofibers on Pt/CNFs electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarar Kaplan, B.; Haghmoradi, N.; Jamil, E.; Merino, C.; Alkan Gürsel, S. Platinum nanoparticles decorated carbon nanofiber hybrids as highly active electrocatalysts for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 8351–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, T.; Kaneko, K.; Alexander, V.N.; James, P.O.; Francisco, R.-R.; Jean, R.; Kenneth, S.W.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2024, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M.P.; Poddubnaya, O.I.; Barbara, G.; Magdalena, S. Comparison of heterogeneous pore models QSDFT and 2D-NLDFT and computer programs ASiQwin and SAIEUS for calculation of pore size distribution. Adsorption 2016, 22, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.-Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Martin, J.; Wang, H. A Review of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Durability Test Protocols. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9107–9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, E.B.; Trevor, J.D.; Gregory, G.W.; Richard, G.C. Electrocatalysis at Graphite and Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrodes: Edge-Plane Sites and Tube Ends are the Reactive Sites. Chem. Commun. 2005, 7, 829–841. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.; Liang, X.; Huawei, C.; Zhengkai, T.; Siew, H.C. Partial Flooding and Its Effect on the Performance of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 207, 112537. [Google Scholar]

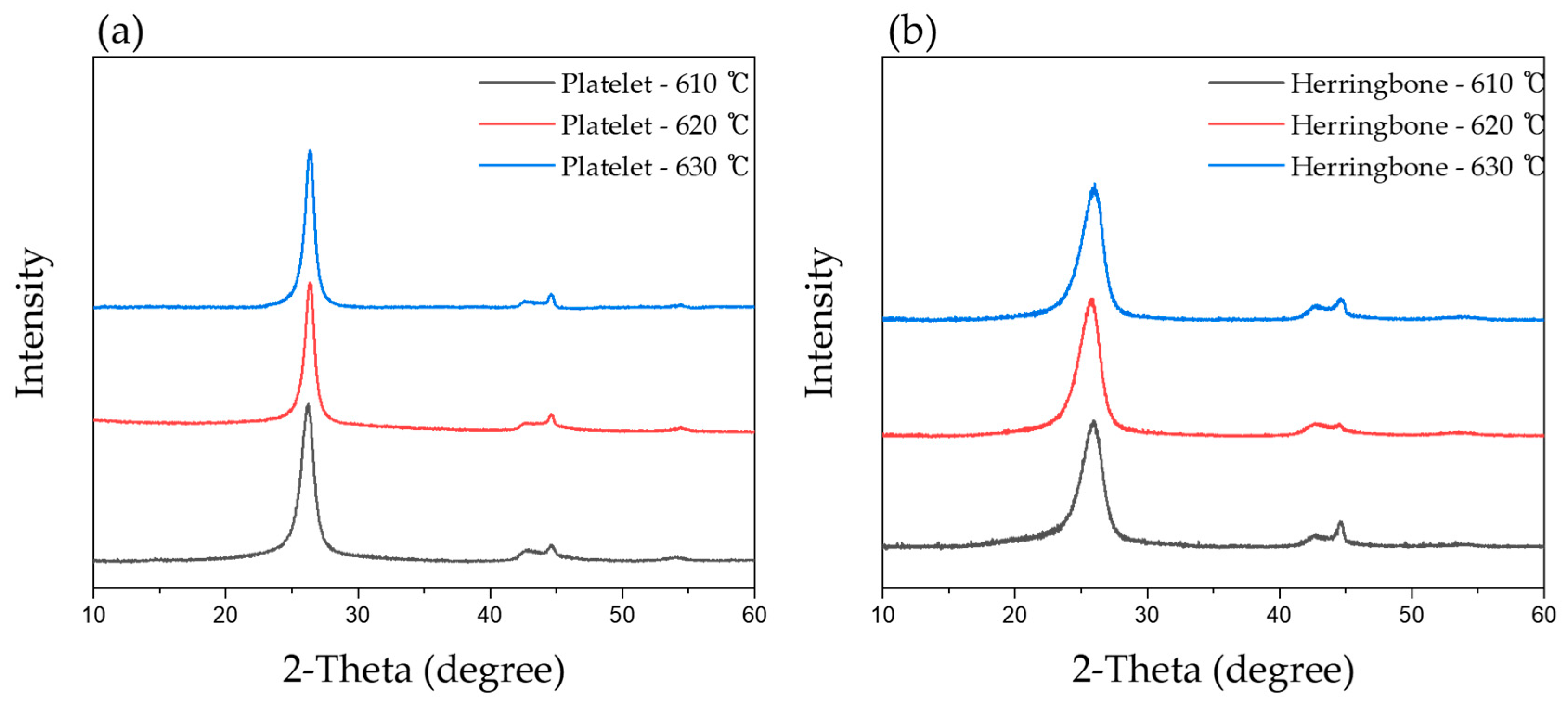

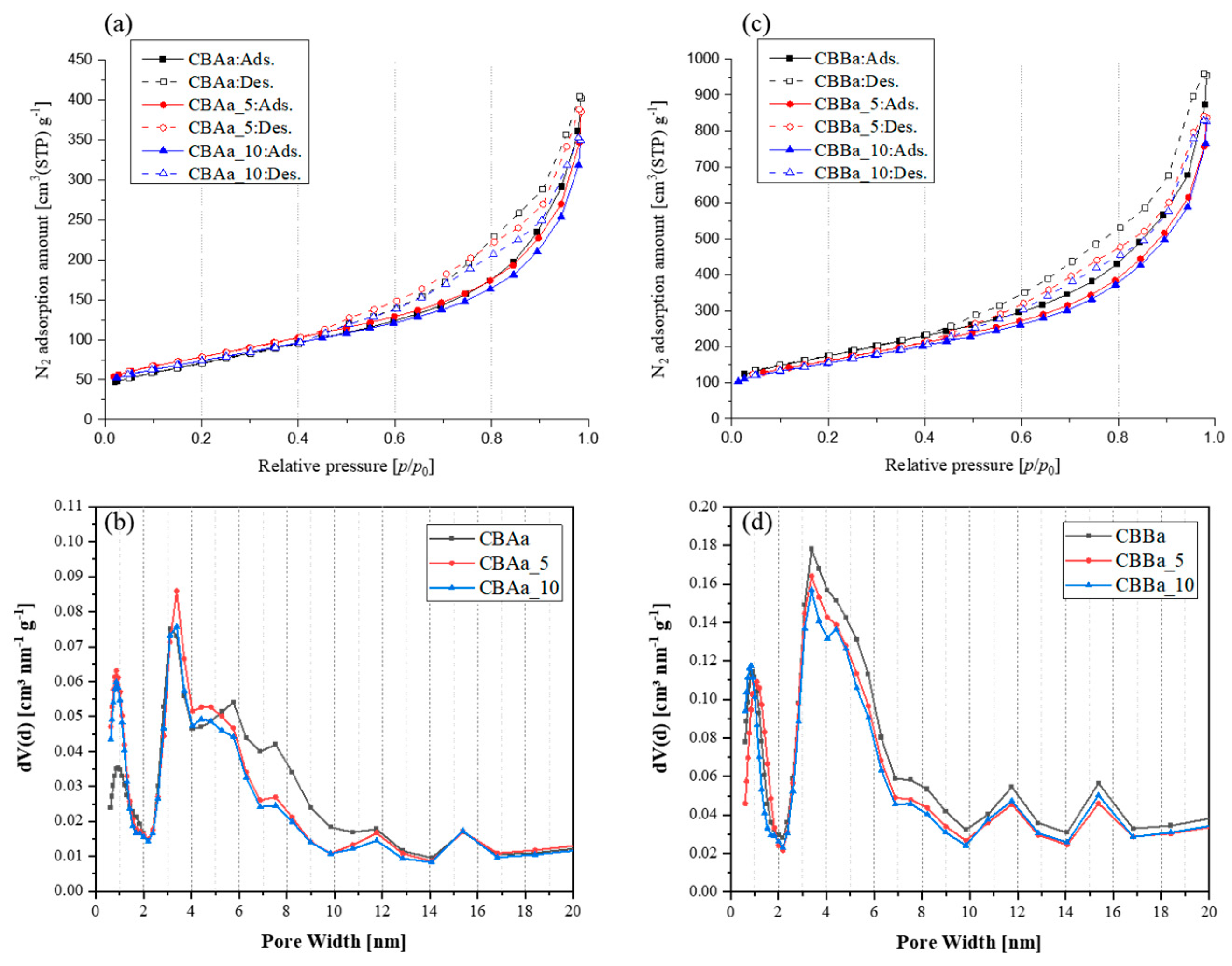



| Carbon Nano Fiber Type | CVD Reactant Gases (Total 200 mL/min) | Temp. (°C) | Time (Min) | Yield *1 | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Diameter *2 (nm) | XRD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d002 (nm) | Lc(002) (nm) | |||||||
| Platelet | CO/H2 = 4/1 (Vol/Vol) | 610 | 240 | 61.2 | 76 | 54–140 | 0.341 | 7.2 |
| 620 | 240 | 62.2 | 104 | 53–214 | 0.339 | 10.1 | ||
| 630 | 240 | 62.1 | 68 | 52–108 | 0.338 | 8.4 | ||
| Herringbone | C2H4/H2 = 1/1 (Vol/Vol) | 610 | 60 | 27.1 | 39 | 78–134 | 0.340 | 4.4 |
| 620 | 60 | 35.0 | 38 | 43–125 | 0.340 | 4.8 | ||
| 630 | 60 | 30.4 | 33 | 109–155 | 0.342 | 4.2 | ||
| Sample | Pore Structural Parameters | XRD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Mesopore Volume (cm3/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Mesopore Ratio (%) | Lc (nm) | d002 (nm) | |
| CBAa | 295.54 | 0.5437 | 0.5919 | 91.86 | 3.06 | 0.3544 |
| CBAa_5 | 281.02 | 0.5231 | 0.5887 | 88.86 | 3.35 | 0.3541 |
| CBAa_10 | 264.16 | 0.4869 | 0.5412 | 89.97 | 3.48 | 0.3500 |
| CBBa | 628.59 | 1.3750 | 1.4784 | 93.01 | 2.99 | 0.3532 |
| CBBa_5 | 580.04 | 1.2129 | 1.2985 | 93.41 | 3.26 | 0.3501 |
| CBBa_10 | 554.65 | 1.1883 | 1.2797 | 92.86 | 3.57 | 0.3488 |
| V@0.16 A/cm2 | V@0.4 A/cm2 | V@1.0 A/cm2 | V@1.6 A/cm2 | Degradation Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBAa | 0.820 | 0.766 | 0.673 | 0.572 | Complete degradation |
| CBAa After AST | 0.670 | 0.475 | - | - | |
| CBAa_5 | 0.811 | 0.762 | 0.684 | 0.599 | Complete degradation |
| CBAa_5 After AST | 0.806 | 0.751 | 0.654 | - | |
| CBAa_10 | 0.809 | 0.758 | 0.678 | 0.595 | 6.22 |
| CBAa_10 After AST | 0.812 | 0.759 | 0.670 | 0.558 | |
| 58CBBa | 0.775 | 0.738 | 0.673 | 0.598 | Complete degradation |
| CBBa After AST | 0.657 | 0.395 | - | - | |
| CBBa_5 | 0.804 | 0.749 | 0.667 | 0.589 | Complete degradation |
| CBBa_5 After AST | 0.758 | 0.653 | 0.490 | - | |
| CBBa_10 | 0.814 | 0.761 | 0.680 | 0.601 | 21.80 |
| CBBa_10 After AST | 0.808 | 0.708 | 0.590 | 0.470 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, M.; Yi, H.; Han, J.; Lee, J.B.; Yoon, S.-H.; Park, J.-I. Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Carbon Black Support for Enhancing the Durability of Catalysts Used in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Against Carbon Corrosion. Membranes 2025, 15, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15010003
Sung M, Yi H, Han J, Lee JB, Yoon S-H, Park J-I. Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Carbon Black Support for Enhancing the Durability of Catalysts Used in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Against Carbon Corrosion. Membranes. 2025; 15(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Minki, Hyeonseok Yi, Jimin Han, Jong Beom Lee, Seong-Ho Yoon, and Joo-Il Park. 2025. "Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Carbon Black Support for Enhancing the Durability of Catalysts Used in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Against Carbon Corrosion" Membranes 15, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15010003
APA StyleSung, M., Yi, H., Han, J., Lee, J. B., Yoon, S.-H., & Park, J.-I. (2025). Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Carbon Black Support for Enhancing the Durability of Catalysts Used in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Against Carbon Corrosion. Membranes, 15(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15010003







