Research on Reverse Osmosis (RO)/Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes Based on Thin Film Composite (TFC) Structures: Mechanism, Recent Progress and Application
Abstract
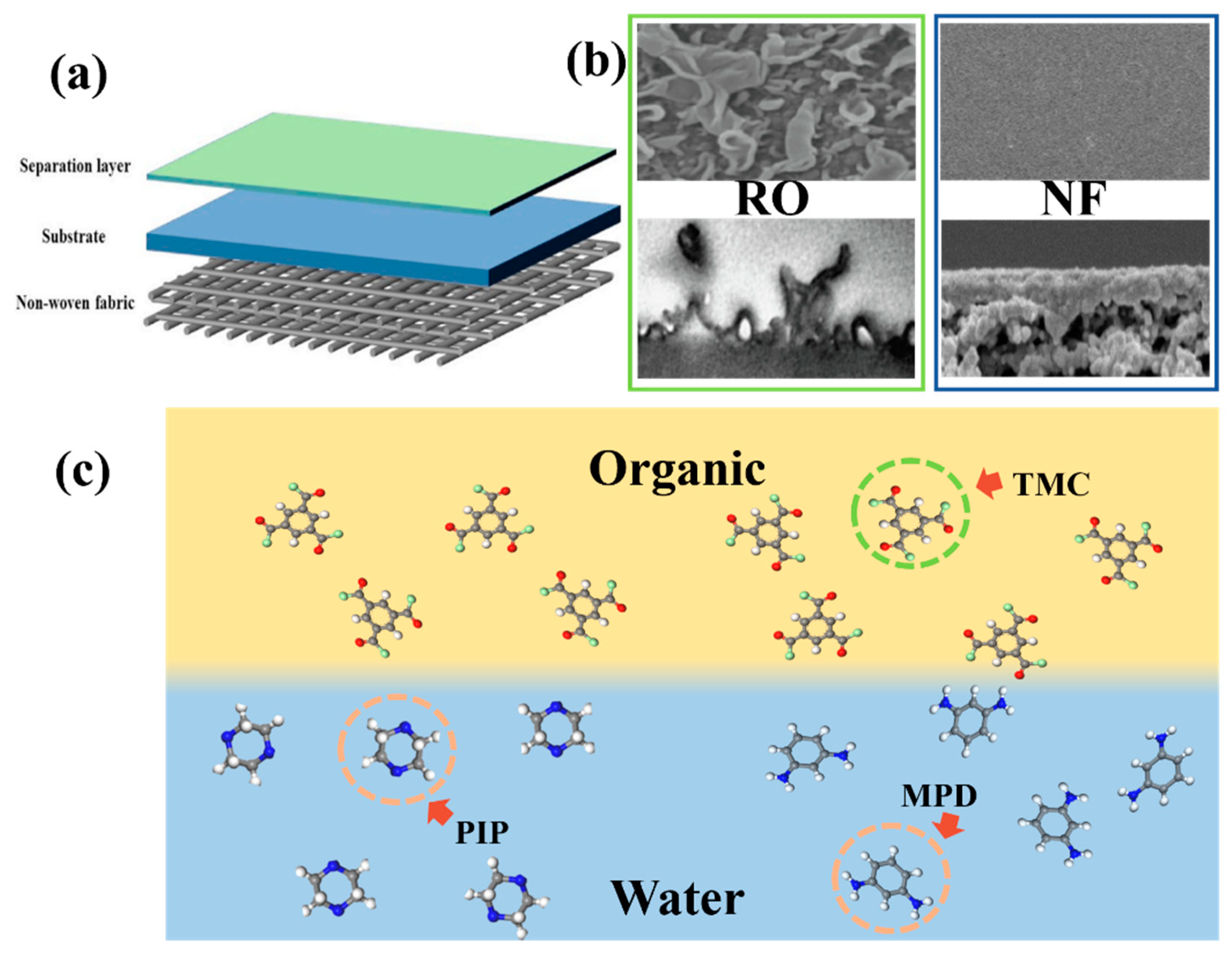
1. Introduction
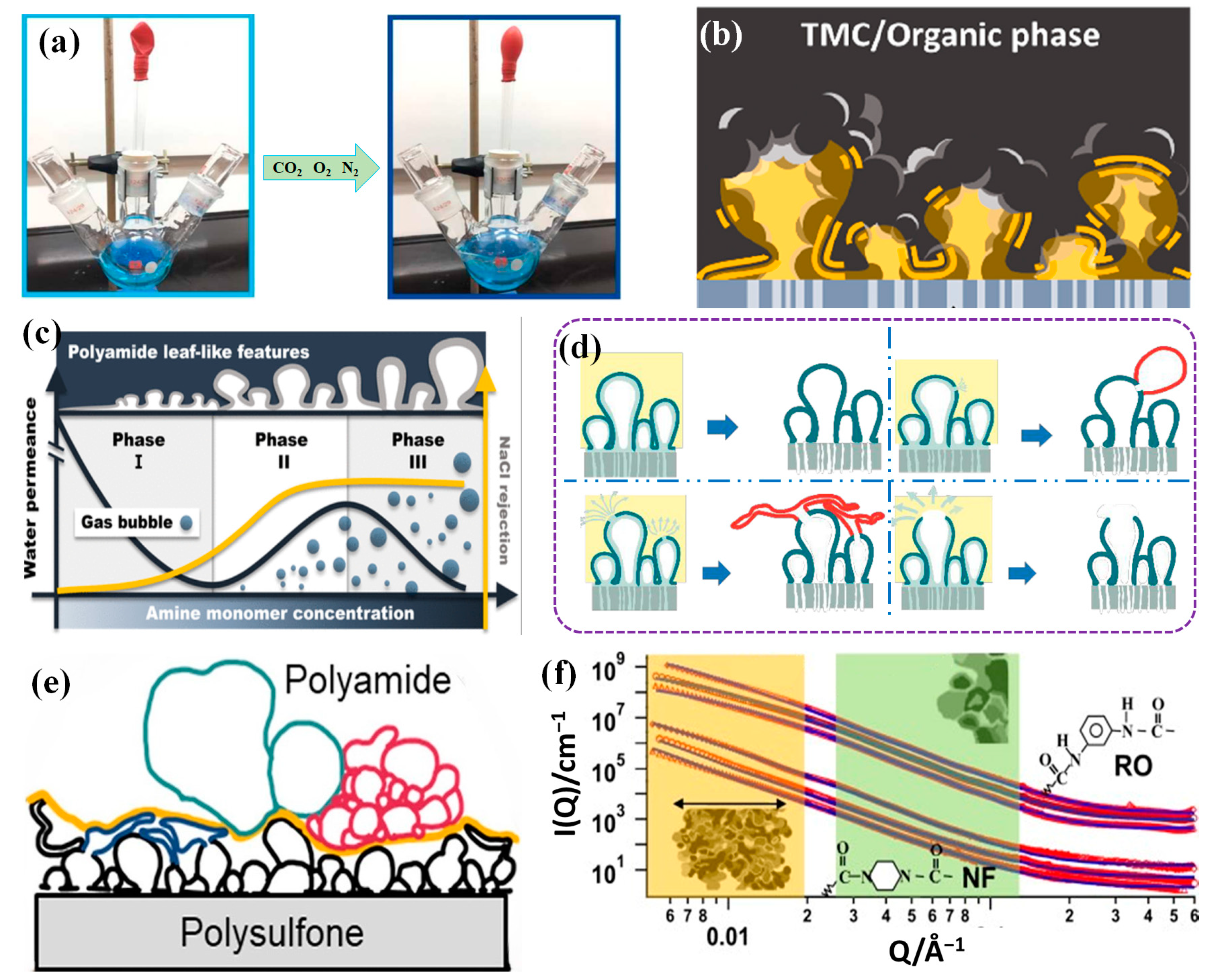
2. Mechanism of PA Layer Formation
3. Modification Methods and Latest Research Progress
3.1. Application of New Monomers
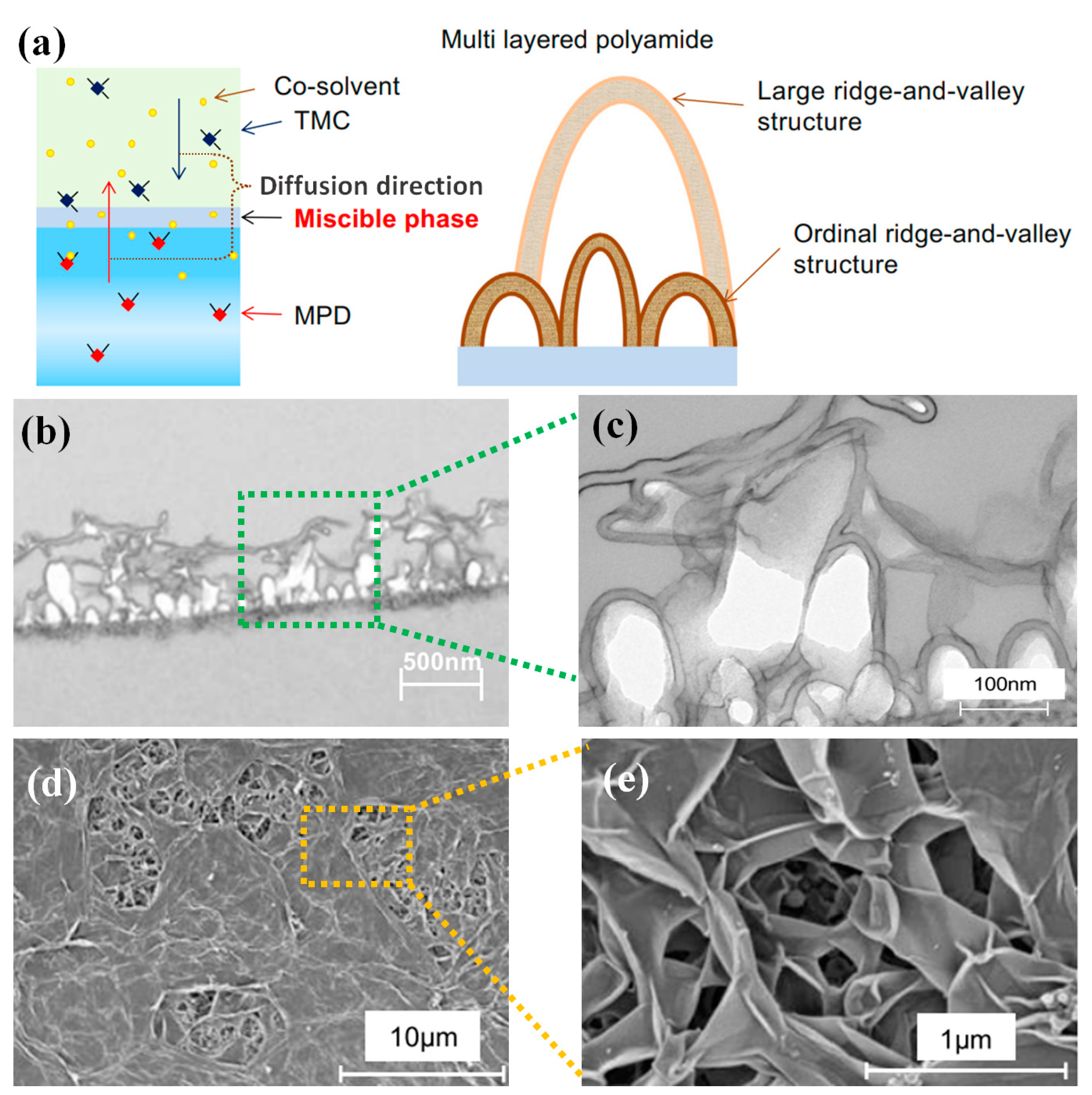
3.2. Modification of Two-Phase Solution
3.3. New Modification Methods
4. Application
4.1. Applications in Different Fields
4.1.1. Treatment of Industrial Wastewater
4.1.2. Desalination
4.1.3. Micropollutant
4.1.4. Resource Recovery
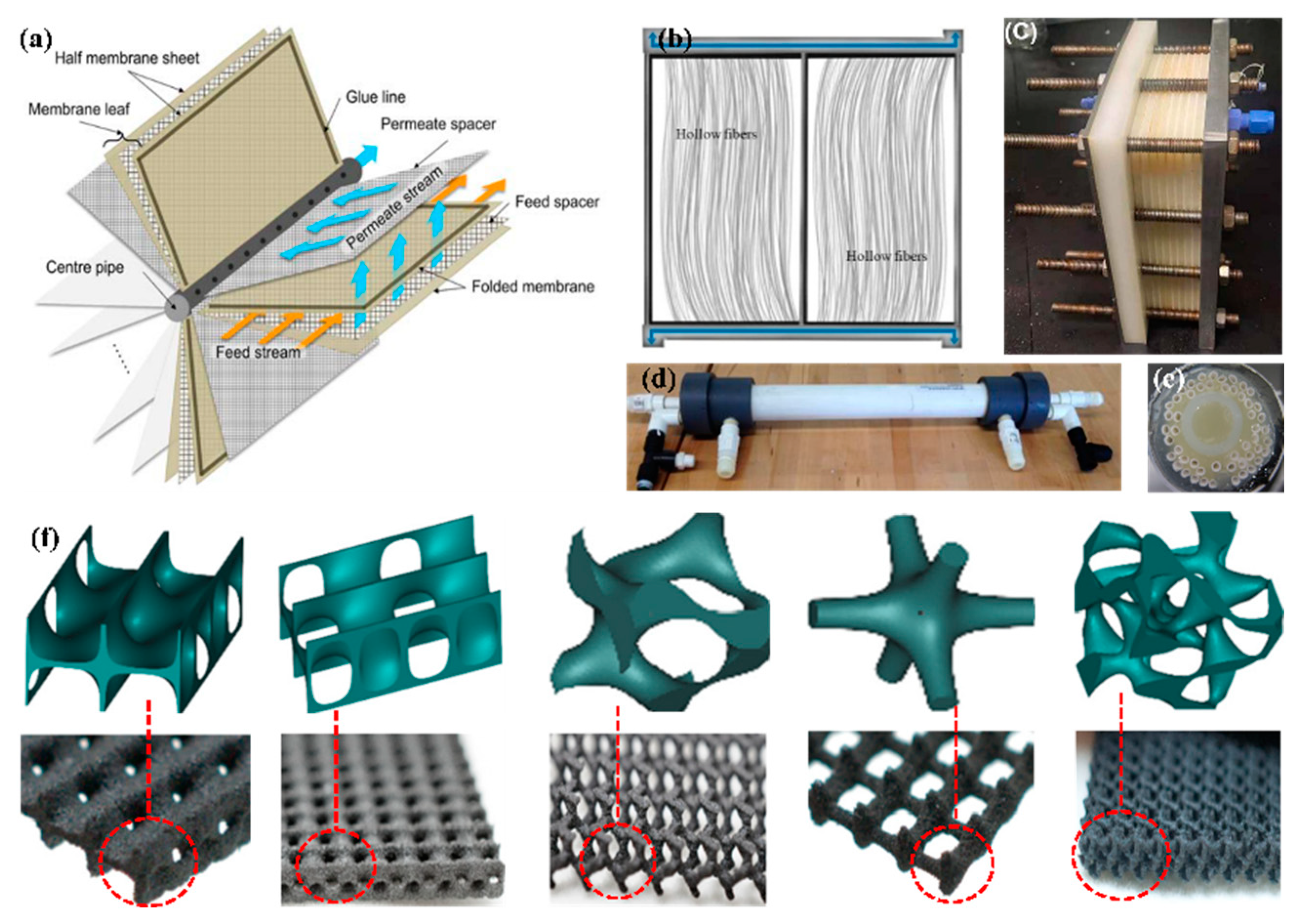
4.2. Membranes Module
4.3. Membrane Fouling and Damage
4.3.1. Membrane Fouling
4.3.2. Membranes Damage
5. Conclusions
6. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, D.; Yao, Z.; Jiao, L.; Waheed, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L. Separation mechanism, selectivity enhancement strategies and advanced materials for mono-/multivalent ion-selective nanofiltration membrane. Adv. Membr. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, J.H.; Chae, H.-R.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K.; Won, Y.-J.; Kim, I.-C. A facile route to enhance the water flux of a thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane: Incorporating thickness-controlled graphene oxide into a highly porous support layer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22053–22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.; Ismail, A.; Misdan, N.; Kassim, M. A recent progress in thin film composite membrane: A review. Desalination 2012, 287, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, P.-F.; Li, X.; Gan, B.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Park, H.-D.; Tang, C.Y. A Critical Review on Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes with Interlayered Structure: Mechanisms, Recent Developments, and Environmental Applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15563–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Karki, S.; Ingole, P.G. Current advances and opportunities in the development of nanofiltration (NF) membranes in the area of wastewater treatment, water desalination, biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tong, T.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Reid, E.M.; Chen, Y. Differentiating Solutes with Precise Nanofiltration for Next Generation Environmental Separations: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, J.; Vatanpour, V.; Khoshnam, M.; Zargar, M. Recent advancements in the application of new monomers and membrane modification techniques for the fabrication of thin film composite membranes: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 166, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Lai, G.S.; Zhao, Y.; Torres, J.; Wang, R. Unraveling the role of support membrane chemistry and pore properties on the formation of thin-film composite polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. A support surface pore structure re-construction method to enhance the flux of TFC RO membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.E.; Yao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. Dissecting the Role of Substrate on the Morphology and Separation Properties of Thin Film Composite Polyamide Membranes: Seeing Is Believing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6978–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.D.; Yan, H.; Cahill, D.G.; Coronell, O.; Mariñas, B.J. Growth dynamics of interfacially polymerized polyamide layers by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and Rutherford backscattering spectrometry. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lopez, R.; Ramon, G.Z.; Coronell, O. Investigating the void structure of the polyamide active layers of thin-film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, F.; Wang, J. Regulating the interfacial polymerization process toward high-performance polyamide thin-film composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Zhou, S.; Long, L.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Vacuum-assisted MPD loading toward promoted nanoscale structure and enhanced water permeance of polyamide RO membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, M.Q.; Lau, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. Greener synthesis of functionalized-GO incorporated TFN NF membrane for potential recovery of saline water from salt/dye mixed solution. Desalination 2022, 523, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, S.; Zhao, X. The influence of RO membrane surface properties on surfactant fouling in radioactive wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; Yong, N.G.H.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Bi, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, D. Low feed water temperature effects on RO membrane fouling development for municipal wastewater reclamation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M. The relationship between polymer molecular structure of RO membrane skin layers and their RO performances. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 123, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.E.; Yao, Z.; Liu, X.; Deng, B.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. Tailoring Polyamide Rejection Layer with Aqueous Carbonate Chemistry for Enhanced Membrane Separation: Mechanistic Insights, Chemistry-Structure-Property Relationship, and Environmental Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9764–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Guo, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Tuning roughness features of thin film composite polyamide membranes for simultaneously enhanced permeability, selectivity and anti-fouling performance. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.E.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, L.; Guo, H.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Does interfacial vaporization of organic solvent affect the structure and separation properties of polyamide RO membranes? J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.E.; Yang, Z.; Long, L.; Zhou, S.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. A critical review on porous substrates of TFC polyamide membranes: Mechanisms, membrane performances, and future perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gan, B.; Qi, S.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Intrinsic Nanoscale Structure of Thin Film Composite Polyamide Membranes: Connectivity, Defects, and Structure–Property Correlation, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3559–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-Q.; Tang, Y.-J.; Xu, Z.-L. Can the NF membrane directly obtained by the interfacial polymerization of MPD and TMC? J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 656, 120618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, K.-R.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Elimelech, M.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometre pores for sub-1 Å precision separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzebyk, K.; Armstrong, M.D.; Coronell, O. Accessing greater thickness and new morphology features in polyamide active layers of thin-film composite membranes by reducing restrictions in amine monomer supply. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 644, 120112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Ray, P.; Xie, Z.; Hoang, M. Synchrotron SAXS to probe cross-linked network of polyamide ‘reverse osmosis’ and ‘nanofiltration’ membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, J.; Huang, S.; Agostino, A.; Kuchel, R.P.; Leslie, G.; Tang, C.Y.; Fane, A.G. Kinetics of support-free interfacial polymerization polyamide films by in-situ absorbance spectroscopy. Desalination 2023, 549, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowbahar, A.; Mansard, V.; Mecca, J.M.; Paul, M.; Arrowood, T.; Squires, T.M. Measuring Interfacial Polymerization Kinetics Using Microfluidic Interferometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3173–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, J.M.; Xie, X.; Murphy, C.J.; Cahill, D.G. Density; Constants, E. and Thermal Conductivity of Interfacially Polymerized Polyamide Films for Reverse Osmosis Membranes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5008–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikheibari, S.; Lei, W.; Dumée, L.F.; Barlow, A.J.; Baskaran, K. Novel thin film nanocomposite membranes decorated with few-layered boron nitride nanosheets for simultaneously enhanced water flux and organic fouling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, B.; Thundat, T.; Fleck, B.A.; Sadrzadeh, M. A Novel Approach Toward Fabrication of High Performance Thin Film Composite Polyamide Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Shi, Y.; Sun, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Thin-film composite membranes formed by interfacial polymerization with natural material sericin and trimesoyl chloride for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, R.; Yang, F.; Kang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Probing influences of support layer on the morphology of polyamide selective layer of thin film composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Niu, Q.J.; Hou, Y.; Sun, H. Effect of interfacial polymerization monomer design on the performance and structure of thin film composite nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, G.; Yu, H.; Du, W.; Shi, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Thin-film composite nanofiltration membrane based on polyurea for extreme pH condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, G.; Liu, Y. The morphology of fully-aromatic polyamide separation layer and its relationship with separation performance of TFC membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-J.; Shen, Q.; Luo, L.-H.; Tong, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Zhang, H.-Z. Surfactants attached thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration (NF) membrane via intermolecular interaction for heavy metals removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 642, 119930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, N.; Hu, P.; Chen, K.; Jiang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; You, M.; et al. Aliphatic polyamide nanofilm with ordered nanostripe, synergistic pore size and charge density for the enhancement of cation sieving. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.Q. An acid resistant nanofiltration membrane prepared from a precursor of poly(s-triazine-amine) by interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.; Sanchuan, Y.; Meihong, L.; Congjie, G. Polyamide thin film composite membrane prepared from m-phenylenediamine and m-phenylenediamine-5-sulfonic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, P.R.; Mohan, D.J.; Reddy, A.V.R. Preparation, characterization and chlorine stability of aromatic–cycloaliphatic polyamide thin film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dong, R.; Evans, A.M.; Biere, N.; Ebrahim, M.A.; Li, S.; Anselmetti, D.; Dichtel, W.R.; Livingston, A.G. Aligned macrocycle pores in ultrathin films for accurate molecular sieving. Nature 2022, 609, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Study on a novel polyamide-urea reverse osmosis composite membrane (ICIC–MPD) I. Preparation and characterization of ICIC–MPD membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Preparation and characterization of polyamide-urethane thin-film composite membranes. Desalination 2005, 180, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, G. Polyamide thin film composite membranes prepared from 3,4′,5-biphenyl triacyl chloride, 3,3′,5,5′-biphenyl tetraacyl chloride and m-phenylenediamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S. Enhanced both water flux and salt rejection of reverse osmosis membrane through combining isophthaloyl dichloride with biphenyl tetraacyl chloride as organic phase monomer for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Dong, G.; Tian, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y. A critical review on polyamide and polyesteramide nanofiltration membranes: Emerging monomeric structures and interfacial polymerization strategies. Desalination 2024, 577, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Song, Q.; Jelfs, K.E.; Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Livingston, A.G. Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.H.H.; Anjum, D.H.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Nunes, S.P. Thin porphyrin composite membranes with enhanced organic solvent transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, L.F.; Huang, T.; Peinemann, K. Cyclodextrin Films with Fast Solvent Transport and Shape-Selective Permeability. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tian, L.; Hou, Y.; Niu, Q.J. Nanofiltration membranes with enhanced microporosity and inner-pore interconnectivity for water treatment: Excellent balance between permeability and selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ghanem, B.S.; Wang, Y.; Pacheco, F.; Ogieglo, W.; Vovusha, H.; Genduso, G.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Han, Y.; Pinnau, I. Finely Tuned Submicroporous Thin-Film Molecular Sieve Membranes for Highly Efficient Fluid Separations. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgojo, P.; Karan, S.; Wong, H.C.; Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Cabral, J.T.; Livingston, A.G. Ultrathin Polymer Films with Intrinsic Microporosity: Anomalous Solvent Permeation and High Flux Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4729–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, B.; Shao, R.; Min, C.; Xu, Z.; Deng, H. Extra-thin composite nanofiltration membranes tuned by γ-cyclodextrins containing amphipathic cavities for efficient separation of magnesium/lithium ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hu, L. Controlling structure and properties of polyamide nanofilms by varying amines diffusivity in organic phase. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.W.; Kwolek, S.L. Interfacial polycondensation. II. Fundamentals of polymer formation at liquid interfaces. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 531–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Cai, P.; Wen, Z. Fast Water Transport Through Sub-5 nm Polyamide Nanofilms: The New Upper-Bound of the Permeance-Selectivity Trade-Off in Nanofiltration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4948–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, Y.-R.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Demystifying viscous isoalkanes as the organic solvent in interfacial polymerization for manufacturing desalination membranes. Desalination 2023, 545, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kwon, S.J.; Kwon, H.; Shin, M.; Park, S.; Park, H.; Park, Y.; Nam, S.; Lee, J.-H. Aromatic solvent-assisted interfacial polymerization to prepare high performance thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes based on hydrophilic supports. Polymer 2018, 144, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X. Combining co-solvent-optimized interfacial polymerization and protective coating-controlled chlorination for highly permeable reverse osmosis membranes with high rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wang, R.; Bae, T.-H. A comprehensive understanding of co-solvent effects on interfacial polymerization: Interaction with trimesoyl chloride. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 583, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.-Y.; Jung, S.G.; Kim, S.H. Structure-Motion-Performance Relationship of Flux-Enhanced Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes Composed of Aromatic Polyamide Thin Films. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4334–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Wang, B.; An, L.; Xu, F.; Cao, Z.; Meng, J. Different roles of aqueous and organic additives in the morphology and performance of polyamide thin-film composite membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 165, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, G.S.; Wang, R. Investigation of aqueous and organic co-solvents roles in fabricating seawater reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 645, 120187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, B.; Soltannia, B.; Thundat, T.; Sadrzadeh, M. Synthesis of thin film composite polyamide membranes: Effect of monohydric and polyhydric alcohol additives in aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Kamada, T.; Ohara, T.; Shintani, T.; Tsuru, T. Controlled surface morphology of polyamide membranes via the addition of co-solvent for improved permeate flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-L.; Fu, P.; Lin, W.-T.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Luo, X.-W.; Yu, Y.-H.; Xu, Z.-K.; Wan, L.-S. High-performance thin-film composite (TFC) membranes with. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hobaib, A.S.; AL-Sheetan, K.M.; Shaik, M.R.; Al-Andis, N.M.; Al-Suhybani, M.S. Characterization and Evaluation of Reverse Osmosis Membranes Modified with Ag2O Nanoparticles to Improve Performance. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Xue, S.; Tang, Y.-J.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-L. Polyamide Membranes with Net-Like Nanostructures Induced by Different Charged MOFs for Elevated Nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Wang, R. The coming of age of water channels for separation membranes: From biological to biomimetic to synthetic. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4537–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. Artificial channels for confined mass transport at the sub-nanometre scale. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Hong, Z.; Xie, Q.; Lu, Y. Fabrication of pH-sensitive thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes with enhanced performance by incorporating amine-functionalized graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded Permeation of Water through Helium-Leak–Tight Graphene-Based Membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X. 1-methylimidazole as a novel additive for reverse osmosis membrane with high flux-rejection combinations and good stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, T.; Sasaki, S.; Kamada, T.; Shintani, T.; Ohara, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Nishida, K.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T. Multilayered polyamide membranes by spray-assisted 2-step interfacial polymerization for increased performance of trimesoyl chloride (TMC)/m-phenylenediamine (MPD)-derived polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F. Interfacial polymerized polyamide nanofiltration membrane by demulsification of hexane-in-water droplets through hydrophobic PTFE membrane: Membrane performance and formation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Long, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, Z. Distinct impact of substrate hydrophilicity on performance and structure of TFC NF and RO polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 662, 120966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Tang, S.; Feng, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, P.; Niu, Q.J. Nanofiltration membranes with enhanced performance by constructing an interlayer integrated with dextran nanoparticles and polyethyleneimine coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 654, 120537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets for Thin-Film Composite Membranes with Enhanced Permeability and Selectivity. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 9238–9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. A gelatin-zirconium phosphate nanoparticles composite interlayer for enhancing compaction resistance and antifouling performance of TFC NF membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 698, 122567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Chang, K.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Tang, H.; Li, B.; Chang, Z. Bubble-template-assisted synthesis of hollow fullerene-like MoS2 nanocages as a lithium ion battery anode material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gan, B.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y.; Gao, C. Confined nanobubbles shape the surface roughness structures of thin film composite polyamide desalination membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Karan, S.; Livingston, A.G. Water Transport through Ultrathin Polyamide Nanofilms Used for Reverse Osmosis. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Chung, T.-S. Ultrathin Polyamide Membranes Fabricated from Free-Standing Interfacial Polymerization: Synthesis, Modifications, and Post-treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Choi, W.; Nam, S.-E.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.-H. Fabrication of polyamide thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes via support-free interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, C.; Zhu, L. Tailoring ultrathin microporous polyamide films with rapid solvent transport by molecular layer-by-layer deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 628, 119249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lee, S.; Stafford, C.M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, W.; Kim, B.; Baek, K.; Chan, E.P.; Chung, J.Y.; Bang, J.; et al. Molecular Layer-by-Layer Assembled Thin-Film Composite Membranes for Water Desalination. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4778–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, A.; Sarkar, S.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. 1-Membranes for industrial wastewater recovery and reuse. In Resource Recovery in Industrial Waste Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E. Membrane technology for water production in agriculture: Desalination and wastewater reuse. Desalination 2015, 364, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aani, S.; Mustafa, T.N.; Hilal, N. Ultrafiltration membranes for wastewater and water process engineering: A comprehensive statistical review over the past decade. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Ng, C.Y.; Lim, Y.P.; Ng, G.H. Ultrafiltration in Food Processing Industry: Review on Application, Membrane Fouling, and Fouling Control. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.F.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Effects of polyaniline nanoparticles in polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes: Fouling behaviours by different types of foulant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3134–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wen, J.; Shi, L.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, Z. A top-down approach to estimate global RO desalination water production considering uncertainty. Desalination 2020, 488, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E. Membrane Engineering for Green Process Engineering. Engineering 2017, 3, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.S.; Lau, W.J.; Liang, Y.Y.; Yusof, N.; Ismail, A.F. Surface modification of PA layer of TFC membranes: Does it effective for performance Improvement? J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 102, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Lecithin decorated thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration membranes for enhanced sieving performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 677, 121632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo-Diaz, J.L.; Morelos-Gomez, A.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Matsumoto, A.; Ueno, Y.; Takeuchi, N.; Kitamura, K.; Miyakawa, H.; Tejima, S.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Antifouling performance of spiral wound type module made of carbon nanotubes/polyamide composite RO membrane for seawater desalination. Desalination 2022, 523, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Kurihara, M.; Wang, R. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: Current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutchkov, N. Considerations for selection of seawater filtration pretreatment system. Desalination 2010, 261, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, M.; Zhao, L.; He, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. Semi batch dual-pass nanofiltration as scaling-controlled pretreatment for seawater purification and concentration with high recovery rate. Desalination 2021, 506, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhari, R.; Bide, Y.; Hosseini, S.S.; Shokrollahzadeh, S. Modification of polyacrylonitrile TFC-FO membrane by biowaste-derived hydrophilic N-doped carbon quantum dots for enhanced water desalination performance. Desalination 2023, 565, 116888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Karki, S.; Gohain, M.B.; Ingole, P.G. Development of micropollutants removal process using thin-film nanocomposite membranes prepared by green new vapour-phase interfacial polymerization method. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryczkowska, B.; Przywara, L. Removal of microplastics from industrial wastewater utilizing an ultrafiltration composite membrane rGO/PAN application. DWT 2021, 214, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Gao, S.; Ruan, Y.; Qi, G.; Guo, K.; Zeng, J. Distribution and removal mechanism of microplastics in urban wastewater plants systems via different processes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Graham, N.J.D.; Jiang, L. Evaluation of a novel polyamide-polyethylenimine nanofiltration membrane for wastewater treatment: Removal of Cu2+ ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chang, H.; Gao, S.; Zhang, R. How to fabricate a negatively charged NF membrane for heavy metal removal via the interfacial polymerization between PIP and TMC? Desalination 2020, 491, 114499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiya, M.; Zhang, J.-C.; Wu, B.; Yin, M.-J.; An, Q.-F. Nanofiltration membranes for sustainable removal of heavy metal ions from polluted water: A review and future perspective. Desalination 2024, 578, 117441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Lau, S.K.; Yong, W.F. Recent advances of thin film composite nanofiltration membranes for Mg2+/Li+ separation. Adv. Membr. 2024, 4, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Elimelech, M. Toward Resource Recovery from Wastewater: Extraction of Phosphorus from Digested Sludge Using a Hybrid Forward Osmosis–Membrane Distillation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Li, S.; Yin, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, N. Lithium extraction from salt lake brines with high magnesium/lithium ratio: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ma, P.; Zhu, C.; He, Q.; Deng, X. Preliminary study on recovering lithium chloride from lithium-containing waters by nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avlonitis, S.A.; Pappas, M.; Moutesidis, K. A unified model for the detailed investigation of membrane modules and RO plants performance. Desalination 2007, 203, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.Y.; Davies, P.A. Concentration polarization model of spiral-wound membrane modules with application to batch-mode RO desalination of brackish water. Desalination 2015, 368, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Xu, X.Y.; Adjiman, C.S. A predictive model for spiral wound reverse osmosis membrane modules: The effect of winding geometry and accurate geometric details. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 96, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shirazi, M.M.A.; Nthunya, L.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Ismail, N.; Tavajohi, N.; Zaragoza, G.; Quist-Jensen, C.A. Progress in module design for membrane distillation. Desalination 2024, 581, 117584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bai, B.; He, R.; Song, J.; He, T. Lithium solvent extraction by a novel multiframe flat membrane contactor module. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 328, 125061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Novel designs for improving the performance of hollow fiber membrane distillation modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Li, L.; Obusckovic, G.; Chau, J.; Sirkar, K.K. Novel cylindrical cross-flow hollow fiber membrane module for direct contact membrane distillation-based desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Sreedhar, N.; Al-Ketan, O.; Rowshan, R.; Al-Rub, R.K.A.; Arafat, H. 3D printed triply periodic minimal surfaces as spacers for enhanced heat and mass transfer in membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 443, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, F.; Lin, G.; Tang, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y. The enhancement of separation performance of hollow fiber membrane modules: From the perspective of membranes and membrane modules structural optimization design. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 280, 119106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Martínez, J.; García-Payo, C.; Arribas, P.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Khayet, M. Recycled reverse osmosis membranes for forward osmosis technology. Desalination 2021, 519, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Steffes, J.; Huey, B.D.; McCutcheon, J.R. 3D printed polyamide membranes for desalination. Science 2018, 361, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Anvari, A.; Hoek, E.M.V.; McCutcheon, J.R. Advancements in conventional and 3D printed feed spacers in membrane modules. Desalination 2023, 556, 116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.V.; Charlton, A.J.; Li, Q.; Kim, Y.C.; Taylor, R.A.; Le-Clech, P.; Barber, T. Can 3D-printed spacers improve filtration at the microscale? Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, N.; Thomas, N.; Al-Ketan, O.; Rowshan, R.; Hernandez, H.; Al-Rub, R.K.A.; Arafat, H.A. 3D printed feed spacers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for flux enhancement and biofouling mitigation in RO and UF. Desalination 2018, 425, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Z.-X.; Chua, Y.T.; Ray, B.M.; Mattia, D.; Metcalfe, I.S.; Patterson, D.A. Perspective on 3D printing of separation membranes and comparison to related unconventional fabrication techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Y.; Karayel, E. D printing technology; methods; biomedical applications, future opportunities and trends. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1430–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Kallem, P.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Kang, S.; Choi, H. A New era of water treatment technologies: 3D printing for membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tan, W.S.; An, J.; Chua, C.K.; Tang, C.Y.; Fane, A.G.; Chong, T.H. The potential to enhance membrane module design with 3D printing technology. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, A.; Lerman, S.; Ramon, G.Z.; Dosoretz, C.G. Experimental characterization and numerical simulation of the anti-biofuling activity of nanosilver-modified feed spacers in membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamaraiselvan, C.; Carmiel, Y.; Eliad, G.; Sukenik, C.N.; Semiat, R.; Dosoretz, C.G. Modification of a polypropylene feed spacer with metal oxide-thin film by chemical bath deposition for biofouling control in membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Doan, H.; Lohi, A.; Cheng, C. Contaminated particle characteristics influence on membrane fouling. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Samieirad, S. Chemical cleaning of reverse osmosis membrane fouled by wastewater. Desalination 2010, 257, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogler, A.; Lin, S.; Bar-Zeev, E. Biofouling of membrane distillation, forward osmosis and pressure retarded osmosis: Principles, impacts and future directions. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-H.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Deshmukh, K.P.; Schäfer, A.I. Renewable energy powered membrane technology: Implications of adhesive interaction between membrane and organic matter on spontaneous osmotic backwash cleaning. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Wang, N.; Fang, X.; Cao, J.; Tao, M.; Cao, Z. Interfacial polymerization nanofiltration membrane with visible light photocatalytic self-cleaning performance by incorporation of CQD/TiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yan, L.; Tripp, M.W.; Kachel, S.R.; Chen, M.; Foster, A.S.; Koert, U.; Liljeroth, P.; Gottfried, J.M. Biphenylene network: A nonbenzenoid carbon allotrope. Science 2021, 372, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Meng, K.; Ming, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Rong, J.; Li, X. Computational simulation of self-cleaning carbon-based membranes with zeolite porous structure for desalination. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 109925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z. Photo-Fenton reaction derived self-cleaning nanofiltration membrane with MOFs coordinated biopolymers for efficient dye/salt separation. Desalination 2023, 553, 116459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Bruggen, B.V.D.; Zhang, Y. MOF laminates functionalized polyamide self-cleaning membrane for advanced loose nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-F.; Cai, Z.-B.; Shen, J.-N.; Wu, L.-X.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Gao, C.-J. Fabrication and characterization of a novel poly(amide-urethane@imide) TFC reverse osmosis membrane with chlorine-tolerant property. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolov, M.; Freger, V. Degradation of Polyamide Membranes Exposed to Chlorine: An Impedance Spectroscopy Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, R.; Gómez, V.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Chlorine-resistance of reverse osmosis (RO) polyamide membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inukai, S.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Ortiz-Medina, J.; Morelos-Gomez, A.; Takeuchi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Tanioka, A.; Araki, T.; Tejima, S.; Noguchi, T.; et al. High-performance multi-functional reverse osmosis membranes obtained by carbon nanotube·polyamide nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Hyeon, D.H.; Chun, J.H.; Chun, B.-H.; Kim, S.H. Nanocomposite poly(arylene ether sulfone) reverse osmosis membrane containing functional zeolite nanoparticles for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Q. Polyester Nanofiltration Membranes for Efficient Cations Separation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiba, K.; Nakai, S.; Ohno, M.; Nishijima, W.; Gotoh, T.; Iizawa, T. Deterioration Mechanism of a Tertiary Polyamide Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Hypochlorite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9109–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Q. Quaternization-spiro design of chlorine-resistant and high-permeance lithium separation membranes. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.; Hu, Z.; Xie, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Gong, C.; Wu, Y. Osmotic cleaning to control inorganic fouling of nanofiltration membrane for seawater desalination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalanta, F.; Handoko, D.T.; Hadiyanto, H.; Kusworo, T.D. Recent implementations of process intensification strategy in membrane-based technology: A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 202, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, J.M.; Suresh, A.K. Chlorine attack on reverse osmosis membranes: Mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Jia, C.; Sun, L.; Tong, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. Advances and promotion strategies of membrane-based methods for extracting lithium from brine. Desalination 2023, 566, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouzi, M.M.A.; Tang, D.Y.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.; Allouzi, S.M.A.; Show, P.L. Micro (nano) plastic pollution: The ecological influence on soil-plant system and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Name | Framework | Operating Condition | Performances | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amine monomer | m-Phenylenediamine (MPD) |  | 1.5 MPa, 25 °C 2000 ppm NaCl | 45–60 L/m2h 98.8% | [37] |
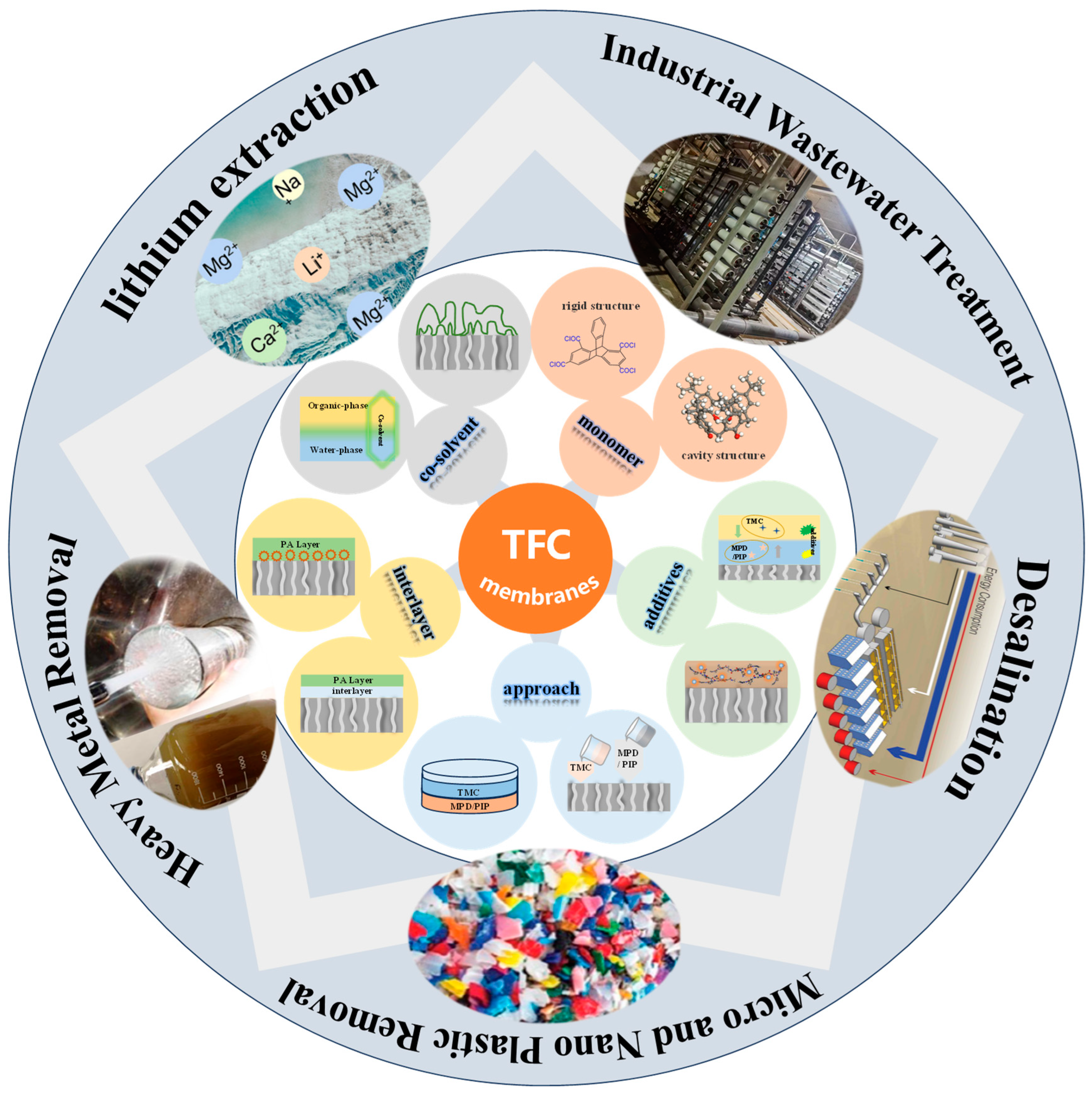
| piperazine (PIP) | 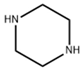 | 3.5 bar, 500 mg/L MgSO4 | 14.3 (L/m2hbar) (98.6%) | [38] | |
| Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (TAEA) | 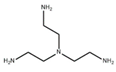 | 1.0 MPa, 25 ℃ 2000 ppm |
135.9 (L/m2h) SLi+/Mg2+ = 25.94 | [39] | |
| 1,3,5(Tri-piperazine)-triazine (TPT) |  | 100 psi, 25 ± 1 °C 2000 ppm MgSO4 |
8.68 (L/m2hbar) 98.6% | [40] | |
| m-phenylenediamine-5-sulfonic acid (SMPD) | 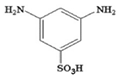 | 15 bar, 2000 ppm, NaCl |
30.0–55.7 (L/m2hbar) 47–94% | [41] | |
| 1,3cyclohexanebis(methylamine) (CHMA) | 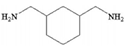 | 10 bar, 2000 ppm, NaCl |
56 (L/m2hbar) 77% | [42] | |
| Chloride monomer | Trimesoyl chloride (TMC) | 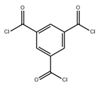 | 1.6 MPa, 25 °C 2000-ppm NaCl |
3.31 ± 0.10(L/m2hbar) 99.3 ± 0.1% | [34] |
| terephthaloyl chloride (TPC) | 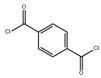 | 10 bar, 25 °C | 7.64 ± 0.1 (L/m2hbar) | [43] | |
| 5-isocyanato-isophthaloyl chloride (ICIC) | 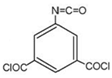 | 1.55 MPa, 25 °C NaCl | ---- | [44] | |
| 5-chloroformyloxy-isophthaloyl chloride (CFIC) | 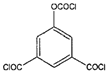 | 1–3 MPa 25 °C 500–8000 mg/L NaCl |
20 (L/m2h) 50.2% | [45] | |
| 3,4′,5-biphenyl triacyl chloride (BTRC) | 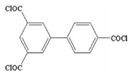 |
20 bar, 2000 ppm, NaCl |
33 (L/m2h) 98.9% | [46] | |
|
3,3′,5,5′-biphenyltetraacyl chloride (BTEC) |  |
55 bar, 32,800 ppm, NaCl |
30.2–48.3 (L/m2h) 99.3–99.7% | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Shao, W.; Wang, H. Research on Reverse Osmosis (RO)/Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes Based on Thin Film Composite (TFC) Structures: Mechanism, Recent Progress and Application. Membranes 2024, 14, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090190
Geng H, Zhang W, Zhao X, Shao W, Wang H. Research on Reverse Osmosis (RO)/Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes Based on Thin Film Composite (TFC) Structures: Mechanism, Recent Progress and Application. Membranes. 2024; 14(9):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090190
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Huibin, Weihao Zhang, Xiaoxu Zhao, Wei Shao, and Haitao Wang. 2024. "Research on Reverse Osmosis (RO)/Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes Based on Thin Film Composite (TFC) Structures: Mechanism, Recent Progress and Application" Membranes 14, no. 9: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090190
APA StyleGeng, H., Zhang, W., Zhao, X., Shao, W., & Wang, H. (2024). Research on Reverse Osmosis (RO)/Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes Based on Thin Film Composite (TFC) Structures: Mechanism, Recent Progress and Application. Membranes, 14(9), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090190






