High-Temperature Water Electrolysis Properties of Membrane Electrode Assemblies with Nafion and Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Membranes by Using a Decal Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
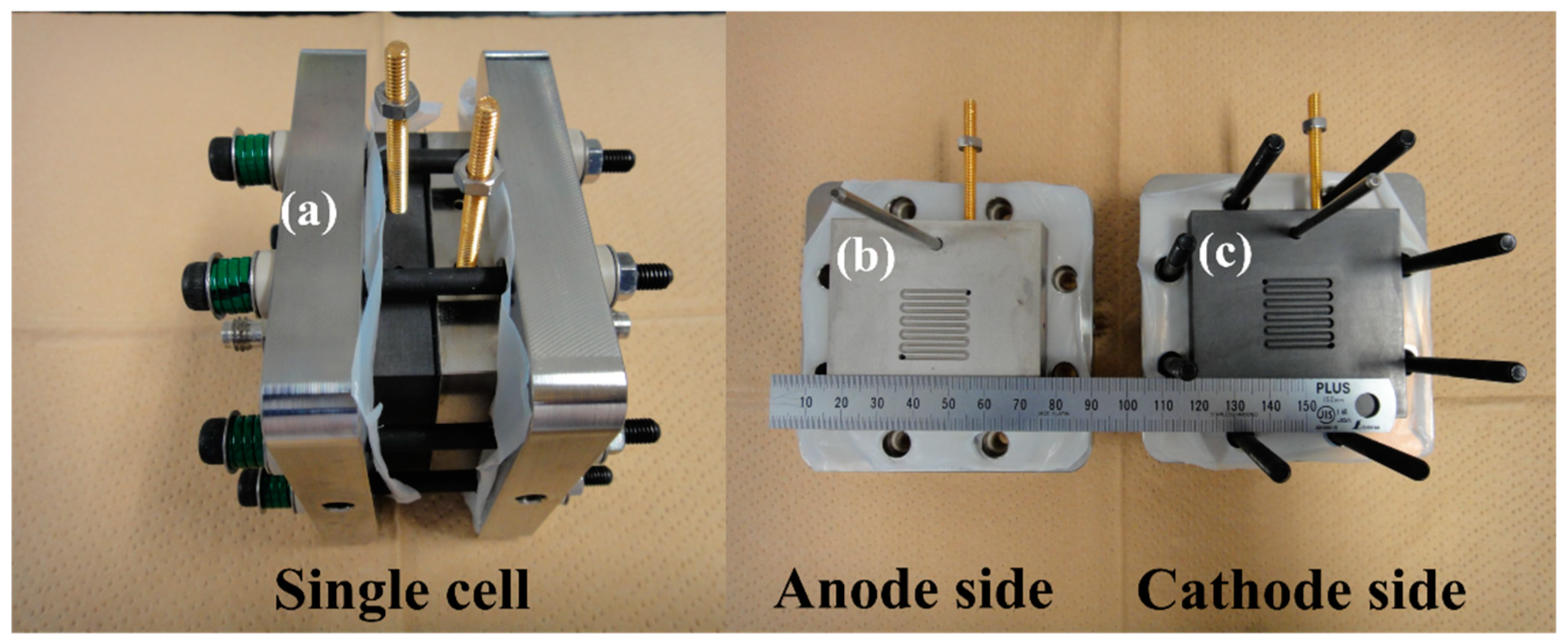
2. Experimental Section
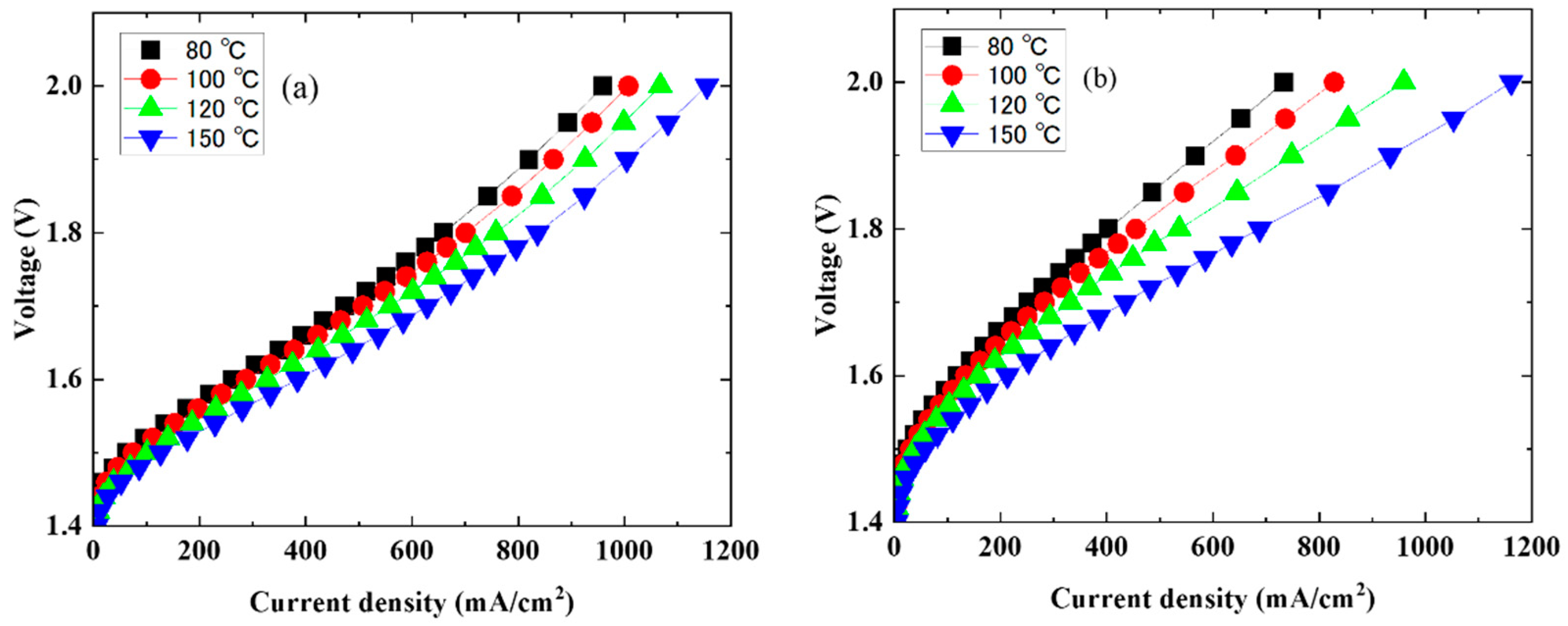
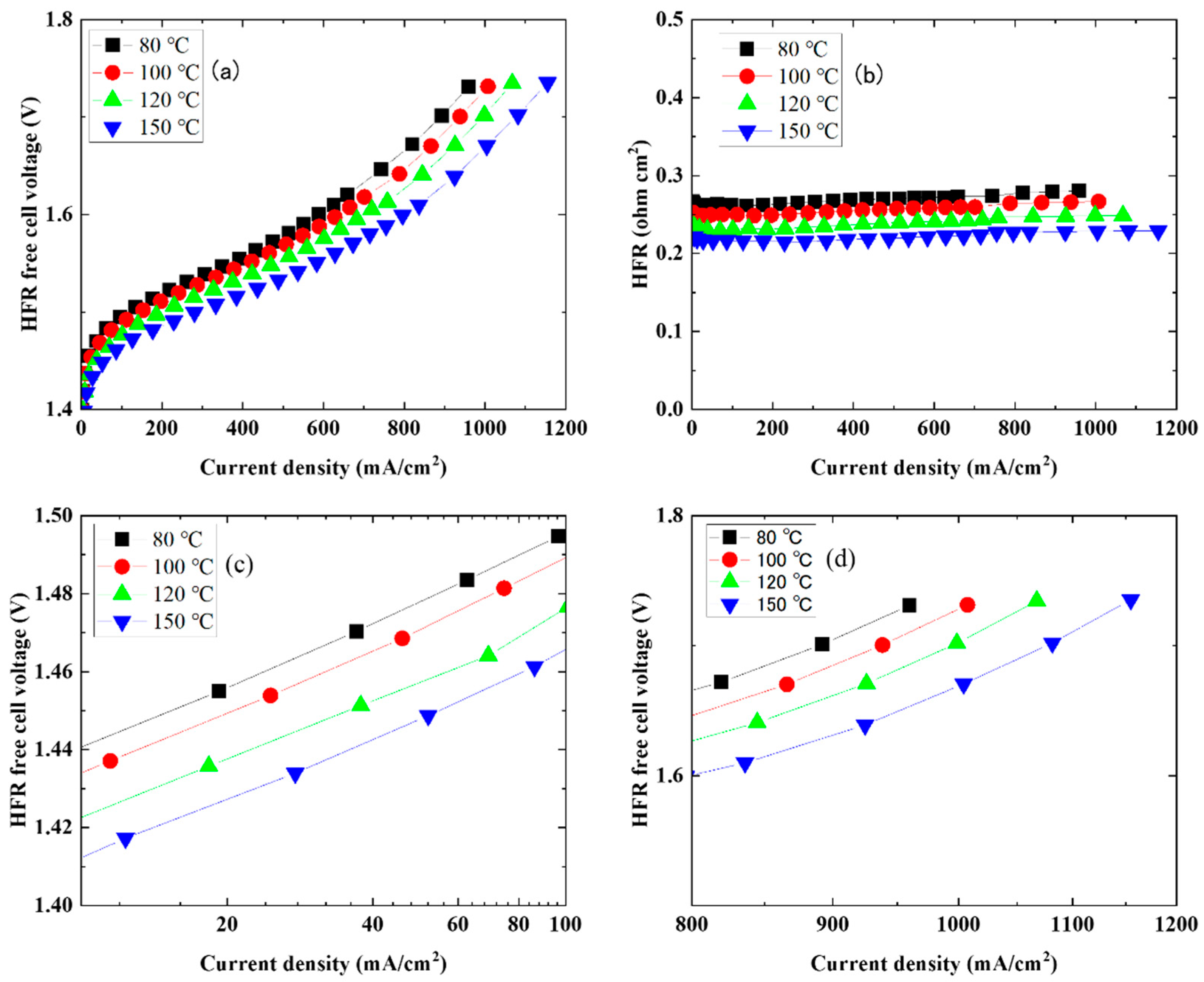
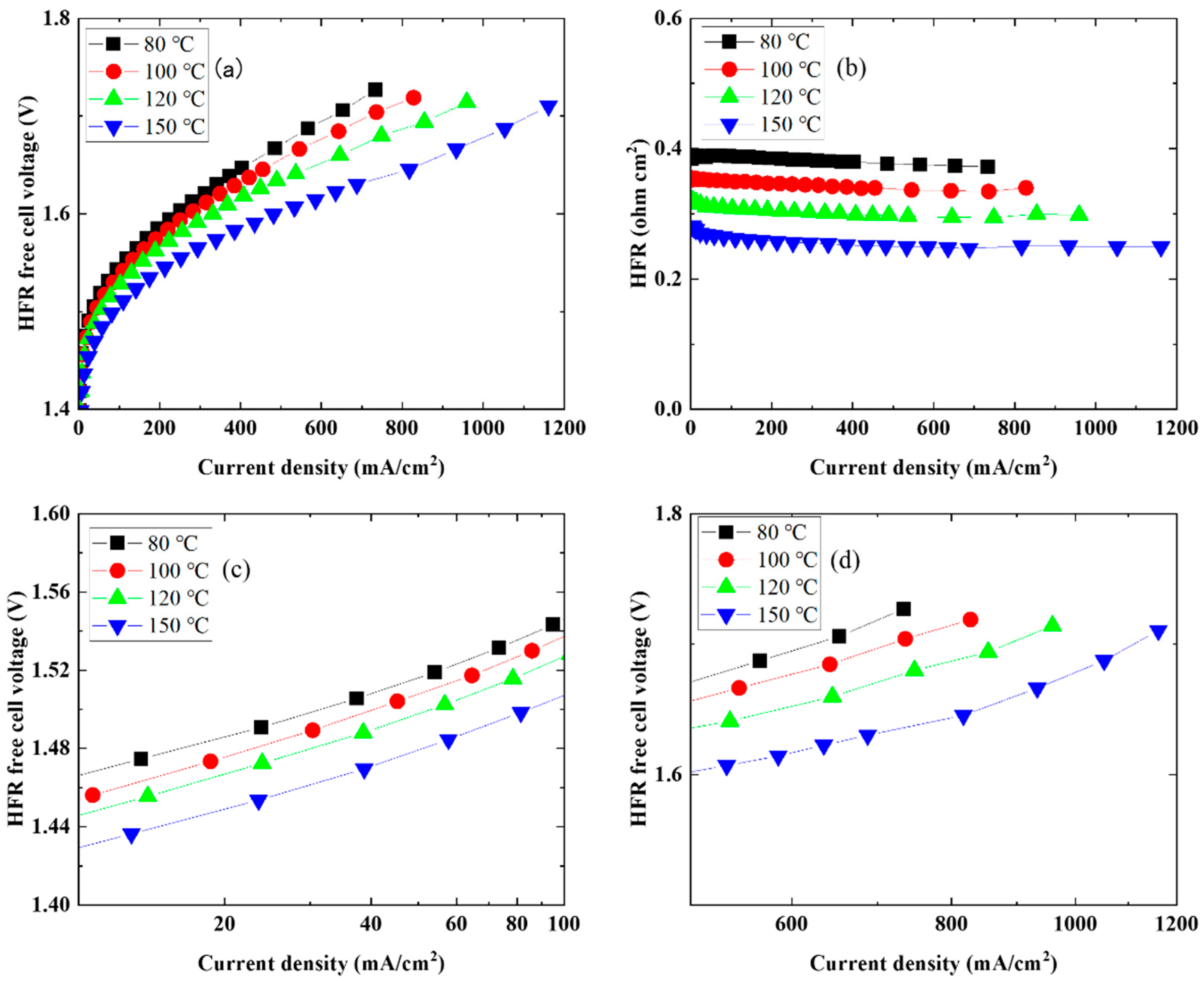
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NEDO Hydrogen Energy White Paper; NEDO: Tokyo, Japan, 2015.
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, V.; Shoji, R.; Matsuzaki, H.; Furube, A.; Lin, L.; Hisatomi, T.; Kaneko, M.; Yamashita, K.; Domen, K.; Seki, K. Unveiling charge dynamics of visible light absorbing oxysulfide for efficient overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7055–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Cobos, L.; Abril-Gonzalez, M.; Pinos-Velez, V. Production of hydrogen from lignocellulosic biomass: A review of technologies. Catalysts 2023, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, H.; El-Emam, R.S.; Horri, B.A. Thermochemical looping technologies for clean hydrogen production—Current status and recent advances. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135295–135308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Motz, A.R.; Bae, C.; Fujimoto, C.; Yang, G.; Zhang, F.-Y.; Ayers, K.E.; Kim, Y.S. Durability of anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3393–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Yu, L.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Water splitting by electrolysis at high current densities under 1.6 volts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostakola, M.F.; Ozcan, H.; El-Emam, R.S.; Horri, B.A. Recent advances in high-temperature steam electrolysis with solid oxide electrolyzes for green hydrogen production. Energies 2023, 16, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arges, C.G.; Wang, L.; Parrondo, J.; Ramani, V. Best practices for investigating anion exchange membrane suitability for alkaline electrochemical devices: Case study using quaternary ammonium poly(2,6-dimethyl 1,4-phenylene)oxide anion exchange membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F1258–F1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, J.; Torchio, C.; Versaci, D.; Dessantis, D.; Marchisio, A.; Caldera, F.; Bella, F.; Francia, C.; Bodoardo, S. Nanosponge-based composite gel polymer electrolyte for safer Li-O2 batteries. Polymers 2021, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, G.; Ricciardi, M.; Bella, F.; Cucciniello, R.; Proto, A.; Gerbaldi, C. Poly(glycidyl ether)s recycling from industrial waste and feasibility study of reuse as electrolytes in sodium-based batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122934–122940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, A.; Sakata, W.; Ishida, E.; Mitsuru, T.; Sato, Y. Application of high-performance hydrocarbon-type sulfonated polyethersulfone for vanadium redox-flow battery. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 19405–19412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Advanced anion exchange membranes with selective swelling-induced ion transport channels for vanadium flow battery application. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 642, 119985–119992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, B.G.; Vaudreuil, S. Review—Recent membranes for Vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 070553–070573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haro, J.C.; Tatsi, E.; Fagiolari, L.; Bonomo, M.; Barolo, C.; Turri, S.; Bella, F.; Griffini, G. Lignin-based polymer electrolyte membranes for sustainable aqueous dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8550–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, H.R. Polymer electrolytes for low and high temperature PEM electroyzers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 36, 101109–101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Ohira, A. Water electrolysis using a porous IrO2/Ti/IrO2 catalyst electrode and Nafion membranes at elevated temperatures. Membranes 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ohira, A. Crosslinked sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (CSPPSU) membranes for elevated-temperature PEM water electrolysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, M.; Müller, K.; Bensmann, B.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R.; Peach, R.; Thiele, S. Evaluation of the efficiency of an elevated temperature proton exchange membrane water electrolysis system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 094504–094517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, M.; Müller, K.; Bensmann, B.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R.; Aili, D.; Franken, T.; Chromik, A.; Peach, R.; Freiberg, A.T.S.; Thiele, S. Review and prospects of PEM water electrolysis at elevated temperature operation. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2300281–2300305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, P.; Bühler, M.; Van Pham, C.; Hegge, F.; Böhm, T.; McLaughlin, D.; Breitwieser, M.; Thiele, S. Directly coated membrane electrode assemblies for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 110, 106640–106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Valls, A.; Gangnus, N.; Secanell, M. Analysis of inkjet printed catalyst coated membranes for polymer electrolyte electrolyzers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F543–F552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhler, M.; Holzapfel, P.; McLaughlin, D.; Thiele, S. From catalyst coated membranes to porous transport electrode based configurations in PEM water electrolyzers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F1070–F1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Carmo, M.; Bender, G.; Everwand, A.; Lickert, T.; Young, J.L.; Smolinka, T.; Stolten, D.; Lehnert, W. Performance enhancement of PEM electrolyzers through iridium-coated titanium porous transport layers. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 97, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Gasteiger, H.A. Influence of ionomer content in IrO2/TiO2 electrodes on PEM water electrolyzer performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F3179–F3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-D.; Ohira, A.; Nakao, H. Chemically crosslinked sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (CSPPSU) membranes for PEM fuel cells. Membranes 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbe, S.; Futter, J.; Schmidt, T.J.; Gubler, L. Insight into elevated temperature and thin membrane application for high efficiency in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 377, 138046–138057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, S.; Guan, C.; Wang, H.; Nakajima, H.; Ito, K.; Wang, Y. Experimental optimization of the Nafion® ionomer content in the catalyst layer for polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis at high temperatures. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1313451–1313459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Scott, K.; Basu, S. Performance of a high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyser. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8918–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Ledesma-Garcia, J.; Arriaga, L.; Aricò, A. High temperature operation of a composite membrane-based solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyser. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Aili, D.; Li, Q.; Christensen, E.; Jensen, J.O.; Zhang, W.; Hansen, M.K.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Bjerrum, N.J. Oxygen evolution catalysts on supports with a 3-D ordered array structure and intrinsic proton conductivity for proton exchange membrane steam electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mališ, J.; Mazúr, P.; Paidar, M.; Bystron, T.; Bouzek, K. Nafion117 stability under conditions of PEM water electrolysis at elevated temperature and pressure. Int. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 41, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, S.; Lee, B.-S.; Cho, M.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Henkensmeier, D.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S. Electrodeposited IrO2/Ti electrodes as durable and cost-effective anodes in high-temperature polymer-membrane-electrolyte water electrolyzers. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2018, 226, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nafion 115 | CSPPSU | |
|---|---|---|
| IEC (meq/g), 25 °C | ∼1.0 | 1.8 |
| Crosslink rate (%), 25 °C | - | 50 |
| Water uptake (%), 100 °C | 38 | 37 |
| l, 25 °C | 21.1 | 11.4 |
| Elongation strength (MPa), 25 °C | 31 | 53 |
| Elongation stain (%), 25 °C | 200 | 33 |
| Flexural modulus (MPa), 25 °C | 196 | 986 |
| Conductivity, 80 °C, 90%RH, mS/cm | 47 | 12 |
| Cell Temperature (°C) | Nafion 115 | CSPPSU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mA/cm2 at 1.8 V | mA/cm2 at 2 V | mA/cm2 at 1.8 V | mA/cm2 at 2 V | |
| 80 | 659 | 960 | 403 | 734 |
| 100 | 701 | 1008 | 455 | 828 |
| 120 | 758 | 1068 | 537 | 959 |
| 150 | 836 | 1155 | 688 | 1161 |
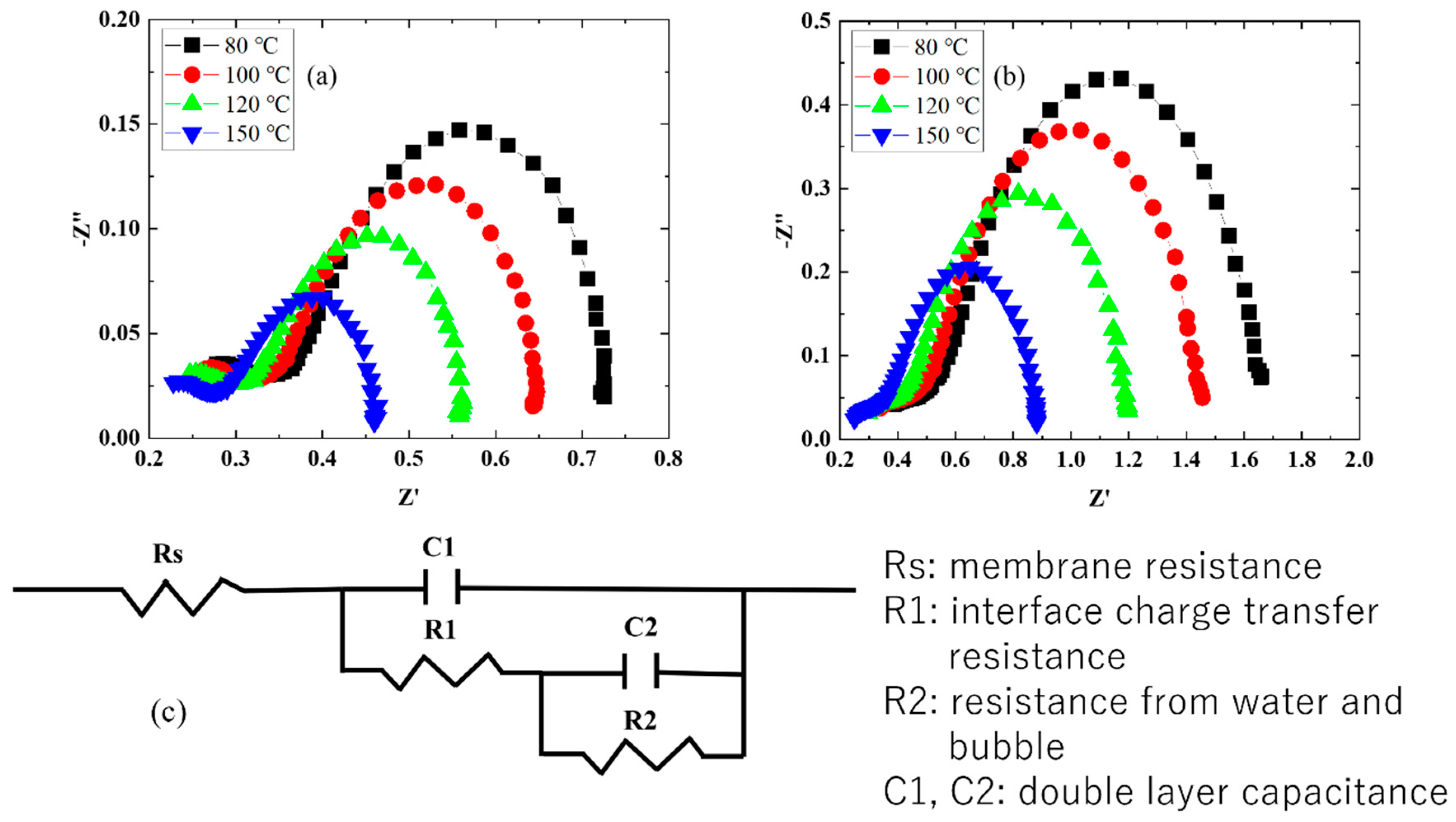
| Nafion 115 | CSPPSU | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Temperature (°C) | Cell Temperature (°C) | |||||||
| 80 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 150 | |
| Rs (ohm) | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| R1 (ohm) | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| C1 (mF) | 0.474 | 0.481 | 0.417 | 0.412 | 0.447 | 0.354 | 0.378 | 0.422 |
| R2 (ohm) | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 1.1 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.52 |
| C2 (mF) | 90.8 | 78.0 | 71.0 | 68.8 | 40.9 | 36.3 | 34.3 | 34.7 |
| Ref. | Temp. (°C) | Pressure (Bar) | Opera. Cond. | Operating Time (h) | Membrane | Catalyst (Loading) | PTL or PTE or CCM | GDL | Degradation Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anode (mg/cm2) | Cathode (mg/cm2) | |||||||||
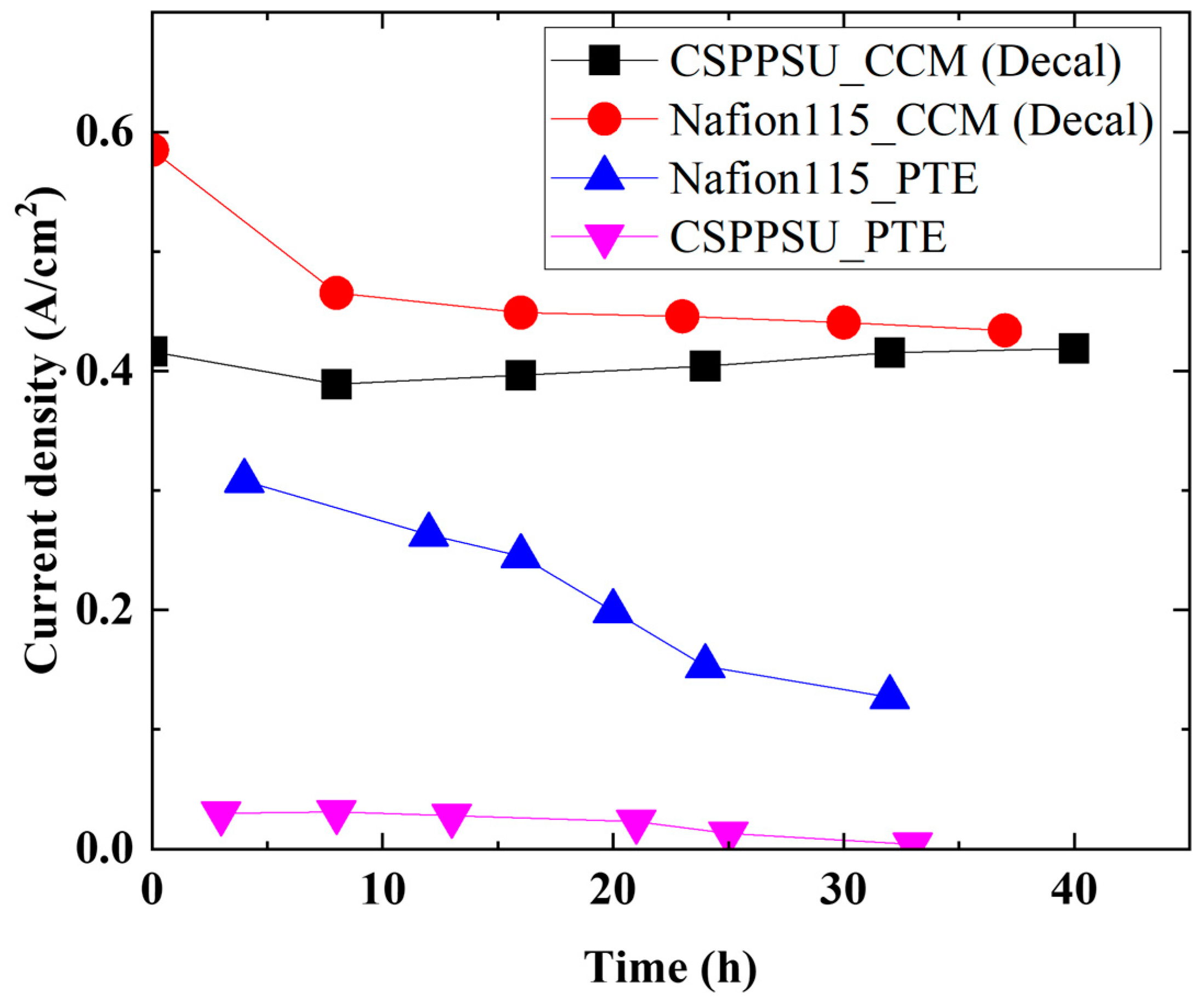
| This study | 120 | 1 | 1.7 V, 0.58 A/cm2 | 37 | Nafion 115 | IrO2 (1) | Pt (1) | CCM (Decal), Pt backing | Carbon cloth (0.291 mm) | −4.1 mA/cm2/h |
| This study | 120 | 1 | 1.7 V, 0.42 A/cm2 | 40 | CSPPSU | IrO2 (1) | Pt (1) | CCM (Decal), Pt backing | Carbon cloth (0.291 mm) | 0 mA/cm2/h |
| [18] | 120 | 1 | 1.7 V, 0.31 A/cm2 | 8 | Nafion 115 | IrO2 (7.5) | Pt (0.3) | PTE: Ti powder porous sheets (plating) (500 mm) | Carbon fiber paper (0.235 mm) | −18.9 mA/cm2/h |
| [19] | 120 | 1 | 1.7 V, 0.03 A/cm2 | 8 | CSPPSU | IrO2 (7.5) | Pt (0.3) | PTE: Ti powder porous sheets (plating) (500 mm) | Carbon fiber paper (0.235 mm) | Separation of membrane and electrode |
| [31] | 120 | 3 | 1.5 V, 0.4 A/cm2 | 300 | Composite SiO2-Nafion | IrO2 (5) | Pt (0.8) | CCM, Ti backing | Carbon cloth | −0.39 mA/cm2/h |
| [32] | 130 | 1 | 1.9 V, 0.35 A/cm2 | ~1200 | PA-doped Aquivion | IrO2 (0.7) | Pt (0.7) | CCM (Decal) Ta-coated stainless steel felt | Non-woven carbon cloth | +0.09 mV/h |
| [33] | 150 | 5 | 1.7 V, 1.2 A/cm2 | 160 | Nafion 117 | IrO2 (0.8) | Pt (0.5) | PTE: Ti felt | Pt-based GDE | −2.5 mA/cm2/h |
| [34] | 120 | 2.5 | 1.72 V, 1.25 A/cm2 | 300 (e-dep) or 150 (spray) | Nafion 212 | IrO2 (0.4) | Pt (0.4) | PTE: Ti-based | Carbon fiber paper (0.325 mm) | −1.5 mA/cm2/h −3.93 mA/cm2/h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-D. High-Temperature Water Electrolysis Properties of Membrane Electrode Assemblies with Nafion and Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Membranes by Using a Decal Method. Membranes 2024, 14, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080173
Kim J-D. High-Temperature Water Electrolysis Properties of Membrane Electrode Assemblies with Nafion and Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Membranes by Using a Decal Method. Membranes. 2024; 14(8):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080173
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Je-Deok. 2024. "High-Temperature Water Electrolysis Properties of Membrane Electrode Assemblies with Nafion and Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Membranes by Using a Decal Method" Membranes 14, no. 8: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080173
APA StyleKim, J.-D. (2024). High-Temperature Water Electrolysis Properties of Membrane Electrode Assemblies with Nafion and Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Membranes by Using a Decal Method. Membranes, 14(8), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080173






