Cationic/Anionic Poly(p-Phenylene Oxide) Membranes: Preparation and Electrodialysis Performance for Nickel Recovery from Industrial Effluents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.2.1. Cationic Membranes
2.2.2. Anionic Membranes
2.3. Membrane Characterization
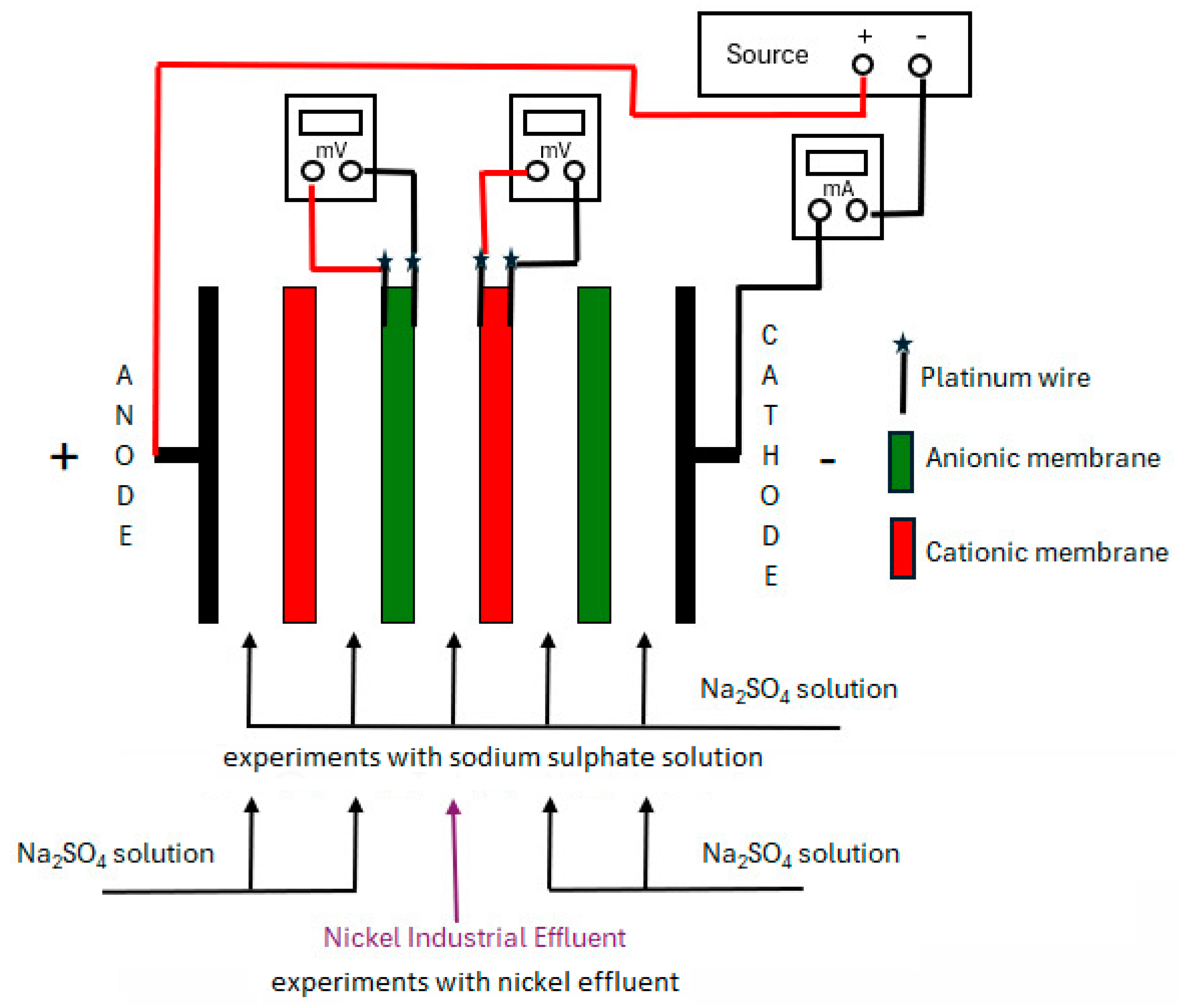
2.4. Electrodialysis Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.1.1. Production, Ion-Exchange Capacity, and Conductivity of Cationic Membranes
3.1.2. Production, Ion-Exchange Capacity, and Conductivity of Anionic Membranes
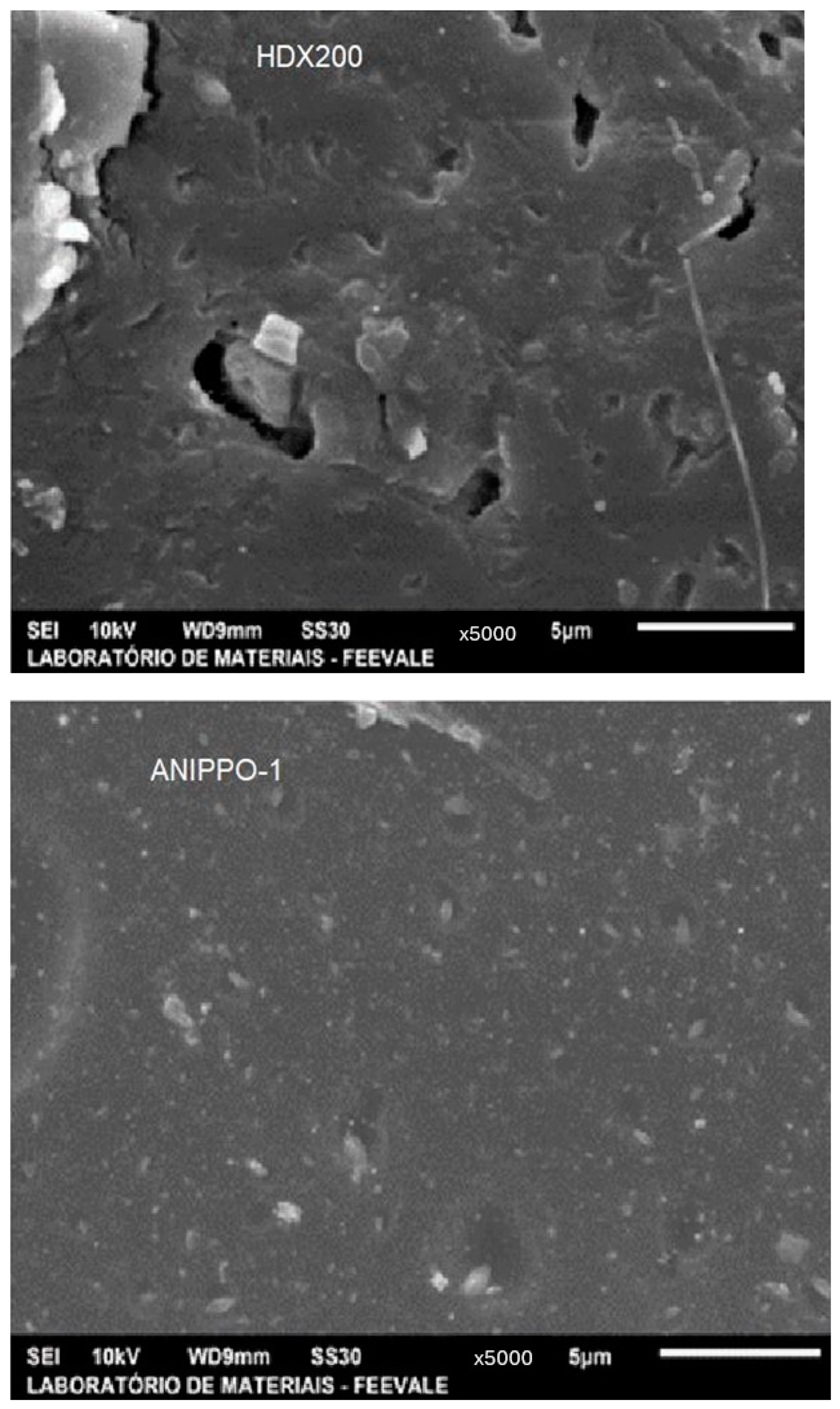
3.1.3. Surface Morphology
3.1.4. Thermal Stability
3.2. Electrodialysis Experiments
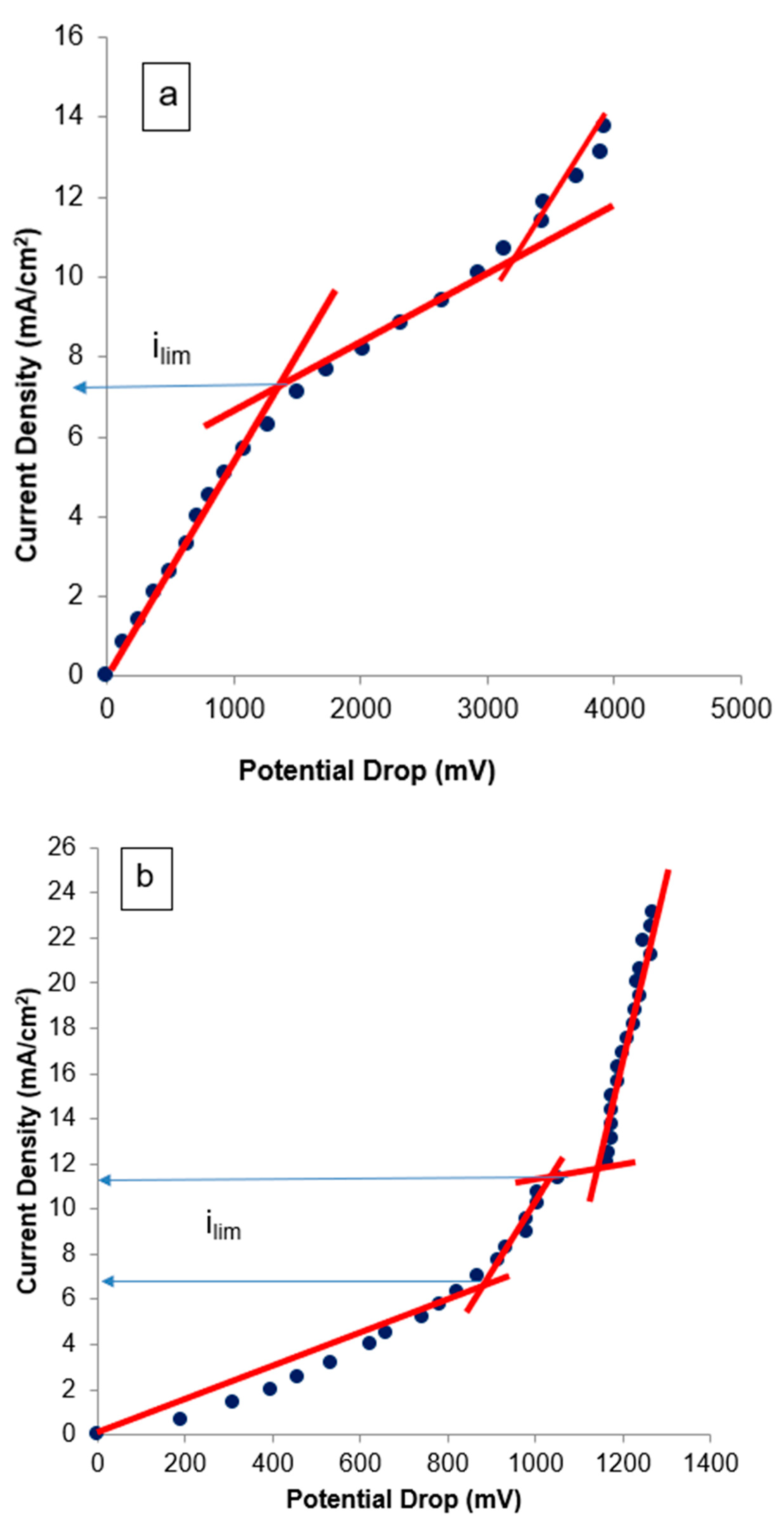
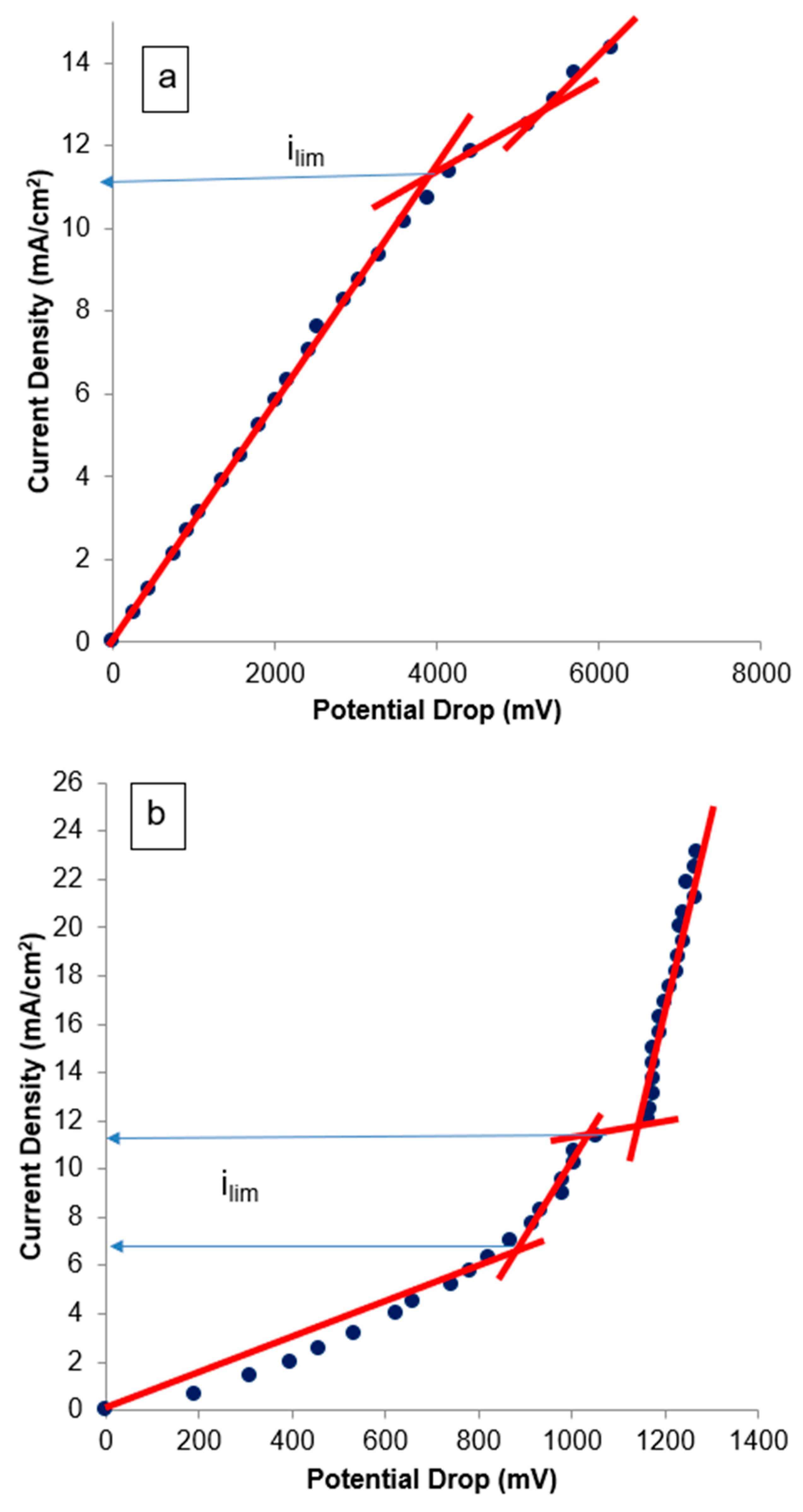
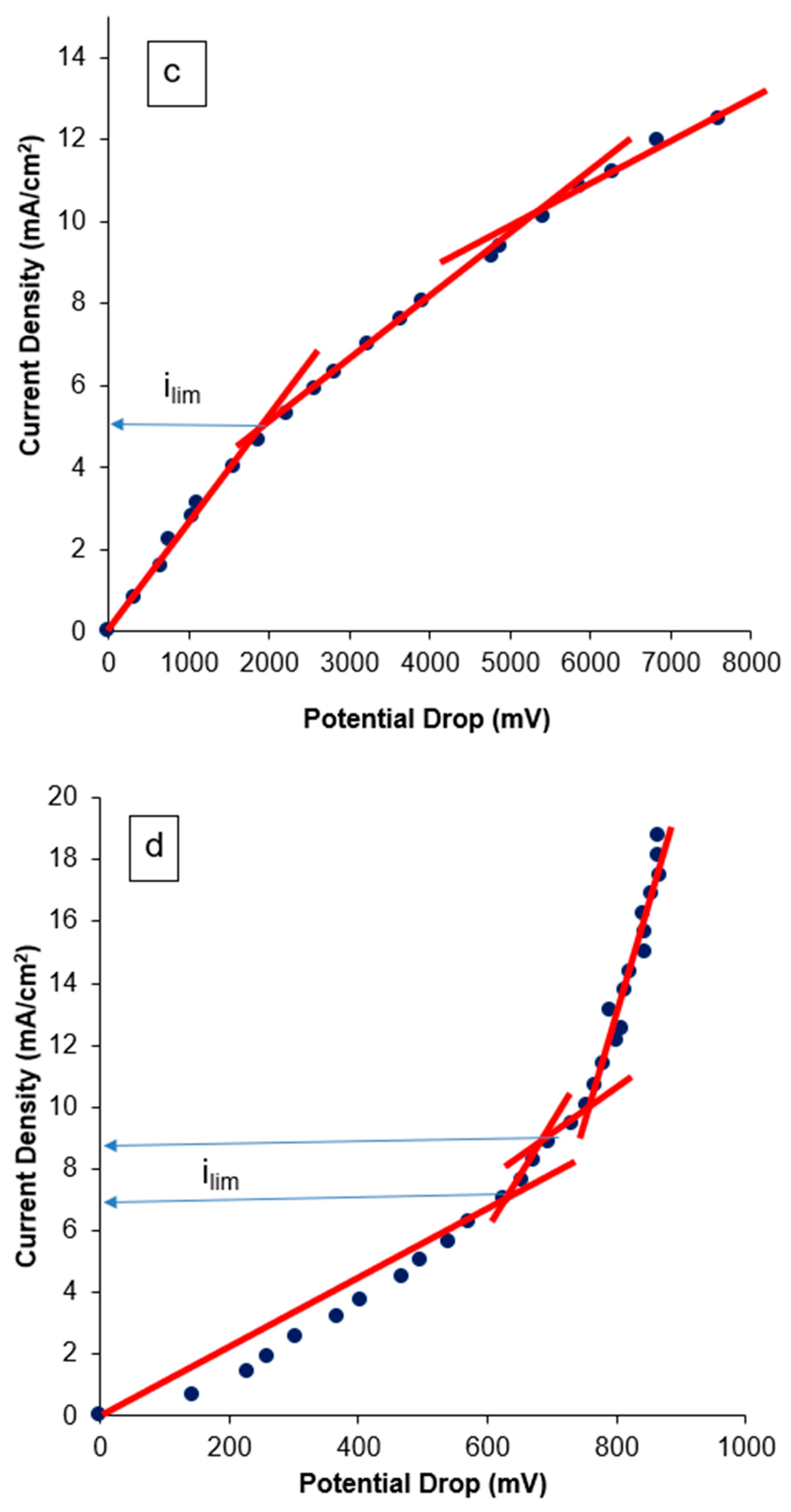
3.2.1. Current–Voltage Curves
3.2.2. Ion Extraction by Electrodialysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yan, J. A pilot-scale study and evaluation of the melting process and vitrification characteristics of electroplating sludge by oxygen enrichment melting. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Ferreira, J.Z.; Bernardes, A.M.; Costa, R.F.D.; Falavera, V.; Trevisan, M.D. Electrochemistry as a clean technology to the treatment of metal plating industries effluents: The application of electrodialysis. Met. Finish. 2000, 98, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Xu, H.; Ahmed, A. Recovery of copper and water from copper electroplating wastewater by the combination process of electrolysis and electrodialysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Y.; Peisen, H.; Mingzhu, X.; Xingen, X.; Lin, S.; Wu, L. An efficient Two-Chamber Electrodeposition-Electrodialysis combination craft for nickel recovery and phosphorus removal from spent electroless nickel plating bath. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121283. [Google Scholar]
- Yaoxing, L.; Rui, L.; Xiaoyun, W.; Liping, D.; Jianguo, D.; Xiaoyu, W.; Xin, Y.; Riya, C.; Rui, D.; Jianxi, L.; et al. Nickel recovery from electroplating sludge via bipolar membrane electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 637, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Yaoxing, L.; Rui, L.; Xiaoyun, W.; Liping, D.; Jianguo, D.; Xiaoyu, W.; Xin, Y.; Riyao, C.; Rui, D.; Jianxi, L.; et al. Recovery of nickel, phosphorus and nitrogen from electroless nickel-plating wastewater using bipolar membrane electrodialysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135326–135345. [Google Scholar]
- Dorota, B.; Piotr, D.; Agata, J.K.; Andrzej, M.; Danuta, B.; Aneta, F.; Ryszard, N.; Babilas, D. The effectiveness of nickel recovery from spent electroplating baths by electrodialysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 64, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Yao, Z. A comprehensive review on the synthesis and applications of ion exchange membranes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarasu, S.; Oh, T.W. Progress in poly(phenylene oxide) based cation exchange membranes for fuel cells and redox flow batteries applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 38381–38415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Esteban, P.; Gupta, G.; Fulton, D.; Mamlouk, M. Highly conductive partially cross-linked poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) as anion exchange membrane and ionomer for water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 37137–37151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, T. Fundamental studies of homogeneous cation exchange membranes from poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4- phenylene oxide): Membranes prepared by simultaneous aryl-sulfonation and aryl-bromination. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.W.; Popkin, S. Sulfonated Polyphenylene ether cation exchange resin. U.S. Patent 3, 5 July 1966. [Google Scholar]
- LaConti, A.B.; Chludzinski, P.J.; Fickett, A.P. Morphology and Reverse Osmosis Properties of Sulfonated 2,6-Dimethyl Polyphenylene Oxide Membranes. In Reverse Osmosis Membrane Research; Lonsdale, H.K., Podall, H.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, J.L.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Linares, A.; Casanova, M.J. Characterization of polymer systems based on sulfonated poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide). Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanqin, W.; Yuhui, H.; Guangmin, C. Preparation and Characterization of Sulfonated Poly(phenylence oxide). Polym. J. 1995, 27, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhasivam, T.; Kim, H.; Park, W.; Lim, H.; Ryi, S.; Roh, S.; Jung, H. Low permeable composite membrane based on sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide) (sPPO) and silica for vanadium redox flow battery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19035–19043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.; Ju, H. Fabrication of low-methanol-permeability sulfonated poly (phenylene oxide) membranes with hollow glass microspheres for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of proton conducting polymer membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 225, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Huang, Y.; Yip, N.Y.H. Advancing the conductivity-permselectivity tradeoff of electrodialysis ion-exchange membranes with sulfonated CNT nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T.; Dhadake, Y.N. Property evaluation of custom-made ion exchange membranes for electrochemical performance in reverse electrodialysis application. J. Electroan. Chem. 2019, 850, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Arniegas, R.A.; Narducci, R.; Ercolani, G.; Antonaroli, S.; Sgreccia, E.; Pasquini, L.; Knauth, P.; Vona, M.L. Alkaline stability of model anion exchange membranes based on poly (phenylene oxide) (PPO) with grafted quaternary ammonium groups: Influence of the functionalization route. Polymer 2019, 185, 121931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, D.C.; Viegas, L.S.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S. Water recovery from acid mine drainage by electrodialysis. Miner. Eng. 2013, 40, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, C.R.; Benvenuti, T.; Trindade, C.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Bernardes, A.M. Electrodialysis for the tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater: Efficiency of ion removal and ageing of ion exchange membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzke, C.D.; Giacobbo, A.; Ferreira, J.Z.; Bernardes, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S. Increasing water recovery rate of membrane hybrid process on the petrochemical wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, E.H.; Marder, L.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Bernardes, A.M. Characterization of an anion-exchange membrane subjected to phosphate and sulfate separation by electrodialysis at overlimiting current density condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, T.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Ortega, E.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J. Influence of the co-ions on the transport of sulfate through anion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kucera, F.; Jancar, J. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Sulfonation of Polymers: A Review. Polym. Engin. Sci. 1998, 3, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y. Fouling resistant nanocomposite cation exchange membrane with enhanced power generation for reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 516, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Guang, R.; Shu, Y.; Chuang, F.; Tsen, W. Effect of sulfonic group on solubility parameters and solubility behavior of poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4- phenylene oxide). Polym. Adv. Tech. 2007, 18, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arges, C.; Wang, L.; Parrondo, J.; Ramani, V. Best Practices for Investigating Anion Exchange Membrane Suitability for Alkaline Electrochemical Devices: Case Study Using Quaternary Ammonium Poly(2,6-dimethyl 1,4-phenylene)oxide Anion Exchange Membranes. J. Electroc. Soc. 2013, 160, 1258–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Overview of ion-exchange membrane processes. In Ion-Exchange Membrane Separation Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 9, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tongwen, X.; Zha, F.F. Fundamental studies on a new series of anion exchange membranes: Effect of simultaneous amination-crosslinking processes on membranes ion-exchange capacity and dimensional stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 199, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrin, H.; Wu, J.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. High durable PEK-based anion exchange membrane for elevated temperature alkaline fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Paturzo, L.; Iulianelli, A.; Gatto, I.; Passalacqua, E. Sulfonated PEEK-WC membranes for proton-exchange membrane fuel cell: Effect of the increasing level of sulfonation on electrochemical performances. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreanu, I.; Ebrasu, D.; Sisu, C.; Varlam, M. Thermal analysis of sulfonated polymers tested as polymer electrolyte membrane for PEM fuel cells. J Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 110, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Echtermeyer, D.; Barthel, A.; Urban, G.; Pliquett, U. Multichannel cell detection in microcompartments by means of true parallel measurements using the Solartron S-1260. J. Electr. Impedance 2020, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailenko, S.D.; Wang, K.; Kaliaguine, S.; Xing, P.; Robertson, G.; Guiver, M. Proton conducting membranes based on cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK). J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, S.; Kumar, P.; Mandal, J.R.; Shahi, V.K. Functionalized graphene oxide-modified sulfonated poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) based thermal-resistance anti-fouling bi-functional cation exchange membrane for electrodialytic desalination. Desalination 2024, 578, 117454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhzad, H.; Kikhavani, T.; Monnaie, F.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Van Gerven, T.; Van der Bruggen, B. Novel composite cation exchange films based on sulfonated PVDF for electromembrane separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Ge, S.; Wang, C. Water uptake, ionic conductivity and swelling properties of anion-exchange membrane. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofer, D.; Nair, B.; Stoler, E.; Kovar, B. Composite Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. US Patent Application Publication, 10 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Formato, R.M.; Kovar, R.F.; Osenar, P.; Landrau, N.; Rubin, L.S. Composite Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. U.S. Patent US 7.052.793 B2, 30 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sedkaoui, Y.; Szymczyk, A.; Lounici, H.; Arous, O. A new lateral method for characterizing the electrical conductivity of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: State of their development and perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Guan, R.; Zhang, P. Effect of heating and stretching membrane on ionic conductivity of sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide). J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, B.; Hong, J.G. A Novel Hybrid Poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA)/Poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) (PPO) Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis Power System. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 239, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarazzato, T.; Buzzi, D.C.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Current-voltage curves for treating effluent containing HEDP: Determination of the limiting current. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gong, C.; Guan, R.; Zou, H.; Dai, H. Sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide) membranes as promising materials for new proton exchange membranes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreanu, I.; Marinoiu, S.; Sisu, C.; Varlam, M.; Fierascu, R.; Stanescu, P.; Teodorescu, M. Synthesis and testing of a composite membrane based on sulfonated polyphenylene oxide and sílica compounds as proton exchange membrane PEM fuel cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 96, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, N.U.; Ji, W.; Wu, B.; Shehzad, M.A.; Ge, L.; Xu, T. SPPO-based cation exchange membranes with a positively charged layer for cation fractionation. Desalination 2019, 472, 114145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khraisheh, M.; Almonani, F. Innovative BPPO Anion Exchange Membranes Formulation Using Diffusion Dialysis-Enhanced Acid Regeneration System. Membranes 2021, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, K.S.; Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Scarazzato, T.; Bernardes, A.M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Investigation of ion-exchange membranes by means of chronopotentiometry: A comprehensive review on this highly informative and multipurpose technique. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 293, 102439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Effect of the equilibria of multivalent metal sulfates on the transport through cation-exchange membranes at different current regimes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, E.D.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Bazinet, L.; Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.V. Effect of ampholyte nature on current-voltage characteristic of anion-exchange membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 285, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Auclair, B.; Pourcelly, G. Transport of weak-electrolyte anions through anion exchange membranes: Current–voltage characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 189, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.L.; Saad, S.; Lan, R.; Goodfellow, R.J.; Tao, S. Anionic membrane and ionomer based on poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4- phenylene oxide) for alkaline membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8272–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, G.G.; Barros, K.S.; Scarazzato, T.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Electrodialisys for concentrating cobalt, chromium, manganese, and magnesium from a synthetic solution based on a nickel laterite processing route. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Mondal, A.N.; Tong, B.; Jiang, C.; Emmanuel, K.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Development of BPPO-based anion exchange membranes for electrodialysis desalination applications. Desalination 2016, 391, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.; Yadav, V.; Rajput, R.; Sharma, J.; Shukla, D.K.; Kulshresha, V. New class of composite anion exchange membranes based on Quaternized poly(phenylene oxide) and functionalized boron nitride. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 336, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Min, C.M.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.S. Enhanced conductivity and stability of anion exchange membranes depending on chain lenghts with crosslinking based on poly(phenylene oxide). Polymer 2020, 192, 122331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubari, M.Q.; Zwain, H.M.; Alekseeva, N.V.; Baziyani, G.I. Features of feed concentration and temperature effects on membranes operation in electrodialysis systems—A review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 012178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liao, J.; Yang, S.; Li, J. Stable cycloaliphatic quaternary ammonium-tethered anion exchange membranes for electrodialysis. Reac. Func. Polym. 2018, 130, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | HDX100 | HDX200 | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic group attached | -SO3− | -NR3+ | -- |
| Water content | 35–50 | 30–45 | % |
| Ion-exchange capacity | ≥2.0 | ≥1.8 | mol/kg (dry) |
| Membrane surface resistance (0.1 mol NaCl) | ≤20 | ≤20 | Ω cm2 |
| Permselectivity (0.1 mol KCl/0.2 mol KCl) | ≥90 | ≥89 | % |
| Burst strength | ≥0.6 | ≥0.6 | MPa |
| Dimension change rate (longitudinal and lateral) | ≤2 | ≤2 | % |
| Water flux | ≤0.1 (below 0.2 MPa) | ≤0.2 (below 0.035 MPa) | mL/h·cm2 |
| Nickel | 10.2 mmol.L−1 |
| Sodium | 123.5 mmol.L−1 |
| Sulfate | 29.6 mmol.L−1 |
| Chloride | 16.8 mmol.L−1 |
| Conductivity (25 °C) | 3 mS.cm−1 |
| pH | 4.4 |
| Membrane | PPO:H2SO4 Molar Ratio | Reaction Time (h) | SD (%) | IEC (meq/g) | Conductivity (mS/cm) (25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CATPPO-1 | 1:4.4 | 0.5 | 20.80 | 1.52 ± 0.012 | 15.3 |
| CATPPO-2 | 1:4.4 | 2.0 | 19.93 | 1.47 ± 0.003 | 13.0 |
| CATPPO-3 | 1:5.5 | 0.5 | 19.93 | 1.47 ± 0.002 | 13.0 |
| SPPO (ref. [11]) | - | - | 17.2 | 1.28 | 0.57 |
| SPPO-FGO (7%) (ref. [30]) | - | - | 1.76 | 100 | |
| HDX100 (ref. [23]) | 2.4 | 5.45 |
| Membrane | PPO:NBS Molar Ratio | IEC (meq/g) | Conductivity (mS/cm) (25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANIPPO-1 | 1:0.5 | 1.88 ± 0.029 | 2.24 |
| ANIPPO-2 | 1:0.7 | 1.07 ± 0.011 | 0.605 |
| HDX200 (ref. [23]) | - | 1.67 | 2.96 |
| Membranes | Nickel PE (%) | Sodium PE (%) | Sulfate PE (%) | Chloride PE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CATPPO-1 + HDX200 | 85.5 | 41.3 | n.d. | n.d. |
| HDX100 + HDX200 | 55.4 | 39.6 | 76.5 | 77.2 |
| ANIPPO-1 + HDX100 | n.d | n.d. | 90.9 | 91.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilbert, F.; Corte, J.F.; do Nascimento, F.T.; Jahno, V.D.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Celso, F.; da Silva, S.W.; Bernardes, A.M. Cationic/Anionic Poly(p-Phenylene Oxide) Membranes: Preparation and Electrodialysis Performance for Nickel Recovery from Industrial Effluents. Membranes 2024, 14, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120268
Wilbert F, Corte JF, do Nascimento FT, Jahno VD, Rodrigues MAS, Celso F, da Silva SW, Bernardes AM. Cationic/Anionic Poly(p-Phenylene Oxide) Membranes: Preparation and Electrodialysis Performance for Nickel Recovery from Industrial Effluents. Membranes. 2024; 14(12):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120268
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilbert, Fabrício, Joana Farias Corte, Felipe Tiago do Nascimento, Vanusca Dalosto Jahno, Marco Antônio Siqueira Rodrigues, Fabrício Celso, Salatiel W. da Silva, and Andrea Moura Bernardes. 2024. "Cationic/Anionic Poly(p-Phenylene Oxide) Membranes: Preparation and Electrodialysis Performance for Nickel Recovery from Industrial Effluents" Membranes 14, no. 12: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120268
APA StyleWilbert, F., Corte, J. F., do Nascimento, F. T., Jahno, V. D., Rodrigues, M. A. S., Celso, F., da Silva, S. W., & Bernardes, A. M. (2024). Cationic/Anionic Poly(p-Phenylene Oxide) Membranes: Preparation and Electrodialysis Performance for Nickel Recovery from Industrial Effluents. Membranes, 14(12), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120268







