Fabrication and Characterization of Cu2+-Driven PTFE-Reinforced Artificial Muscle Polymer Membrane for Water Purification and Energy Harvesting Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fabrication of Cu-IPMC by Chemical Deposition Technique
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Microscopy Study
2.2.2. Mechanical Characterizations
2.2.3. Surface-Wetting Characterization
2.2.4. Scratch Test
2.2.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
2.2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.8. Electric Properties
3. Results and Discussion
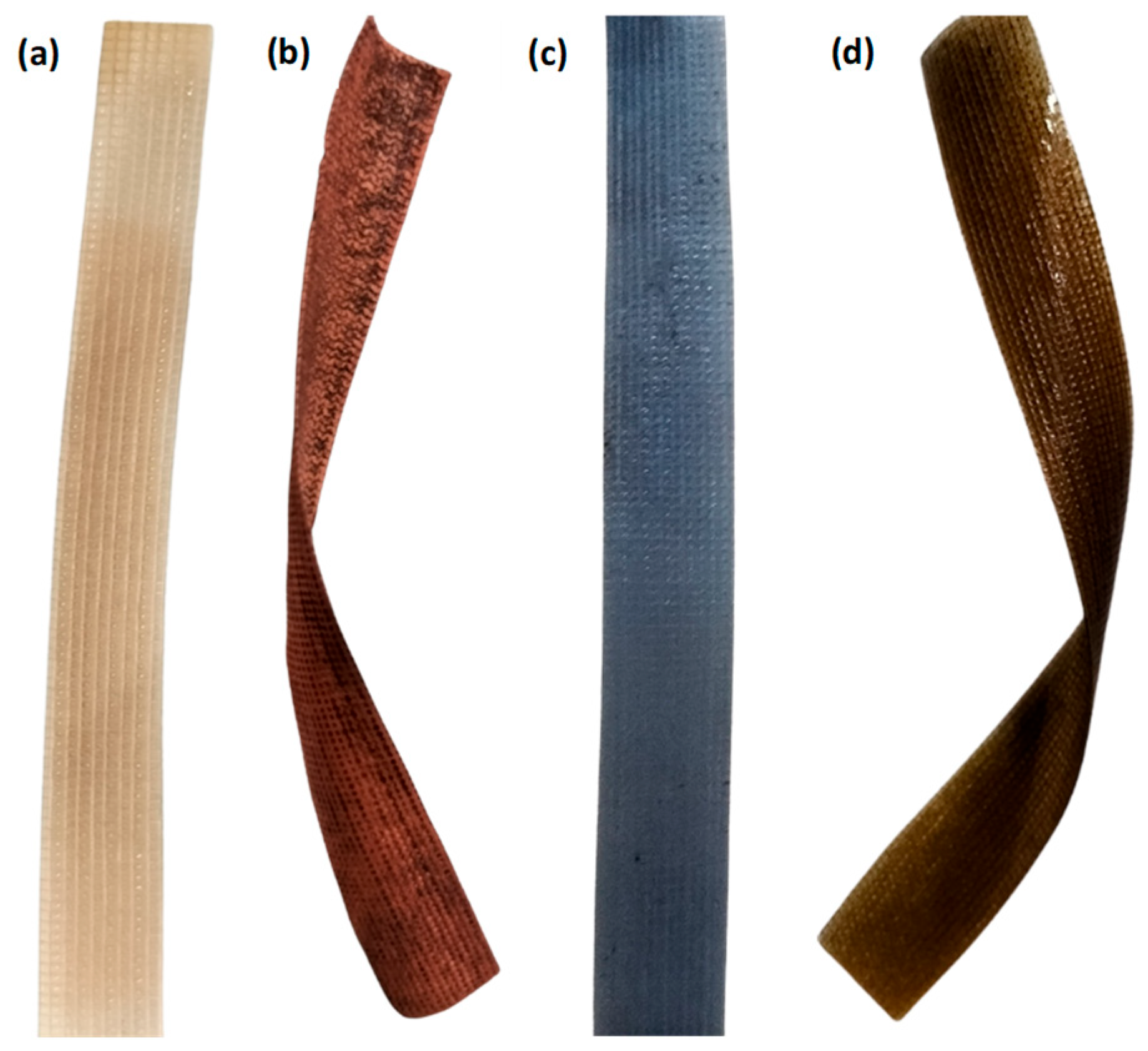
3.1. Morphology and Microstructure
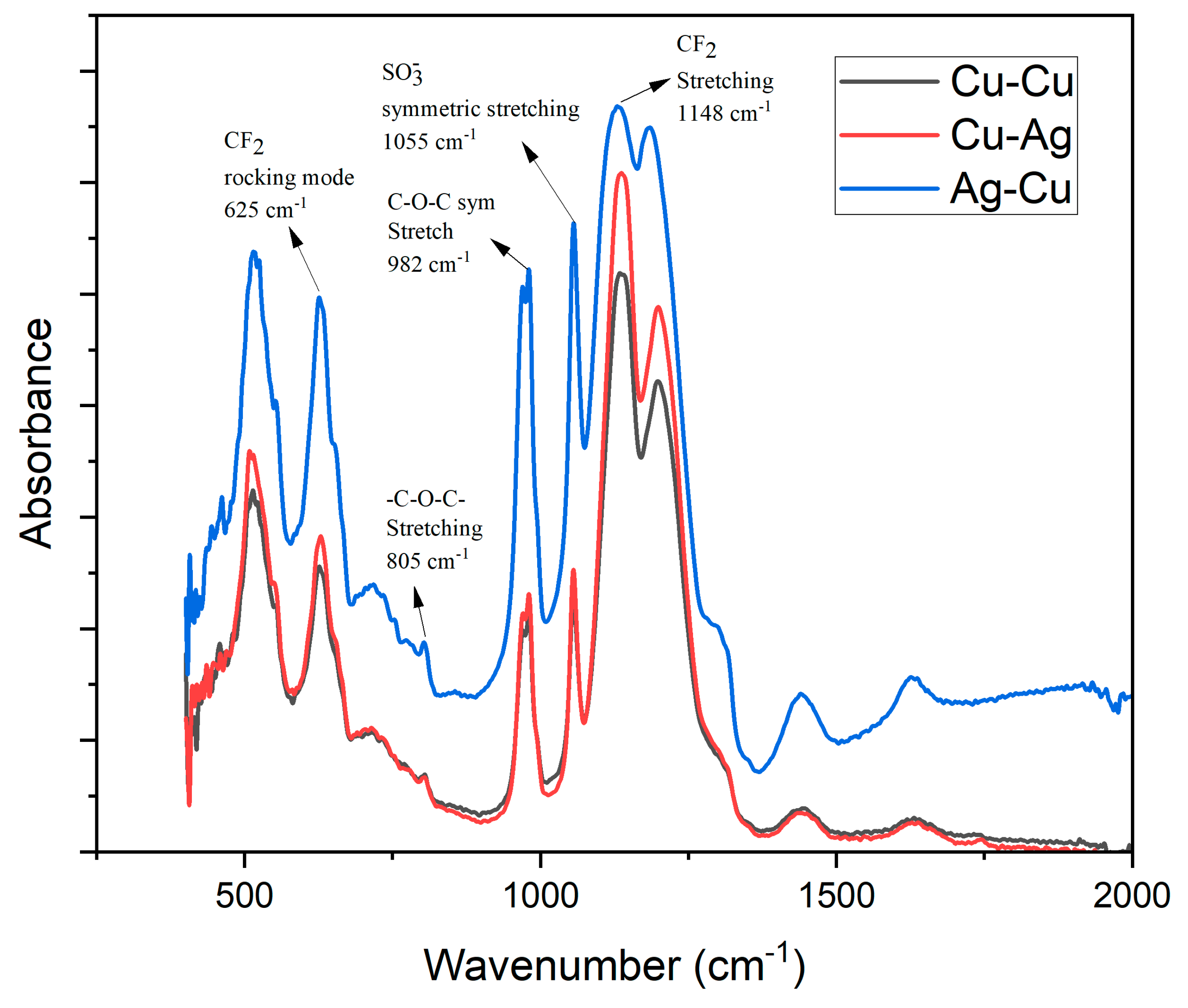
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
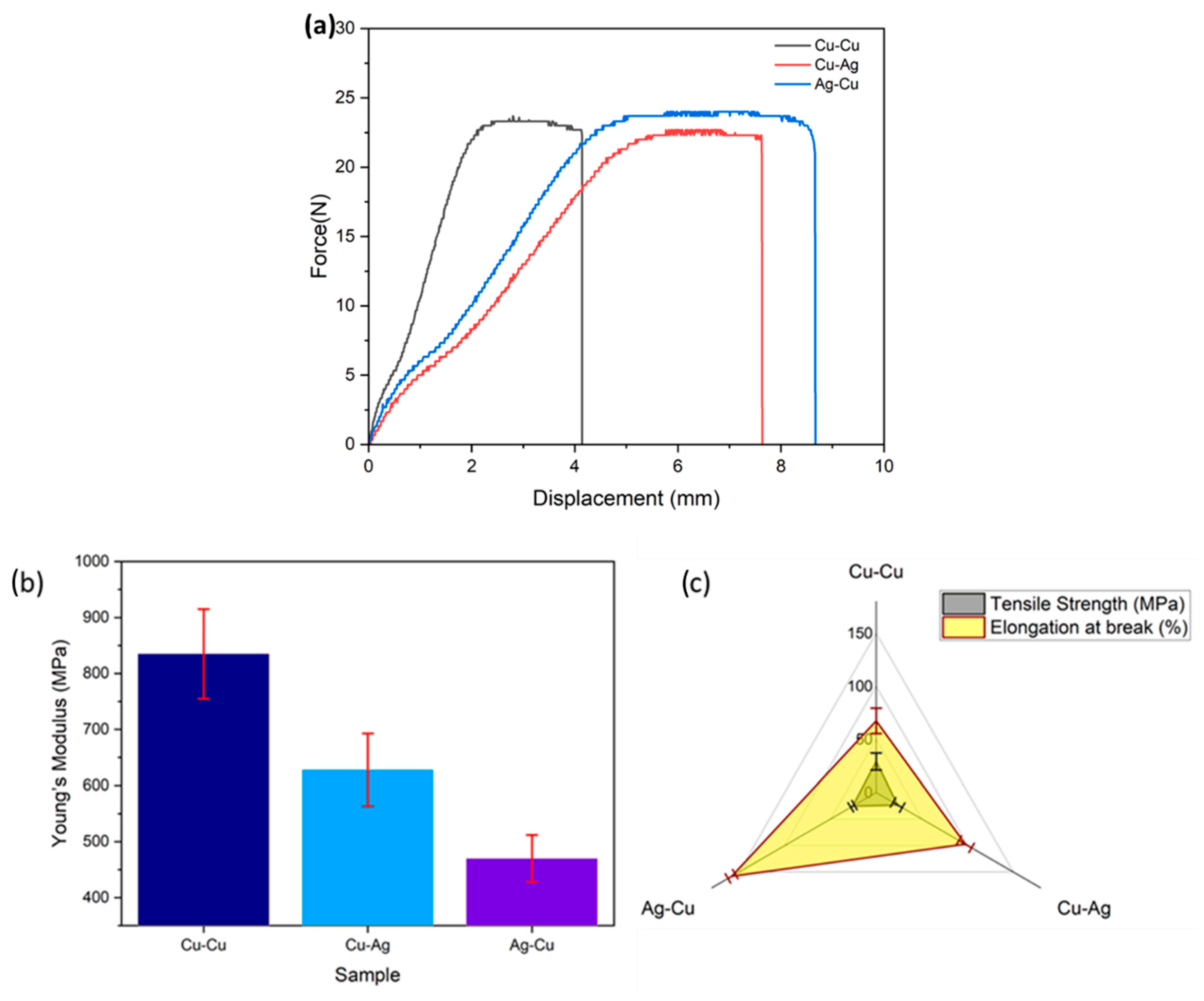
3.3. Mechanical Properties
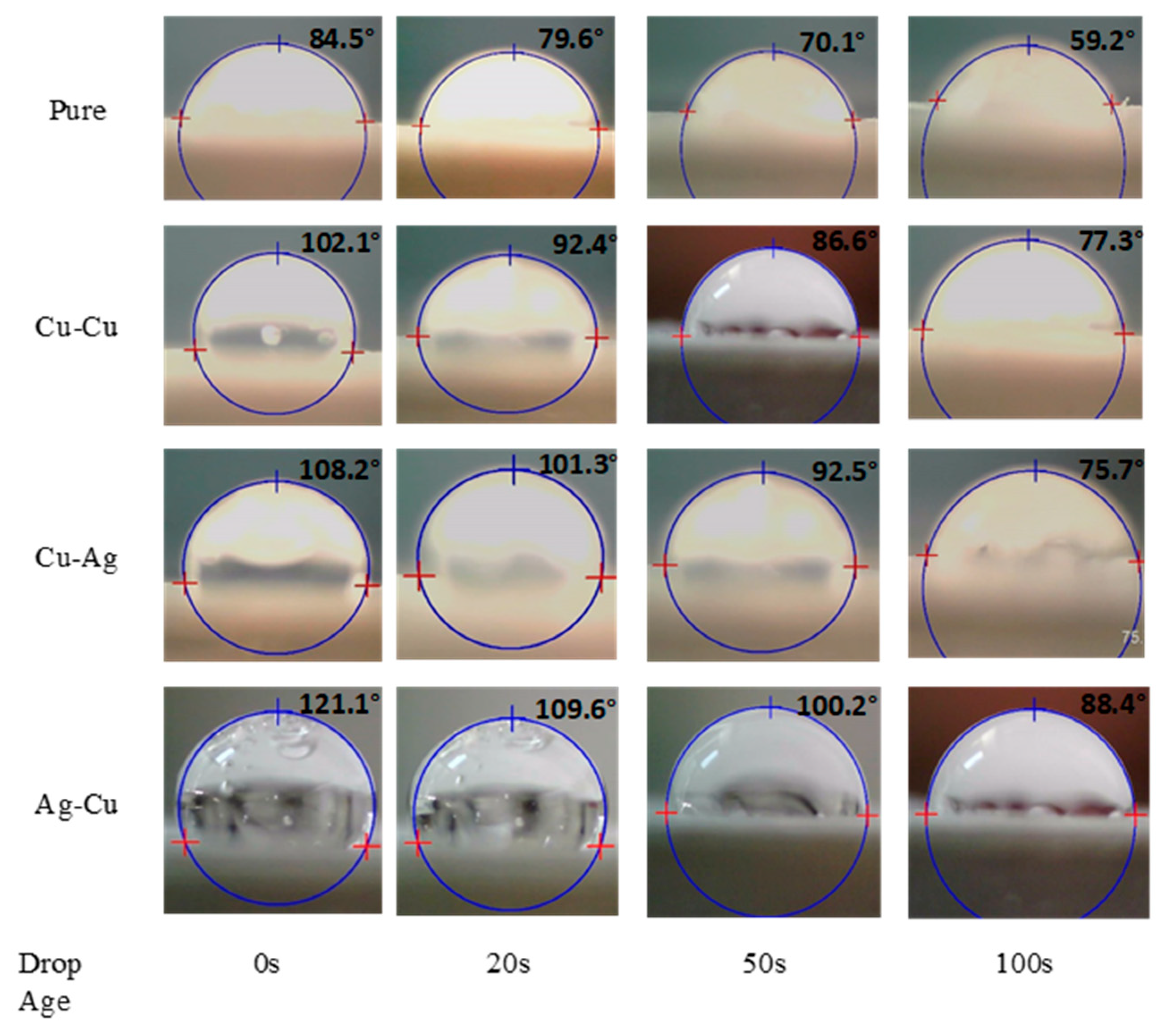
3.4. Contact Angle Measurement
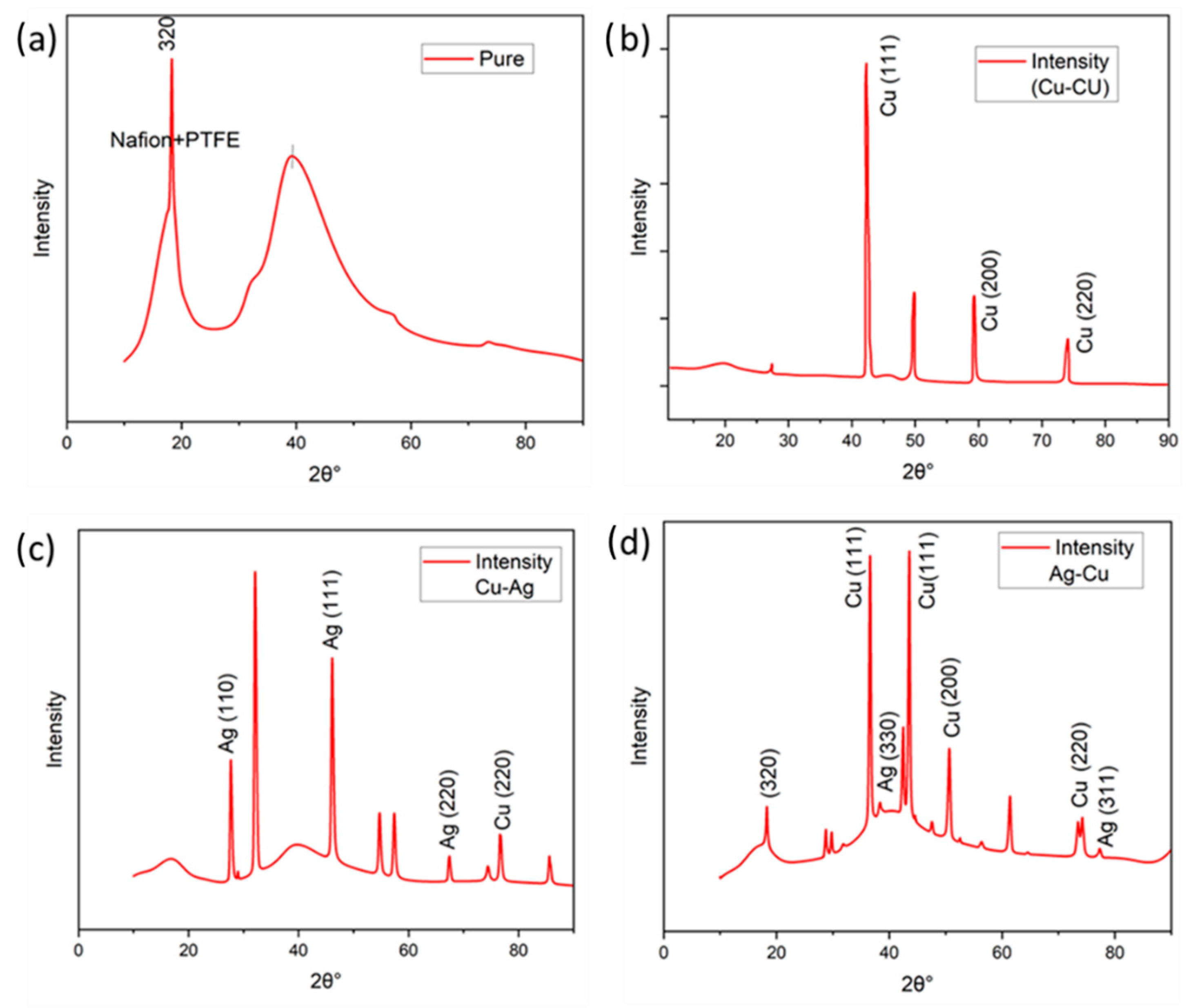
3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
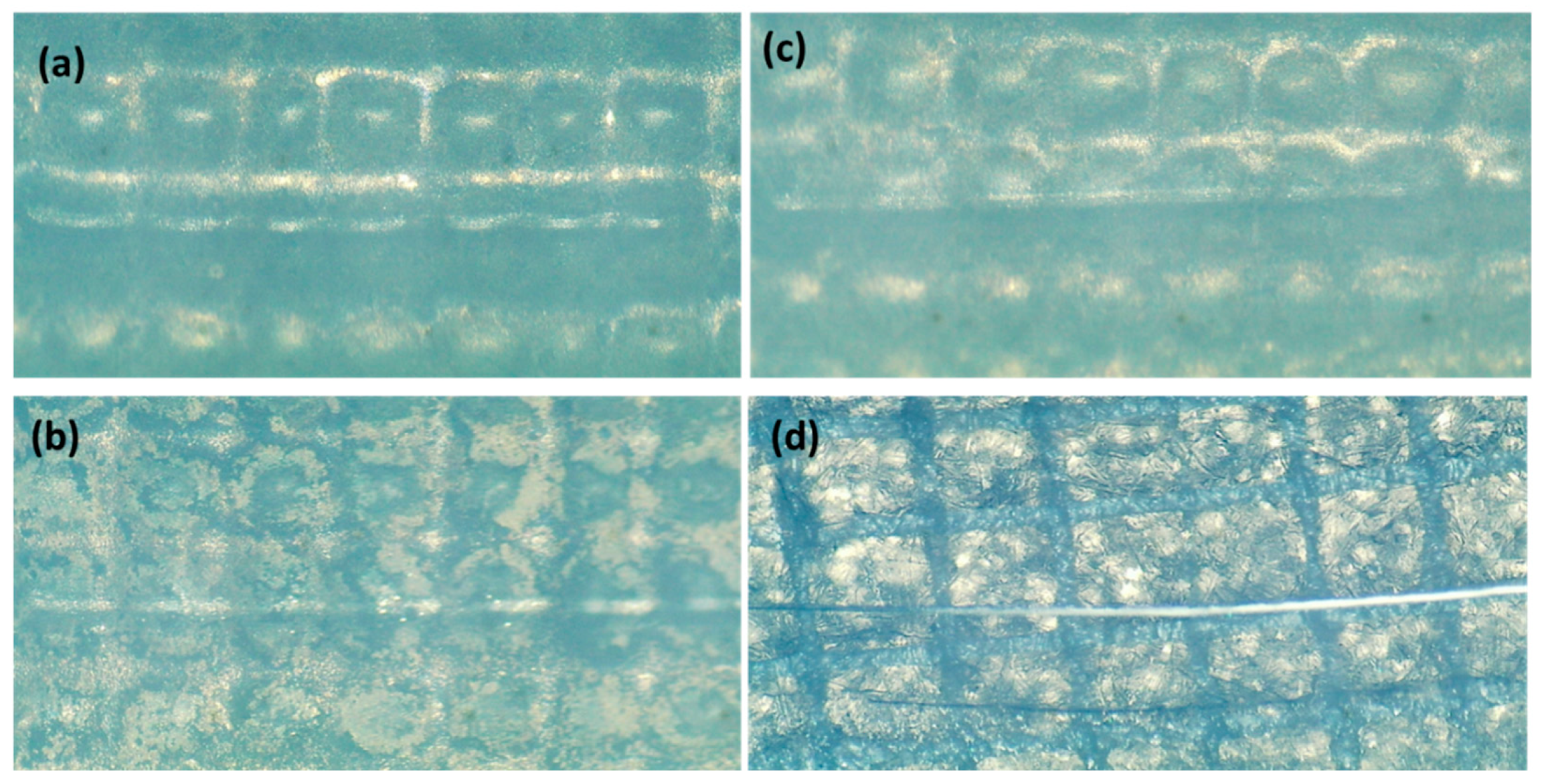
3.6. Scratch Test Analysis
3.7. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
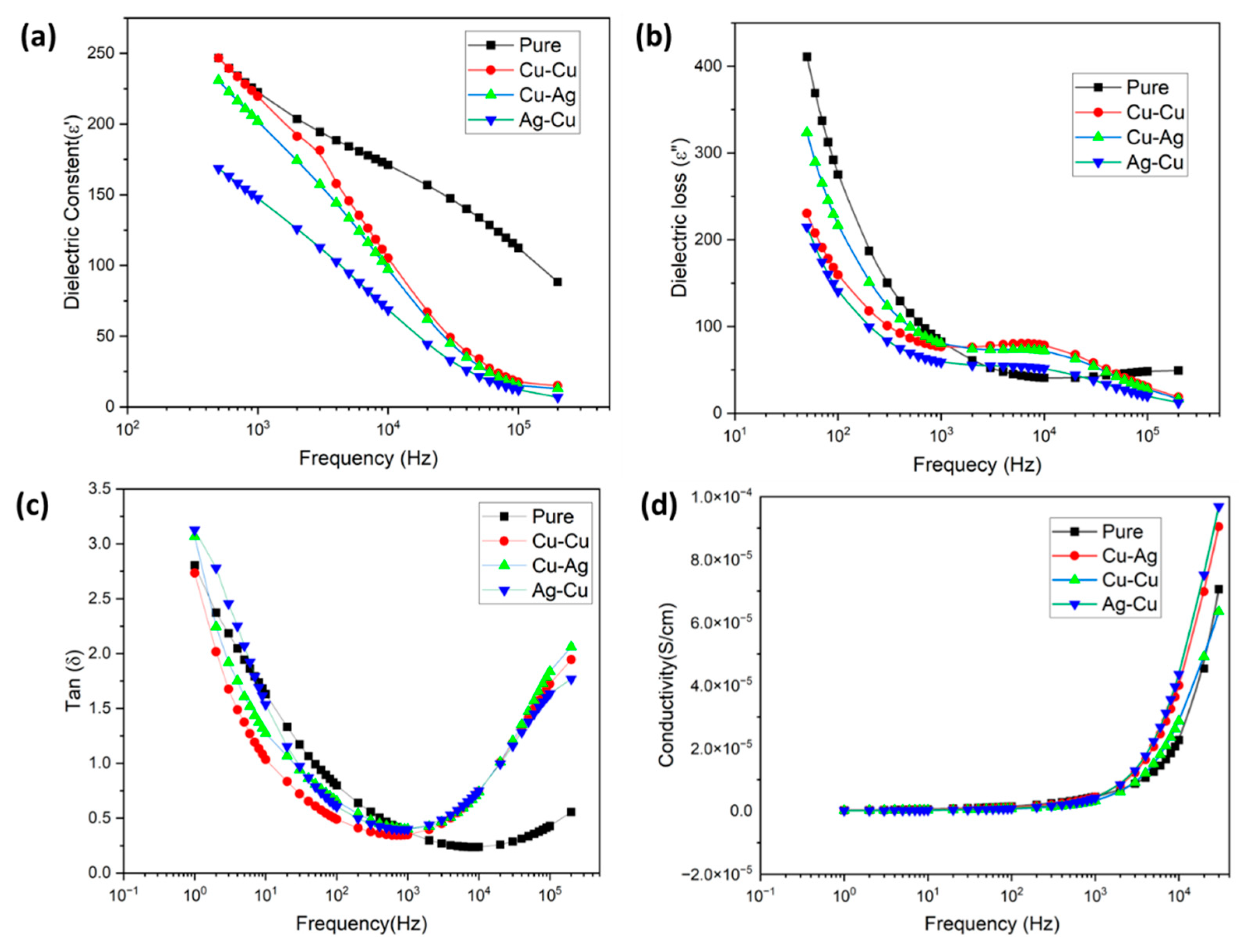
3.8. Dielectric Properties
4. Conclusions
- Enhanced mechanical properties were gained by metal ion deposition in addition to the reinforcement when compared with the unmodified membrane.
- The membranes that have been altered through a chemical deposition technique exhibit a more hydrophobic nature. This is due to the strong attraction between positively and negatively charged ions, which results in an adhesive nature and a 50% increase in the contact angle of Ag-Cu.
- Scratch test indicated that the adhesive strength between membrane and metal electrode was higher for Ag-Cu coated membrane.
- Increased crystallinity and phase transformation succeeded, and it would help in the generation of electrical energy.
- The Ag-Cu membrane demonstrates the highest Tg when compared with Cu-Cu and Cu-Ag. The observed outcome entails an increase in the rigidity of chain macromolecules, which could potentially enhance their ability to cope with elevated pressure during water purification processes.
- The successful achievement of improved conductivity outcomes was observed in specimens that underwent treatment in a reducing solution along with the presence of metal ions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maia, B.A.; Magalhães, N.; Cunha, E.; Braga, M.H.; Santos, R.M.; Correia, N. Designing Versatile Polymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.; Yoon, C. Advances in Biodegradable Soft Robots. Polymers 2022, 14, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.W.; Islam Bhat, S.; Al Qahtani, H.S.; Aamir, M.; Amin, M.N.; Farhan, M.; Aldabal, S.; Khan, M.S.; Jeelani, I.; Nawaz, A.; et al. Recent Progress, Challenges, and Trends in Polymer-Based Sensors: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, A.M.; Murcia, M.D. Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, I.; Imoto, I.; Okaue, D.; Imai, M.; Kumagai, S.; Makita, T. Electronic excitation spectra of organic semiconductor/ionic liquid interface by electrochemical attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; He, Q.; Zhu, D.; Luo, M. A Compact Review of IPMC as Soft Actuator and Sensor: Current Trends, Challenges, and Potential Solutions from Our Recent Work. Front. Robot. AI 2019, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfiri, M. Sensing mechanical deformation via ionic polymer metal composites: A primer. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2019, 22, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, B.; Schäfer, C.; Kokel, A. Chapter 2—Solid catalysts for environmentally benign synthesis. In Heterogeneous Catalysis in Sustainable Synthesis; Török, B., Schäfer, C., Kokel, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 23–80. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Yin, G.; Vokoun, D.; Shen, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, X. Review on Improvement, Modeling, and Application of Ionic Polymer Metal Composite Artificial Muscle. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadevi, T.S.; Goo, B.H.; Paek, S.Y.; Choi, O.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H. Nafion composite membranes impregnated with polydopamine and poly (sulfonated dopamine) for high-performance proton exchange membranes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12956–12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Datta, S.; Majumder, S. Design and Control of an EMG Driven IPMC Based Artificial Muscle Finger. In Computational Intelligence in Electromyography Analysis—A Perspective on Current Applications and Future Challenges; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dhapola, P.S.; Singh, P.K.; Bhattacharya, B.; Surana, K.; Mehra, R.; Gupta, M.; Singh, A.; Singh, V.; Sahoo, N.G. Electrical, thermal, and dielectric studies of ionic liquid-based polymer electrolyte for photoelectrochemical device. High Perform. Polym. 2018, 30, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Kim, K.J. IPMC as a mechanoelectric energy harvester: Tailored properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 015017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Electroless copper deposition: A critical review. Thin Solid Films 2019, 669, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtamäki, T.; Tian, X.; Korhonen, J.T.; Ras, R.H.A. Surface-wetting characterization using contact-angle measurements. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, K.; Crasta, V.; Kumar, N.B.R.; Shetty, G.; Rekha, P.D. Structural, optical, mechanical and dielectric properties of titanium dioxide doped PVA/PVP nanocomposite. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamarlapudi, S.L.R.K.; Chintalpudi, V.K.; Muddada, S. Application of Biosorption for Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. In Biosorption; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Yu, H.; Kang, G.; Cao, Y. Fabrication and characterization of a novel Nafion-PTFE composite hollow fiber membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiaxerli, A.; Karagianni, A.; Ouranidis, A.; Kachrimanis, K. Polyelectrolyte Matrices in the Modulation of Intermolecular Electrostatic Interactions for Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesaswi, C.S.; Sreekanth, P.R. Evaluation of dynamic mechanical properties of teflon fabric reinforced artificial muscle material. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Costa, C.M.; Correia, D.M.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Martins, P.; Correia, D.M.; Correia, V.; Ribeiro, C.; Pedro Martins, P.M.; et al. Chapter 1—Electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride)-based materials: Recent progress, challenges, and opportunities. In Fascinating Fluoropolymers and Their Applications; Ameduri, B., Fomin, S., Eds.; Progress in Fluorine Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kusoglu, A.; Weber, A.Z. New Insights into Perfluorinated Sulfonic-Acid Ionomers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 987–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaki, M.; Fadaei Tehrani, A.; Niroumand, B.; Gupta, M. Wettability in Metal Matrix Composites. Metals 2021, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, A. Electroless copper deposition and interface characteristics of ionic electroactive polymer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Han, R.; Ren, J.; Li, L.; Han, N.; Feng, X.; Zhu, J. A review on the mechanical properties for thin film and block structure characterised by using nanoscratch test. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesaswi, C.S.; Sreekanth, P.S.R. Characterisation of Silver-coated Teflon fabric-reinforced Nafion ionic polymer metal composite with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoparticles. Iran Polym. J. 2022, 31, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, S.M. Dielectric Polymers. In Polymers and Polymeric Composites; Jafar Mazumder, M., Sheardown, H., Al-Ahmed, A., Eds.; Functional Polymers. A Reference Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
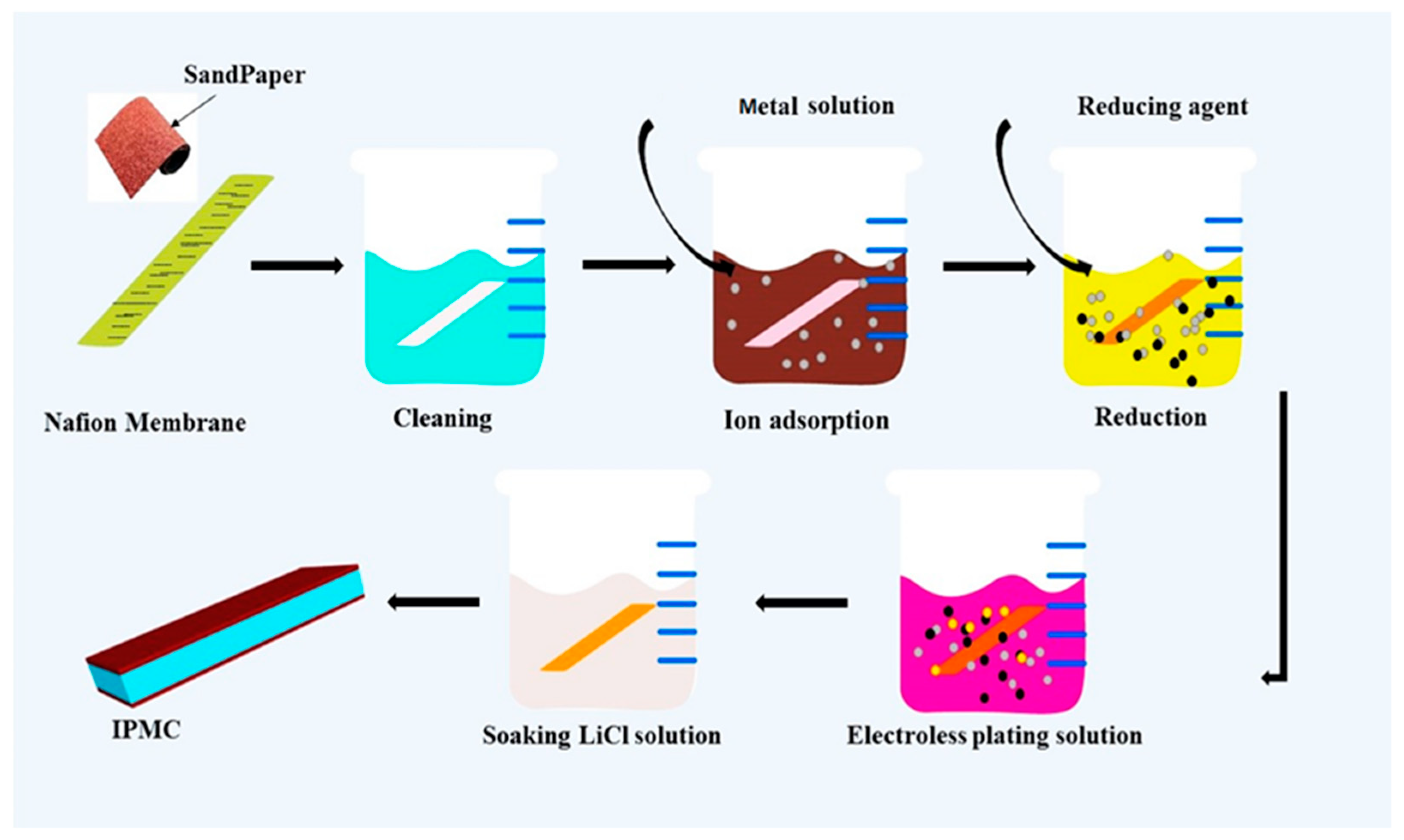



| CuSO4·5H2O | EDTA·2Na | 2,2-Dipyridine | HCHO | NaOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 g/L | 35 g/L | 0.05 g/L | 25 mL/L | Until PH-12.5 |
| Membrane | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-Cu | 779 ± 80 | 29.1 ± 8 | 67.3 ± 12 |
| Cu-Ag | 628 ± 65 | 23.5 ± 5 | 97.4 ± 7 |
| Ag-Cu | 470 ± 42 | 25.8 ± 2 | 158 ± 4 |
| Membrane | Adhesive Strength (P) N/mm2 | Max. Coefficient of Friction (CoF) |
|---|---|---|
| Cu-Cu | 0.032 | 0.019 |
| Cu-Ag | 0.051 | 0.014 |
| Ag-Cu | 0.068 | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avvari, V.D.; Sreekanth, P.S.R. Fabrication and Characterization of Cu2+-Driven PTFE-Reinforced Artificial Muscle Polymer Membrane for Water Purification and Energy Harvesting Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090766
Avvari VD, Sreekanth PSR. Fabrication and Characterization of Cu2+-Driven PTFE-Reinforced Artificial Muscle Polymer Membrane for Water Purification and Energy Harvesting Applications. Membranes. 2023; 13(9):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090766
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvvari, Venkata Dinesh, and P. S. Rama Sreekanth. 2023. "Fabrication and Characterization of Cu2+-Driven PTFE-Reinforced Artificial Muscle Polymer Membrane for Water Purification and Energy Harvesting Applications" Membranes 13, no. 9: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090766
APA StyleAvvari, V. D., & Sreekanth, P. S. R. (2023). Fabrication and Characterization of Cu2+-Driven PTFE-Reinforced Artificial Muscle Polymer Membrane for Water Purification and Energy Harvesting Applications. Membranes, 13(9), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090766






