Simultaneous Urea and Phosphate Recovery from Synthetic Urine by Electrochemical Stabilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membranes
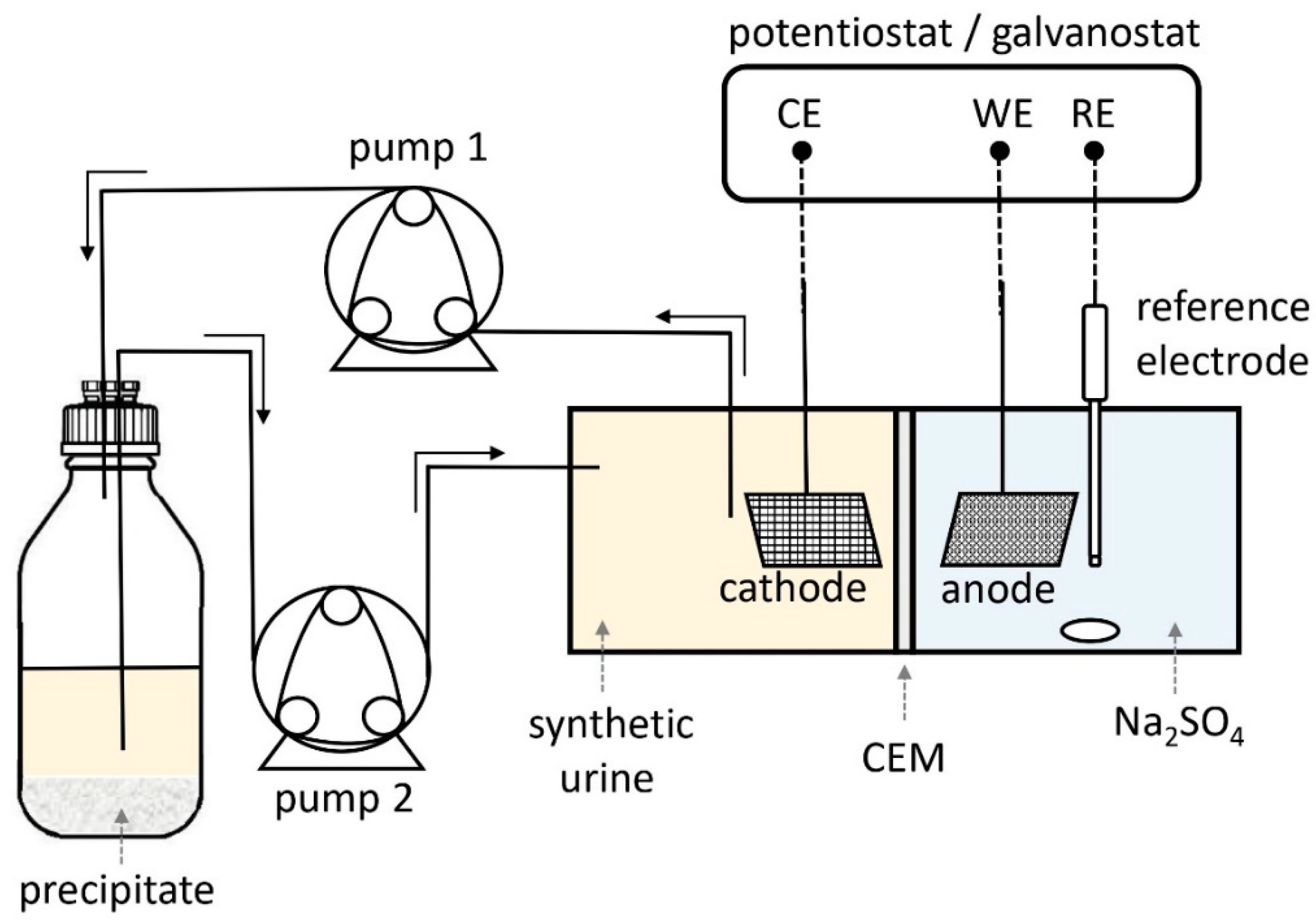
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Elecrochemical Stabilization Process
2.4. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
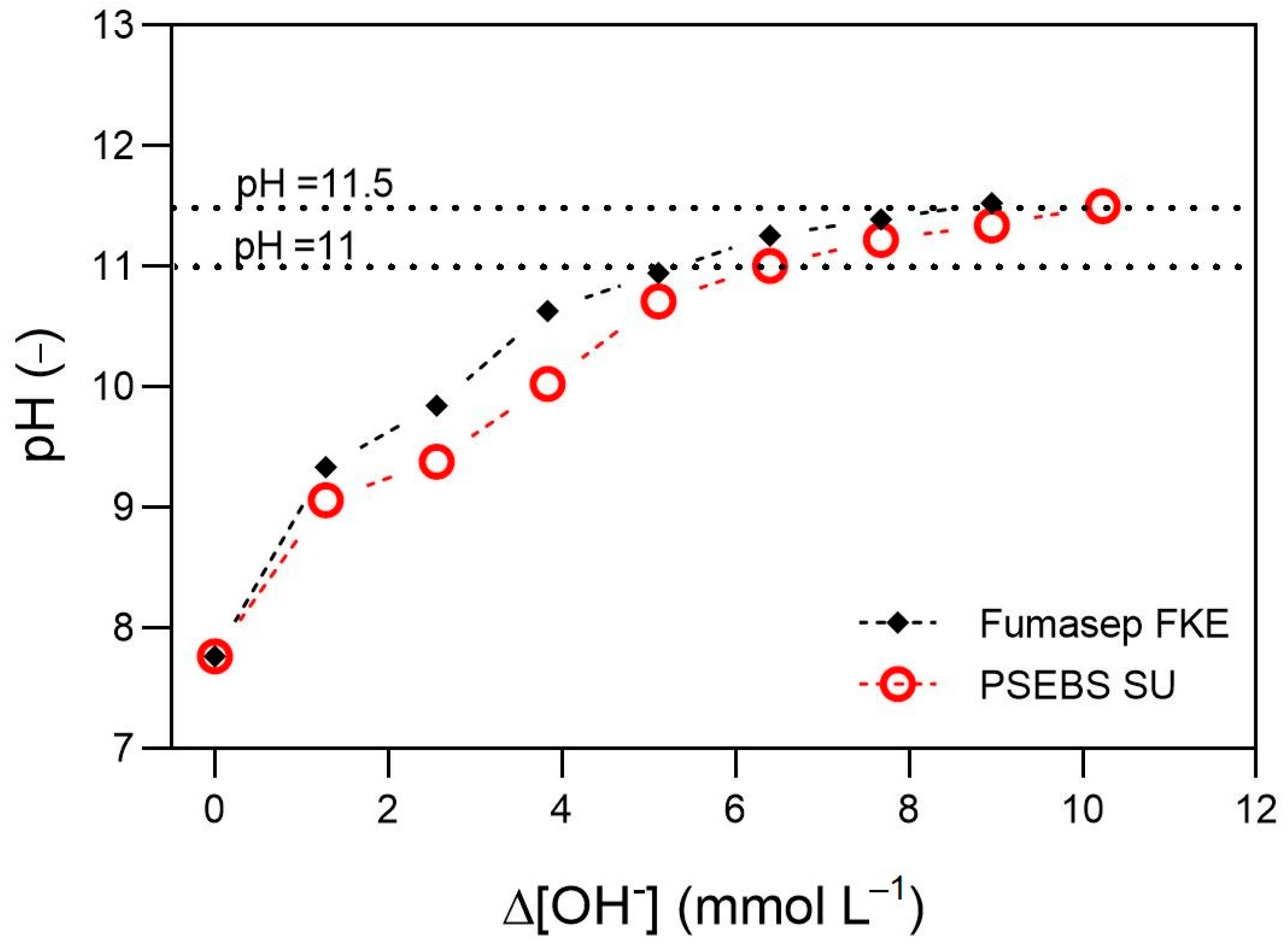
3.1. Electrochemical pH-Shift of Synthetic Urine
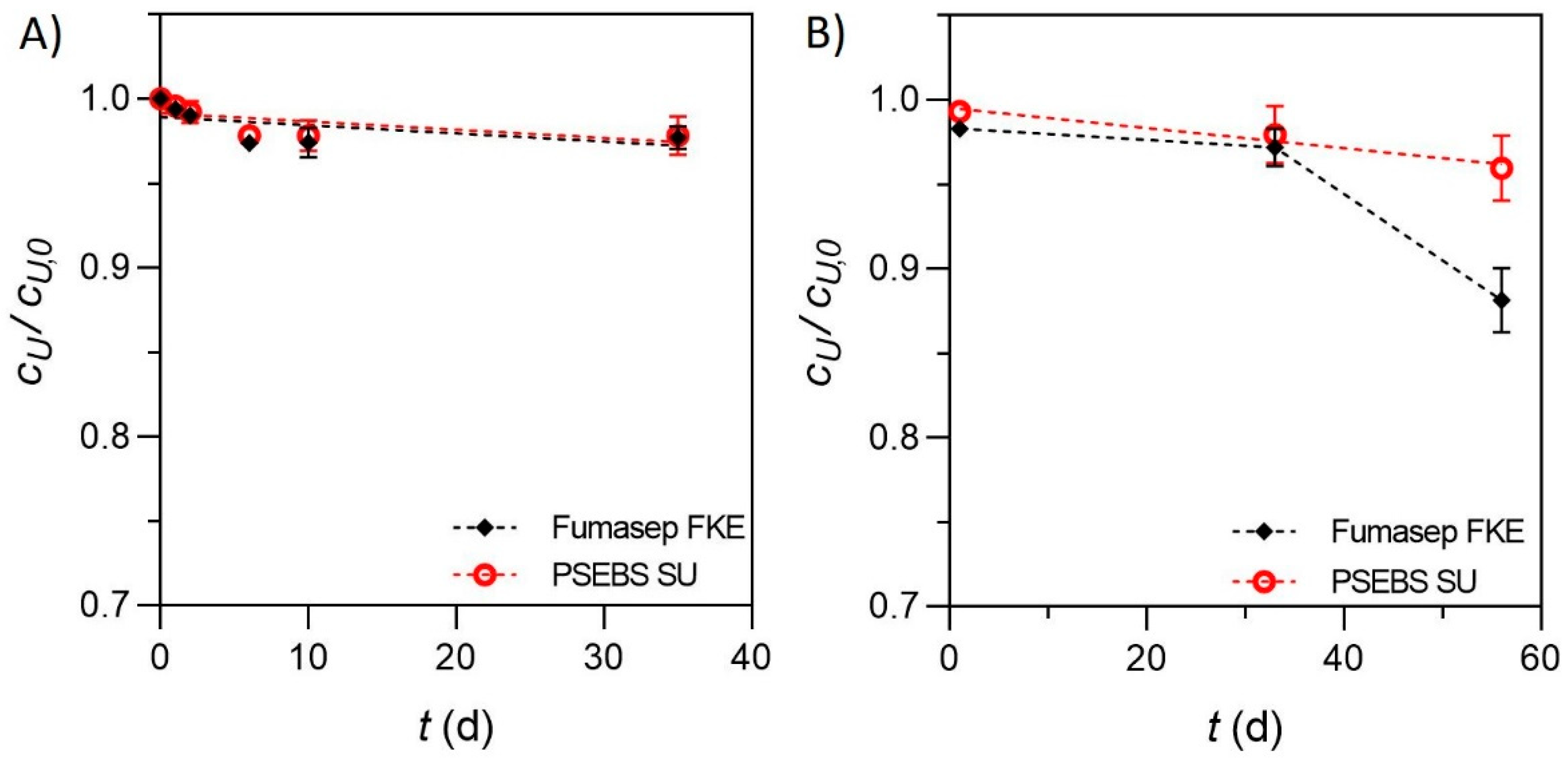
3.2. Assessment of Electrochemical Urea Stabilization
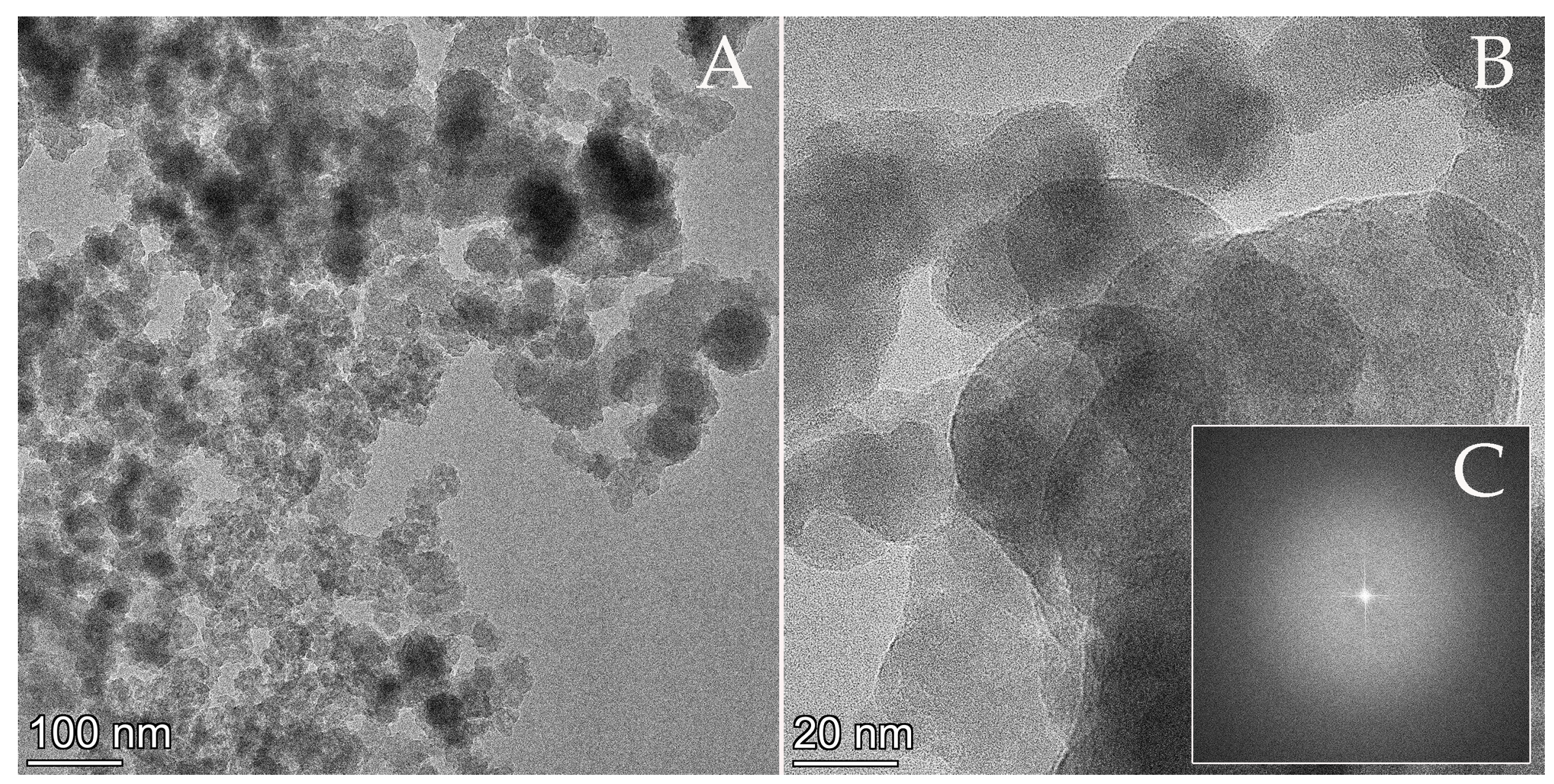
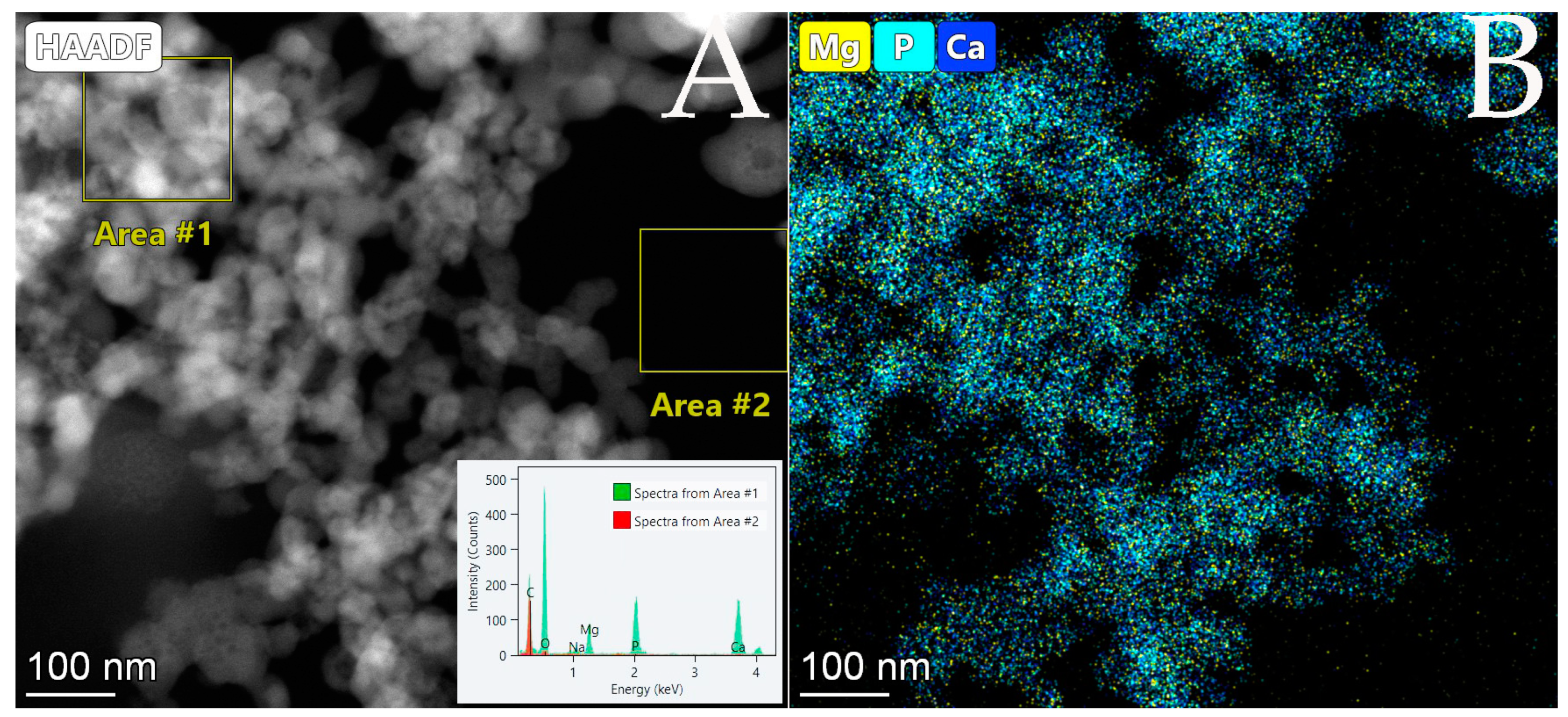
3.3. Efficiency of Simultaneous Phosphorous Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kavvada, O.; Tarpeh, W.A.; Horvath, A.; Nelson, K.L. Life-cycle cost and environmental assessment of decentralized nitrogen recovery using ion exchange from source-separated urine through spatial modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12061–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.F.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G.M.; Liu, H. Recent progress on the recovery of valuable resources from source-separated urine on-site using electrochemical technologies: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma, P.; Kuntke, P.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S. Source-separated urine opens golden opportunities for microbial electrochemical technologies. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, H.L.T.; Hausinger, R.P. Microbial ureases: Significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, H.; Saetta, D.; Boyer, T.H. Characterization of urea hydrolysis in fresh human urine and inhibition by chemical addition. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udert, K.M.; Larsen, T.A.; Gujer, W. Fate of major compounds in source-separated urine. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.A.; Udert, K.M.; Lienert, J. Source Separation and Decentralization for Wastewater Management; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Udert, K.M.; Larsen, T.A.; Biebow, M.; Gujer, W. Urea hydrolysis and precipitation dynamics in a urine-collecting system. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udert, K.M.; Larsen, T.A.; Gujer, W. Estimating the precipitation potential in urine-collecting systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.A.; Riechmann, M.E.; Udert, K.M. State of the art of urine treatment technologies: A critical review. Water Res. X 2021, 13, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arve, P.H.; Popat, S.C. Stabilization of Urea for Recovery from Source-Separated Urine Using Electrochemically Synthesized Hydrogen Peroxide. ACS ES&T Eng. 2021, 1, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arve, P. Stabilization of Urea in Urine through the Electrochemical Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2022, MA2022-02, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, R.; Mao, Y.; Peng, S.; Li, Z.; Zong, Y.; Wu, D. Selective recovery of phosphorus and urea from fresh human urine using a liquid membrane chamber integrated flow-electrode electrochemical system. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.K.; Englehardt, J.D. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater by electrochemical pH modulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, J.; De Pryck, L.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Rabaey, K.; Clauwaert, P. Electrochemically Induced Precipitation Enables Fresh Urine Stabilization and Facilitates Source Separation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Im, S.J.; Muthuraj, V.; Jang, A. Electrochemical recovery of H2 and nutrients (N, P) from synthetic source separate urine water. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.K.; Englehardt, J.D.; Cohn, J.L.; Dauer, E.A.; Shukla, D. Electrohydromodulation for phosphate recovery from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, D.; Johansson, E.; Grennberg, K. Storage of human urine: Acidification as a method to inhibit decomposition of urea. Ecol. Eng. 1999, 12, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Mahmood, I.B. Stabilization of source-separated human urine by chemical oxidation. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.G.; Naidoo, V. Urine: The liquid gold of wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.G.; Krähenbühl, M.; Köpping, I.; Larsen, T.A.; Udert, K.M. A novel approach for stabilizing fresh urine by calcium hydroxide addition. Water Res. 2016, 95, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Rosa, L.F.M.; Harnisch, F.; Žitka, J.; Otmar, M.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bakonyi, P.; Kretzschmar, J. Functional stability of novel homogeneous and heterogeneous cation exchange membranes for abiotic and microbial electrochemical technologies. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 658, 120705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigul, N.; Korkmaz, F.; Kurultak, İ. A New Artificial Urine Protocol to Better Imitate Human Urine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseney, R.C.; Finney, K.F. Spectrophotometric Determination of Urea, Thiourea, and Certain of Their Substitution Products with p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde and Diacetylmonoxime. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, W.A.; Tabatabai, M.A. Determination of Orthophosphate in Aqueous Solutions Containing Labile Organic and Inorganic Phosphorus Compounds. J. Environ. Qual. 1977, 6, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, C.A.; Jasper, J.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Phosphate Recovery from Human Waste via the Formation of Hydroxyapatite during Electrochemical Wastewater Treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koók, L.; Nagy, K.B.; Nyirő-Kósa, I.; Kovács, S.; Žitka, J.; Otmar, M.; Bakonyi, P.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. Simultaneous Urea and Phosphate Recovery from Synthetic Urine by Electrochemical Stabilization. Membranes 2023, 13, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080699
Koók L, Nagy KB, Nyirő-Kósa I, Kovács S, Žitka J, Otmar M, Bakonyi P, Nemestóthy N, Bélafi-Bakó K. Simultaneous Urea and Phosphate Recovery from Synthetic Urine by Electrochemical Stabilization. Membranes. 2023; 13(8):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080699
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoók, László, Kristóf Bence Nagy, Ilona Nyirő-Kósa, Szilveszter Kovács, Jan Žitka, Miroslav Otmar, Péter Bakonyi, Nándor Nemestóthy, and Katalin Bélafi-Bakó. 2023. "Simultaneous Urea and Phosphate Recovery from Synthetic Urine by Electrochemical Stabilization" Membranes 13, no. 8: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080699
APA StyleKoók, L., Nagy, K. B., Nyirő-Kósa, I., Kovács, S., Žitka, J., Otmar, M., Bakonyi, P., Nemestóthy, N., & Bélafi-Bakó, K. (2023). Simultaneous Urea and Phosphate Recovery from Synthetic Urine by Electrochemical Stabilization. Membranes, 13(8), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080699







