Monitoring of Particulate Fouling Potential of Feed Water with Spectroscopic Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models
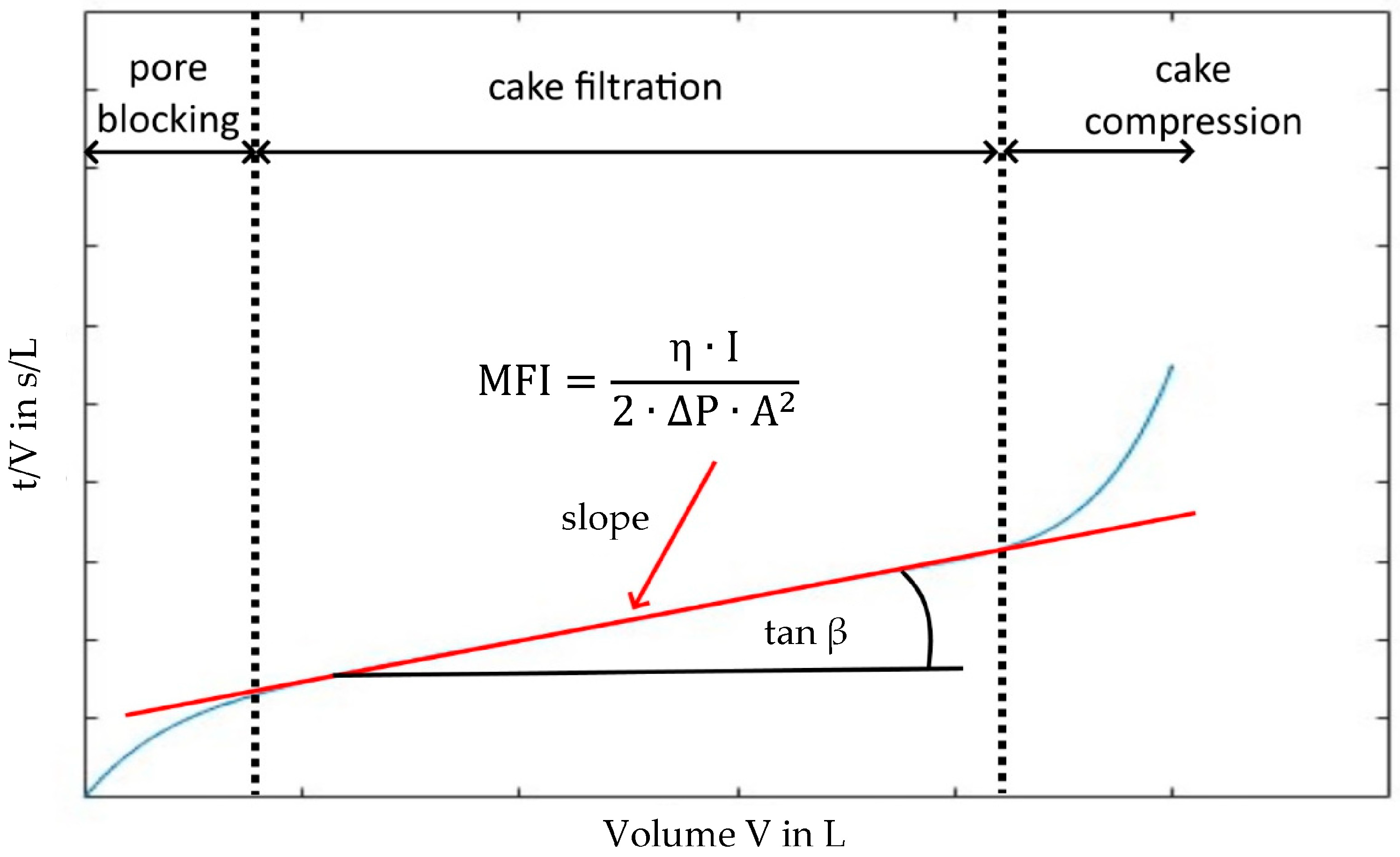
2.1. Modified Fouling Index (MFI)
2.2. Basics of the Spectral Extinction Method
2.2.1. Beer–Lambert Law and Light Scattering
- : Rayleigh regimehomogeneous scattering around the particle;
- : Mie regimecomplex scattering distribution around the particle;
- : Fraunhofer regimescattering according to geometrical optics.
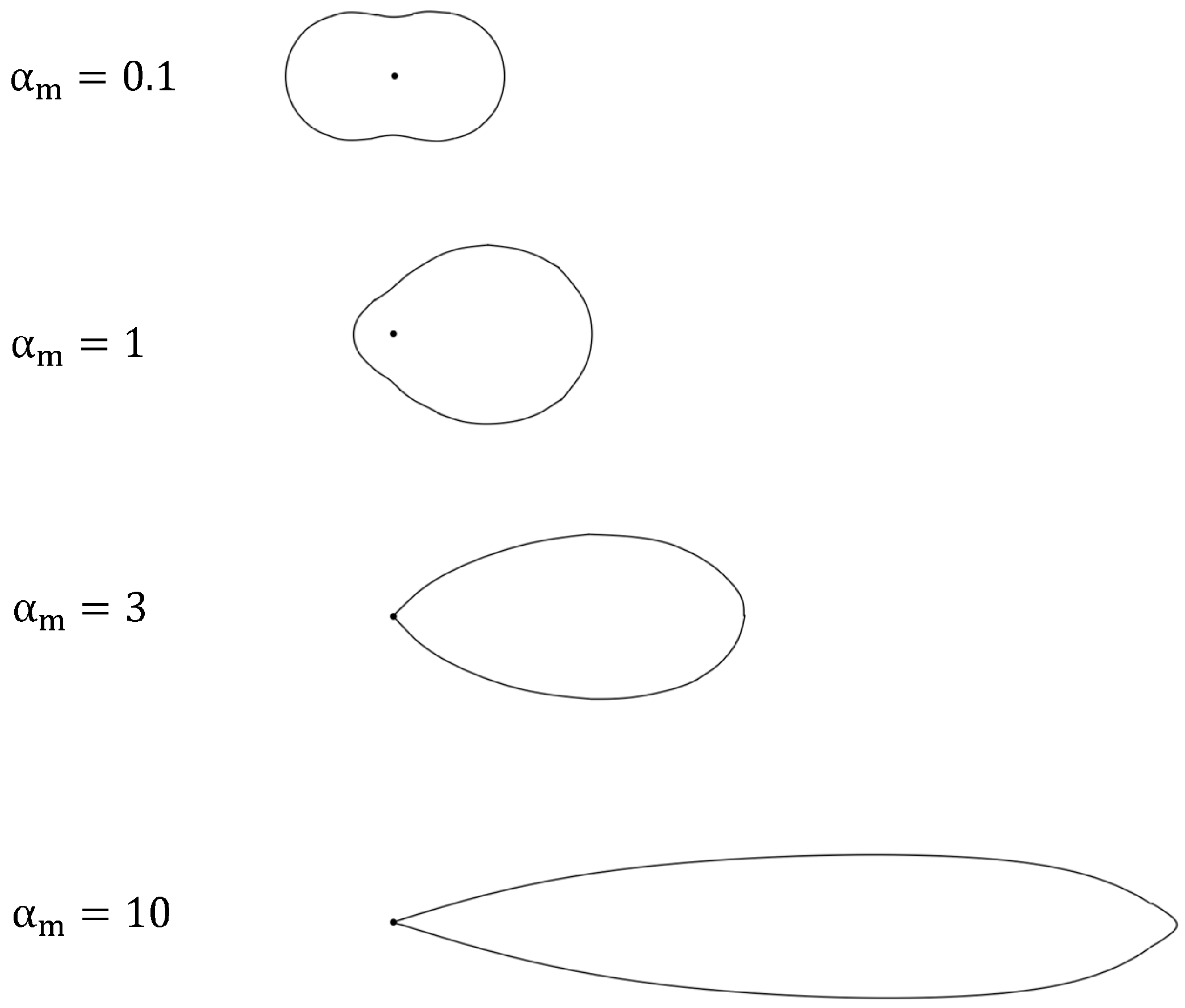
2.2.2. Mie Theory and BH Algorithm
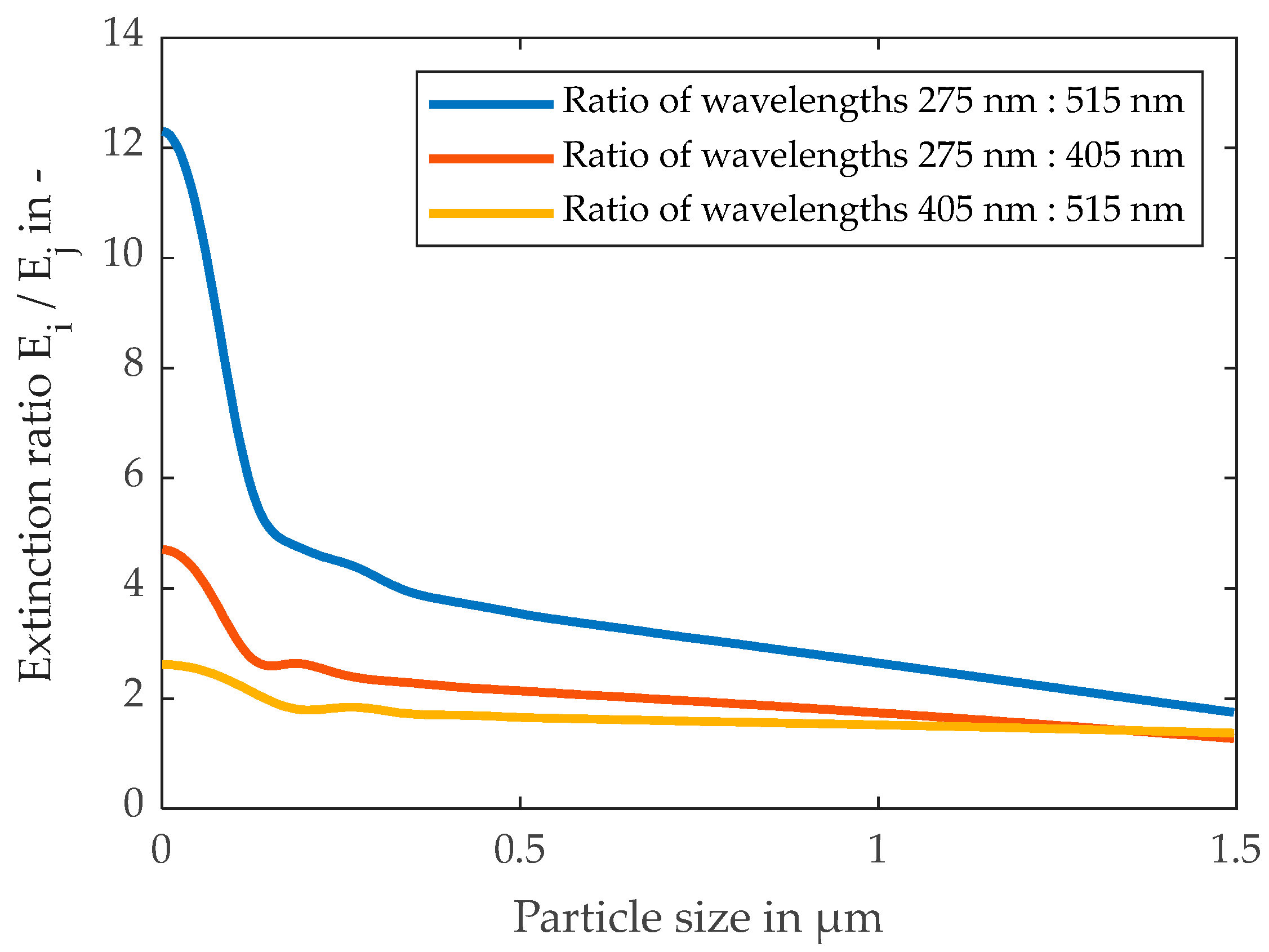
2.2.3. Spectral Extinction Method
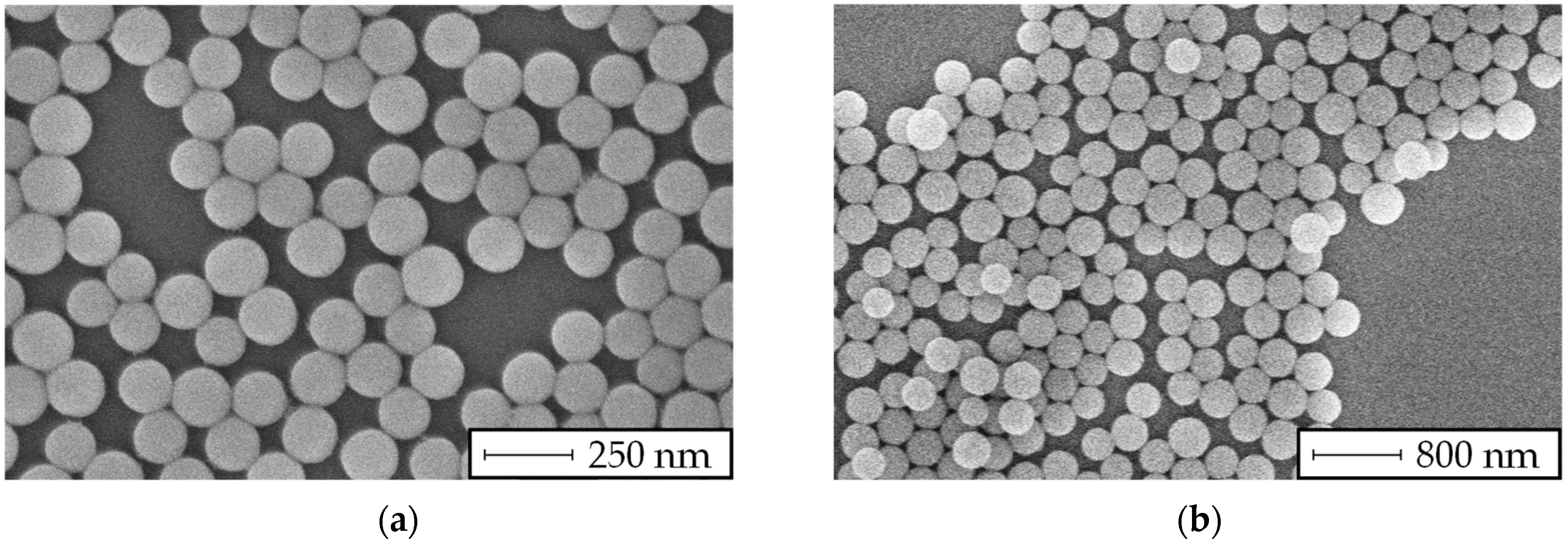
2.3. Modified Stöber Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals for the Particle Synthesis by the Modified Stöber Process
3.2. Materials for MFI Testing
3.3. Experimental Setup for Combined Fouling Potential Measurements and Test Conditions
4. Results
4.1. Experiments with Monomodal Silica Foulants
4.1.1. Light Transmission of the Model Foulants
4.1.2. MFI Measurement with 0.45 µm PES Membrane
4.1.3. Comparison of MFI0.45 and Spectroscopic Measurements
4.2. Experiments with Bimodal Silica Foulants
4.2.1. Comparison of MFI0.45 and Spectroscopic Measurements
4.2.2. Comparison of MFI0.1 and Spectroscopic Measurements
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Online monitoring of the particulate fouling potential of RO feedwater is theoretically possible as shown through measurements with a silica model foulant.
- Different foulants and therefore specific filter cake resistances are distinguishable by the extinction ratio of different wavelengths. Yet, the results show a significant measurement error and the test setup needs improvement.
- A linear correlation between MFI and the extinction of UV275nm light is given as long as sufficient filter cake is formed during the test filtration.
- The shown correlation improves, if the test membrane’s pore size is smaller than the smallest particle fraction of the feedwater. Therefore, it is advisable to perform an MFI-UF test instead of the standardized MFI0.45 test to evaluate the fouling potential of real-world RO feed water.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, N.N.; Fane, A.G.; Ho, W.W.; Matsuura, T. Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; (AIChE-100); Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Missimer, T.M.; Jones, B.; Maliva, R.G. Environmental Science and Engineering: Intakes and Outfalls for Seawater Reverse-Osmosis Desalination Facilities: Innovations and Environmental Impacts; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Melián-Martel, N.; Nuez, I. Short Review on Predicting Fouling in RO Desalination. Membranes 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D4189-14; Standard Test Method for Silt Density Index (SDI) of Water. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- EPA 815-R-06-009; Membrane Filtration Guidance Manual. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Alhadidi, A.; Kemperman, A.J.; Schippers, J.C.; Wessling, M.; Van Der Meer, W.G. The influence of membrane properties on the Silt Density Index. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, J.C.; Verdouw, J. The modified fouling index, a method of determining the fouling characteristics of water. Desalination 1980, 32, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Amy, G.L.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D. The Modified Fouling Index Ultrafiltration constant flux for assessing particulate/colloidal fouling of RO systems. Desalination 2015, 365, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunada, M.; Dhakal, N.; Gulrez, R.; Ajok, P.; Li, Y.; Abushaban, A.; Smit, H.; Moed, D.; Ghaffour, N.; Schippers, J.C.; et al. Prediction of particulate fouling in full-scale reverse osmosis plants using the modified fouling index—Ultrafiltration (MFI-UF) method. Desalination 2023, 553, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunada, M.; Dhakal, N.; Andyar, W.Z.; Ajok, P.; Smit, H.; Ghaffour, N.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D. Improving MFI-UF constant flux to more accurately predict particulate fouling in RO systems: Quantifying the effect of membrane surface porosity. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D8002-15; Standard Test Method for Modified Fouling Index (MFI-0.45) of Water. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Mosset, A.; Bonnelye, V.; Petry, M.; Sanz, M.A. The sensitivity of SDI analysis: From RO feed water to raw water. Desalination 2008, 222, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujundzic, E.; Greenberg, A.R.; Fong, R.; Hernandez, M. Monitoring protein fouling on polymeric membranes using ultrasonic frequency-domain reflectometry. Membranes 2011, 1, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, Y.; Hazut, A.; Spanier, A. Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method. Membranes 2022, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, L. Messverfahren zum Monitoring von Fällungsprozessen sowie Untersuchung eines neuen Verfahrens zur CaCo3-Fällung. Doctoral Dissertation, Technische Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ripperger, S.; Gösele, W.; Alt, C.; Loewe, T. Filtration, 1. Fundamentals. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Benz, N.; Lösch, P.; Antonyuk, S. Influence of the Measurement Resolution on the Filtration Analysis: An Improved Test Setup According to VDI 2762 Guideline. Processes 2023, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer. Bestimmung der Absorption des rothen Lichts in farbigen Flüssigkeiten. Ann. Der Phys. Und Chem. 1852, 162, 78–88. [CrossRef]
- Bouguer, P. Essai D’optique sur la Gradation de la Lumière; Claude Jombert: Paris, France, 1729. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.H. Photometrie: (Photometria, sive De Mensura et Gradibus Luminis, Colorum et Umbrae (1760)); W. Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1892. [Google Scholar]
- Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann. Der Phys. Und Chem. 1908, 330, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchener, B.G.; Wainwright, J.; Parsons, A.J. A review of the principles of turbidity measurement. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2017, 41, 620–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru, A. Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hulst, H.C.; van de Hulst, H.C. Light Scattering by Small Particles; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA; Melbourne, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schaber, K.; Schenkel, A.; Zahoransky, R.A. Drei-Wellenlängen-Extinktionsverfahren zur Charakterisierung von Aerosolen unter industriellen Bedingungen. tm-Tech. Mess. 1994, 61, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, L.; Wessely, B.; Ripperger, S. Optische Extinktionsmessverfahren zur Inline-Kontrolle Disperser Stoffsysteme. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2009, 81, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Gao, H. Spectrometric characterization of suspension liquid and light extinction model update. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 296, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Blaaderen, A.; Kentgens AP, M. Particle morphology and chemical microstructure of colloidal silica spheres made from alkoxysilanes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 149, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, N. Herstellung von Größenkontrollierten, Modifizierten SiO2-Partikeln nach Stöber und ihr Einfluss auf das Tribologische Verhalten von Epoxidharz-Kompositen. Doctoral Dissertation, Technische Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, T. Zum Fällungsprozess und Wachstum kugelförmiger SiO2-Partikel. Doctoral Dissertation, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, N.; Ripperger, S.; Antonyuk, S. Investigations on the Capability of the Statistical Extinction Method for the Determination of Mean Particle Sizes in Concentrated Particle Systems. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N. Messfähigkeit der Statistischen Extinktionsmethode zur Inline-Messung der Partikelgröße, der Partikelkonzentration und der Partikelgeschwindigkeit; Technische Universität Kaiserslautern: Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hund, D.; Lösch, P.; Kerner, M.; Ripperger, S.; Antonyuk, S. CFD-DEM study of bridging mechanisms at the static solid-liquid surface filtration. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI 2762 Blatt 2; Mechanical Solid-Liquid Separation by Cake Filtration–Determination of Filter Cake Resistance. Accuris Standards: Englewood, CO, USA, 2010.
- Hesse, R.; Lösch, P.; Antonyuk, S. CFD-DEM analysis of internal packing structure and pressure characteristics in compressible filter cakes using a novel elastic–plastic contact model. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, H.; Jin, Y.O.; Hong, S. Application of multiple modified fouling index (MFI) measurements at full-scale SWRO plant. Desalination 2017, 407, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
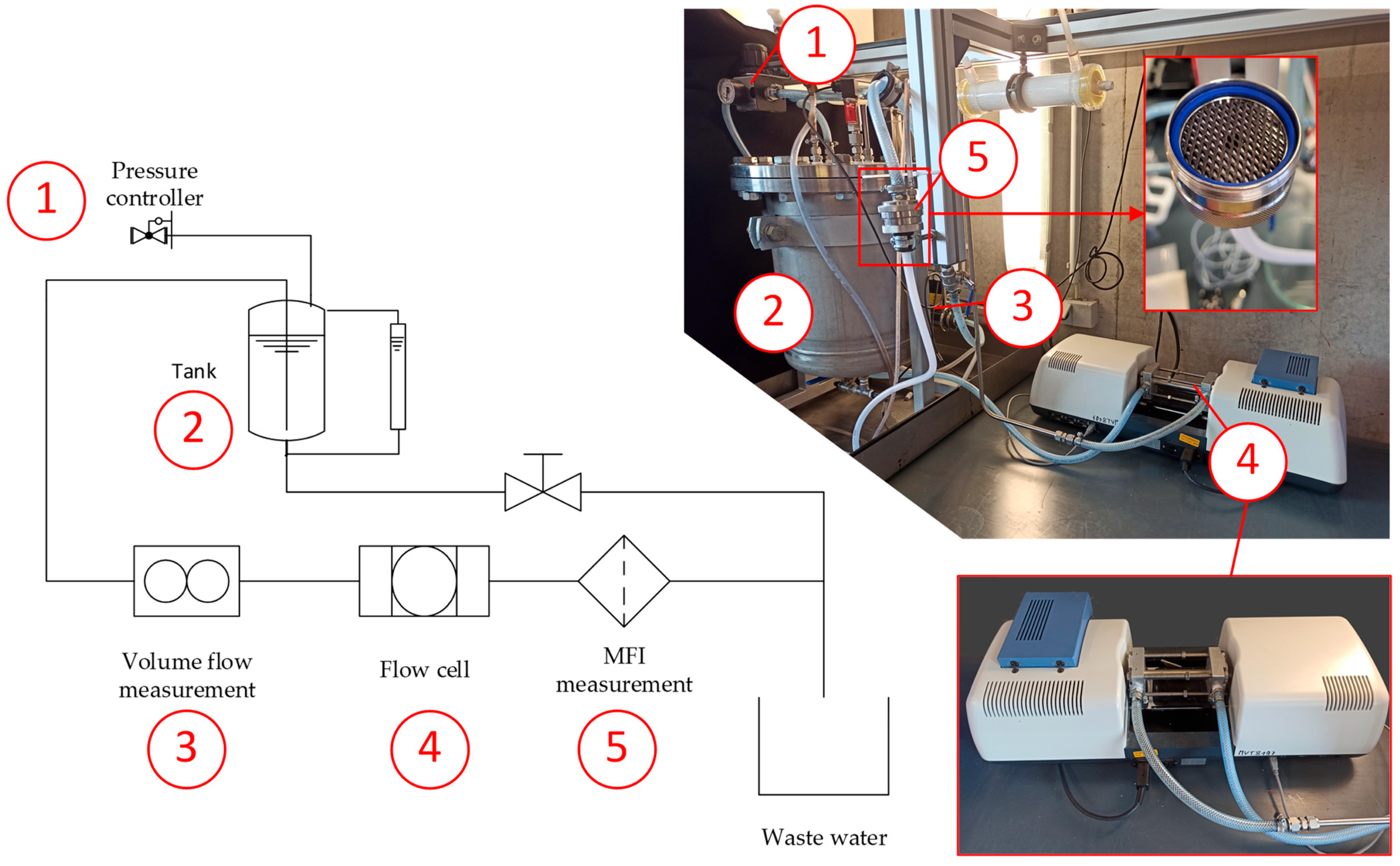

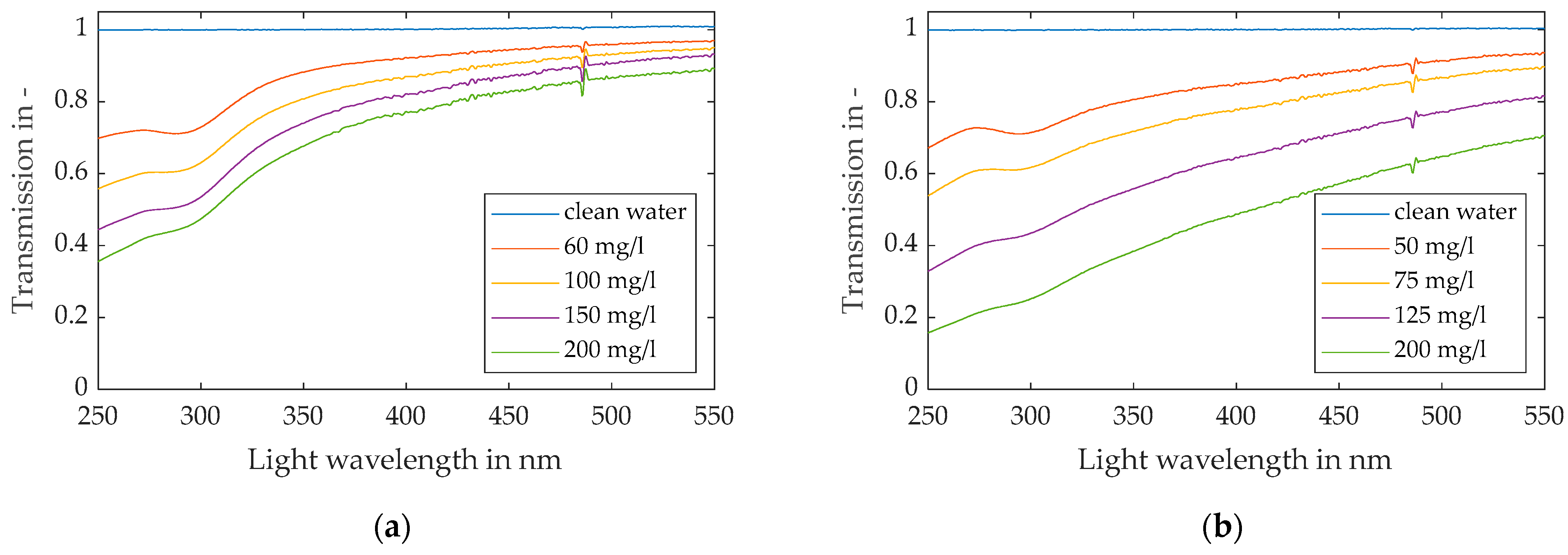
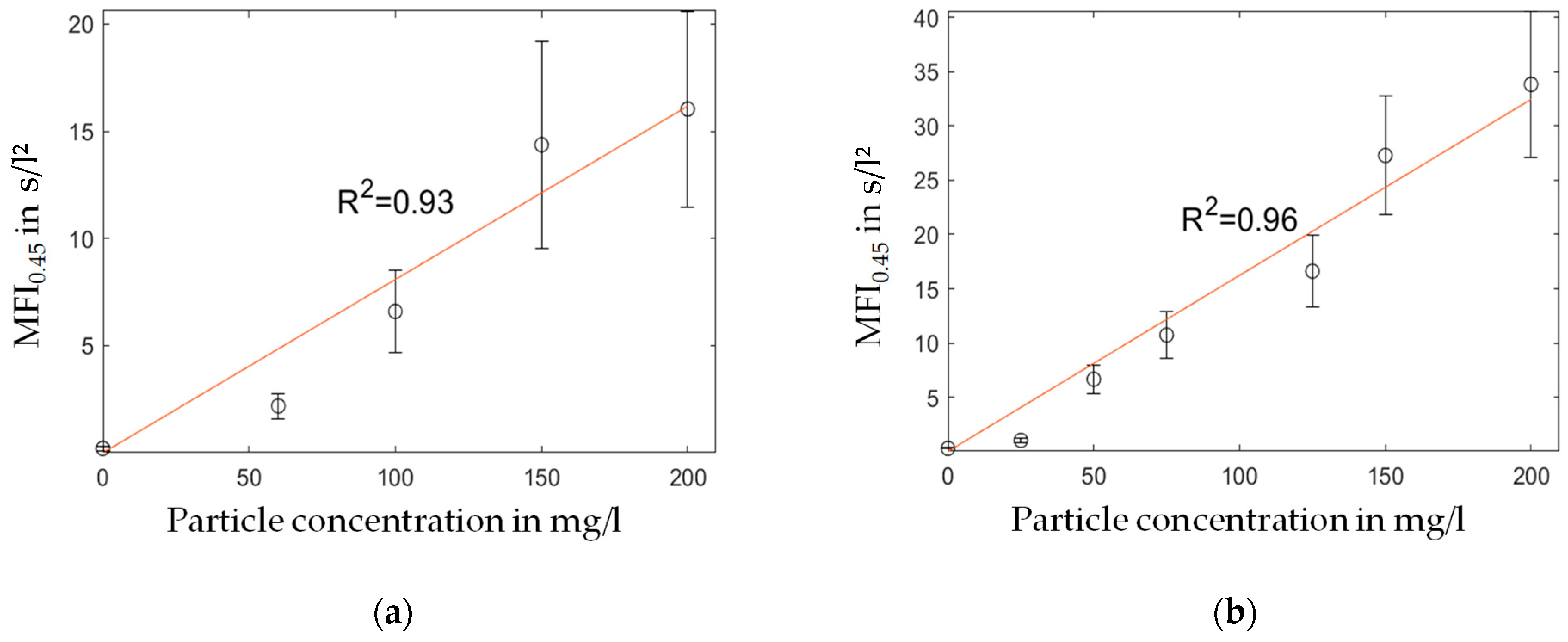
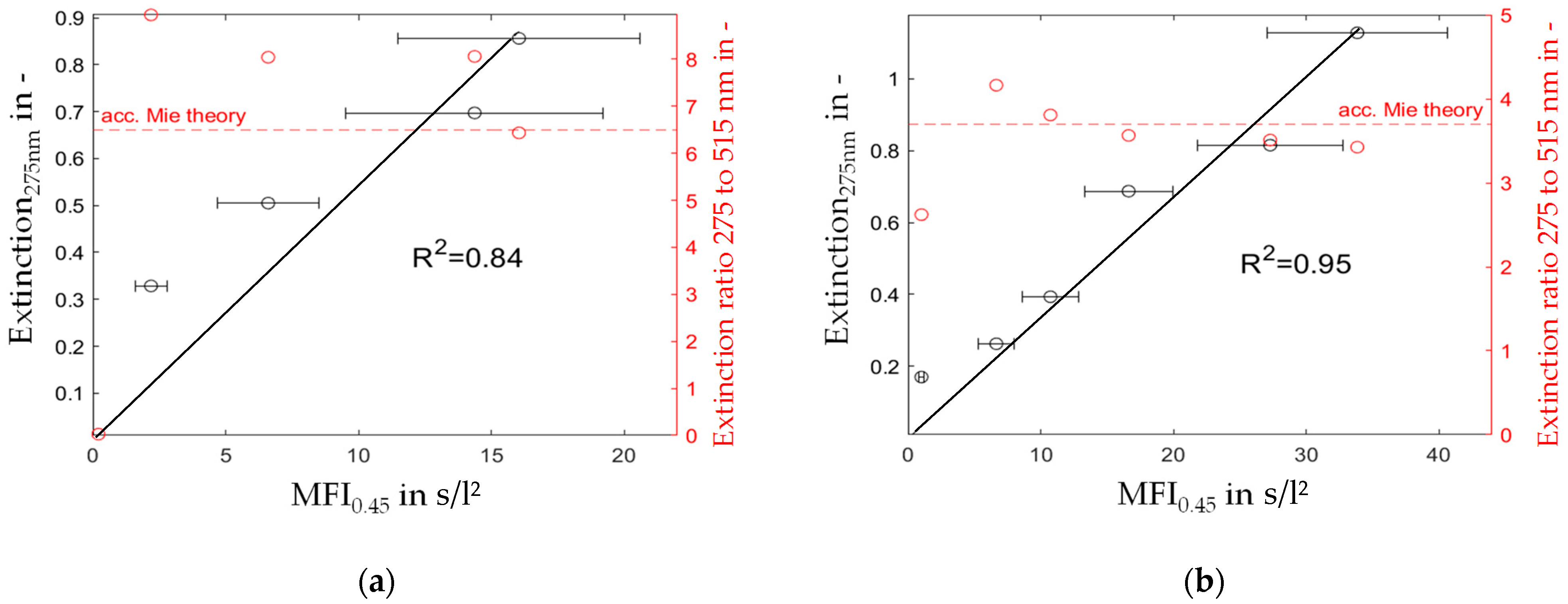
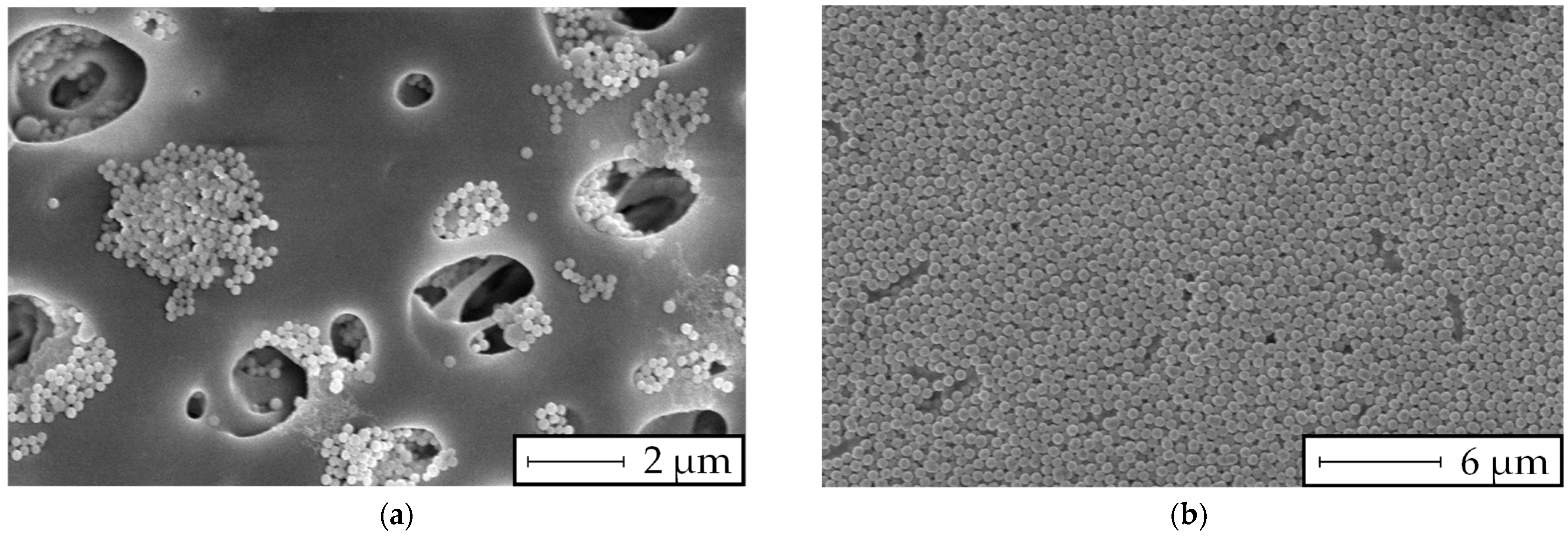

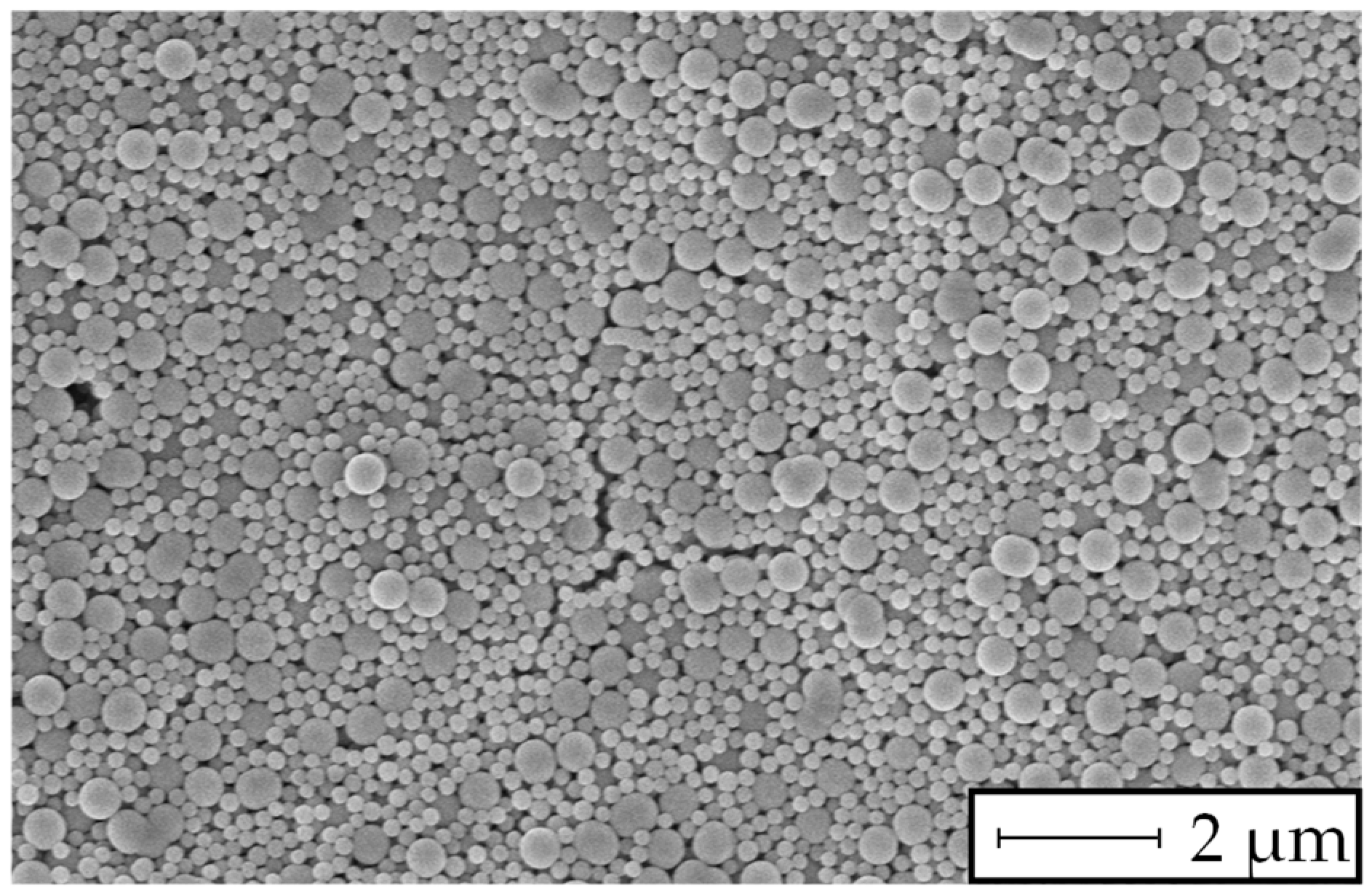

| Chemical | Ammonia | Ethanol | TEOS | TMED | Isopropanol | Di water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | 25 wt% | 99.9% | >99% | >99% | 99.5% | < 0.1 µS/cm |
| Supplier | Grüssing GmbH, Filsum, Germany | Th. Geyer GmbH & Co. KG, Renningen, Germany | Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Taufkirchen, Germany | Merck Schuchardt OHG, Hohenbrunn, Germany | Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Germany | RO system + mixed bed desalination |
| Function | Catalyst | Co-solvent | Silicon source | Catalyst | Co-solvent | Solvent |
| Particle Size | 120 (±10) nm | 400 (±80) nm |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction temperature | 55 °C | 30 °C |
| Reaction time | 1 h | 2 h |
| Stirrer speed | 900 rpm | 900 rpm |
| Ethanol | - | 70 mL |
| Isopropanol | 70 mL | - |
| DI-water | 25 mL | 10 mL |
| Ammonia solution | 1.5 mL | 30 mL |
| TEOS | 6 mL | 12 mL |
| TMED | 0.4 mL | 3 mL |
| MFI Test Parameters | Optical Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test duration: | 15 min | Measurement interval: | 60 s | ||
| Filter media pore size: | 0.45 µm or 0.1 µm | Optical path length: | 150 mm | ||
| Filter media diameter: | 47 mm | Light wavelengths: | 275, 405 and 515 nm | ||
| Filtration pressure: | 2.07 bar (30 psi) | ||||
| Feed temperature: | 21 °C | ||||
| Mean Particle Size in nm: | 120 (±10) | 400 (±80) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 25 | ||
| 100 | 50 | ||
| Particle concentration in mg/L: | 150 | 75 | |
| 200 | 125 | ||
| 150 | |||
| 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weirich, M.; Antonyuk, S. Monitoring of Particulate Fouling Potential of Feed Water with Spectroscopic Measurements. Membranes 2023, 13, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070664
Weirich M, Antonyuk S. Monitoring of Particulate Fouling Potential of Feed Water with Spectroscopic Measurements. Membranes. 2023; 13(7):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070664
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeirich, Marc, and Sergiy Antonyuk. 2023. "Monitoring of Particulate Fouling Potential of Feed Water with Spectroscopic Measurements" Membranes 13, no. 7: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070664
APA StyleWeirich, M., & Antonyuk, S. (2023). Monitoring of Particulate Fouling Potential of Feed Water with Spectroscopic Measurements. Membranes, 13(7), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070664







