X-ray-Fluorescence-Based Screening Method for Uranium in Contaminated Brackish Water Using Graphene Oxide Nanosheets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Sampling of Seawater, Brackish Water, and River Water
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Standard Samples for Examination of the Solid–Liquid Ratio
2.3.2. River Water, Brackish Water, and Seawater Samples
2.3.3. Standard Samples for the Standard Addition Method and the Calibration Curve Method
2.3.4. Standard Samples for Determination of the Fitting Parameters
2.4. XRF Measurements
2.5. Peak Fitting
3. Results
3.1. Measured XRF Spectra for the Standard Sample
3.2. XRF Spectra of the River Water, Brackish Water, and Seawater Samples
3.3. Relationship between the Salinity and the Signal Intensity
3.4. Determination of the Uranium Concentration in Seawater
3.5. Calibration Curve and Determination of the DL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leggett, R.W. The behavior and bhemical toxicity of U in the kidney: A reassessment. Health Phys. 1989, 57, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.M.; Taylor, S.K. Environmental uranium and human health. Rev. Environ. Health 1997, 12, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma-Takeda, S.; Kokubo, T.; Terada, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Ueno, S.; Hayao, T.; Inoue, T.; Kitahara, K.; Blyth, B.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Uranium dynamics and developmental sensitivity in rat kidney. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T. Radioactivity of Fission Product and Heavy Nuclides Deposited on Soil in Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 1116–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Iizawa, Y.; Terada, Y.; Adachi, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Nakai, I. Detection of uranium and chemical state analysis of individual radioactive microparticles emitted from the Fukushima nuclear accident using multiple synchrotron radiation x-ray analyses. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8521–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grella, A.W. A Review of Selected Nuclear Transport Event Case Histories. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials, New Orleans, LA, USA, 15–20 May 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bleise, A.; Danesi, P.R.; Burkart, W. Properties, Use and health effects of depleted uranium (DU): A general overview. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 64, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDiarmid, M.A.; Engelhardt, S.; Oliver, M.; Gucer, P.; Wilson, P.D.; Kane, R.; Kabat, M.; Kaup, B.; Anderson, L.; Hoover, D.; et al. Health effects of depleted uranium on exposed gulf war veterans: A 10-year follow-up. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2004, 67, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Caritat, P. Chemical Elements in the Environment: Factsheets for the Geochemist and Environmental Scientist; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, S.; Tagami, K.; Tabei, K.; Hirai, I. Concentrations of REEs, Th and U in river waters collected in Japan. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, A.; Sugiyama, M. Natural background concentration of dissolved uranium in Japanese rivers. Jpn. J. Limnol. 2012, 73, 89–107. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboon, S.; Inoue, K.; Fukushi, M.; Tsuruoka, H.; Shimizu, H.; Kasar, S.; Arae, H.; Kavasi, N.; Sahoo, S.K. Distribution of uranium in Japanese river waters determined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2019, 319, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Kawabata, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Sakurai, N.; Kondo, K. Horizontal distribution profiles of 238U, 137Cs and stable elements in the bottom sediments of the brackish lake Obuchin in Aomori prefecture. Jpn. J. Limnol. 1998, 59, 159–173. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunk, R.M.; Mills, R.A.; Jenkins, W.J. A reevaluation of the oceanic uranium budget for the Holocene. Chem. Geol. 2002, 190, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Not, C.; Brown, K.; Ghaleb, B.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Conservative behavior of uranium vs. salinity in Arctic Sea ice and brine. Mar. Chem. 2012, 130, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, C.; Sander, J.M.; Kautenburger, R. New approach of a transient ICP-MS measurement method for samples with high salinity. Talanta 2017, 164, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, H.; Uwatoko, T.; Takahashi, H.; Sakai, Y. Determination of trace levels of uranium in waste solutions by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence following adsorption on graphene oxide. X-ray Spectrom. 2022, 51, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, Z.; Shi, W. Uranium(VI) adsorption on graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanchuk, A.Y.; Slesarev, A.S.; Kalmykov, S.N.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Tour, J.M. Graphene oxide for effective radionuclide removal. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Janik, P.; Zawisza, B.; Talik, E.; Margui, E.; Queralt, I. Green approach for ultratrace determination of divalent metal ions and arsenic species using total-reflection x-ray fluorescence spectrometry and mercapto-modified graphene oxide nanosheets as a novel adsorbent. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Helvenston, E.M.; Shuller-Nickles, L.C.; Powell, B.A. Surface complexation modeling of Eu(III) and U(VI) interactions with graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Izumoto, Y.; Matsuyama, T.; Yoshii, H. Trace determination of uranium preconcentrated using graphene oxide by total reflection x-ray fluorescence spectrometry. X-ray Spectrom. 2019, 48, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Izumoto, Y.; Ishii, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshii, H. Development of methods to evaluate several levels of uranium concentrations in drainage water using total reflection x-ray fluorescence technique. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, H.; Takamura, K.; Uwatoko, T.; Takahashi, H.; Sakai, Y. Screening of uranium contamination on waste surfaces using X-ray fluorescence analysis. Spectrochim. Acta B 2022, 189, 106368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumoto, Y.; Fukutsu, K.; Takamura, K.; Sakai, Y.; Oguri, Y.; Yoshii, H. Rapid detection of plutonium contamination with and without uranium contamination in wounds by x-ray fluorescence. J. Radiol. Prot. 2020, 40, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslattes, R.D.; Kessler, E.G., Jr.; Indelicato, P.; de Billy, L.; Lindroth, E.; Anton, J. X-ray transition energies: New approach to a comprehensive evaluation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 35–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Website of the Secretariat of the Nuclear Regulation Authority (S/NRA/R) of Japan. Available online: https://www.nsr.go.jp/data/000045581.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2022). (In Japanese)
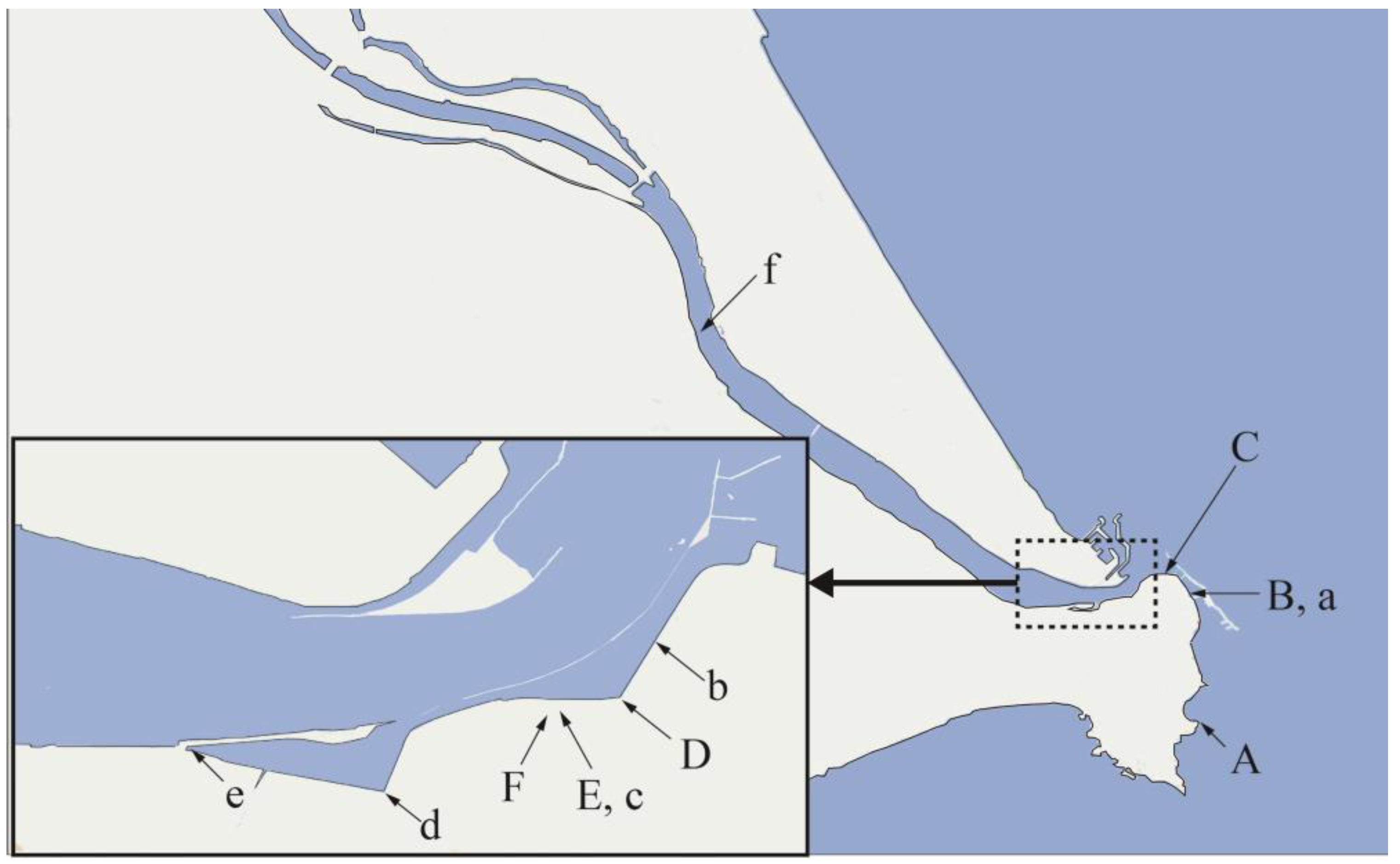
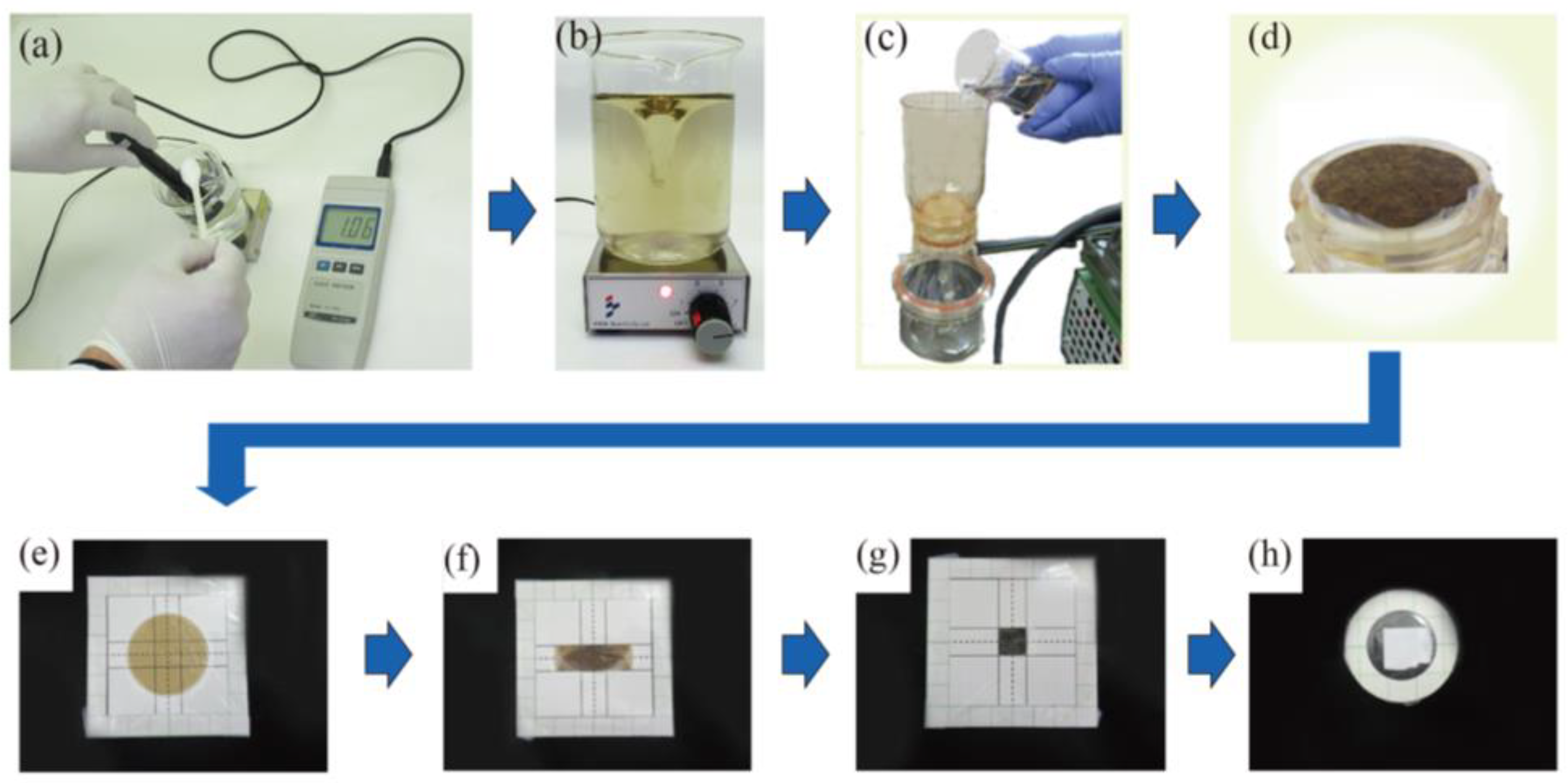

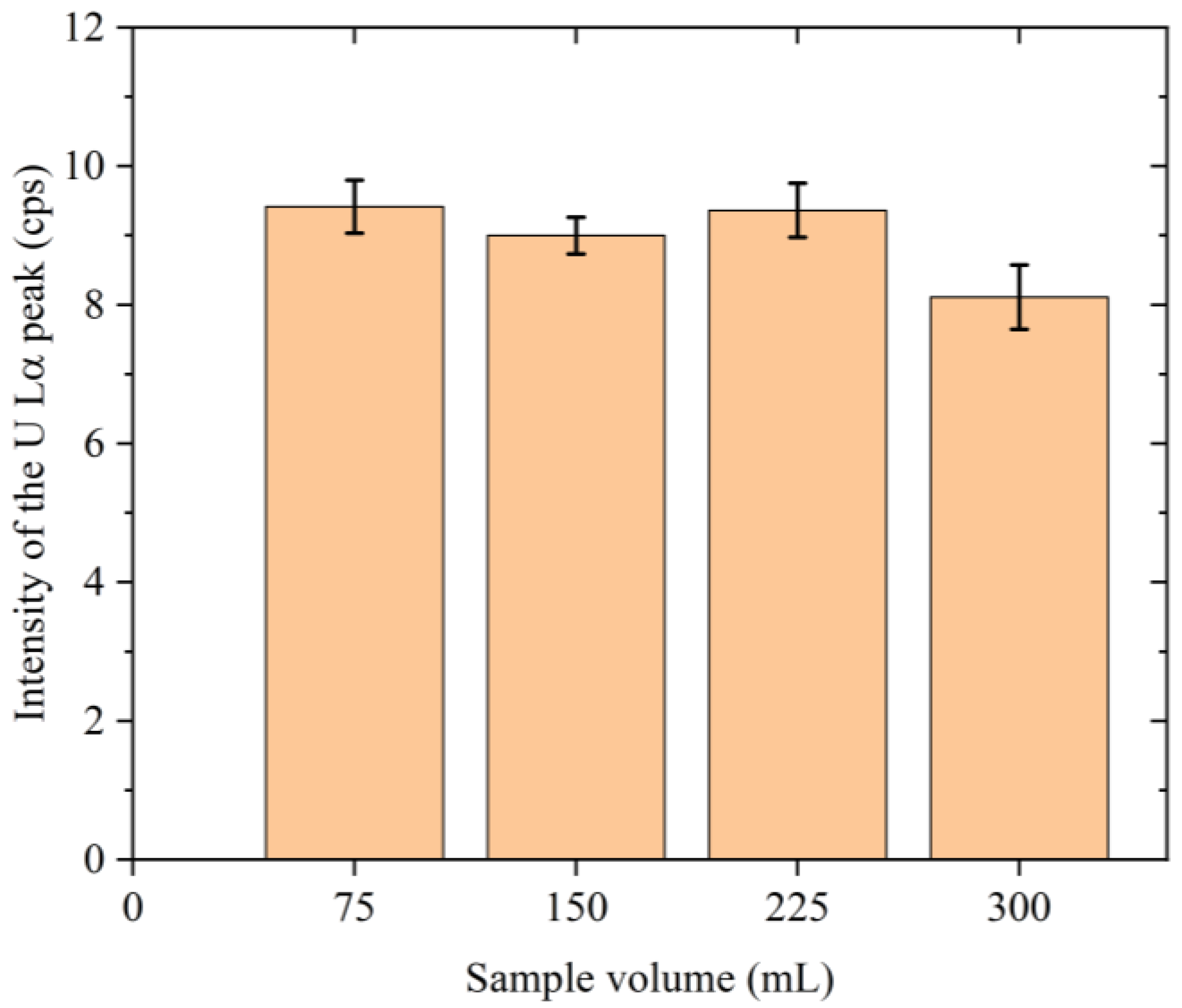
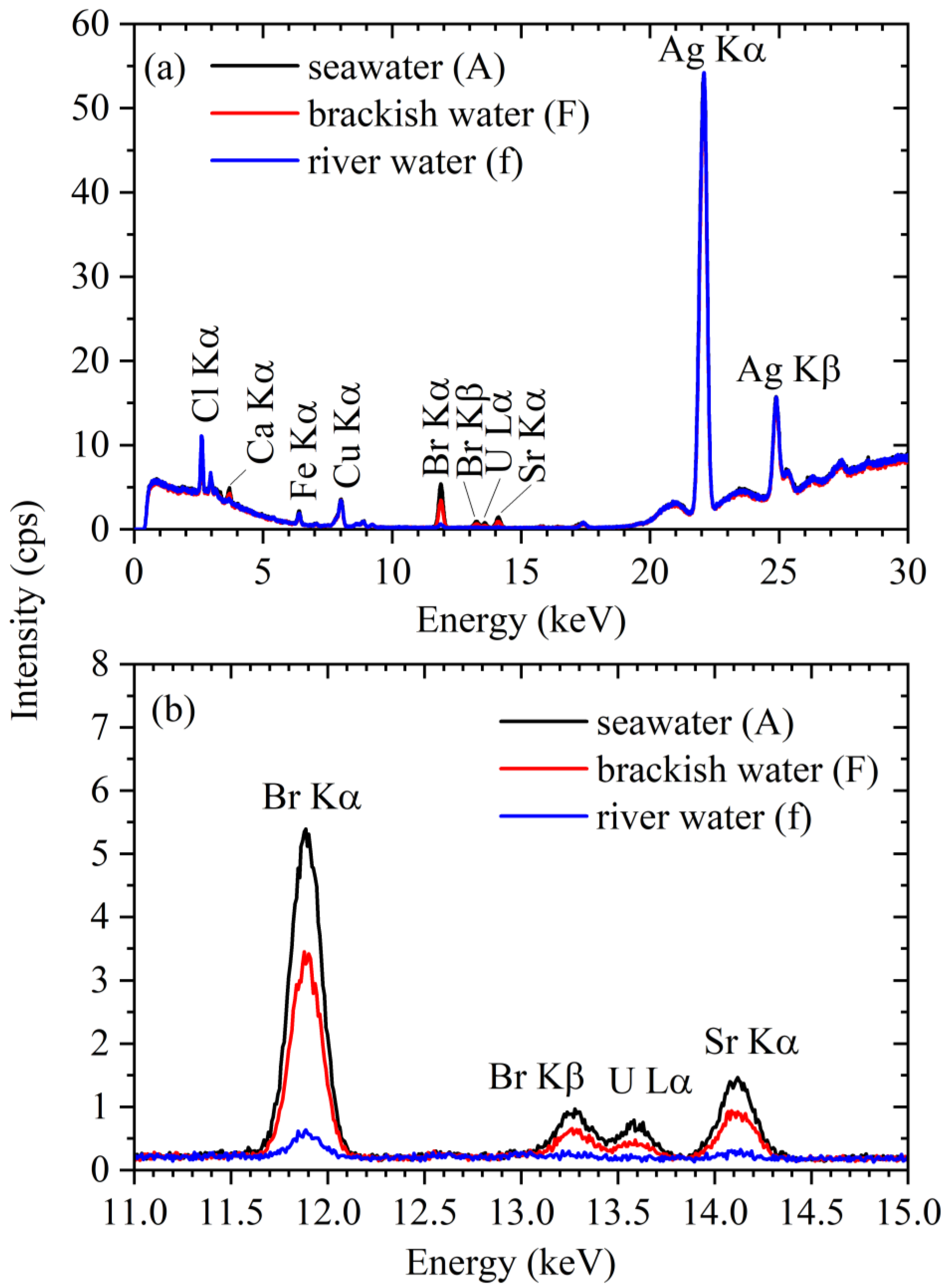
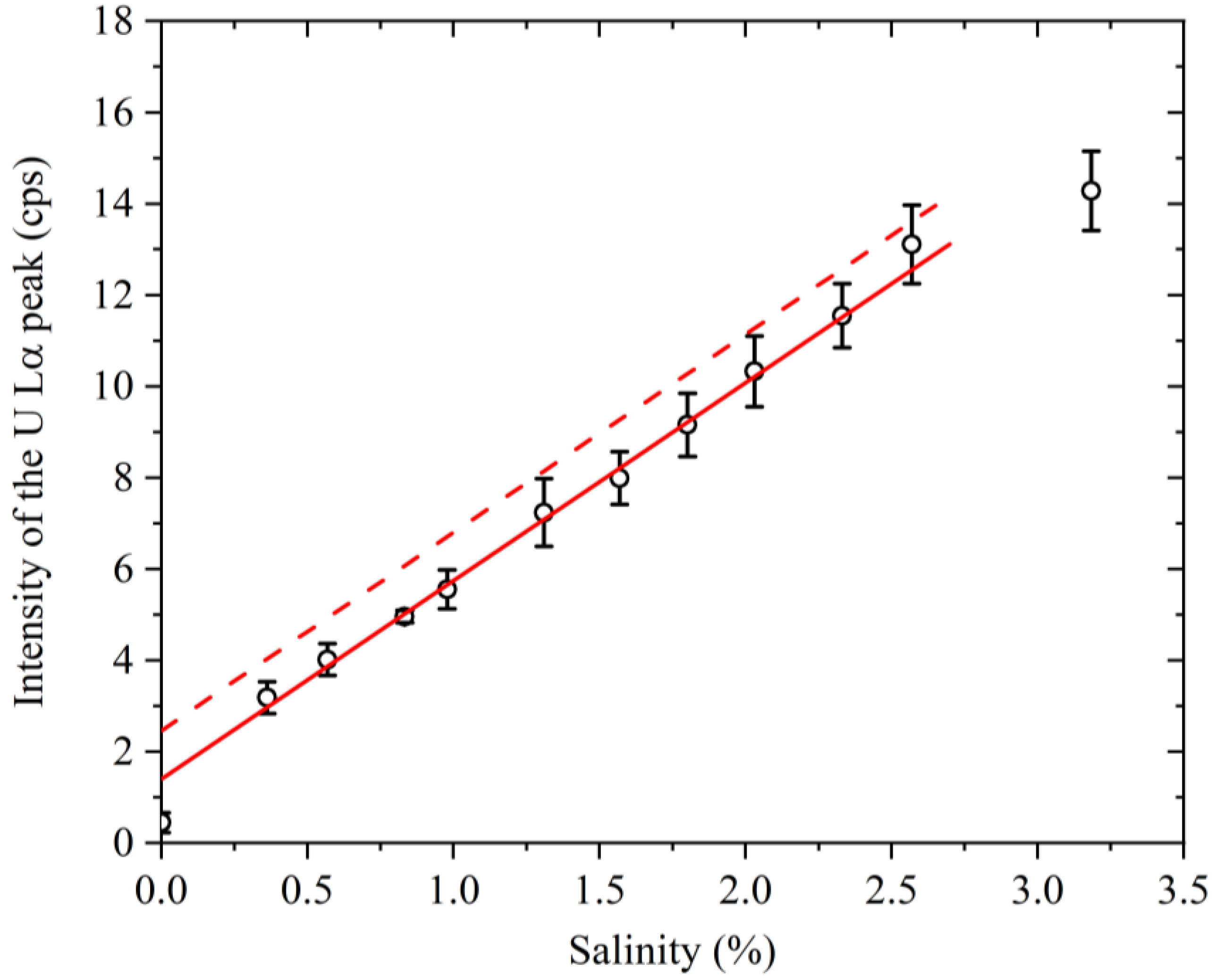
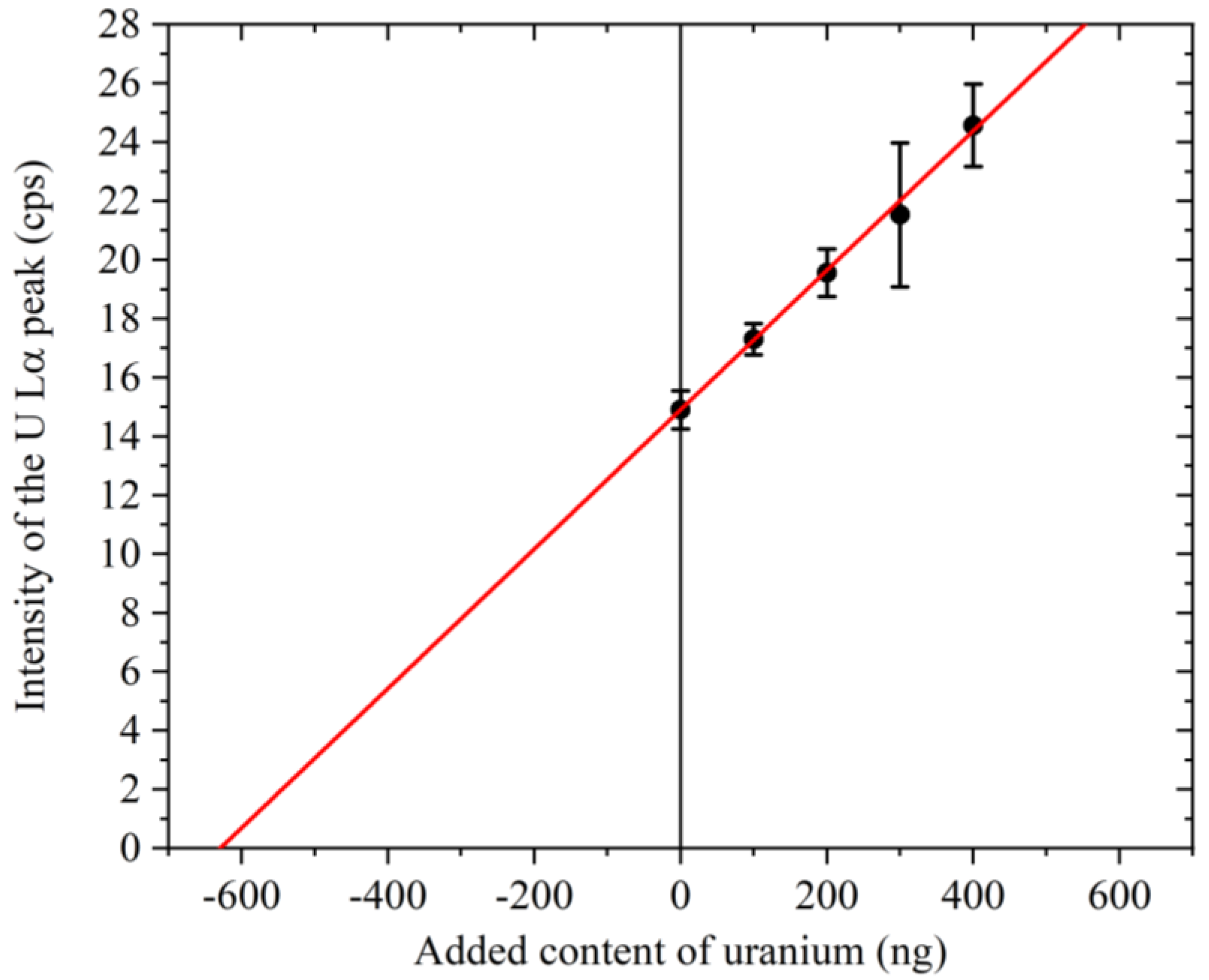
| Sampling Point | Salinity (%) | U Lα (cps) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3.18 | 14.3 ± 0.9 |
| B | 2.57 | 13.1 ± 0.9 |
| C | 2.33 | 11.5 ± 0.7 |
| D | 2.03 | 10.3 ± 0.8 |
| E | 1.80 | 9.2 ± 0.7 |
| F | 1.57 | 8.0 ± 0.6 |
| a | 1.31 | 7.2 ± 0.7 |
| b | 0.98 | 5.6 ± 0.4 |
| c | 0.83 | 5.0 ± 0.1 |
| d | 0.36 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| e | 0.57 | 4.0 ± 0.4 |
| f | 0.00 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshii, H.; Takamura, K.; Uwatoko, T.; Sakai, Y. X-ray-Fluorescence-Based Screening Method for Uranium in Contaminated Brackish Water Using Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Membranes 2023, 13, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030299
Yoshii H, Takamura K, Uwatoko T, Sakai Y. X-ray-Fluorescence-Based Screening Method for Uranium in Contaminated Brackish Water Using Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Membranes. 2023; 13(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshii, Hiroshi, Kodai Takamura, Tetsuaki Uwatoko, and Yasuhiro Sakai. 2023. "X-ray-Fluorescence-Based Screening Method for Uranium in Contaminated Brackish Water Using Graphene Oxide Nanosheets" Membranes 13, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030299
APA StyleYoshii, H., Takamura, K., Uwatoko, T., & Sakai, Y. (2023). X-ray-Fluorescence-Based Screening Method for Uranium in Contaminated Brackish Water Using Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Membranes, 13(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030299







