Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol)–b–poly(propylene glycol)–b–poly(ethylene glycol)/Silicon Dioxide Nanofibrous Adsorbents for Selective Copper (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Electrospun PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
2.3. Characterization of Prepared PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
2.4. Removal of Heavy Metals by Adsorption Process
2.5. Kinetics and Isotherm Models for Adsorption Study
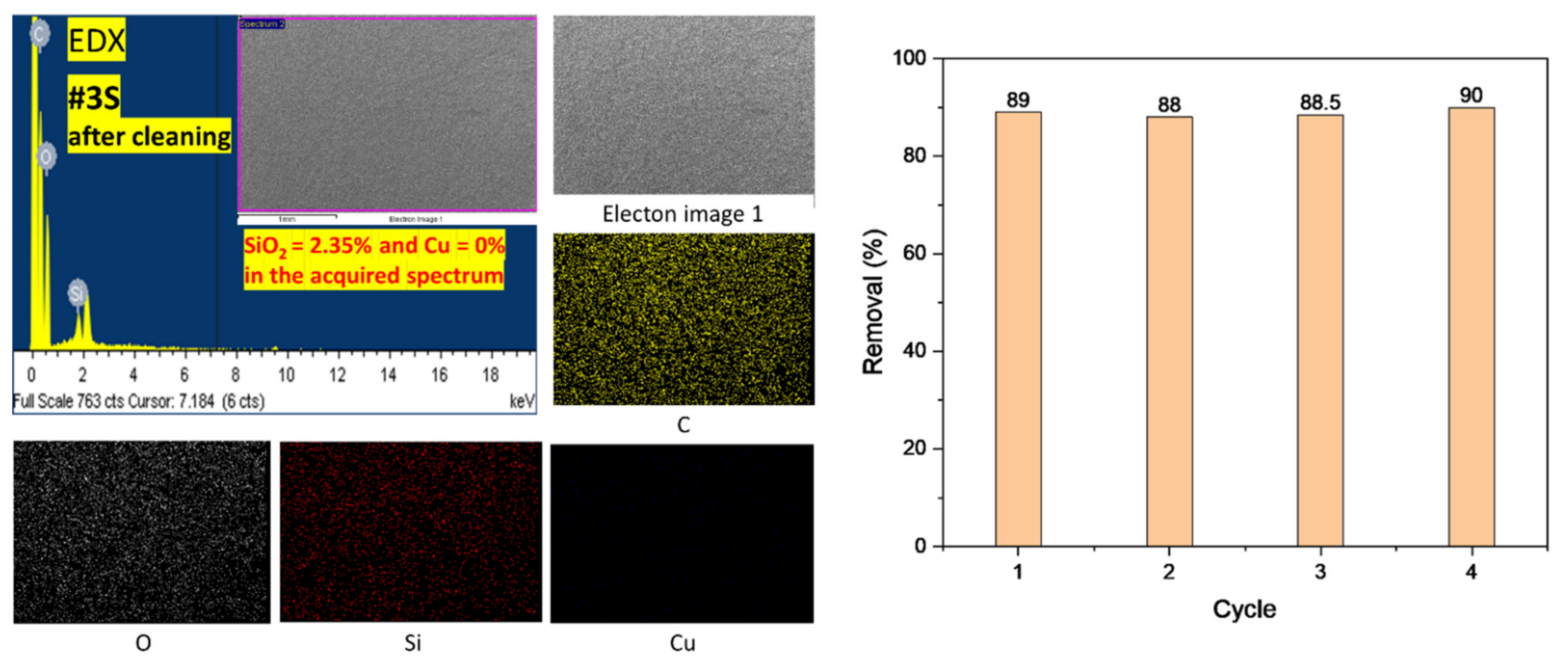
2.6. Recyclability Study of the Prepared Nanofibrous Adsorbents
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of the Electrospun PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
3.1.1. Morphological Analysis of PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
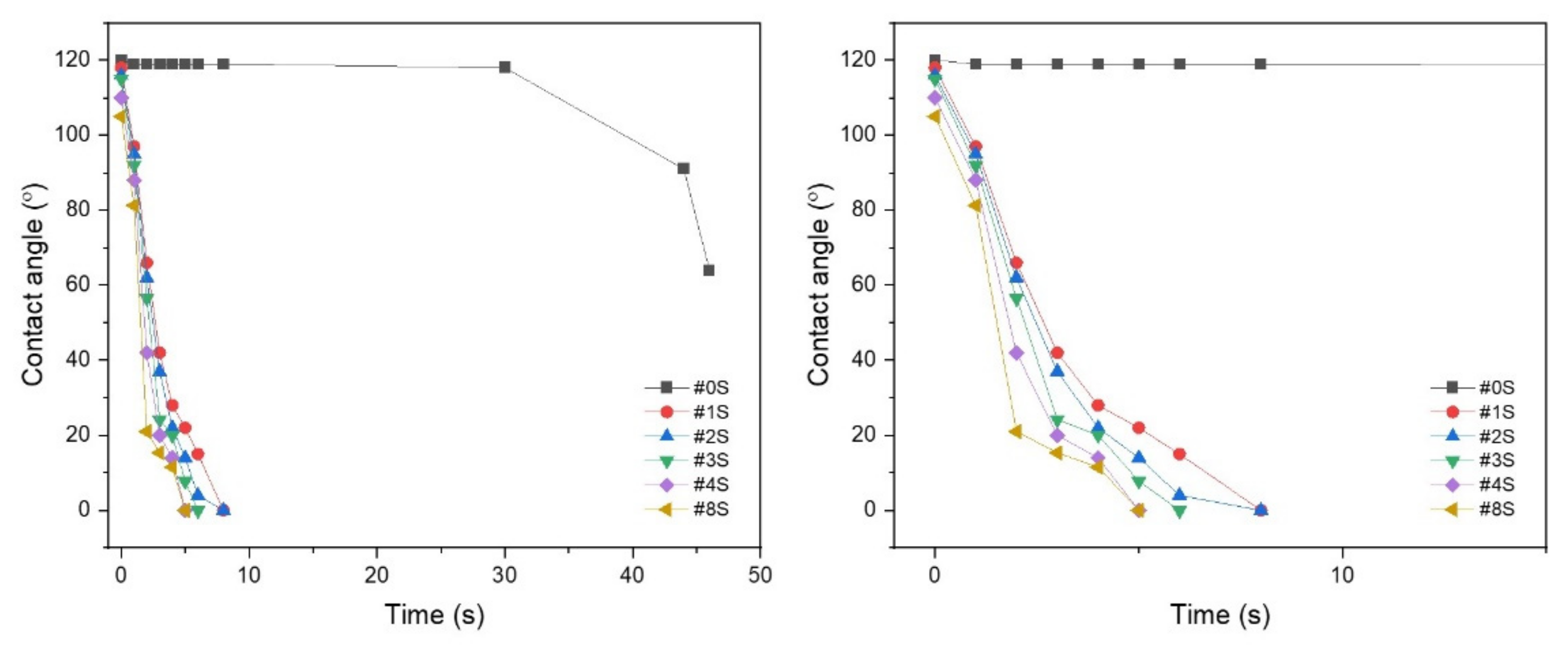
3.1.2. Contact Angle of PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
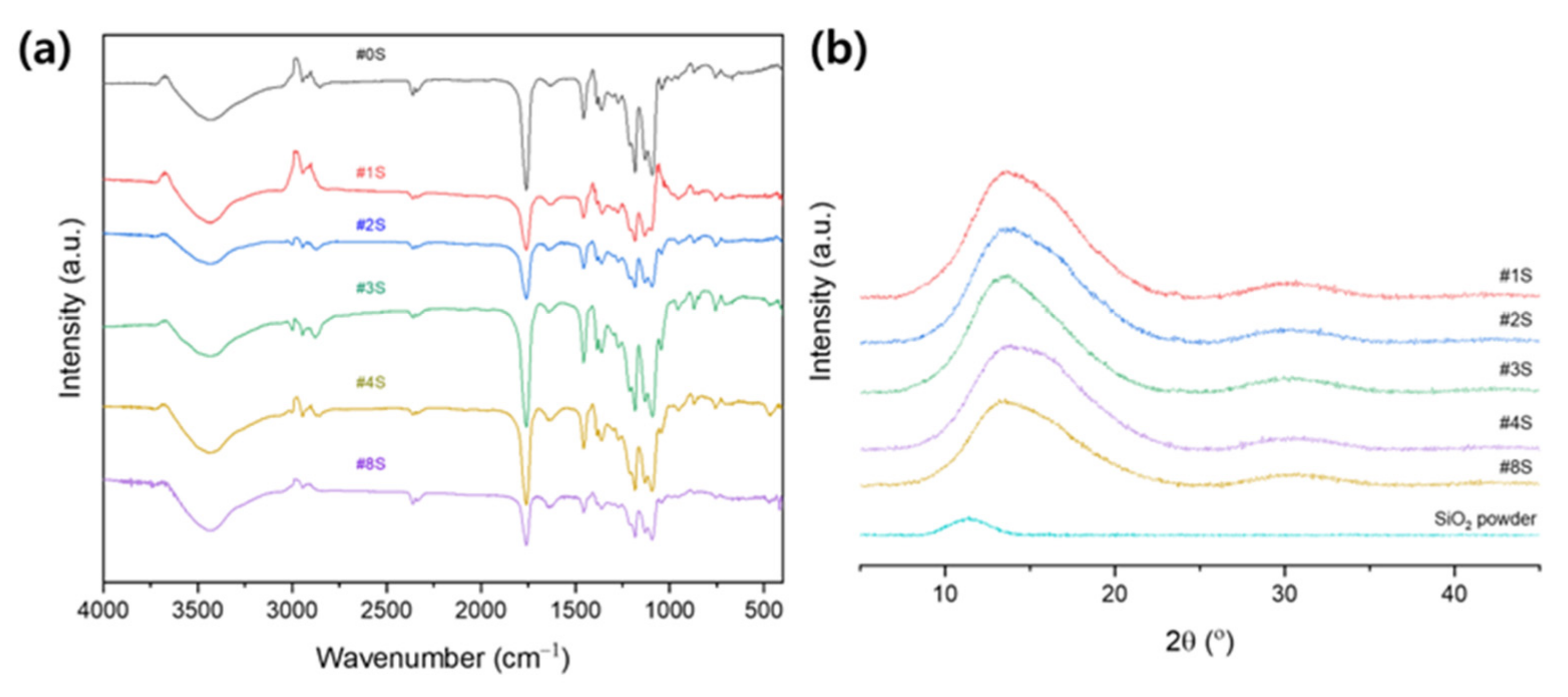
3.1.3. Chemical Structure Analysis of PLA/PEG-PPG-PEG/SiO2 Nanofibrous Adsorbents
3.2. Evaluation of Nanofibrous Adsorbents in Adsorption Applications
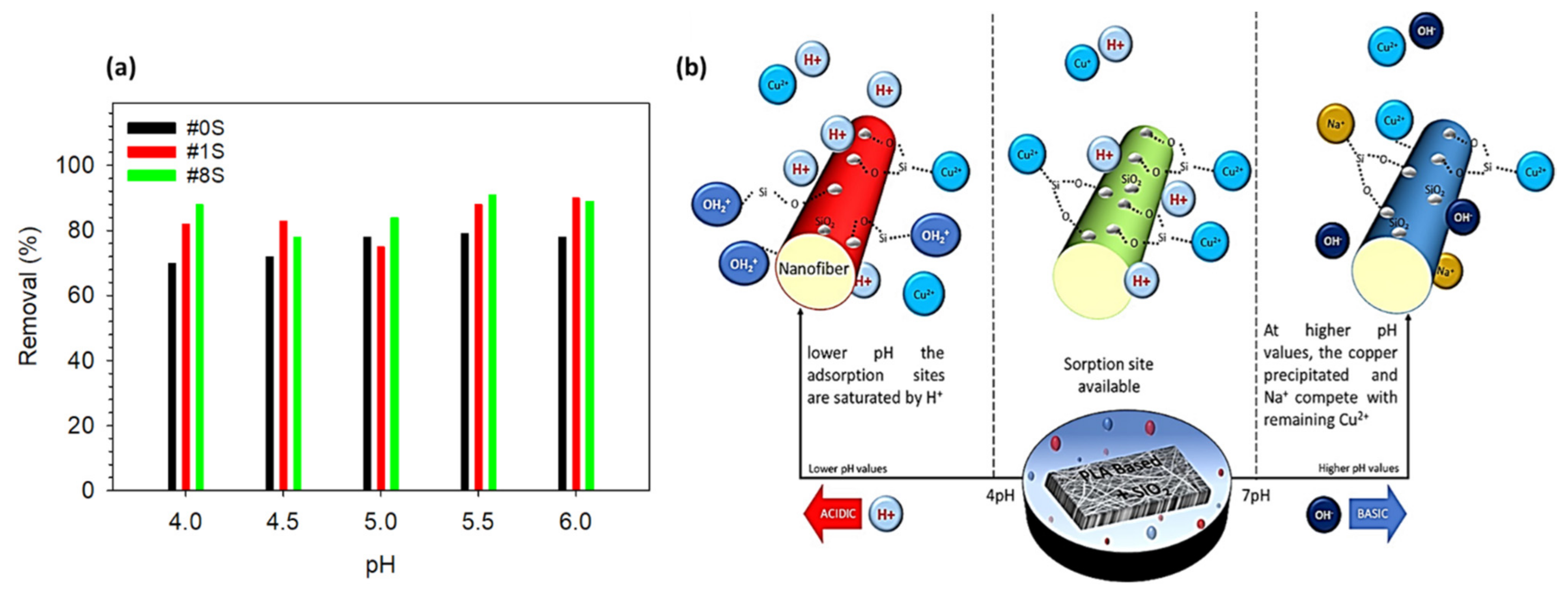
3.2.1. Effect of pH on Adsorption Capacity
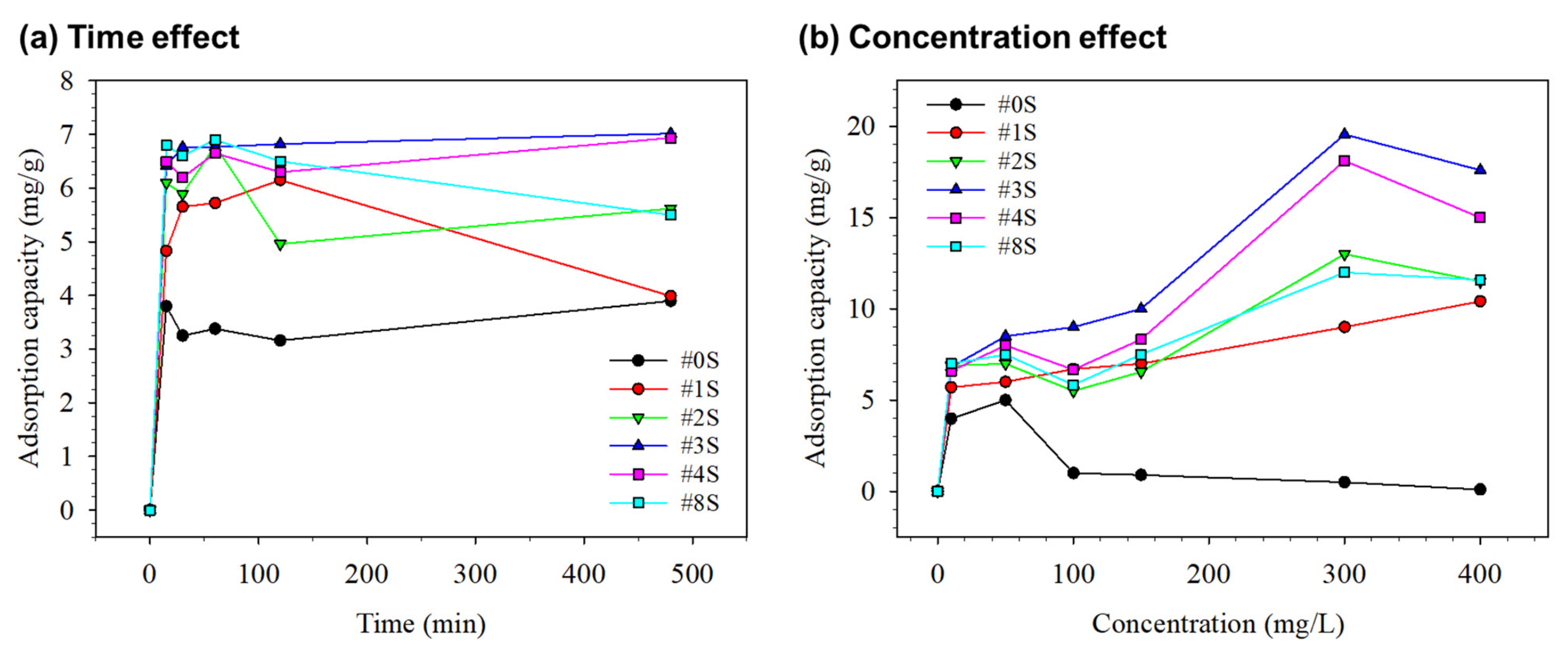
3.2.2. Effect of Time Interval on Adsorption Capacity
3.2.3. Effect of Concentration on Adsorption Capacity
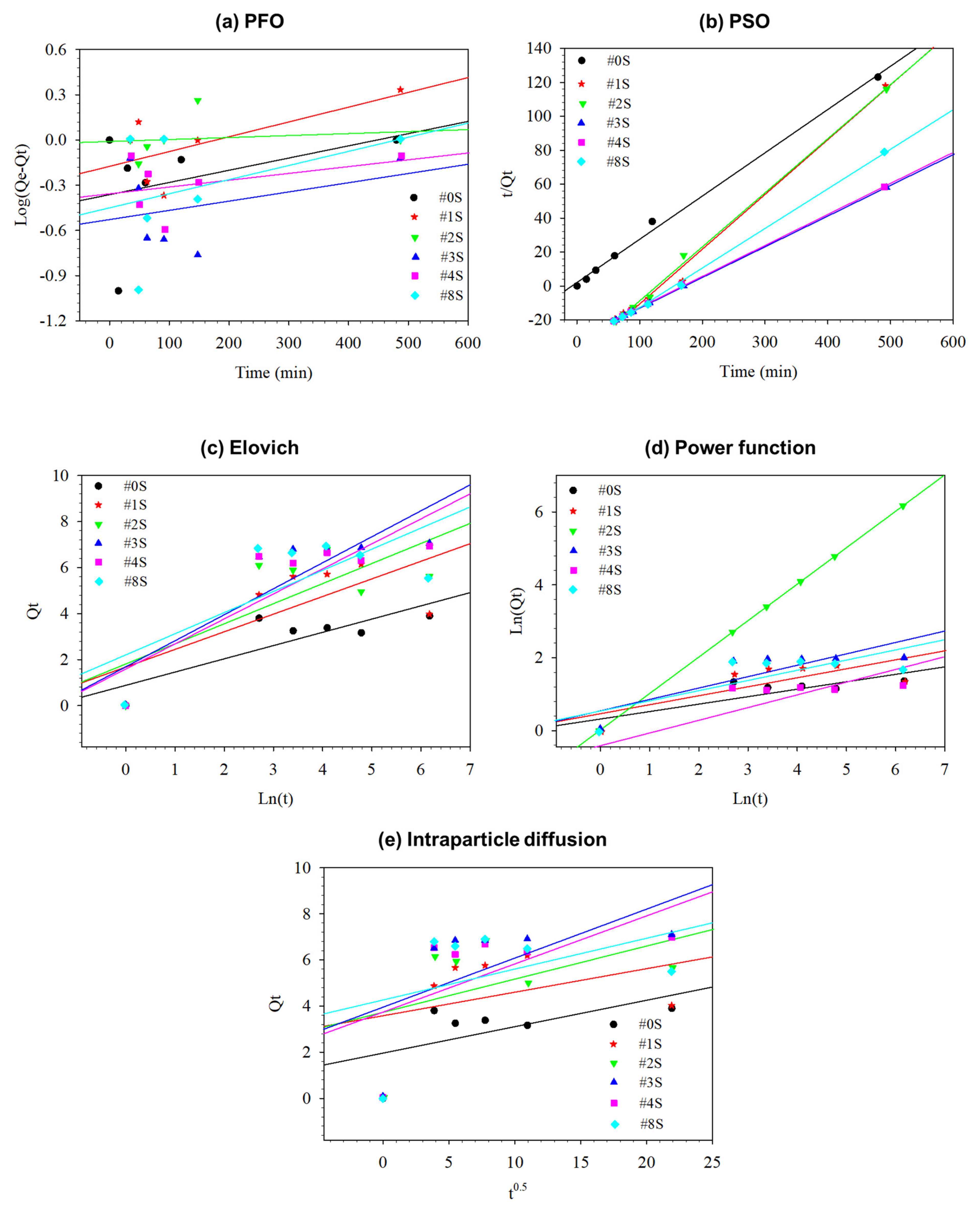
3.3. Kinetics and Isotherm Models for Adsorption Study
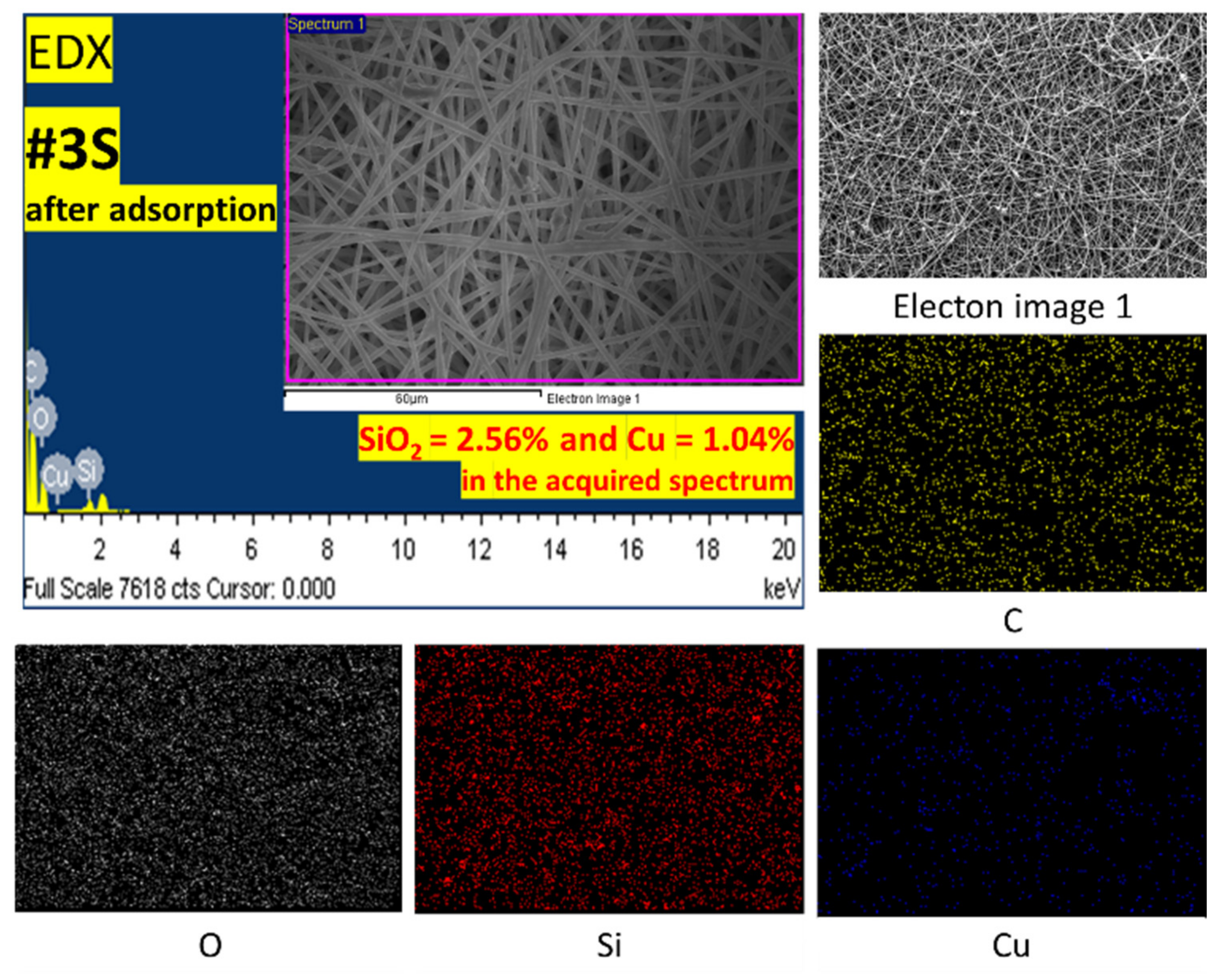
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism and Reusability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, N.K.; Majumder, C.B. Novel biofiltration methods for the treatment of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancosu, N.; Snyder, R.L.; Kyriakakis, G.; Spano, D. Water Scarcity and Future Challenges for Food Production. Water 2015, 7, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Kapri, A.; Goel, R. Heavy Metal Pollution: Source, Impact, and Remedies. In Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils; Khan, M.S., Zaidi, A., Goel, R., Musarrat, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Sheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wyckoff, K.N.; He, C.; He, Q. Characteristics of Cadmium Sorption by Heat-Activated Red Mud in Aqueous Solution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheriji, J.; Tabassi, D.; Hamrouni, B. Removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.-L. Effect of anions on electrochemical coagulation for cadmium removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hamouz, O.C.S.; Estatie, M.; Saleh, T.A. Removal of cadmium ions from wastewater by dithiocarbamate functionalized pyrrole based terpolymers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Verma, Y.; Choubey, S.; Pandey, M.; Chandrasekhar, K. Biosorptive removal of cadmium from contaminated groundwater and industrial effluents. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4420–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Kumar, V.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-C. Review on solvent extraction of cadmium from various solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 111–112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Karim, M.R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Alharthi, N.H. Novel optimised highly aligned electrospun PEI-PAN nanofibre mats with excellent wettability. Polymer 2019, 180, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Khraisheh, M.; Alharthi, N.H.; Luqman, M.; Islam, A.; Rezaul Karim, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Khaleque, M.A. Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Lim, T.-C.; Ma, Z. Electrospinning Process. In An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2005; pp. 90–154. [Google Scholar]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and superhydrophilic surfaces and materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Superhydrophilic (superwetting) surfaces: A review on fabrication and application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Yang, S.B.; Karim, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Alnaser, I.A. Preparation and Characterization of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly (ethylene glycol)-Poly(propyl glycol)-Poly(ethylene glycol) Blended Nanofiber Membranes for Fog Collection. Membranes 2023, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Preparation of Antimicrobial Ultrafine Cellulose Acetate Fibers with Silver Nanoparticles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Liu, J.; Kumar, S.; Kyu, T. Experimental and Theoretical Investigations of Porous Structure Formation in Electrospun Fibers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, K.L.; Jones, L. The Impact of Contact Angle on the Biocompatibility of Biomaterials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.M.; Wang, L.; Reipa, V.; Murphy, T.E. Porous silicon biosensor for detection of viruses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayıcı, Ş.; Yar, A.; Pehlivan, E.; Avcı, A. ZnO-TiO2 doped polyacrylonitrile nano fiber-Mat for elimination of Cr (VI) from polluted water. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikal, N.R.; Sadjadi, S.; Rajabi-Hamane, M.; Ahmadi, S.J.; Iravani, E. Decoration of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with ZnO nanoparticles and their application for removal of Pb ions from waste water. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastbaz, A.; Keshtkar, A.R. Adsorption of Th4+, U6+, Cd2+, and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a novel modified polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber adsorbent prepared by electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.Y.; Alharbi, H.F.; Karim, M.R.; Aijaz, M.O.; Alharthi, N.H. Preparation of TiO2 incorporated polyacrylonitrile electrospun nanofibers for adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Lim, C.X.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Lee, S.M.; Goh, K.L.; Chang, H.; Chan, E.S. Electrospun functionalized polyacrylonitrile–chitosan Bi-layer membranes for water filtration applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53882–53893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, A.R.; Tabatabaeefar, A.; Vaneghi, A.S.; Moosavian, M.A. Electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone/silica/3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane composite nanofiber adsorbent: Preparation, characterization and its application for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sadaawy, M.; Abdelwahab, O. Adsorptive removal of nickel from aqueous solutions by activated carbons from doum seed (Hyphaenethebaica) coat. Alex. Eng. J. 2014, 53, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Saber-Tehrani, M.; Bagheri, H. Simultaneous removal of heavy-metal ions in wastewater samples using nano-alumina modified with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhmunsiama; Lee, S.M.; Tiwari, D. Manganese oxide immobilized activated carbons in the remediation of aqueous wastes contaminated with copper(II) and lead(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Rafique, M.I.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Engineered biochar composites with zeolite, silica, and nano-zerovalent iron for the efficient scavenging of chlortetracycline from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15136–15152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Faraj, A.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Hussain, Q.; Abduljabbar, A.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I. An efficient phosphorus scavenging from aqueous solution using magnesiothermally modified bio-calcite. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Lee, S.S.; Oh, S.-E.; Mohan, D.; Moon, D.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Ok, Y.S. Modeling adsorption kinetics of trichloroethylene onto biochars derived from soybean stover and peanut shell wastes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8364–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.R.; Aijaz, M.O.; Alharth, N.H.; Alharbi, H.F.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Awual, M.R. Composite nanofibers membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan for selective lead(II) and cadmium(II) ions removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, C.L.; Chouyyok, W.; Mackie, K.E.; Neiner, D.; Saraf, L.V.; Droubay, T.C.; Warner, M.G.; Addleman, R.S. Manganese Doping of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Tailoring Surface Reactivity for a Regenerable Heavy Metal Sorbent. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3931–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous environment using polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/ZSM-5 zeolite membrane. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, C.; Soontarapa, K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Geetha Balakrishna, R. Environmental friendly and cost effective caramel for congo red removal, high flux, and fouling resistance of polysulfone membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, F.; El Haitami, A.; Ober, P.; Backus, E.H.G.; Cantin, S. Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(propylene glycol)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) Copolymer 2D Single Network at the Air–Water Interface. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9142–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.W.; Ibrahim, N.; Yunus, W.; Hussein, M. Effects of Graphene Nanopletelets on Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Polymer Nanocomposites. Polymers 2013, 6, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; Dybal, J.; Šturcová, A. ATR FTIR investigation of interactions and temperature transitions of poly(ethylene oxide), poly(propylene oxide) and ethylene oxide–propylene oxide–ethylene oxide tri-block copolymers in water media. Vib. Spectrosc. 2009, 50, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.H.; Gan, S.N.; Chan, C.H.; Yahya, R. ATR-FTIR studies on ion interaction of lithium perchlorate in polyacrylate/poly(ethylene oxide) blends. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 76, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, X. Effect of molecular weight of polyethylene glycol on crystallization behaviors, thermal properties and tensile performance of polylactic acid stereocomplexes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 42120–42127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, R.L.; Devaki, S.J. Design and Development of Biogel Through Hierarchical Self-Organisation of Biomolecule for Sustainable Antibacterial Applications. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Dubey, R. Synthesis of SiO2 nanoparticles by sol-gel method and their optical and structural properties. Rom. J. Inf. Sci. Technol 2020, 23, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Naga, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Inui, M.; Noguchi, K.; Murase, S. Crystallization of amorphous poly(lactic acid) induced by organic solvents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasoulia, I.-G.; Tarantili, P.A. Preparation and characterization of polyethylene glycol/poly(L-lactic acid) blends. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.B.; Nikzad, S.; Yan, H.; Ochiai, Y.; Lai, J.-C.; Yu, Z.; Chen, G.; Kang, J.; Bao, Z. High Energy Density Shape Memory Polymers Using Strain-Induced Supramolecular Nanostructures. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Karim, M.R.; Usman, A.R.A.; Assaifan, A.K. Carbon Nanodots-Embedded Pullulan Nanofibers for Sulfathiazole Removal from Wastewater Streams. Membranes 2022, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, G.; Hassan, H. Removal of copper ions from aqueous solution using silica derived from rice straw: Comparison with activated charcoal. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Ma, L.; Pang, X.; Li, L. Preparation of Chitosan Stacking Membranes for Adsorption of Copper Ions. Polymers 2019, 11, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Jacobs, N.V.; Luyt, A. Electrospun alginate nanofibres as potential bio-sorption agent of heavy metals in water treatment. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, B.; Alem, A.; Marcotte, S.; Pantet, A.; Ahfir, N.-D.; Bizet, L.; Duriatti, D. Experimental investigation on removal of heavy metals (Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) from aqueous solution by flax fibres. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Karim, M.R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Alharthi, N.H.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Abdo, H.S. Magnetic/Polyetherimide-Acrylonitrile Composite Nanofibers for Nickel Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution. Membranes 2021, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaifan, A.K.; Aijaz, M.O.; Luqman, M.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Karim, M.R.; Alharbi, H.F. Removal of cadmium ions from water using coaxially electrospun PAN/ZnO-encapsulated PVDF nanofiber membranes. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2831–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

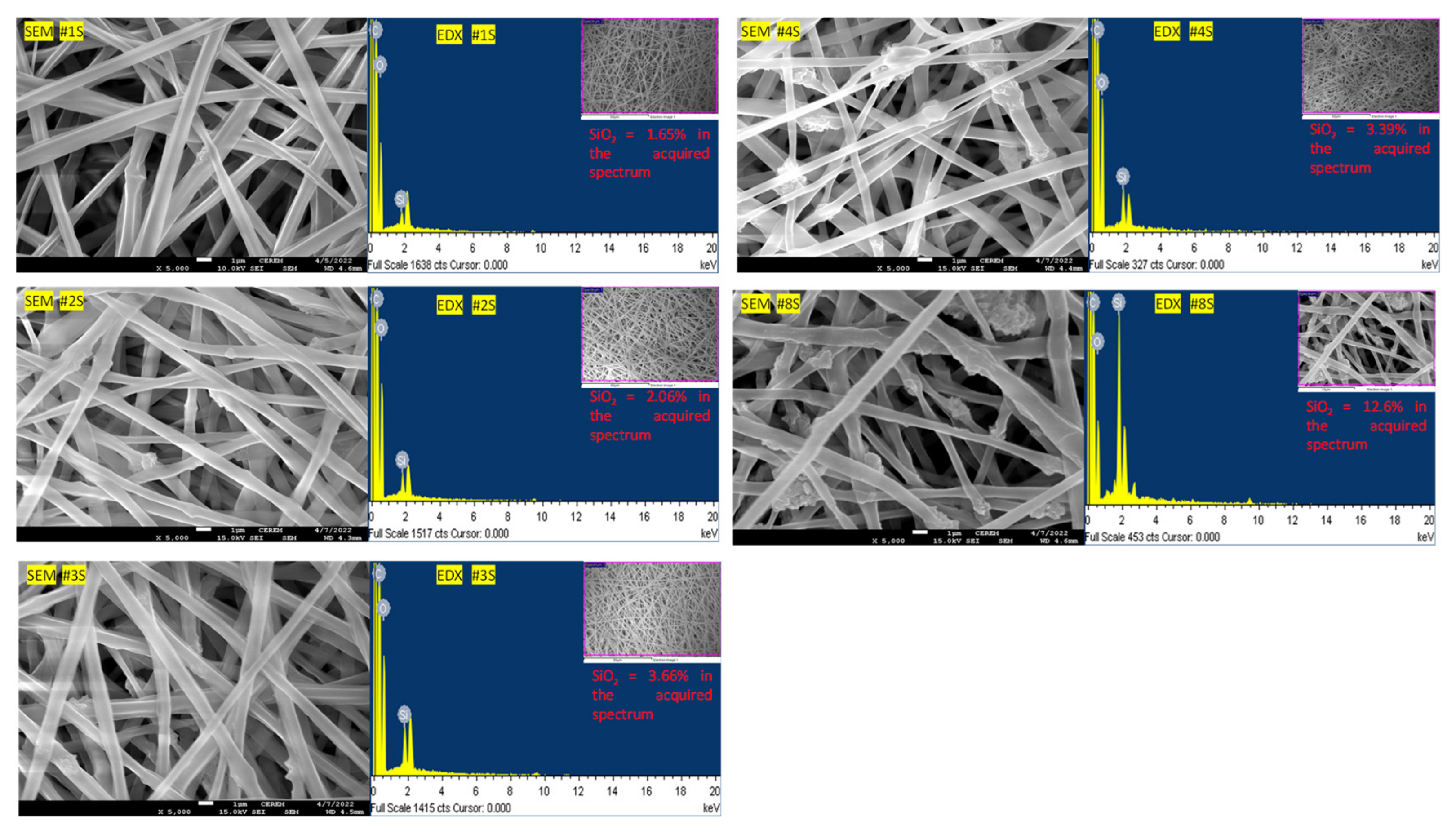

| Sample Name of Electro-spun Nanofibrous Adsorbents | PLA Concentration (%w/v) | PEG-PPG-PEG Concentration (%w/v) | SiO2 Concentration (%w/w) in PLA: PEG-PPG-PEG (4:1) Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| #0S | 12 | 9 | 0 |
| #1S | 1 | ||
| #2S | 2 | ||
| #3S | 3 | ||
| #4S | 4 | ||
| #8S | 8 |
| Model | Equation | Plot | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetic model * | |||
| Pseudo-first-order | [31] | ||
| Pseudo-second-order | [31] | ||
| Elovich | [32] | ||
| Power function | [33] | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | [34] | ||
| Isotherm model ** | |||
| Langmuir | [35] | ||
| Freundlich | [34] | ||
| Temkin | [31] | ||
| Standard Error | Equation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| The standard error of estimate (SEE) | [36,37] | |
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | [32] |
| Kinetics Models | Parameter | #0S | #1S | #2S | #3S | #4S | #8S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order (PFO) | k1 | 0.001863442 | 0.0021 | 0.0003 | 0.0015 | 0.0011 | 0.002 |
| Qe | 0.434461381 | 0.7255 | 0.99 | 0.373 | 0.55 | 0.376 | |
| R2 | 0.154773071 | 0.43 | 0.0267 | 0.133 | 0.165 | 0.159 | |
| SEE | 0.386 | 0.216 | 0.1526 | 0.3325 | 0.216 | 0.414 | |
| Pseudo-second-order (PSO) | k2 | 0.0316 | −0.0193 | −1.5966 | 0.0874 | 0.039 | −0.0250 |
| Qe | 3.9242 | 3.9425 | 5.5906 | 7.0332 | 6.8906 | 5.4547 | |
| R2 | 0.9965 | 0.9924 | 0.9979 | 1.0000 | 0.9991 | 0.9984 | |
| SEE | 3.1037 | 4.5408 | 1.6874 | 0.2005 | 0.901 | 1.4762 | |
| Elovich | α | 2.6709 | 6.8989 | 6.9980 | 4.8554 | 4.7240 | 9.4631 |
| β | 1.7364 | 1.3057 | 1.1462 | 0.8855 | 0.9200 | 1.0885 | |
| R2 | 0.6871 | 0.4971 | 0.5494 | 0.8575 | 0.7286 | 0.5164 | |
| SEE | 0.9122 | 1.8083 | 1.8550 | 1.5908 | 1.5572 | 2.0871 | |
| Power function | Kf | 0.2041 | 0.2464 | 1.0000 | 0.3128 | 0.3065 | 0.2793 |
| B | 1.3779 | 1.6573 | 1.0000 | 1.6296 | 1.6167 | 1.7628 | |
| R2 | 0.6879 | 0.5609 | 1.0000 | 0.7084 | 0.7056 | 0.5879 | |
| SEE | 0.3227 | 0.5117 | 0 | 0.4711 | 0.4646 | 0.5488 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | Kid | 0.1146 | 0.1021 | 0.1435 | 0.2127 | 3.6935 | 0.1339 |
| c | 1.9605 | 3.5351 | 3.6993 | 3.8593 | 0.2087 | 4.2687 | |
| R2 | 0.3569 | 0.1158 | 0.1948 | 0.3421 | 0.3522 | 0.1437 | |
| SEE | 1.3078 | 2.3978 | 2.4795 | 2.5077 | 2.4059 | 2.7771 |
| Isotherm Models | Parameters | #0S | #1S | #2S | #3S | #4S | #8S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | 0.1217 | 9.9897 | 12.5628 | 19.3290 | 16.9314 | 0.0283 | |
| KL | −0.0183 | 0.0425 | 0.0225 | 0.0219 | 0.0192 | 12.2638 | |
| R2 | 0.6755 | 0.9758 | 0.8681 | 0.8849 | 0.8279 | 0.9234 | |
| SEE | 5.5 | 2.5786 | 5.0406 | 2.9690 | 4.3124 | 3.8200 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 28.2586 | 4.5949 | 5.5356 | 5.1851 | 4.9133 | 5.8857 |
| n | −1.3236 | 9.4395 | 11.5455 | 5.5873 | 6.3083 | 12.3893 | |
| R2 | 0.6824 | 0.7025 | 0.2469 | 0.6704 | 0.4868 | 0.3092 | |
| SEE | 0.3963 | 0.0588 | 0.1446 | 0.1182 | 0.1500 | 0.1172 | |
| Temkin | A | 0.0015 | 3.9 | 6.12 | 2.02 | 2.23 | 8.2 |
| B | −1.0302 | 1.27 | 1.39 | 2.45 | 2.11 | 1.31 | |
| R2 | 0.6730 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.62 | |
| SEE | 1.4667 | 1.75 | 3.25 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 3.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aijaz, M.O.; Yang, S.B.; Karim, M.R.; Alnaser, I.A.; Alahmari, A.D.; Almubaddel, F.S.; Assaifan, A.K. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol)–b–poly(propylene glycol)–b–poly(ethylene glycol)/Silicon Dioxide Nanofibrous Adsorbents for Selective Copper (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater. Membranes 2023, 13, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010054
Aijaz MO, Yang SB, Karim MR, Alnaser IA, Alahmari AD, Almubaddel FS, Assaifan AK. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol)–b–poly(propylene glycol)–b–poly(ethylene glycol)/Silicon Dioxide Nanofibrous Adsorbents for Selective Copper (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleAijaz, Muhammad Omer, Seong Baek Yang, Mohammad Rezaul Karim, Ibrahim Abdullah Alnaser, Abdulelah Dhaifallah Alahmari, Fahad S. Almubaddel, and Abdulaziz K. Assaifan. 2023. "Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol)–b–poly(propylene glycol)–b–poly(ethylene glycol)/Silicon Dioxide Nanofibrous Adsorbents for Selective Copper (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater" Membranes 13, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010054
APA StyleAijaz, M. O., Yang, S. B., Karim, M. R., Alnaser, I. A., Alahmari, A. D., Almubaddel, F. S., & Assaifan, A. K. (2023). Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol)–b–poly(propylene glycol)–b–poly(ethylene glycol)/Silicon Dioxide Nanofibrous Adsorbents for Selective Copper (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater. Membranes, 13(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010054








