Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
2.2. Reconstitution of hBK Channels into Liposomes
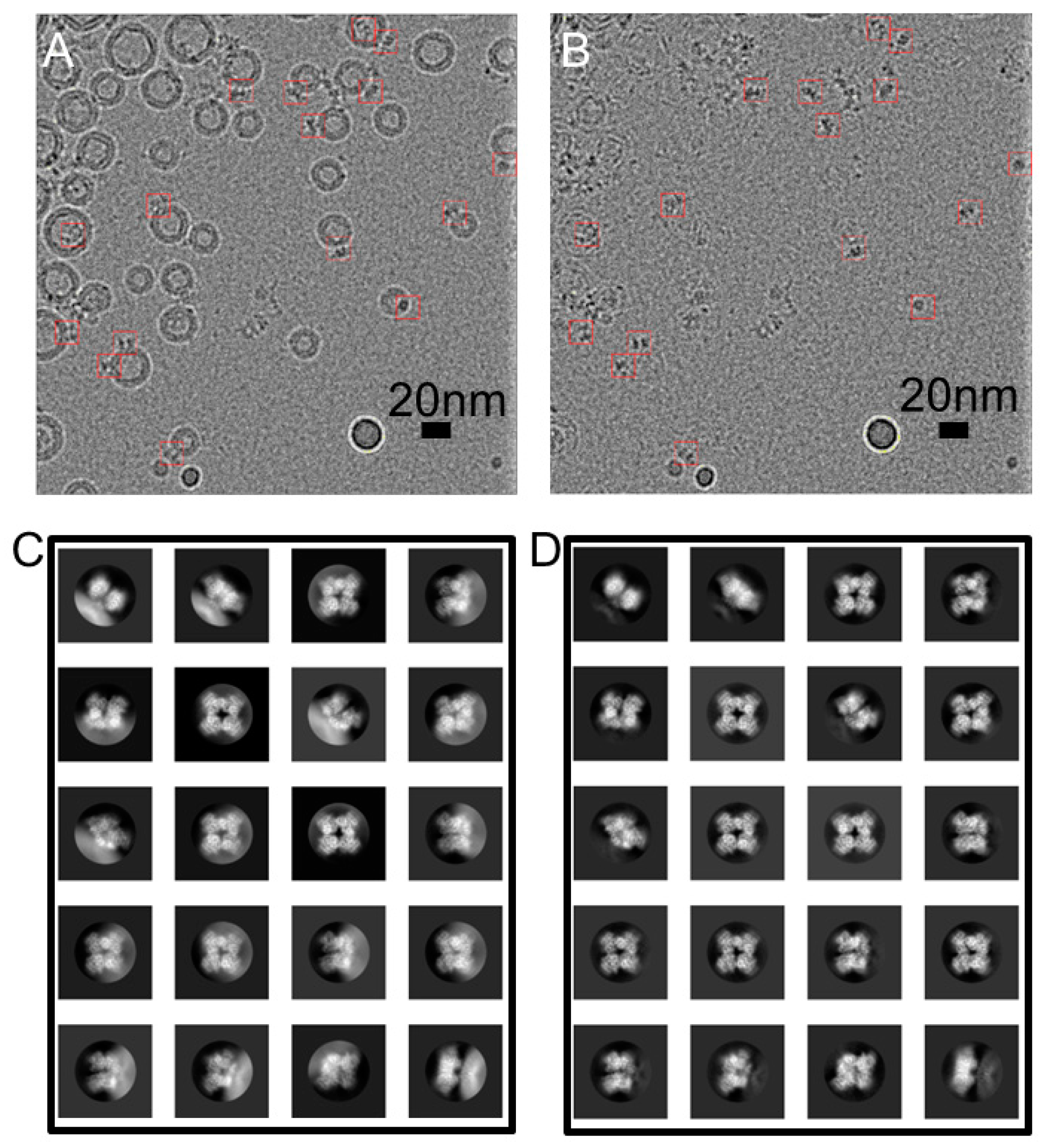
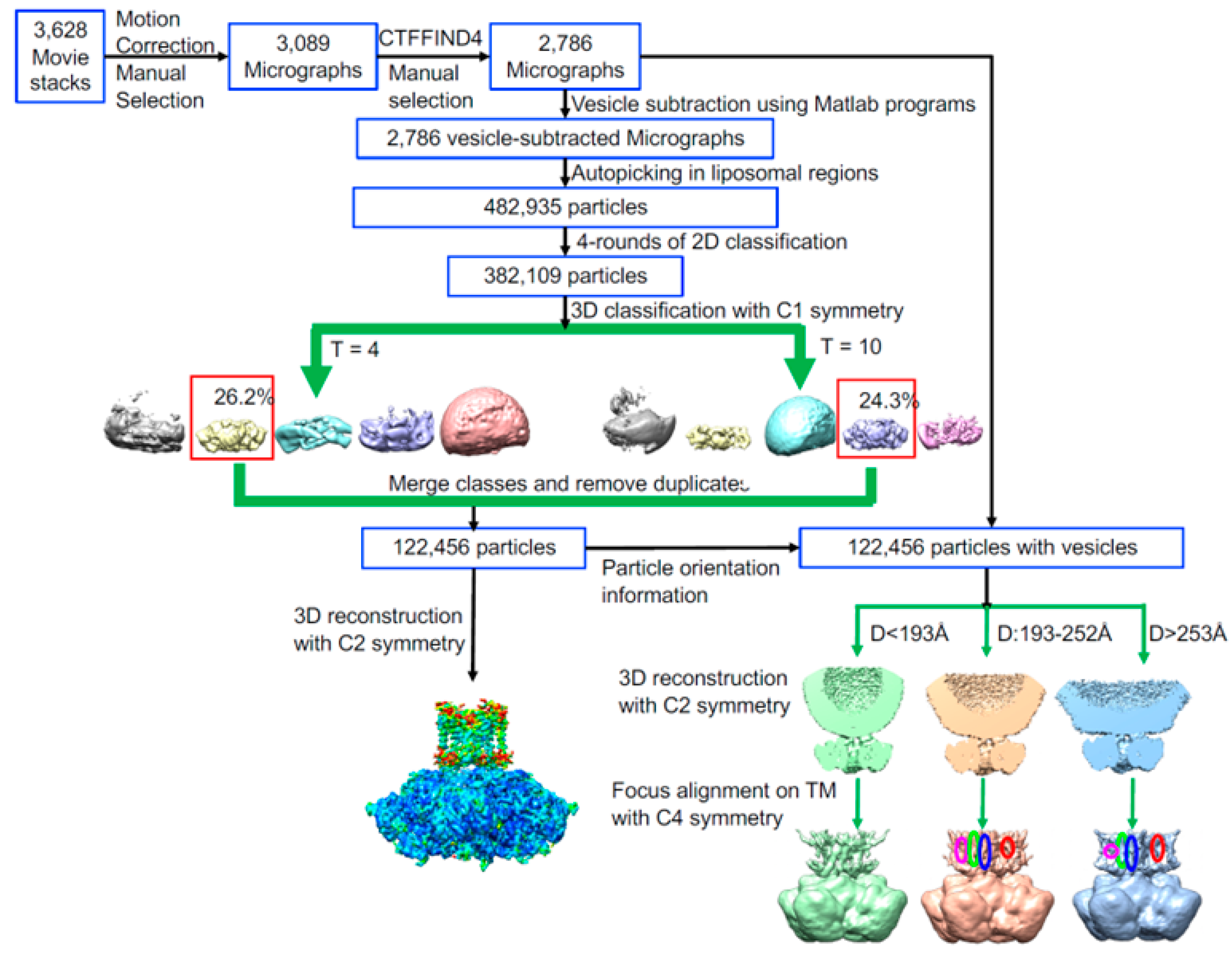
2.3. CryoEM Grid Prepartion, Data Collection, and Data Processing
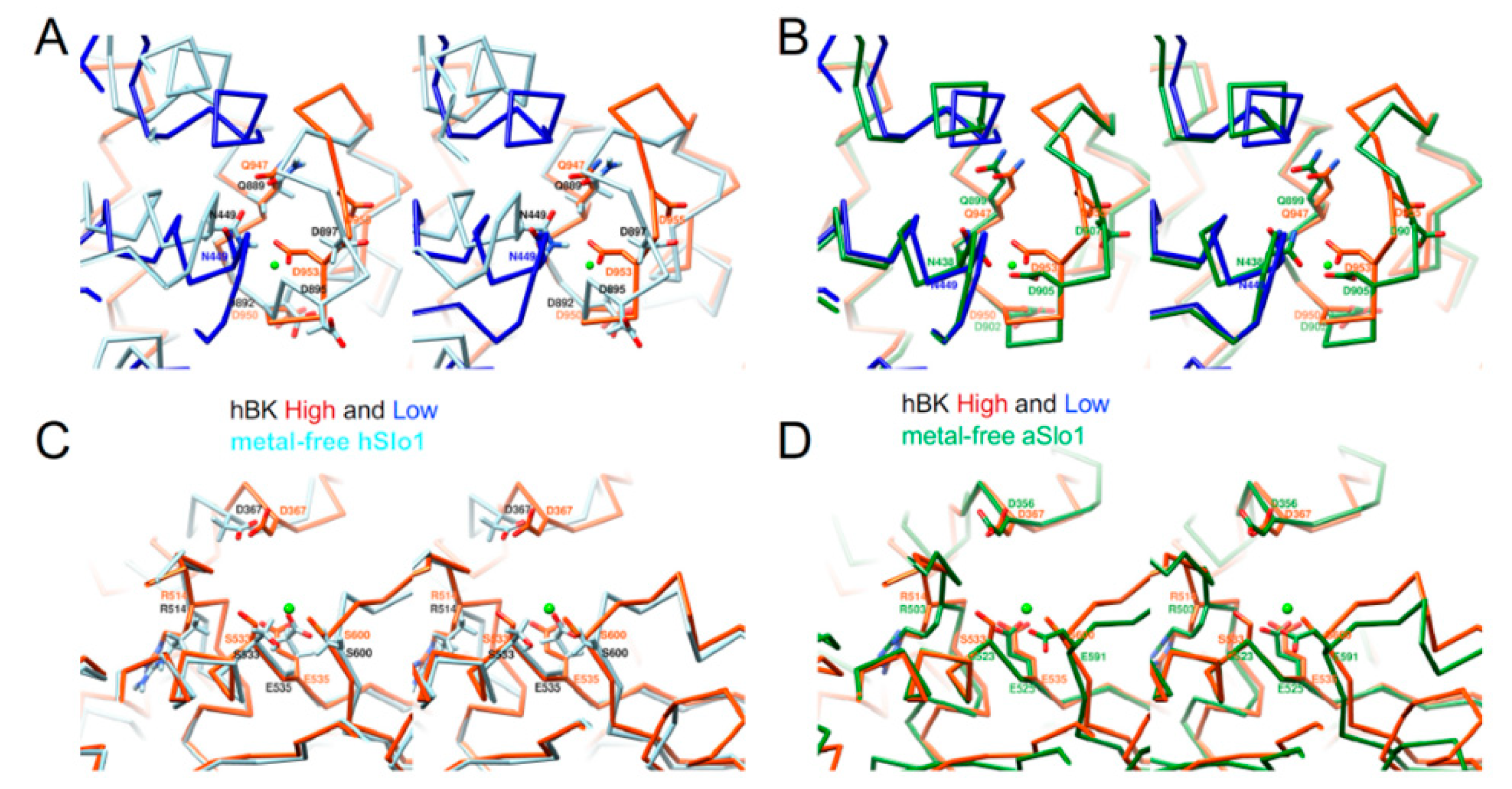
3. Results
3.1. Overall Structure of hBK in Liposomes
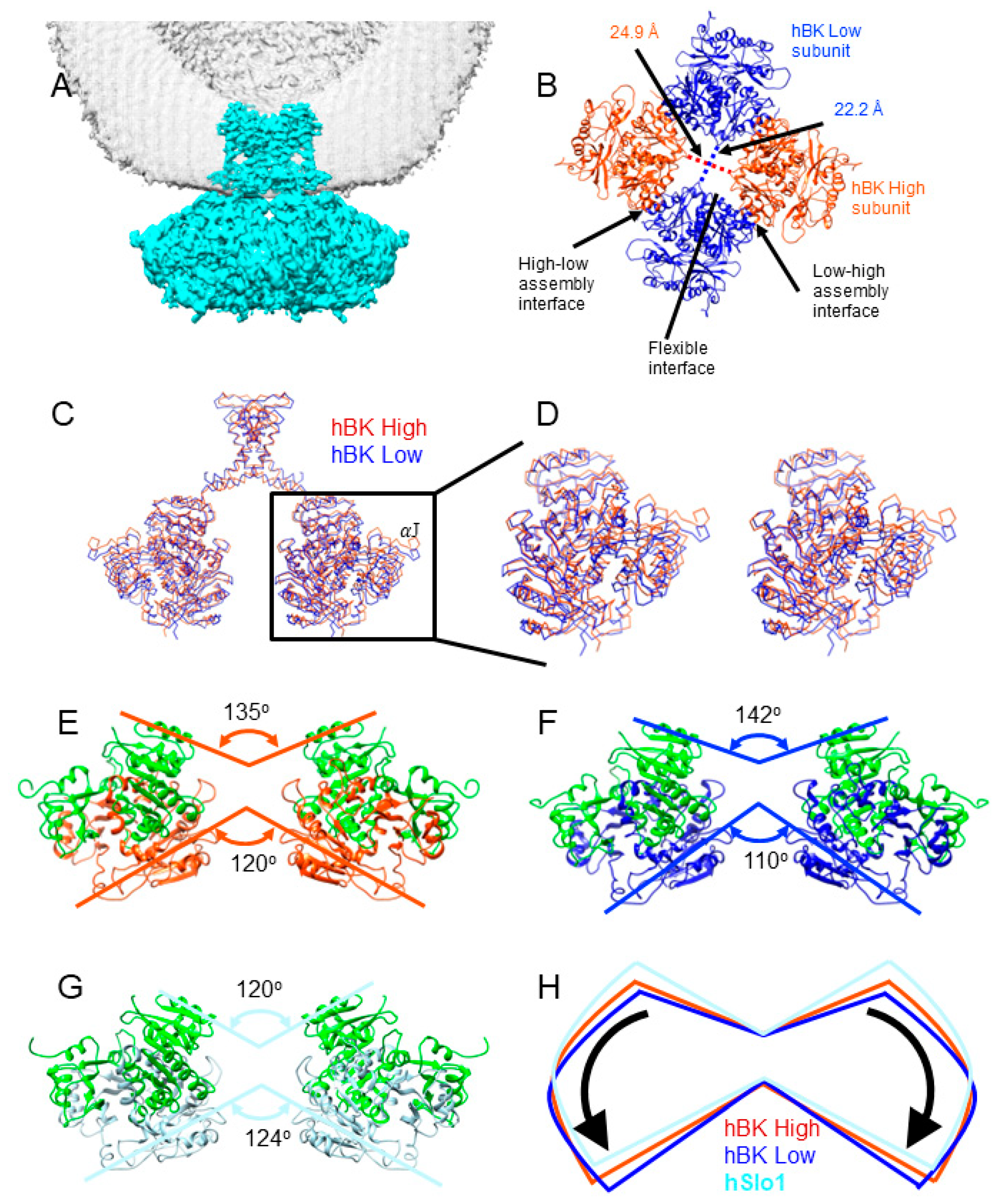
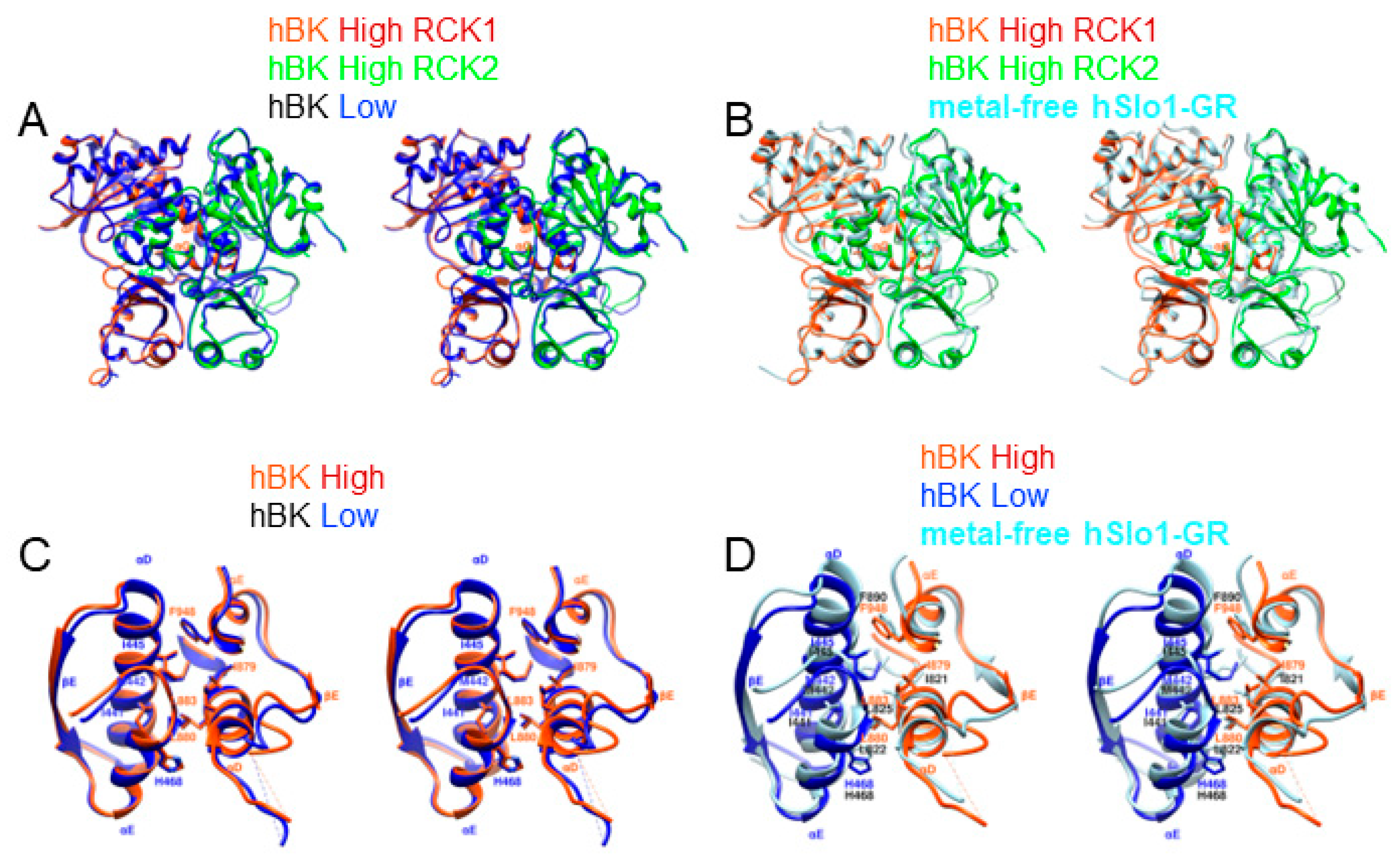
3.2. An Intermediate State of the BK Channel
3.3. Rotational Flexibility in the TM Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, J.; Yang, H.; Lee, U.S. Molecular mechanisms of BK channel activation. CMLS 2009, 66, 852–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribkoff, V.K.; Starrett, J.E.; Dworetzky, S.I. Maxi-K potassium channels: Form, function, and modulation of a class of endogenous regulators of intracellular calcium. Neuroscientist 2001, 7, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horrigan, F.T.; Aldrich, R.W. Coupling between voltage sensor activation, Ca2+ binding and channel opening in large conductance (BK) potassium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 120, 267–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasquel-Ursulaez, W.; Segura, I.; Díaz-Franulic, I.; Echeverría, F.; Lorenzo-Ceballos, Y.; Espinoza, N.; Rojas, M.; Garate, J.A.; Perozo, E.; Alvarez, O.; et al. Mechanism of voltage sensing in Ca2+- and voltage-activated K+ (BK) channels. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204620119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Pico, A.; Cadene, M.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of the RCK domain from the E. coli K+ channel and demonstration of its presence in the human BK channel. Neuron 2001, 29, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Cadene, M.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. Crystal structure and mechanism of a calcium-gated potassium channel. Nature 2002, 417, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Cadene, M.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature 2002, 417, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.X. Crystal Structures of a Ligand-free MthK Gating Ring: Insights into the Ligand Gating Mechanism of K+ Channels. Cell 2006, 126, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, M.; Salkoff, L. A novel calcium-sensing domain in the BK channel. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, L.; Chaturvedi, N.; Harilal, D.; Qin, J.; Cui, J. Mechanism of magnesium activation of calcium-activated potassium channels. Nature 2002, 418, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, T.B.; Cox, D.H. Measurements of the BKCa Channel’s High-Affinity Ca2+ Binding Constants: Effects of Membrane Voltage. J. Gen. Physol. 2008, 132, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.M.; Zeng, X.; Lingle, C.J. Multiple regulatory sites in large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Nature 2002, 418, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Huang, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Moller, A.; Zou, X.; Cui, J. Ion sensing in the RCK1 domain of BK channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18700–18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Kaldany, C.; Holmstrand, E.C.; Cox, D.H. Mapping the BKCa Channel’s “Ca2+ Bowl”: Side-chains Essential for Ca2+ Sensing. J. Gen. Physol. 2004, 123, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Leonetti, M.D.; Pico, A.R.; Hsiung, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of the Human BK Channel Ca2+-Activation Apparatus at 3.0 Å Resolution. Science 2010, 329, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ye, S.; Jiang, Y.X. Structure of the gating ring from the human large-conductance Ca2+-gated K+ channel. Nature 2010, 466, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Leonetti, M.D.; Hsiung, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Open structure of the Ca2+ gating ring in the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Nature 2012, 481, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Hite, R.K.; MacKinnon, R. Cryo-EM structure of the open high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Nature 2017, 541, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, R.K.; Tao, X.; MacKinnon, R. Structural basis for gating the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Nature 2017, 541, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T.; Cheng, Y.; Sliz, P.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Harrison, S.C.; Walz, T. Lipid-protein interactions in double-layered two-dimensional AQP0 crystals. Nature 2005, 438, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W. Getting ready for the decade of the lipids. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B.; Dickson, E.J.; Kruse, M.; Vivas, O.; Suh, B.C. Phosphoinositides regulate ion channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.G. Biological membranes: The importance of molecular detail. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.B.; Tao, X.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature 2007, 450, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Jiang, Q.X.; MacKinnon, R. Phospholipids and the origin of cationic gating charges in voltage sensors. Nature 2006, 444, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayburt, T.H.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Sligar, S.G. Self-Assembly of Discoidal Phospholipid Bilayer Nanoparticles with Membrane Scaffold Proteins. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, T.J.; Finka, R.; Smith, C.; Lin, Y.; Dafforn, T.; Overduin, M. Membrane Proteins Solubilized Intact in Lipid Containing Nanoparticles Bounded by Styrene Maleic Acid Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7484–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 structures in nanodiscs reveal mechanisms of ligand and lipid action. Nature 2016, 543, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumroy, R.A.; Samanta, A.; Liu, Y.; Hughes, T.E.T.; Zhao, S.; Yudin, Y.; Rohacs, T.; Han, S.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.Y. Molecular mechanism of TRPV2 channel modulation by cannabidiol. eLife 2019, 8, e48792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Kusakizako, T.; Dung Nguyen, T.H.; Nishizawa, T.; Hino, T.; Tominaga, M.; Nureki, O. The structure of lipid nanodisc-reconstituted TRPV3 reveals the gating mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autzen, H.E.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Campbell, M.G.; Asarnow, D.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the human TRPM4 ion channel in a lipid nanodisc. Science 2018, 359, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.; van Goor, M.K.; Asarnow, D.; Wang, Y.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y.; van der Wijst, J. Structural insight into TRPV5 channel function and modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8869–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoldrick, L.L.; Singh, A.K.; Saotome, K.; Yelshanskaya, M.V.; Twomey, E.C.; Grassucci, R.A.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Opening of the human epithelial calcium channel TRPV6. Nature 2018, 553, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; She, J.; Zeng, W.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Bai, X.C.; Jiang, Y.X. Structure of mammalian endolysosomal TRPML1 channel in nanodiscs. Nature 2017, 550, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.; Feng, S.; Tien, J.; Peters, C.J.; Bulkley, D.; Lolicato, M.; Zhao, J.; Zuberbühler, K.; Ye, W.; Qi, L.; et al. Cryo-EM structures of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel. Nature 2017, 552, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.H.; Stam, N.J.; Hryc, C.F.; Couoh-Cardel, S.; Pintilie, G.; Chiu, W.; Wilkens, S. The 3.5-Å CryoEM Structure of Nanodisc-Reconstituted Yeast Vacuolar ATPase Vo Proton Channel. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 993–1004.e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.S.; Yang, X.; DeCaen, P.G.; Liu, X.; Bulkley, D.; Clapham, D.E.; Cao, E. The Structure of the Polycystic Kidney Disease Channel PKD2 in Lipid Nanodiscs. Cell 2016, 167, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Kao, T.Y.; Cheng, C.C.; Chiang, Y.W. Structure and regulation of the BsYetJ calcium channel in lipid nanodiscs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30126–30134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yan, N. Structural Basis of the Modulation of the Voltage-Gated Calcium Ion Channel Cav1.1 by Dihydropyridine Compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 60, 3131–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.M.I.; Manolaridis, I.; Jackson, S.M.; Kowal, J.; Stahlberg, H.; Locher, K.P. Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nature 2017, 546, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Manolaridis, I.; Kowal, J.; Zechner, M.; Taylor, N.M.I.; Bause, M.; Bauer, S.; Bartholomaeus, R.; Bernhardt, G.; Koenig, B.; et al. Structural basis of small-molecule inhibition of human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.S.; Kern, D.M.; Brohawn, S.G. Cryo-EM structure of the potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC4 in lipid nanodiscs. eLife 2020, 9, e352505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.P.; Luo, M.; Zhou, W.; Symersky, J.; Bai, D.; Chambers, M.G.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Liao, M.; Mueller, D.M. High-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the yeast ATP synthase in a lipid membrane. Science 2018, 360, eaas9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, H.; Wang, J.; Tama, F.; Chollet, L.; Gogol, E.P.; Collier, R.J.; Fisher, M.T. Three-dimensional structure of the anthrax toxin pore inserted into lipid nanodiscs and lipid vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3453–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bose, P.S.; Sigworth, F.J. Using cryo-EM to measure the dipole potential of a lipid membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18528–18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sigworth, F.J. Structure of the BK potassium channel in a lipid membrane from Electron CryoMicroscopy. Nature 2009, 461, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.H.; Brandt, S.S.; Shigematsu, H.; Sigworth, F.J. Statistical modeling and removal of lipid membrane projections for cryo-EM structure determination of reconstituted membrane proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 194, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Fan, X.; Yan, N. Cryo-EM analysis of a membrane protein embedded in the liposome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18497–18503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Palovcak, E.; Armache, J.P.; Verba, K.A.; Cheng, Y.; Agard, D.A. MotionCor2: Anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 2017, 4, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tonggu, L. Membrane protein reconstitution for functional and structural studies. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brohawn, S.G.; del Marmol, J.; MacKinnon, R. Crystal structure of the human K2P TRAAK, a lipid- and mechano-sensitive K+ ion channel. Science 2012, 335, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tonggu, L.; Tang, L.; Wang, L. Effects of N-glycosylation on hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.N.; Long, S.B. Crystal structure of the human two-pore domain potassium channel K2P1. Science 2012, 335, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Brown, E.C.; Wang, W.; MacKinnon, R. Novel cell-free high-throughput screening method for pharmacological tools targeting K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5748–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonggu, L.; Wang, L. Cryo-EM sample preparation method for extremely low concentration liposomes. Ultramicroscopy 2020, 208, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suloway, C.; Pulokas, J.; Fellmann, D.; Cheng, A.; Guerra, F.; Quispe, J.; Stagg, S.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. Automated Molecular Microscopy: The New Leginon System. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohou, A.; Grigorieff, N. CTFFIND4: Fast and accurate defocus estimation from electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 192, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheres, S.H.W. RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.; Sali, A.; Baker, M.L.; Carragher, B.; Devkota, B.; Downing, K.H.; Egelman, E.H.; Feng, Z.; Frank, J.; Grigorieff, N.; et al. Outcome of the First Electron Microscopy Validation Task Force Meeting. Structure 2012, 20, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Jain, S.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. The Phenix software for automated determination of macromolecular structures. Methods 2011, 55, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannuzzu, L.M.; Isacoff, E.Y. Independence and Cooperativity in Rearrangements of a Potassium Channel Voltage Sensor Revealed by Single Subunit Fluorescence. J. Gen. Physol. 2000, 115, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, M.; Kurtz, L.; Tombola, F.; Isacoff, E. The Cooperative Voltage Sensor Motion that Gates a Potassium Channel. J. Gen. Physol. 2005, 125, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalstrup, T.; Blunck, R. Dynamics of internal pore opening in KV channels probed by a fluorescent unnatural amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8272–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonggu, L.; Wang, L. Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment. Membranes 2022, 12, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080758
Tonggu L, Wang L. Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment. Membranes. 2022; 12(8):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080758
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonggu, Lige, and Liguo Wang. 2022. "Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment" Membranes 12, no. 8: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080758
APA StyleTonggu, L., & Wang, L. (2022). Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment. Membranes, 12(8), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080758






