Resin-Loaded Heterogeneous Polyether Sulfone Ion Exchange Membranes for Saline Groundwater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Heterogeneous Cation and Anion Exchange Membranes
2.3. Membrane Characterisation
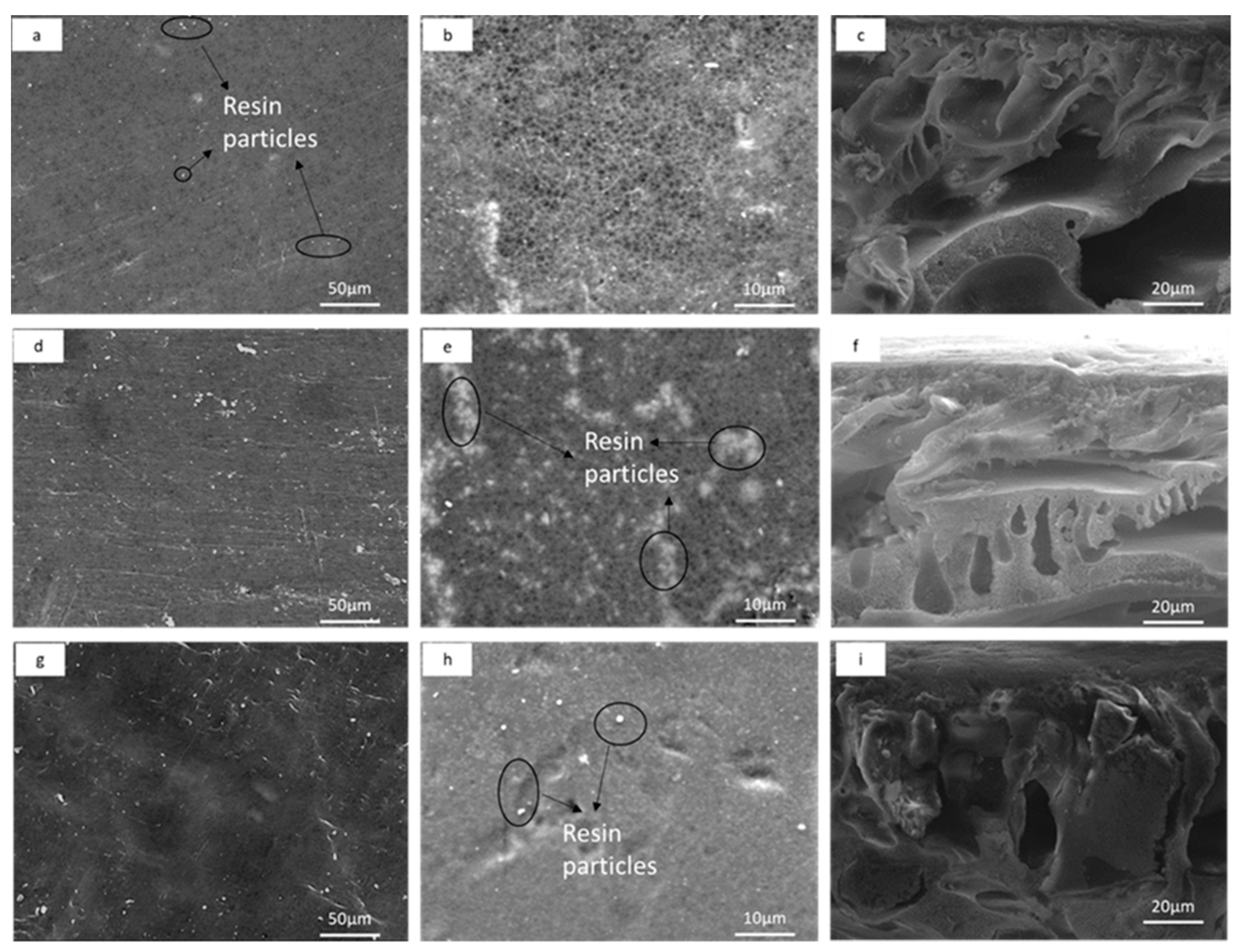
2.3.1. Membrane Morphology and Topography
2.3.2. Hydrophilicity
2.3.3. Water Uptake
2.3.4. Ion Exchange Capacity (IEC) and Fixed Ion Concentration (FIC)
2.3.5. Membrane Potential, Transport Number and Permselectivity
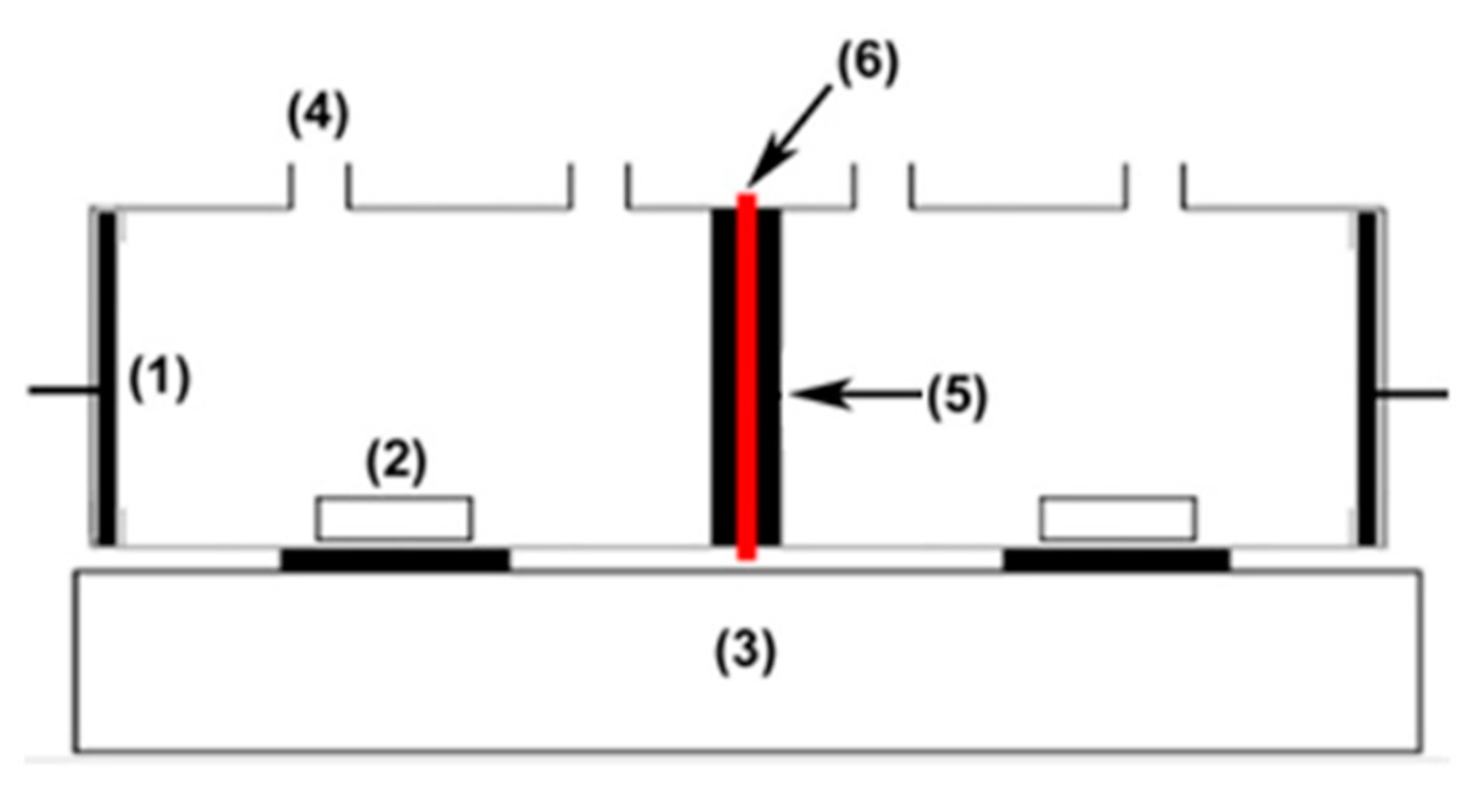
2.4. Membrane Testing and Application
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Characterisation
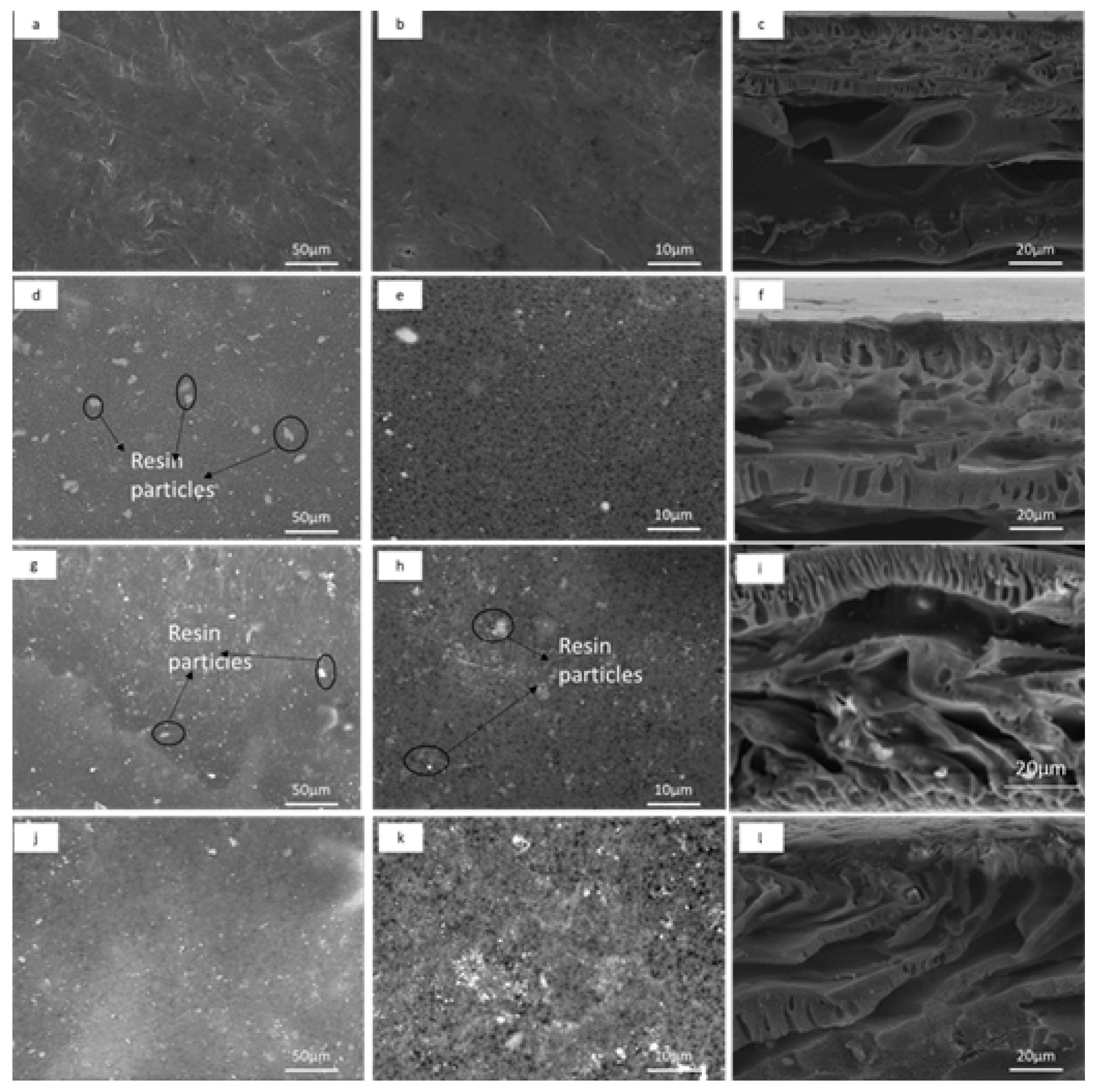
3.1.1. Membrane Morphology
3.1.2. Membrane Topography
3.1.3. Hydrophilicity
3.1.4. Water Uptake
3.1.5. Ion Exchange Capacity and Fixed Ion Concentration
3.1.6. Membrane Potential, Transport Number and Permselectivity
3.2. Membrane Application
3.2.1. Pure Water Flux
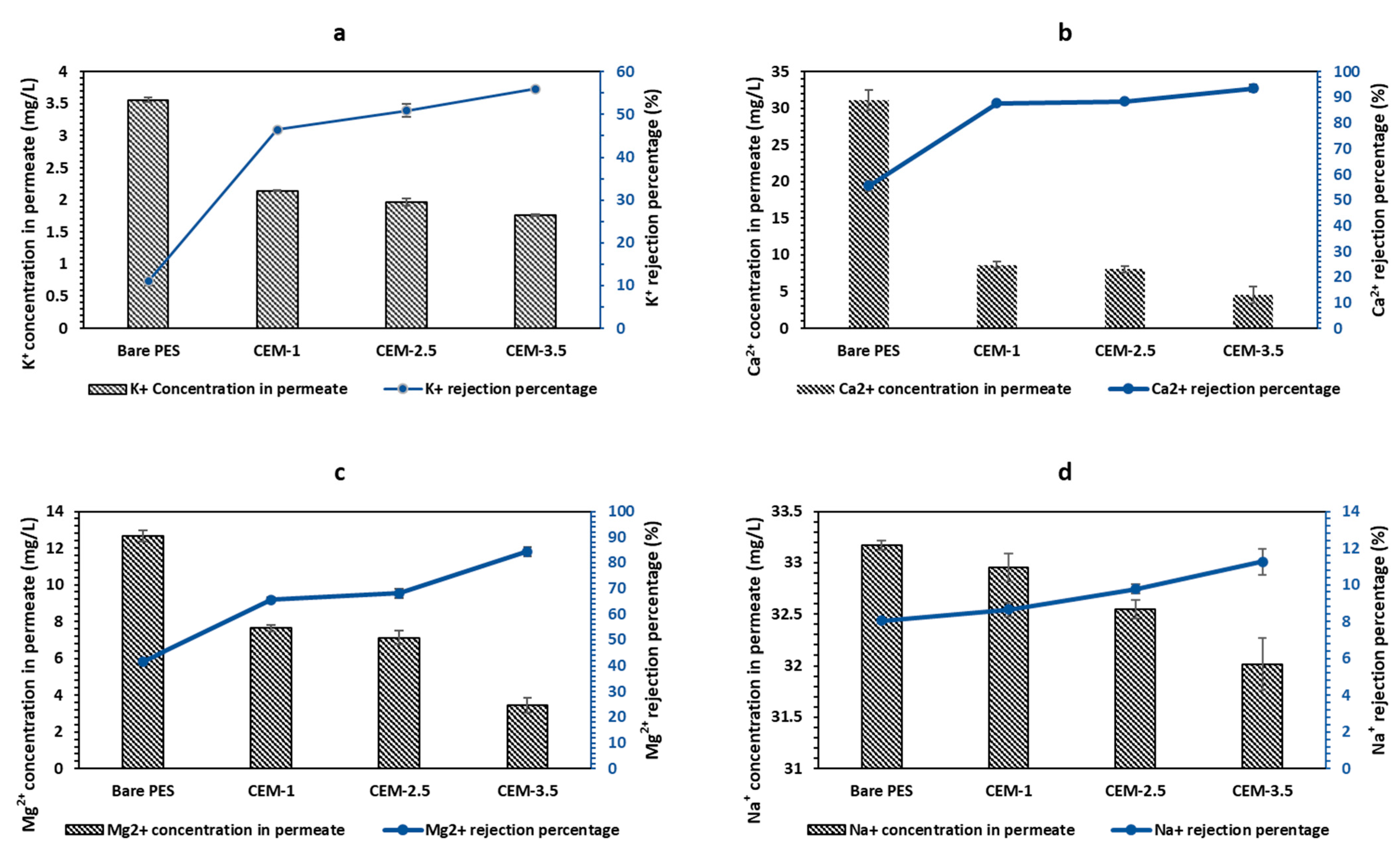
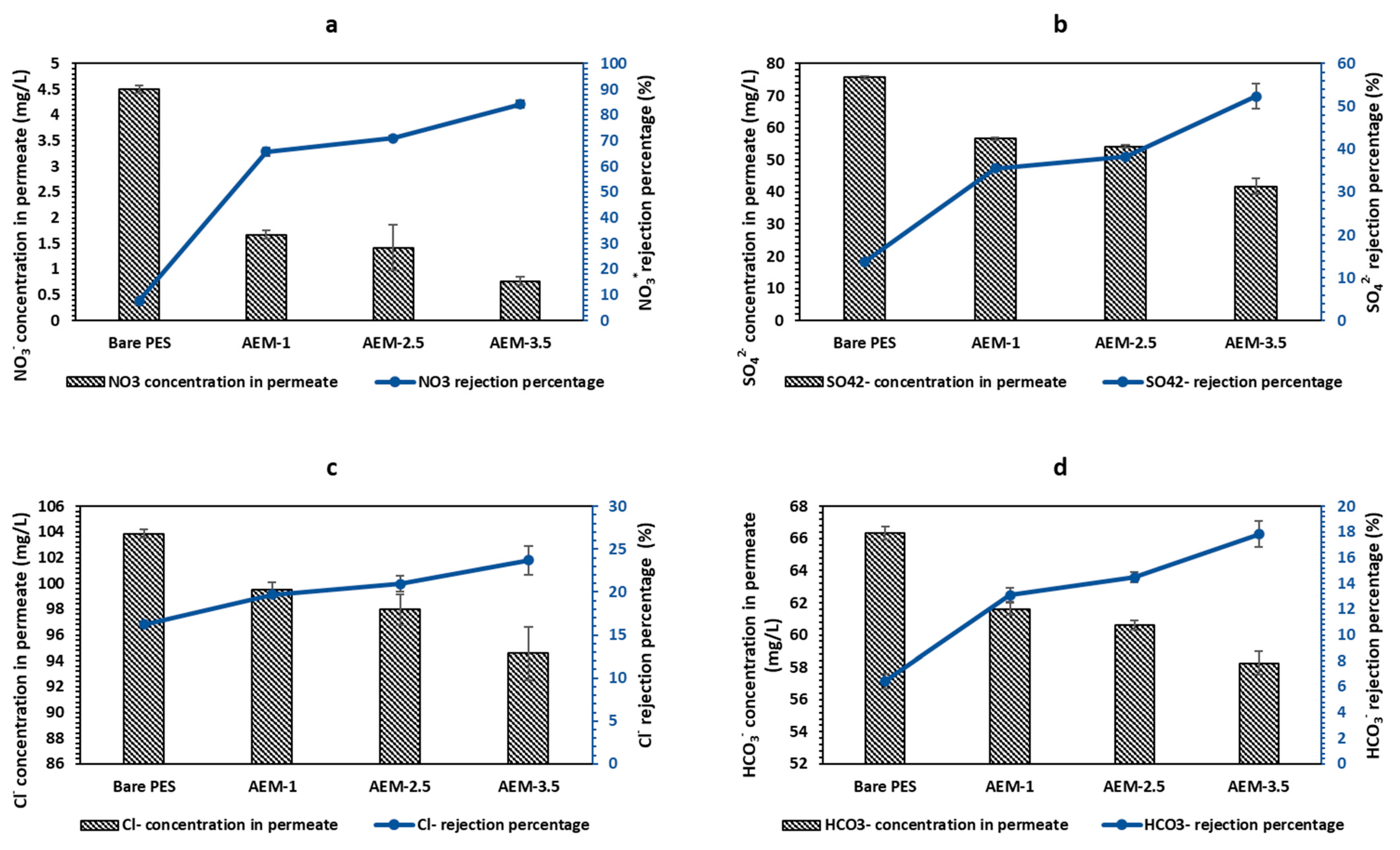
3.2.2. Salt Rejection Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, P.; Capito, M.; Cath, T. Selective removal of arsenic and monovalent ions from brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Desalination for Safe Water Supply: Guidance for the Health and Environmental Aspects Applicable to Desalination; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Verberk, J.; Verhack, J. Comparison of pressure-driven membrane processes and traditional processes for drinking water production in Europe based on specific impact criteria. Water SA 2004, 30, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salama, R.B.; Otto, C.J.; Fitzpatrick, R. Contributions of groundwater conditions to soil and water salinization. Appl. Hydrogeol. 1999, 7, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, A.; Molina, L.; Llop, A.; MacDonald, A.M. Impact of irrigated agriculture on groundwater-recharge salinity: A major sustainability concern in semi-arid regions. Appl. Hydrogeol. 2018, 26, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Salinization of groundwater in arid and semi-arid zones: An example from Tajarak, western Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2007, 52, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWS. National Groundwater Strategy—Draft 4; Department of Water and Sanitation: Pretoria, South Africa, 2016; pp. 1–89.
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osomosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter-Varbanets, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Swartz, C.; Pronk, W. Decentralized systems for potable water and the potential of membrane technology. Water Res. 2009, 43, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Manna, A.; Pal, P. Removal of arsenic from contaminated groundwater by membrane intergrated hybrid treatment system. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion exchange membranes: Classification charaterization and strategies of preventation and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: State of their development and perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Gohil, G.S.; Shahi, V.K. Recent developments on ion exchange membranes and electro-membrane processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 119, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariduranganavar, M.Y.; Nagarale, R.K.; Kulkami, D.D. Electrodialytic transport properties of heterogenous cation exchange membranes prepared by gelation and solvent evapouration methods. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Davies, G.L.; Guriko, Y.K.; Vigues, N.; Munoz-Berbel, X.; Macanas, J.; Mas, J.; Munoz, M.; Muraviev, D. Ecologically friendly polymer-metal and polymer metal oxide nanocomposites for complex water treatment. In New Trends and Developments; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 187–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Nagarale, R.K.; Kittur, A.A.; Kulkarni, S.S. Ion exchange membranes: Perparative methods for electridialysis and fuel cell applications. Desalination 2006, 197, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Heidari, A.R.; Khodabakhshi, A.R. Preparation and charaterization of poly(vinyl chloride)-blend-poly(carbonate) heterogeneous cation exchange membrane: Investigation of solvent type and ratio effects. Desalination 2012, 285, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.V.; Shah, B.; Trivedi, G.; Ray, P.; Adhikary, S.; Rangarajan, R. Studies on heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 44, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.-L.; Jia, Y.-X.; Liu, X. An attempt for improving electrodialytic transport properties of a heterogeneous anion exchange membrane. Desalination 2014, 351, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.V.; Shah, B.G.; Trivedi, G.S.; Ray, P.; Adhikary, S.K.; Rangarajan, R. Charaterization of heterogenous anion exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 187, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.V.; Ray, P.; Adhikary, S.K.; Shah, B.G.; Rangarajan, R. Studies of the effect of variation of blend ratio on permselectivity and heterogeniety of ion exchange membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 127–134, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Klaysom, C.; Moon, S.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.M.; Wang, L. Preparation of porous ion exchange membrane (IEMs) and ther characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubita, T.; Porada, S.; Aerts, P.; van der Wal, A. Heterogeneous anion exchange membranes with nitrate selectivity and low electrical resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 607, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinertova, K.; Honorato, R.S.; Stranska, E.; Nedela, D. Comparison of heterogeneous anion-exchange membranes for nitrate ion removal from mixed salt solution. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křivčík, J.; Neděla, D.; Hadrava, J.; Brozova, L. Increasing selectivity of a heterogeneous ion-exchange membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 56, 3160–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubenko, D.V.; Karavanova, Y.A.; Melnikov, S.S.; Achoh, A.R.; Pourcelly, G.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. An approach to increase the premselectivity and mono-valent ion selectivity of cation exchange membranes by introduction of amorphous zicronium phosphate. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Oaiser, A.; Huda, N.; Saeed, A. Heterogeneous ion exchange membranes based on thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU): Effect of PSS/DVB resin on morphology and electrodialysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Madaeni, S.; Khodabakhshi, A. Heterogeneous cation exchange membrane: Preparation, charaterization and comparison of transport properties of mono and bivalent cations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2308–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadja, V.; Makwana, S.; Maiti, S.; Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, U. Comparative efficacy study of different type of ion exchange membrane for production of ultrapure water via electrodeionzation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 10974–10982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, L.; Ladewig, B.P.; Mulcany, D. Synthesis and Charaterization of superhydrophilic conductive heterogeneous PANI/PVDF anion exchange membranes. Desalination 2015, 362, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, A.; Madaeni, S.; Hosseini, S. Investigation of electrochemical and morphological properties of S-PVC based heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes modified by sodium dodecyl sulphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 77, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akberova, E.; Vasiléva, V. Effect of resin content in cation-exchange membranes on development of electroconvection. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 111, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarita, C.; Mulyati, S.; Arahman, N.; Bilad, M.; Shamsuddin, S.; Ismali, N. Improvement of properties and performances of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by blending with bio-based dragonbloodin resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C. Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 272, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chazaro-Ruiz, L. Porous PVDF/PANI ion exchange membrane (IEM) modified by polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and lithium chloride in the application of membrane capacitive deionisation (MCDI). Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Alled, J.M.; Abdel-Karim, A.; Alberto, M.; Leaper, S.; Perez-Page, M.; Huang, K.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; El-Kalliny, A.S.; Holmes, S.M.; Gorgojo, P. Polyethersulfone membranes: From ultrafiltration to nanofiltration via the incorporation of APTS functionalized-graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.-H.; Chen, L.-W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination 1995, 103, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienk, I.M.; Boomgaard, T.V.D.; Smolders, C.A. The formation of nodular structures in the top layer of ultrafiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 53, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, T.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Mixed-Matrix Membrane Fabrication for Water Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, N.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Alamry, K.A.; Asiri, A.M. Modified polyether-sulfone membrane: A mini review. Des. Monomers Polym. 2017, 20, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, J.; Ray, P. Preparation of heterogeneous cation and anion exchange membranr by eco-friendly method: Electrochemical charaterization and desalination performance. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rameetse, M.; Aberefa, O.; Daramola, M. Effect of loading and functionalizatopn of carbon nanotube on the performance of blended polysulfone/polyethersulfone membrane during treatment of wastewater containing phenol and benzene. Membranes 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, M.; Kikhavani, T.; Ashrafizadeh, S. Synthesis and charaterization of enhanced heterogeneous cation exchange membrane via nanoclay. Ionics 2017, 23, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNair, R.; Szekely, G.; Dryfe, R.A.W. Ion-Exchange Materials for Membrane Capacitive Deionization. ACS ES&T Water 2020, 1, 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Jashni, E.; Hosseini, S.; Shen, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Electrochemical charaterization of mixed matrix electrodialysis cation exchange membrane incorporated with carbon nanofibres for desalination. Ionics 2019, 25, 5595–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariono, D.; Prabandari, D.; Wulandari, R.; Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin. Preparation and charaterization of polysulfone/PEG heterogenous ion exchange membrane for reverse electrodialysis (RED). J. Phys. 2017, 877, 012075. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, M.; Hosseini, S.; Bagheripour, E.; Madaeni, S. Surface modifiation of cation exchange membranes by graft polymerization of PAA-co-PANI/MCNTs nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Rahzani, B.; Asiani, H.; Khodabakhshi, A.; Seidypoor, A. Surface modification of heterogenous cation exchange membranes by simultaneous using polymerization of (acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) membrane charaterization in desalination process. Desalination 2014, 345, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Rafiuddin. Transport phenomena of inorganic-organic cation exchange nanocomposite membrane: A comparative study with different methods. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2014, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.; Cassady, H.; Paul, D.; Logan, B.; Hickner, M. Specific ion effects on membrane potential and permselectivity of ion exchange membranes. R. Soc. Chem. 2014, 16, 21673–21681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Mondal, A.N.; Tong, B.; Jiang, C.; Emmanuel, K.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Development of BPPO-based anion exchange membranes for electrodialysis desalination applications. Desalination 2016, 391, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Koranian, P.; Gholami, A.; Madaeni, S.; Moghadassi, A.; Sakinejad, P.; Khodabakhshi, A. Fabrication of mixed matrix heterogeneous ion exchange membrane by multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Electrochemical charaterization and transport properties of mono and bivalent cations. Desalination 2013, 329, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinkhameh, M.; Zendehnam, A.; Hosseini, S.M. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite heterogeneous cation exchange membranes modified by silver nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Hosseini, S.; Shabanian, M. Novel electrodialysis cation exchange membrane prepared by 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid; heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 337, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Zheng, C.; Mondal, A.N.; Hossain, M.; Wu, B.; Emmanuel, K.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Preparation of anion exchange membranes from BPPO and dimethylethanolamine for electrodialysis. Desalination 2017, 402, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, I.; Golubenko, D.; Nikonenko, V.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Selectivity of Transport Processes in Ion-Exchange Membranes: Relationship with the Structure and Methods for Its Improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, X. Enhancement in flux and antifouling properties of polyvinylidene fluoride/polycarbonate blend membranes for water environmntal improvements. Am. Chem. Soc. Omega 2020, 5, 30201–30209. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggen, B.; Verberk, J.; Verhack, J. A review of pressure-driven membrane process in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Enviromental Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ghyselbrecht, K.; Meesschaert, B.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Electrodialysis on RO concentrate to improve water recovery in wastewater reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Kang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Preparation and performance of a charge-mosaic nanofiltration membrane with novel salt concentration sensitivity for the separation of salts and dyes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Abdu, S.; Wessling, M. Selectivity of ion exchange membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Ion Rejection in Covalent Organic Frameworks: Revealing the Overlooked Effect of In-Pore Transport. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45246–45255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, P.; Vaezi, F.; Mahvi, A.; Naddaffi, K.; Rahmani, A. Nitrate removal from drinking water by piont of use ion exchange. J. Res. Health Sci. 2010, 10, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nujic, M.; Milinkovic, D.; Habuda-Stanic, M. Nitrate removal from water by ion exchange. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada, H. Guidelines for Canada Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Total Dissolved Solids (TDS); Healthy Living: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]

| Membrane Type | Sample | PES (wt %) | PEG (wt %) | Resin Powder (wt %) | NMP (wt %) | Membrane Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare PES membrane | PES | 15 | 2 | 0 | 83 | 190.7 |
| Cation exchange membrane (CEM) | CEM-1 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 82 | 197.5 |
| CEM-2.5 | 15 | 2 | 2.5 | 80.5 | 199.6 | |
| CEM-3.5 | 15 | 2 | 3.5 | 79.5 | 216.8 | |
| Anion exchange membrane (AEM) | AEM-1 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 82 | 207.6 |
| AEM-2.5 | 15 | 2 | 2.5 | 80.5 | 220.8 | |
| AEM-3.5 | 15 | 2 | 3.5 | 79.5 | 223.2 |
| Membrane Type | Sa (nm) | Sq (nm) | Contact Angle (°) | Water Uptake (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare PES | 471.107 | 584.916 | 88.89 ± 4.34 | 58.89 ± 1.23 |
| CEM-1 | 42.1155 | 68.6434 | 86.13 ± 3.10 | 61.20 ± 0.50 |
| CEM-2.5 | 102.084 | 149.473 | 84.10 ± 2.05 | 62.79 ± 0.80 |
| CEM-3.5 | 317.252 | 365.124 | 76.26 ± 2.68 | 65.55 ± 0.52 |
| AEM-1 | 68.5571 | 99.1441 | 88.02 ± 2.27 | 63.44 ± 1.45 |
| AEM-2.5 | 153.511 | 189.011 | 73.56 ± 4.62 | 63.58 ± 0.53 |
| AEM-3.5 | 295.952 | 354.847 | 74.49 ± 4.50 | 63.96 ± 0.32 |
| Membrane Type | IEC (meq·g−1) | FIC (meq·g−1) | Membrane Potential (mV) | Transport Number (t) | Permselectivity (Ps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare PES | 0 | 0 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.50 ± 0.0001 | 0.17 ± 0.0002 |
| CEM-1 | 0.06 ± 0.003 | 0.10 ± 0.004 | 6.44 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.0001 | 0.26 ± 0.001 |
| CEM-2.5 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.50 ± 0.07 | 13.67 ± 0.12 | 0.62 ± 0.001 | 0.37 ± 0.002 |
| CEM-3.5 | 0.58 ± 0.07 | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 18.97 ± 0.21 | 0.66 ± 0.002 | 0.44 ± 0.003 |
| AEM-1 | 0.5 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 7.64 ± 0.15 | 0.57 ± 0.001 | 0.28 ± 0.002 |
| AEM-2.5 | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 1.26 ± 0.09 | 19.5 ± 0.32 | 0.67 ± 0.003 | 0.45 ± 0.004 |
| AEM-3.5 | 1 ± 0.09 | 1.56 ± 0.14 | 26.0 ± 0.10 | 0.72 ± 0.001 | 0.54 ± 0.001 |
| Membrane Type | Pure Water Flux (L·m−2·h−1) |
|---|---|
| Bare PES | 8.71 ± 0.40 |
| CEM-1 | 10.78 ± 0.75 |
| CEM-2.5 | 12.50 ± 0.48 |
| CEM-3.5 | 14.90 ± 0.45 |
| AEM-1 | 11.58 ± 0.35 |
| AEM-2.5 | 14.93 ± 0.20 |
| AEM-3.5 | 17.79 ± 0.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mudau, F.; Motsa, M.; Hassard, F.; de Kock, L.-A. Resin-Loaded Heterogeneous Polyether Sulfone Ion Exchange Membranes for Saline Groundwater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080736
Mudau F, Motsa M, Hassard F, de Kock L-A. Resin-Loaded Heterogeneous Polyether Sulfone Ion Exchange Membranes for Saline Groundwater Treatment. Membranes. 2022; 12(8):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080736
Chicago/Turabian StyleMudau, Fulufhelo, Machawe Motsa, Francis Hassard, and Lueta-Ann de Kock. 2022. "Resin-Loaded Heterogeneous Polyether Sulfone Ion Exchange Membranes for Saline Groundwater Treatment" Membranes 12, no. 8: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080736
APA StyleMudau, F., Motsa, M., Hassard, F., & de Kock, L.-A. (2022). Resin-Loaded Heterogeneous Polyether Sulfone Ion Exchange Membranes for Saline Groundwater Treatment. Membranes, 12(8), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080736









