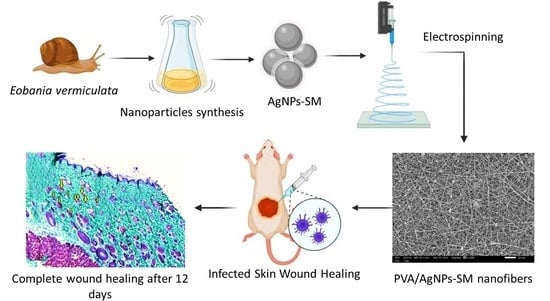
Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
2.2. Snail Samples and Mucus Collection
2.3. Snails’ Identification
2.4. Snails’ Mucus Collection
2.5. Snail Mucus Composition
2.6. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles—Snail Mucus Nanocomposite Dispersion
Physico-Chemical Characterization of AgNPs-SM
2.7. Antibacterial Activity of Snail Mucus and AgNPs-SM
2.8. Manufacturing of Nanofibrous Membranes
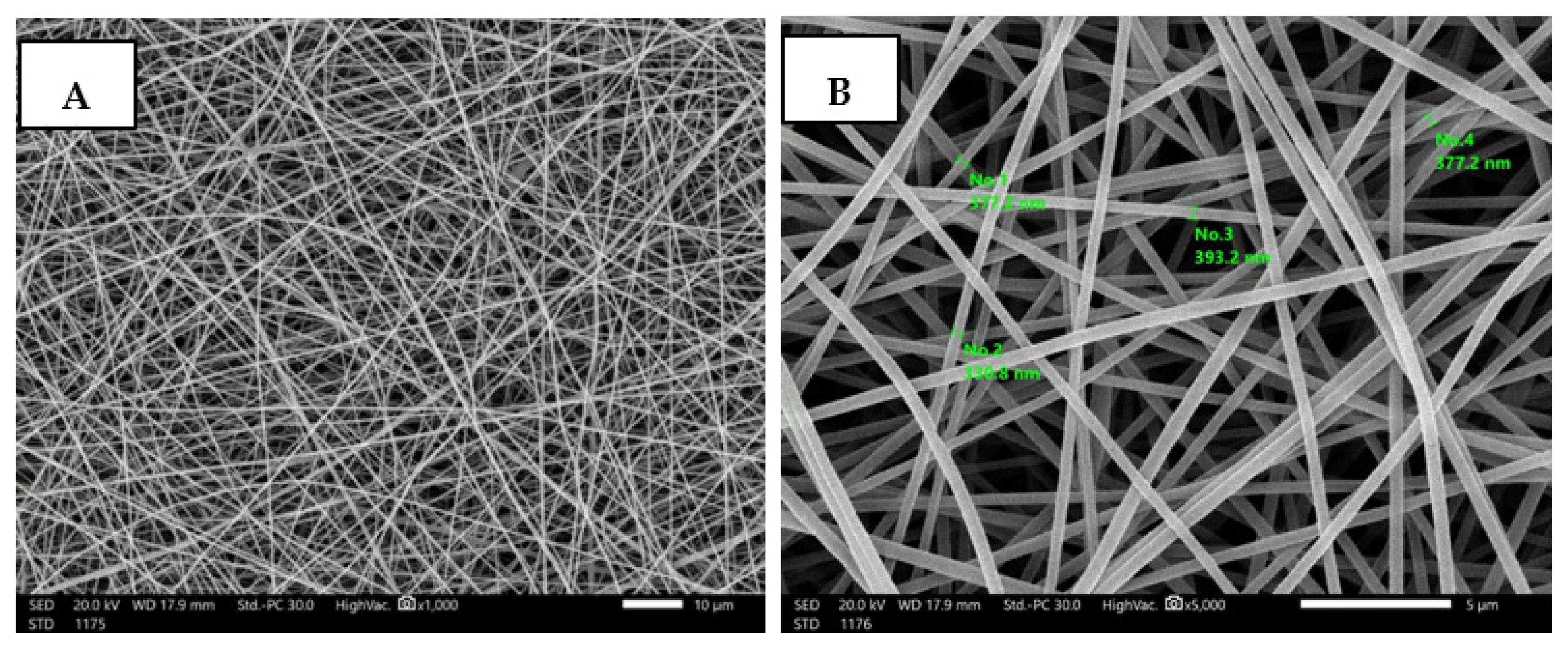
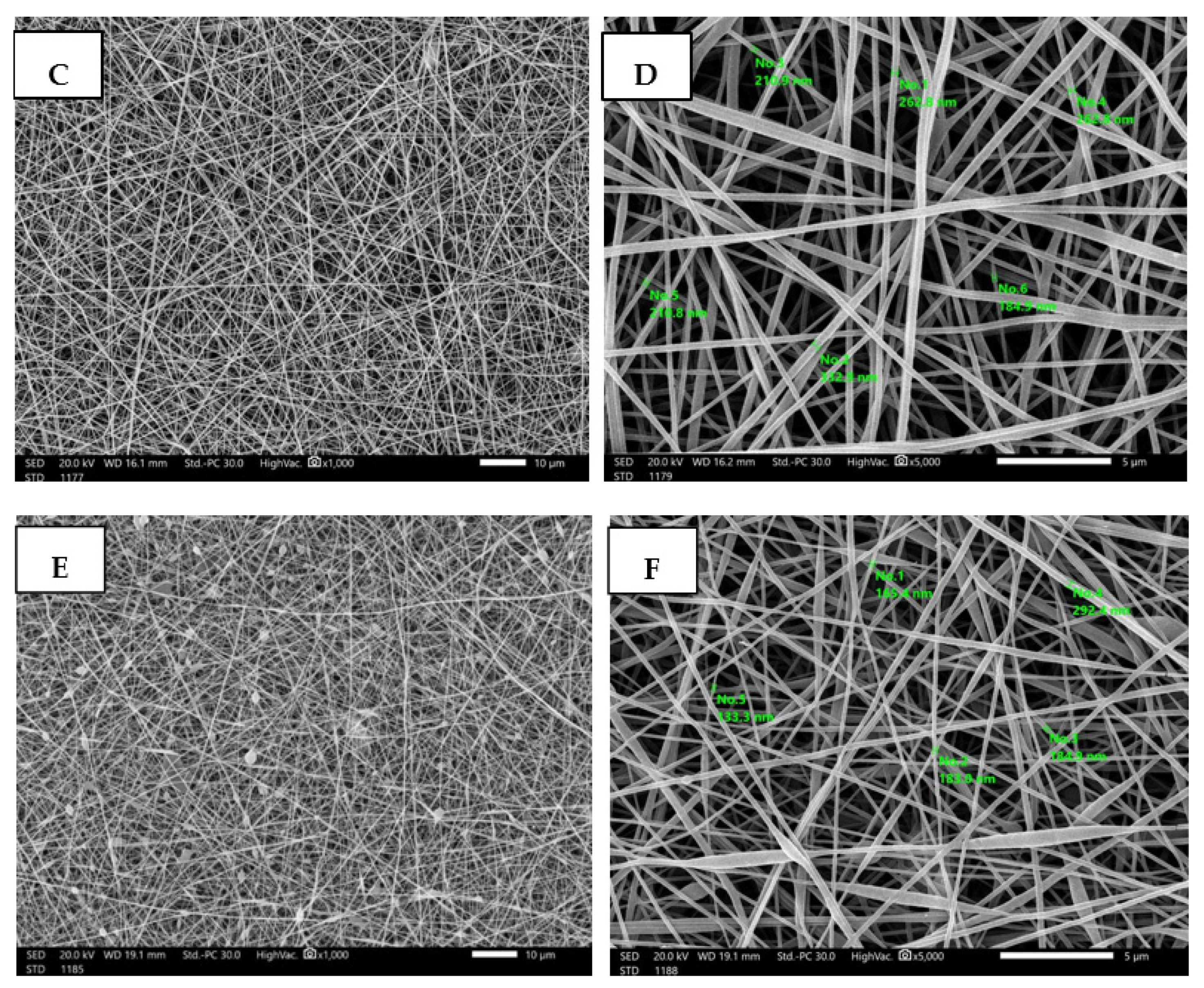
2.8.1. Morphological and Physical Characterizations of the Prepared Electrospun Nanofibers
2.8.2. Loading Analysis
2.9. In Vitro Studies
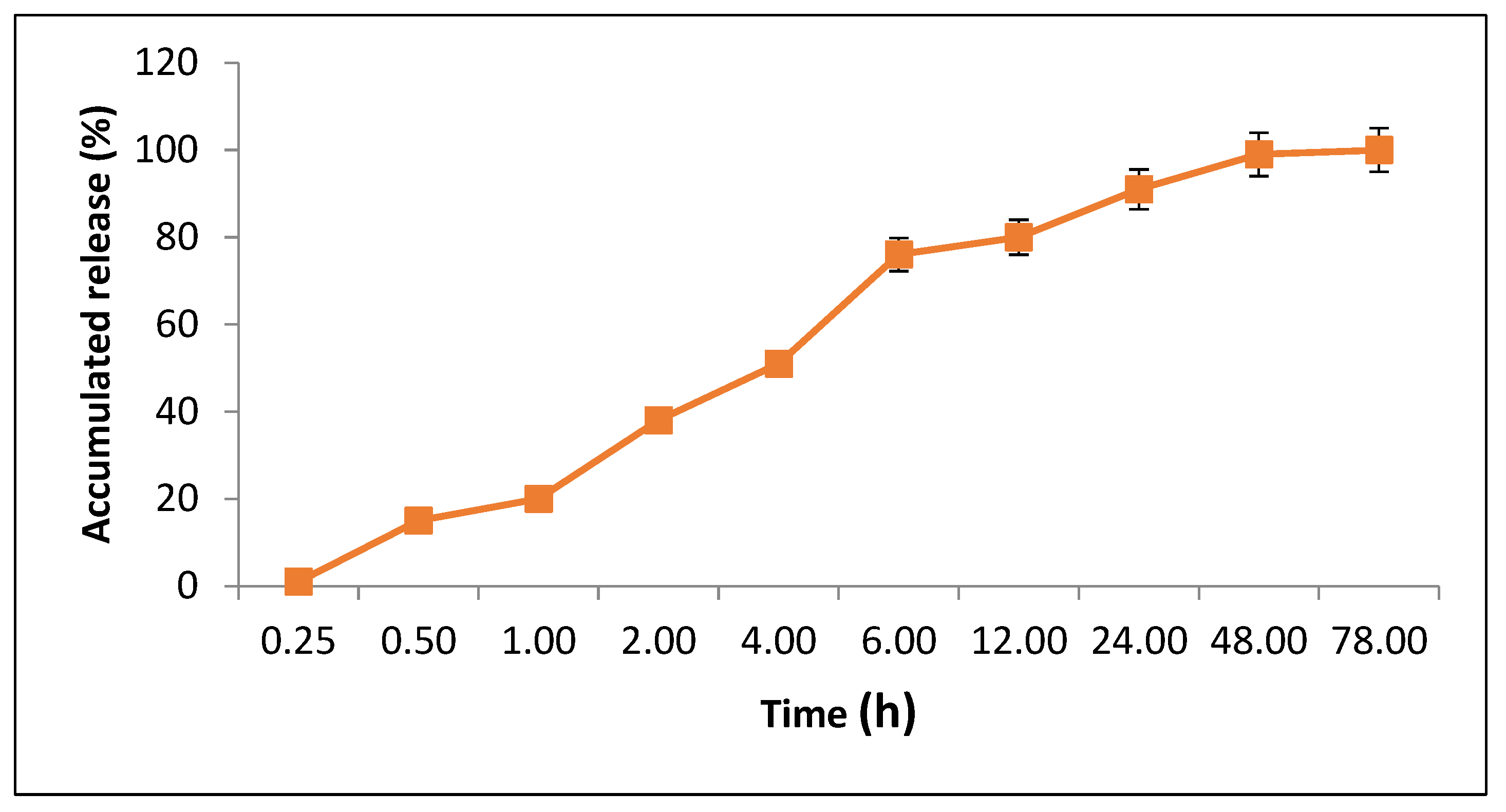
2.9.1. Release Profile Assay
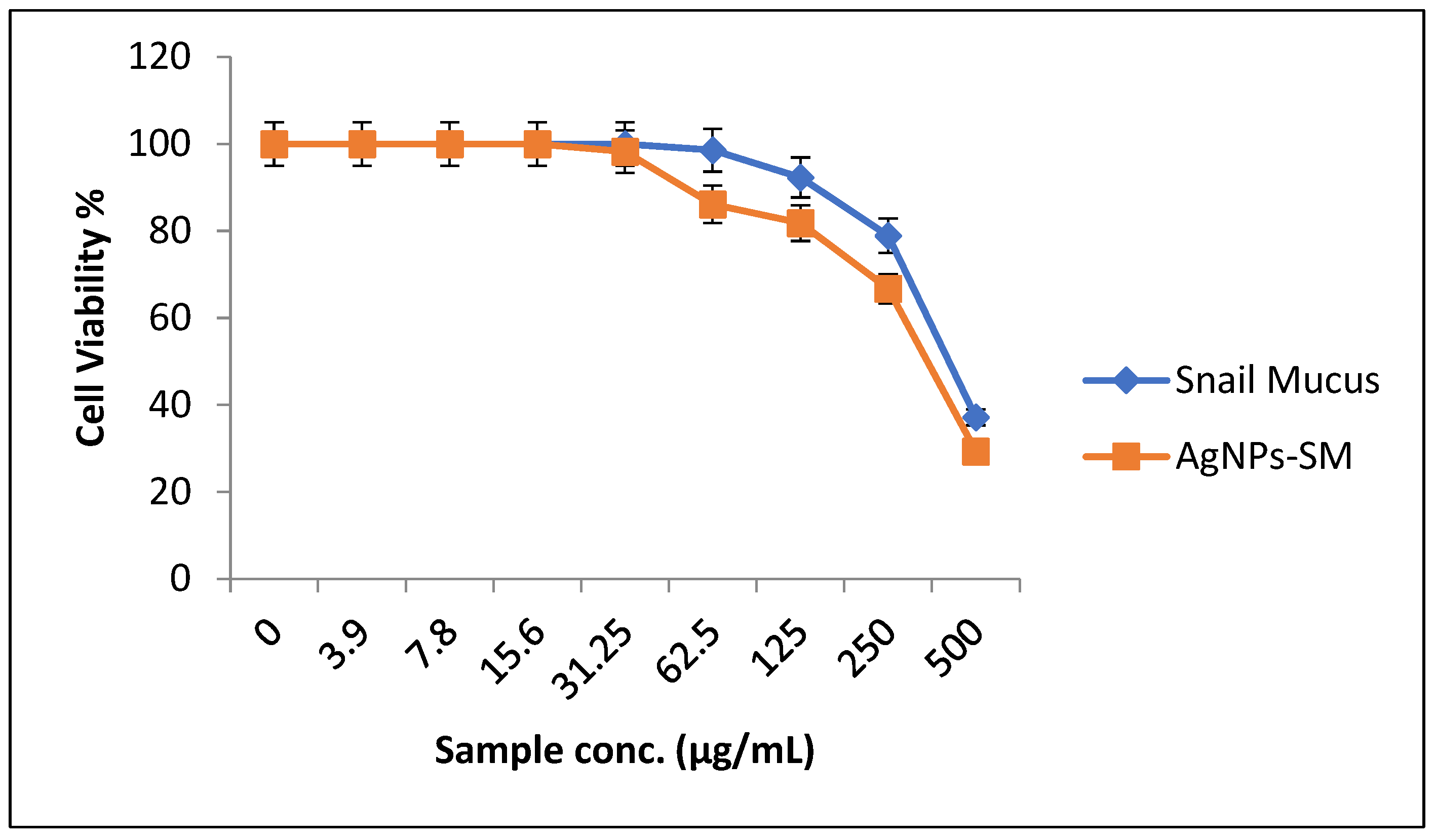
2.9.2. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Effect of the Prepared Electrospun Nanofibers
2.9.3. Antibacterial Activity of the Prepared Electrospun Nanofibers
2.10. In Vivo Skin Wound Healing Experiment
2.10.1. Animals and Ethics
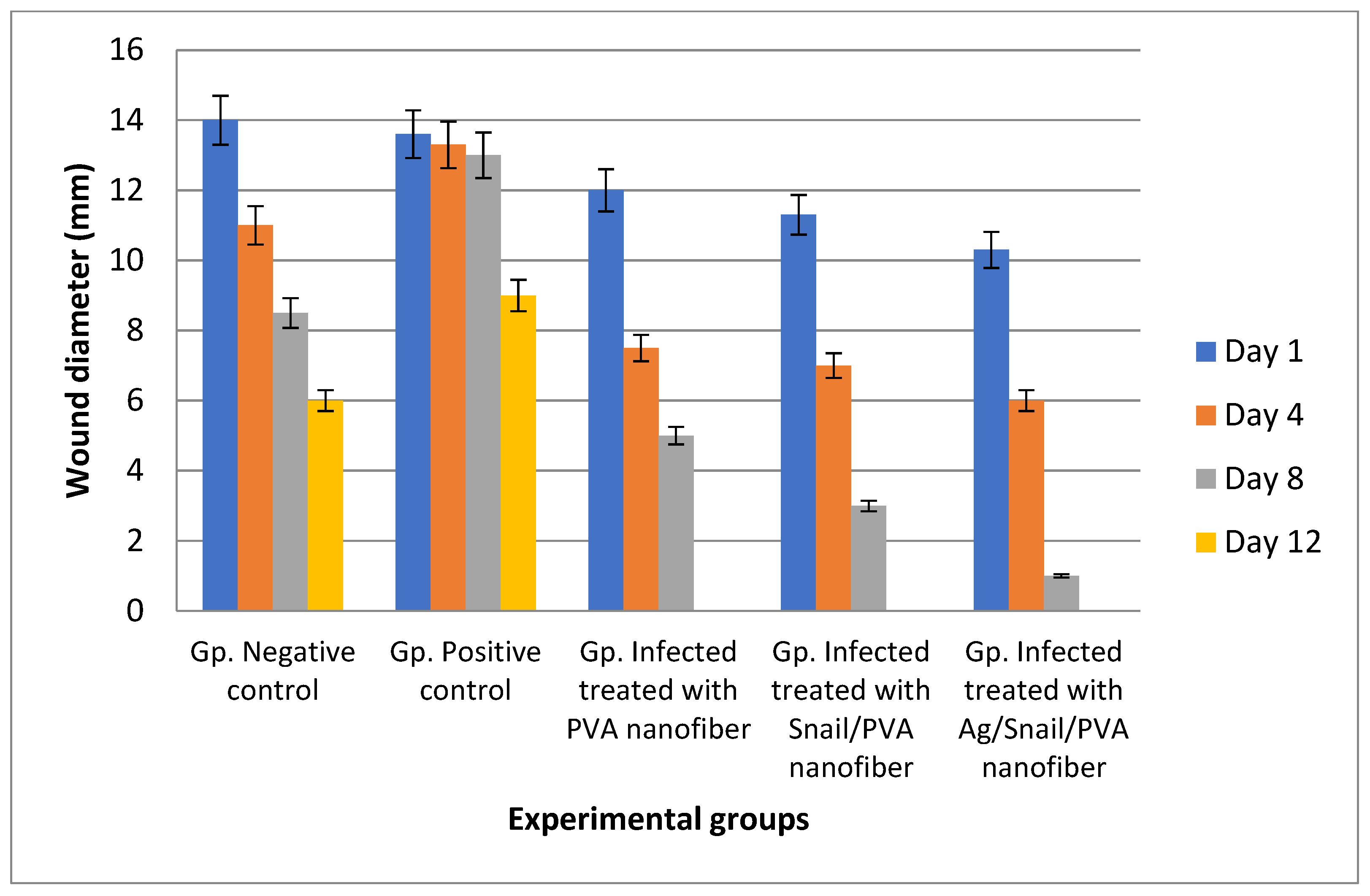
2.10.2. Wound Healing Assessment
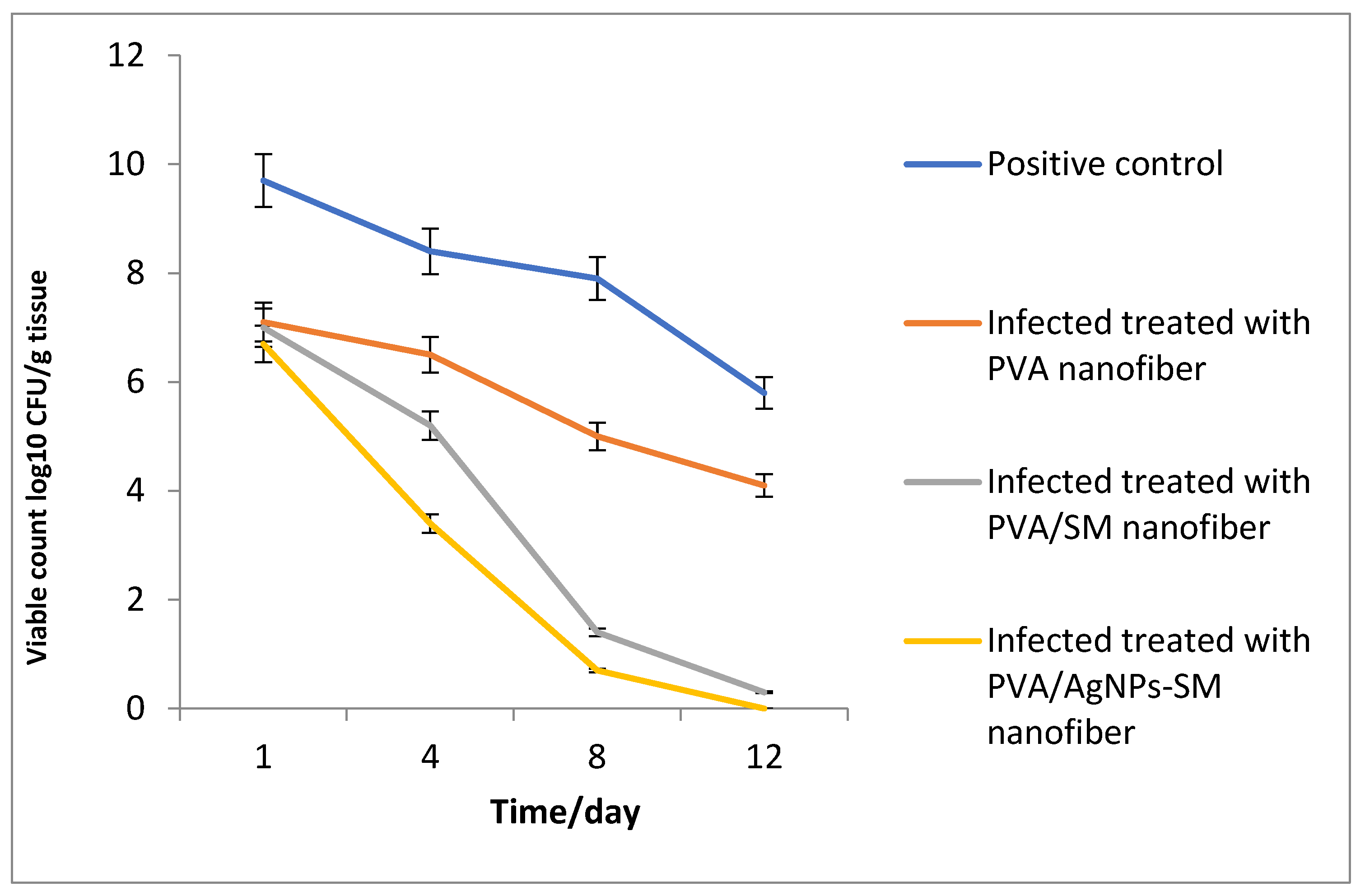
2.10.3. Bacterial Load Assessment
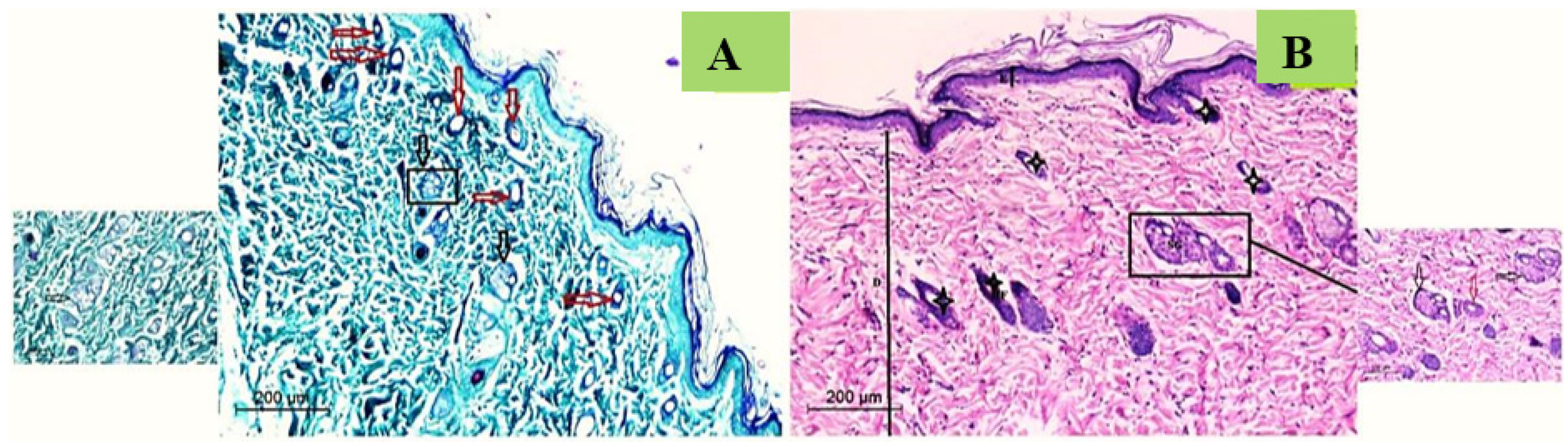
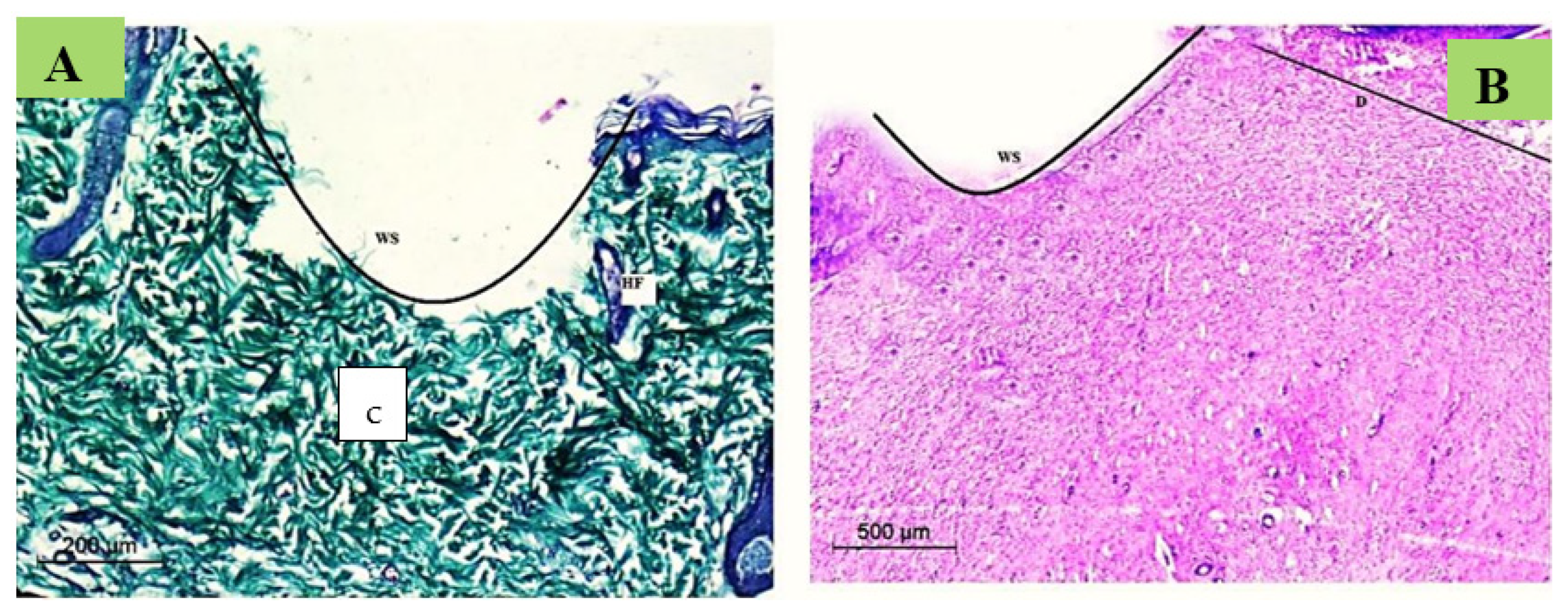
2.10.4. Histologic Examination
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition of Snail Mucus
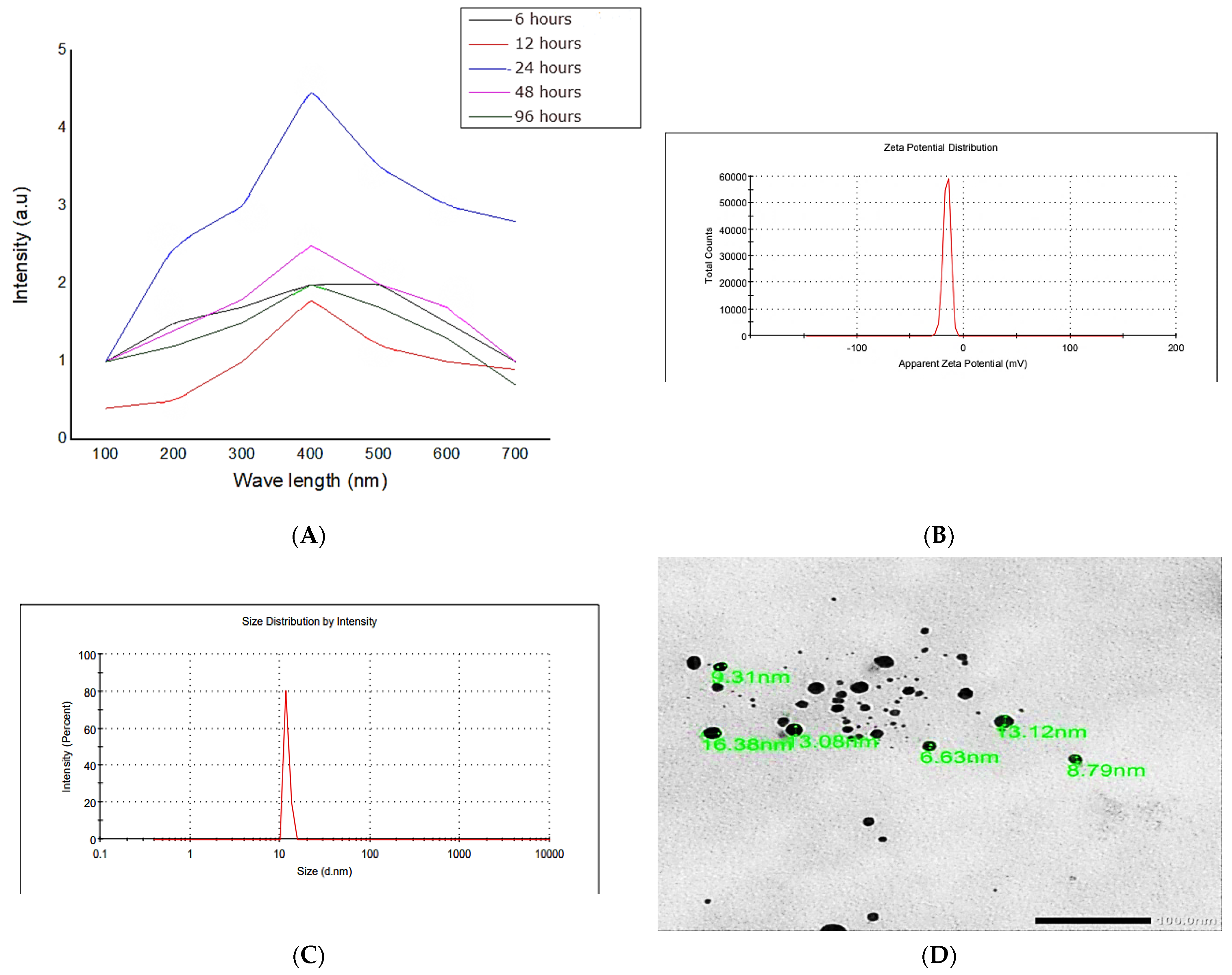
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles—Snail Mucus Nanocomposite Dispersion
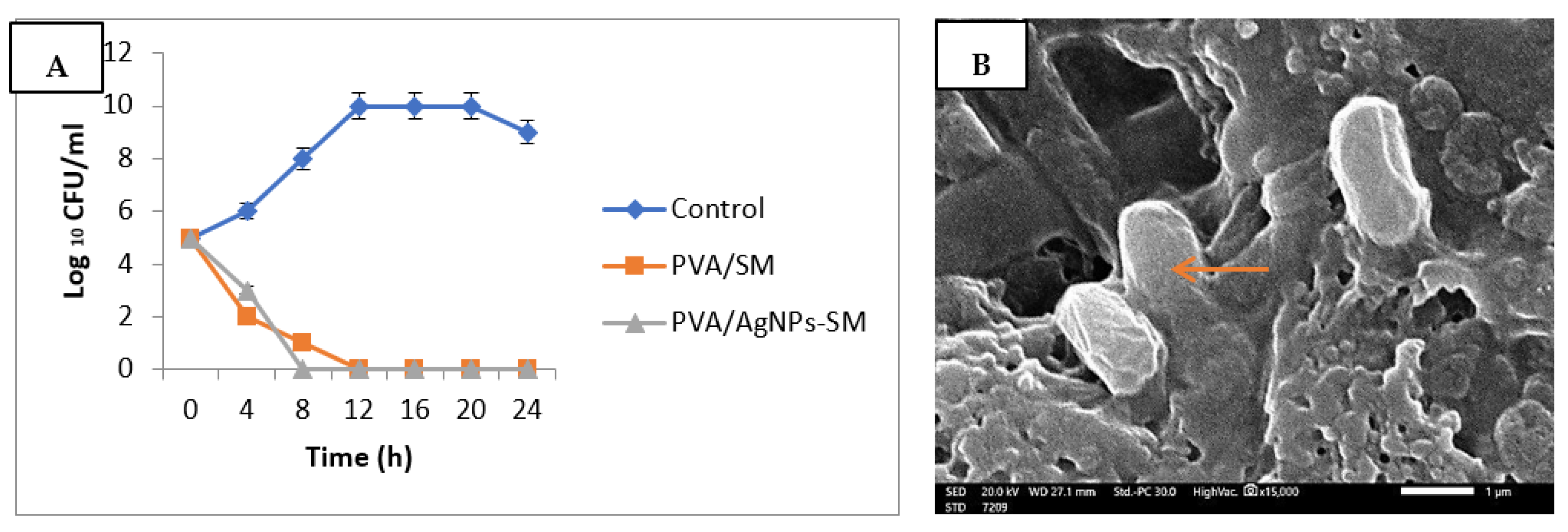
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of Snail Mucus and AgNPs-SM
3.4. Fabrication and Characterization of Nanofibrous AgNPs-SM/PVA
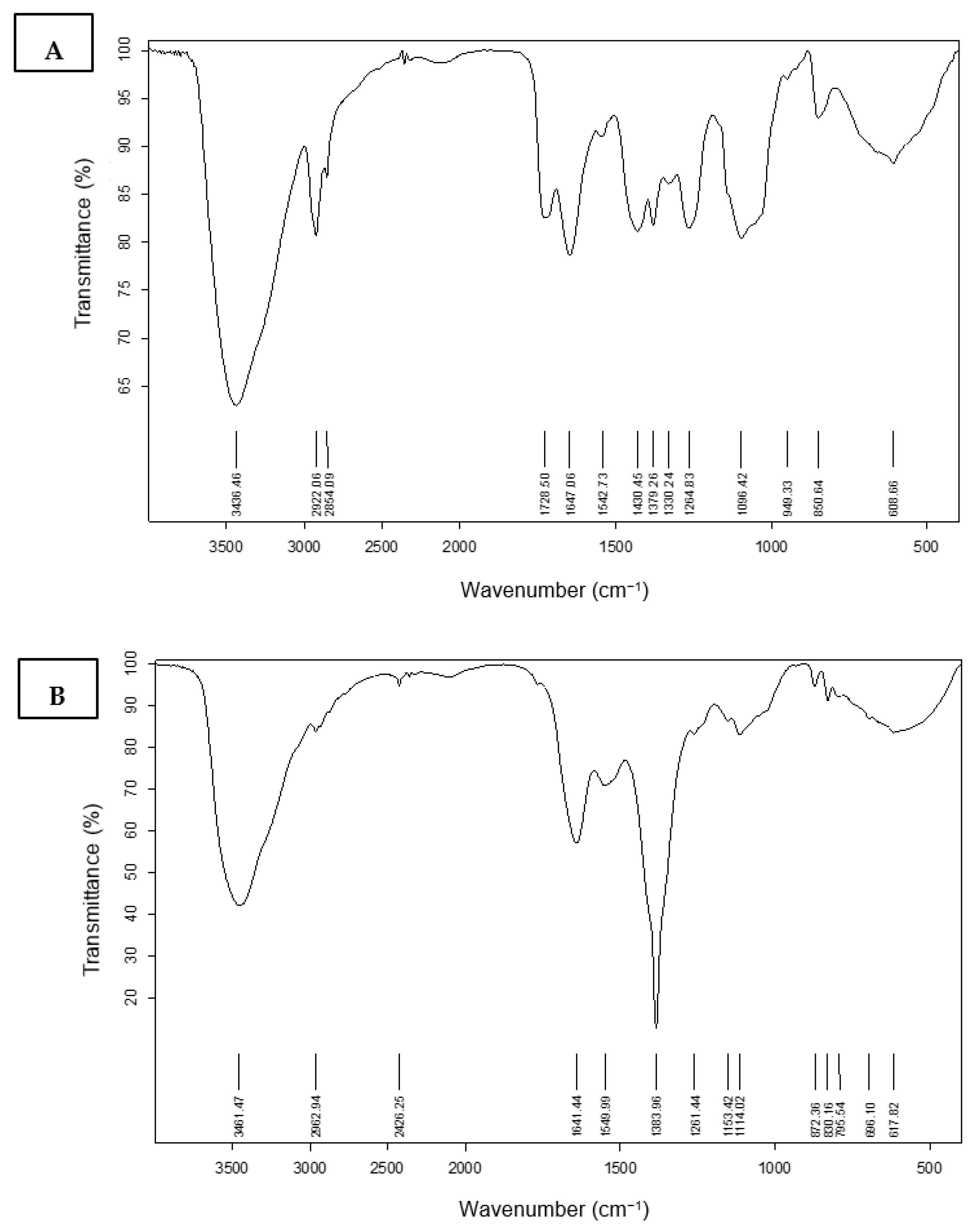
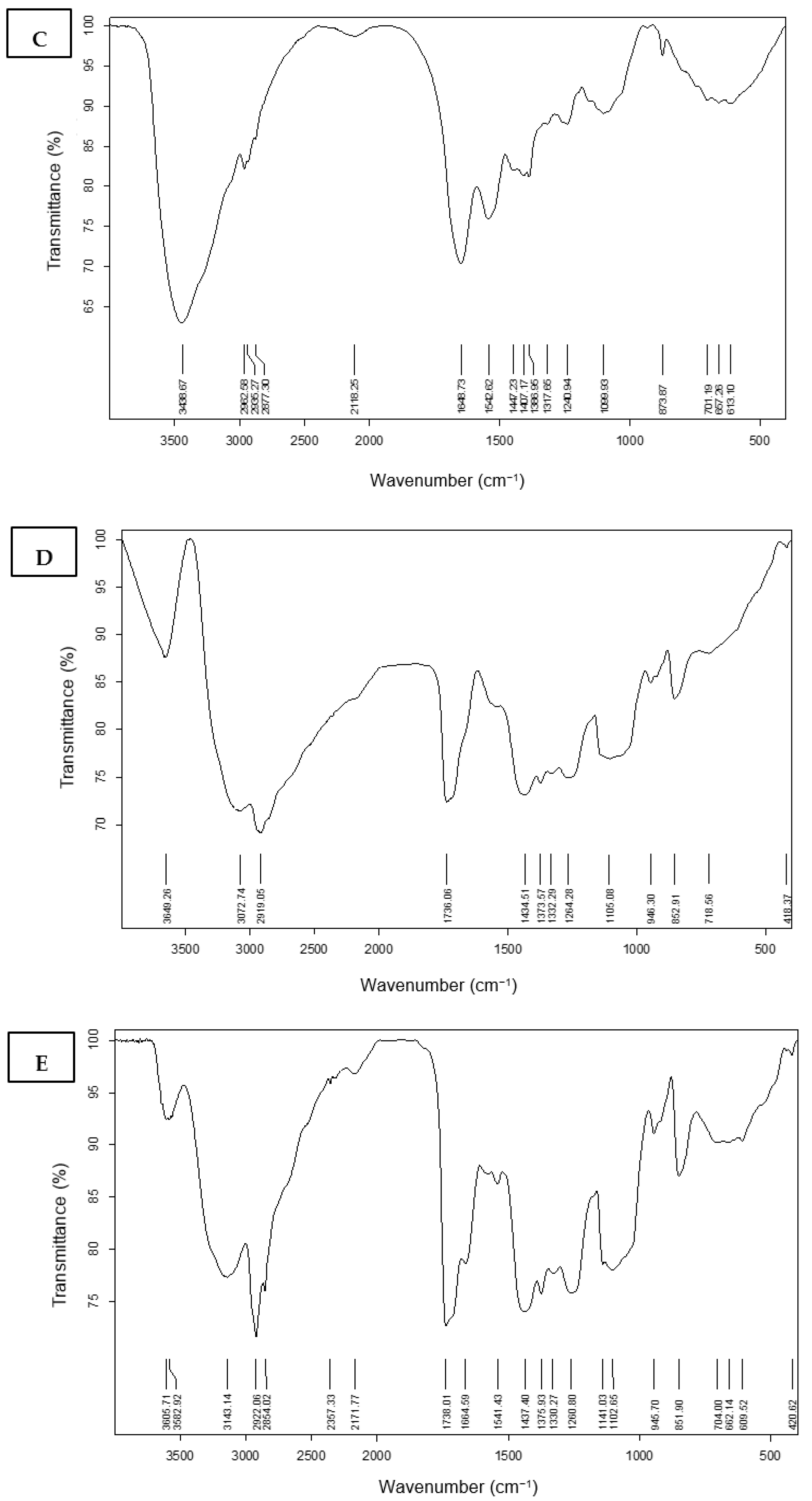
3.4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Characterization
3.4.2. Loading Analysis and Release Profile
3.5. Evaluation of Cytotoxic Effects of the Synthesized AgNPs-SM
3.6. Antibacterial Activity of the Prepared Nanofibers
3.7. In Vivo Experiments
3.7.1. Skin Wound Healing Experiment
3.7.2. Bacterial Load Assessment
3.7.3. Histological Study
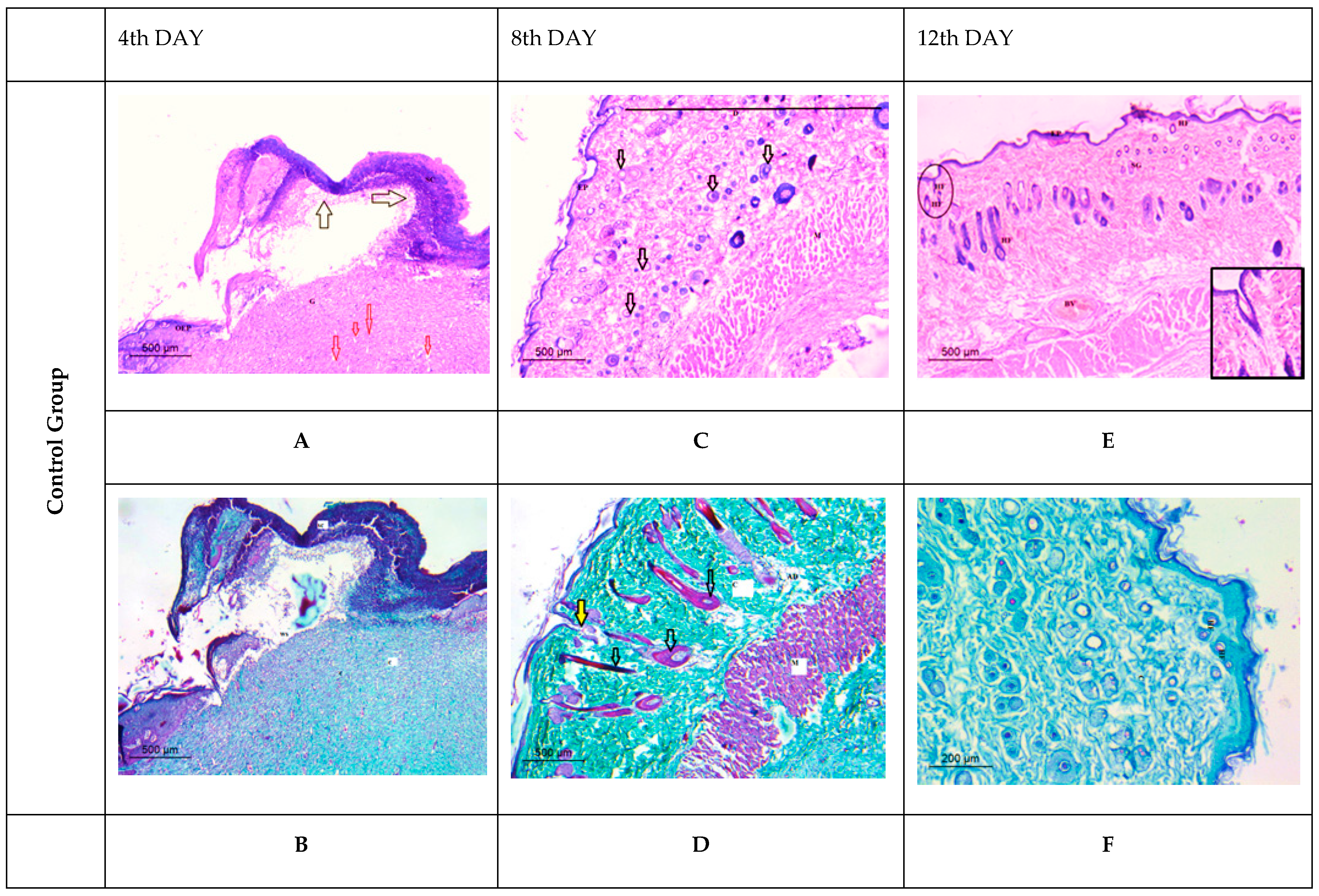
Normal Skin Histology
Wound Degree
Histological Observation of Skin of the Negative Control Wounded Rats (Group 1)
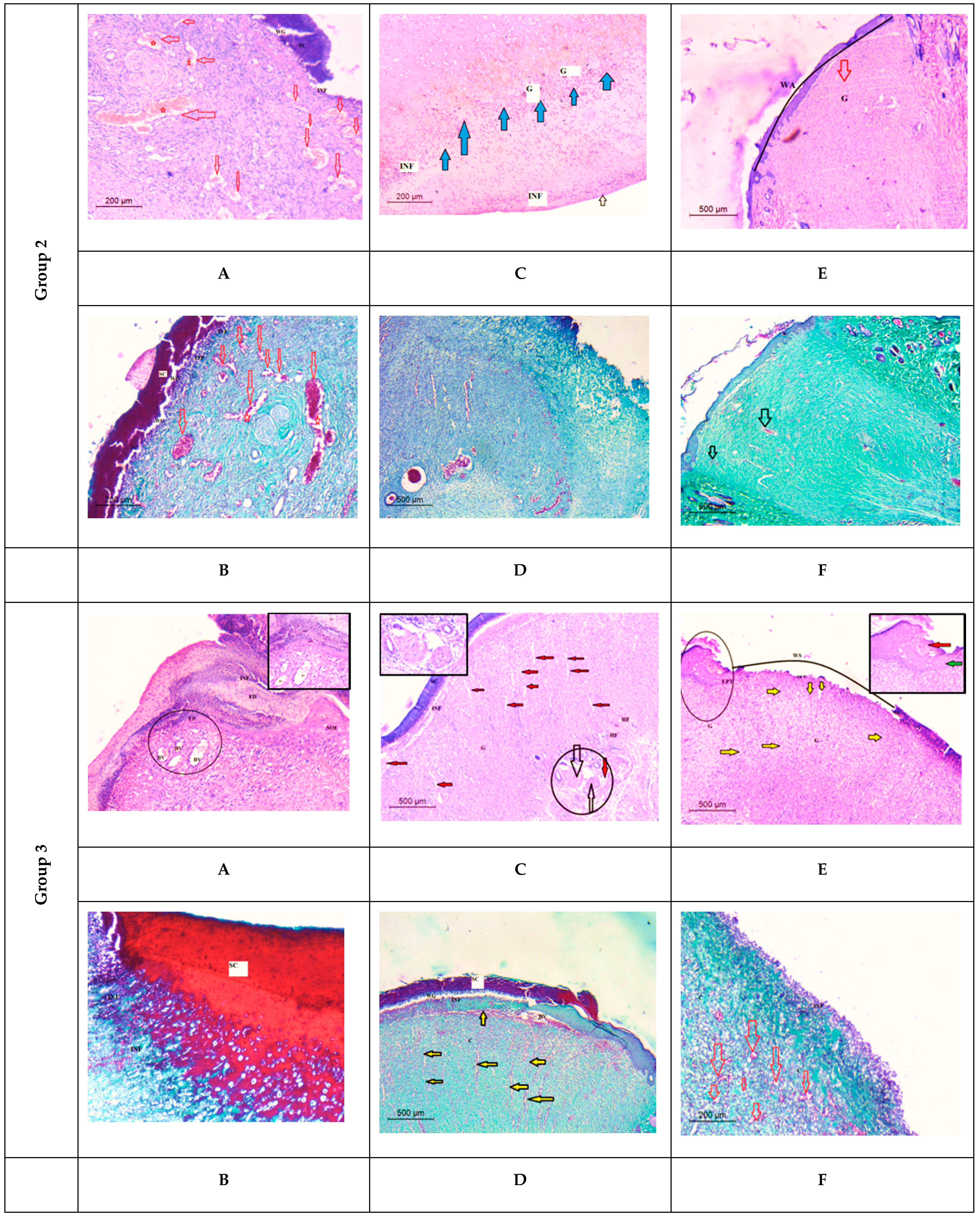
Histological Observation of Skin of the Positive Control Wounded Rats (Group 2)
Histological Observation of Skin of the PVA Nanofiber-Treated Wounded Rats (Group 3)
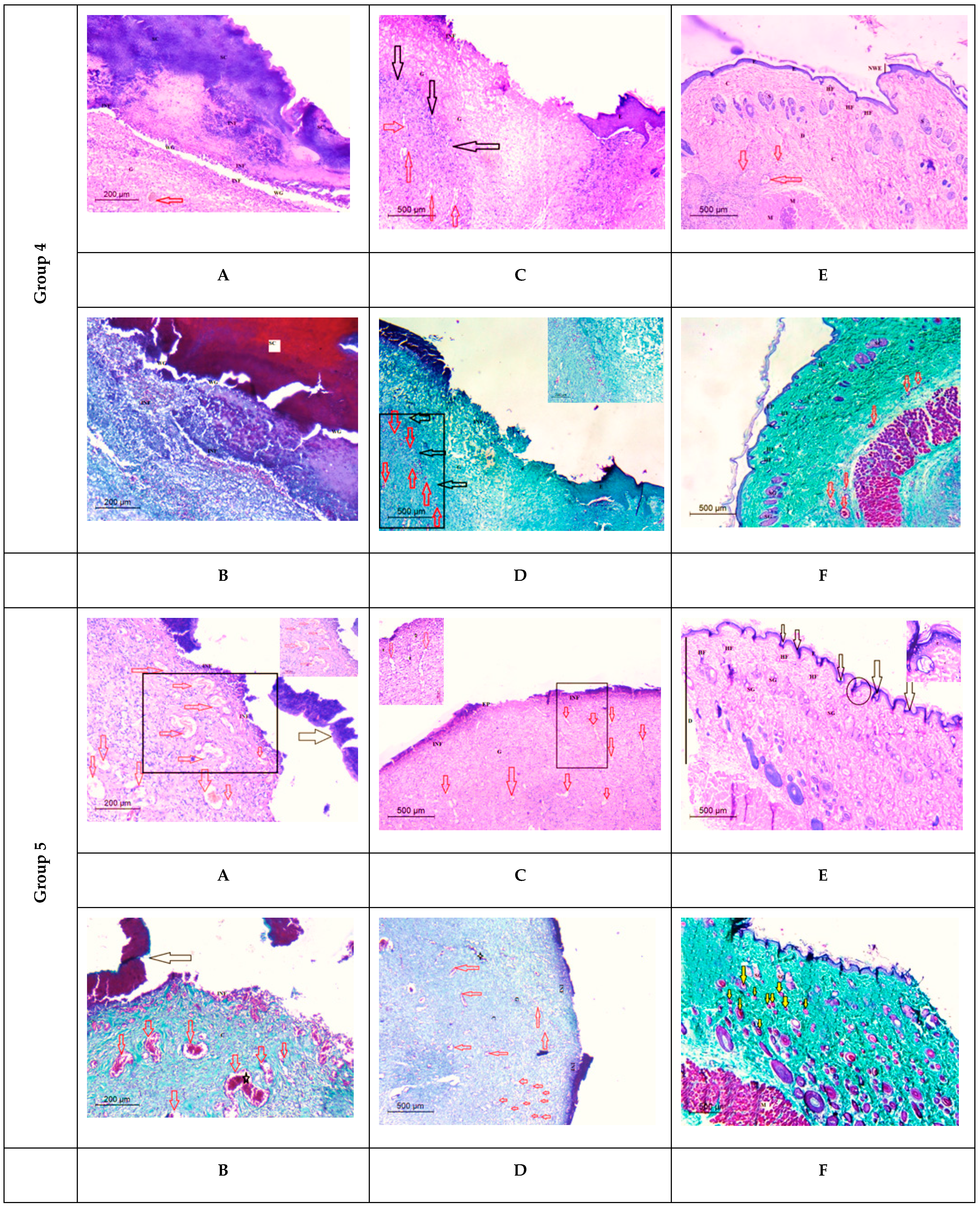
Histological Observation of Skin of the PVA/SM Nanofibers Treated Wounded Rats (Group 4)
Histological Observation of Skin of the PVA/AgNPs-SM Nanofiber-Treated Wounded Rats (Group 5)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benkendorff, K. Molluscan biological and chemical diversity: Secondary metabolites and medicinal resources produced by marine molluscs. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.B.; Liu, L.; Kotiw, M.; Benkendorff, K. Review of anti-inflammatory, immune-modulatory and wound healing properties of molluscs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, S.J.; Graham, M.A.; Dedi, C.G.; Taylor-Harris, P.M.; Gunn, A. Antimicrobial properties of mucus from the brown garden snail Helix aspersa. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 72, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harti, A.S.; Sulisetyawati, S.D.; Murharyati, A.; Oktariani, M.; Wijayanti, I.B. The effectiveness of snail slime and chitosan in wound healing. Int. J. Pharma Med. Biol. Sci. 2016, 5, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanto, Y.B.; Hasan, C.Y.; Rahardjo, R.; Pangestiningsih, T.W. Effect of snail mucus on angiogenesis during wound healing. F1000Research 2021, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh Asiabi, P.; Ramazani, A.; Khoobi, M.; Amin, M.; Shakoori, M.; Mirmohammad Sadegh, N.; Farhadi, R. Regenerated silk fibroin-based dressing modified with carnosine-bentonite nanosheets accelerates healing of second-degree burn wound. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3243–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Díez-Vicente, A.L. Wound healing bionanocomposites based on castor oil polymeric films reinforced with chitosan-modified ZnO nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, J.; Hadidi, M.; Nazarpak, M.H.; Mansouri, M.; Hasannasab, M. Physicochemical and antibacterial characterization of nanofibrous wound dressing from silk fibroin-polyvinyl alcohol-elaeagnus angustifolia extract. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Wakil, H.B.; Banaja, A.E.A.; Amer, S.A.M. Morphometric and genetic insights for three terrestrial snails in Taif province of Saudi Arabia. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 14, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Godan, D. Pest Slugs and Snails; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 445, p. 443. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, A.A.A.; El-Massry, S.A.; Nasr, I.N. Chemical analysis of mucus from certain land snails under Egyptian conditions. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2009, 42, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Min, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, B. Controlled self-assembly of glycoprotein complex in snail mucus from lubricating liquid to elastic fiber. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13806–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mane, P.C.; Sayyed, S.A.; Kadam, D.D.; Shinde, M.D.; Fatehmulla, A.; Aldhafiri, A.M.; Chaudhari, R.D. Terrestrial snail-mucus mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and in vitro investigations on their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M.T.; Bakr, B.A.; Shahin, Y.H.; Elwakil, B.H.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Aljohani, F.S.; Bekhit, A.A. Novel synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles: Biological activity and acute toxicity study. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 8171786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freag, M.S.; Elnaggar, Y.; Abdallah, O.Y. Lyophilized phytosomal nanocarriers as platforms for enhanced diosmin delivery: Optimization and ex vivo permeation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Aljohani, F.S.; Hamed, M.T.; Bakr, B.A.; Shahin, Y.H.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Awaad, A.K.; El-Kady, H.; Elwakil, B.H. In vivo bio-distribution and acute toxicity evaluation of greenly synthesized ultra-small gold nanoparticles with different biological activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, Y.S.; Elwakil, B.H.; Elshewemi, S.S.; El-Naggar, M.Y.; Bekhit, A.A.; Olama, Z.A. Novel Siwa propolis and colistin-integrated chitosan nanoparticles: Elaboration; in vitro and in vivo appraisal. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.W.; Sosiati, H.; Wijongko, P. The Fabrication and characterization of electrospun PVA-snail mucin nanofiber membrane. Int. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Res. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Omran, N.; Elwakil, B.H.; Hamed, M.T.; Abdallah, S.M.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Shehata, N.; Hagar, M. Elastic nanofibrous membranes for medical and personal protection applications: Manufacturing, anti-COVID-19, and anti-colistin resistant bacteria evaluation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalalinia, F.; Taherzadeh, Z.; Jirofti, N.; Amiri, N.; Foroghinia, N.; Beheshti, M.; Bazzaz, B.S.F.; Hashemi, M.; Shahroodi, A.; Movaffagh, J. Evaluation of wound healing efficiency of vancomycin-loaded electrospun chitosan/poly ethylene oxide nanofibers in full thickness wound model of rat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Nurunnabi, M.D.; Shahriar, S.M.; Ahammad, A.J.; Shim, Y.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Green chemistry synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their potential anticancer effects. Cancers 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santiago-Morales, J.; Amariei, G.; Letón, P.; Rosal, R. Antimicrobial activity of poly (vinyl alcohol)-poly (acrylic acid) electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnahas, R.A.; Elwakil, B.H.; Elshewemi, S.S.; Olama, Z.A. Egyptian Olea europaea leaves bioactive extract: Antibacterial and wound healing activity in normal and diabetic rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilia, G.; Fratini, F. Antimicrobial properties of terrestrial snail and slug mucus. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Laurenzana, A.; Fibbi, G.; Veiga-Villauriz, C.; Fanelli, F.; Fracassi, F.; Onzo, A.; Cosma, P. Biomolecules from snail mucus (Helix aspersa) conjugated gold nanoparticles, exhibiting potential wound healing and anti-inflammatory activity. Soft Matter. 2020, 16, 10876–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.E.; Hoda, H.; Osman, G.Y.; El-Sabbagh, S.M.; Sheir, S.K. Antibacterial activity of some terrestrial gastropods from Egypt against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Egypt. J. Zool. 2020, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Hagar, M.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Abozaid, G.M.; Abdallah, S.M.; Shehata, N.; Ahmed, H.; Hassanin, A.H.; Hassanin, A.H. Hybrid nanofibrous membranes as a promising functional layer for personal protection equipment: Manufacturing and antiviral/antibacterial assessments. Polymers 2021, 13, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, V.; Hartwell, R.; Yang, H.; Ghahary, A.; Ko, F. Bioactive nanofibres for wound healing applications. J. Fiber Bioeng. Inform. 2011, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Shin, H.S. Development of coaxial alginate-PCL nanofibrous dressing for controlled release of Spirulina extract. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-de la Cruz, M.C.; Sanz-Rodríguez, F.; Zamarrón, A.; Reyes, E.; Carrasco, E.; González, S.; Juarranz, A. A secretion of the mollusk Cryptomphalus aspersa promotes proliferation, migration and survival of keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 34, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, R.; Aval, S.F.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; Zarghami, N. Recent advances in cell electrospining of natural and synthetic nanofibers for regenerative medicine. Drug Res. 2018, 68, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brieva, A.; Philips, N.; Tejedor, R.; Guerrero, A.; Pivel, J.P.; Alonso-Lebrero, J.L.; Gonzalez, S. Molecular basis for the regenerative properties of a secretion of the mollusk Cryptomphalus aspersa. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 21, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, M.; Aziz, A.S.; Ubaidulla, U.; Hemalatha, P.; Saravanakumar, A.; Ravikumar, R.; Peng, M.M.; Choi, E.Y.; Jang, H.T.; Jang, H.T. Sulfanilamide and silver nanoparticles-loaded polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan composite electrospun nanofibers: Synthesis and evaluation on synergism in wound healing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 39, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, R.; Khorshidi, A.; Shojaei, A.F.; Mashayekhi, F.; Moghaddam, M.J.M. Skin wound healing acceleration by Ag nanoparticles embedded in PVA/PVP/Pectin/Mafenide acetate composite nanofibers. Polym. Test. 2019, 79, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Amino Acid | Concentration (mg/gm) |
|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 3.350 |
| Therionine | 1.376 |
| Serine | 1.489 |
| Glutamic acid | 3.360 |
| Proline | 1.754 |
| Glysine | 1.241 |
| Alanine | 1.522 |
| Valine | 1.167 |
| Methionine | 0.051 |
| Iso leucine | 0.835 |
| Leucine | 2.303 |
| Tyrosine | 1.655 |
| Phenyl alanine | 2.044 |
| Histidine | 2.565 |
| Lysine | 1.053 |
| Tested Strains | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | MIC (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM | AgNPs-SM | SM | AgNPs-SM | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 45.0 | 60.0 | 128.0 | 4.0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 49.0 | 65.0 | 64.0 | 2.0 |
| Acinetobacter baumanii | 44.0 | 50.0 | 128.0 | 32.0 |
| Escherichia coli | 37.0 | 52.0 | 128.0 | 16.0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 48.0 | 58.0 | 64.0 | 16.0 |
| Nanofiber | Average Fiber Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|
| PVA | 170 |
| PVA/SM | 126 |
| PVA/AgNPs-SM | 110 |
| Tested Groups | Day 1 | Day 4 | Day 8 | Day 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative control |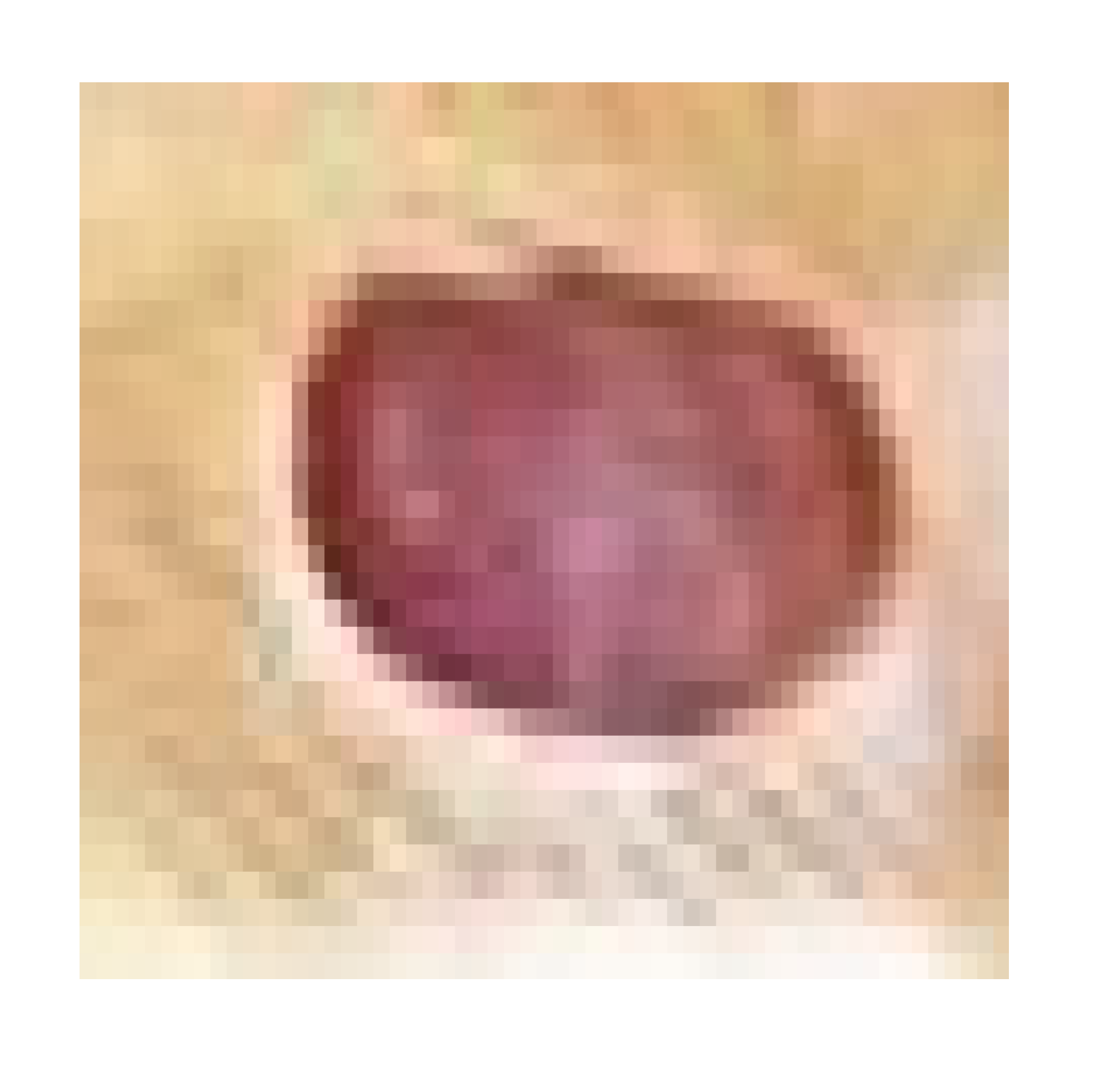  |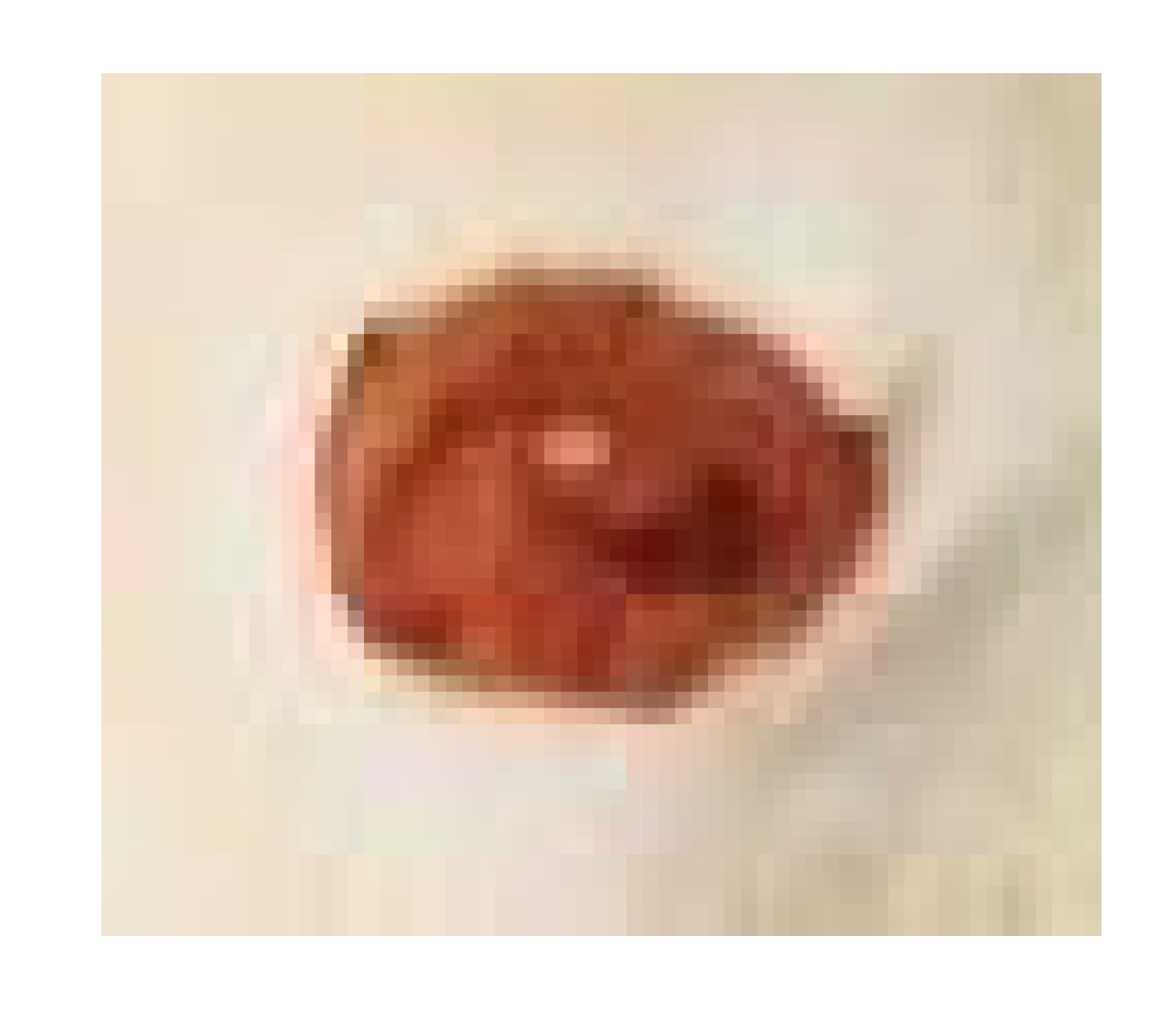  |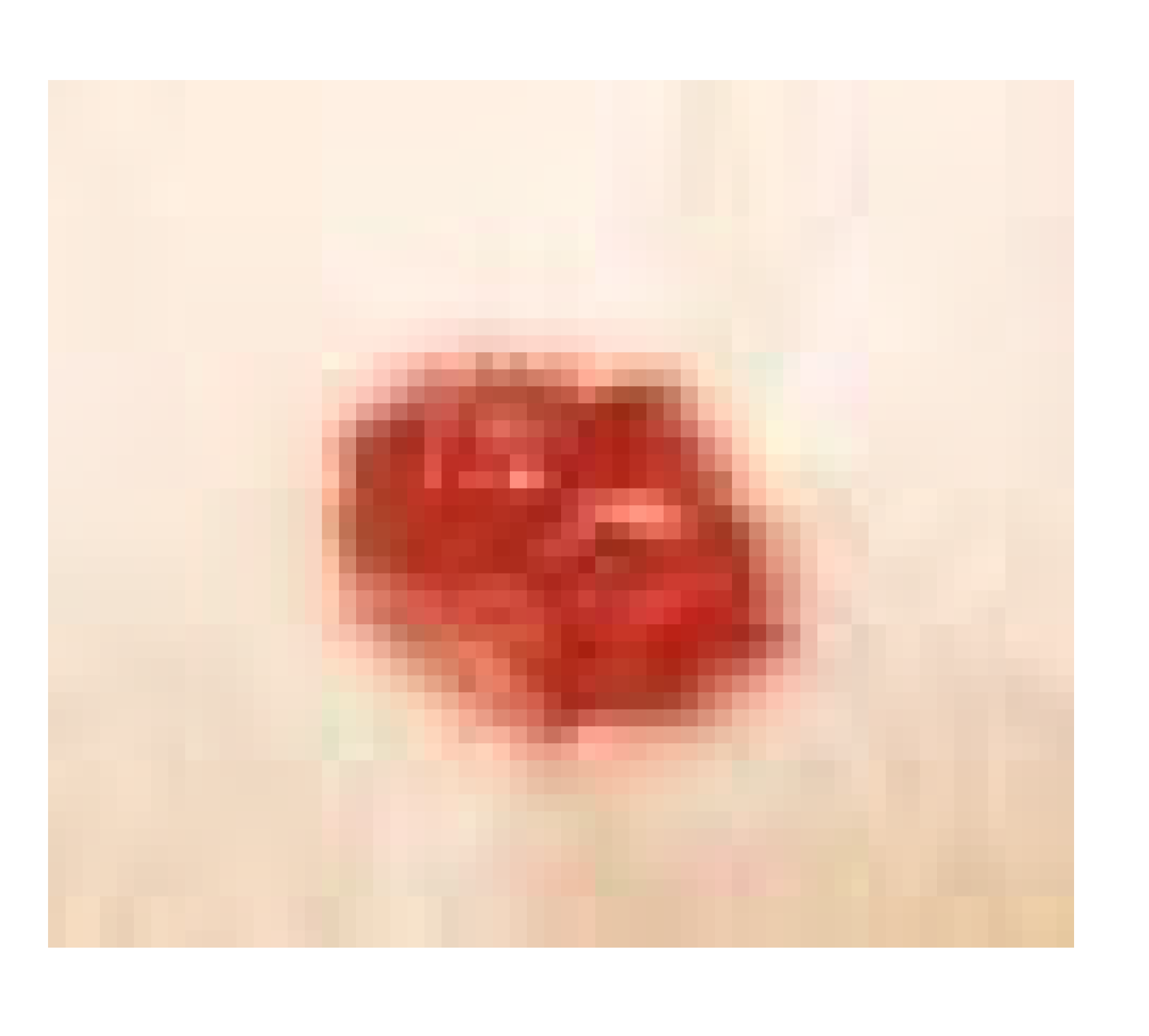  |  |
| Positive control |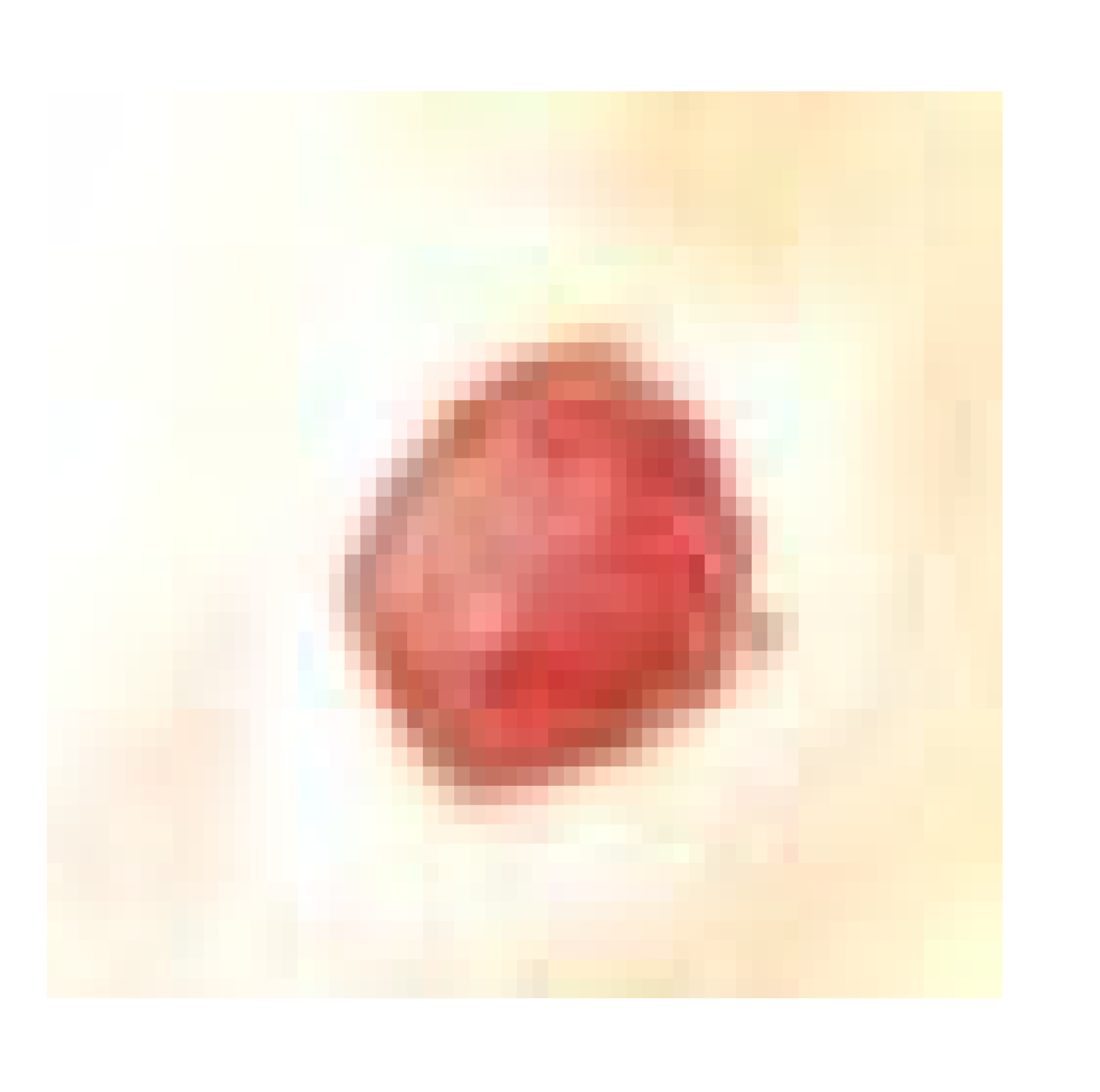  |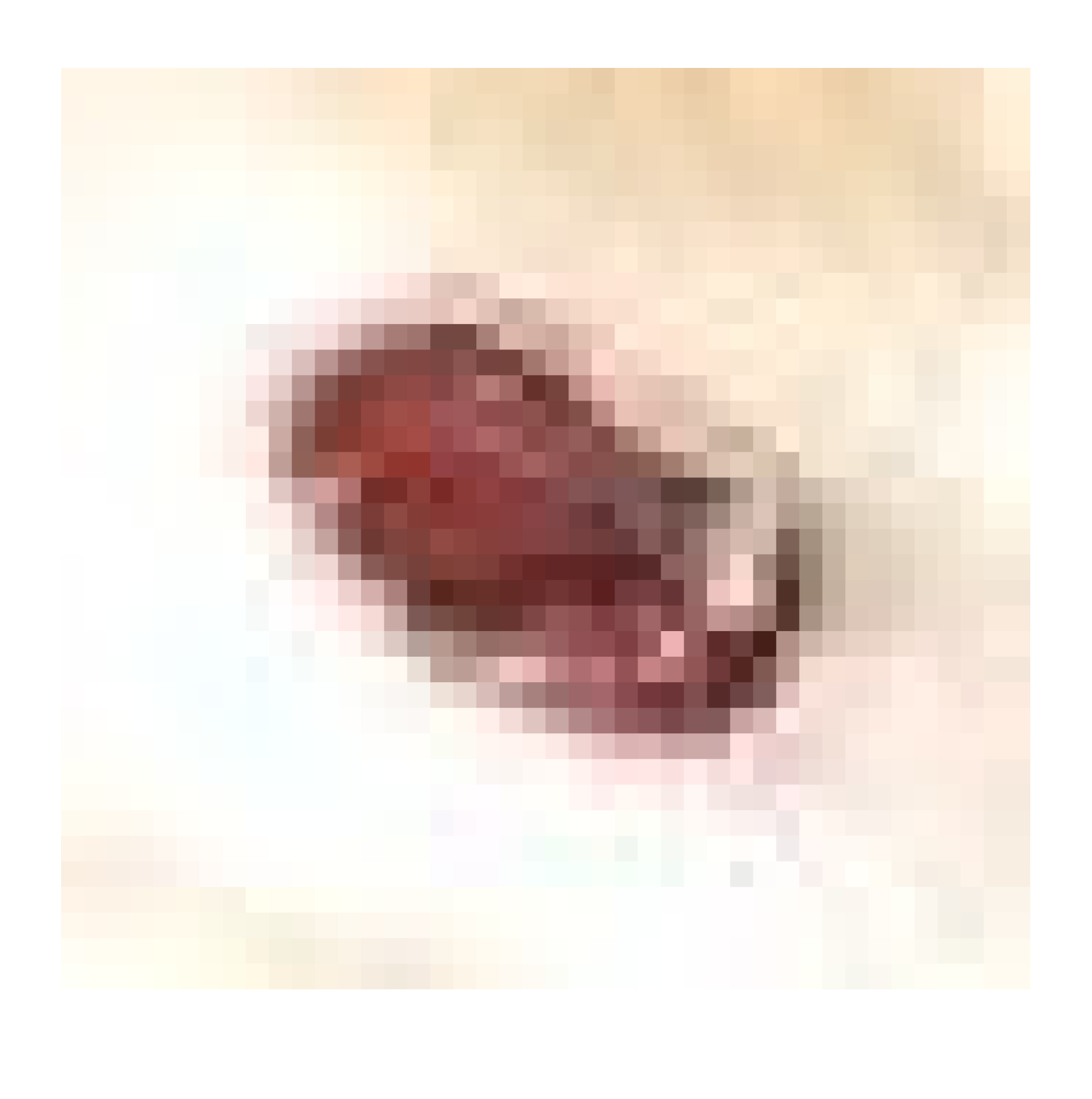  |  | |
| Infected + treated with PVA nanofiber |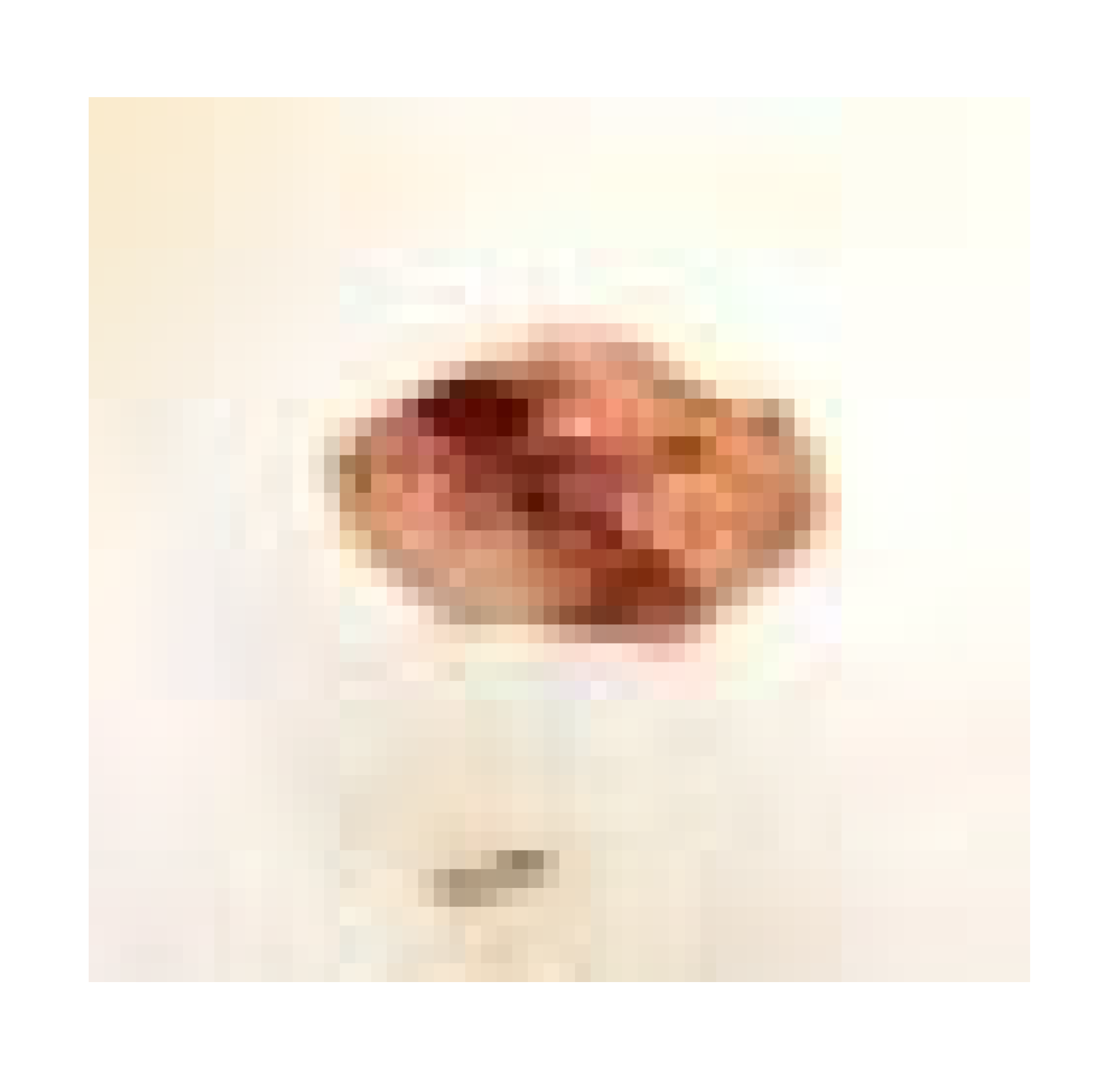  |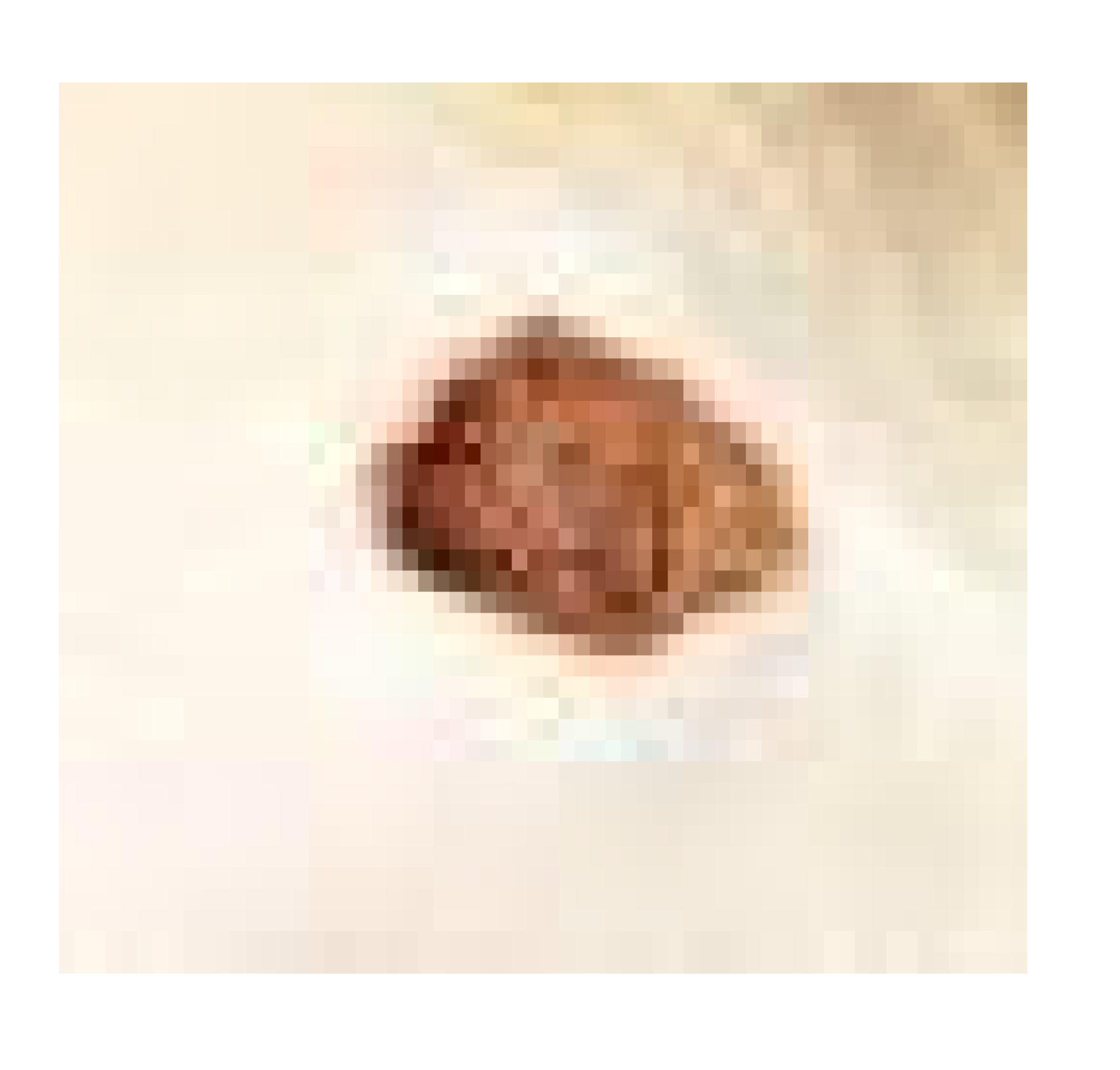  |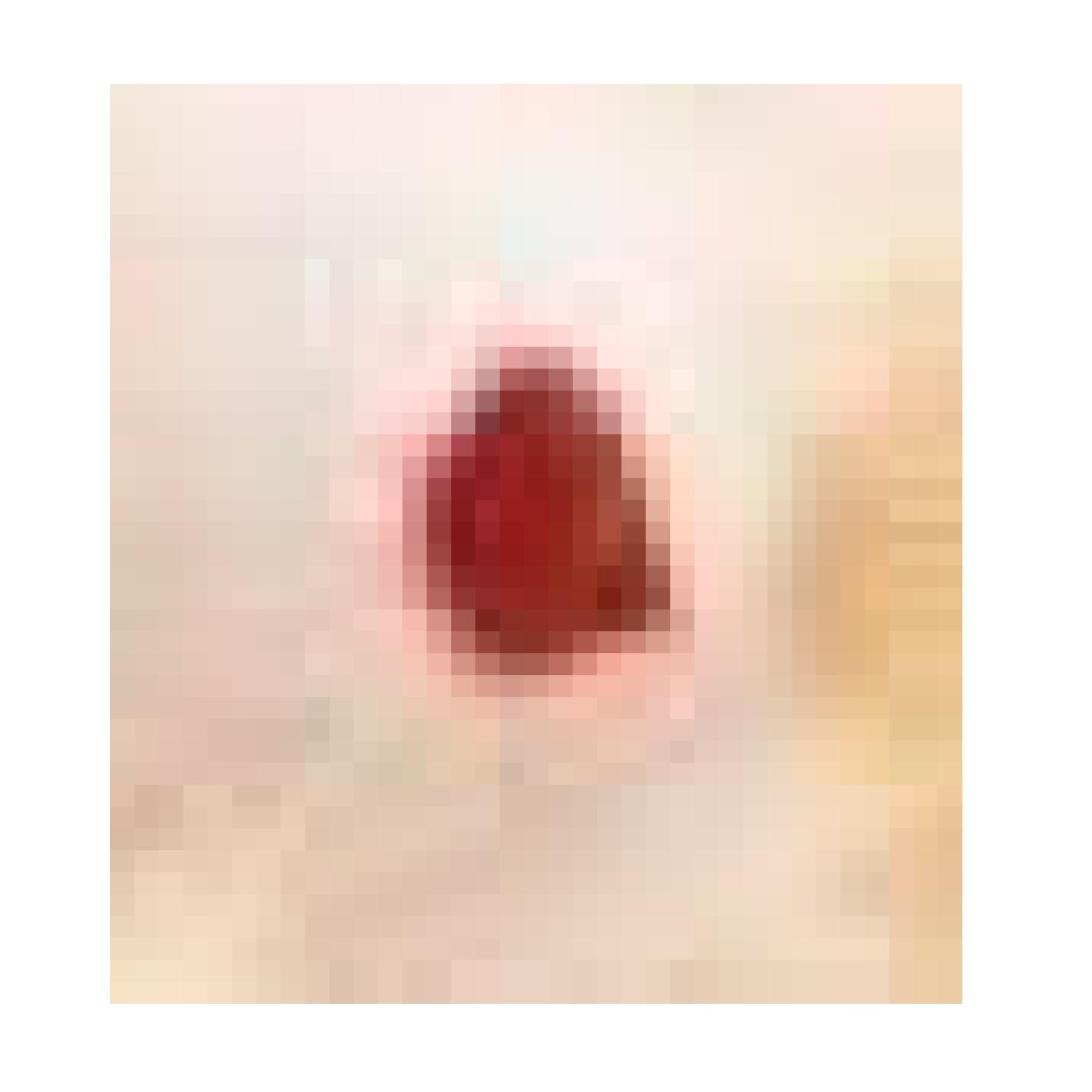  | |
| Infected + treated with PVA/SM nanofiber |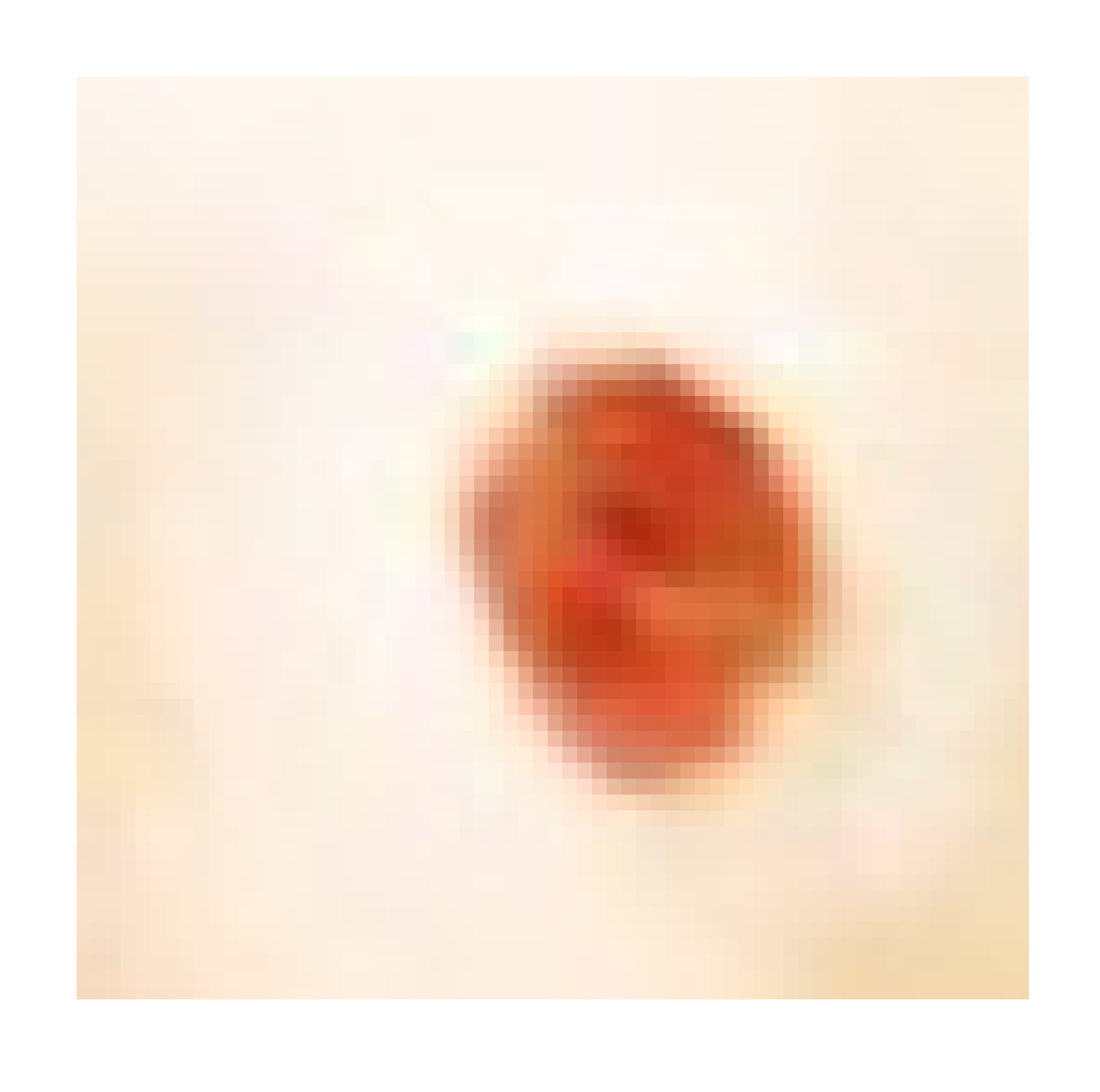  | 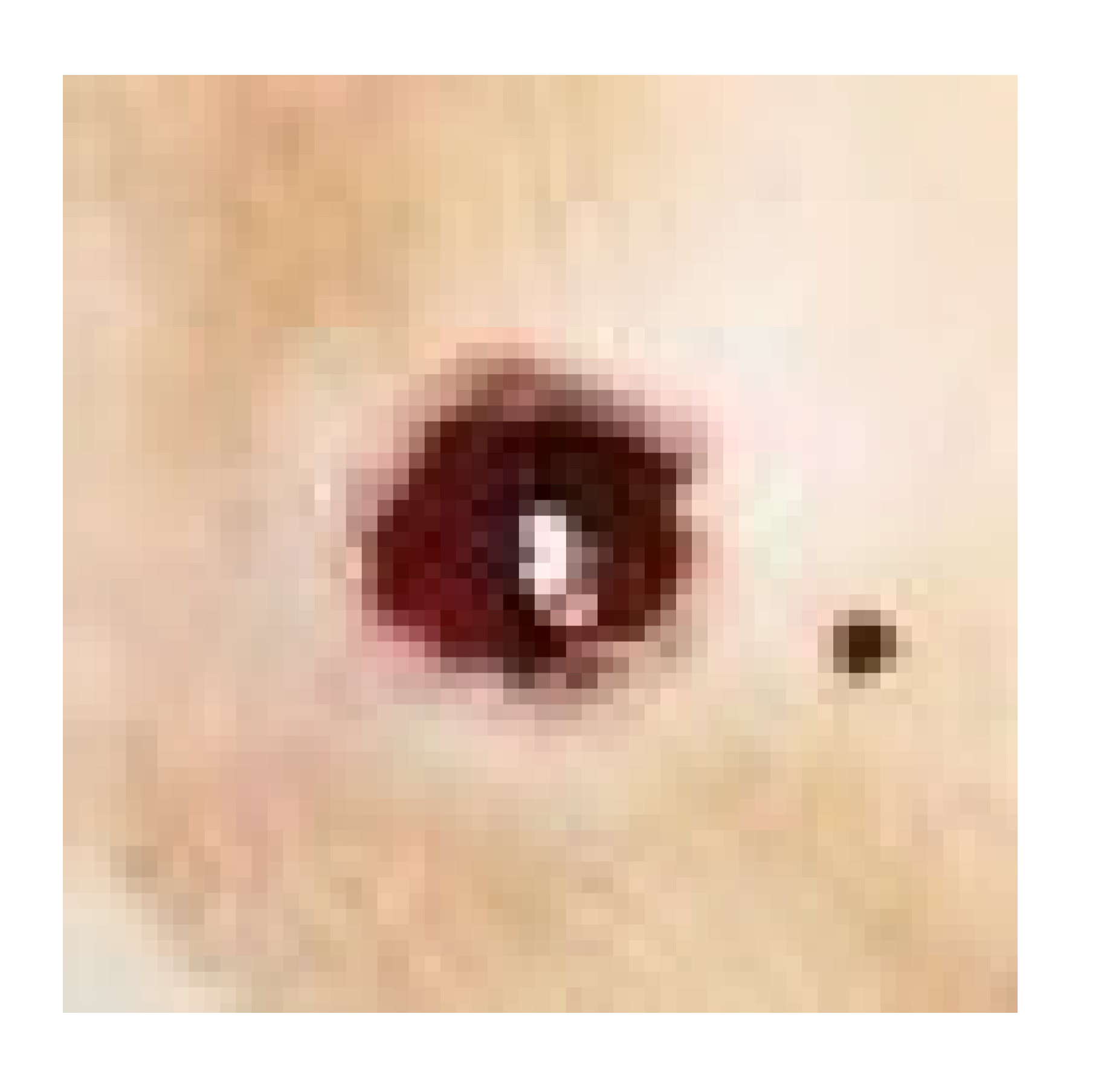 |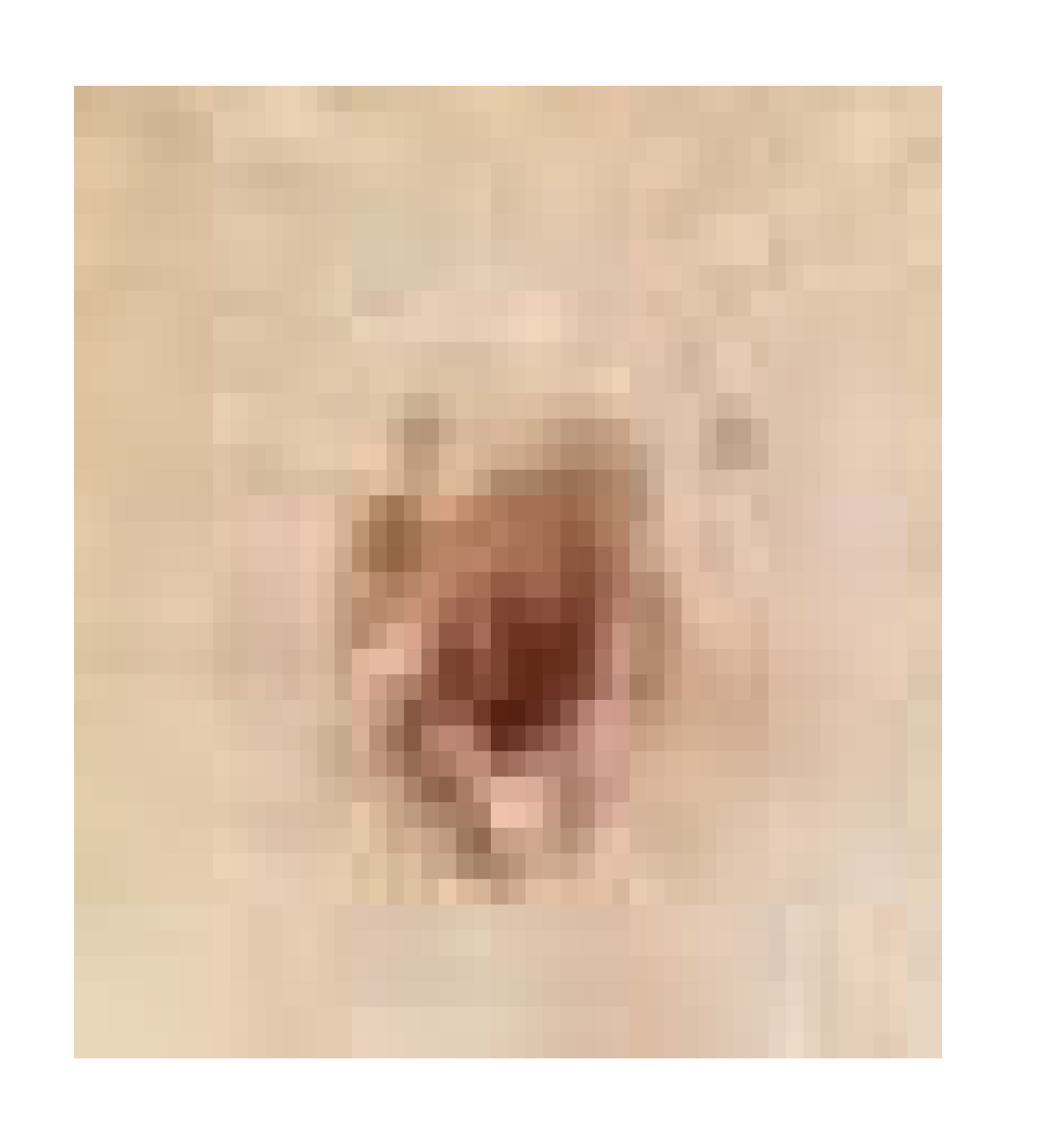  | |
| Infected + treated with PVA/AgNPs-SM nanofiber | 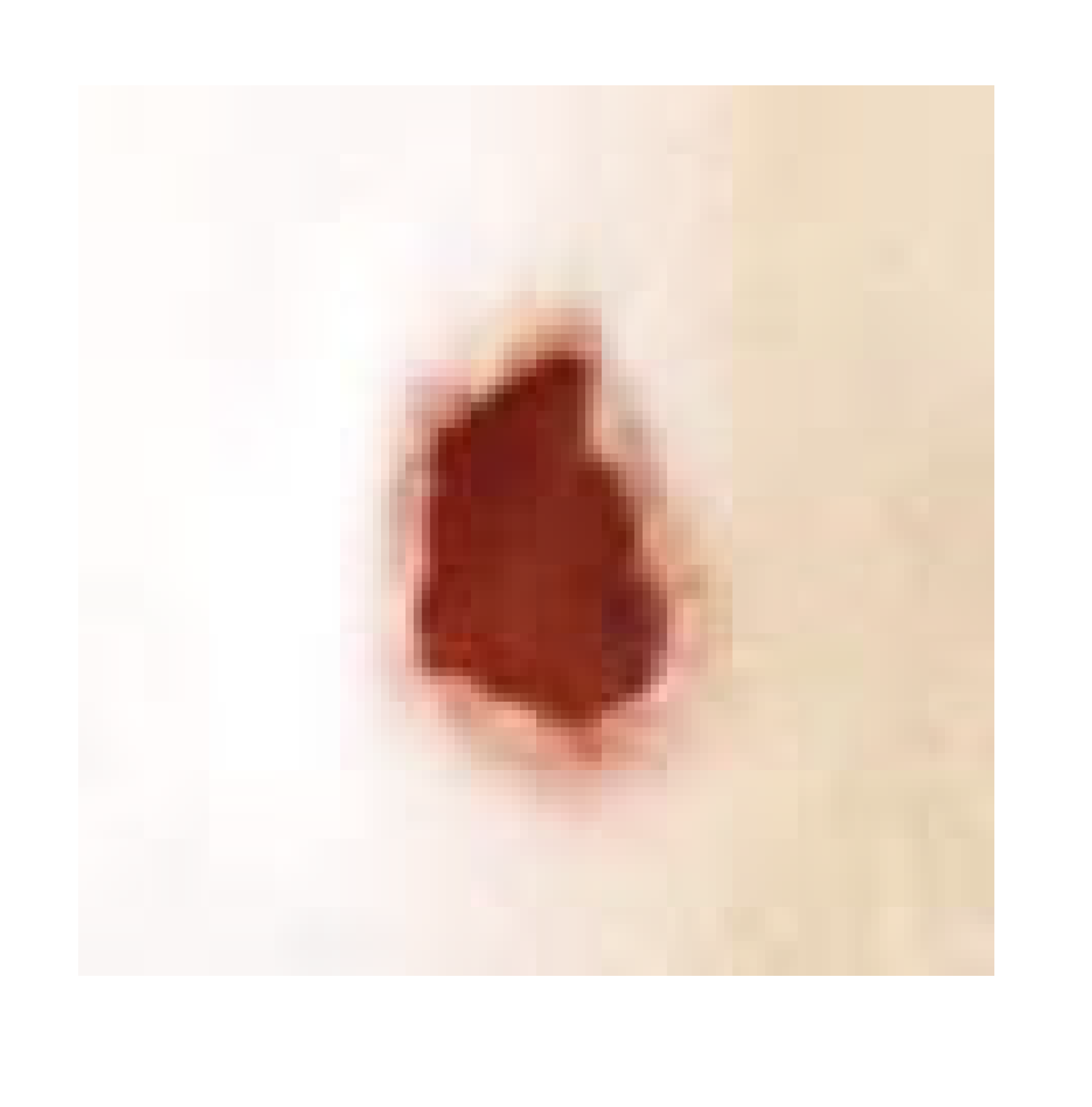 |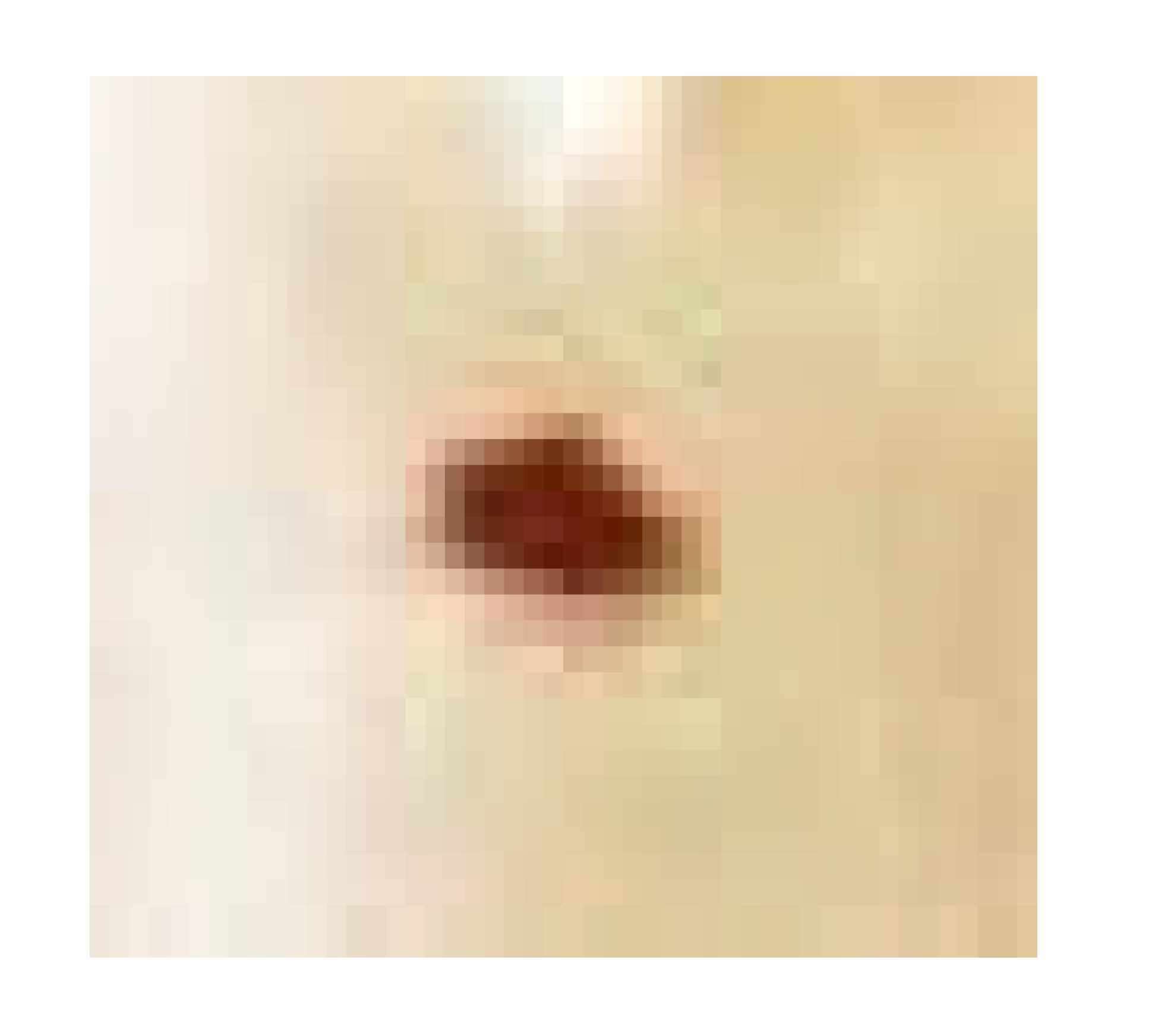  |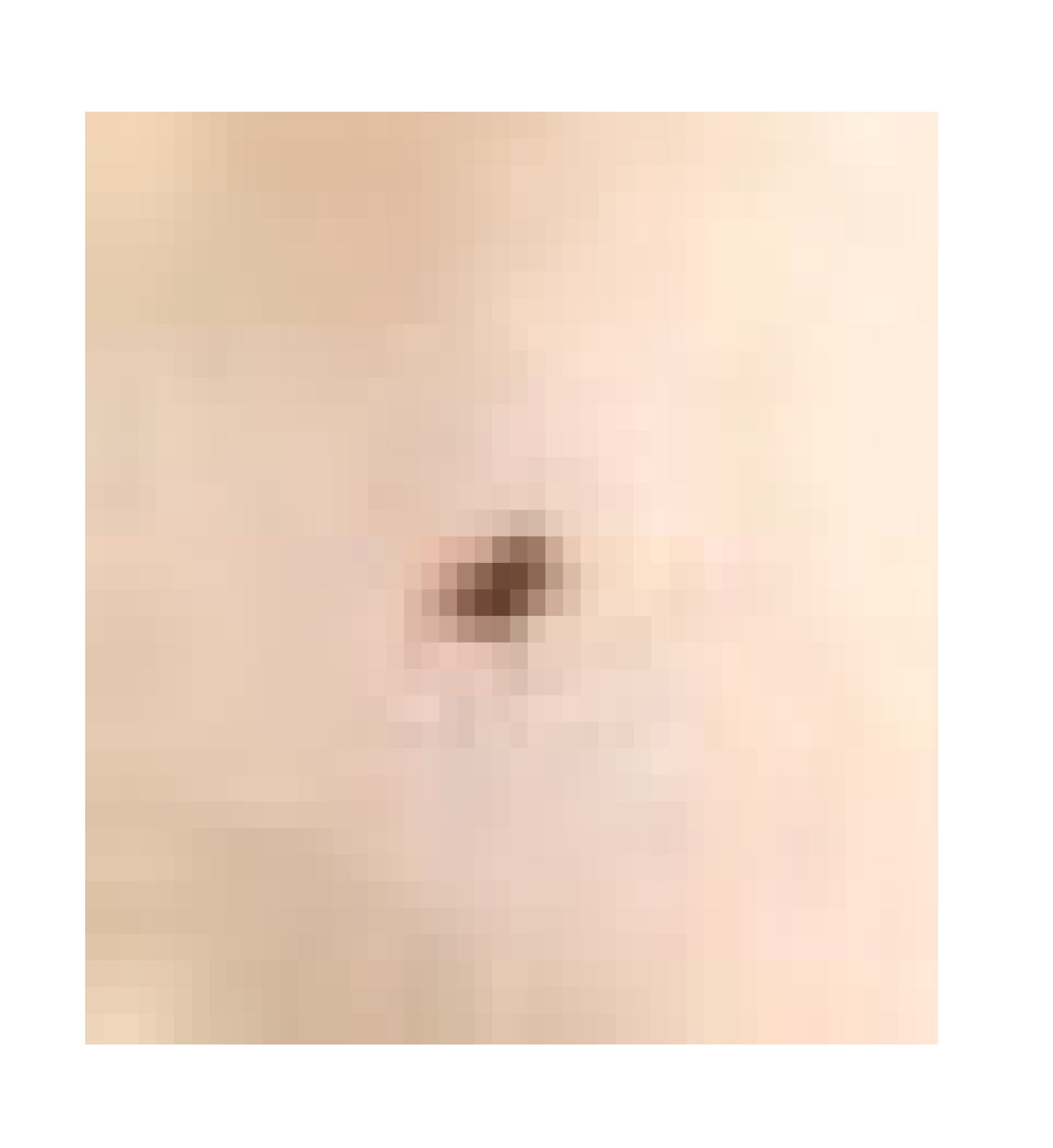  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Attar, A.A.; El-Wakil, H.B.; Hassanin, A.H.; Bakr, B.A.; Almutairi, T.M.; Hagar, M.; Elwakil, B.H.; Olama, Z.A. Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities. Membranes 2022, 12, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050536
El-Attar AA, El-Wakil HB, Hassanin AH, Bakr BA, Almutairi TM, Hagar M, Elwakil BH, Olama ZA. Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities. Membranes. 2022; 12(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Attar, Aalaa A., Hamdy B. El-Wakil, Ahmed H. Hassanin, Basant A. Bakr, Tahani M. Almutairi, Mohamed Hagar, Bassma H. Elwakil, and Zakia A. Olama. 2022. "Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities" Membranes 12, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050536
APA StyleEl-Attar, A. A., El-Wakil, H. B., Hassanin, A. H., Bakr, B. A., Almutairi, T. M., Hagar, M., Elwakil, B. H., & Olama, Z. A. (2022). Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities. Membranes, 12(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050536