New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for Bacteria Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.4. Water Uptake
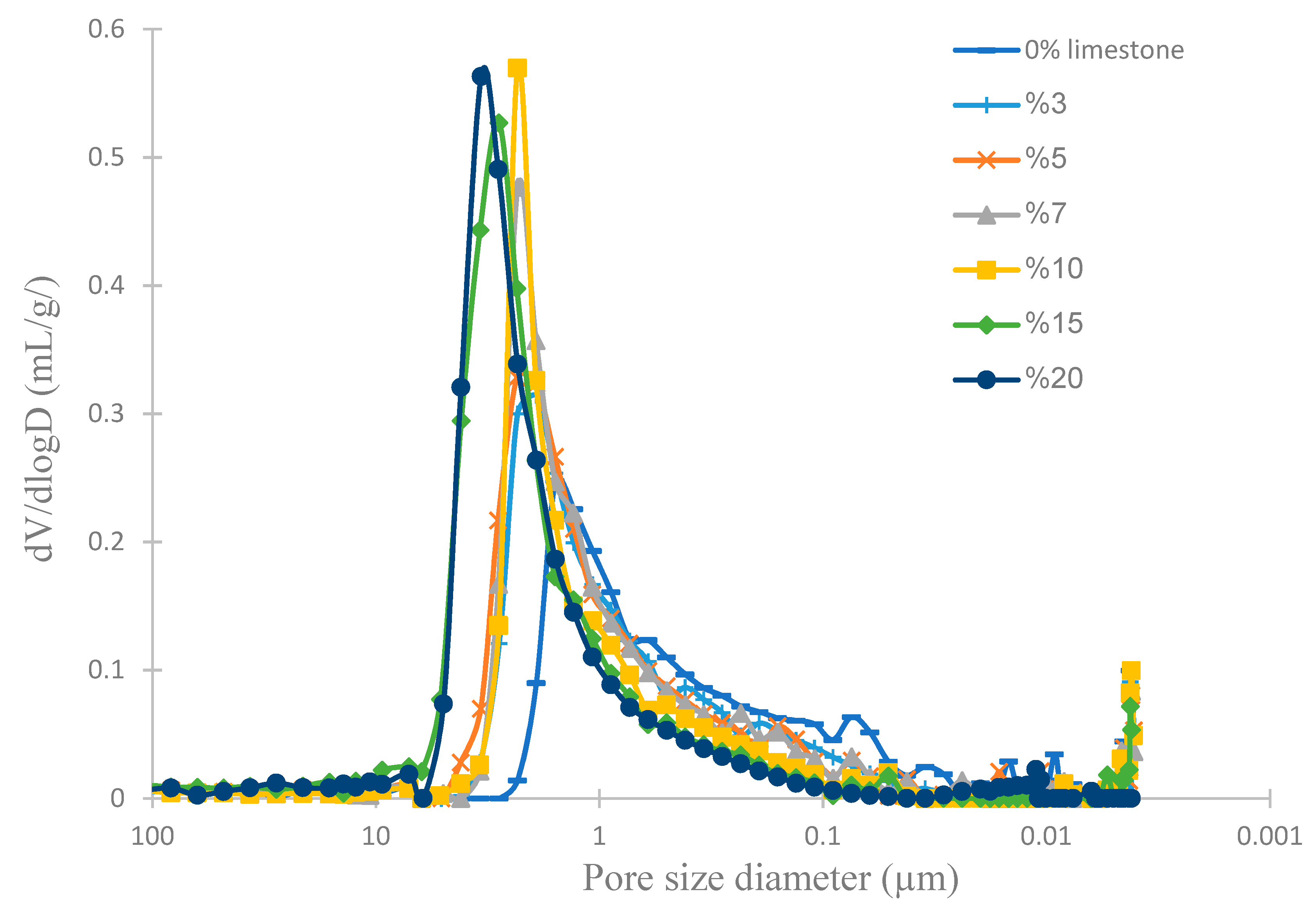
2.5. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)
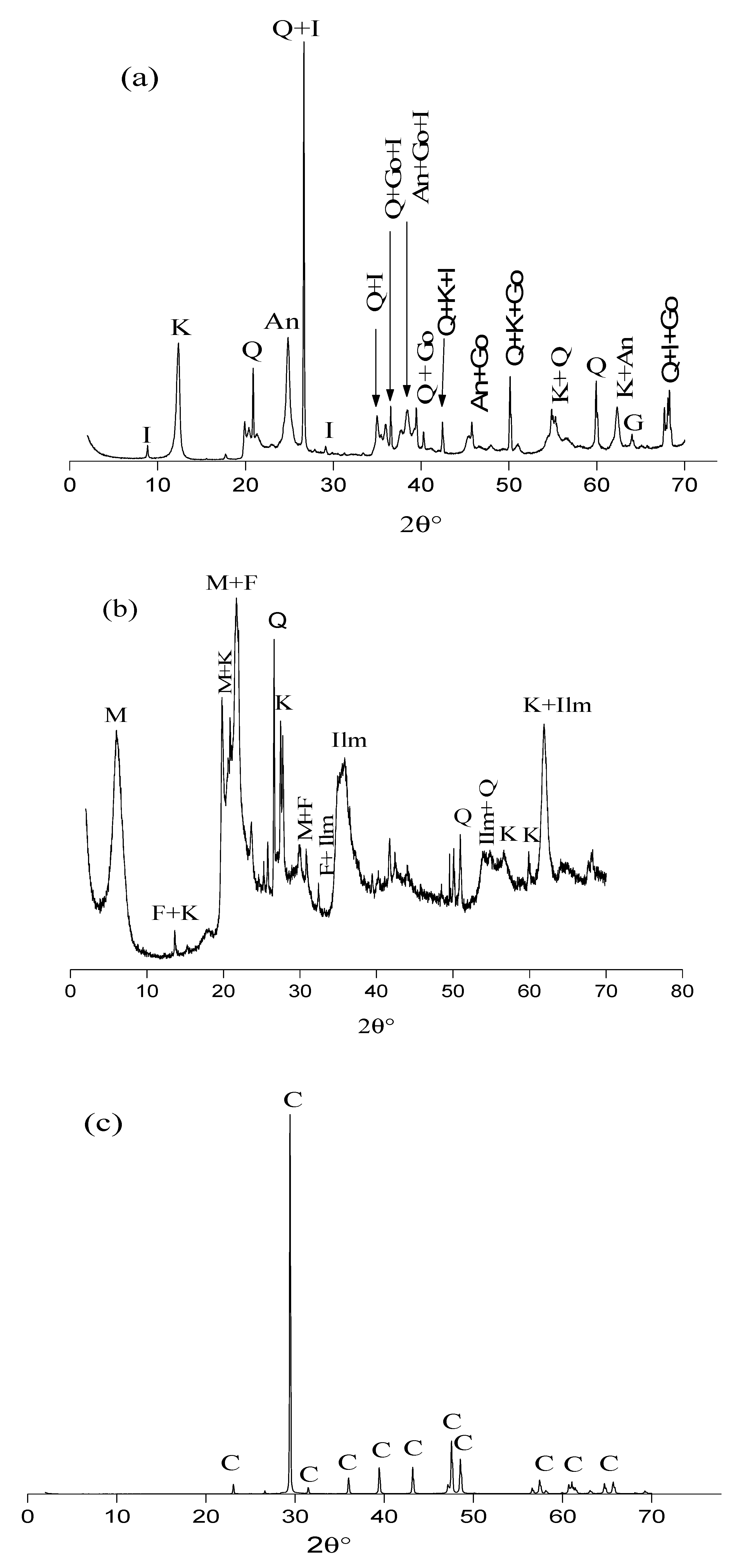
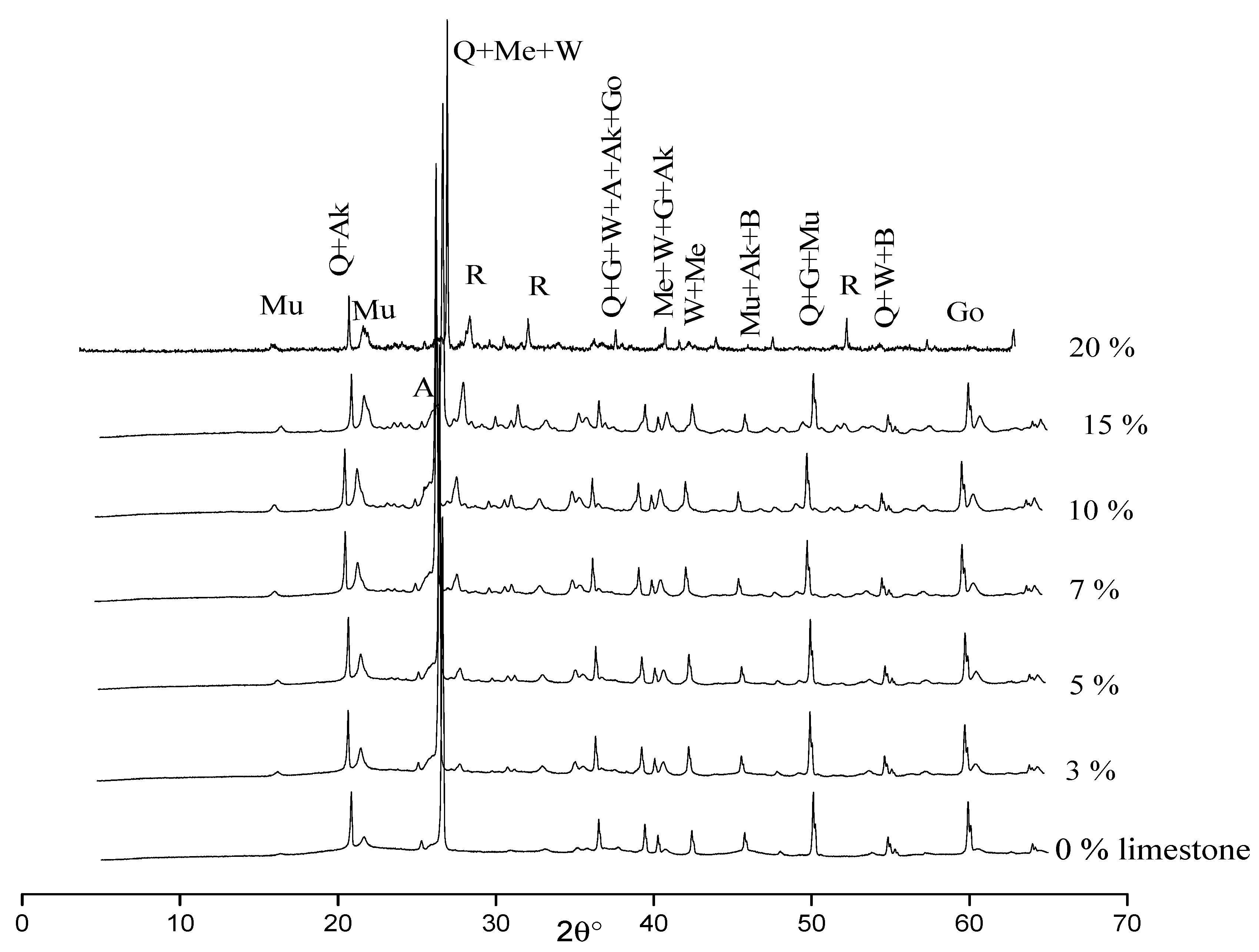
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
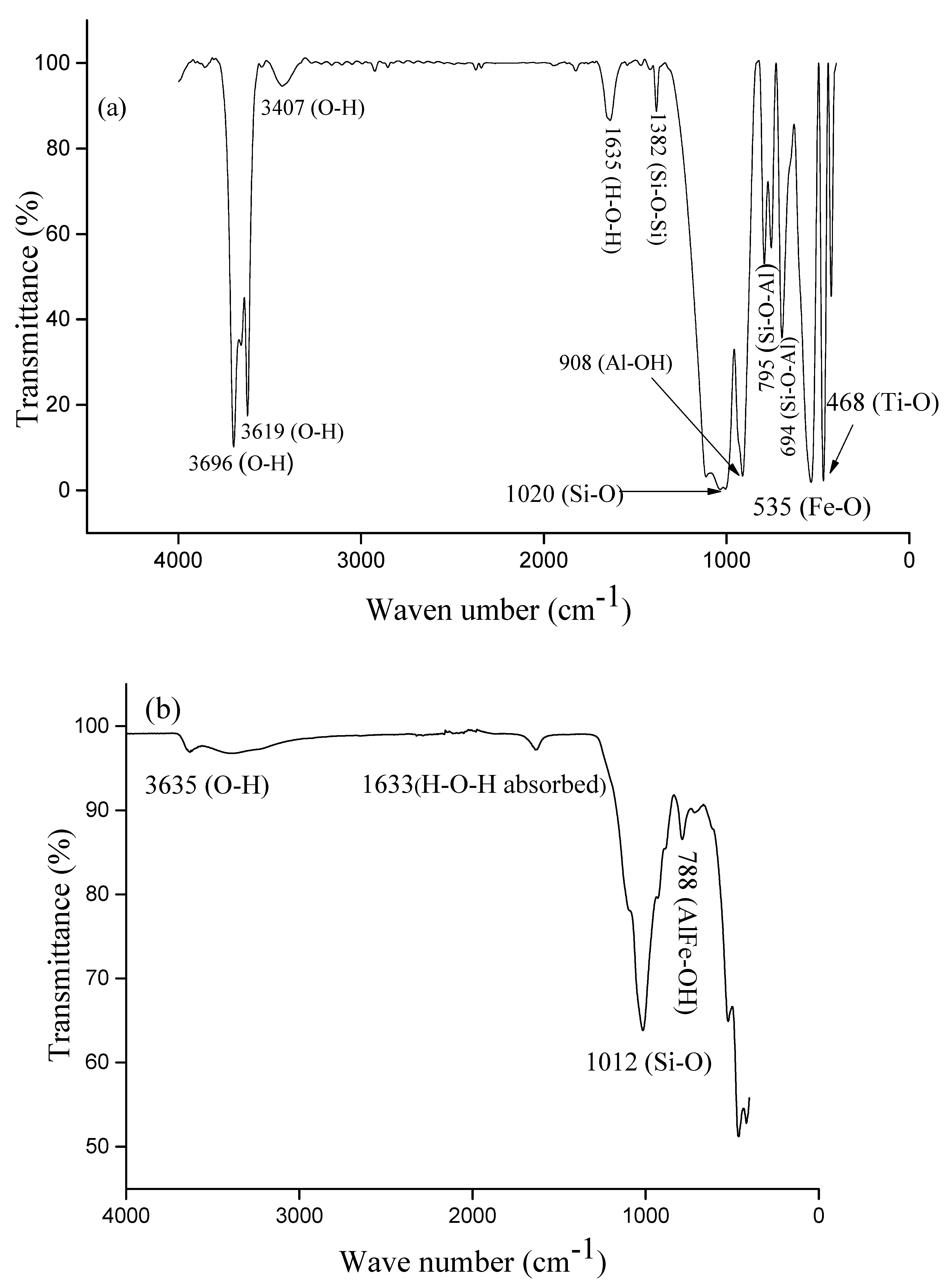
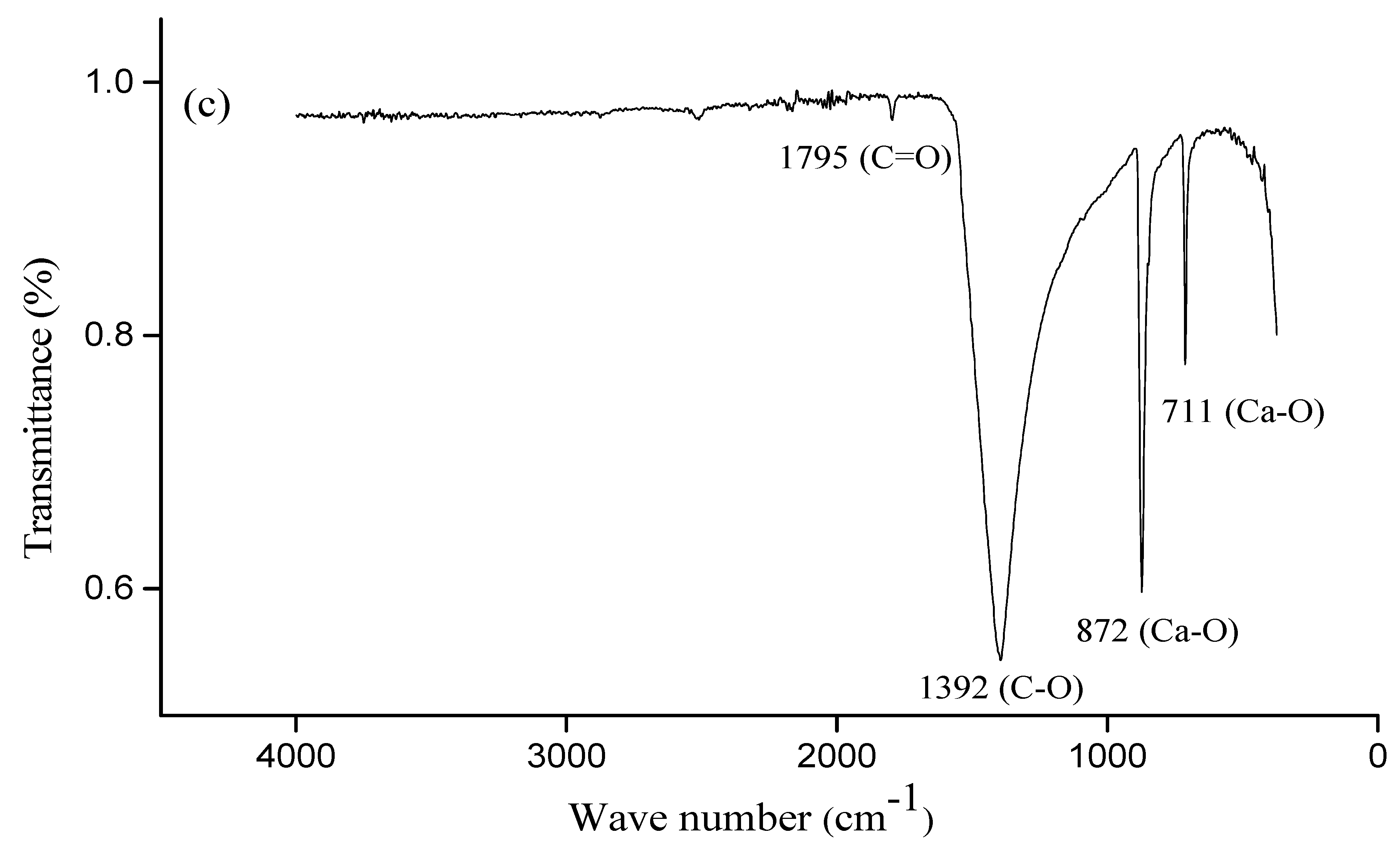
2.7. Attenuated Total Reflectance—Fourier-Transform InfraRed (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
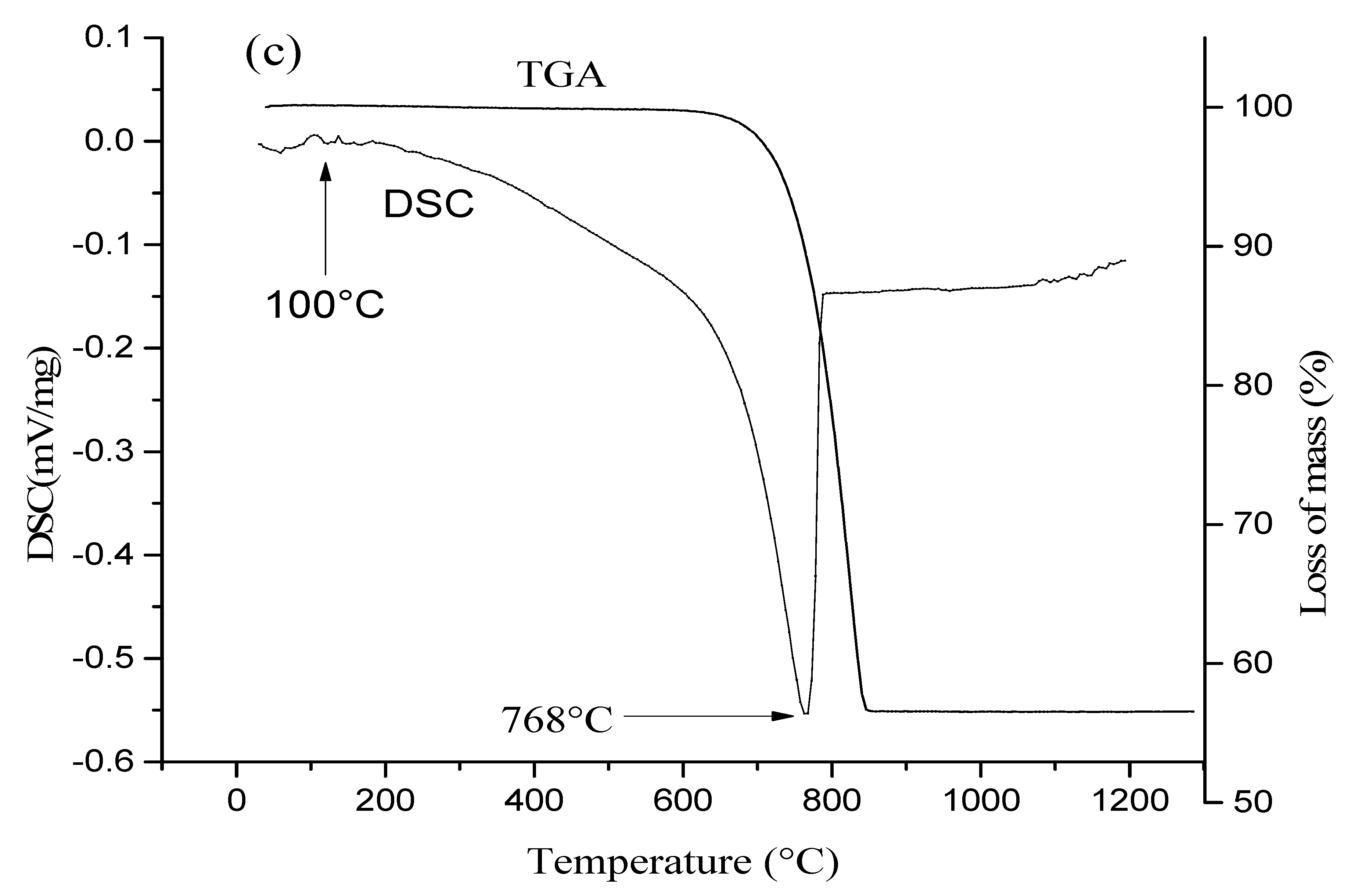
2.8. Chemical and Thermal Analyses
2.9. Membrane-Separation Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Raw Materials
3.2. Membrane Characterization
3.3. Membrane Separation Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Xin, X. Reduction of Escherichia coli using Ceramic Disk Filter Decorated by Nano-TiO2: A Low-cost Solution for Household Water Purification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, J.M.; Evans, N.; Mash, H.; Rosenblum, L.; Schenck, K.; Glassmeyer, S.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Wilson, V.S. Comparison of in Vitro Estrogenic Activity and Estrogen Concentrations in Source and Treated Waters From 25 US Drinking Water Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Fu, H.; Gao, P.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X. An Integrated Gravity-driven Ecological Bed for Wastewater Treatment in Subtropical Regions: Process Design, Performance Analysis, and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Noel, M.; Mohan, R. Removal of Nitrate Ion from Water by Electro-chemical Approaches. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Drinking-Water Fact Sheet. 2021. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs391/en/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Bain, R.E.S.; Wright, J.A.; Christenson, E.; Bartram, J.K. Rural: Urban in Equalities in Post 2015 Targets and Indicators for Drinking-water. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukura, N.; Katengeza, G.; Gwenzi, W.; Mbiriri, C.I.; Nkambule, T.T.; Moyo, M.; Kuvarega, A.T. Development and Evaluation of a Low-cost Ceramic FIlter for the Removal of Methylorange, Hexavalent Chromium, and Escherichia coli from Water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 249, 122965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial Contamination of Drinking Water and Disease Outcomes in Developing Regions. Toxicology 2004, 198, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J. The Urban Environment and Health in a World of Increasing Globalization: Issues for Developing Countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 9, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Pinelo, G.; Jonsson, A.; Meyer, S. Membrane Technology for Purification of Enzymatically Produced Oligosaccharides: Molecular and Operational Features Affecting Performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-González, M.; Ahmed, A.; Maamo, K.; Salem, M.; Jordan, C.; Harasek, M. Evaluation of Nanofiltration Membranes for Pure Lactic Acid Permeability. Membranes 2022, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentama, J.; Ouazzani, K.; Elgarouani, A. New Membranes Made of Sintered Clay Application to Crossflow Microfiltration. Afr. J. Sci. Techol. 2003, 4, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemakhema, S.; Larbot, A.; Ben Amar, R. New Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes from Tunisian Natural Materials: Application for the Cuttlefish Effluents Treatment. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talidi, A.; Saffaj, N.; Kacem, E.K.; Alami Younssi, S.; Albizane, A.; Chakir, A. Processing and Characterization of Tubular Ceramic Support for Microfiltration Membrane Prepared from Pyrophyllite Clay. Sci. Study Res. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2011, 12, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Jona, S.; Purkait, M.K.; Mohanty, K. Preparation and Characterization of Low-cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for the Removal of Chromate from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2009, 47, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Clarification of 1,3-Propanediol Fermentation Broths by Using a Ceramic Fine UF Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Application of Capillary Polypropylene Membranes for Microfiltration of Oily Wastewaters: Experiments and Modeling. Fibers 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, M.; Bernat, k.; Mikucka, W. Membrane Bioreactor Technology: The Effect of Membrane Filtrationon Biogas Potential of the Excess Sludge. Membranes 2020, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Comparison of Polypropylene and Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes Applied for Separation of 1,3-PD Fermentation Broths and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast Suspensions. Membranes 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batouti, M.; Alharny, N.F.; Elewa, M.M. Rewies of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membranes Separation Processes in Water treatment Application. Separation 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Cross-Flow Microfiltration of Glycerol Fermentation Broths with Citrobacter freundii. Membranes 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomczak, W.; Grubecki, I.; Gryta, M. The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achiou, B.; Elomari, H.; Ouammou, M.; Albizane, A.; Bennazha, J.; Alami Younssi, S.; El Amrani, I.E.; Aaddane, A. Elaboration and Characterization of Flat Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane Made from Natural Moroccan Pozzolan (Central Middle Atlas). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Samhari, O. Membranes Céramiques et Polymères Modifées par de l’Oxyde de Graphène pour la Rétention de Molécules Organiques et le Dessalement d’Eaux Saumâtres et d’Eau de Mer. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Rennes 1, Rennes, France and Université Hassan II, Casablanca, Morocco, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moslehyani, A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Goh, P.S. Chapter 3—Recent Progresses of Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes and Processes in Water Treatment. Membr. Sep. Princ. Appl. 2019, 3, 85–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gruskevica, K.; Mezule, L. Cleaning Methods for Ceramic Ultrafiltration Membranes Affected by Organic Fouling. Membranes 2021, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Development of Ceramic Membranes from Low-cost Clays for the Separation of Oil–water Emulsion. Desalin. Water. Treat. 2014, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammache, Z.; Bensaadi, S.; Berbar, Y.; Audebrand, N.; Szymczyk, A. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Electronic Waste by Diffusion Dialysis Biosensors and Bioelectronics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Puttaswamy, K.R.; Xu, M.; Dong, Y. Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification. Membranes 2019, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaniganti, C.M.; Emani, S.; Thorat, P.; Uppaluri, R. Microfiltration of Synthetic Bacteria Solution Using Low Cost Ceramic Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, J.S.; Characklis, G.W.; Noble, R.T. Attachment of Fecal Indicator Bacteria to Particles in the Neuse River Estuary. J. Envir. Energ, ASCE. 2006, 132, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, N.E.; Macquillan, M.F.; Campbell, J.J. The Enumeration of Thermophilic Bacteria by the Plate Count Method. Can. J. Microbiol. 1957, 3, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang-Syapnjeu, P.; Njoya, D.; Kamseu, E.; Cornette de Saint Cyr, L.; Marcano-Zerpa, A.; Balme, S.; Bechelany, M.; Soussan, L. Elaboration of a New Ceramic Membrane Support from Cameroonian Clays, Coconut Husks and Eggshells: Application for Escherichia coli Bacteria Retention. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 198, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, O.; Araus, K.; Temelli, F. Separation of Lipid Mixtures using a Coupled Supercritical CO2–Membrane Technology System. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyburg, S.; Schwarz, A. Influence of the Clay Type on the Pore Structure of Structural Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaiman, I.; Messaoudi, L. Preparation of New Ceramic Supports Macro-porous for Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration Membranes based Moroccan Clay. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 11, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Echajia, M.; Hajjaji, M.; Kacim, S. Mineralogy, Technological Properties and Firing Structural Changes of a Clay Pottery of safi. Sil. Ind. 2003, 68, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjaji, M. Minéralogie et Transformation Thermique des Minéraux Argileux de la Région de Marrakech. Eur. J. Eng. Res. Sci. 2014, 101, 5–80. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Pecanha, L.A.; Vieira, C.M.F. Reformulation of Roofing Tiles Body with Addition of Granite Waste from Sawing Operations. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffo, E.; Bike Mbah, J.B.; Belibi, P.D.; Yankwa Djobo, J.N.; Elimbi, A. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Unheated and Heated Kaolin Based-geopolimers With Partial Replacement of Aluminium Hydroxide. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, J.; Dias, M.I.; Coroado, J.; Rocha, F. Mineralogical Transformations of Calcareous Rich Clays with Firing: A Comparative Study Between Calcite and Dolomite Rich Clays from Algarve. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2009, 42, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boch, P. Matériaux et Processus Céramique; Hermes Science: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F. Influence of Firing Temperature on the Ceramic Properties of Clays from Campos dos Goytacazes. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2004, 27, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Domínguez-Ríos, R.C.; Bocanegra-Bernal, M.H.; Aguilar-Elguézabal, A. Use of Thermally Treated Bentonitic Clay in the Formulation of Ceramic Tiles. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2009, 46, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra, C.V.; Cultrone, G.; Cerezo, P.; Aguzzi, C.; Baschini, M.T.; Vallés, J.; López Galindo, A. Characterization of Northern Patagonian Bentonites for Pharmaceutical Uses. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2006, 31, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimbi, A.; Jopwouo, D.; Wandji, R. Propriétés des Produits de Cuisson des Argiles Kaolinitiques de Bomkoul (Cameroun). In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on the Valorization of Clay Material, Yaounde, Cameroon, 11–12 April 2001; pp. 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yakoubi, E.N.; Aberkan, M.; Ouadia, M. Potentialité d’Utilisation d’Argiles Marocaines de Jbel Kharrou dans l’Industrie Céramique. C. R. Geosci. 2006, 338, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreola, F.; Siligardi, C.; Manfredini, T.; Carbonchi, C. Rheological Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Porcelain Stone Ware Bodies Containing Italian Clay Added with Bentonites. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptáceka, P.; Kubátováb, D.; Halica, J.; Brandstetr, J.; Soukal, F.; Opravil, T. Isothermal Kinetic Analysis of the Thermal Decomposition of Kaolinite: The Thermogravimetric Study. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 501, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoune, F.; Heraiz, M.; Belhouchet, H.; Sahe, N.; Redaoui, D. Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Algerian Tamazarte Kaolin by Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA). Acta Phys. Pol. A. 2017, 131, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, R.D.; Wu, J.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Glass–ceramics: Their Production from Wastes. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 733–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madejová, J.; Komdel, P.; Cicel, B. Infrared Study of Octahedral Site Populations in Smectites. Clay. Miner. 1994, 29, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaji, M.; Kacim, S.; Boulmane, M. Mineralogy and Firing Characteristics of Clay from the Valley of Ourika (Morocco). Appl. Clay. Sci. 2001, 21, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valanciene, V.; Siauciunas, R.; Baltusnikaite, J. The Influence of Mineralogical Composition on the Colour of Clay Body. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qacimi, N.E.; Baraka, N.E.; Safaj, N.; Mamouni, R.; Laknifi, A.; Alami Younssi, S.; Faouzi, A.; Zidouh, H. Preparation and Characterization of Flat Membrane Support Based on Sahar Moroccan Clay: Application to the Filtration of Textile Effluents. Desal. Water. Treat. 2019, 143, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majouli, A.; Alami Younssi, S.; Tahiri, S.; Albizane, A.; Loukili, H.; Belhaj, M. Characterization of Flat Membrane Support Elaborated from Local Moroccan Perlite. Desalination 2011, 277, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; Larbot, A.; ElFeki, H.; Ben Amar, R. Elaboration and Characterisation of Apatite based Mineral Supports for Microfltration and Ultrafltration Membranes. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Characterization of Kaolinite from Assam and Meghalaya, Northeastern India. J. Mod. Phys. 2010, 12, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ptáceka, P.; Kubátováb, D.; Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J.; Soukal, F.; Opravil, T. The Non-isothermal Kinetic Analysis of the Thermal Decomposition of Kaolinite by Thermogravimetric Analysis. J. Power. Technol. 2010, 204, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Frost, R.L. A Spectroscopic Comparison of Selected Chinese Kaolinite, Coal Bearing Kaolinite and Halloysite—A Mid-infrared and Near-infrared Study. Spectrochim. Acta A 2010, 77, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mache, J.R.; Signing, P.; Njoya, A.; Kunyu, F.; Mbey, J.A.; Njopwouo, D.; Fagel, N. Smectite Clay from Sabga Deposit (Cameroon): Mineralogical and Physicochemical Properties. Clay Miner. 2013, 48, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, F.; Touzé, P. La Spectrométrie Infrarouge à Transformée de Fourier (IRTF): Une Méthode Intéressante pour la Caractérisation des Ciments. Bull. Lab. Ponts Chaussées 2001, 4350, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetto, G.E.; Laviano, R.; Sabbatini, L.; Zambonin, P.G. Infrared Spectroscopy in the Mineralogical Characterization of Ancient pottery. J. Cult. Herit. 2002, 3, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsell Color. Munsell Soil Color Charts; Munsell Color: New Windsor, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mouafon, M.; Njoya, D.; Hajjaji, M.; Njoya, A.; Lecomte-Nana, G.L.; Njopwouo, D. Effect of Porogenic Agent Type and Firing Temperatures on Properties of Low-cost Microfiltration Membranes from Kaolin. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Iaich, S.; Messaoudi, L. Mise au Point et Caractérisation des Membranes Minérales de Micro-filtration Déposées sur des Supports Céramiques Tubulaires à base d’une Argile Marocaine Naturelle (Development and Characterization of Inorganic Membranes for mMicro-filtration Deposited on Tubular Supports Ceramic based on Natural Moroccan clay). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, B.K.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Preparation and Characterization of Low Cost Ceramic Membranes for Micro-filtration Applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, D.D.S.; Bortoluz, J.; Zeni, M.; Bergmann, C.P.; Santos, V.D. Characterization of Mullite Ceramic Membranes and their Application in the Removal Escherichia coli. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kuk, K.N.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Park, C.Y.; Hwang, Y.K.; et al. Antimicrobial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticle and Graphene Oxid Nanosheet Composites as a Bactericidal Agent for Water Disinfection. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłodzińska, E.; Szumski, M.; Dziubakiewicz, E.; Hrynkiewicz, K.; Skwarek, E.; Janusz, W.; Buszewski, B. Effect of Zeta potential Value on Bacterial Behavior during Electrophoretic Separation. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrouk, I.; Alami Younssi, S.; Kabbabi, A.; Persin, M.; Albizane, A.; Tahiri, S. Elaboration and Characterization of Ceramic Membranes made from Natural and Synthetic Phosphates and Their Application in Filtration of Chemical Pre-treated Textile Effluent. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, J.; Besser, B.; Brandes, C.; Kroll, S.; Rezwan, K. Production of Ceramic Membranes with Different Pore Sizes for Virus Retention. Water. Res. 2014, 4, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Kaolin (%) | 90 | 87 | 85 | 83 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bentonite (%) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Limestone (%) | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Sample | Content (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | L.O.I. | Total | |
| Kaolin | 48.50 | 32.24 | 1.51 | - | 0.28 | 0.05 | - | 1.16 | 2.36 | 0.19 | 13.69 | 99.98 |
| Bentonite | 67.52 | 15.08 | 5.09 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.70 | 0.75 | 1.25 | 0.26 | - | 9.06 | 100 |
| Limestone | CaO (56.04) | |||||||||||
| Minerals (%) Sample | Kaolinite | Montmorillonite | Illite | Feldspar (Albite) | Anatase | Quartz | Ilmenite | Goethite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolin | 63 | - | 8 | - | 1 | 26 | - | 1 |
| Bentonite | 2 | 54 | - | 18 | - | 25 | 1 | - |
| Limestone | Calcite (99.99) | |||||||
| Limestone (%) | Porosity (%) | Average Pore Size (µm) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Water Uptake (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 36 | 1.5 | 4.48 | 15.0 |
| 3 | 38 | 2.0 | 4.10 | 15.6 |
| 5 | 39 | 2.3 | 3.78 | 16.0 |
| 7 | 40 | 2.3 | 1.96 | 16.0 |
| 10 | 42 | 2.7 | 1.17 | 16.5 |
| 15 | 43 | 2.8 | 0.39 | 17.0 |
| 20 | 44 | 3.4 | 0.26 | 18.4 |
| Limestone (%) | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water permeability (L·h−1·m−2·bar−1) | 179 ± 15 | 357 ± 14 | 513 ± 18 | 566 ± 18 | 577 ± 7 | 579 ± 8 | 755 ± 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mountoumnjou, O.; Szymczyk, A.; Lyonga Mbambyah, E.E.; Njoya, D.; Elimbi, A. New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for Bacteria Removal. Membranes 2022, 12, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050490
Mountoumnjou O, Szymczyk A, Lyonga Mbambyah EE, Njoya D, Elimbi A. New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for Bacteria Removal. Membranes. 2022; 12(5):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050490
Chicago/Turabian StyleMountoumnjou, Olivier, Anthony Szymczyk, Emilia Enjema Lyonga Mbambyah, Dayirou Njoya, and Antoine Elimbi. 2022. "New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for Bacteria Removal" Membranes 12, no. 5: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050490
APA StyleMountoumnjou, O., Szymczyk, A., Lyonga Mbambyah, E. E., Njoya, D., & Elimbi, A. (2022). New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes for Bacteria Removal. Membranes, 12(5), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050490







