State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
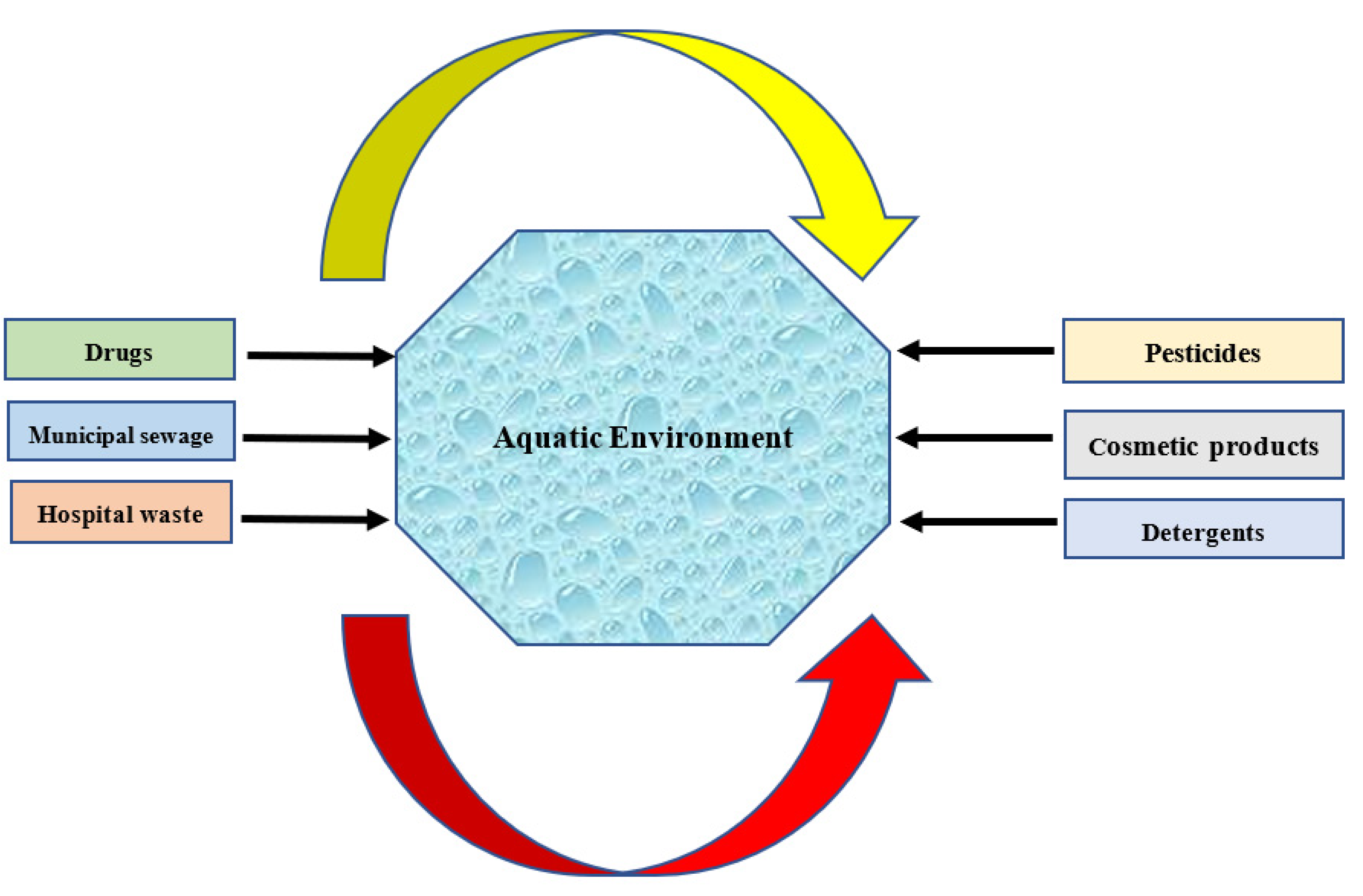
2. Various Types of Micro-Contaminants in Water/Wastewater Sources and Their Potential Detriments for Health
3. Different Technologies towards Micro-Contaminants Removal
3.1. Prevalent Physico-Chemical Treatment Procedures for Micro-Contaminant Removal
3.1.1. ACA Technique
3.1.2. Coagulation–Flocculation (G-F) Technique
3.2. Biological Treatment Procedures
3.2.1. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
3.2.2. Constructed Wetland (CW) Technique
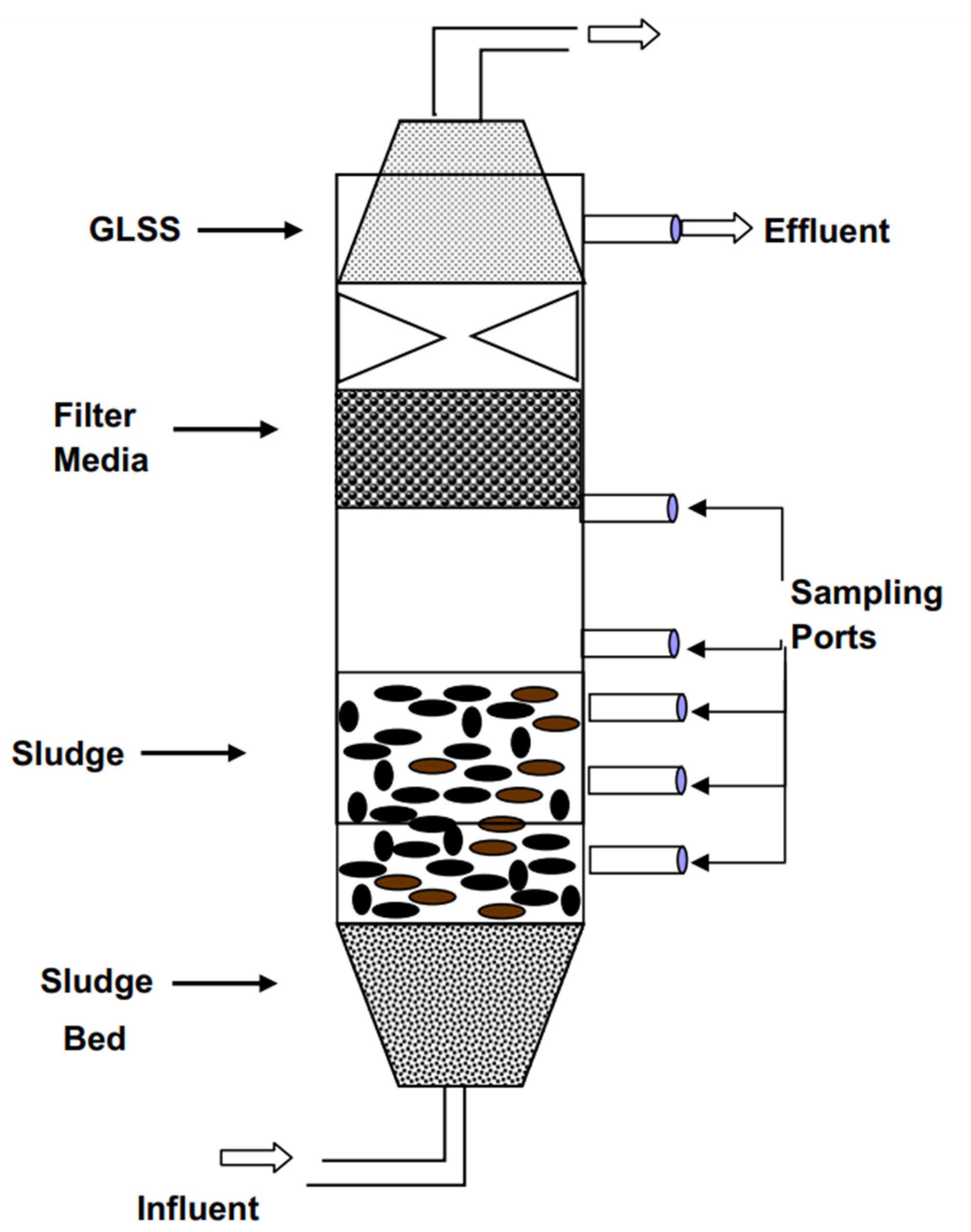
3.2.3. Hybrid Reactor System (HRS)
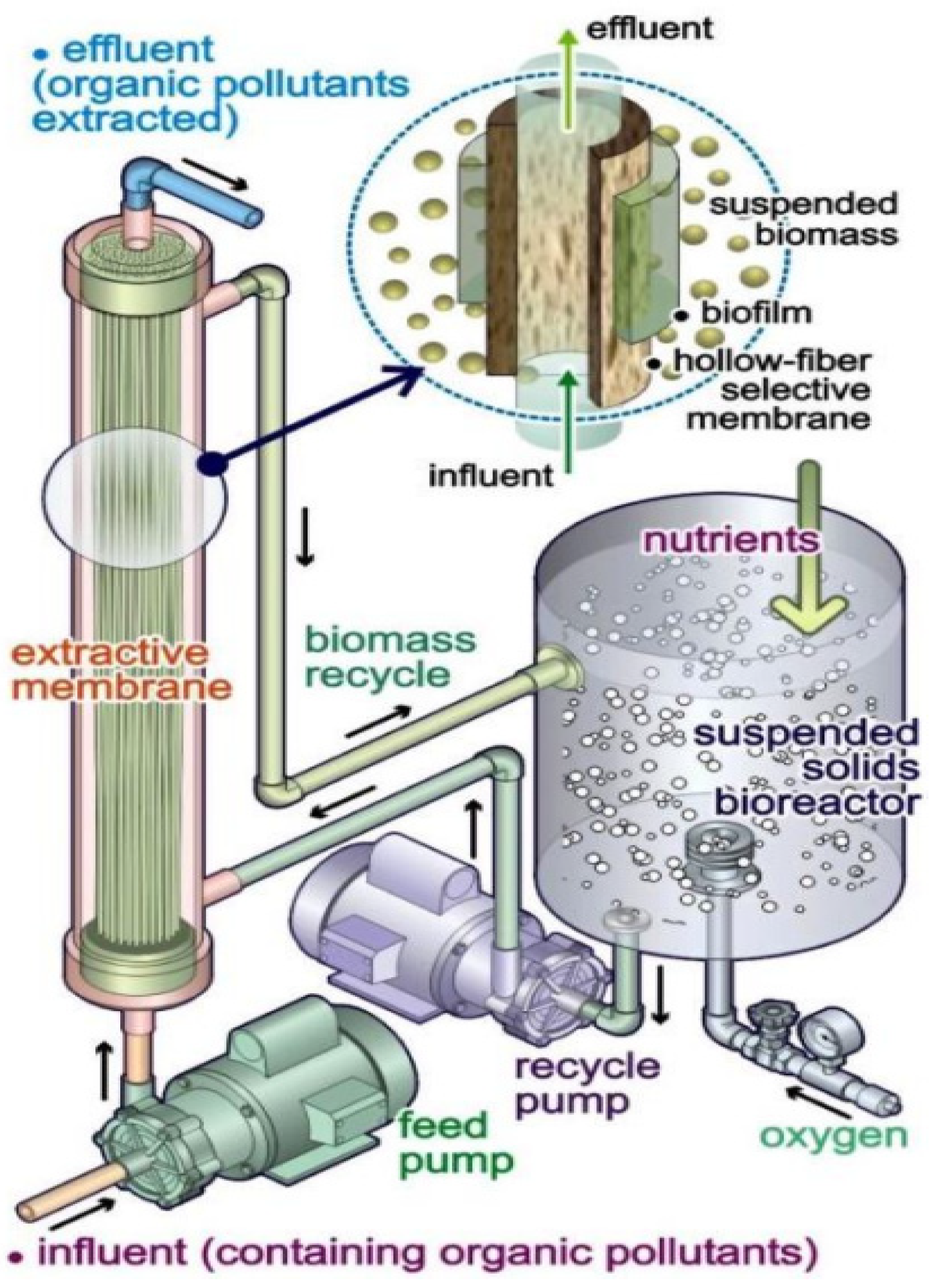
3.2.4. Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
4. Challenges and Limitations towards the Use of MBR
4.1. Membrane Fouling and Its Mitigation in MBRs
4.2. Different Techniques to Mitigate Membrane Fouling/Biofouling
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, H.; Robinson, Z.P.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, F. The feasibility and challenges of energy self-sufficient wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, C.; Bae, J. Current status of the pilot-scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatments of domestic wastewaters: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besha, A.T.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Tufa, R.A.; Bekele, D.N.; Curcio, E.; Giorno, L. Removal of emerging micropollutants by activated sludge process and membrane bioreactors and the effects of micropollutants on membrane fouling: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2395–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Ngo, H.H. Micropollutants removal and health risk reduction in a water reclamation and ecological reuse system. Water Res. 2018, 138, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngweme, G.N.; al Salah, D.M.M.; Laffite, A.; Sivalingam, P.; Grandjean, D.; Konde, J.N.; Mulaji, C.K.; Breider, F.; Poté, J. Occurrence of organic micropollutants and human health risk assessment based on consumption of Amaranthus viridis, Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Seyssiecq, I.; Piram, A.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Vanot, G.; Tiliacos, N.; Roche, N.; Doumenq, P. From the conventional biological wastewater treatment to hybrid processes, the evaluation of organic micropollutant removal: A review. Water Res. 2017, 111, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francesco, P.; Coppola, G.; Curcio, S. Modeling aspects in simulation of phase change materials used for thermal regulation of buildings. J. Phase Change Mater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Alizadeh, S.M.S.; Fouladvand, M.T.; Khan, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Heidari, Z.; Pelalak, R.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Albadarin, A.B. Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of CO2 capture using MDEA-based nanofluids in nanostructure membranes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Air–Organic Solvent and Air–Water Partitioning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 181–212. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, L.; Kumar, R.V.; Borah, S.N.; Manikandan, N.A.; Pakshirajan, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Membrane bioreactor and integrated membrane bioreactor systems for micropollutant removal from wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Khan, A.; Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Agustiono Kurniawan, T.; Rezakazemi, M. Recent advancements in molecular separation of gases using microporous membrane systems: A comprehensive review on the applied liquid absorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, H.; Joss, A. Review on the fate of organic micropollutants in wastewater treatment and water reuse with membranes. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjani, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Pishnamazi, M.; Shirazian, S. Evaluation of potassium glycinate, potassium lysinate, potassium sarcosinate and potassium threonate solutions in CO2 capture using membranes. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacouba, Z.A.; Mendret, J.; Lesage, G.; Zaviska, F.; Brosillon, S. Removal of organic micropollutants from domestic wastewater: The effect of ozone-based advanced oxidation process on nanofiltration. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Adimi, M.; Jirandehi, H.F.; Shirazian, S. Effect of graphene oxide on modifying polyethersulfone membrane performance and its application in wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadiri, M.; Hemmati, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Shirazian, S. Modelling tyramine extraction from wastewater using a non-dispersive solvent extraction process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39068–39076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Derome, C.; Buleté, A.; Vulliet, E.; Bressy, A.; Varrault, G.; Chebbo, G.; Rocher, V. Removal of emerging micropollutants from wastewater by activated carbon adsorption: Experimental study of different activated carbons and factors influencing the adsorption of micropollutants in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Paola, M.G.; Paletta, R.; Lopresto, C.G.; Calabrò, V. Multiple light scattering as a preliminary tool for starch-based film formulation. J. Phase Change Mater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M.; Abdullatif, N.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Ghadiri, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Marjani, A.; Pishnamazi, M. Intensification of CO2 absorption using MDEA-based nanofluid in a hollow fibre membrane contactor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, S.S.; Mahanta, C.; Mishra, P. Simultaneous influence of indigenous microorganism along with abiotic factors controlling arsenic mobilization in Brahmaputra floodplain, India. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 213, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Hiasa, M.; Mahmood, T.; Matsuo, T. Direct solid-liquid separation using hollow fiber membrane in an activated sludge aeration tank. In Water Pollution Research and Control Brighton; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Clech, P. Membrane bioreactors and their uses in wastewater treatments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.J. The status of industrial and municipal effluent treatment with membrane bioreactor technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 305, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Current state and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenten, I.G.; Friatnasary, D.L.; Khoiruddin, K.; Setiadi, T.; Boopathy, R. Extractive membrane bioreactor (EMBR): Recent advances and applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagle, A.; Freeman, B. Fundamentals of membranes for water treatment. Future Desalin. Tex. 2004, 2, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Dickhout, J.M.; Moreno, J.; Biesheuvel, P.; Boels, L.; Lammertink, R.; De Vos, W. Produced water treatment by membranes: A review from a colloidal perspective. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 487, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutamim, N.S.A.; Noor, Z.Z.; Hassan, M.A.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Olsson, G. Membrane bioreactor: Applications and limitations in treating high strength industrial wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.K.; Kashif, A.; Rout, P.R.; Aslam, M.; Fuwad, A.; Choi, Y.; Park, J.H.; Kumar, G. A brief review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors emphasizing recent advancements, fouling issues and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.; Babanezhad, M.; Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. Prediction of thermal distribution and fluid flow in the domain with multi-solid structures using Cubic-Interpolated Pseudo-Particle model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. Evaluation of product of two sigmoidal membership functions (psigmf) as an ANFIS membership function for prediction of nanofluid temperature. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.M. Membrane bioreactors for industrial wastewater treatment: Applicability and selection of optimal system configuration. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2006, 2006, 3233–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, T.; Soeprijanto, A.A. Effect of powdered activated carbon addition on a submerged membrane adsorption hybrid bioreactor with shock loading of a toxic compound. J. Math. Technol. 2010, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-S.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, A.-C.; Erdei, L.; Vigneswaran, S. Long-term operation of submerged membrane bioreactor for the treatment of high strength acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) wastewater: Effect of hydraulic retention time. Desalination 2006, 191, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Deng, L.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, X. A review on membrane fouling control in anaerobic membrane bioreactors by adding performance enhancers. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Behroyan, I.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. High-performance hybrid modeling chemical reactors using differential evolution based fuzzy inference system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Matošić, M.; Mijatović, I.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) as an advanced wastewater treatment technology. In Emerging Contaminants from Industrial and Municipal Waste; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 37–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Ji, J.; Li, Y.-Y. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment with a focus on multicomponent biogas and membrane fouling control. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2641–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjiri, A.T.; Roudsari, M.H. Modeling and simulation of natural convection heat transfer process in porous and non-porous media. Appl. Res. J. 2016, 2, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.H.; Nierychlo, M.; Christensen, M.L.; Nielsen, P.H.; Jørgensen, M.K. Fouling of membranes in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: Planktonic bacteria can have a significant contribution. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Shi, Q.; Wu, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y. Fouling behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic modified membrane in anammox membrane bioreactor: Role of gel layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, A.; Ujang, Z.; Salim, M. The influenced of PAC, zeolite, and Moringa oleifera as biofouling reducer (BFR) on hybrid membrane bioreactor of palm oil mill effluent (POME). Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4341–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. Developing intelligent algorithm as a machine learning overview over the big data generated by Euler–Euler method to simulate bubble column reactor hydrodynamics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20558–20566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Sheng, G.-P.; Shi, B.-J.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. A novel electrochemical membrane bioreactor as a potential net energy producer for sustainable wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulliet, E.; Cren-Olivé, C. Screening of pharmaceuticals and hormones at the regional scale, in surface and groundwaters intended to human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, N.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Membrane fouling in nanofiltration/reverse osmosis membranes coupled with a membrane bioreactor used for municipal wastewater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 18, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.L. Micropollutants in wastewater irrigation systems: Impacts and perspectives. Ann. Adv. Chem. 2019, 3, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goswami, L.; Manikandan, N.A.; Pakshirajan, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Simultaneous heavy metal removal and anthracene biodegradation by the oleaginous bacteria Rhodococcus opacus. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.S.M.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.; Metin, M.; Altay, V.; Bhat, R.A.; Ejaz, M.; Gul, A.; Unal, B.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nibir, L.; Nahar, K. Arsenic and human health: Genotoxicity, epigenomic effects, and cancer signaling. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 200, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.; Basu, N.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Dórea, J.G.; McSorley, E.; Sakamoto, M.; Chan, H.M. Current progress on understanding the impact of mercury on human health. Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mergler, D. Ecosystem approaches to mercury and human health: A way toward the future. Ambio 2021, 50, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking water nitrate and human health: An updated review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egbi, C.D.; Anornu, G.K.; Ganyaglo, S.Y.; Appiah-Adjei, E.K.; Li, S.-L.; Dampare, S.B. Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Lower Volta River Basin of Ghana: Sources and related human health risks. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boink, A.; Speijers, G. Health effects of nitrates and nitrites, a review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Problems Associated with Nitrogen Fertilisation of Field Grown Vegetable Crops 563, Potsdam, Germany, 30 August–1 September 1999; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, C.M.; Cordier, S.; Font-Ribera, L.; Salas, L.A.; Levallois, P. Overview of disinfection by-products and associated health effects. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, S.D. Tackling unknown disinfection by-products: Lessons learned. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Mitch, W.A. Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs) and Human Health Effects: Multidisciplinary Challenges and Opportunities; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Zarei, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asghari, F.B.; Haghighat, G.A. Fluoride contamination in groundwater resources in the southern Iran and its related human health risks. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 153, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, C.; Whelton, H.; O’mullane, D. Water fluoridation. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2009, 10, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, S.; Awofeso, N. Water fluoridation: A critical review of the physiological effects of ingested fluoride as a public health intervention. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 293019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilden, R.C.; Huffling, K.; Sattler, B. Pesticides and health risks. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2010, 39, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencko, V.; Foong, F.Y.L. The history of arsenical pesticides and health risks related to the use of Agent Blue. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucic, A.; Duca, R.C.; Galea, K.S.; Maric, T.; Garcia, K.; Bloom, M.S.; Andersen, H.R.; Vena, J.E. Reproductive health risks associated with occupational and environmental exposure to pesticides. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in drinking water—A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman Jr, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keerthanan, S.; Jayasinghe, C.; Biswas, J.K.; Vithanage, M. Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in the environment: Plant uptake, translocation, bioaccumulation, and human health risks. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1221–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, Z.; Zare, E.N.; Ghomi, M.; Ahmadijokani, F.; Amini, M.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Arjmand, M.; Sharma, G.; Ali, H.; Ahmad, A. Toxicity and remediation of pharmaceuticals and pesticides using metal oxides and carbon nanomaterials. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusaucy, J.; Gateuille, D.; Perrette, Y.; Naffrechoux, E. Microplastic pollution of worldwide lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, M.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y.; Fu, W.; Li, C. A comparative review of microplastics in lake systems from different countries and regions. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith Jr, K. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iannilli, V.; Corami, F.; Grasso, P.; Lecce, F.; Buttinelli, M.; Setini, A. Plastic abundance and seasonal variation on the shorelines of three volcanic lakes in Central Italy: Can amphipods help detect contamination? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14711–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, F.; Hanif, K.; Rafey, A.; Khalid, U.; Zafar, A.; Ameen, M.; Lima, E.C. Removal of micropollutants from municipal wastewater using different types of activated carbons. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acero, J.L.; Benitez, F.J.; Real, F.J.; Teva, F. Micropollutants removal from retentates generated in ultrafiltration and nanofiltration treatments of municipal secondary effluents by means of coagulation, oxidation, and adsorption processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillossou, R.; Le Roux, J.; Mailler, R.; Vulliet, E.; Morlay, C.; Nauleau, F.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V. Organic micropollutants in a large wastewater treatment plant: What are the benefits of an advanced treatment by activated carbon adsorption in comparison to conventional treatment? Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Pattern recognition of the fluid flow in a 3D domain by combination of Lattice Boltzmann and ANFIS methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dai, R.; Chen, M.; Khan, S.J.; Wang, Z. Applications of membrane bioreactors for water reclamation: Micropollutant removal, mechanisms and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, A.; Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Adimi, M.; Fathinejad Jirandehi, H.; Shirazian, S. Modification of polyethersulfone membrane using MWCNT-NH2 nanoparticles and its application in the separation of azeotropic solutions by means of pervaporation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Ramamurthy, R. Progress in the removal of organic microcontaminants from wastewater using high retention membrane bioreactors: A critical review. Environ. Res. 2021, 110930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, S.; Tu, Y.; Hao, X. Capabilities and mechanisms of microalgae on removing micropollutants from wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Langenhoff, A.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H. Sorption of micropollutants on selected constructed wetland support matrices. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, M.; García-Galán, M.J.; Matamoros, V.; Fernández-Gatell, M.; Rousseau, D.P.; Du Laing, G.; Garfí, M.; Puigagut, J. Constructed wetlands operated as bioelectrochemical systems for the removal of organic micropollutants. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsigiannis, A.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mantziaras, J.; Gioldasi, M. Removal of emerging pollutants through granular activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, N.; Capparelli, A.; Navarro, A.; Marino, D. Pharmaceutical emerging pollutants removal from water using powdered activated carbon: Study of kinetics and adsorption equilibrium. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyrides, I.; Conteras, P.; Stuckey, D. Post-treatment of a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAMBR) saline effluent using powdered activated carbon (PAC). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Masoumian, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Influence of number of membership functions on prediction of membrane systems using adaptive network based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/446192/What-is-activated-carbon-or-activated-charcoal (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- Das, S.; Ray, N.M.; Wan, J.; Khan, A.; Chakraborty, T.; Ray, M.B. Micropollutants in wastewater: Fate and removal processes. Phys. -Chem. Wastewater Treat. Resour. Recovery 2017, 3, 75–117. [Google Scholar]
- López-Vinent, N.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; Ganiyu, S.O.; Sable, S.; Messele, S.A.; Lillico, D.; Stafford, J.; Sans, C.; Giménez, J.; Esplugas, S. Coagulation-flocculation followed by catalytic ozonation processes for enhanced primary treatment during wet weather conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wan, Y.; Shi, B.; Shi, J. Effects of powdered activated carbon on the coagulation-flocculation process in humic acid and humic acid-kaolin water treatment. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, R.; Ahmad, Z. Physico-Chemical Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Babanezhad, M.; Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Functional input and membership characteristics in the accuracy of machine learning approach for estimation of multiphase flow. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, W.; Cao, B.; Xia, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, D. Characterization of changes in floc morphology, extracellular polymeric substances and heavy metals speciation of anaerobically digested biosolid under treatment with a novel chelated-Fe2+ catalyzed Fenton process. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, S.; Lema, J.M.; Omil, F. Pre-treatment of hospital wastewater by coagulation–flocculation and flotation. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, H.; Matsuto, T. Experimental study of behavior of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in leachate treatment process and evaluation of removal efficiency. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thuy, P.T.; Moons, K.; Van Dijk, J.; Viet Anh, N.; Van der Bruggen, B. To what extent are pesticides removed from surface water during coagulation–flocculation? Water Environ. J. 2008, 22, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Yoon, Y.; Snyder, S.; Wert, E. Fate of endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical, and personal care product chemicals during simulated drinking water treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6649–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.M.; Tuhkanen, T.; Kronberg, L. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in effluents from a sewage treatment plant and in the recipient water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8220–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Laski, E.; García-Cañibano, C.; De Vidales, M.M.; Encinas, Á.; Kuch, B.; Marugán, J. Micropollutants removal by full-scale UV-C/sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E.; Ross, A.B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. JPCRD 1988, 17, 1027–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Deng, W.-J.; Ying, G.-G. Removal of steroid hormones and biocides from rural wastewater by an integrated constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivant, A.-L.; Boutin, C.; Prost-Boucle, S.; Papias, S.; Hartmann, A.; Depret, G.; Ziebal, C.; Le Roux, S.; Pourcher, A.-M. Free water surface constructed wetlands limit the dissemination of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in the natural environment. Water Res. 2016, 104, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Carvalho, P.N.; Müller, J.A.; Manoj, V.R.; Dong, R. Sanitation in constructed wetlands: A review on the removal of human pathogens and fecal indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, L.; Pan, X.-M.; Lee, D.-J. Pollution tolerant protozoa in polluted wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 240, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. Removal processes of disinfection byproducts in subsurface-flow constructed wetlands treating secondary effluent. Water Res. 2014, 51, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Liu, H. Purification ability and carbon dioxide flux from surface flow constructed wetlands treating sewage treatment plant effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babanezhad, M.; Behroyan, I.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Computational modeling of transport in porous media using an adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30826–30835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruchlik, Y.; Linge, K.; Joll, C. Removal of organic micropollutants in waste stabilisation ponds: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, A.; Surampalli, R.Y. Performance of anaerobic hybrid reactors for the treatment of complex phenolic wastewaters with biogas recirculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondor, A.C.; Jakab, G.; Vancsik, A.; Filep, T.; Szeberényi, J.; Szabó, L.; Maász, G.; Ferincz, Á.; Dobosy, P.; Szalai, Z. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in the Danube and drinking water wells: Efficiency of riverbank filtration. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driezum, I.H.; Derx, J.; Oudega, T.J.; Zessner, M.; Naus, F.L.; Saracevic, E.; Kirschner, A.K.; Sommer, R.; Farnleitner, A.H.; Blaschke, A.P. Spatiotemporal resolved sampling for the interpretation of micropollutant removal during riverbank filtration. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alobaidi, R.A.K.; Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Mhemid, R.K.S.; Manav-Demir, N.; Cinar, O. Biodegradation of Emerging Pharmaceuticals from Domestic Wastewater by Membrane Bioreactor: The Effect of Solid Retention Time. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marszałek, A.; Bohdziewicz, J.; Puszczało, E. Co-treatment of municipal landfill leachate with dairy wastewater in membrane bioreactor. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2020, 27, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpuz, M.V.A.; Borea, L.; Senatore, V.; Castrogiovanni, F.; Buonerba, A.; Oliva, G.; Ballesteros Jr, F.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Choo, K.-H. Wastewater treatment and fouling control in an electro algae-activated sludge membrane bioreactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Valéro, J.R. Membrane processes for removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) from water and wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadkaew, N.; Hai, F.I.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Nghiem, L.D. Removal of trace organics by MBR treatment: The role of molecular properties. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadkaew, N.; Sivakumar, M.; Khan, S.J.; McDonald, J.; Nghiem, L.D. Effect of mixed liquor pH on the removal of trace organic contaminants in a membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.B.; Weiss, S.; Reemtsma, T. Pathways and metabolites of microbial degradation of selected acidic pharmaceutical and their occurrence in municipal wastewater treated by a membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeganroudsari, M.; Soltani, M.; Heydarinasab, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Hossain, M.K.; Khiyavi, A.A. Mathematical modeling and simulation of molecular mass transfer across blood brain barrier in brain capillary. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, M.; Müller, J.; Knepper, T.P. Biodegradation of persistent polar pollutants in wastewater: Comparison of an optimised lab-scale membrane bioreactor and activated sludge treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3419–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, B.C.; Ra, J.S.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S.; Chang, N.I.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.D. Comparison of the removal efficiency of endocrine disrupting compounds in pilot scale sewage treatment processes. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cases, V.; Alonso, V.; Argandoña, V.; Rodriguez, M.; Prats, D. Endocrine disrupting compounds: A comparison of removal between conventional activated sludge and membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2011, 272, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Namdeo, M.; Mehta, R.; Agrawala, V. Effect of arsenic contamination in potable water and its removal techniques. Int. J. Water Wastewater Treat 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, N.; Sockan, V.; Jayakaran, P. Waste water treatment by coagulation and flocculation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2014, 3, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe, M.; Farner, J.M.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Understanding and improving microplastic removal during water treatment: Impact of coagulation and flocculation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8719–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaie Nakhjiri, A.; Sanaeepur, H.; Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Shirazi, M.M.A. Recovery of precious metals from industrial wastewater towards resource recovery and environmental sustainability: A critical review. Desalination 2022, 527, 115510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A. Potential applications of nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: Nanoadsorbents performance. In Research Anthology on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Nanomaterials; IGI Global: Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA, 2021; pp. 1230–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Ghadiri, M. Numerical investigation of ibuprofen removal from pharmaceutical wastewater using adsorption process. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’na, E. Amine-Modified SBA-15 (Prepared by Co-Condensation) for Adsorption of Copper from Aqueous Solutions; University of Ottawa: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lofrano, G.; Meric, S. A comprehensive approach to winery wastewater treatment: A review of the state-of the-art. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3011–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Díaz, C.; Canizares, P.; Fernández, F.; Natividad, R.; Rodrigo, M.A. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: An overview of the current applications to actual industrial effluents. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petre, C.F.; Piché, S.; Normandin, A.; Larachi, F. Advances in chemical oxidation of total reduced sulfur from kraft mills atmospheric effluents. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2007, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordio, A.; Carvalho, A.J.P.; Pinto, A.P.H. Wetlands: Water “living filters”? In Wetlands: Ecology, Conservation and Restoration; Russo, R.E., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 15–71. [Google Scholar]
- Almasi, A.; Dargahi, A.; Ahagh, M.; Janjani, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Tabandeh, L. Efficiency of a constructed wetland in controlling organic pollutants, nitrogen, and heavy metals from sewage. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 9, 2924–2928. [Google Scholar]
- Gizińska-Górna, M.; Czekała, W.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Lewicki, A.; Dach, J.; Marzec, M.; Pytka, A.; Janczak, D.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Listosz, A. The possibility of using plants from hybrid constructed wetland wastewater treatment plant for energy purposes. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Arora, M. Suitability of Grey Water Recycling as decentralized alternative water supply option for Integrated Urban Water Management. IOSR J. Eng. 2012, 2, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassew, F.A.; Bergland, W.H.; Dinamarca, C.; Kommedal, R.; Bakke, R. Granular sludge bed processes in anaerobic digestion of particle-rich substrates. Energies 2019, 12, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, M.; Tawfik, A.; Samhan, F.; El-Gohary, F. Sewage treatment using an integrated system consisting of anaerobic hybrid reactor (AHR) and downflow hanging sponge (DHS). Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 4, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Du, R. Feasibility of partial-denitrification/anammox for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment in a hybrid biofilm reactor. Water Res. 2022, 208, 117856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Behroyan, I.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Performance and application analysis of ANFIS artificial intelligence for pressure prediction of nanofluid convective flow in a heated pipe. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Feng, K.; Gapeeva, A.; Meurisch, K.; Kaps, S.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Mishra, Y.K.; Adelung, R.; Baum, M. Functional Polymer Materials for Modern Marine Biofouling Control. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 127, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Biofouling: Lessons from nature. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 2381–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Oh, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shin, H.-S.; Chae, S.-R. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Res. 2017, 114, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.-S.; Le Clech, P.; Jefferson, B.; Judd, S. Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, I.; Sinha, A. A review on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors: Control and mitigation. In Environmental Contaminants; Gupta, T., Agarwal, A.K., Agarwal, R.A., Labhesetwar, N.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 281–315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceri, H.; Fischer, K.; Schulze, A.; Moheimani, N.R. Membrane fouling control for sustainable microalgal biodiesel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigómez, I.; González, E.; Rodríguez-Gómez, L.; Vera, L. Fouling control strategies for direct membrane ultrafiltration: Physical cleanings assisted by membrane rotational movement. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Lohrengel, B.; Nghiem, L.D. Membrane fouling and chemical cleaning in water recycling applications. Desalination 2010, 250, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, N.; Uzal, N.; Koseoglu, H.; Harman, I.; Yukseler, H.; Yetis, U.; Civelekoglu, G.; Kitis, M. Treatment of a denim producing textile industry wastewater using pilot-scale membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2009, 240, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lina, C.; Xiuhua, L.; Zhijian, M.; Zhang, Z. Startup and operation of anaerobic EGSB reactor treating palm oil mill effluent. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayon, S.; Noor, M.M.M.; Ahmad, J.; Ghani, L.A.; Nagaoka, H.; Aya, H. Effects of mixed liquor suspended solid concentrations on membrane bioreactor efficiency for treatment of food industry wastewater. Desalination 2004, 167, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, A.; Ujang, Z.; Noor, Z.Z. Performance of bio-fouling reducers in aerobic submerged membrane bioreactor for palm oil mill effluent treatment. Desalination 2008, 316, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhin, S.G.; Banadda, N.; Komakech, A.J.; Kabenge, I.; Wanyama, J. Membrane fouling control in low pressure membranes: A review on pretreatment techniques for fouling abatement. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Classification | Micro-Contaminant | Average Concentration in Surface Water (ng L−1) | Average Concentration in Wastewater (ng L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pesticides | Carbaryl | --- | 1.6 |
| Dimethoate | 22 | --- | |
| Diethyltoluamide (DEET) | 135 | 593 | |
| Diazinon | 15 | 173 | |
| Hormone active substances | Estradiol | 2 | 3 |
| Estrone | 2 | 15 | |
| Nonylphenol | 441 | 267 | |
| Pharmaceuticals (NSAID, over the counter (OTC) drugs and veterinary drugs | Diclofenac | 65 | 647 |
| Erythromycin | 25 | 42 | |
| Ethinylestradiol | 5 | 2 | |
| Ibuprofen | 35 | 394 | |
| Mefenamic acids | 7 | 870 | |
| Metformin | 713 | 10,347 | |
| Naproxen | 37 | 462 | |
| Penicillin V | --- | 28.7 | |
| Codeine | --- | 70.6 | |
| Citalopram | --- | 33.8 | |
| Azithromycin | 12 | 175 | |
| Atenolol | 205 | 843 | |
| Detergents and personal care/food products | Gadolinium | --- | 115 |
| Buprenorphine | --- | 3.9 | |
| Maprotiline | --- | 0.4 | |
| Duloxetine | --- | 0.1 | |
| Chlorpromazine | --- | 0.1 | |
| Acesulfame | 4010 | 22,500 | |
| Sucralose | 540 | 4600 |
| Micro-Contaminant | Health Detriments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Arsenic |
| [51,52] |
| Mercury |
| [53,54] |
| Nitrate |
| [55,56,57] |
| Disinfection by-products |
| [58,59,60] |
| Fluoride |
| [61,62,63] |
| Pesticides |
| [64,65,66,67] |
| Pharmaceutical drugs |
| [68,69,70,71] |
| Coagulant/Flocculent | Micro-Contaminant | Source | Removal (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric chloride/Aluminium sulfate | Ibuprofen | Hospital wastewater | 4.8 | [100] |
| Diclofenac | 19.4 | |||
| Naproxen | 10.2 | |||
| Carbamazepine | 15.9 | |||
| Sulfamethoxazole | 9.5 | |||
| Tonalide | 14.3 | |||
| Galaxolide | 9.9 | |||
| Ferric chloride | Bisphenol A | Landfill leachate | 20 | [101] |
| Nonylphenol | 90 | |||
| Aluminium sulfate | Aldrin | Surface water | 46 | [102] |
| Bentazon | 15 | |||
| Aluminium sulfate | Estradiol | Drinking water treatment pant | 2 | [103] |
| Estrone | 5 | |||
| Progesterone | 6 | |||
| Fluoxetine | 15 | |||
| Hydrocodone | 24 | |||
| Chlordane | 25 | |||
| Erythromycin | 33 | |||
| DDT | 36 | |||
| Ferric sulfate | Diclofenac | Lake water with dissolved humic acid | 77 | [104] |
| Ibuprofen | 50 | |||
| Bezafibrate | 36 | |||
| Carbamazepine | Less than 10 | |||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Less than 10 |
| Classification | Micro–Contaminant | Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Non–steroidal anti–inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Ibuprofen | 73–99.8 |
| Ketoprofen | 3.7–91.9 | |
| Naproxen | 40.1–99.3 | |
| Diclofenac | 15–87.4 | |
| Anti–epileptics/anti–depressant | Acetaminophen | 95.1–99.9 |
| Carbamazepine | 42–51 | |
| Diazepam | 67 | |
| Hormones and EDCs | Estrone | 76.9–99.4 |
| 17β–estradiol | Higher than 99.4 | |
| 17α–Ethinylestradiol | 0–93.5 | |
| Bisphenol A | 88.2–97 | |
| Antibiotics | Sulfamethoxazole | 20–91.9 |
| Erythromycin | 25.2–90.4 | |
| Beta blockers | Atenolol | 5–96.9 |
| Metoprolol | 29.5–58.7 | |
| Lipid regulator/cholesterol lowering drugs | Bezafibrate | 88.2–95.8 |
| Clofibric acid | 25–71 | |
| Gemfibrozil | 32.5–85 |
| Micro-Contaminants Removal Approach | Positive Points | Drawbacks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coagulation/flocculation |
|
| [131,132,133,134] |
| ACA |
|
| [135,136,137] |
| AOP |
|
| [138,139,140] |
| CW |
|
| [141,142,143,144] |
| HRS |
|
| [145,146,147] |
| MBRs |
|
| [121,122,140] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, M.-L.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Kamal, M.; Mohamed, A.; Algarni, M.; Yu, S.T.; Wang, F.-M.; Su, C.-H. State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment. Membranes 2022, 12, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040429
Nguyen M-L, Nakhjiri AT, Kamal M, Mohamed A, Algarni M, Yu ST, Wang F-M, Su C-H. State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040429
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, My-Linh, Ali Taghvaie Nakhjiri, Mehnaz Kamal, Abdullah Mohamed, Mohammed Algarni, Subbotina Tatyana Yu, Fu-Ming Wang, and Chia-Hung Su. 2022. "State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment" Membranes 12, no. 4: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040429
APA StyleNguyen, M.-L., Nakhjiri, A. T., Kamal, M., Mohamed, A., Algarni, M., Yu, S. T., Wang, F.-M., & Su, C.-H. (2022). State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment. Membranes, 12(4), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040429








