Polypropylene Hollow-Fiber Membrane Made Using the Dissolution-Induced Pores Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Preparation of Hollow-Fiber Membranes
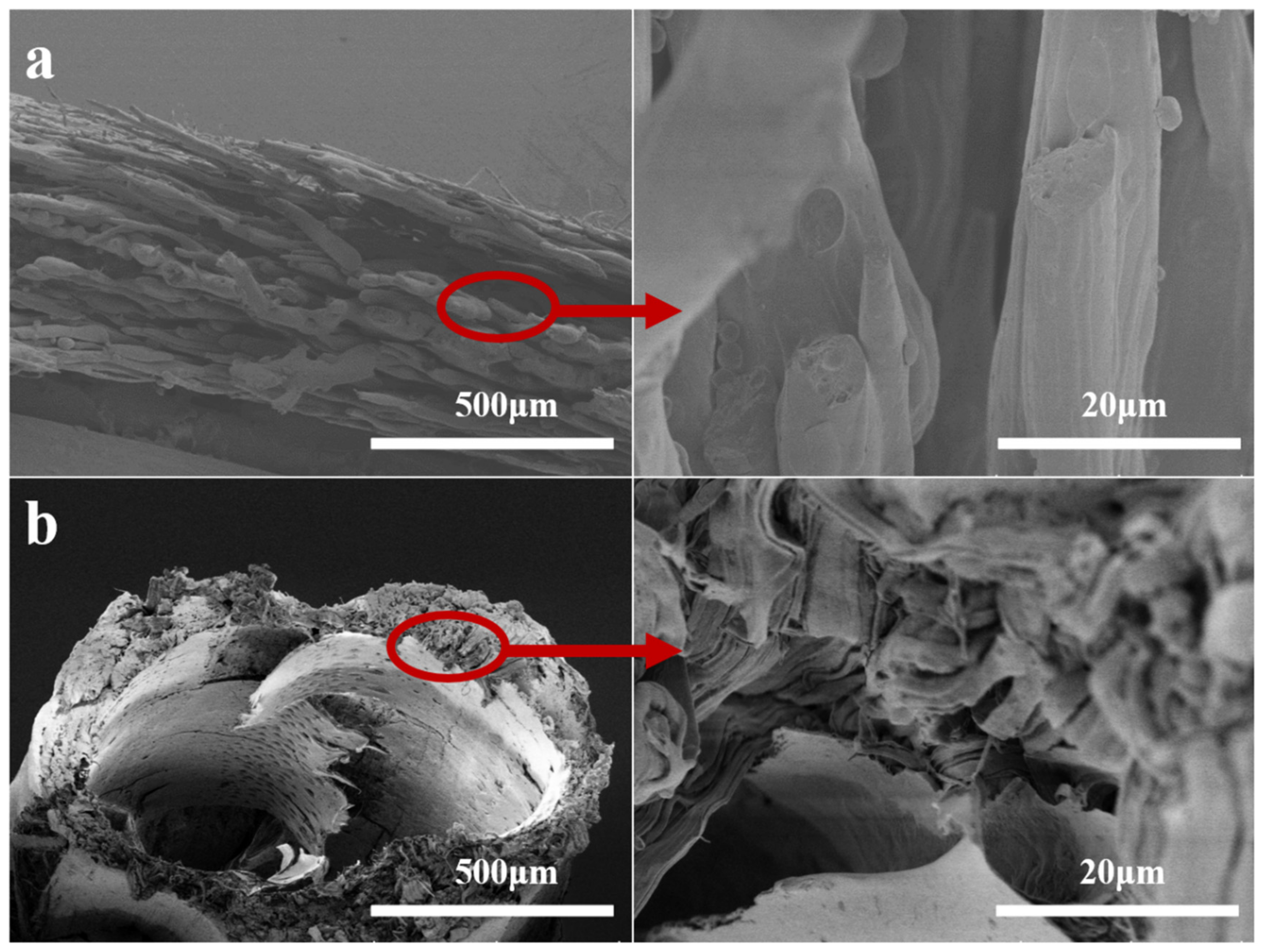
2.3. FTIR, Particle Size/Zeta Potential, Pore Size Testing, and SEM Testing
2.4. Embedded and Blocked Factor
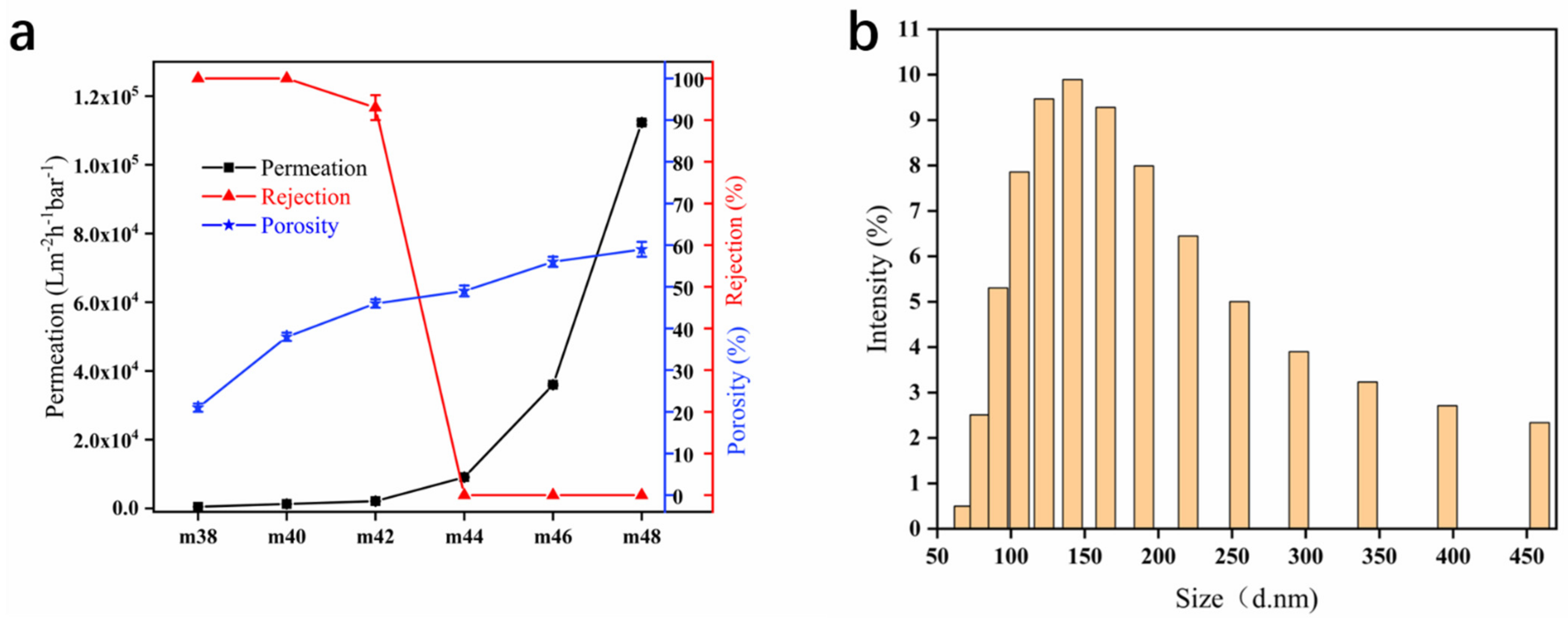
2.5. Filtration Performance and Porosity
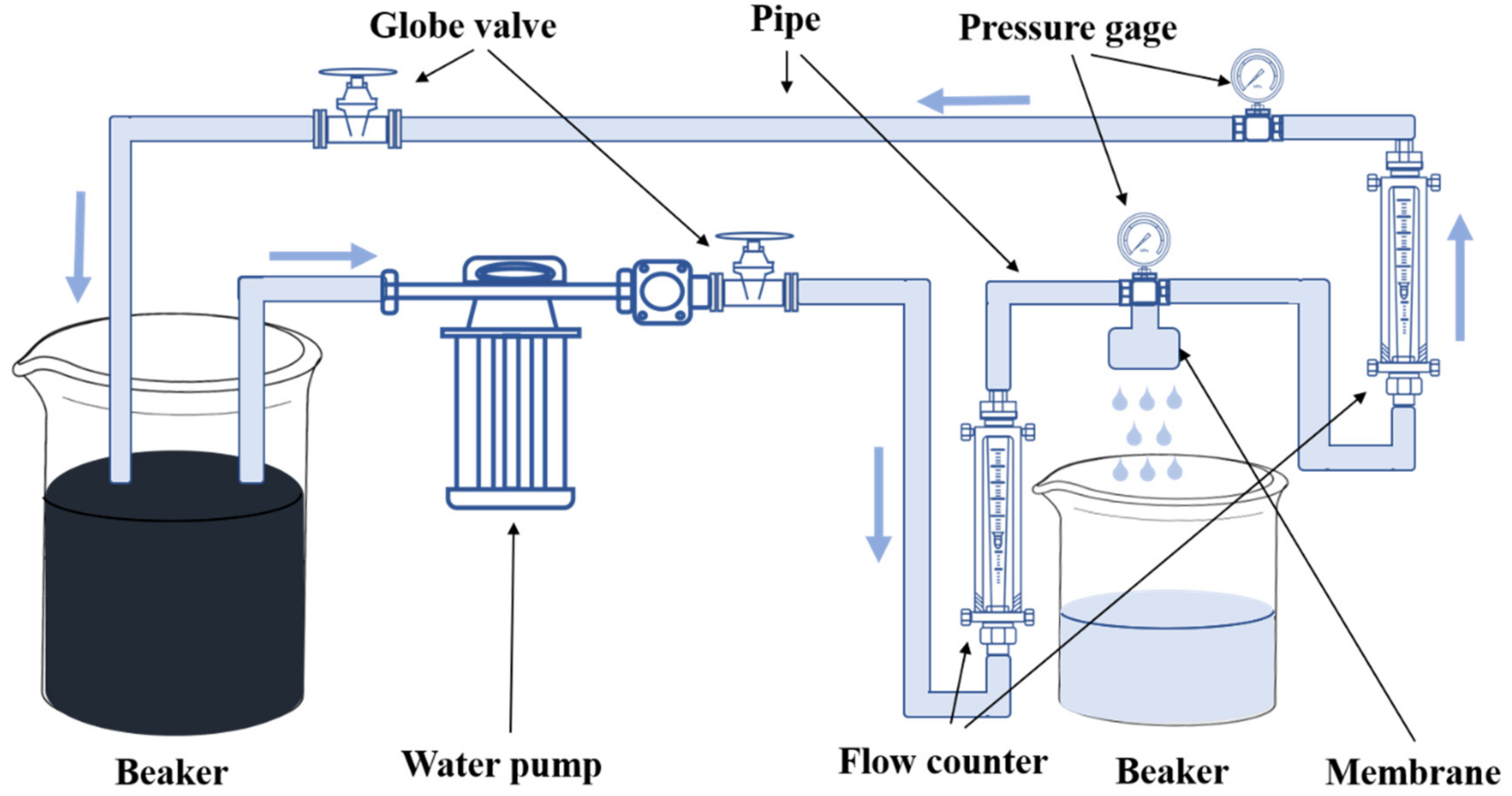
2.6. Mechanical Test
3. Results and Discussion
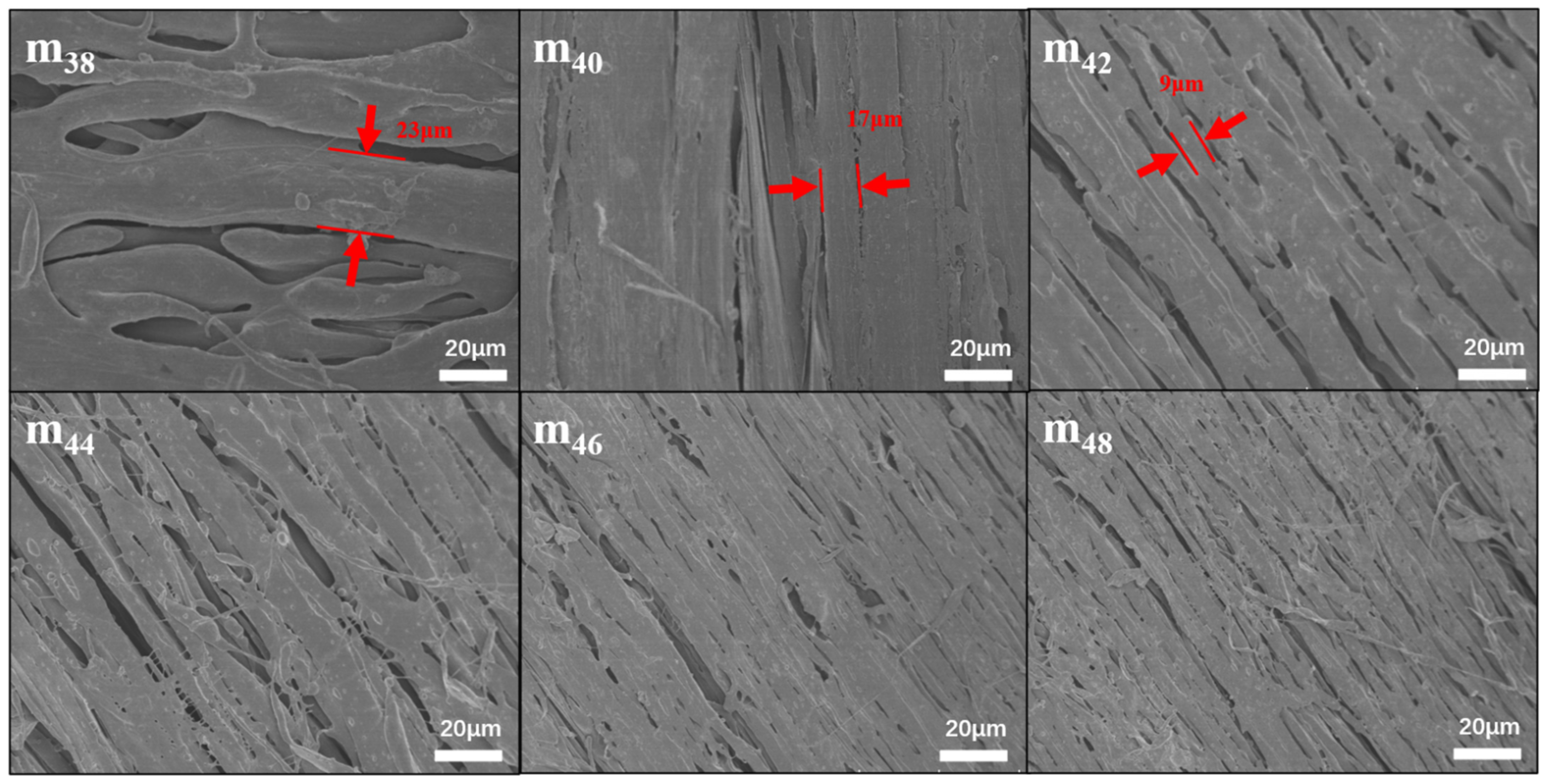
3.1. Preparation of Hollow-Fiber Membranes (with Different Contents of EVOH)
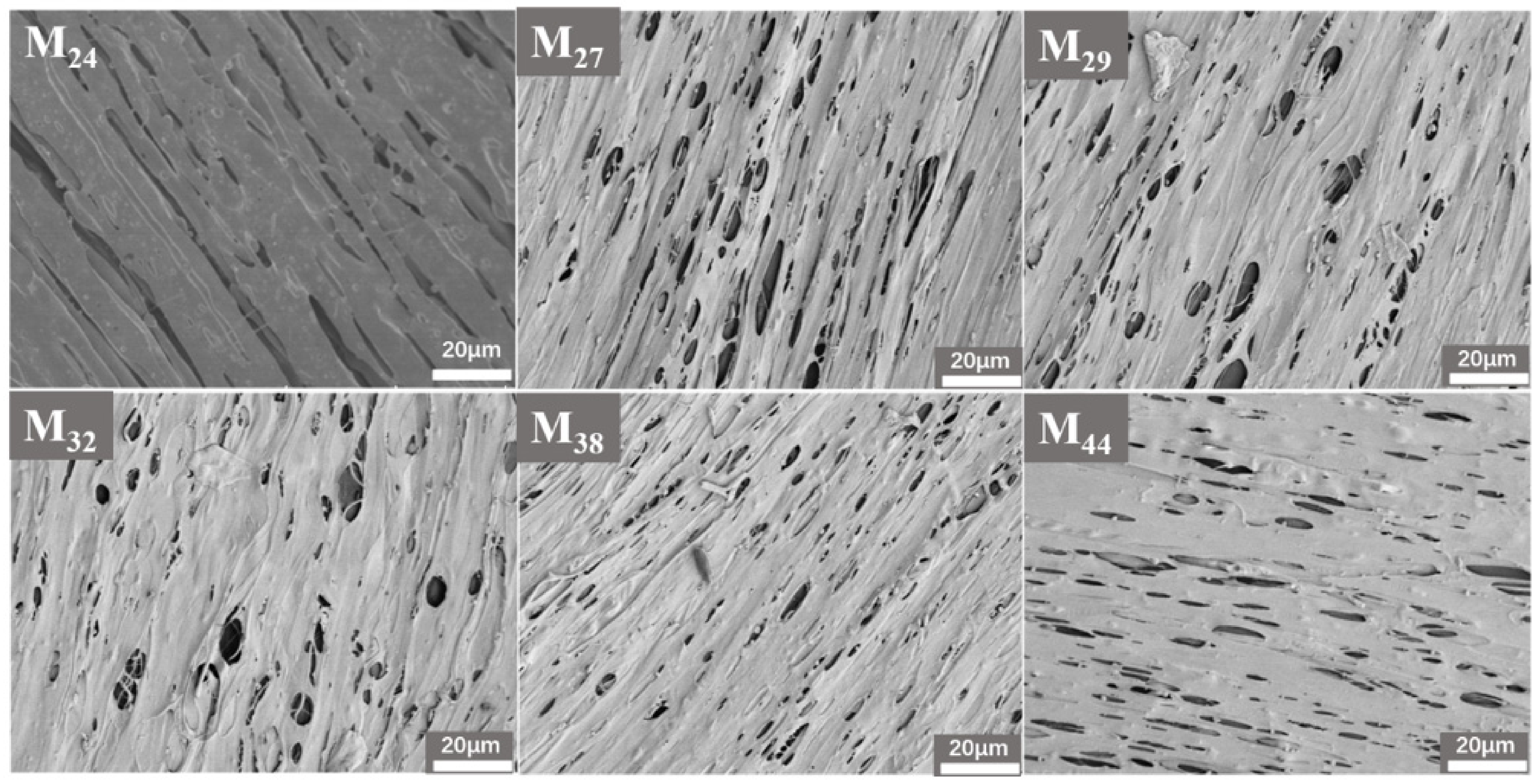
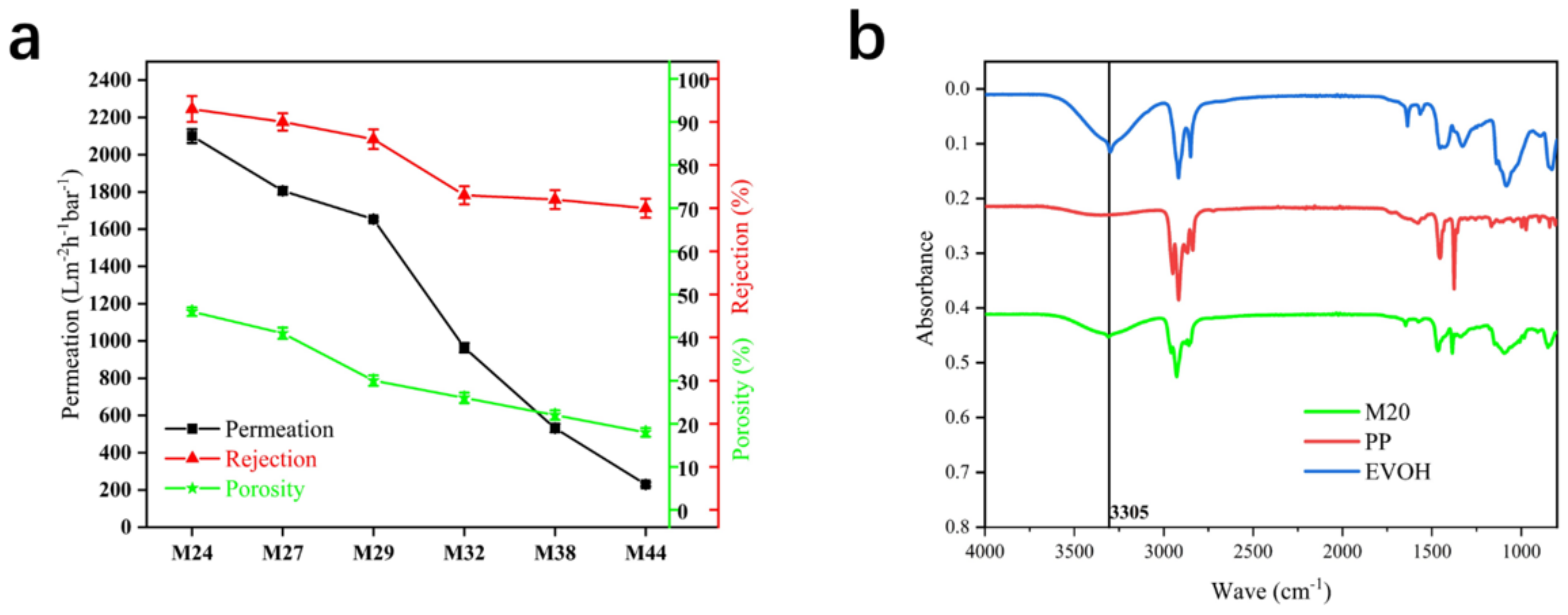
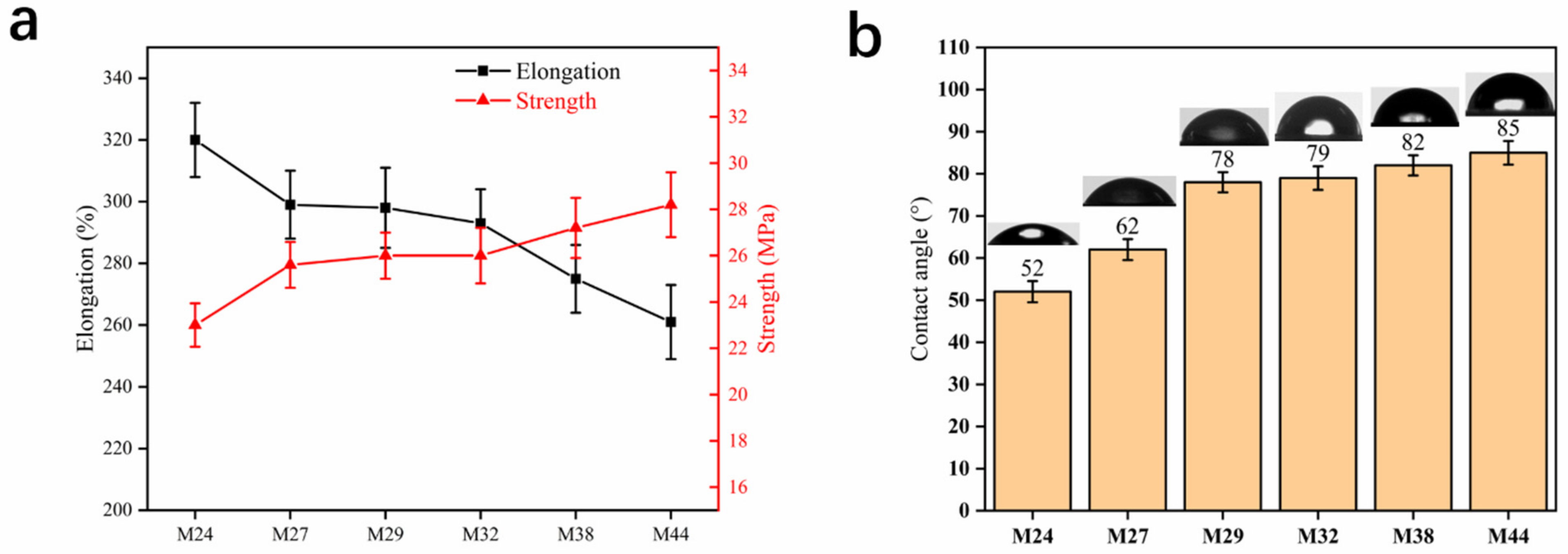
3.2. Preparation of Hollow-Fiber Membranes (EVOH with Different Ethylene Segments)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Mao, T.; Zheng, C.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Niu, Z.; Wu, X. A polypropylene melt-blown strategy for the facile and efficient membrane separation of oil-water mixtures. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 29, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Fan, R. Covalent modification of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt on microporous polypropylene membrane and its antibacterial properties. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2021, 40, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, X.; Gao, C.; Xue, L. Super-hydrophobic F-TiO2@PP membranes with nano-scale ?coral?-like synapses for waste oil recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 267, 118579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, C. The polypropylene membrane modified by an atmospheric pressure plasma jet as a separator for lithium-ion button battery. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gu, J.; Yin, Y. A biaxial stretched β-isotactic polypropylene microporous membrane for lithium-ion batteries. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, C.G.; Dietrich, M.; Gromann, K.; Frese, J.; Krueger, S.; Sachweh, J.S.; Jockenhoevel, S. Fibronectin coating of oxygenator membranes enhances endothelial cell attachment. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Tatebe, K.; Onishi, M.; Seita, Y.; Takahara, K. Influence of Molecular-Weight of Polypropylene and A Nuclenting-Agent on Polypropylene Miroporous Hollow-Fiber Membranes for Artificial Lungs. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 1993, 50, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, A.; Tatebe, K.; Onishi, M.; Seita, Y.; Takahara, K. Morphological Change of Microporous Hollow-Fiber Membranes for Artificial Lungs Induced by Cooling. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 1993, 50, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wei, F.; Wu, B.; Zhang, K.; Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, S. Effects of annealing stress field on the structure and properties of polypropylene hollow fiber membranes made by stretching. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4271–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Mao, H.; Zhao, Z.-P. Fabrication of PP hollow fiber membrane via TIPS using environmentally friendly diluents and its CO2 degassing performance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19164–19170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, J. Design and preparation of polypropylene ultrafiltration membrane with ultrahigh permeation for both water and oil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabedi, P.; Akbari, A.; Yegani, R. Fabrication of hydrophobic PP/CH3SiO2 composite hollow fiber membrane for membrane contactor application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, F.; Habib, E.; Reza, Y.; Saber, Z. Fouling characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle embedded polypropylene membrane in oil refinery wastewater treatment using membrane bioreactor (MBR). Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 90, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghaddosi, S.; Akbari, A.; Yegani, R. Preparation, characterization and anti-fouling properties of nanoclays embedded polypropylene mixed matrix membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 125, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, Z.; Hua, X. Study on structure and hydrophobicity of PP/EVA co-blending membrane: Quenching rate. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zwirner, U.; Hoeffler, K.; Pflaum, M.; Korossis, S.; Haverich, A.; Wiegmann, B. Identifying an optimal seeding protocol and endothelial cell substrate for biohybrid lung development. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Zhao, Z.-P.; Xi, Z.-Y.; Yan, S.-Y. Microporous polypropylene membrane prepared via TIPS using environment-friendly binary diluents and its VMD performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Yan, S.Y.; Zhao, Z.P.; Xi, Z.Y. Isothermal Crystallization of iPP in Environment-friendly Diluents: Effect of Binary Diluents and Crystallization Temperature on Crystallization Kinetics. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Fan, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, L. Effect of stretching on continuous oil/water separation performance of polypropylene hollow fiber membrane. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, G.; MacInnis, K.; Olah, A.; Baer, E. Structure-property relationships of microporous membranes produced by biaxial orientation of compatibilized PP/Nylon 6 blends. Polymer 2018, 145, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, W.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yao, L. Preparation and characterization of antibacterial microporous membranes fabricated by poly(AMS-co-DMAEMA) grafted polypropylene via melt-stretching method. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, W.; Huang, T.; Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Q. Microporous membrane fabricated by AMS-GMA-TPE terpolymer grafted polypropylene prepared via extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46020–46025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ajji, A.; Guo, S.; Xiong, C. Preparation of Microporous Polypropylene/Titanium Dioxide Composite Membranes with Enhanced Electrolyte Uptake Capability via Melt Extruding and Stretching. Polymers 2017, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, S.; Xie, G. A high-barrier PP/EVOH membrane prepared through the multistage biaxial-stretching extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45016–45027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, G.; MacInnis, K.; Olah, A.; Baer, E. Formation of microporous membranes by biaxial orientation of compatibilized PP/Nylon 6 blends. Polymer 2017, 123, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, W.; Xia, Y.; Gu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Tao, S.; Geng, H.; Tao, G.; et al. Improving amphiphilic polypropylenes by grafting poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate segments on a polypropylene microporous membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Ni, L.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X.-S.; Ji, L. Technology study of polypropylene hollow fiber membranes-like artificial lung made by the melt-spinning and cold-stretching method. In Materials Processing Technology; Advanced Materials Research; Liu, X.H., Jiang, Z., Han, J.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 418–420, pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, X.T.; Yan, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.B. Effect of Annealing Temperature on PP Microporous Membranes Obtained by a Melt-Extrusion-Stretching Method. Int. Polym. Proc. 2019, 34, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wei, F.; Shao, H.; Xie, L.; Cui, Z.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Microstructure construction of polypropylene-based hollow fiber membranes with bimodal microporous structure for water permeation enhancement and rejection performance rejection. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.W.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, D.J.; Park, O.O.; Nam, S.Y. Effect of annealing on the morphology of porous polypropylene hollow fiber membranes. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q. Morphology structure study of polypropylene hollow fiber membrane made by the blend-spinning and cold-stretching method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijie, X.; Jiayi, X.; Ziqin, T.; Henghui, H.; Xiande, C.; Caihong, L.; Xingqi, Z. Pore growth and stabilization in uniaxial stretching polypropylene microporous membrane processed by heat-setting. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.T.; Song, K.; Kim, S.S. Effects of Nucleating Agents on Preparation of Polypropylene Hollow Fiber Membranes by Melt Spinning Proces. Macromol. Res. 2002, 10, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, K.; Du, X.; Yang, J. Synthesis of polydopamine-mediated PP hollow fibrous membranes with good hydrophilicity and antifouling properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Qi, Y.; Luo, D.; Liang, S.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Fabrication of antifouling polypropylene hollow fiber membrane breaking through the selectivity-permeability trade-off. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 105, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-N.; Au-Duong, A.-N.; Lee, C.-K. Facile coating on microporous polypropylene membrane for antifouling microfiltration using comb-shaped poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) with multivalent catechol. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardani, A.K.; Ariono, D.; Subagjo, S.; Wenten, I.G. Fouling tendency of PDA/PVP surface modified PP membrane. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 19, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin, K.; Wardani, A.K.; Aryanti, P.T.P.; Astuti, D.I.; Komaladewi, A.A.I.A.S. Preparation of antifouling polypropylene/ZnO composite hollow fiber membrane by dip-coating method for peat water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Qi, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Interface engineering of polypropylene hollow fiber membrane through ultrasonic capillary effect and nucleophilic substitution. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 3125–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Qi, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Polypropylene composite hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes with an acrylic hydrogel surface by in situ ultrasonic wave-assisted polymerization for dye removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 136, 47099–47109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Yan, B.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, L.; Chen, V. Self-cleaning PDA/ZIF-67@PP membrane for dye wastewater remediation with peroxymonosulfate and visible light activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M.; Lü, Z.; Yu, S.; Gao, C. Cross-flow deposited hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)/polypropylene (PP) thin-film composite membrane for aqueous and non-aqueous nanofiltration. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 153, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.A.; Ernst, T.; Sucksdorff, C.; Pirjola, R.; Ryno, J. Experiences of a filter method and a standard curve method for determining k-indices. Ann. Geophys. Atmos. Hydrospheres Space Sci. 1988, 6, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Gryta, M. Influence of polypropylene membrane surface porosity on the performance of membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Z. Experimental study of the effect of membrane porosity on membrane absorption process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 3245–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Chen, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-Z. In situ reinforced and flame-retarded polycarbonate by a novel phosphorus-containing thermotropic liquid crystalline copolyester. Polymer 2011, 52, 4150–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnooshi, M.; Javadi, A.; Nazockdast, H.; Ottermann, K.; Altstädt, V. Rheological rationalization of in situ nanofibrillar structure development: Tailoring of nanohybrid shish-kebab superstructures of poly (lactic acid) crystalline phase. Polymer 2020, 211, 123040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Umetsu, K.; Miyasaka, K. Mechanical properties of biaxially drawn films of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene dried gels. Polymer 1993, 34, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, Z.; He, C. Polypropylene Hollow-Fiber Membrane Made Using the Dissolution-Induced Pores Method. Membranes 2022, 12, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040384
Qiu Z, He C. Polypropylene Hollow-Fiber Membrane Made Using the Dissolution-Induced Pores Method. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040384
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Zhongyong, and Chunju He. 2022. "Polypropylene Hollow-Fiber Membrane Made Using the Dissolution-Induced Pores Method" Membranes 12, no. 4: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040384
APA StyleQiu, Z., & He, C. (2022). Polypropylene Hollow-Fiber Membrane Made Using the Dissolution-Induced Pores Method. Membranes, 12(4), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040384




