Lithium Salt Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerized Solid-State Electrolyte with Comparable Ionic Conductivity and Better Interface Compatibility for Li-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments and Measurements
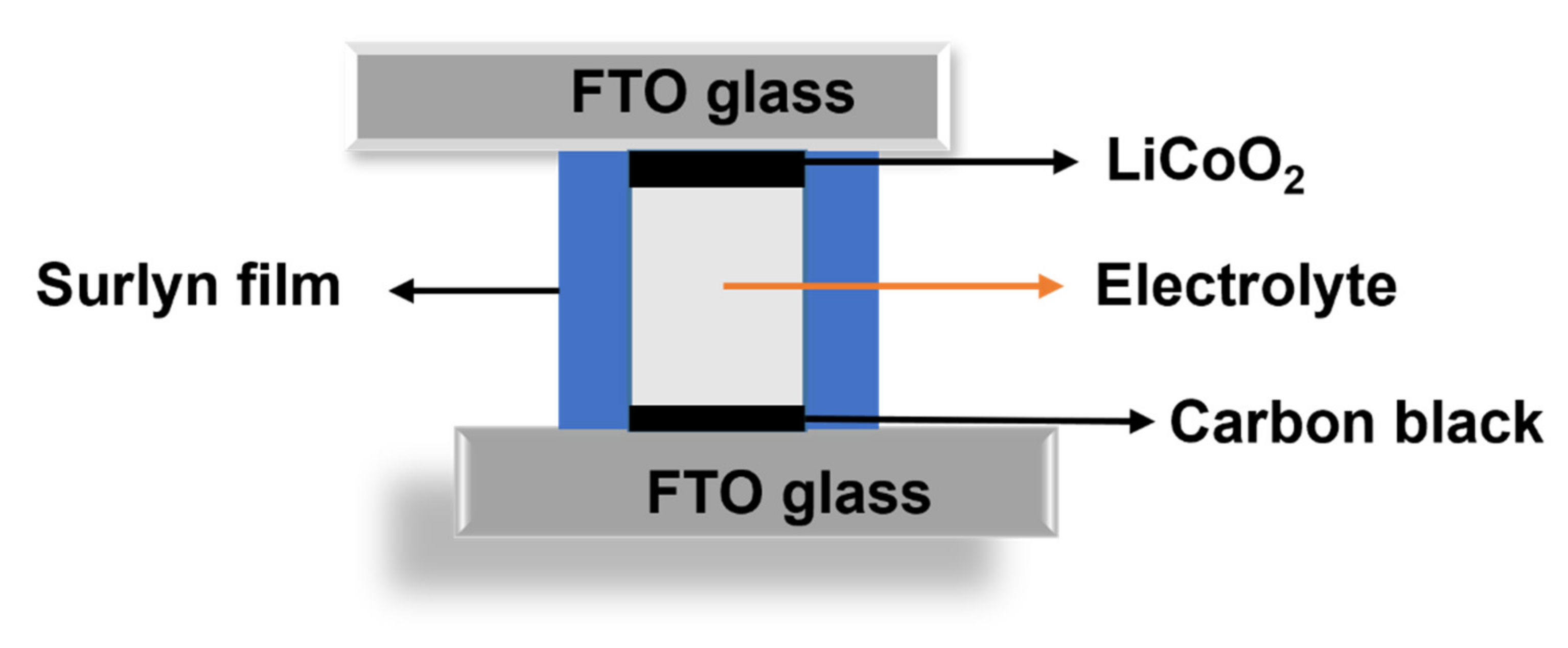
2.3. Fabrication of Asymmetry Dummy Cell
2.4. In Situ Thermal Polymerization
2.5. Electrochemical Performances
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Structure Characterization
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of SPEs
3.3. Electrochemical Performances
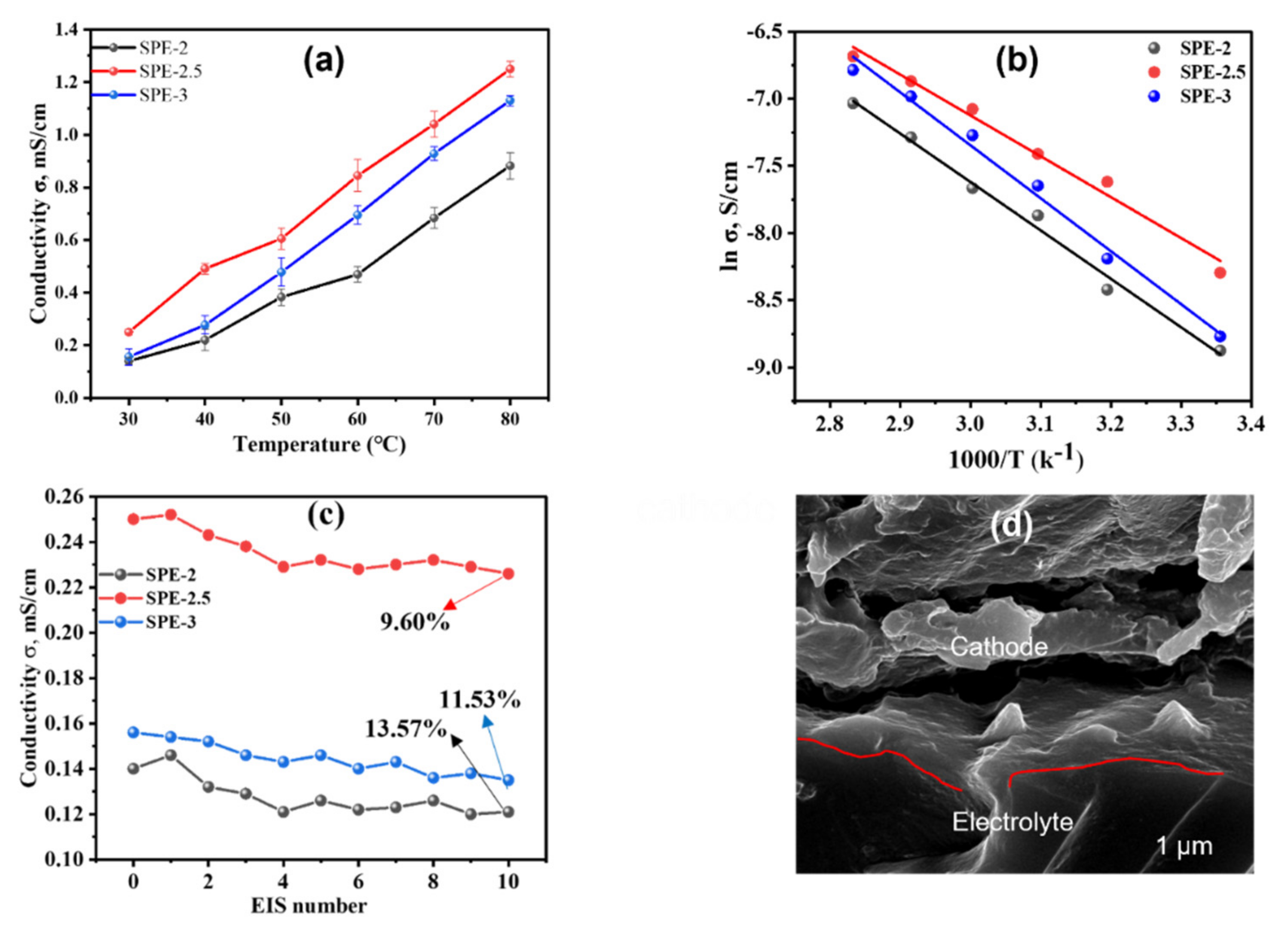
3.3.1. Ionic Conductivity and Impedimetric Stability
3.3.2. Electrochemical Stability Window and tLi+ Measurement
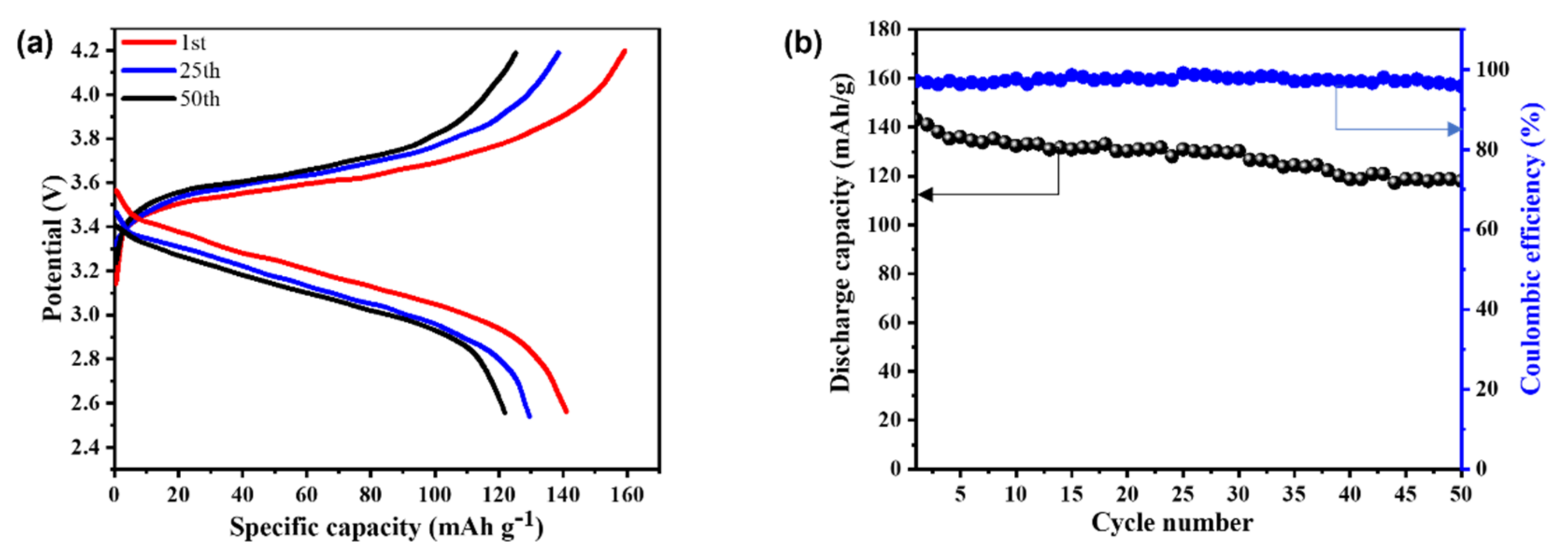
3.3.3. Electrochemical Performances
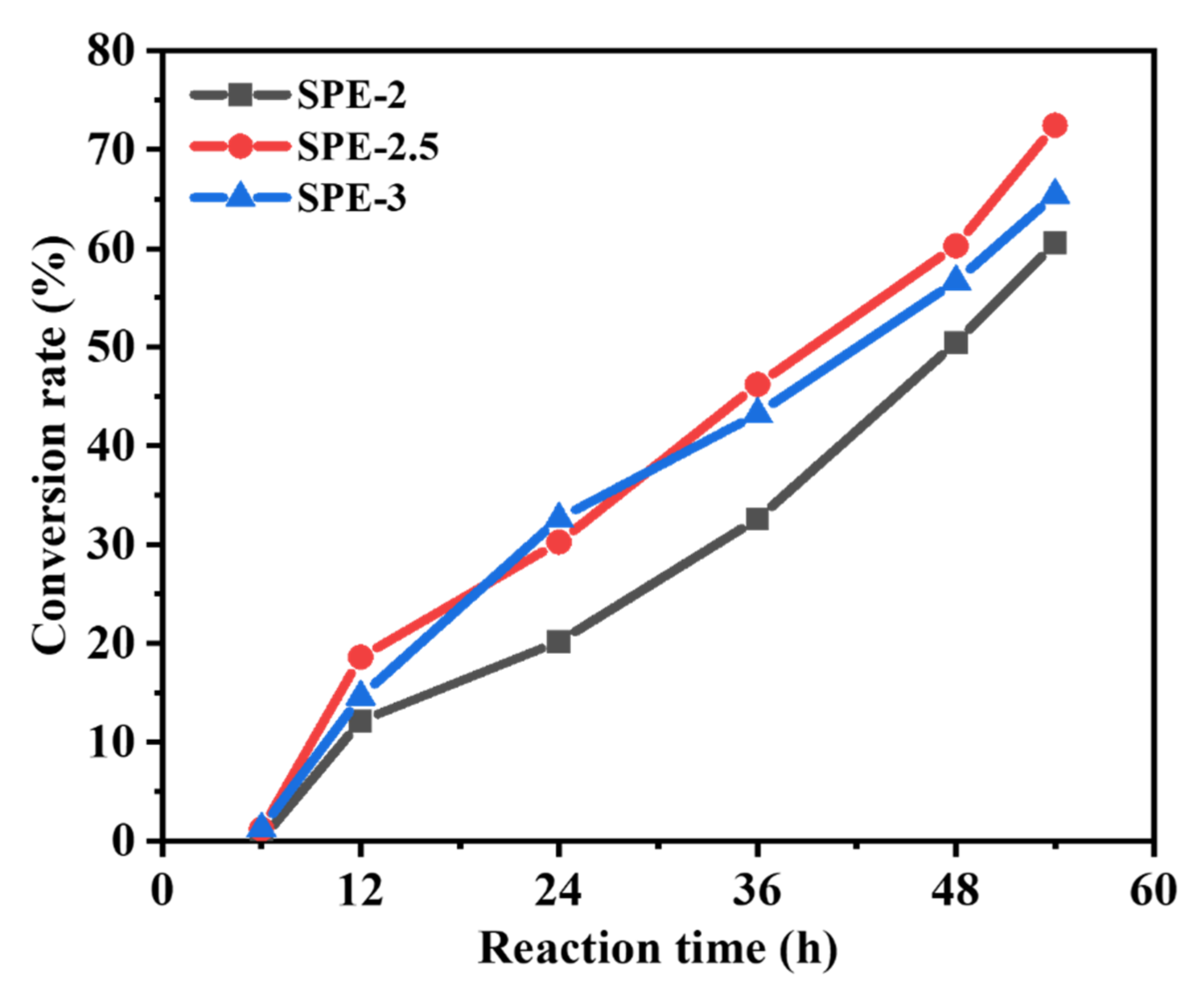
3.3.4. Mechanism of In Situ Cationic Ring Opening of Poly (EOM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Pei, A.; Cui, Y. Materials for lithium-ion battery safety. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, aas9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Cui, Z.; Qiao, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Tang, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. An in-situ polymerized solid polymer electrolyte enables excellent interfacial compatibility in lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, X.; Chai, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Feng, J. High Performance Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Batteries: A Self-Catalyzed Strategy toward Facile Synthesis. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Lin, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Yu, H. Polymer electrolytes and interfaces in solid-state lithium metal batteries. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 449–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, R.; Cao, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, H. In-situ polymerized solid-state electrolytes with stable cycling for Li/LiCoO2 batteries. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Anothumakkool, B.; Kurungot, S.; Winter, M.; Nair, J.R. In situ polymerization process: An essential design tool for lithium polymer batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2708–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyken, O.; Pask, S. Ring-Opening Polymerization—An Introductory Review. Polymers 2013, 5, 361–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crivello, J.V. Investigations of the reactivity of “kick-started” oxetanes in photoinitiated cationic polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2015, 53, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Tsutsumi, H. Ionic conducting behavior of solvent-free polymer electrolytes prepared from oxetane derivative with nitrile group. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, Y.; Tsutsumi, H.; Oishi, T. New Type Polymer Electrolytes Based on Bis-Oxetane Monomer with Oligo(ethylene oxide) Units. Polym. J. 2001, 33, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Song, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, L. Li salt initiated in-situ polymerized solid polymer electrolyte_new insights via in-situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Stephan, A.M.; Chan, C.H.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Electrochemical studies on composite gel polymer electrolytes for lithium sulfur-batteries. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44594–44601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.T.; Liebig, A.; Cook, J.; Marsh, P.; Ciocanel, C.; Lindberg, G.E.; Browder, C.C. Development of a PEO-based lithium ion conductive epoxy resin polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 2018, 326, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.; Stalin, S.; Khan, K.; Archer, L.A. Solid-state polymer electrolytes with in-built fast interfacial transport for secondary lithium batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, R.; Tsutsumi, H. Fire-retardant solid polymer electrolyte films prepared from oxetane derivative with dimethyl phosphate ester group. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.-B.; Zhou, S.-S.; Zhang, D.-J.; Feng, S.-W.; Li, L.-F.; Liu, K.; Feng, W.-F.; Nie, J.; Li, H.; Huang, X.-J. Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) as conducting salt for nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: Physicochemical and electrochemical properties. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Park, K.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, H. Unraveling the role of LiFSI electrolyte in the superior performance of graphite anodes for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkrob, I.A.; Marin, T.W.; Zhu, Y.; Abraham, D.P. Why Bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide Is a “Magic Anion” for Electrochemistry. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19661–19671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jang, G.; Lim, H.; Zhang, W.; Kim, W.; Jang, H. An In Situ Polymeric Electrolyte with Low Interfacial Resistance on Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 9, 2101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, G.; Dong, S.; Cui, G. Review—In Situ Polymerization for Integration and Interfacial Protection Towards Solid State Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Feng, Z.-g.; Su, Y.-f.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, G.-q. Synthesis and characterization of homo- and copolymers of 3-(2-cyano ethoxy)methyl- and 3-[methoxy(triethylenoxy)]methyl-3′-methyl-oxetane. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Choi, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Jang, H.; Ryu, T.; Yoon, S.; Jin, L.; Jin, Y.; Kim, W. Remarkable Conductivity of a Self-Healing Single-Ion Conducting Polymer Electrolyte, Poly(ethylene-co-acrylic lithium (fluoro sulfonyl)imide), for All-Solid-State Li-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34930–34938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Du, Y.; Jin, Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. Epoxy containing solid polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pan, X.; Huang, F.; Li, K. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose fibers grafted with hyperbranched poly(3-methyl-3-oxetanemethanol). Cellulose 2011, 18, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Rahman, M.M.; Sutradhar, S.C.; Lopa, N.S.; Ryu, T.; Yoon, S.; Choi, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of an imidazolium based Li salt as electrolyte with Li fluorinated sulfonylimides as additives for Li-Ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 302, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.R.; Shaji, I.; Ehteshami, N.; Thum, A.; Diddens, D.; Heuer, A.; Winter, M. Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Battery via Thermally Induced Cationic Ring-Opening Polymerization (CROP) with an Insight into the Reaction Mechanism. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3118–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, G.; Stolz, L.; Nair, J.; Laskovic, I.C.; Winter, M.; Kasnatscheew, J. Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-based Electrolyte for Solid-State-Lithium-Batteries with High Voltage Positive Electrodes: Evaluating the Role of Electrolyte Oxidation in Rapid Cell Failure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, M.; Plylahan, N.; Scheers, J.; Johansson, P. Thermal stability and decomposition of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) salts. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23327–23334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Han, H.; Li, H.; Nie, J.; Armand, M.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, X. Transport and Electrochemical Properties and Spectral Features of Non-Aqueous Electrolytes Containing LiFSI in Linear Carbonate Solvents. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A74–A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.B.; Liu, G.; Curtiss, L.A.; Redfern, P.C. Towards room-temperature performance for lithium–polymer batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2305–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croy, J.R.; Abouimrane, A.; Zhang, Z. Next-generation lithium-ion batteries: The promise of near-term advancements. MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.; Ryou, M.-H.; Lee, Y.M. Effect of LiFePO4 cathode density and thickness on electrochemical performance of lithium metal polymer batteries prepared by in situ thermal polymerization. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 154, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huai, L.; Hu, G.; Yang, S.; Ren, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Peng, Z.; Shen, C. Effect of LiFSI Concentrations to Form Thickness- and Modulus-Controlled SEI Layers on Lithium Metal Anodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 9825–9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, C.; Huang, B.; Lu, M.; Yang, Y. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of PEO-based polymer electrolytes with room temperature ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 5789–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yin, Y.X.; Zeng, X.X.; Li, J.Y.; Shi, J.L.; Shi, Y.; Wen, R.; Guo, Y.G.; Wan, L.J. In situ plasticized polymer electrolyte with double-network for flexible solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 10, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.T.; Tran, B.T.; Subramani, R.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Rajamani, A.; Lee, M.Y.; Hou, S.S.; Lee, Y.L.; Teng, H. Free-standing polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium batteries operated at room temperature. J. Power Sources 2020, 449, 227518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.F.; Aparicio, M.; Mosa, J. Covalent silica-PEO-LiTFSI hybrid solid electrolytes via sol-gel for Li-ion battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popall, M.; Andrei, M.; Kappel, J.; Kron, J.; Olma, K.; Olsowski, B. ORMOCERs as inorganic-organic electrolytes for new solid state lithium batteries and supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Yoon, S.; Jin, L.; Lim, H.; Jeon, M.; Jang, H.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, W. Lithium Salt Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerized Solid-State Electrolyte with Comparable Ionic Conductivity and Better Interface Compatibility for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes 2022, 12, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030330
Zhang W, Yoon S, Jin L, Lim H, Jeon M, Jang H, Ahmed F, Kim W. Lithium Salt Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerized Solid-State Electrolyte with Comparable Ionic Conductivity and Better Interface Compatibility for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030330
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Sujin Yoon, Lei Jin, Hyunmin Lim, Minhyuk Jeon, Hohyoun Jang, Faiz Ahmed, and Whangi Kim. 2022. "Lithium Salt Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerized Solid-State Electrolyte with Comparable Ionic Conductivity and Better Interface Compatibility for Li-Ion Batteries" Membranes 12, no. 3: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030330
APA StyleZhang, W., Yoon, S., Jin, L., Lim, H., Jeon, M., Jang, H., Ahmed, F., & Kim, W. (2022). Lithium Salt Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerized Solid-State Electrolyte with Comparable Ionic Conductivity and Better Interface Compatibility for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes, 12(3), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030330








