Effect of Aeration Intensity on Performance of Lab-Scale Quorum-Quenching Membrane Bioreactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CIBs
2.2. Survival Test of Rhodococcus sp. BH4 after Completion of MBR Operation
2.3. MBR Design and Basic Operational Conditions
2.4. Analysis of Water Quality Parameters
2.5. Different Research Conditions of MBR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Successful Immobilization of Rhodococcus sp. BH4 in CIBs
3.2. Survival of Rhodococcus sp. BH4 upon Completion of MBR Operation
3.3. Analysis of Water Quality Parameters
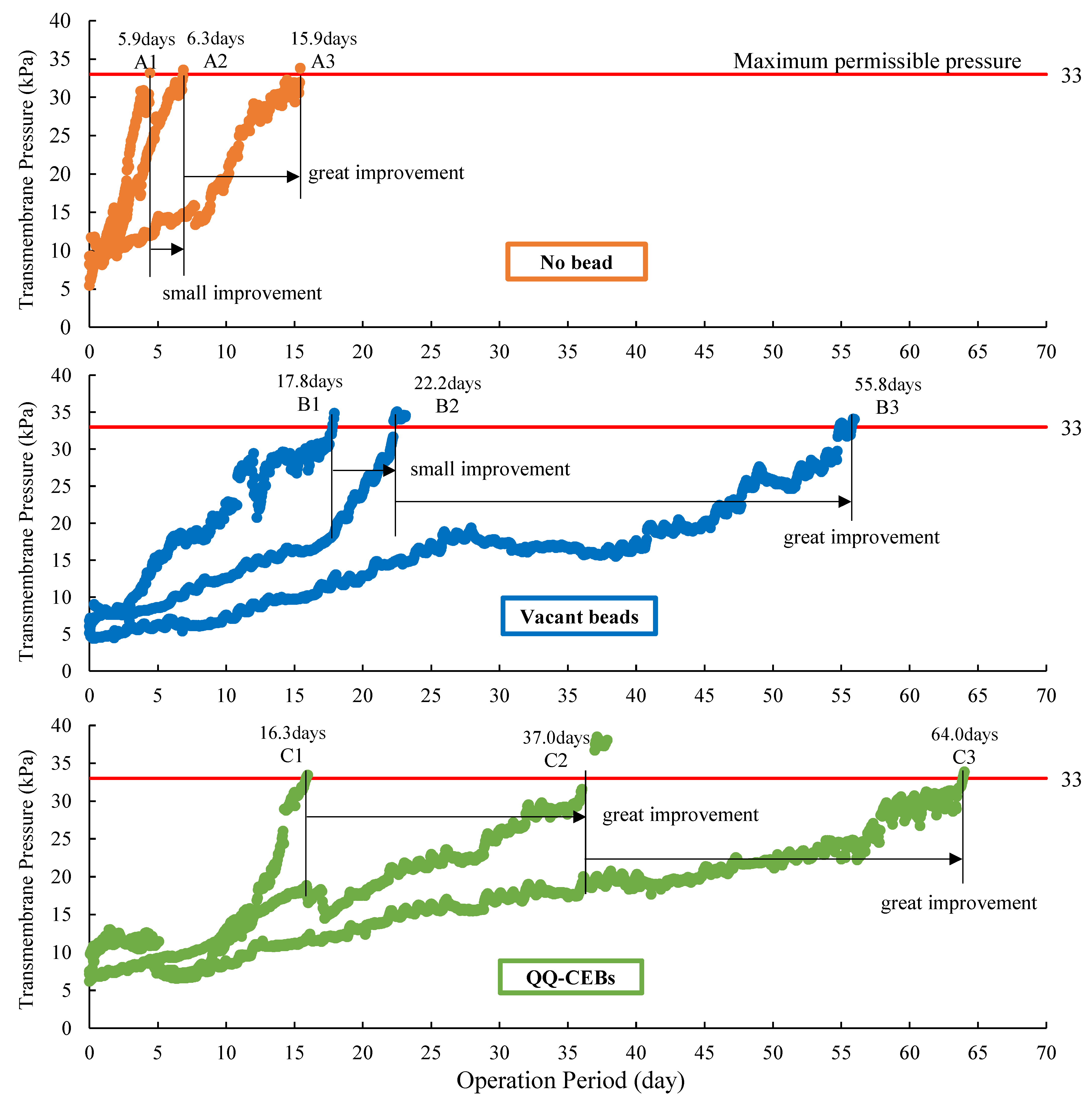
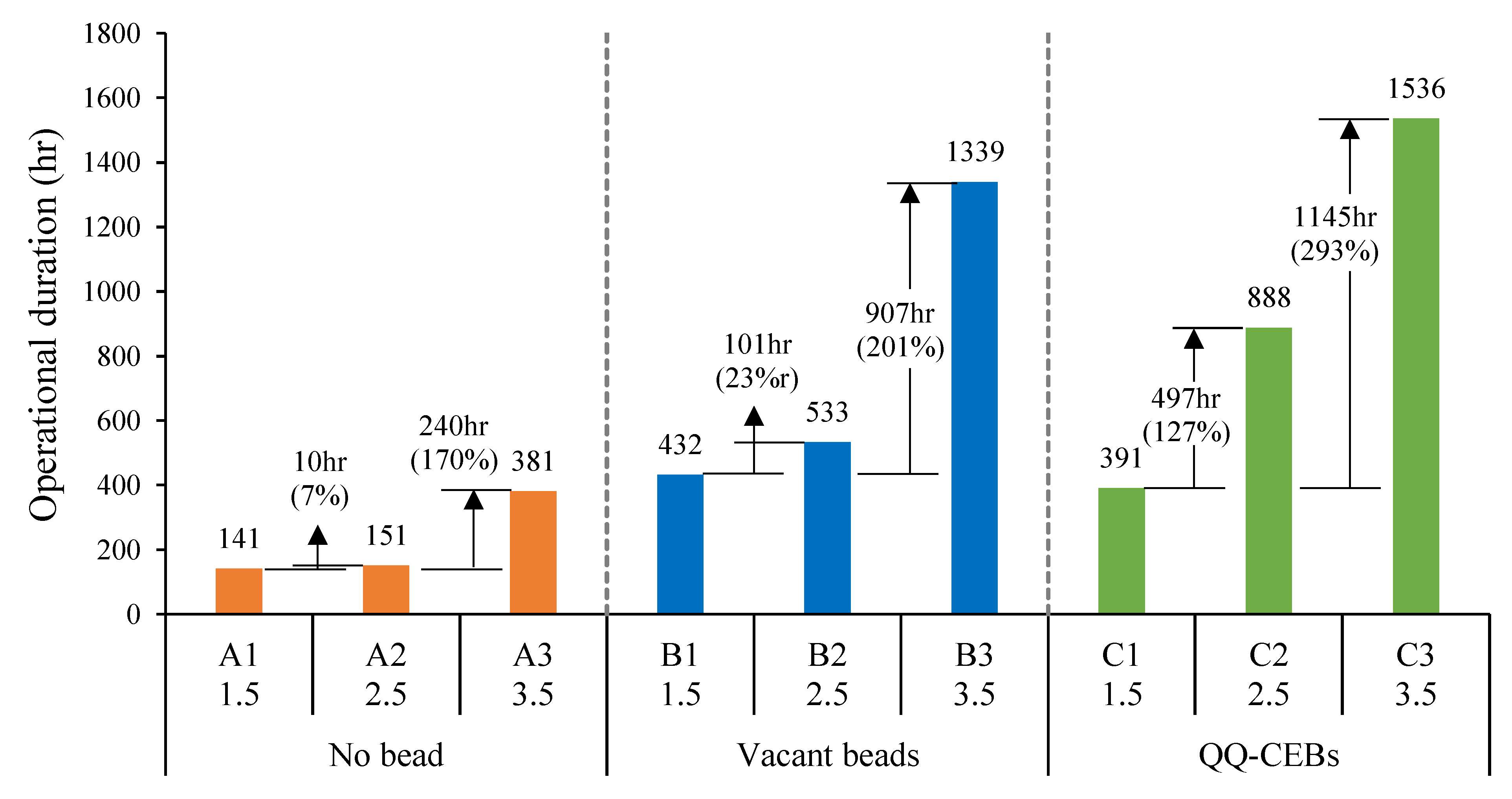
3.4. Comparisons of Different Operations of MBRs
3.5. Effect of Bead Type on MBR Performance
3.6. Effect of Aeration Intensity on MBR Performance
3.7. Separation of QQ Effect from Combined Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimura, K.; Yamato, N.; Yamamura, H.; Watanabe, Y. Membrane fouling in pilot-scale membrane bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6293–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasekara, N.A.; Choo, K.H.; Lee, C.H. Biofouling control: Bacterial quorum quenching versus chlorination in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2016, 103, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaludin, R.; Abdul Majid, L.; Othman MH, D.; Mansur, S.; Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Khongnakorn, W.; Puteh, M.H. Polyvinylidene Difluoride (PVDF) Hollow Fiber Membrane Incorporated with Antibacterial and Anti-Fouling by Zinc Oxide for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, L.; Pulido-Beltran, L.; Kruithof, J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Farhat, N.M. Phosphorus concentration in water affects the biofilm community and the produced amount of extracellular polymeric substances in reverse osmosis membrane systems. Membranes 2021, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, J.J.; Vo TK, Q.; Kim, H.S. Application of physical and chemical enhanced backwashing to reduce membrane fouling in the water treatment process using ceramic membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Leverette, L.; Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. Membrane bioreactors–a review on recent developments in energy reduction, fouling control, novel configurations, LCA and market prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.S.; Yeon, K.M.; Yang, C.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, C.H.; Park, S.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.K. Control of membrane biofouling in MBR for wastewater treatment by quorum quenching bacteria encapsulated in microporous membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4877–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lade, H.; Paul, D.; Kweon, J.H. Quorum quenching mediated approaches for control of membrane biofouling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; He, J.; Xu, G.; Hu, H.; Li, G. Biofouling control by biostimulation of quorum-quenching bacteria in a membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 2624–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Oh, H.S.; Jo, S.J.; Yeon, K.M.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, D.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.K. Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: Physical and biological effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouayed, N.; Dietrich, N.; Lafforgue, C.; Lee, C.H.; Guigui, C. Process-oriented review of bacterial quorum quenching for membrane biofouling mitigation in membrane bioreactors (MBRs). Membranes 2016, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.C.; Yeon, K.M.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, C.H. Enzyme-immobilized nanofiltration membrane to mitigate biofouling based on quorum quenching. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergön-Can, T.; Köse-Mutlu, B.; Koyuncu, I.; Lee, C.-H. Biofouling control based on bacterial quorum quenching with a new application: Rotary microbial carrier frame. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, T.; Ikeda, K.; Ijima, H.; Kawakami, K. Fabrication of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads crosslinked using sodium sulfate for microorganism immobilization. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, J.E.; Won, Y.J.; Yeon, K.M.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, D.J. Macroencapsulation of quorum quenching bacteria by polymeric membrane layer and its application to MBR for biofouling control. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Shi, Y.; Shi, L. Biofouling control and sludge properties promotion through quorum quenching in membrane bioreactors at two aeration intensities. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasnain, G.; Khan, S.J.; Arshad, M.Z.; Abdullah, H.Y. Combined impact of quorum quenching and backwashing on biofouling control in a semi-pilot scale MBR treating real wastewater. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2017, 39, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, Z.; Rose, J.; Ahmed, S.; Chung, S. Quorum Quenching Cell Entrapping Bead by Polyvinyl Alcohol Method for Biofouling Mitigation in Lab-scale MBR, NUST. J. Eng. Sci. 2020, 13, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Chung, S.; Sohail, N.; Qazi, I.A.; Justin, A. Application of cell entrapping beads for Quorum Quenching technique in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Khan, S.J.; Waheed, H.; Lee, C.H.; Hashmi, I.; Iqbal, H. Membrane biofouling retardation and improved sludge characteristics using quorum quenching bacteria in submerged membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 483, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.-K.; Kwon, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.; Nahm, C.H.; Jo, S.J.; Oh, H.-S.; Park, P.-K.; Choo, K.-H.; et al. Crossing the border between laboratory and field: Bacterial quorum quenching for anti-biofouling strategy in an MBR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pham, D.; Bach, L.T. Immobilized bacteria by using PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol) crosslinked with Sodium sulfate. Int. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Nahm, C.H.; Kwon, H.; Oh, H.-S.; Won, Y.-J.; Choo, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K. More efficient media design for enhanced biofouling control in a membrane bioreactor: Quorum quenching bacteria entrapping hollow cylinder. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8596–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, C.H.; Choi, D.-C.; Kwon, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.; Choo, K.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K. Application of quorum quenching bacteria entrapping sheets to enhance biofouling control in a membrane bioreactor with a hollow fiber module. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse-Mutlu, B.; Ergön-Can, T.; Koyuncu, I.; Lee, C.H. Quorum quenching MBR operations for biofouling control under different operation conditions and using different immobilization media. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 17696–17706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujang, Z.; Ng, S.S.; Nagaoka, H. Package plant of extended aeration membrane bioreactors: A study on aeration intensity and biofouling control. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.N.; Kim, S.R.; Jo, S.J.; Yeon, K.M.; Lee, C.H. Evaluation of mechanical membrane cleaning with moving beads in MBR using Box–Behnken response surface methodology. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 56, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasekara, N.A.; Choo, K.H.; Lee, C.H. Hybridization of physical cleaning and quorum quenching to minimize membrane biofouling and energy consumption in a membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2014, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, K.H.; Park, P.K.; Oh, H.S. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in membrane bioreactors. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; van der Graaf, J.H.; van Lier, J.B. Specific energy consumption of membrane bioreactor (MBR) for sewage treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, M.; Saeed, N.; Chung, S.; Nawaz, M.S.; Ghaffour, N. Physical and economical evaluation of laboratory-scale membrane bioreactor by long-term relative cost–benefit analysis. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2020, 10, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Eds.; American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.A.; Boyle, W.C.; Popel, H.J. Aeration: Principles and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Psoch, C.; Schiewer, S. Long-term flux improvement by air sparging and backflushing for a membrane bio-reactor, and modeling permeability decline. Desalination 2008, 230, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Tay, J.H. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Membrane fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


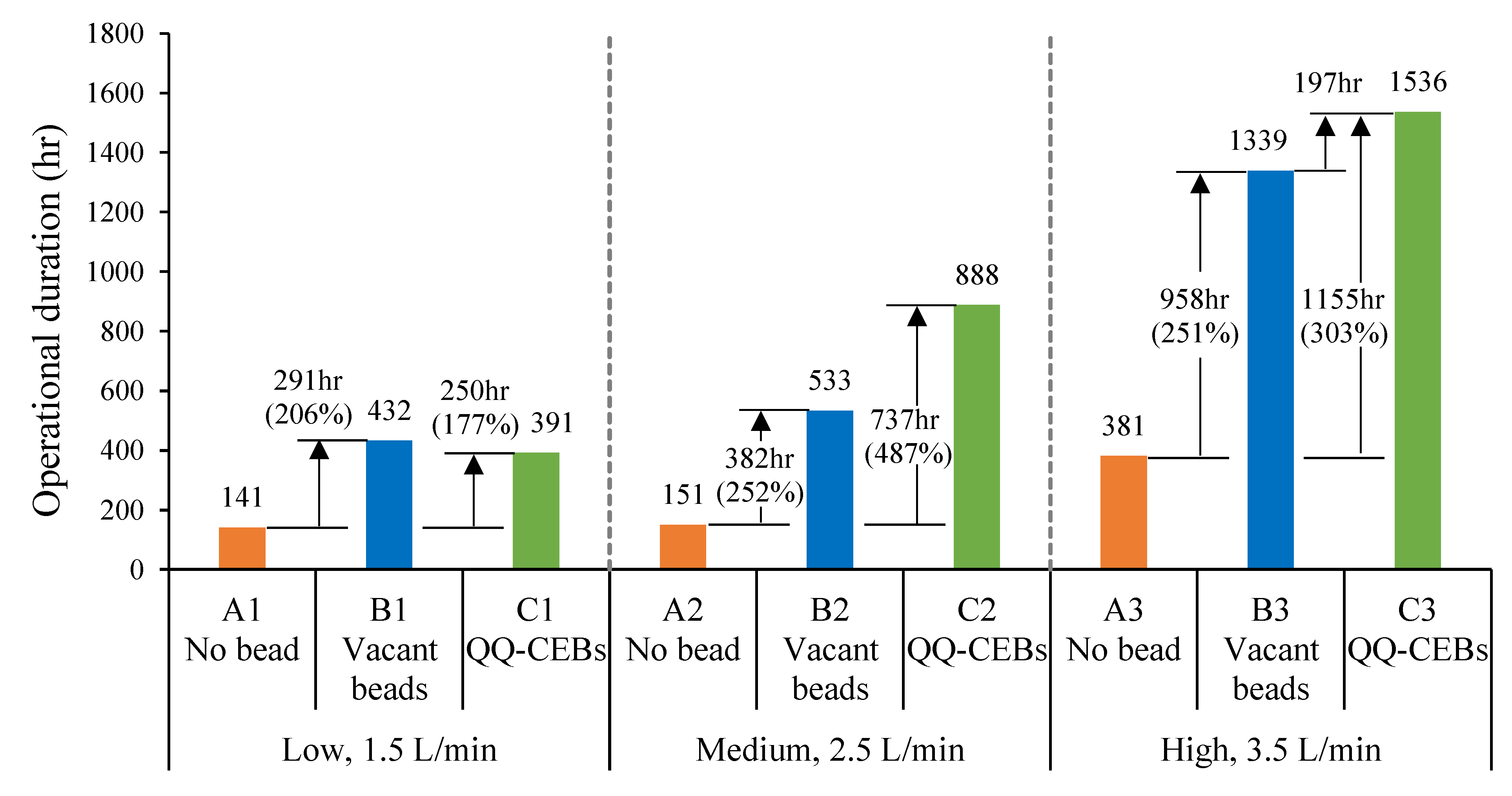

| Parameters | Description or Values | Parameters | Description or Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of MBR | Single stage, submerged | Manufacturer | PHILOS Korea |
| Working volume | 4 L/reactor | Membrane material | Hydrophilic PVDF |
| Permeate flow rate | 13 mL/min | Pore size | 0.1 µm |
| Backwash flow rate | 26 mL/min | Module design | U-shape |
| SBW frequency | 1 min after every 10 min | Membrane dimension | φ 2.3 mm, length 50 cm, 8 fibers |
| HRT | 5.1 h | Effective surface area | 289 cm2/module |
| SRT | 17~20 days | No. of module | 1 module/reactor |
| MLSS | 8000 mg/L | Flux | 27 L/m2/h |
| MLVSS | 7080 mg/L | Influent COD | 205~250 mg/L |
| Food/Microorganism | 0.12~0.15 gCOD/gVSS·day | Influent Ammonia-N | 26~33 mg/L |
| Operation Names | Research Variable1: Bead Type | Research Variable2: Aeration Intensity (L/min) | SADm (m3/m2/h) | Velocity Gradient G (/s) a | Beads Size φ (mm) | Filling Ratio of Beads in Reactor (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | No bead | 1.5 | 3.1 | 92 | - | - |
| A2 | No bead | 2.5 | 5.2 | 119 | - | - |
| A3 | No bead | 3.5 | 7.3 | 140 | - | - |
| B1 | Vacant beads | 1.5 | 3.1 | 92 | 3.4 | 1% |
| B2 | Vacant beads | 2.5 | 5.2 | 119 | 3.4 | 1% |
| B3 | Vacant beads | 3.5 | 7.3 | 140 | 3.4 | 1% |
| C1 | QQ-CIBs | 1.5 | 3.1 | 92 | 3.4 | 1% |
| C2 | QQ-CIBs | 2.5 | 5.2 | 119 | 3.4 | 1% |
| C3 | QQ-CIBs | 3.5 | 7.3 | 140 | 3.4 | 1% |
| Operation Name | COD | Ammonia (Nitrification) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Removal (%) | Standard Deviation (%) | n | Average Removal (%) | Standard Deviation (%) | n | |
| A1 | 92.2 | 7.6 | 5 | 96.5 | 5.6 | 4 |
| A2 | 91.9 | 5.8 | 5 | 99.5 | 0.1 | 4 |
| A3 | 93.9 | 4.2 | 5 | 98.9 | 0.9 | 4 |
| B1 | 92.5 | 7.1 | 9 | 95.5 | 5.0 | 5 |
| B2 | 94.5 | 4.9 | 9 | 96.6 | 5.1 | 5 |
| B3 | 94.6 | 8.5 | 5 | 96.2 | 5.8 | 4 |
| C1 | 90.5 | 1.1 | 4 | 97.1 | 4.0 | 3 |
| C2 | 93.2 | 10.7 | 10 | 99.6 | 0.5 | 8 |
| C3 | 92.9 | 7.7 | 18 | 99.3 | 0.7 | 13 |
| One-way ANOVA | p-value = 0.992 > 0.05 | p-value = 0.237 > 0.05 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, Z.U.; Ayub, M.; Chung, S.; Oh, H. Effect of Aeration Intensity on Performance of Lab-Scale Quorum-Quenching Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes 2022, 12, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030289
Islam ZU, Ayub M, Chung S, Oh H. Effect of Aeration Intensity on Performance of Lab-Scale Quorum-Quenching Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030289
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Zia Ul, Mariam Ayub, Shinho Chung, and Heekyong Oh. 2022. "Effect of Aeration Intensity on Performance of Lab-Scale Quorum-Quenching Membrane Bioreactor" Membranes 12, no. 3: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030289
APA StyleIslam, Z. U., Ayub, M., Chung, S., & Oh, H. (2022). Effect of Aeration Intensity on Performance of Lab-Scale Quorum-Quenching Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes, 12(3), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030289








