Abstract
This work provides a comprehensive review on the incorporation of ionic liquid (ILs) into polymer blends and their utilization as proton exchanges membranes (PEM). Various conventional polymers that incorporate ILs are discussed, such as Nafion, poly (vinylidene fluoride), polybenzimidazole, sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone), and sulfonated polyimide. The methods of synthesis of IL/polymer composite membranes are summarized and the role of ionic liquids as electrolytes and structure directing agents in PEM fuel cells (PEMFCs) is presented. In addition, the obstacles that are reported to impede the development of commercial polymerized IL membranes are highlighted in this work. The paper concludes that the presence of certain ILs can increase the conductivity of the PEM, and consequently, enhance the performance of PEMFCs. Nevertheless, the leakage of ILs from composite membranes as well as the limited long-term thermal and mechanical stability are considered as the main challenges that limit the employment of IL/polymer composite membranes in PEMFCs, especially for high-temperature applications.
1. Introduction
Over recent decades, renewable energy systems have been utilized to meet the increasing demand for power and energy. Among these renewable energy systems, fuel cells seem to be receiving extra attention. A fuel cell produces electricity by utilizing hydrogen or other fuels via an electrochemical reaction. Fuel cells are suitable for stationary and portable applications. In addition, they serve as a potential candidate for transportation due to their high power density, low operating temperature, and dynamic characteristics [1]. Fuel cells operate at a higher efficiency compared to combustion engines [2]. Fuel cells have been reported to convert chemical energy to electricity with a theoretical efficiency of about 83% for hydrogen fuel cells specifically [3]. This efficiency is defined based on the ratio of the amount of Gibbs free energy divided by the enthalpy or the heat of combustion for the overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell. As a result, fuel cells offer several advantages when compared to conventional combustion engines. In addition to superior efficiency, fuel cells have less carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions compared to combustion engines [4]. In fact, during the operation of hydrogen fuel cells, there are no carbon dioxide or air pollutants emissions. Another advantage of fuel cells is their silent operation, as they possess fewer dynamic parts when compared to combustion engines.
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have received considerable research interest recently. PEMFCs have an all-solid structure that makes them ideal for transport applications, stationary, and portable applications. These fuel cells utilize a special polymer electrolyte membrane for conducting protons. PEMFCs can produce clean energy while operating at temperatures lower than other types of fuel cells. PEMFCs are also distinguished by their silent operation and all-solid membrane structure due to the polymer electrolyte. Lately, research has been conducted to enhance their durability, cost, and overall performance. However, improvements in the technical and economical aspects of the fuel cell are still required for commercialization. Research has been focusing on the optimization of the fuel cell by optimizing the configuration, materials, conformation, and structure of the catalyst layer [5,6,7,8,9]. For instance, several research studies have focused on decreasing the cost of PEMFCs by enhancing the electrolyte conductivity [10,11,12,13]. Simultaneously, in order to enhance the safety of the fuel cells, nonflammable and nonvolatile electrolytes have been investigated.
PEMFCs have been investigated for their application in electric vehicles. Although the industry is predominantly reliant on lithium-ion batteries, PEMFCs have great potential in powering and improving the performance of electric vehicles [14]. Moreover, PEMFCs are able to tap into the market and compete with lithium-ion batteries to offer electric vehicles that have a long driving range, high utilization, and low cost [14,15]. The main advantage of PEMFCs over batteries, especially in the long-range market, is the high specific energy and energy density of hydrogen [16]. In addition, for future high-utilization transportation, hydrogen is a natural fit when looking at grid compatibility and fast refueling.
Ionic liquids (ILs) possess desired characteristics such as excellent ionic conductivity even at anhydrous conditions [17]. Many research efforts have been conducted on the incorporation of ILs into PEMFCs, yet, review articles pertaining to the subject are either outdated or focused only on certain types of polymers or ILs [18,19]. This work provides a comprehensive review on the recent use of ILs in PEMFCs, focusing mainly on systems employing IL/polymer composite membranes while outlining the future research needs and challenges. This review has also presented the opportunities for the use of ILs in high-temperature operations and focused on presenting all types of polymers evaluated in the literature for this purpose.
2. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
A PEMFC consists of electrodes, an electrolyte, a catalyst, and diffusion layers. Figure 1 depicts a diagram of a PEMFC [18]. The membrane and the catalyst layers create the membrane electrode assembly. The PEM serves a vital role, as it is responsible for separating the gaseous reactants, conducting protons, and electrically insulating the electrons. Membranes ideal for PEMFCs should be of low cost and possess desirable properties such as high proton conductivity, high mechanical strength, high thermal, chemical, and electrochemical stability, and low oxygen and fuel crossover. In that regard, perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membrane, i.e., Nafion of Dupont, is most commonly in PEMFCs, due to its superb chemical stability, outstanding strength, and high ionic conductivity [20,21]. Nevertheless, the conductivity of the membrane decreases significantly when the temperature exceeds 100 °C, rendering it undesirable for high-temperature processes.
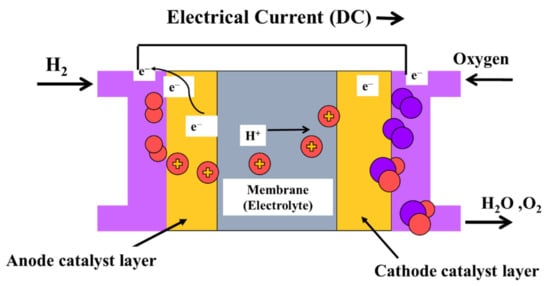
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a PEMFC.
Proton exchange membranes could be classified based on their properties and functions. The structure of the PFSA membranes consists of a fluorinated backbone with a fluorocarbon side chain, in addition to sulphonic acid ion clusters attached to the side chains of the backbone. These membranes are prone to dehydration at temperatures above 80 °C, which, consequently, reduces their proton conductivity. In order to overcome the challenges faced by PFSA membranes, researchers have adopted partially fluorinated membranes [22]. The structure of the partially fluorinated membranes consists of a fluorocarbon base with a hydrocarbon side chain grafted on the backbone. Hence, the structure allows for the use of inexpensive base films with a low crossover, in addition to forming a relatively stronger compound compared to PFSA membranes. Moreover, the cost of the membrane is reduced since a less fluorinated polymer is needed; nevertheless, the reduction in the cost comprises the proton conductivity resulting in low performance and less durable membrane compared to a perfluorinated polymer.
Researchers have studied the use of nonfluorinated membranes as alternatives to conventional PFSA membranes in PEMFCs. The nonfluorinated membranes consist of a hydrocarbon base, normally altered by the addition of polar or sulphonic groups. The polymer membranes should have a proton conductor component. Research in this context focused first on poly (arylene ether) materials, due to their high stability, availability, and processibility [23]. Nevertheless, due to the short lifetime and excessive swelling of poly (arylene ether) membranes, efforts were directed towards optimizing other nonfluorinated materials and acid–base membranes. The latter involves the incorporation of acid components (such as sulfonated compounds) into an alkaline polymer base such as polybenzimidazole (PBI). The mixture of the acid–base membrane allows for high thermal and chemical stabilities, in addition to a proton conductivity in the same range as, or even higher than, that of Nafion. Among the strong acids, phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and sulphuric acid (H2SO4) show valuable proton conductivities in both wet and anhydrous forms [24,25]. PBI is known for its high chemical and thermal stability. However, the main disadvantage of the acid–base membrane is the leaching of acid during operation, which limits the durability of the membrane [18]. Table 1 provides a summary of the classification of membranes in terms of their category and structure. A detailed summary of the structure, physical properties, and performance of membranes can be found in [26].

Table 1.
Summary of membranes classification.
Significant research has been performed on developing novel proton exchange membranes for use in fuel cells [12,13,27]. These efforts have achieved moderate success. However, it is clear that these membranes still need improvement to become commercially viable. Researchers have investigated the modification of Nafion membranes by incorporating bifunctional compounds, such as silica, zeolites, and carbon nanotubes, to enhance water retention and increase proton conductivity at higher temperatures [28].
The electrodes of the proton exchange membrane represent another vital component in PEMFCs arrangement. In order to overcome the challenges halting the utilization of PEMFCs as an efficient and competitive energy source, the performance and durability of the electrolyte and electrodes need to be improved. Typically, the electrodes consist of three layers: backing, gas diffusion, and catalyst layers [29]. The catalyst layer usually consists of noble metals, such as platinum, as a catalyst; however, platinum is quite expensive and accounts for 55% of the PEMFC cost. In order to lower the cost without significantly compromising the performance of PEMFCs, platinum alloys (such as Pt–Ru, Pt–Co, Pt–Pd, etc.) are employed as catalysts [29]. Another method is the use of platinum bimetal, which involves adding metals such as Fe, Cu, Co, and Ni to the platinum catalyst. Moreover, the catalyst ink distribution and the agglomeration of catalyst particles are crucial to the performance of the catalyst layer.
In the subsequent sections, the focus will be on discussing the recent developments in the incorporation of ILs in PEMFCs polymer membranes.
3. Ionic Liquids Applications in PEM
ILs are salts in the liquid state, typically defined as liquid electrolytes composed entirely of ions without the use of solvents. Some ILs flow freely as liquids at room temperature. These ILs are referred to as room-temperature ILs (RTILs). Furthermore, ILs possess a number of desirable properties for electrochemical applications, such as: very low volatility, nonflammable characteristics, high thermal and electrochemical stability, and high ionic conductivity under anhydrous conditions [19]. Given the excellent properties of ILs, and the fact that they are made up entirely from ions and do not contain solvents, ILs can be combined and/or modified to tailor their properties that are desirable for specific applications. For instance, extensive research has been carried for the employment of IL as electrolytes in solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells [30,31,32].
The critical aspect of the fuel-cell performance is stability, which is heavily impacted by the conductivity of the IL. Typically, ILs possess conductivities that are in the range 1.0 × 10−4–1.8 × 10−4 S/cm [19]. For instance, ILs based on imidazolium cations exhibit conductivity of approximately 1 mS/cm [19]. Other ILs, such as those based on pyrrolidinium, piperidinium, pyridinium, and tetraalkylammonium cations, show lower conductivities (in the range 1.0 × 10−4–5 × 10−3 S/cm). The counter ion influences the reduction potential of the cation or the anion. It has been reported that the presence of halide anions, such as F− and Br−, limits the stability to 2–3 V. However, in the case of the bis(trifluoromethylsulphonyl)imide (TFSI−) anion, higher stability in the region of 4.5 V could be obtained due to the oxidization of the anion at a high anodic potential [33]. ILs with tetraalkylammonium cations display improved stability in the range of 4.0–5.7 V due to the cathodic reduction occurring at temperately negative potentials [34].
ILs can be either protic or aprotic. Protic ILs are suitable for application in fuel cells due to the reactivity of the active proton available at the cation. On the other hand, aprotic ILs, i.e., not protic, possess low melting points owing to the padding of large irregular cations with small anions. Hence, aprotic ILs are good candidates for lithium batteries applications due to their high mobility and ion concentration.
Protic ILs result from combining a Brønsted acid and a base. The hydrogen-bonded network is formed by the availability of proton acceptor and donor sites caused by the migration of the protons from the acid to the base. Protic ILs could be formed with protons existing on the cation, such as triethylammonium bromide, 1-methylimidazolium chloride, and pyridinium bromide [19]. Another method for forming protic ILs is by attaching acidic functional groups such as sulfonate or sulfone-amide to the cation as the basis of protons in the architecture. Another type of protic ILs called multiprotic ILs are characterized by the presence of a functional group and a proton on the anion or the cation. These ILs are referred to as multiprotic since multiple protons exist in their structure.
3.1. Preparation of Polymerized Ionic Liquid Membranes
Polymerization of ILs containing a polymeric group appears to be the most commonly used technique for creating polymeric electrolytes. Polymerised ILs (PILs) comprise a wide variety of structures depending on the nature of the final application. Figure 2 shows a summary of poly(ILs).
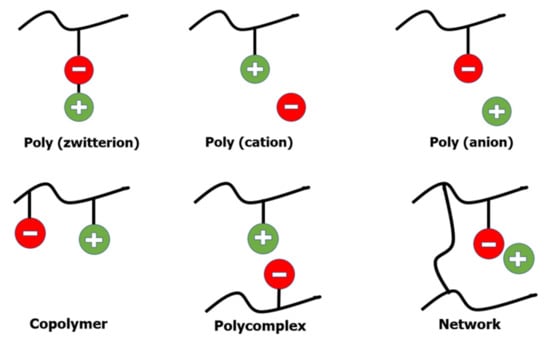
Figure 2.
Depiction of poly (ILs).
Mainly, PILs can be synthesized by direct polymerization of IL monomers or by chemical modification of existing polymers. Direct polymerization can be achieved by techniques such as free or controlled radical polymerization, reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT), and atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). The IL monomers that are usually employed in this method include methacryloyl, styrenic, and 1-vinylimidazolium groups. Controlled radical polymerization offers the advantage of designing and controlling the macromolecular construction of the IL species [18]. The ATRP and RAFT, on the other hand, are mainly utilized for the preparation of homopolymers and block copolymers of IL. Besides these, photopolymerization can be used, which is an intuitive method for the formation of PILs composites based on imidazolium-based monomer for application of gas separation membranes [35]. The PILs synthesized using the chemical alteration of existing polymers will adopt the structure of the original polymer in addition to a certain degree of polymerization.
The ionic conductivity of the IL monomer decreases as the glass temperature increases and the mobility and number of mobile ions decreases. The decrease in ionic conductivity is the most common disadvantage of PILs. This limitation can be addressed by increasing the concentration of carrier ions or modifying the polymer structure to increase the mobility of ions. For example, Põhako-Esko et al. [36] investigated the addition of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [EMIM][BF4] to methacrylate-type PILs. It was reported that an increase in the amount of [EMIM][BF4] resulted in an increased ionic conductivity (0.1 mS/cm compared to only 0.01 mS/cm for the unmodified PIL).
The addition of the ILs manipulates the morphology of the membranes, where ILs are known to be structure-directing agents. For instance, GSaiz et al. [37] studied the effect of ILs on the morphology of a PVDF-HFP membrane. The Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) results showed the presence of several morphologies and different hydrophobic properties depending on the selected IL. Figure 3 shows the cross-sectional SEM view of PVDF-HFP-based membranes with the presence of ILs. It can be seen that the pristine PVDF-HFP membranes show a high degree of porosity; however, membranes with ILs possess a different structure. For instance, PVDF-HFP/[dema][TfO] composites show no pores when prepared at room temperature, or heated at 100 °C. Nevertheless, a spherulites structure is observed when the solvent evaporates at 80 °C. Meanwhile, PVDF-HFP/[MIm][NTf2] composites showed no porosity. This indicates that hydrophilic ILs induce porosity when compared to hydrophobic ones. In general, the addition of ILs improves the morphology of the membranes as they reduce the occurrence and extent of variations on the membrane that causes local heat spots and leads to holes in membranes [38,39].
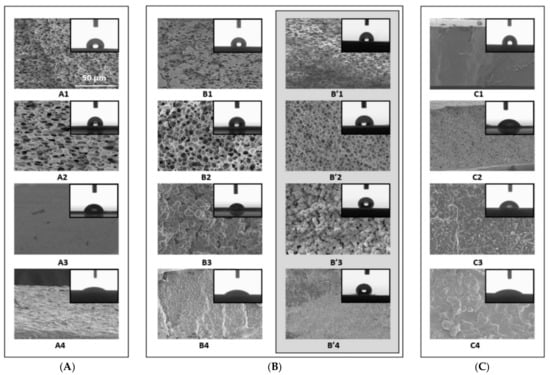
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional SEM images for of PVDF-HFP membranes (1), PVDF-HFP/[MIm][Cl] (2), PVDF-HFP/[dema][TfO] (3) and PVDF-HFP/[MIm][NTf2] (4), prepared at room temperature (A), 80 °C (B) and 100 °C (C). B′ represents the membranes prepared at 80 °C after immersion in water for 48 h [37], Reproduced with permission from Paula GSaiz, et al., Materials & Design; published by Elsevier, 2018.
3.2. Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes in PEMFCs
Protic ILs represent promising candidates in PEM membranes due to several advantages including thermal stability, low volatility, and high conductivity above 100 °C. As established, Protic ILs are in base–acid equilibrium since they are created by the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base. Hence, the protic IL’s structure consists of a neutral species, a cation, and an anion. The neutral species are formed by the transport process of the back proton, where in case of incomplete proton transport, the ILs’ boiling could occur prior to the decomposition resulting in a decrease in the thermal stability, especially at high temperatures.
The proton transfer occurs via Grotthuss and vehicle mechanisms [19]. In the former mechanism, the proton moves from one water molecule to another utilizing the availability of hydrogen bonds. In the vehicle mechanism, the protons move by migration. In some cases, both mechanisms can coincide in one system. For protic ILs, the proton transport is generally conducted by the vehicle mechanism, as there are no sites in the structure to receive the protons, therefore the cations carrying active protons travel to transport those protons. In protic ILs containing hydrogen phosphite and hydrogen sulphate anion, the anions can serve as a proton donor or acceptor, hence allowing the coexistence of the Grotthuss and vehicle mechanisms. Nonetheless, the viscosity affects the ionic conductivity of the protic ILs [40].
The employed IL greatly affects the performance of PEMFC. The effect of the IL on the PEM can be easily studied by observing the values of the open circuit potential (OCP). The OCP mainly depends on the solubility and mass transfer coefficient of the reactants oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2), where a higher OCP means better performance. Miran et al. [41] were among the researchers who studied hydrogen fuel cells and acid dissociation constant (pKa) and its influence on proton transfer from acids to bases in protic ILs. They concluded that the OCP increased with increasing equilibrium constant up to 17, after which it decreased. This led to the conclusion that the proton migration is hindered by the value of pKa and the strong N-H bond.
Numerous research has been conducted to study the feasibility of employing protic ILs as proton conductors for PEMFC. Table 2 shows the conductivity values of common protic ILs used in fuel-cell applications. Nakamoto et al. [42] prepared protic ILs and melts by combining Benzimidazolium (bzlm) and bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide (TFSI) at different molar ratios. The resulting protic IL showed thermal stability at 350 °C and remained stable under oxygen reduction and hydrogen oxidation reactions. The measured conductivity at 140 °C was 8.3 mS/cm. Moreover, it was shown that [Bzlm][TFSI] melts can be utilized as an electrolyte at 150 °C for dry conditions. Nevertheless, at identical operating parameters, H3PO4 electrolyte exhibited larger open-circuit potentials than [Bzlm][TFSI]. Noda et al. [43] prepared protic IL using imidazole (Im) and TFSI at various molar ratios. The resulting protic IL showed thermal stability at 300 °C and above while increasing the oxygen reduction and hydrogen oxidization reactions. Nonetheless, the adsorption of imidazolium on the electrode caused the electric current to decline. Wippermann et al. [44] produced an IL of (2-sulfoethylammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate) [2-sea][TfO] (95 wt%) dissolved in water that displayed a conductivity 20 times less than H3PO4 at a temperature of 130 °C. However, at a lower temperature of 90 °C, the solution showed a higher activity for oxygen reduction reaction when compared to H3PO4. Moreover, protic IL [2-FPy]TF improved the fuel performance by displaying an increase of 15% in the polarization curve represented for a 0.1 V cell potential increase at 80 °C [45].

Table 2.
Conductivity of common protic IL in fuel cells.
Some attempts have been made to improve the physical and chemical properties of protic ILs. This includes the incorporation of organic and inorganic compounds. For instance, [EMIM]HSO4 was tested as an electrolyte in a PEMFC [59]. The results showed that [EMIM]HSO4 is a promising electrolyte especially at elevated temperatures above 145 °C. [EMIM][TFSI] has also been tested as an electrolyte for PEMFC, and it showed good thermal stability for temperatures of 350 °C and above with a conductivity of 5.4 mS/cm [63]. 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [BMIM][BF4] has been tested as an electrolyte for fuel-cell applications and displayed a conductivity of 1.2 mS/cm [64]. Li et al. [65] established hybrid PEMs based on [dema][TfO] and SiO2 monoliths. The membranes showed extremely high conductivity of 10 mS/cm; however, the membrane brittleness required improvement. Moreover, clay multistructures were studied due to their low cost, ease of availability, and high sorption capacity. Takashi et al. [66] intercalated three different ILs into montmorillonite clay, namely 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium octylsulfate [EMIM][OCSO4], N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide [TMPA][TFSI], and N,N-diethyl-N-methyl-N-(2-methoxyethyl) ammonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide [DEMET][TFSI]. The ionic conductivities achieved for [DEMET][TFSI] and [TMPA][TFSI] were 1.88 and 1.99 mS/cm, respectively. Protic ILs based on morpholinium (N-ethylmorpholinium, N-methylmorpholinium, and morpholinium cations) were synthesized by Yoshizawa-Fujita et al. [49]. In their work, the protic ILs showed proton conductivities around 10–16.8, 21–29, and 1 mS/cm at 25, 100, and 150 °C, respectively.
The previous literature shows that ILs are promising alternatives to conventional electrolytes as proton conductors for PEMs. The main attractive feature of utilizing ILs as electrolytes is the high conductivities they possess at high temperatures, even in anhydrous conditions. The ILs are synthesized as film-like membranes by supporting them on polymers for PEMFC applications. In the following sections, the various polymers used in PEMFCs are discussed.
3.3. Polymer-Ionic Liquids Membranes
Solid-state electrolytes are the desirable method for preparing ILs electrolytes since the film structure is required by electronic devices. In order to achieve the film-like membrane, IL can be mixed with ordinary polymers. This results in a change in the glass transition temperature and enhances the properties of hydrogen transport. Nevertheless, this technique comprises the properties of the IL and the strength of the membrane [67]. An example of the technique is the polymerization of methylmethacrylatein1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C2mim][TFSI]) in the presence of a cross-linking agent to synthesize a self-standing polymer gel with a proton conductivity of 10 mS/cm at room temperature [68]. In the following sections, we provide a review of all types of membranes that have been investigated with ILs. It should be noted here that these membranes can be classified into sulfonated fluorine-based (e.g., Nafion) and hydrocarbon-based membranes. Hydrocarbon-based membranes are generally categorized into aliphatic-based (such as polyimide) or aromatic-based, such as PBI. They are generally characterized by low proton conduction properties as opposed to the PFSA membranes. In addition, there is a difficulty encountered in forming a distinct phase between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, which is another drawback that has limited their application in PEM fuel-cell membranes. Therefore, the most widely used hydrocarbon-based polymer materials that also involve ionic liquids include Nafion, PBI, PI, PVDF, PMMA, and PSS.
3.3.1. Nafion-Based PEM
The conductivity of Nafion membranes mainly depends on their water content. A dramatic decrease in Nafion’s conductivity is observed for temperatures higher than the boiling point of water. Since high temperature is preferred in PEMFCs due to several advantages, including enhanced kinetics and better water management, Nafion membranes have been modified with a variety of materials including ILs. Diaz et al. [69] studied the behaviour of Nafion 112 membranes modified with 1-butyl-3-(4-sulphobutyl)-imidazoliumtri-fluoromethanesulphonate ([HSO3-BBIm][TfO]) and 1-methyl-3-(4-sulphobutyl)-imidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulphonyl)imide([HSO3-BMIm][TFSI]) ILs. The presence of the electrochemically stable imidazolium cation and the highly conductive anions allowed for the enhanced performance of these membranes. The existence of ([HSO3–BBIm][TfO]) improved the current density of the fuel-cell membrane to 217 mA/cm with the humidification of the inlet gasses. Yuso et al. [70] explored the properties of Nafion 112 membranes combined with n-dodecyltrimethylammonium (DTA+). The optimum volume fraction occurred at 68% DTA+ after 22 h of contact and resulted in higher thermal stability when the membranes are compared at 120 °C. Noto et al. [71] studied Nafion 117 membranes modified with triethylammonium methanesulphonate (TMS) and triethylammonium perfluorobutanesulphonate (TPFBu). The addition of the IL increased the uptake of the membranes (20 and 39 wt.% for TMS and TPFBu, respectively). The synthesized membrane showed thermal stability up to 140 °C. Sun et al. [72] evaluated the conductivity of anhydrous Nafion membranes impregnated with imidazole-based molten salts in addition to three ILs, namely: 1,2-dimethyl imidazolium trifluoroacetate, imidazolium tri-fluoroacetate, and 1, 2-di-methyl imidazolium trifluoromethane sulfonate. The conductivity was high, at around 3–4 mS/cm. Sood et al. [73] modified Nafion membranes with triethylammmonium trifluorosulfonate. It was found that an increase in the triethylammmonium trifluorosulfonate (TEA-TF) content led to enhanced membrane conductivity and water uptake properties.
The most important factor to consider while manufacturing polymerized IL electrolytes is the compatibly between the IL and the polymer, as it greatly affects the uptake degree of the IL by the polymer. For instance, Schauer et al. [74] examined the compatibility of protic IL, 1-ethylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate [EIM][TfO] and aprotic IL, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate [BMIM][TfO] with Nafion, and other polymers including Udel-type polysulfone, polybenzimidazole derivative containing benzofuranone moieties (PBI-O-Ph), and poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropene) (fluoroelastomer). The results showed that owing to the low solubility of the two IL, they were completely incompatible with the polysulfone polymer. Thus, the conductivity was negligible, as the ionic conductivity structure did not form due to the low solubility. However, in the case of PBI-O-Ph, the IL was partially compatible. Hence, low conductivities were recorded for temperatures above 90 °C. In the case of charged polymers such as Nafion, a marginally higher conductivity was recorded. Lojoiu et al. [75] evaluated the effect of different ILs on Nafion conductivity and found a direct proportional relationship between conductivity and IL uptake. Hence, to maximize the conductivity of the membrane, optimization of the uptake of the IL by the polymer is an important consideration. For instance, [HSO3-BBIM][TfO] showed an uptake degree of 9.4% by Nafion, which is higher when compared to 1.6% for [HSO3-BBIM][TFSI]. Consequently, the performance of the resulting membranes was enhanced and a current density of 0.217 A/cm was observed [69]. Zanchet et al. [76] fabricated Nafion composite membranes and varied the ILs content, namely 3-triethylammonium propane sulfonic acid tetrafluoroborate (TEA-PSBF4), 3-triethylammonium propane sulfonic acid hydrogen sulphate (TEA-PSHSO4), and 3-triethylammonium propane sulfonic acid trifluoromethanesulfonate (TEA-PSCF3SO3). The ILs were reported to improve the proton conductivity and stability of the resulting membrane. The results showed that the conductivity increased from 0.093 S/cm (for unmodified Nafion) to 0.159 S/cm for 5 wt.% (TEA-PSHSO4)/Nafion at 80 °C.
The proton transfer mechanism between the anion and the cation in polymerized IL membranes was also investigated in the literature. Kumar and Venkatnathan [77] investigated the proton transfer in polymerized IL membranes in an attempt to aid the selection process of a suitable IL that will boost the conductivity of the polymer. It was reported that the modification enhanced the proton conduction paths. The conductivity of the Nafion/IL membranes was also affected by the dispersion of the IL within the membrane matrix. Under anhydrous conditions and at a temperature of 130 °C, the conductivity was 6 mS/cm [78].
The addition of silica (SiO2) showed an improvement in membranes along with ILs. For example, for Nafion/(SiO2)3.67(TEA)/(TEA-TF)1.2, a conductivity of 4.7 mS/cm was reported at 105 °C [79]. Another example is the Nafion/1-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborid [C3OHMIM]BF4/SiO2 (50/10 wt%) membrane, which was found to be stable up to a temperature of 405 °C due to the formation of hydrogen bonds. Moreover, the membrane achieved a conductivity of 55 mS/cm above 160 °C and a 100% increase in the tensile strength compared to pristine Nafion [80]. In another study, the protic IL1-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [TMSPMIM]BF4 was employed to functionalize mesoporous SiO2 in order to prevent IL retention. The resulting Nafion membrane showed a 7-fold increase in conductivity when 3 wt% functionalized SiO2 were utilized, where a conductivity of 375 mS/cm was obtained [81]. The use of graphene oxide (GO) to enhance the conductivity of Nafion-based membranes, especially at higher temperatures, has been investigated. Maiti et al. [82] synthesized a membrane using GO, [DMBIM]H2PO4, and Nafion 117. At 110 °C, the conductivity was 6.1 mS/cm. Figure 4 shows the influence of temperature on the proton conductivity of the membranes, as well as the effect of the current density on the voltage and power density of the PEMFC operating with hydrogen at 110 °C. The figure shows an enhancement in conductivity and fuel-cell performance (as seen by the polarization curve) upon the modification of Nafion using ILs or additives (e.g., GO).
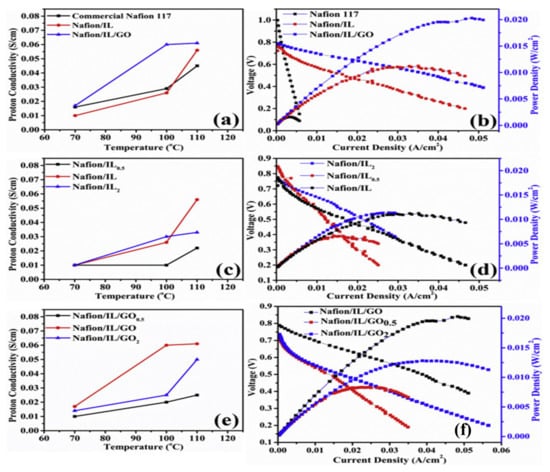
Figure 4.
(a) Proton conductivities at different temperatures under anhydrous conditions. (b) I–V and power density, fuel: H2, operating conditions: 110 °C, 1 atm. (c) Proton conductivities of Nafion/IL membranes at different temperatures under anhydrous conditions, (d) I–V and power density curves of Nafion/IL membranes, fuel: H2, operating conditions: 110 °C, 1 atm. (e) Proton conductivity of Nafion/IL/GO membranes at different temperatures under anhydrous conditions and (f) I–V and power density curves of Nafion/IL/GO membranes, fuel: H2, operating conditions: 110 °C, 1 atm [82], Reproduced with permission from Elsevier, 2017.
The structure and length of the side chain of fluorine-based membranes significantly affect the conductivity of the polymer membrane. Fluorine-based polymer electrolyte membranes can also include other types such as Aciplex and Flermon membranes, but to the best of our knowledge, they have not yet been used in PEM fuel-cell membranes with ILs in particular. When it comes to the side chain, and upon the examination of fluorine-based membranes, it can be clearly seen that Nafion is characterized by a long side chain. Aquivion (Solvay) and PFSA (3M) ionomers, on the other hand, have short side chains. The short side chains appear to exhibit more durability, however, they can also affect the crystallinity and eventually the glass transition temperature. PFSA (3M) ionomers were found to be investigated in only one study that involved the modification with imidazole ionic liquid [83]. The limited number of studies is probably due to their poor mechanical properties and decreased conductivities as opposed to Nafion.
In general, the strategy to improve the conductivity while maintaining the mechanical properties of the semicrystalline backbone is usually by the utilization of a multi-acid side chain. For instance, some side chains contain two sulfonyl fluoride groups that are hydrolysed to sulfonic acid. Others rely on bis(perfluooalkylsulfonyl)imide which competes with the acid strength of a perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acid. A recent development is the production of perfluoroimide acid (PFIA) ionomers with the addition of several bis(sulfonyl)imides added to the side chain to produce perfluoroalkyl ionene chain extended (PFICE) ionomers [84].
The previous literature has summarized the recent work on Nafion/IL membranes. Researchers mainly discussed the enhancement in the properties of the Nafion membranes caused by incorporating IL. In this context, the compatibility of IL and the polymer matrix is an important consideration that affects the degree of uptake of the IL by the polymer, and consequently, the conductivity of the resulting membrane. Table 3 shows a summary of the conductivity of Nafion-based membranes.

Table 3.
Conductivity values of some Nafion-based membranes.
3.3.2. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)-Based PEM
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and its copolymers are widely used in polymer/IL blends. These polymers are characterized by the production of stable film possessing outstanding thermal and mechanical properties, since the presence of an amorphous region allows for a large number of liquid electrolytes. Martinella et al. [85] studied the possibility of using PVDF-HFP as a matrix polymer for EIMTFSI by investigating the thermophysical properties of polymer/IL membrane. It was demonstrated that by increasing the polymer concentration, the thermomechanical stability increases. The conductivity was measured to be 10 mS/cm for the highest IL content of 80 wt.%. Lee et al. [86] synthesized composite membranes using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluor hydrogenates [EMIM](FH)nF) ILs and the fluorinated polymer compounds (S-DFBP-HFDP) and (PVDF-HFP). The conductivity of the membrane that had a weight ratio of 1/0.3/1.75 was around 34.7 mS/cm at 130 °C. Furthermore, the reported open-circuit voltage, power density, and current density were reported to be 1 V, 0.020 W/cm2, and 0.06 A/cm2, respectively. Gao et al. [87] examined the performance of a PVDF/IL composite membrane by varying the following cations: [Epdy], [N1114]+, and [EMIM]. Using [N1114] HSO4, a 60-fold increase in maximum power density was observed when compared to imidazolium-based IL. The incorporation of the protic IL and PVDF-HFP resulted in a composite membrane with a high melting temperature and a conductivity of 10 mS/cm at 140 °C [52]. Superacids have also been studied to complement the composite membranes, as they are famous proton conductors and carriers. Nair and Mohapatra [88] synthesized HClO4SiO2/[dema][TfO]/PVDF-HFP composite membranes. The SiO2 particles were employed to foil the leak of [dema][TfO] from the membrane, in addition to serving as a substrate to immobilize HClO4 that was utilized for conductivity enhancement. The optimum weight percent of [dema][TfO] occurred at 80 wt.%, where the recorded conductivities of the membrane were 0.02 and 0.6 mS/cm at 30 and 100 °C, respectively. Protic IL based on amides has also been utilized. For instance, at 150 °C, ITSA exhibits a high ionic conductivity of 32.6 mS/cm. Xiang et al. [53] studied the physicochemical properties of ITSA/PVDF. A higher amount of PVDF decreased the conductivity. This issue was solved by the addition of PAI as a polymeric additive. Thus, an ionic conductivity of 7.5 mS/cm was achieved for PAI/PVDF (60/5 wt.%) composite membrane.
In case of PVDF-HFP membranes, the conductivity can be enhanced by incorporating additives such as aluminium oxide particles and Polyethylene glycol (PEG) [89]. Another method is the addition of copolymers to the PVDF/IL composite membrane. Inan et al. [90] combined SPEEK with PVDF-HPF membrane and observed that the conductivity and mechanical and chemical stabilities were enhanced. Nanocomposites such as titania and silica have also been incorporated with PVDF-HPF membrane to produce similar enhancements [91,92]. Mališ et al. [93] synthesized polymer/IL membranes by mixing PVDF-HPF and Nafion polymers with BMIMTfO and EIMTfO aprotic and protic IL, respectively. The synthesized membranes were employed in fuel cells (90–160 °C) and compared with PBI reference fuel cells. The conductivity of the composite membranes, especially those based on EIMTfO, increased with the presence of water. For instance, adding 5 wt.% water increased the ionic conductivity by 170% to a value of 13.5 mS/cm. The operating conditions played a vital part in the performance of the composite membranes. Under wet conditions, Nafion/BMIMTfO membranes displayed the most superior conductivity, mainly due to the weak interaction between BMIMTfO and the polymer. However, in dry conditions, the highest conductivity observed was for PVDF-HFP/EIMTfO membrane due to the late interaction between the polymer and IL, which permitted the water to stay in the structure, hence causing the superior conductivity. Nevertheless, the fuel cell did not outperform the PBI reference cell. Table 4 shows a summary of the conductivity of PVDF-based membranes.

Table 4.
Conductivity values of some PVDF-based membranes.
3.3.3. Polybenzimidazole (PBI)-Based PEM
PBI is commercially available and is the furthermost widely investigated and utilized polymer for high-temperature fuel-cell applications [94]. This is attributed to its low cost and good thermal and mechanical stabilities. Eguizábal et al. [95] synthesized hybrid membranes containing 1-H-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide [HMI][TFSI] and PBI polymer for high-temperature PEMFCs application. The optimal membrane composition achieved a conductivity of 54 mS/cm at 200 °C. Van de Ven et al. [96] combined 1-H-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide with PBI to produce a hybrid membrane with a proton conductivity of 1.86 mS/cm at 190 °C, exceeding that of Nafion 117. Ye et al. [97] produced a composite membrane based on H3PO4/1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogen phosphate (PMIH2PO4)/PBI for high-temperature PEMFCs. The PEMFC exhibited a proton conductivity of 2.0 mS/cm when operated at 150 °C under anhydrous conditions. Liu et al. [98] investigated the compatibility between PBI and protic IL diethylmethylammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate [dema][TfO], and developed a hybrid membrane exhibiting a conductivity of 20.73 mS/cm at 160 °C. Wang et al. [99] created a cross-linked structure PBI-IPTS grafted to PBIOH30 backbone (IPTS30)/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogenphosphate [BMIM]H2PO4 hybrid membranes. Due to the aromatic ring structure of the [BMIM]H2PO4 cation, the compatibility with PBI was increased, which consequently enhanced the proton conductivity. The measured conductivity at 160 °C was 133 mS/cm. Nevertheless, the presence of the cation increased the spacing between the polymeric chains leading to a reduction in the mechanical strength. For instance, compared to neat PBI membranes, a 35% decline in tensile strength and a 30% decline in Young’s modulus were observed for PBI/[BMIm]H2PO4 (10 wt.%).
Protic ILs have also been added to porous PBI to form composite PEMs. Eguizábal et al. [100] manufactured porous PBI treated with microporous titanosilicate (ETS-10) and combined with methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide [MIM][TFSI] IL to form a PEM. The membrane achieved an in-plane conductivity of 100 mS/cm and a through-plane conductivity of 40 mS/cm at 160 °C. However, durability tests up to 500 h revealed a severe degradation in the proton conductivity, where values of 15 and 6 mS/cm were achieved at 150 and 200 °C, respectively. In addition, the rise in the temperature resulted in the improvement of the power and current densities of the composite membranes. For example, the rise in temperature from 25 to 180 °C raised the power and current densities by 96% and 200%, respectively, for compact PBI membranes at 0.5 V. Lemus et al. [101] prepared membranes utilizing porous PBI and 1-H-3-vinylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide [IMVH][TFSI]. Synthesis was performed using ultraviolet photopolymerization and reported conductivities were 371 mS/cm when synthesized with 2.5 mol% divinylbenzene (DVB) crosslinker and 309 mS/cm when synthesized with a pre-existing PBI with 80% porosity. The stability of conductivity tests showed a decrease in conductivity for the 500 h, and then the conductivity approximately stayed constant at a value of 250 mS/cm for both membranes. Kallem et al. [102] prepared PBI membranes infiltered with [IMVH][TFSI]. The presence of the IL repressed the transport of the proton, yet it improved both the thermal and mechanical stability. The measured conductivity at 200 °C was around 53.3 mS/cm for a hybrid membrane PBI/IL/DVB (0.88/58.5/1%). The tensile strength was reported to be 10.0 MPa. To enhance the membrane conductivity, [IMVH][TFSI] was added to hierarchical porous polybenzimidazole (HPBI). A conductivity of 85 mS/cm at 200 °C was obtained for a HPBI (49.5 wt.%)/IL (58.5 wt.%)/DVB (1%) composite membrane [103]. Nawn et al. [104] synthesized membranes consisting of polybenzimidazole membranes (PBI4N) impregnated with zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) nanofillers. The content of the ZrO2 filler varied between 0 and 22 wt.%. The results show that the content of the filler plays a vital role in the performance of the PEM. For instance, as the content increased from 0 to 8%, the thermal and mechanical stabilities increased. However, when increasing from 8 to 22%, the opposite effect is demonstrated, where the stabilities decreased. The [PBI4N(ZrO2)0.231] (H3PO4)13 membrane attained a conductivity of 104 mS/cm at 180 °C. Hybrid membranes consisting of PBI/[dema][TfO] were employed in fuel cells. The membrane showed a conductivity of 20.73 mS/cm at 160 °C. In addition, for PBI/[dema][TfO], membranes showed a conductivity reduction of 10% (with 83 wt.% [dema][TfO]) and 18% (with 80 wt.% [dema][TfO]) after 400 hr. Moreover, PBI/[dema][TfO] (83 wt.%) membrane exhibited power density of 26.50 and 29.64 mW/cm2 at 120 °C and 140 °C, respectively [98]. Xu et al. [105] prepared PEM by incorporating IL graphite oxide (ILGO) with PBI loaded with polymer acid (PA). At 175 °C, the proton conductivity was measured as 35 mS/cm, while the power density was measured to be 320 mW/cm2. It was concluded that ILGO filler could enhance the conductivity of the PEM. Hooshyari et al. [106] developed composite membranes incorporating PBI with 1,3-di(3-methylimidazolium) propane bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide (PDC3) and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide (PMC6) dicationic IL. The membrane was tested for PEMFC applications under anhydrous conditions and 180 °C, and PBI/PA/PDC3 attained an ionic conductivity and power density of 78 mS/cm and 400 mW/cm2, respectively. Liu et al. [107] synthesized functional silica IL into PBIOH to produce composite membranes for PEMFC applications. Subsequent to investigating the trade-off between the conductivity and stability of the PEM based on the weight percent of the IL, an optimum content of 5 wt.% was reached. At that ratio, the proton conductivity was measured as 106 mS/cm at 170 °C.
For PBI/IL composite membranes, numerous studies showed that proton conductivity improved and remained stable for a longer duration. However, the presence of IL amplified the space between the polymeric chains of PBI and caused a deterioration in the intermolecular forces and mechanical strength. Table 5 shows a summary of the conductivity of PBI-based membranes.

Table 5.
Conductivity values of some PBI-based membranes.
3.3.4. Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketones) (SPEEK)-Based PEM
SPEEK membranes are widely investigated in PEMFC owing to their high thermal and chemical stability and their ability to retain water to enhance proton conductivity. Jothi and Dharmalingam [108] prepared and tested SPEEK/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethyl phosphate [EMIM][DEP] membrane by casting. Under anhydrous conditions at 145 °C, an ionic conductivity of 3 mS/cm was recorded as well as a power density of 203 mW/cm2 with OCP of 0.83 V. Li et al. [109] added silicon oxide particles SiOx to a SPEEK/[dema][TfO] membrane and investigated the resulting hybrid membranes. The addition of the SiOx decreased the IL leakage and the inflammation degree of the membrane due to the promoted interaction between SPEEK, the IL, and siloxane. Under dry conditions, the SPEEK based membrane showed a conductivity of 20.03 mS/cm at 220 °C. Sulfonated SPEEK/[dema][TfO] IL/with modified montmorillonite clay and dema+ cation (Mmtdema) exhibited an ionic conductivity of 78 mS/cm at 70 °C [110]. Wang et al. [111] introduced mesoporous SiO2 to SPEEK/IL membranes and discovered that the presence of silica improved the IL preservation in SPEEK. For instance, SPEEK/[BMIM][BF4]/SiO2 (50 wt.%/7.5 wt.%) membranes displayed a conductivity of 15 mS/cm. Batalha et al. [112] improved the conductivity of SPEEK/[dema][TfO] composite membranes by the addition of ZrO2. The interaction between the IL and the elongated architecture of zirconia allowed for the existence of new proton transport channels. For instance, the proton conductivity of SPEEK increased from 70 to 660 mS/cm with the addition of [dema][TfO] and 6 wt% of ZrO2. SPEEK and [BMIm]+ cations show excellent interaction, which allows for the retention of IL by SPEEK [113]. For example, at 160 °C and dry conditions, the hybrid membrane SPEEK/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [BMIm]PF6 (50%)/PA (4.6 doping level) exhibited a conductivity of 30 mS/cm. The durability test displayed a stable conductivity of 20 mS/cm for periods more than 600 hr. da Trindade et al. [114] aimed at enhancing the SPEEK membranes’ performance by the addition of (ImHSO4), (MIHSO4) and BMIHSO4 IL. The conductivity increased by 50% and 30% when the membranes were doped with 5 wt.% of (MIHSO4) and BMIHSO4, respectively. Moreover, for PEMFC applications SPEEK/BMIHSO4 PEM showed a power density of 530 mW/cm2 in the range of 80 to 100 °C. Che et al. [39] prepared a multicomponent hybrid membrane based on SPEEK, polyurethane (PU), and BMIm+ IL using layer-by-layer fabrication. After 100 layers, the PEM was obtained and doped on PA to be tested for PEMFC. The PEM (SPEEK/PU/SPEEK/BMIM)100/60%PA exhibited conductivity and tensile strength of 103 mS/cm (at 160 °C) and 2.38 MPa, respectively. Elumalai et al. [115] synthesized composite membranes based on phosphonate IL immobilised mesoporous silica SBA-15 as a filler to the SPEEK polymer matrix. In this case, the observed conductivity was 10.2 mS/cm with 6% SBA-15/SPEEK at 140 °C. At the same temperature, the mechanical strength was measured as 23 MPa, while a power density of 183 mW/cm2 was also obtained. Table 6 shows the conductivity values of some SPEEK-based membranes.

Table 6.
Conductivity values of some SPEEK-based membranes.
3.3.5. Sulfonated Polyimide (SPI)-Based PEM
Among other promising polymers for PEMFC is sulfonated polyimide (SPI), which exhibits high mechanical strength, high thermal stability, and low permeability. Chen et al. [116] manufactured hybrid membranes by combining 1-vinylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate [ImVH][TfO], 1-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate [MIm][TfO] IL with SPI. The resulting polymer structure is strengthened due to ionic bonds formed between the IL cations and SPI sulfonic acid groups at elevated temperatures, in turn improving the polymer’s preservation of the IL, increasing the long-term stability and conductivity. Under dry conditions, SPI/[ImVH][TfO](50 wt.%) membrane showed an ionic conductivity of 3–6 mS/cm at 120 °C. Another composite membrane consisting of SPI/[MIm]BF4/H2SO4 was tested for fuel-cell applications [117]. The ionic conductivity achieved was 55.9 mS/cm at 180 °C, however, the value deteriorated to 28.2 mS/cm after three months. Lee et al. [118] tested SPI/[dema][TfO] (67 wt.%) membranes for PEMFC after confirming the compatibility between the IL and the polymer. Under dry conditions, the measured conductivity was 10 mS/cm at 120 °C. For PEMFC performance, a current density of 240 mA/cm2 and a power density of 100 mW/cm2 were achieved at 80 °C under dry conditions. Chen et al. [119] synthesized the hybrid membrane SPI/[ImVH][TfO] (40 wt.%) by employing 1,4-bis(4-aminophenoxy-2-sulfonic acid) benzenesulfonic acid (pBABTS), 3,3′, 4,4′-diphenyl sulfone tetracarboxylic dianhydride (DSDA) as dianhydride, and 4,4′-(9-fluorenylidene) dianiline (9FDA) as diamine. Under dry conditions, the PEM attained a proton conductivity of 16 mS/cm at 120 °C. Kowsari et al. [120] synthesized PEM doped with PA and constructed on SPI/graphene oxide (GO). The GO was functionalized with [MIm]+ and H2PO4−. The measured conductivity of the membrane at 160 and 120 °C were 77.2 and 124.3 mS/cm, respectively.
3.3.6. Other Polymer-Based PEM
Zhang et al. [121] synthesized a hybrid membrane by incorporating 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide [BMIm][TFSI] IL with silicon nanorods (SNR) into poly(2,5-benzimidazole) (ABPBI) polymer. The conductivity was 10 mS/cm under a temperature range of 80–140 °C. The PEMFC performance attained power densities of 150 and 280 mW/cm2 at 80 and 180 °C, respectively. Li et al. [122] synthesized composite membranes using sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone sulfone) (SPAEKS) and 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium phosphotungstate (PWA-IL). At 80 °C, the PEM showed an excellent proton conductivity of 127 mS/cm. Figure 5 shows the variation of the temperature on the conductivity of SPAEKS-based membranes, in addition to the Arrhenius plot. Awasthi et al. [123] synthesized a hybrid membrane based on poly(arylene ether) polymer while incorporating [BMIm][BF4] IL. The hydrophilic length was constant at 8 kDa, while the hydrophobic length was varied (5, 8, and 10 kDa) to produce the polymers (named as P1, P2, and P3 polymers, respectively). The increase in the hydrophobic length resulted in a decline in the proton conductivity of the membrane owing to lower water retention. Moreover, the IL improved the conductivity. For instance, the proton conductivity of P1 increased from 32 to 75 mS/cm when 50 wt.% of IL was added to the PEM. Following the trend, the proton conductivity of P2 rose from 25 to 61 mS/cm and the proton conductivity of P3 increased by 109% with the addition of 50 wt.% [BMIm][BF4].
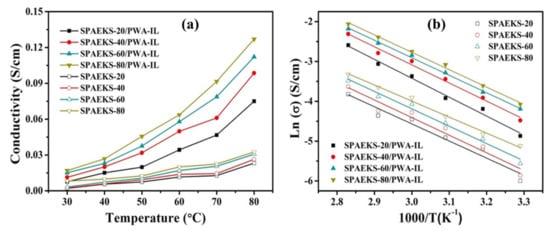
Figure 5.
(a) Proton conductivity and (b) Arrhenius plot (right) of SPAEKS-X membranes and SPAEKS-X/PWA-IL membranes at different temperatures [122], Reproduced with permission from Jatindranath Maiti, et al., Composites Science and Technology; published by Elsevier, 2018.
Dahi et al. [124] synthesized hybrid membranes based on Matrimid® polymer and 1-n-butylimidazolium bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate [BIm][BEHP], 1-n-butylimidazolium dibutylphosphate [BIm][DBP], and 1-n-methylimidazolium dibutylphosphate [MIm][DBP] hydrophilic IL. The hybrid membranes display great stability as most of the IL is reserved in the pores of Matrimid®. In addition, the viscosity of the IL deteriorated with increasing temperature, causing leakage of the IL and decreasing the conductivity. The PEM [BIm][DBP]/Matrimid® attained the most superior proton conductivity of 20 mS/cm when compared to its counterpart at 115 °C. Langevin et al. [55] prepared composite PEM by immersing segments of MAT14PVP7 in TEA-TF IL. The proton conductivity of the PEM at 130 °C was measured as 20 mS/cm, which is higher when compared to the proton conductivity of TEA-TF/Nafion standing at 1.8 mS/cm. The results also revealed that, unlike Nafion, the mechanical resistance of MAT14PVP7-based PEM is barely affected by the increase in temperature.
Zakeri et al. [125] developed and fabricated composite membranes based on [ETFE-g-poly(4-VP)-SO3H]HSO4. At 95 °C, the composite membrane revealed a staggering conductivity enhancement of 62% of that of the Nafion 112 membrane. The membrane also displayed high thermal stability. Moreover, Zakeri et al. [126] also manufactured a similar composite membrane structure of Poly(1-vinyl imidazole) grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) Trifluoromethanesulfonate [ETFE-g-P(1-Vim)Prso3H ]CF3SO3. At 95 °C, the PEM revealed a proton conductivity of 138 mS/cm, with 96% retention at 80 °C and for 50 hr under fully hydrated conditions. Tang et al. [127] synthesized composite membranes using adsorbed and doped [MIM][TfO] over polyacrylamide/polyethylene glycol interpenetrated (PAM/PEG IPN). With the variation in the concentration of the IL (22.84 wt.%, 50 wt.%), the conductivities attained at 150 °C were 10.37 and 17.02 mS/cm, respectively. Tang et al. [128] prepared [MIM][TfO] into poly(acrylic acid)–poly(ethylene glycol) superabsorbent membranes with proton conductivities reaching 40.4 mS/cm. The tests were performed under dry conditions and at a temperature of 200 °C. Chopade et al. [129] studied the structure of N-ethylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [EIM][TFSI]/PEO composite membranes. The thermal and mechanical stabilities were improved due to the cross-linked structured polymer. Hence, even at a high temperature of 180 °C the PEM with 45 wt% of [EIM][TFSI] exhibited a conductivity of 14 mS/cm. Chu et al. [130] synthesized elastic and clear composite membranes utilizing PAMAM dendrimer-based macromolecular IL. The PEM displayed elevated thermal stability until temperatures of 350 °C, and a conductivity of 12 mS/cm at 160 °C and under dry conditions. PEM based on [MIm][TfO] and [APMIm][Br]-GO with a 1.0 wt.% achieved a conductivity of 14.8 mS/cm at 160 °C [131].
Thanganathan and Nogami [132] improved the properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) membranes by incorporating 1–butyl–3–methylimidazolium Bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (BMITFSI) and 1–ethyl–3–methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMI-BF4) ILs. Silica was incorporated as well to improve the stability and conductivity of the PEM. The hybrid membranes displayed conductivities of a maximum of 0.58 mS/cm at 60 °C. Yang et al. [133] synthesized composite membranes based on (PVA)-Citric Acid (CA)-IL for PEMFC applications. The tested results proved that PVA-CA-IL membranes show excellent performance under anhydrous conditions. Furthermore, PVA-CA-EAN (1:0.05:0.4 molar ratio) exhibited the most superior proton conductivity of 7.8 mS/cm at 140 °C. Wu et al. [134] studied the effect of poly(phenylene oxide) (PPO)/methylimidazole (MeIM) composite membranes on the performance of a PEMFC. At 30 °C, the PPO/MeIM membrane recorded a proton conductivity of 67.9 mS/cm in addition to a mechanical strength of 4.8 MPa at a molar ratio of 4:10 Moreover, without the additional humidification the PEMFC displayed a power density of 260 mW/cm2 at 160 °C.
The proton conductivity of Zirconium phosphate (ZrP) powder has been examined and composite membranes prepared from ZrP and porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with and without mineral acids have been also investigated as electrolytes for direct hydrocarbon fuel cells that operate at high temperatures [135,136,137,138]. Moreover, Mohammed et al. [139] synthesized PEM based on ZrP and imidazolium-based IL for high-temperature fuel-cell applications. Five imidazolium based ILs were tested: 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate [EMIM][ESO4], 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide [BMIM][DCA], 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium triflate [BMIM][TFA], 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate [EMIM][AC], 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium Trifluoroacetic [BMIM][TFA]. ZrP/[EMIM][ESO4] recorded the most superior proton conductivity of 22.6 mS/cm when compared to its imidazolium-based IL counterparts. The reported results showed better performance than Nafion membranes, which highlights the great potential of ZrP-based PEM. A similar study by Al-Othman et al. [140] reported on the synthesis of composite membranes based on ZrP polymer, imidazolium-based IL, and glycerol supported on PTFE. The ZrP/[EMIM][SO4]/GLY/PTFE membrane was tested for PEMFC applications and demonstrated a proton conductivity of 70 mS/cm at 200 °C. Ortiz-Martínez et al. [141] copolymerized 1-(4-sulphobutyl)-3-vinylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulphonate [HSO3−BVIm][TfO] IL with methyl methacrylate MMA and perfluoro-3,6-dioxa-4-methyl-7-octene sulfonyl fluoride (hPFSVE) to form PILs for PEMFC applications. Both poly ([HSO3−BVIm] [TfO]-co-MMA) and poly([HSO3-BVIM][TfO]-co-hPFSVE) electrolyte membranes offered high conductivity in the range of (1–10 mS/cm) for wet and dry conditions. The performance of membranes was improved, showing the promising prospects of these PILs as PEM, with power outputs up to 45 mW/cm2. Figure 6 shows the performance of the PEMFC for various mall ratios.
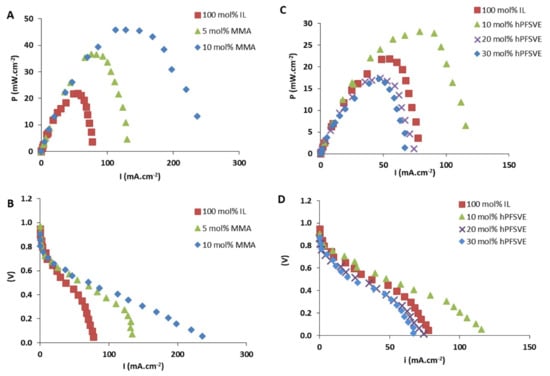
Figure 6.
(A,C) Power curves and (B,D) polarization curves for PEMFC membranes based on poly(IL-co-hPFSVE), poly([IL-co-MMA), and poly(IL) [141]. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier, 2019.
Zhu et al. [142] prepared PILs with precursors of 1,3,5-tris(1-imidazolyl)benzene (TIB) and incorporated them into poly (2,6-dimethyl phenylene oxide) (QPPO) polymer matrix to produce hybrid PEM. The resulting TIB/QPPO hybrid membranes exhibited decent thermal stability, suitable mechanical properties, and improved conductivity and fuel-cell performance. For instance, the highest conductivity and fuel-cell performance recorded were 55 mS/cm and 168.9 mW/cm2 at 80 °C, respectively. Eisa et al. [143] prepared PEMFC based on polyaniline (PANI), 1-Hexyl-3- Methylimidazolium Tricyanomethanide IL, and ZrP. The proposed PEMFC with (50:50 mg) PANI/ZrP and 3.7 wt.% IL showed a promising ionic conductivity of 20 mS/cm at room temperature. Ka’ki et al. [40] synthesized and evaluated nanocomposite PEMFC based on calcium phosphate (CP) and ILs. PEMFC with CP/PTFE/[HMIM][C4N3−] composite membranes possessed a proton conductivity of 100 mS/cm at room temperature and 3.14 mS/cm at 200 °C. Table 7 lists the conductivity values of polymer-based membranes.

Table 7.
Conductivity values of some polymer-based membranes.
Sulfonated polyphenylene oxide (SPPO) has also been investigated as a polymer matrix for PEMFCs. Fu et al. [144] prepared several SPPO membranes for fuel-cell applications. The membranes showed a proton conductivity of 94 mS/cm at 25 °C, which is comparable to that of Nafion 117. Yang et al. [145] prepared SPPO-based membranes in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone solution for PEM applications. The resulting membranes exhibited a proton conductivity of 11.6 mS/cm at 25 °C, which is also comparable to that of Nafion 112. Liu et al. [146] presented a method to stabilize poly(methyl-methylcrylate) (PMMA)-grafted magnetic nanoparticles with sulfonated polystyrene (SPS) in IL/cosolvent mixtures. The experimental results displayed that the highest ionic conductivity in the range of 30 mS/cm occurred while dissolving PMMA-PSS in acetonitrile and ILs. Zhang et al. [147] studied the enhancement of SPAEKS-based PEMS by the introduction of [EMIM][N(Tf)2] IL, MIL-100 metal organic framework, and phosphotungstic acid (HPW). Membranes based on SPAEKS with HPW-ILs@MIL-100 showed an outstanding conductivity of 138 mS/cm at 100 °C. Wang et al. [148] synthesized a series of sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone ketone sulfone) SPAEKKS polymers for PEMFC applications. The resulting membranes reported a proton conductivity of 32 mS/cm at 80 °C, which is comparable to Nafion 117.
4. IL/Polymer PEM: Challenges and Future Work
The durability of PEM membranes is one of the most critical properties. It is affected by various factors that can cause membranes’ degradation either in mechanical, thermal, or chemical modes [149,150]. The mechanical degradation appears in the form of pinholes and cracks that are usually present as a result of manufacturing defects and can be detected in the early life of the PEMFC. The presence of cracks and pinholes lead to fuel crossover, hence, a combustion reaction resulting from the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, instead of an electrochemical reaction. This leads to a severe safety risk [151]. The delamination of the membrane–electrode interface is another issue that has a direct influence on membrane durability of the PEMFCs. Delamination is a result of stress cycling and causes severe interfacial resistance, thus, an intense performance drop. The high-temperature operation is another serious issue that affects the durability of the PEM, as material decomposes around 280 °C for PFSA membranes [151]. Another issue caused by thermal degradation is the membrane thinning. The membrane’s material decomposition causes a reduction in the thickness of the membrane. Membrane thinning can lead to fuel crossover and electrical short circuits. The oxidization of the platinum catalyst under fuel-cell conditions is another important issue in fuel-cell materials’ durability [150].
In order for PEMFC technology to outperform the current technologies, the durability and performance ought to be increased, while decreasing the cost. The performance of the PEMFC highly depends on the power densities obtained. Therefore, an improvement in the conductivity of the PEM and a decline in the electrodes’ polarization losses will surely improve the power densities. Moreover, the PEM should meet the requirement of PEMFC application, especially the required stable performance for high-temperature PEM. Thus, the electrode/membrane interface (whether electrically or chemically) will affect the fuel-cell performance. For instance, the reduced interface will result in elevated electronic resistance and low utilization.
The main challenge facing polymerized IL membranes is the compatibility of ILs with the matrix polymers and the organic–inorganic fillers. There has been a clear compromise between the conductivity and the mechanical strength of the composite materials. Another major issue is the long-term thermal and mechanical stability of the composite membranes, especially under high-temperature PEMFC operation. The leakage of the IL from the membrane structure is another challenge faced in PEMFC operation. Moreover, PEM doped in acids to increase the conductivity should possess the ability to hold the acid, which in turn will improve the long-term stability of the PEM.
Research in the coming future must be directed towards studying several IL cations such as pyrrolidinium or triazolium, since all the present research fixated on ammonium and imidazolium-based IL has been exhausted. Poly ILs have the potential to provide a feasible alternative for conventional and commercially available polymers. Poly ILs are known for their excellent conductivity and high thermal stability, as well as their environmentally friendly and low-cost synthesis compared to Nafion [152]. Further, poly ILs are considered a promising replacement for IL as they are more stable and safe, possess better mechanical properties, and most importantly they offer a solution for the leakage issues. Hence, future research should be dedicated to investigating the employment of poly IL in PEMFC. The molecular and morphological structures of the PEM ought to be studied using molecular dynamics and orbital simulation, as they provide information that cannot be attained experimentally. Research should also focus on studying the proton conduction mechanisms inside the PEM to enable the design of IL-polymer membranes with optimized performance.
5. Conclusions
This review article provided an overview of the employment of polymerized ILs in PEMFC applications. The review focused on the preparation of composite membranes utilizing the most commonly used polymers in PEM: Nafion, PVDF, PBI, SPEEK, and SPI, in addition to other polymers incorporated with ILs. A small section on the methods and techniques available for the synthesis of polymer/IL membranes was also presented. The addition of some carefully selected ILs to the polymer matrix improved the conductivity, thermal and mechanical stability, as well as the mechanical strength of pristine PEM. In terms of conductivity, PBI-based composite membranes revealed the highest conductivity and longest stability when compared to their polymer counterparts. For instance, conductivities of 371 and 309 mS/cm were recorded for PIL 2.5 mol% CL and PIL-PBI composite membranes. The same membranes exhibited a stable conductivity larger than 250 mS/cm and lasted for more than 40 days. With respect to the mechanical properties, it was concluded that protic ILs might produce a plasticizing effect, which causes a decline in the ionic domains’ dipolar interactions. A prominent method to overcome the issue is polymer cross-linking. In that aspect, SPEEK-based polymers exhibited the highest mechanical strength. For example, crosslinking glycerol or glycol with SPEEK to prepare TFAPA/SPEEK improved the membrane’s mechanical strength. The paper also highlighted the current challenges facing the employment of polymer/ILs in PEMFC and suggested various paths for the development of research on polymerized ILs and their application in PEMFC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.-O. and M.T.; methodology, Adnan Alashkar, A.A.-O. and M.T.; validation, A.A.; formal analysis, A.A., A.A.-O., M.T. and M.Q.; investigation, A.A. and A.A.-O.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A., A.A.-O., M.T. and M.Q.; writing—review and editing, A.A., A.A.-O., M.T. and M.Q.; visualization, A.A.-O. and M.T.; supervision A.A.-O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by the American University of Sharjah open access program (OAP), OAP22-CEN-073.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the open access program (OAP) at the American University of Sharjah through grant #OAP22-CEN-073.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| [2-FPy]TF: | 2-fluoropyridinium triflate |
| [2-sea][TfO]: | 2-Sulfoethylammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| 9FDA: | 4,4′-(9-fluorenylidene) dianiline |
| ABPBI: | Poly(2,5-benzimidazole) |
| BG-BF4: | N-butylguanidinium tetrafluoroborate |
| [BIm][BEHP]: | 1-n-butylimidazolium bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate |
| [BIm][DBP]: | 1-n-butylimidazolium dibutylphosphate |
| BMIHSO4: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate |
| [BMIM][DCA]: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide |
| [BMIm]H2PO4: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogenphosphate |
| [BMIM][TFA]: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium triflate |
| [BMIM][TFA]: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium Trifluoroacetic |
| [BMIm][TfO]: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [BMIm][BF4]: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [BMIm]PF6: | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| (Btmps)/HN(Tf)2: | 3-(1-butyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl) propane-1- sulfonate 1,1,1-Trifluoro-N-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) methanesulfoneamide |
| [bzlm][TFSI]: | Benzimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide |
| [C2H3N3]/[CH3SO3H]: | 1H-1,2,4-triazole/methanesulfonic acid |
| [C2mim][TFSI]: | Methylmethacrylatein1-ethyl-3-methylimida- zolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| [C3OHmim]BF4: | 1-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroboride |
| CF3SO3: | Trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| CL: | Crosslinker |
| CP: | Calcium phosphate |
| [dema]HSO4: | Diethylmethylammonium hydrogensulfate |
| [dema][TfO]: | Diethylmethylammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [dema][TFSA]: | Diethylmethylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide |
| [DMBIm]H2PO4: | 2,3 dimethyl-1-butylimidazolium dihydrogen phosphate |
| [DMEIm]H2PO4: | 2,3-dimethyl-1-ethylimidazolium dihydrogenphosphate |
| [DEMET][TFSI]: | N,N-diethyl-N-methyl-N-(2-methoxyethyl) ammonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| DSDA: | 3,3′, 4,4′-diphenyl sulfone tetracarboxylic dianhydride |
| DTA+: | n-dodecyltrimethylammonium |
| DVB: | Divinylbenzene |
| [EIm][TfO]: | 1-ethylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [EIm][TFSI]: | N-ethylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [Emim]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium cation |
| [EMIM][AC]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate |
| [EMIM][BF4]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [EMIm][DEP]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethyl phosphate |
| [EMIM][ESO4]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate |
| [EMIm](FH)nF): | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluor hydrogenates |
| [EMIm]HSO4: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogensulfate |
| [EMIM][OCSO4]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium octylsulfate |
| [EMIM][SO4]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium sulfate |
| [EMIM][TFSI]: | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imid |
| [Emorph][HCOO]: | N-ethylmorpholinium formate |
| [Epdy]: | Ethyl pyridinium |
| ETFE: | poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) |
| ETFE-g-poly(4-VP): | Poly(4-VP) grafted ETFE films |
| ETFE-g-P(1-Vim): | Poly(1-vinyl imidazole) grafted onto ETFE film |
| ETS-10: | Microporous titanosilicate |
| H3PO4: | Phosphoric acid |
| H2SO4: | Sulfuric acid |
| HClO4SiO2: | Perchloric acid immobilized on nano-silica |
| [HMI][TFSI]: | 1-H-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| HPBI: | Hierarchical porous polybenzimidazole |
| HSO3-BBIm][TfO]: | 1-butyl-3-(4-sulphobutyl)-imidazoliumtri-fluoromethanesulphonate |
| [HSO3-BBIm][TFSI]: | 1-methyl-3-(4-sulfobutyl)-imidazolium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide |
| [HSO3-BMIm][TFSI]: | 1-methyl-3-(4-sulphobutyl)-imidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulphonyl)imide |
| IL: Ionic Liquid | |
| ImHSO4: | Imidazolium hydrogen sulfate |
| [ImVH][TfO]: | 1-vinylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [ImVH][TFSI]: | 1-H-3-vinylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| IPTS30: | IPTS grafted to PBIOH30 backbone |
| ITSA: | Isobutyramide trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| MAT14PVP7: | Interconnected porous support prepared from MAT14 and PVP7 |
| [MIm]BF4: | n-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [MImCM]Cl: | 1-carboxylmethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [MIm][DBP]: | 1-n-methylimidazolium dibutylphosphate |
| [MIm][TfO]: | 1-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [MIm][TFSI]: | Methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| MIHSO4: | 1-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate |
| [Mmorph][HCOO]: | N-methylmorpholinium formate |
| Mmtdema: | Modified montmorillonite clay with dema+ cation |
| [morph][HCOO]: | Morpholinium formate |
| [MPz][TFSI]: | 1-methyl-pyrazole N,N-bis(trifluoromethane-sulfonyl)imide |
| [MTBDH]TFSI: | 7-methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [N1114]+: | Trimethylethyl amide cation |
| [N1114]+HSO4: | Trimethylethyl amide hydrogensulfate |
| OCP: | Open circuit potemtial |
| PA: | Polyamide |
| PAA: | Poly(acrylic acid) |
| PEG: | poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PAI: | Polyamide imide |
| PAMAM: | Polyamidoamine |
| PAM/PEG IPN: | Polyacrylamide/polyethylene glycol interpenetrated |
| PANI: | Polyaniline |
| pBABTS: | 1,4-bis(4-aminophenoxy-2-sulfonic acid) benzenesulfonic acid |
| PBI: | Polybenzimidazole |
| PBI-O-Ph: | Polybenzimidazole derivative with benzofuranone moieties |
| PDC3: | 1,3-di(3-methylimidazolium) propane bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide |
| PEM: | Proton Exchange Membrane |
| PEMFC: | Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell |
| PMC6: | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| PMIH2PO4: | 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogen phosphate |
| PPO: | Poly(phenylene oxide) |
| PVA: | Plovinyl alcohol |
| PVDF: | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVDF-HFP: | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropene) |
| PWA: | 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium phosphotungstate |
| [pyrr][C7H15COO]: | Pyrrolidinium octanoate |
| [pyrr][CF3COO]: | Pyrrolidinium trifluoroacete |
| [pyrr][CH3COO]: | Pyrrolidinium acetate |
| [pyrr][HCOO]: | Pyrrolidinium formate |
| [pyrr]HSO4: | Pyrrolidinium hydrogensulfate |
| [pyrr][NO3]: | Pyrrolidinium nitrate |
| [pyrr][TFSA]: | Pyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide |
| QPPO: | Poly (2,6-dimethyl phenylene oxide |
| RTIL: | Room temperature ionic liquid |
| SiO2: | Silicon oxide |
| SPAEKKS: | Sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone ketone sulfone) |
| SPAEKS: | Sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone sulfone) |
| SPEEK: | Sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) |
| SPI: | Sulfonated polyimide |
| SPPO: | Sulfonated Polyphenylene Oxide |
| SPS: | Sulfonated polystyrene |
| TEA: | Triethylammonium |
| TEAH+: | Triethylammonium cation |
| TEA-TF: | Triethylammonium-triflate |
| TFA−: | Triflate anion |
| TFAPA: | Trifluoroacetic propylamine |
| TIB: | 1,3,5-tris(1-imidazolyl)benzene |
| [TMPA][TFSI]: | N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| TMS: | Triethylammonium methanesulphonate |
| [TMSPMIm]BF4: | 1-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| TOA-TF: | Trioctylammonium triflate |
| TPFBu: | Triethylammonium perfluorobutanesulphonate |
| ZrO2: | Zirconium dioxide |
| ZrP: | Zirconium phosphate |
References
- Jayakumar, A.; Chalmers, A.; Lie, T.T. Review of prospects for adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles in New Zealand. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2017, 7, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawalbeh, M.; Al-Othman, A.; Assad, M.E.H. Graphene oxide—Nafion composite membrane for effective methanol crossover reduction in passive direct methanol fuel cells. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Conference on Renewable Energy: Generation and Applications (ICREGA), Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 February 2018; pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Al-Othman, A.; Nancarrow, P.; Tawalbeh, M.; El Haj Assad, M. Direct hydroCarbon fuel cells: A promising technology for improving energy efficiency. Energy 2019, 172, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martis, R.; Al-Othman, A.; Alkasrawi, M.; Tawalbeh, M. Fuel cells for carbon capture and power generation: Simulation studies. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 6139–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnci, M.; Türksoy, Ö. Review of fuel cells to grid interface: Configurations, technical challenges and trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 1353–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Han, T.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yang, N.; Xiao, J.; Kawi, S. Recent progress in direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell: Advanced anode catalysts, diversified carbon fuels, and heat management. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 4283–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, E.; Wilberforce, T.; Ijaodola, O.; Thompson, J.; Olabi, A.G. Review of operating condition, design parameters and material properties for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 1227–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawalbeh, M.; Al-Othman, A.; Singh, K.; Douba, I.; Kabakebji, D.; Alkasrawi, M. Microbial desalination cells for water purification and power generation: A critical review. Energy 2020, 209, 118493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Ijaodola, O.; Emmanuel, O.; Thompson, J.; Olabi, A.; Abdelkareem, M.; Sayed, E.; Elsaid, K.; Maghrabie, H. Optimization of Fuel Cell Performance Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Membranes 2021, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Park, C.J.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated poly ether sulfone/heteropoly acid composite membranes as electrolytes for the improved power generation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.K.; Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Lee, K.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Yoo, D.J. Enhancing Physic Chemical Properties and Single Cell Performance of Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether) (SPAE) Membrane by Incorporation of Phosphotungstic Acid and Graphene Oxide: A Potential Electrolyte for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Escorihuela, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Compañ, V. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs): Advances and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Simonsen, S.; Norby, T.; Chatzitakis, A. Composite Membranes for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells and Electrolysers: A Critical Review. Membranes 2019, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano, Z.P.; Banham, D.; Ye, S.; Hintennach, A.; Lu, J.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Batteries and fuel cells for emerging electric vehicle markets. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, E.; Wilberforce, T.; Ijaodola, O.; Thompson, J.; Olabi, A.G. Selection of proton exchange membrane fuel cell for transportation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 30625–30640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaswad, A.; Omran, A.; Sodre, J.R.; Wilberforce, T.; Pignatelli, G.; Dassisti, M.; Baroutaji, A.; Olabi, A.G. Technical and Commercial Challenges of Proton-Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells. Energies 2020, 14, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancarrow, P.; Al-Othman, A.; Mital, D.K.; Döpking, S. Comprehensive analysis and correlation of ionic liquid conductivity data for energy applications. Energy 2021, 220, 119761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, I. Progress in the use of ionic liquids as electrolyte membranes in fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elwan, H.A.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A review of proton exchange membranes based on protic ionic liquid/polymer blends for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 484, 229197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, K.; Watanabe, M. Recent progress in proton conducting membranes. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 73, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Tawalbeh, M.; Temsah, O.; Al-Murisi, M. Industrial Challenges of MOFs in Energy Applications. In Encyclopedia of Smart Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, F.; Oshima, A.; Kakigi, T.; Mitani, N.; Matsuura, A.; Fujii, K.; Sato, Y.; Li, J.; Washio, M. Synthesis and characterization of PEFC membranes based on fluorinated-polymer-alloy using pre-soft-EB grafting method. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2007, 265, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Economy, J. Preparation of proton-conducting composite membranes from sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) and polyacrylonitrile. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 291, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, L.K.; Masdar, M.S.; Shyuan, L.K. Ionic Liquid in Phosphoric Acid-Doped Polybenzimidazole (PA-PBI) as Electrolyte Membranes for PEM Fuel Cells: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, C.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, G. Impact of Membrane Phosphoric Acid Doping Level on Transport Phenomena and Performance in High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. Membranes 2021, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K. Membrane electrode assemblies for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. In Functional Materials for Sustainable Energy Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 279–311. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-D.; Ohira, A.; Nakao, H. Chemically Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone (CSPPSU) Membranes for PEM Fuel Cells. Membranes 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Yen, C.-Y.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Liao, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-P. High proton-conducting Nafion ®/–SO3H functionalized mesoporous silica composite membranes. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majlan, E.H.; Rohendi, D.; Daud, W.R.W.; Husaini, T.; Haque, M.A. Electrode for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Lin, B.; Yan, F. Ionic liquid/poly(ionic liquid)-based electrolytes for energy devices. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Choi, I.; Hong, J.; Kim, O. Polymer electrolytes integrated with ionic liquids for future electroChemical devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashkar, A.; Ibrahim, T.; Khamis, M.; Alami, A.H. Electrolytes, Dyes, and Perovskite Materials in Third Generation Photovoltaic Cells. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2021, 2, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, R.; Lee, J.S. Ionic Liquids for ElectrChemical Devices. Electrchemistry 2007, 75, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galiński, M.; Lewandowski, A.; Stepniak, I. Ionic liquids as electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5567–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, J.E.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Effect of Anion on Gas Separation Performance of Polymer−Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid Composite Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 9919–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Põhako-Esko, K.; Timusk, M.; Saal, K.; Lõhmus, R.; Kink, I.; Mäeorg, U. Increased conductivity of polymerized ionic liquids through the use of a nonpolymerizable ionic liquid additive. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 3086–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSaiz, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Eizagirre Barker, S.; Fernández de Luis, R.; Arriortua, M.I. Ionic liquids for the control of the morphology in poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) membranes. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, J.T.E.; Abdul Rahim, A.R.; Masdar, M.S.; Shyuan, L.K. Enhanced Performance of Polymer Electrolyte Membranes via Modification with Ionic Liquids for Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Fan, H.; Duan, X.; Feng, F.; Mao, W.; Han, X. Layer by layer self-assembly fabrication of high temperature proton exchange membrane based on ionic liquids and polymers. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka’ki, A.; Alraeesi, A.; Al-Othman, A.; Tawalbeh, M. Proton conduction of novel calcium phosphate nanoComposite membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 30641–30657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, M.S.; Yasuda, T.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. ElectroChemical properties of protic ionic liquids: Correlation between open circuit potential for H2/O2 cells under non-humidified conditions and ΔpKa. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, H.; Noda, A.; Hayamizu, K.; Hayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, H.; Watanabe, M. Proton-Conducting Properties of a Brønsted Acid−Base Ionic Liquid and Ionic Melts Consisting of Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide and Benzimidazole for Fuel Cell Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Kudo, K.; Mitsushima, S.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. Brønsted Acid−Base Ionic Liquids as Proton-Conducting Nonaqueous Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 4024–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wippermann, K.; Wackerl, J.; Lehnert, W.; Huber, B.; Korte, C. 2-Sulfoethylammonium Trifluoromethanesulfonate as an Ionic Liquid for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F25–F37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, J.; Dunn, P.; Holmes, L.; Belieres, J.-P.; Angell, C.A.; Gervasio, D. A Flourinated Ionic Liquid as a High-Performance Fuel Cell Electrolyte. ECS Trans. 2019, 13, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, H.; Watanabe, M. Brønsted acid-base ionic liquids for fuel cell electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 24, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miran, M.S.; Yasuda, T.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Binary Protic Ionic Liquid Mixtures as a Proton Conductor: High Fuel Cell Reaction Activity and Facile Proton Transport. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 27631–27639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Gondosiswanto, R.; Hibbert, D.B.; Zhao, C. Critical assessment of superbase-derived protic ionic liquids as electrolytes for electroChemical applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 298, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; Byrne, N.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H. Proton transport properties in zwitterion blends with Brønsted acids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16373–16380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hu, J.; Saak, W.; Beckhaus, R.; Wittstock, G.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Agert, C.; Conrad, O. Protic ionic liquid and ionic melts prepared from methanesulfonic acid and 1H-1,2,4-triazole as high temperature PEMFC electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10426–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshizawa, M.; Ogihara, W.; Ohno, H. Design of new ionic liquids by neutralization of imidazole derivatives with imide-type acids. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernicola, A.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B.; Tamada, M.; Ohno, H. New Types of Brönsted Acid–Base Ionic Liquids-Based Membranes for Applications in PEMFCs. ChemPhysChem 2007, 8, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Zou, Q. PhysicoChemical properties of new amide-based protic ionic liquids and their use as materials for anhydrous proton conductors. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Sun, B.; He, R. Preparation and characterization of new anhydrous, conducting membranes based on composites of ionic liquid trifluoroacetic propylamine and polymers of sulfonated poly (ether ether) ketone or polyvinylidenefluoride. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4428–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, D.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Marais, S.; Karademir, S.; Sanchez, J.-Y.; Iojoiu, C.; Martinez, M.; Mercier, R.; Judeinstein, P.; Chappey, C. High-Temperature Ionic-Conducting Material: Advanced Structure and Improved Performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15552–15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Conrad, O.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. PhysicoChemical properties of phosphonium-based and ammonium-based protic ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20574–20579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalia, B.S.; Sekhon, S.S. Polymer electrolytes containing ionic liquids with acidic counteranion (DMRImH2PO4, R = ethyl, butyl and oCtyl). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 425, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalsky, S.; Bardeau, J.-F.; Makhno, S.; Babkina, N.; Tarasyuk, O.; Cherniavska, T.; Orlovska, I.; Kozyrovska, N.; Brovko, O. New proton conducting membrane based on bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite film impregnated with guanidinium-based ionic liquid. Polymer 2018, 142, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Xin, Y.; Yin, Y.; Jungu; Zho, Z. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell working at elevated temperature with ionic liquid as electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 6115–6122. [Google Scholar]
- Brigouleix, C.; Anouti, M.; Jacquemin, J.; Caillon-Caravanier, M.; Galiano, H.; Lemordant, D. PhysicoChemical characterization of morpholinium cation based protic ionic liquids used as electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anouti, M.; Caillon-Caravanier, M.; Dridi, Y.; Galiano, H.; Lemordant, D. Synthesis and characterization of new pyrrolidinium based protic ionic liquids. Good and superionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13335–13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, M.A.B.H.; Noda, A.; Mitsushima, S.; Watanabe, M. Brønsted acid–base ionic liquids and their use as new materials for anhydrous proton conductors. Chem. Commun. 2003, 8, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, G.; Nogami, M. Inorganic–organic hybrid membranes with anhydrous proton conduction prepared from tetramethoxysilane/methyl-trimethoxysilane/trimethylphosphate and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide for H2/O2 fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; He, P.; Li, J. A Room-Temperature Ionic-Liquid-Templated Proton-Conducting Gelatinous Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17512–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, F.; Di, Z.; Gu, J. Anhydrous proton-conducting glass membranes doped with ionic liquid for intermediate-temperature fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 59, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Shirai, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Fuji, M. Study of intercalation compounds using ionic liquids into montmorillonite and their thermal stability. Solid State Ion. 2013, 241, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Nakamura, S.; Honda, Y.; Kinugawa, K.; Lee, S.-Y.; Watanabe, M. Effects of Polymer Structure on Properties of Sulfonated Polyimide/Protic Ionic Liquid Composite Membranes for Nonhumidified Fuel Cell Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, T.; Watanabe, M. Macromolecules in Ionic Liquids: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Ortiz, A.; Vilas, M.; Tojo, E.; Ortiz, I. Performance of PEMFC with new polyvinyl-ionic liquids based membranes as electrolytes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 3970–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Yuso, M.d.V.M.; Cuberes, M.T.; Romero, V.; Neves, L.; Coelhoso, I.; Crespo, J.G.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Benavente, J. Modification of a Nafion membrane by n-dodecyltrimethylammonium cation inclusion for potential application in DMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 4023–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noto, V.; Piga, M.; Giffin, G.A.; Lavina, S.; Smotkin, E.S.; Sanchez, J.-Y.; Iojoiu, C. Influence of Anions on Proton-Conducting Membranes Based on Neutralized Nafion 117, Triethylammonium Methanesulfonate, and Triethylammonium Perfluorobutanesulfonate. 1. Synthesis and Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jordan, L.R.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Acid–Organic base swollen polymer membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Iojoiu, C.; Espuche, E.; Gouanvé, F.; Gebel, G.; Mendil-Jakani, H.; Lyonnard, S.; Jestin, J. Proton Conducting Ionic Liquid Doped Nafion Membranes: Nano-Structuration, Transport Properties and Water Sorption. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24413–24423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Sikora, A.; Plíšková, M.; Mališ, J.; Mazúr, P.; Paidar, M.; Bouzek, K. Ion-conductive polymer membranes containing 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate and 1-ethylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iojoiu, C.; Martinez, M.; Hanna, M.; Molmeret, Y.; Cointeaux, L.; Leprêtre, J.-C.; El Kissi, N.; Guindet, J.; Judeinstein, P.; Sanchez, J.-Y. PILs-based Nafion membranes: A route to high-temperature PEFMCs dedicated to electric and hybrid vehicles. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, L.; da Trindade, L.G.; Bariviera, W.; Borba, K.M.N.; Santos, R.D.M.; Paganin, V.A.; de Oliveira, C.P.; Ticianelli, E.A.; Martini, E.M.A.; de Souza, M.O. 3-Triethylammonium propane sulfonate ionic liquids for Nafion-based composite membranes for PEM fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 6928–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Venkatnathan, A. Mechanism of Proton Transport in Ionic-Liquid-Doped Perfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 14449–14456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Gao, X.; Yan, X.; Gao, H.; Shi, L.; Jia, H.; Zheng, L. Preparation and Characterization of Nonaqueous Proton-Conducting Membranes with Protic Ionic Liquids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7626–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayumanasundaram, S.; Piga, M.; Lavina, S.; Negro, E.; Jeyapandian, M.; Ghassemzadeh, L.; Müller, K.; Di Noto, V. Hybrid inorganic–organic proton conducting membranes based on Nafion, SiO2 and triethylammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Mehio, N.; Tan, M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, G.; Dai, S.; Jin, X. More sustainable electricity generation in hot and dry fuel cells with a novel hybrid membrane of Nafion/nano-silica/hydroxyl ionic liquid. Appl. Energy 2016, 175, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.K.; Kuila, T.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Protic ionic liquid-functionalized mesoporous silica-based hybrid membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24366–24372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, J.; Kakati, N.; Woo, S.P.; Yoon, Y.S. Nafion® based hybrid composite membrane containing GO and dihydrogen phosphate functionalized ionic liquid for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 155, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epping Martin, K.; Kopasz, J.P. The U.S. DOEs High Temperature Membrane Effort. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandrasits, M.A.; Lindell, M.J.; Hamrock, S.J. New directions in perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acid–based proton-exchange membranes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 18, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, A.; Matic, A.; Jacobsson, P.; Börjesson, L.; Fernicola, A.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B.; Ohno, H. Physical Properties of Proton Conducting Membranes Based on a Protic Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 12462–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Nohira, T.; Hagiwara, R. Novel composite electrolyte membranes consisting of fluorohydrogenate ionic liquid and polymers for the unhumidified intermediate temperature fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, B.; Qi, L.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Gu, J.; Zou, Z. Impact of cation selection on proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance with trimethylethyl amide, ethylpyridinium and ethylmethyl imidazolium ionic liquid carried by poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane as electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.G.; Mohapatra, S.R. Perchloric acid functionalized nano-silica and protic ionic liquid based non-aqueous proton conductive polymer electrolytes. Mater. Lett. 2019, 251, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Kim, P.; Nahm, K.S.; Elizabeth, R.N. Structural characterization of PVdF-HFP/PEG/Al2O3 proton conducting membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, T.Y.; Doğan, H.; Unveren, E.E.; Eker, E. Sulfonated PEEK and fluorinated polymer based blends for fuel cell applications: Investigation of the effect of type and molecular weight of the fluorinated polymers on the membrane’s properties. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12038–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Kim, P.; Kim, A.R.; Nahm, K.S.; Elizabeth, R.N. Structural, thermal and ion transport studies of different particle size nanoComposite fillers incorporated PVdF-HFP hybrid membranes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. PVDF-HFP-based porous polymer electrolyte membranes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mališ, J.; Mazúr, P.; Schauer, J.; Paidar, M.; Bouzek, K. Polymer-supported 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate and 1-ethylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate as electrolytes for the high temperature PEM-type fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4697–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Olvera-Mancilla, J.; Alexandrova, L.; Felipe del Castillo, L.; Compañ, V. Recent Progress in the Development of Composite Membranes Based on Polybenzimidazole for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguizábal, A.; Lemus, J.; Pina, M.P. On the incorporation of protic ionic liquids imbibed in large pore zeolites to polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Ven, E.; Chairuna, A.; Merle, G.; Benito, S.P.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Ionic liquid doped polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.J.; Kodiweera, N.K.A.C.; Jayakody, J.R.P.; Greenbaum, S.G. New membranes based on ionic liquids for PEM fuel cells at elevated temperatures. J. Power Sources 2008, 178, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F.; Yu, S.; Shao, Z.; Yi, B. Ionic-Liquid-Based Proton Conducting Membranes for Anhydrous H2/Cl2 Fuel-Cell Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Cage-like cross-linked membranes with excellent ionic liquid retention and elevated proton conductivity for HT-PEMFCs. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguizábal, A.; Lemus, J.; Roda, V.; Urbiztondo, M.; Barreras, F.; Pina, M.P. Nanostructured electrolyte membranes based on zeotypes, protic ionic liquids and porous PBI membranes: Preparation, characterization and MEA testing. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 7221–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, J.; Eguizábal, A.; Pina, M.P. Endurance strategies for the preparation of high temperature polymer electrolyte membranes by UV polymerization of 1-H-3-vinylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 3981–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Eguizabal, A.; Mallada, R.; Pina, M.P. Constructing Straight Polyionic Liquid MicroChannels for Fast Anhydrous Proton Transport. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 35377–35389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Drobek, M.; Julbe, A.; Vriezekolk, E.J.; Mallada, R.; Pina, M.P. Hierarchical Porous Polybenzimidazole Microsieves: An Efficient Architecture for Anhydrous Proton Transport via Polyionic Liquids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14844–14857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawn, G.; Pace, G.; Lavina, S.; Vezzù, K.; Negro, E.; Bertasi, F.; Polizzi, S.; Di Noto, V. NanoComposite Membranes based on Polybenzimidazole and ZrO2 for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Scott, K. A polybenzimidazole/ionic-liquid-graphite-oxide composite membrane for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyari, K.; Javanbakht, M.; Adibi, M. Novel composite membranes based on PBI and dicationic ionic liquids for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 205, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Polybenzimidazole/ionic-liquid-functional silica composite membranes with improved proton conductivity for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothi, P.R.; Dharmalingam, S. An efficient proton conducting electrolyte membrane for high temperature fuel cell in aqueous-free medium. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L. Anhydrous conducting composite membranes composed of SPEEK/silica/ionic liquids for high-temperature proton exchange. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.J.R.; Carlos Dutra, J.; Gomes, A.d.S. Hybrid membranes of sulfonated poly ether ether ketone, ionic liquid and organically modified montmorillonite for proton exchange membranes with enhanced ionic conductivity and ionic liquid lixiviation protection. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. The influence of various ionic liquids on the properties of SPEEK membrane doped with mesoporous silica. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 257, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, J.A.F.L.; Dahmouche, K.; Sampaio, R.B.; Gomes, A.d.S. Structure and Properties of New sPEEK/Zirconia/Protic Ionic Liquid Membranes for Fuel Cell Application. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J. Fabrication and characterization of phosphoric acid doped imidazolium ionic liquid polymer composite membranes. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 206, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Trindade, L.G.; Zanchet, L.; Souza, J.C.; Leite, E.R.; Martini, E.M.A.; Pereira, E.C. Enhancement of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)-based proton exchange membranes doped with different ionic liquids cations. Ionics 2020, 26, 5661–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Ganesh, T.; Selvakumar, C.; Sangeetha, D. Phosphonate ionic liquid immobilised SBA-15/SPEEK composite membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2018, 1, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-K.; Wu, T.-Y.; Kuo, C.-W.; Peng, Y.-C.; Shih, I.-C.; Hao, L.; Sun, I.-W. 4,4′-Oxydianiline (ODA) containing sulfonated polyimide/protic ionic liquid composite membranes for anhydrous proton conduction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 11321–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligöz, H.; Yılmazoğlu, M. Development of a new highly conductive and thermomechanically stable complex membrane based on sulfonated polyimide/ionic liquid for high temperature anhydrous fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Fabrication of protic ionic liquid/sulfonated polyimide composite membranes for non-humidified fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5909–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-K.; Wong, J.-M.; Wu, T.-Y.; Chen, L.-C.; Shih, I.-C. Improving the Conductivity of Sulfonated Polyimides as Proton Exchange Membranes by Doping of a Protic Ionic Liquid. Polymers 2014, 6, 2720–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowsari, E.; Zare, A.; Ansari, V. Phosphoric acid-doped ionic liquid-functionalized graphene oxide/sulfonated polyimide composites as proton exchange membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 13964–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S.; Bao, X.; Zhao, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Q. Design of sepiolite-supported ionogel-embedded composite membranes without proton carrier wastage for wide-temperature-range operation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15288–15301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z. Organic-inorganic composite membrane based on sulfonated poly (arylene ether ketone sulfone) with excellent long-term stability for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Gaur, B. Polymer Electrolytes: Ionic Liquid Modified Phenolphthalein Based Hybrid Multiblock Poly (Arylene Ether) Copolymers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, H5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahi, A.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Langevin, D.; Chappey, C.; Rogalsky, S.P.; Tarasyuk, O.; Marais, S. Polyimide/ionic liquid composite membranes for fuel cells operating at high temperatures. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, M.; Abouzari-Lotf, E.; Nasef, M.M.; Ahmad, A.; Miyake, M.; Ting, T.M.; Sithambaranathan, P.; Ming, T.T. Fabrication and characterization of supported dual acidic ionic liquids for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, M.; Abouzari-Lotf, E.; Nasef, M.M.; Ahmad, A.; Ripin, A.; Ting, T.M.; Sithambaranathan, P. Preparation and characterization of highly stable protic-ionic-liquid membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 30732–30742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Huang, M. Anhydrous proton exchange membrane operated at 200 °C and a well-aligned anode catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16010–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wu, J.; Tang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. High-temperature proton exchange membranes from ionic liquid absorbed/doped superabsorbents. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 15836–15844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopade, S.A.; So, S.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Lodge, T.P. Anhydrous Proton Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Membranes via Polymerization-Induced Microphase Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6200–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Lin, B.; Yan, F.; Qiu, L.; Lu, J. Macromolecular protic ionic liquid-based proton-conducting membranes for anhydrous proton exchange membrane application. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 7979–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Yuan, W.; Xu, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Yuan, N.; Chu, F.; Ding, J. Protic ionic liquid/functionalized graphene oxide hybrid membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanganathan, U.; Nogami, M. Investigations on effects of the incorporation of various ionic liquids on PVA based hybrid membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zheng, L. Anhydrous proton exchange membranes at elevated temperatures: Effect of protic ionic liquids and crosslinker on proton conductivity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17683–17689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zou, G.; Fang, X.; Cong, C.; Zhou, Q. Effect of Methylimidazole Groups on the Performance of Poly(phenylene oxide) Based Membrane for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 10227–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Tremblay, A.Y.; Pell, W.; Letaief, S.; Burchell, T.J.; Peppley, B.A.; Ternan, M. Zirconium phosphate as the proton conducting material in direct hydrocarbon polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells operating above the boiling point of water. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Tremblay, A.Y.; Pell, W.; Letaief, S.; Liu, Y.; Peppley, B.A.; Ternan, M. A modified silicic acid (Si) and sulphuric acid (S)-ZrP/PTFE/glycerol composite membrane for high temperature direct hydrocarbon fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 224, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Tremblay, A.Y.; Pell, W.; Liu, Y.; Peppley, B.A.; Ternan, M. The effect of glycerol on the conductivity of Nafion-free ZrP/PTFE composite membrane electrolytes for direct hydrocarbon fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Zhu, Y.; Tawalbeh, M.; Tremblay, A.Y.; Ternan, M. Proton conductivity and morphology of new composite membranes based on zirconium phosphates, phosphotungstic acid, and silicic acid for direct hydrocarbon fuel cells applications. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Al-Othman, A.; Nancarrow, P.; Elsayed, Y.; Tawalbeh, M. Enhanced proton conduction in zirconium phosphate/ionic liquids materials for high-temperature fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 4857–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Nancarrow, P.; Tawalbeh, M.; Ka’Ki, A.; El-Ahwal, K.; El Taher, B.; Alkasrawi, M. Novel composite membrane based on zirconium phosphate-ionic liquids for high temperature PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 6100–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Ortiz, A.; Fernández-Stefanuto, V.; Tojo, E.; Colpaert, M.; Améduri, B.; Ortiz, I. Fuel cell electrolyte membranes based on copolymers of protic ionic liquid [HSO3-BVIm][TfO] with MMA and hPFSVE. Polymer Guildf 2019, 179, 121583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Poly tris (1-imidazolyl) benzene ionic liquids/Poly (2,6-dimethyl phenylene oxide) composite membranes for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11109–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, A.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Sayah, M.; Tawalbeh, M. Novel Composite Membranes Based on Polyaniline/Ionic Liquids for PEM Fuel Cells Applications. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 865, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.-Q.; Julius, D.; Hong, L.; Lee, J.-Y. PPO-based acid–base polymer blend membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gong, C.; Guan, R.; Zou, H.; Dai, H. Sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide) membranes as promising materials for new proton exchange membranes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, D.; Akcora, P. Ion-Containing Polymer-Grafted Nanoparticles in Ionic Liquids: Implications for Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 8108–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Xu, J.; Meng, L.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone sulfone) polymers by incorporating phosphotungstic acid-ionic-liquid-functionalized metal-organic framework. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 630, 119304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Ni, H.; Na, H. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone ketone sulfone) membranes for application in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Ikram Ben Belgacem, I.B.; Emoric, W.; Uzomad, P.C. Nafion degradation mechanisms in proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) system: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 27956–27973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell durability for vehicular applications: Degradation modes and experimental techniques. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 112022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, X.Z.; Martin, J.J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Wu, S.; Merida, W. A review of PEM fuel cell durability: Degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Ali Aboudzadeh, M.; Barandiaran, M.J.; Mecerreyes, D. Facile incorporation of natural carboxylic acids into polymers via polymerization of protic ionic liquids. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).