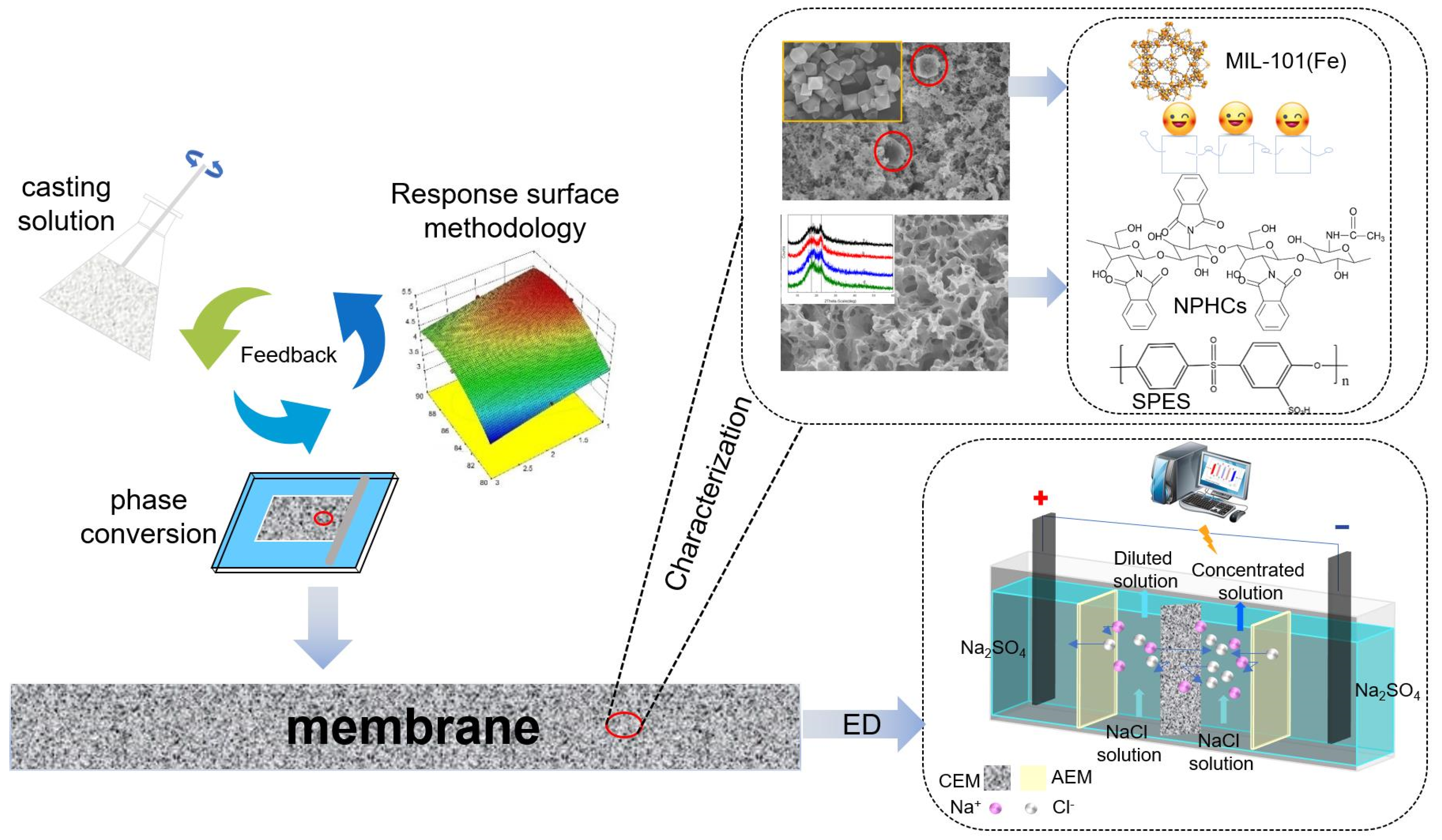
Fabrication of a Cation-Exchange Membrane via the Blending of SPES/N-Phthaloyl Chitosan/MIL-101(Fe) Using Response Surface Methodology for Desalination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MIL-101(Fe)
2.3. Preparation of Sulfonated Polyethersulfone and N-Phthaloyl Chitosan
2.4. Synthesis of Ion Exchange Membranes
2.5. Membrane Characterization
2.5.1. Characterization Method
2.5.2. Water Content and Hydrophilicity
2.5.3. Ion Exchange Capacity and Fixed Ion Concentration
2.5.4. Diffusion Coefficient and Electrochemical Properties of the Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
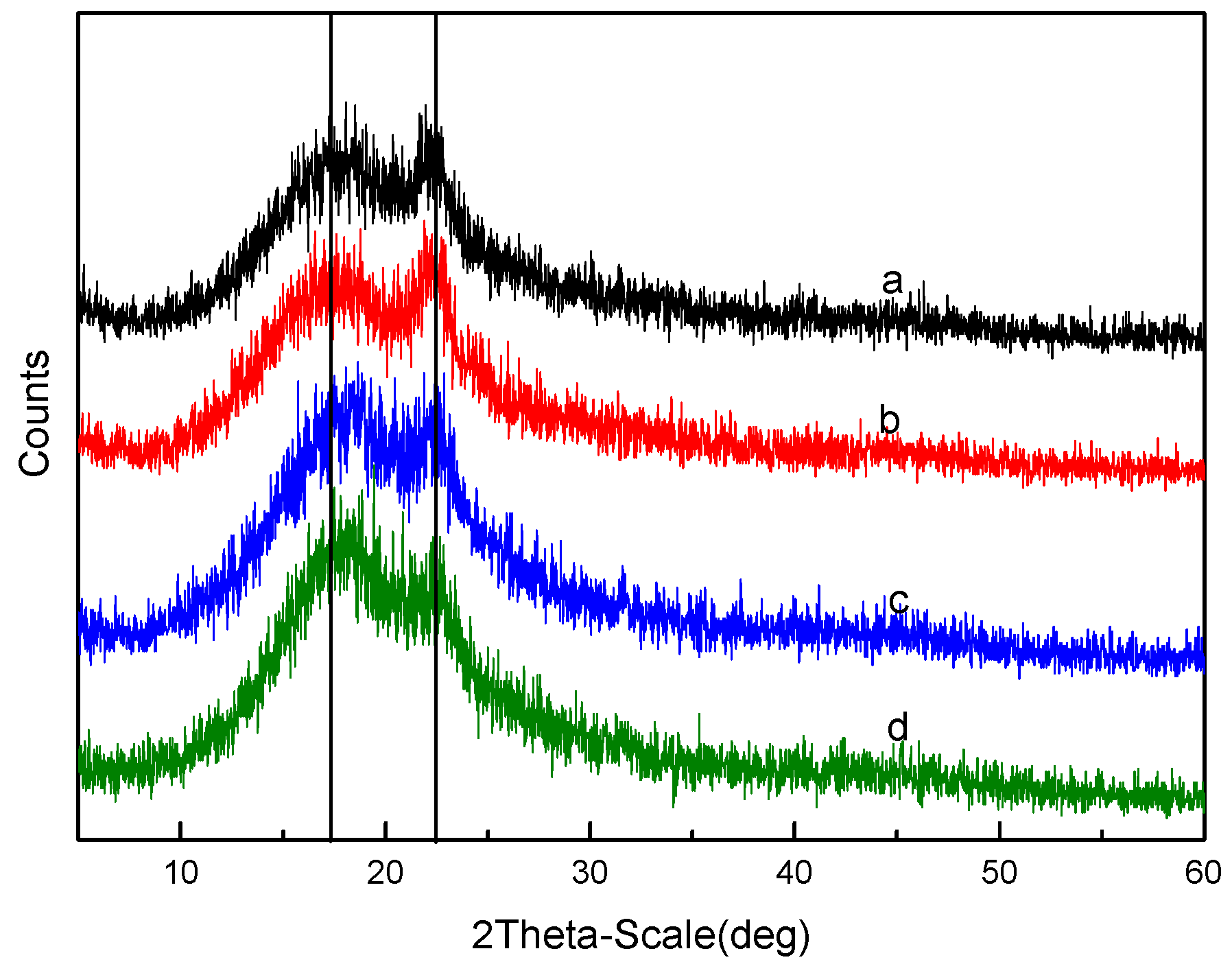
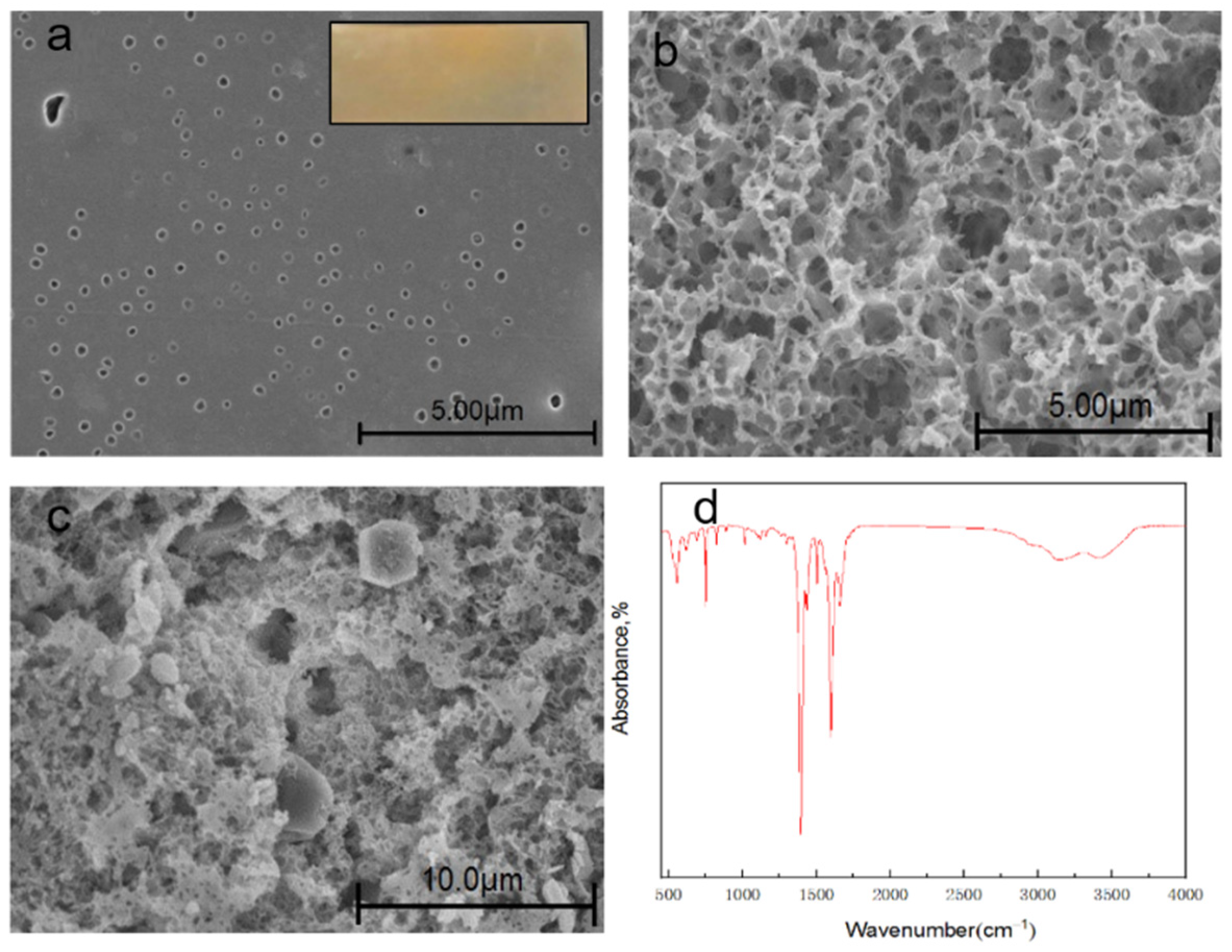
3.1. Characterization of MIL-101(Fe)
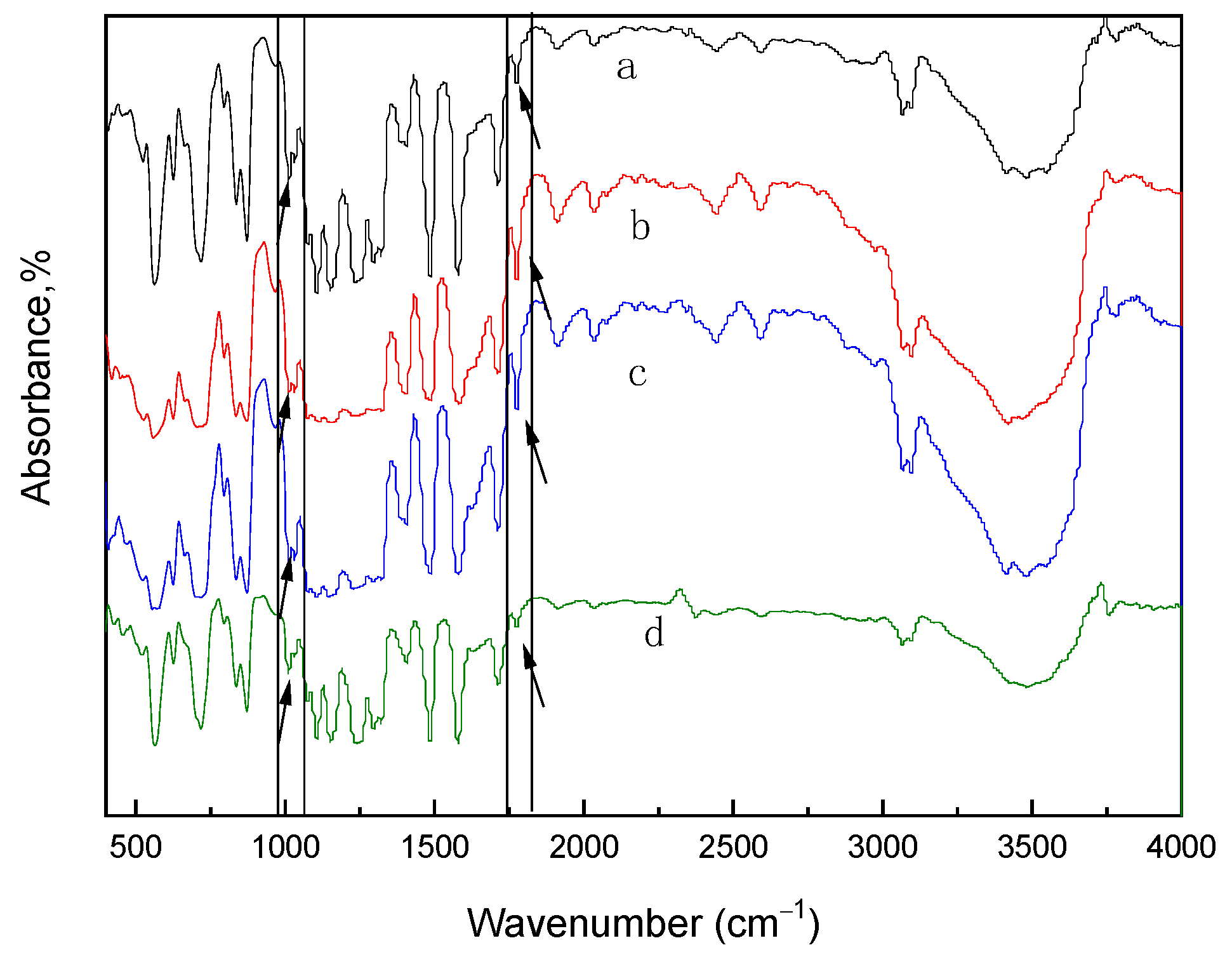
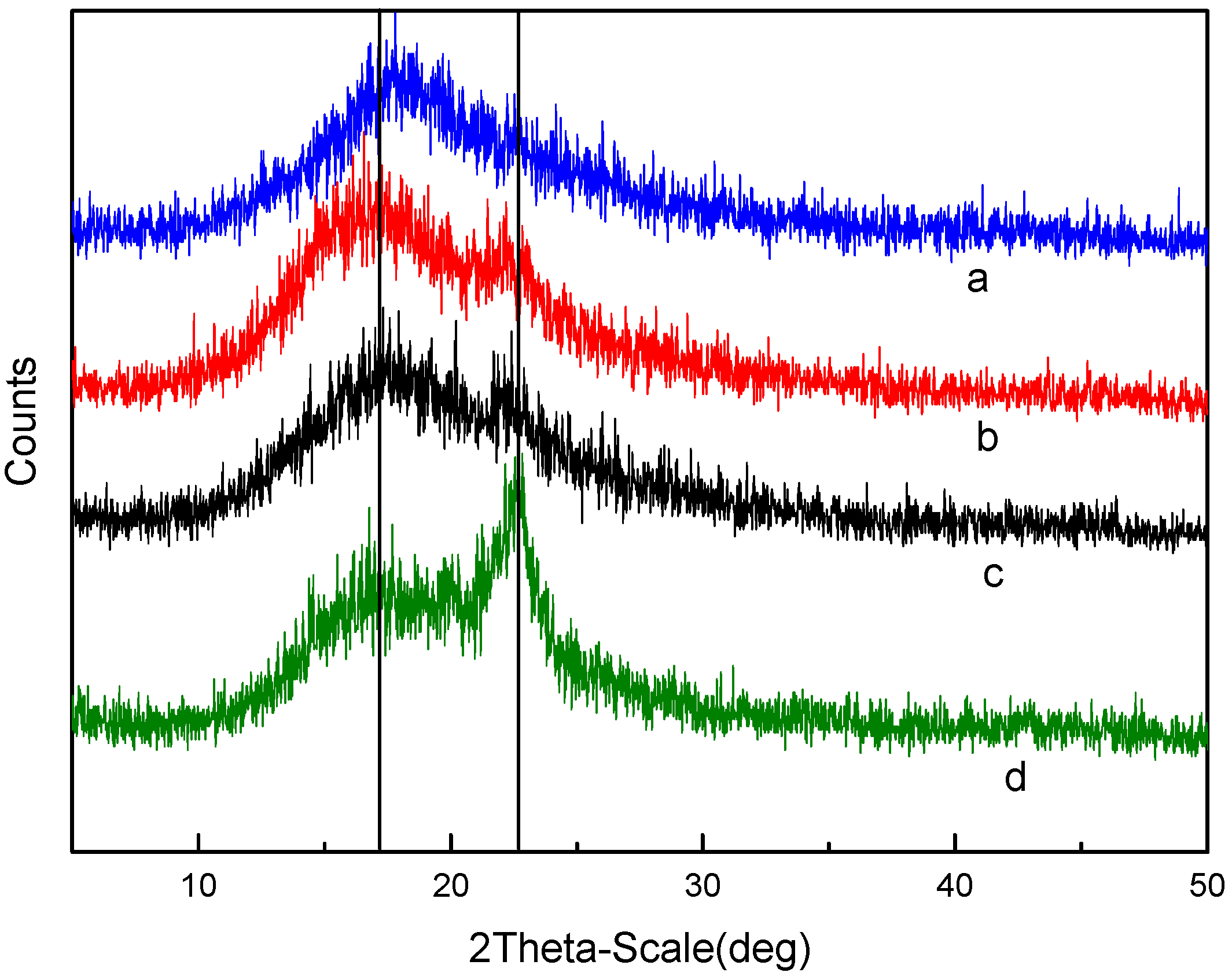
3.2. Characterization of Polymer Structure-Morphology (SPES and NPHCs)
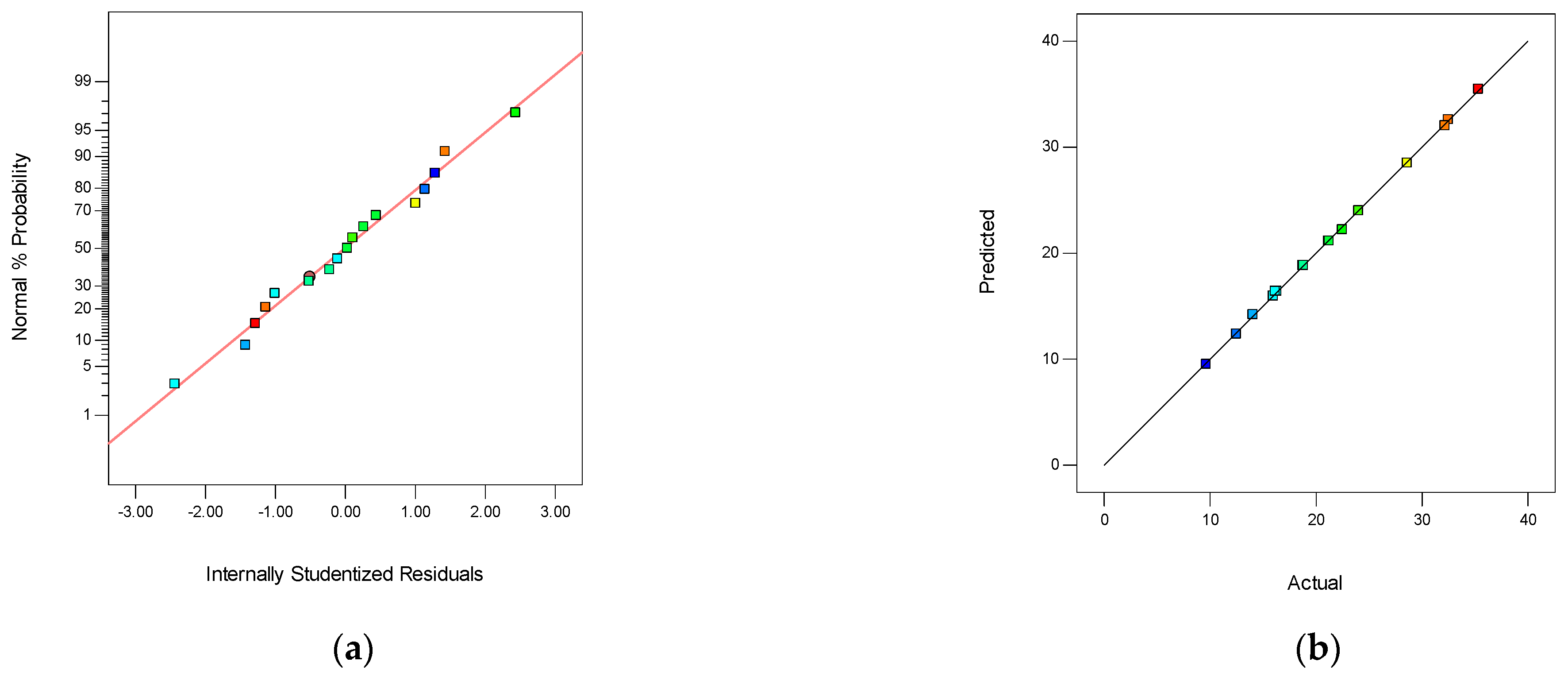
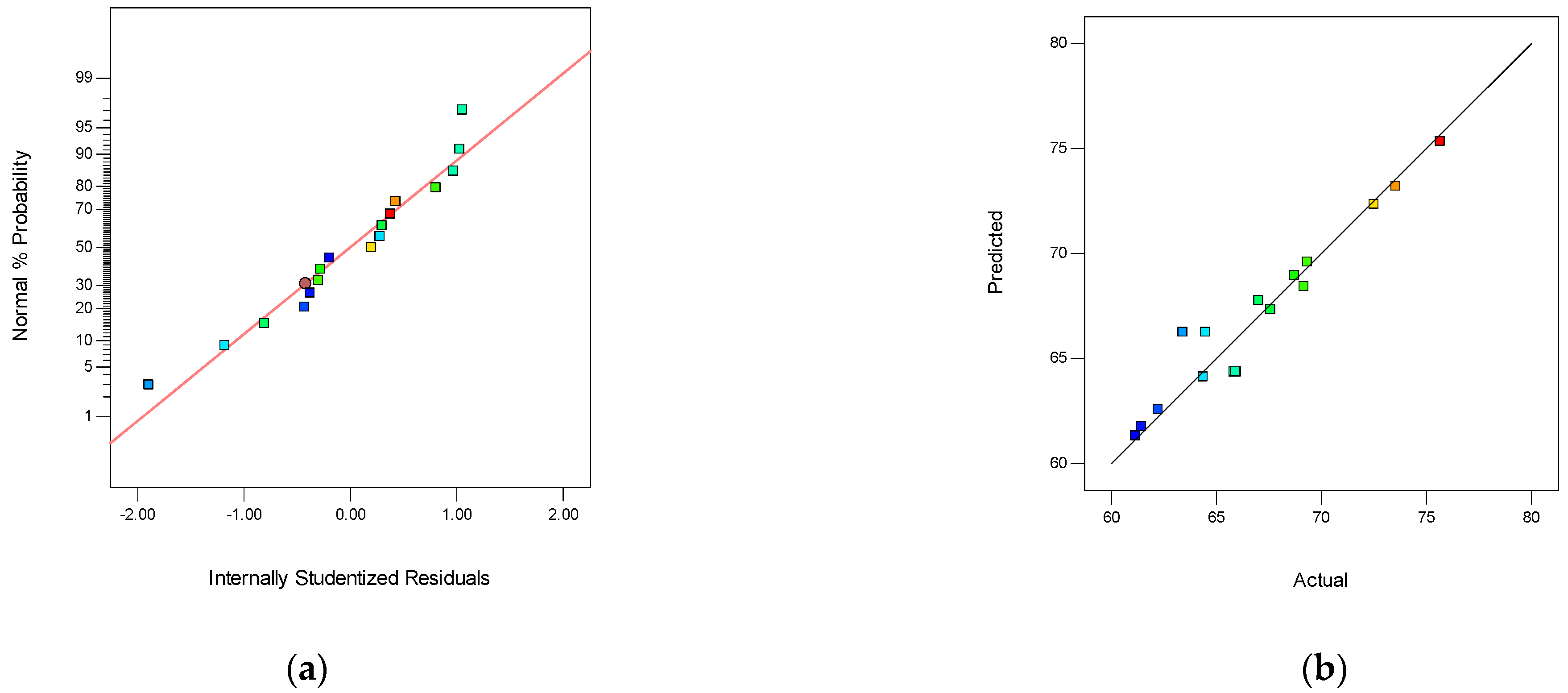
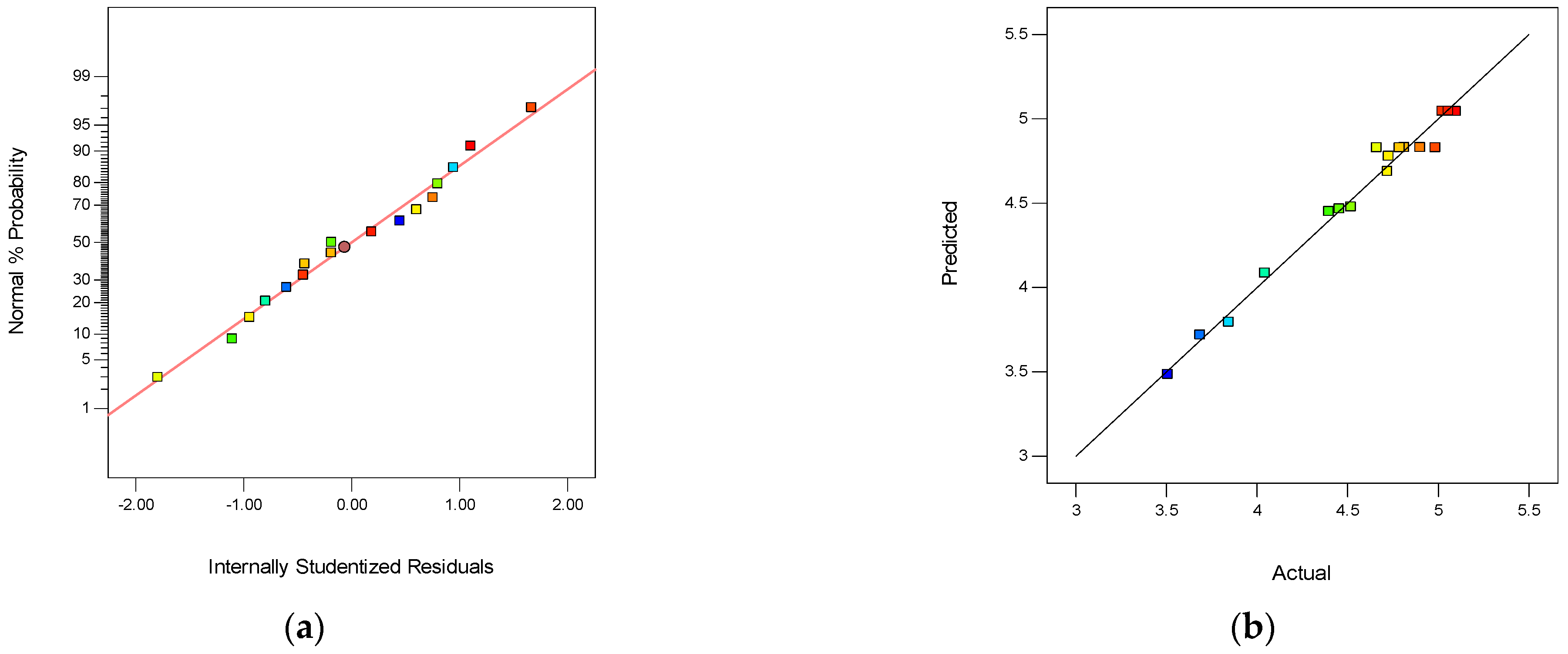
3.3. Optimization of the Procedure by RSM
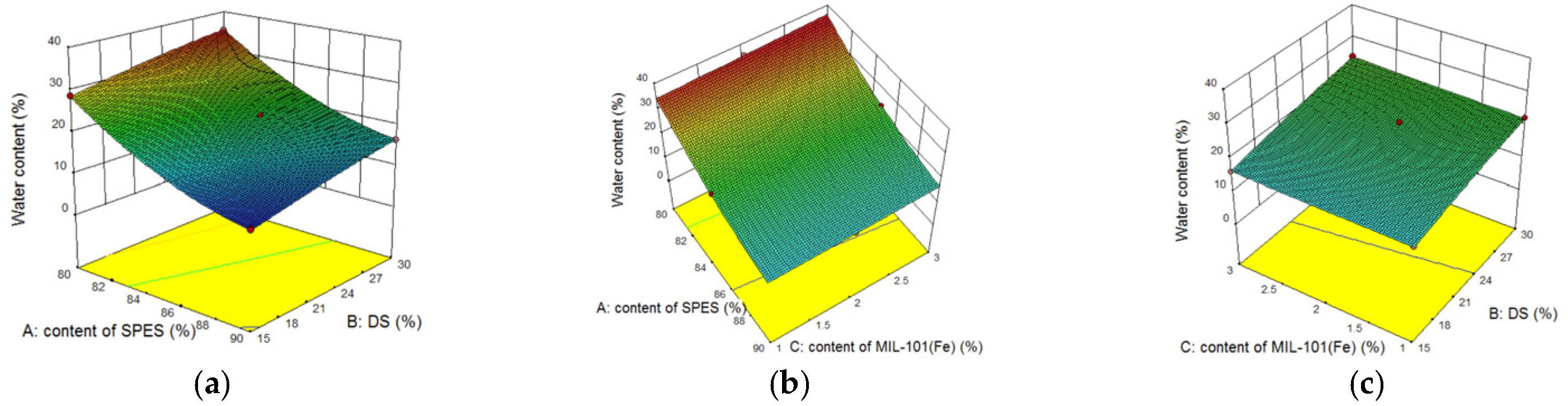
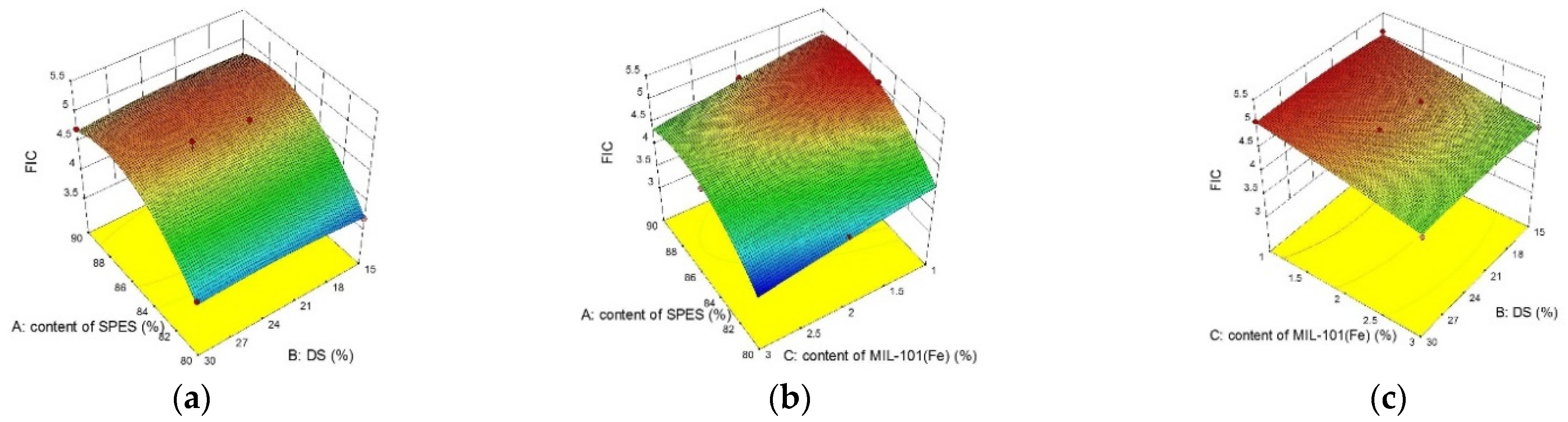
3.3.1. The Box–Behnken Surface Statistical Design on SPES/NPHCs/MIL-101(Fe) CEMs
3.3.2. Effect of MIL-101(Fe) Content on MIL-101(Fe) Hybrid Membrane
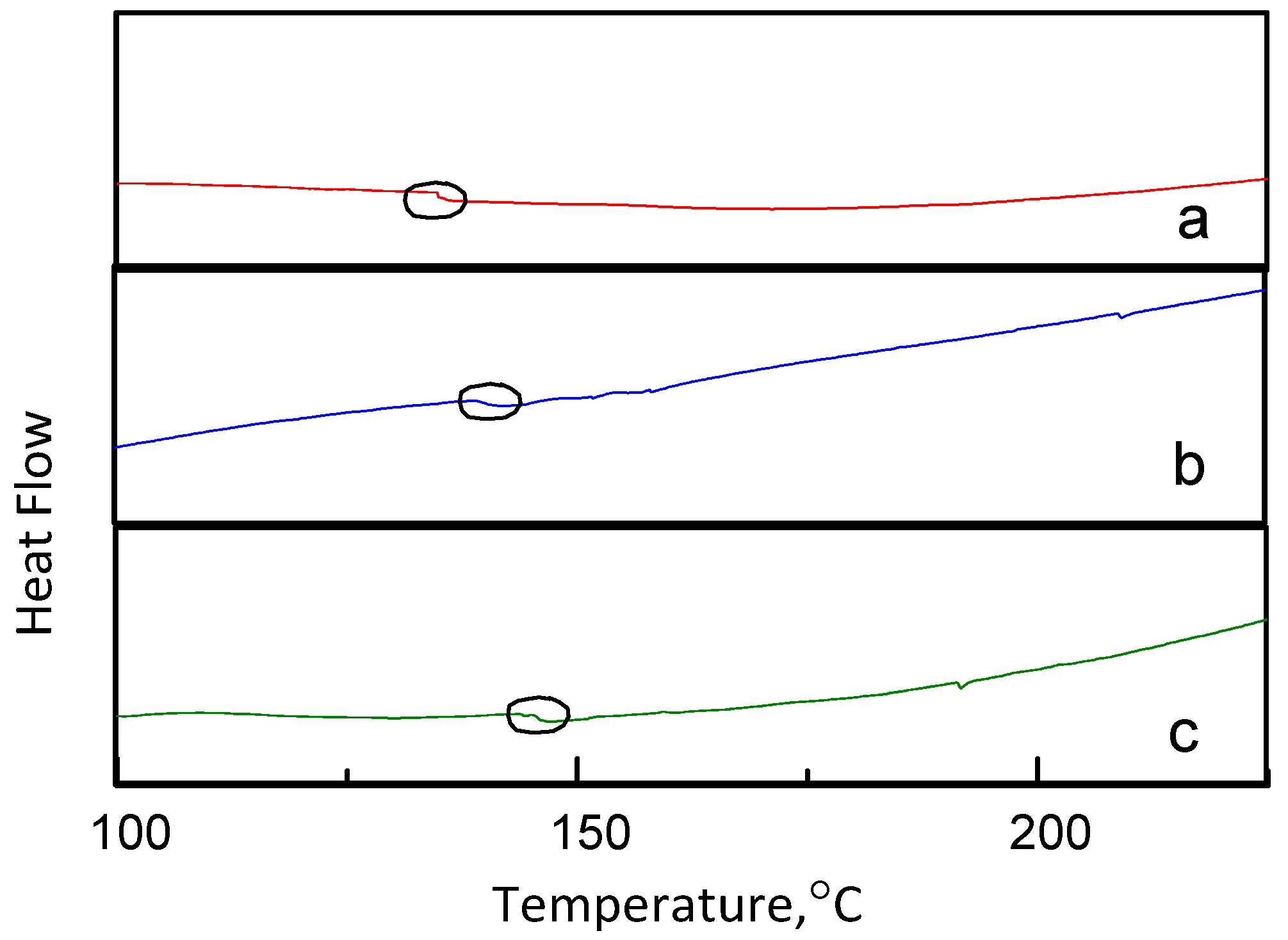
3.4. Membrane Structure—Thermal STABILITY
3.5. Membrane Structure-Morphology
3.6. Water Content, Ion-Exchange Capacity and Hydrophilicity
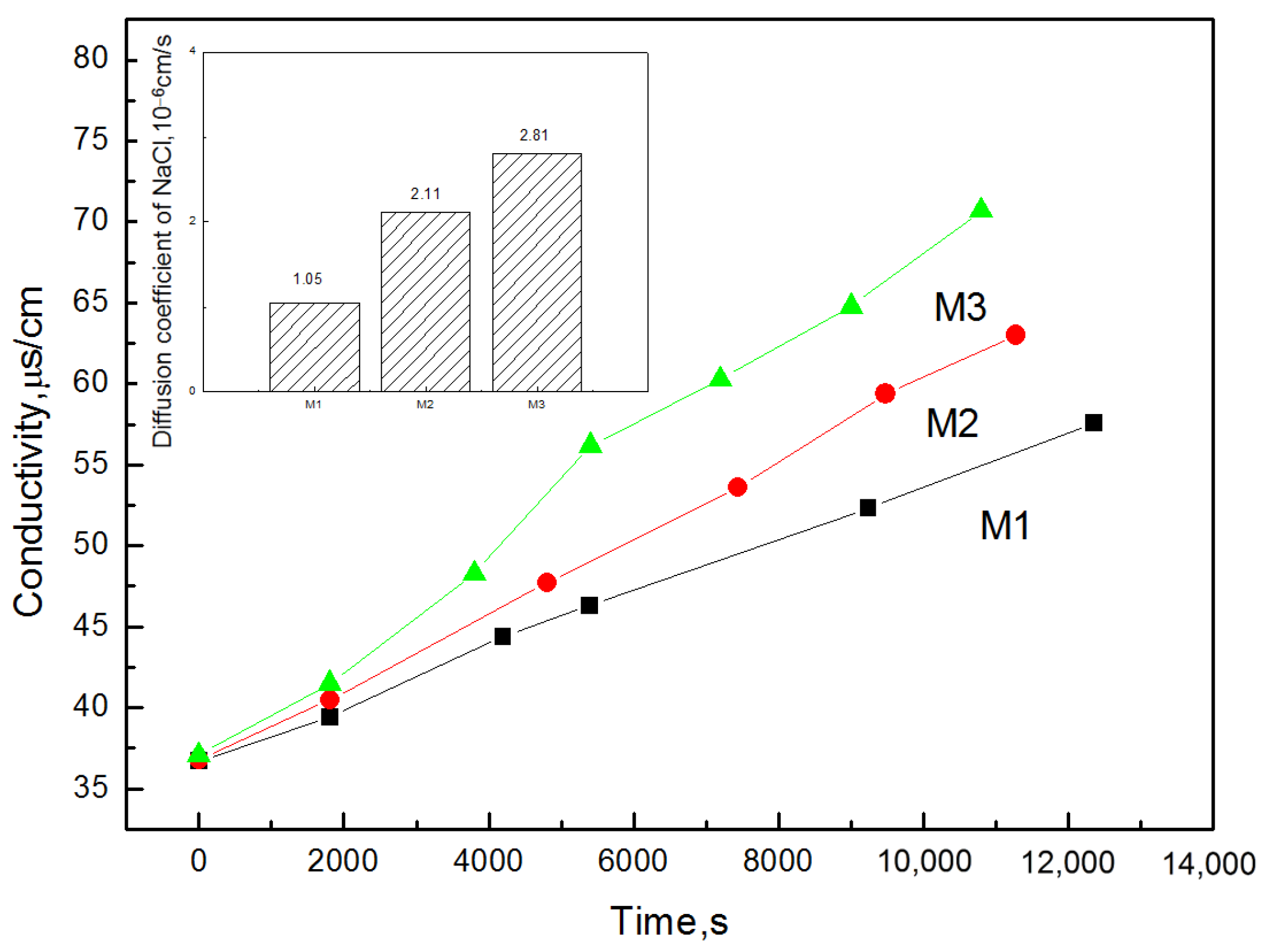
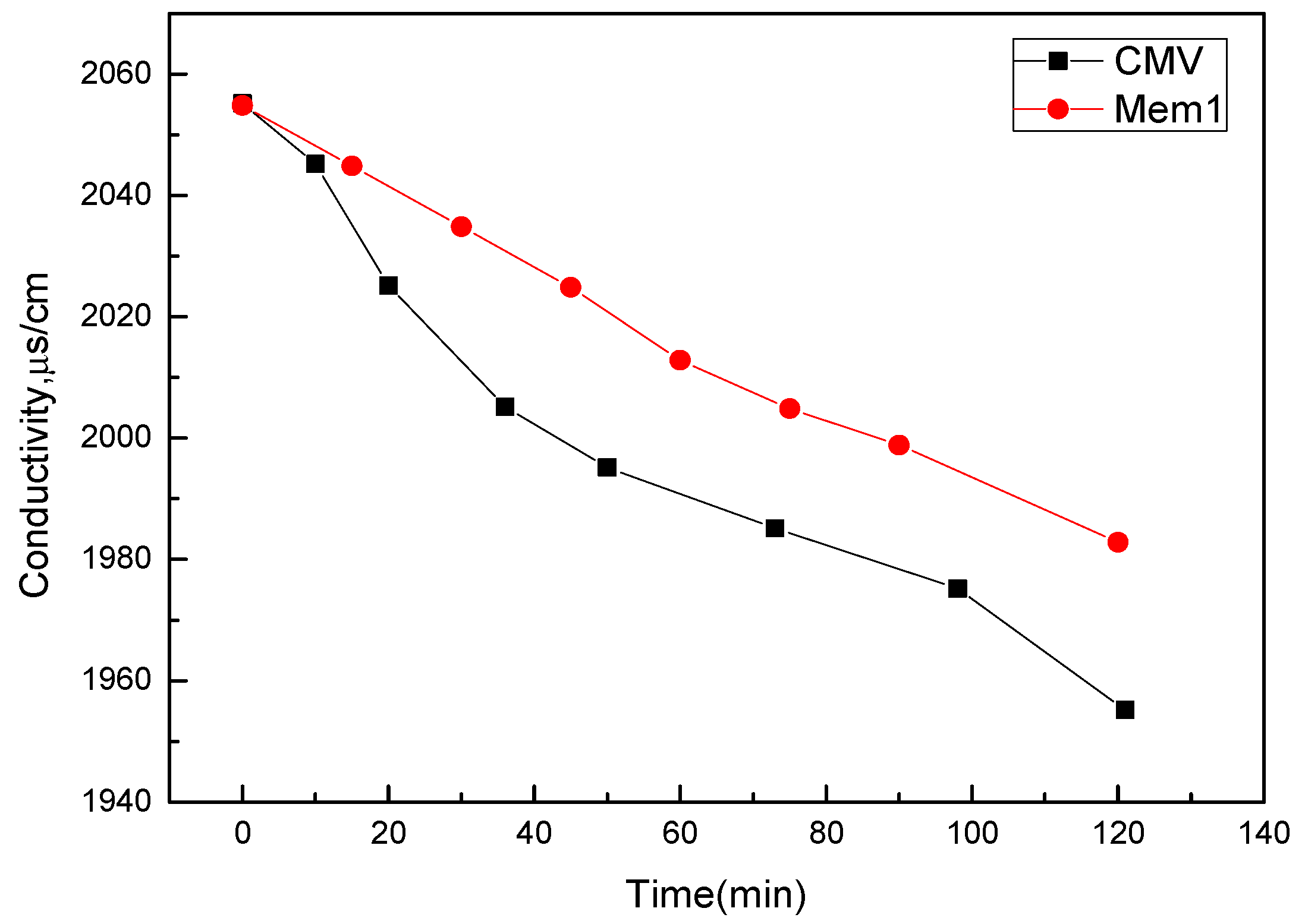
3.7. Membrane Porosity and Desalination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; et al. Fluoride removal from secondary effluent of the graphite industry using electrodialysis: Optimization with response surface methodology. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ma, M. Functionalized electrospun nanofiber membranes for water treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Chen, H.; Srinivasa Raghavan, D.S.; Ting, Y.-P. Removal behaviors of antibiotics in a hybrid microfiltration-forward osmotic membrane bioreactor for real municipal wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, X.; Meng, X.; Yu, G.; Wang, D. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using dithiocarbamate modified chitosan beads with Pb(II) as imprinted ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Improved desalination properties of hydrophobic GO-incorporated PVDF electrospun nanofibrous composites for vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ba, X.; Cui, N.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X. Preparation, characterisation, and desalination performance study of cellulose acetate membranes with MIL-53(Fe) additive. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.H.; Zhu, A.M.; Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L. Achieving efficient proton conduction in a MOF-based proton exchange membrane through an encapsulation strategy. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Xu, T. Optimization of electrodialysis with bipolar membranes by using response surface methodology. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Chew, J.W. Boron transfer during desalination by electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Techno-economic evaluation of preparing high-valued TPAOH from its low-cost bromide via electrodialysis metathesis (EDM). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Gao, X. Towards improved hydrodynamics of the electrodialysis (ED) cell via computational fluid dynamics and cost estimation model: Effects of spacer parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, J. Application of response surface methodology for modeling and optimization of lead (Pb (II)) removal from seaweed extracts via electrodialysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 179, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassady, H.J.; Cimino, E.C.; Kumar, M.; Hickner, M.A. Specific ion effects on the permselectivity of sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) cation exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 508, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Marschall, R.; Moon, S.-H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.Q.M.; Wang, L. Preparation of porous composite ion-exchange membranes for desalination application. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Moon, S.-H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.Q.M.; Wang, L. Preparation of porous ion-exchange membranes (IEMs) and their characterizations. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yue, B.; Yan, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. Proton conducting composite membranes based on sulfonated polysulfone and polysulfone-g-(phosphonated polystyrene) via controlled atom-transfer radical polymerization for fuel cell applications. Solid State Ion. 2019, 338, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Karkooti, A.; Liu, L.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Thundat, T.; Liu, Y.; Narain, R. Fabrication of antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone (PES)/cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Gao, J. Developing homogeneous ion exchange membranes derived from sulfonated polyethersulfone/N-phthaloyl-chitosan for improved hydrophilic and controllable porosity. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Rodríguez, G.; Torres-Rodríguez, L.M.; Montes-Rojas, A. Synthesis and characterization of commercial cation exchange membranes modified electrochemically by polypyrrole: Effect of synthesis conditions on the transport properties. Desalination 2017, 416, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Montoro, C.; Semsarilar, M. Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Alhassan, S.I.; Luo, Z.; Song, B.; Jin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Highly efficient fluoride removal from water using 2D metal-organic frameworks MIL-53(Al) with rich Al and O adsorptive centers. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 8, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Mamrol, N.; Yang, X.; Gao, C.; Bruggen, B.V. Metal-organic framework based membranes for selective separation of target ions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 634, 119407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, L.; Chiao, Y.H.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Qian, X. Cu(I/II) Metal-Organic Frameworks Incorporated Nanofiltration Membranes for Organic Solvent Separation. Membranes 2020, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, J.; Tong, Z.; Shen, C.; Meng, Q. Preparation of Amino-Functional UiO-66/PIMs Mixed Matrix Membranes with [bmim][Tf2N] as Regulator for Enhanced Gas Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Chang, B.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Yoon, J.; Choi, J.W. Battery Electrode Materials with Omnivalent Cation Storage for Fast and Charge-Efficient Ion Removal of Asymmetric Capacitive Deionization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Kaushal, J.; Srivastav, A.L.; Mahajan, P. A critical review on recent developments in MOF adsorbents for the elimination of toxic heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2020, 27, 44771–44796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ren, Y.; Zhai, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Hua, M.; Lv, L.; Pan, B. Integrating cationic metal-organic frameworks with ultrafiltration membrane for selective removal of perchlorate from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 381, 120961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S.; Mishra, B.K.; Giles, D.E.; Singh, P. Review of fluoride removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z. Selective adsorption of Pb (II) over the zinc-based MOFs in aqueous solution-kinetics, isotherms, and the ion exchange mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2017, 24, 14198–14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Pan, N.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Liao, J.; Shen, J. Functional UiO-66 Series Membranes with High Perm Selectivity of Monovalent and Bivalent Anions for Electrodialysis Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4086–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Velasco, G.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L.; Escamilla-Coronado, M.; Turnes-Palomino, G.; Palomino-Cabello, C.; Guzman-Mar, J.L. Iron metal-organic framework supported in a polymeric membrane for solid-phase extraction of anti-inflammatory drugs. Anal Chim. Acta 2020, 1136, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, A.M.; Lin, C.S.K.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Vargas, C.; Luque, R. Iron oxide functionalised MIL-101 materials in aqueous phase selective oxidations. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2013, 455, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, Z.; Luo, F. Ultrahigh uranium extraction performance of COFs/SPES mixed matrix membranes at acidic medium. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 288, 121364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, V.B.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Preparation and characterization of porous polyethersulfone (PES) membranes with improved biocompatibility by blending sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) and cellulose acetate (CA)–A comparative study. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, P.; Pang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wen, L. Engineered PES/SPES nanochannel membrane for salinity gradient power generation. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumeenal, A.; Neelakandan, S.; Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A. Synthesis and properties of novel proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated polyethersulfone and N-phthaloyl chitosan blends for DMFC applications. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarango, L.; Paseta, L.; Navarro, M.; Zornoza, B.; Coronas, J. Controlled deposition of MOFs by dip-coating in thin film nanocomposite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anahidzade, N.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Dinari, M.; Firouz Tadavani, K.; Zhiani, M. Metal-organic framework anchored sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) as a high temperature proton exchange membrane for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploegmakers, J.; Japip, S.; Nijmeijer, K. Mixed matrix membranes containing MOFs for ethylene/ethane separation—Part B: Effect of Cu3BTC2 on membrane transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Lu, X.; Jia, Z. Adjustable pervaporation performance of Zr-MOF/poly(vinyl alcohol) mixed matrix membranes. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2019, 94, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirehpour, A.; Rahimpour, A.; Ulbricht, M. Nano-sized metal organic framework to improve the structural properties and desalination performance of thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Thanh, H.T.; Thu Phuong, T.T.; Le Hang, P.T.; Tam Toan, T.T.; Tuyen, T.N.; Mau, T.X.; Khieu, D.Q. Comparative study of Pb(II) adsorption onto MIL–101 and Fe–MIL–101 from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Devi, A.; Muthumeenal, A.; Sabarathinam, R.M.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication and electrochemical properties of SPVdF-co-HFP/SPES blend proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavangar, T.; Hemmati, A.; Karimi, M.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F. Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide (GO) on sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) substrate for effective dye removal. Polym. Bull. 2018, 76, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y. Separation of mixed amino acids by BMED process using porous SPES and SPSf cation exchange membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C. Accessing of graphene oxide (GO) nanofiltration membranes for microbial and fouling resistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Zhao, Y.; Molina, S.; García-Calvo, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Alternating current enhanced deposition of a monovalent selective coating for anion exchange membranes with antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Gao, J. Response surface modeling and optimization of electrodialysis for reclamation of RO concentrates in coal-fired power plants. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Assay | A-SPES Content (%) | B-DS (%) | C-MIL-101(Fe) Content (%) | Response | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1: WC (%) | Y2: IEC (mM/g) | Y3: Contact Angle (±2°) | Y4: FIC | ||||
| 1 | 85 | 25 | 2 | 21.23 | 1.02 | 65.92 | 4.79 |
| 2 | 80 | 30 | 2 | 35.33 | 1.36 | 61.44 | 3.85 |
| 3 | 80 | 25 | 1 | 32.48 | 1.31 | 64.37 | 4.04 |
| 4 | 80 | 20 | 3 | 32.16 | 1.13 | 61.15 | 3.51 |
| 5 | 85 | 20 | 2 | 18.80 | 0.92 | 64.48 | 4.90 |
| 6 | 85 | 25 | 2 | 21.16 | 1.05 | 65.84 | 4.98 |
| 7 | 90 | 30 | 2 | 16.30 | 0.77 | 69.33 | 4.72 |
| 8 | 90 | 25 | 1 | 14.05 | 0.71 | 72.51 | 5.02 |
| 9 | 85 | 15 | 1 | 15.95 | 0.81 | 73.55 | 5.10 |
| 10 | 90 | 15 | 2 | 9.65 | 0.46 | 75.67 | 4.73 |
| 11 | 85 | 30 | 3 | 24.01 | 1.06 | 62.23 | 4.40 |
| 12 | 85 | 15 | 3 | 16.14 | 0.72 | 69.17 | 4.45 |
| 13 | 85 | 30 | 1 | 22.48 | 1.14 | 67.01 | 5.06 |
| 14 | 85 | 20 | 2 | 18.75 | 0.90 | 63.40 | 4.81 |
| 15 | 90 | 20 | 3 | 12.49 | 0.56 | 68.71 | 4.52 |
| 16 | 80 | 15 | 2 | 28.61 | 1.05 | 67.58 | 3.69 |
| 17 | 85 | 25 | 2 | 21.20 | 0.99 | 65.96 | 4.66 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Probe > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 860.62 | 9 | 95.62 | 2338.01 | <0.0001 | highly significant |
| A-content of SPES | 723.83 | 1 | 723.83 | 17,697.52 | <0.0001 | |
| B-DS | 104.97 | 1 | 104.97 | 2566.48 | <0.0001 | |
| C-content of MIL-101(Fe) | 2.42 | 1 | 2.42 | 59.05 | 0.0001 | |
| AB | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.025 | 0.8795 | |
| AC | 0.36 | 1 | 0.36 | 8.92 | 0.0203 | |
| BC | 0.45 | 1 | 0.45 | 11.07 | 0.0126 | |
| A2 | 33.59 | 1 | 33.59 | 821.17 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 0.63 | 1 | 0.63 | 15.38 | 0.0057 | |
| C2 | 0.007 | 1 | 7.019 × 10−3 | 0.17 | 0.6911 | |
| Residual | 0.29 | 7 | 0.041 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.28 | 4 | 0.071 | 50.67 | 0.0044 | |
| Pure Error | 0.004 | 3 | 0.001 | |||
| Cor Total | 860.91 | 16 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Probe > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.96 | 9 | 0.11 | 237.40 | <0.0001 | highly significant |
| A-content of SPES | 0.70 | 1 | 0.70 | 1549.59 | <0.0001 | |
| B-DS | 0.22 | 1 | 0.22 | 490.62 | <0.0001 | |
| C-content of MIL-101(Fe) | 0.010 | 1 | 0.010 | 22.90 | 0.0020 | |
| AB | 0.00002 | 1 | 2.256 × 10−5 | 0.050 | 0.8290 | |
| AC | 0.00005 | 1 | 4.879 × 10−4 | 1.09 | 0.3319 | |
| BC | 0.00004 | 1 | 4.422 × 10−5 | 0.098 | 0.7628 | |
| A2 | 0.00351 | 1 | 3.512 × 10−3 | 7.82 | 0.0266 | |
| B2 | 0.00300 | 1 | 3.001 × 10−3 | 6.68 | 0.0362 | |
| C2 | 0.000245 | 1 | 2.461 × 10−4 | 0.55 | 0.4832 | |
| Residual | 0.00314 | 7 | 4.490 × 10−4 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.00074 | 4 | 1.841 × 10−4 | 0.23 | 0.9055 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 0.00241 | 3 | 8.022 × 10−4 | |||
| Cor Total | 0.96 | 16 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Probe > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 259.33 | 9 | 28.81 | 9.97 | 0.0031 | significant |
| A-content of SPES | 125.49 | 1 | 125.49 | 43.43 | 0.0003 | |
| B-DS | 69.96 | 1 | 69.96 | 24.21 | 0.0017 | |
| C-content of MIL-101(Fe) | 48.50 | 1 | 48.50 | 16.78 | 0.0046 | |
| AB | 0.009 | 1 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.9570 | |
| AC | 0.094 | 1 | 0.094 | 0.032 | 0.8623 | |
| BC | 0.041 | 1 | 0.041 | 0.014 | 0.9081 | |
| A2 | 3.54 | 1 | 3.54 | 1.22 | 0.3052 | |
| B2 | 21.02 | 1 | 21.02 | 7.27 | 0.0308 | |
| C2 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.70 | 0.24 | 0.6370 | |
| Residual | 20.23 | 7 | 2.89 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 19.64 | 4 | 4.91 | 25.22 | 0.0121 | |
| Pure Error | 0.58 | 3 | 0.19 | |||
| Cor Total | 279.56 | 16 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Probe > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3.83 | 9 | 0.43 | 38.59 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-content of SPES | 1.91 | 1 | 1.91 | 172.93 | <0.0001 | |
| B-DS | 1.044 × 10−4 | 1 | 1.044 × 10−4 | 9.463 × 10−3 | 0.9252 | |
| C-content of MIL-101(Fe) | 0.67 | 1 | 0.67 | 60.86 | 0.0001 | |
| AB | 6.943 × 10−3 | 1 | 6.943 × 10−3 | 0.63 | 0.4536 | |
| AC | 1.246 × 10−4 | 1 | 1.246 × 10−4 | 0.011 | 0.9183 | |
| BC | 6.956 × 10−5 | 1 | 6.956 × 10−5 | 6.308 × 10−3 | 0.9389 | |
| A2 | 1.16 | 1 | 1.16 | 104.95 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 0.011 | 1 | 0.011 | 1.03 | 0.3440 | |
| C2 | 2.635 × 10−3 | 1 | 2.635 × 10−3 | 0.24 | 0.6399 | |
| Residual | 0.077 | 7 | 0.011 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.020 | 4 | 5.049 × 10−3 | 0.27 | 0.8835 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 0.057 | 3 | 0.019 | |||
| Cor Total | 3.91 | 16 |
| Membrane | Water Content % | IEC (mM·g−1) | Contact Angle(°) | FIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (SPES + NPHCs): MOFs 100:0 | 21.90 | 1.14 | 67.96 ± 2 | 5.21 |
| (SPES + NPHCs): MOFs 99:1 | 22.41 | 1.29 | 65.43 ± 2 | 5.76 |
| (SPES + NPHCs): MOFs 98:2 | 24.62 | 1.37 | 63.21 ± 2 | 5.56 |
| (SPES + NPHCs): MOFs 97:3 | 26.73 | 1.54 | 60.45 ± 2 | 5.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; Xue, J.; Gao, X. Fabrication of a Cation-Exchange Membrane via the Blending of SPES/N-Phthaloyl Chitosan/MIL-101(Fe) Using Response Surface Methodology for Desalination. Membranes 2022, 12, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020144
Wang X, Wang Q, Zhao M, Zhang L, Ji X, Sun H, Sun Y, Ma Z, Xue J, Gao X. Fabrication of a Cation-Exchange Membrane via the Blending of SPES/N-Phthaloyl Chitosan/MIL-101(Fe) Using Response Surface Methodology for Desalination. Membranes. 2022; 12(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaomeng, Qun Wang, Mengjuan Zhao, Lu Zhang, Xiaosheng Ji, Hui Sun, Yongchao Sun, Zhun Ma, Jianliang Xue, and Xueli Gao. 2022. "Fabrication of a Cation-Exchange Membrane via the Blending of SPES/N-Phthaloyl Chitosan/MIL-101(Fe) Using Response Surface Methodology for Desalination" Membranes 12, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020144
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Q., Zhao, M., Zhang, L., Ji, X., Sun, H., Sun, Y., Ma, Z., Xue, J., & Gao, X. (2022). Fabrication of a Cation-Exchange Membrane via the Blending of SPES/N-Phthaloyl Chitosan/MIL-101(Fe) Using Response Surface Methodology for Desalination. Membranes, 12(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020144








