Current–Voltage Characteristics and Solvent Dissociation of Bipolar Membranes in Organic Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Current–Voltage Characteristics and pH Change Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
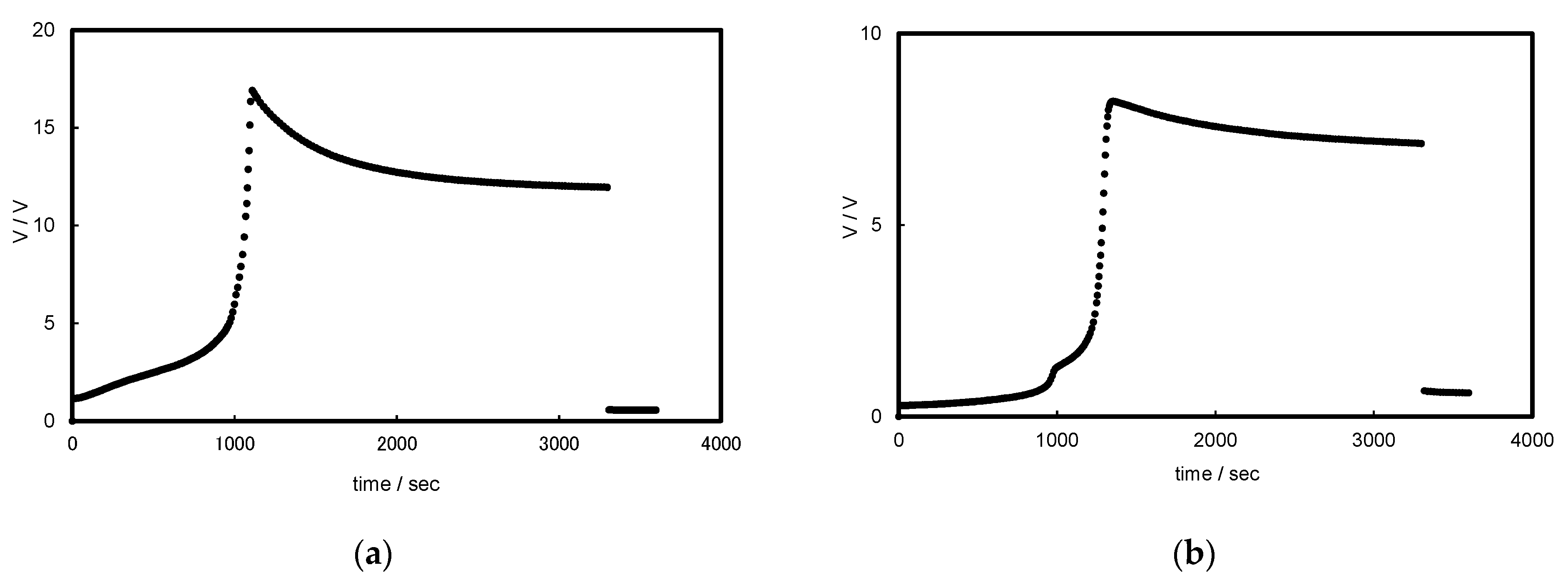
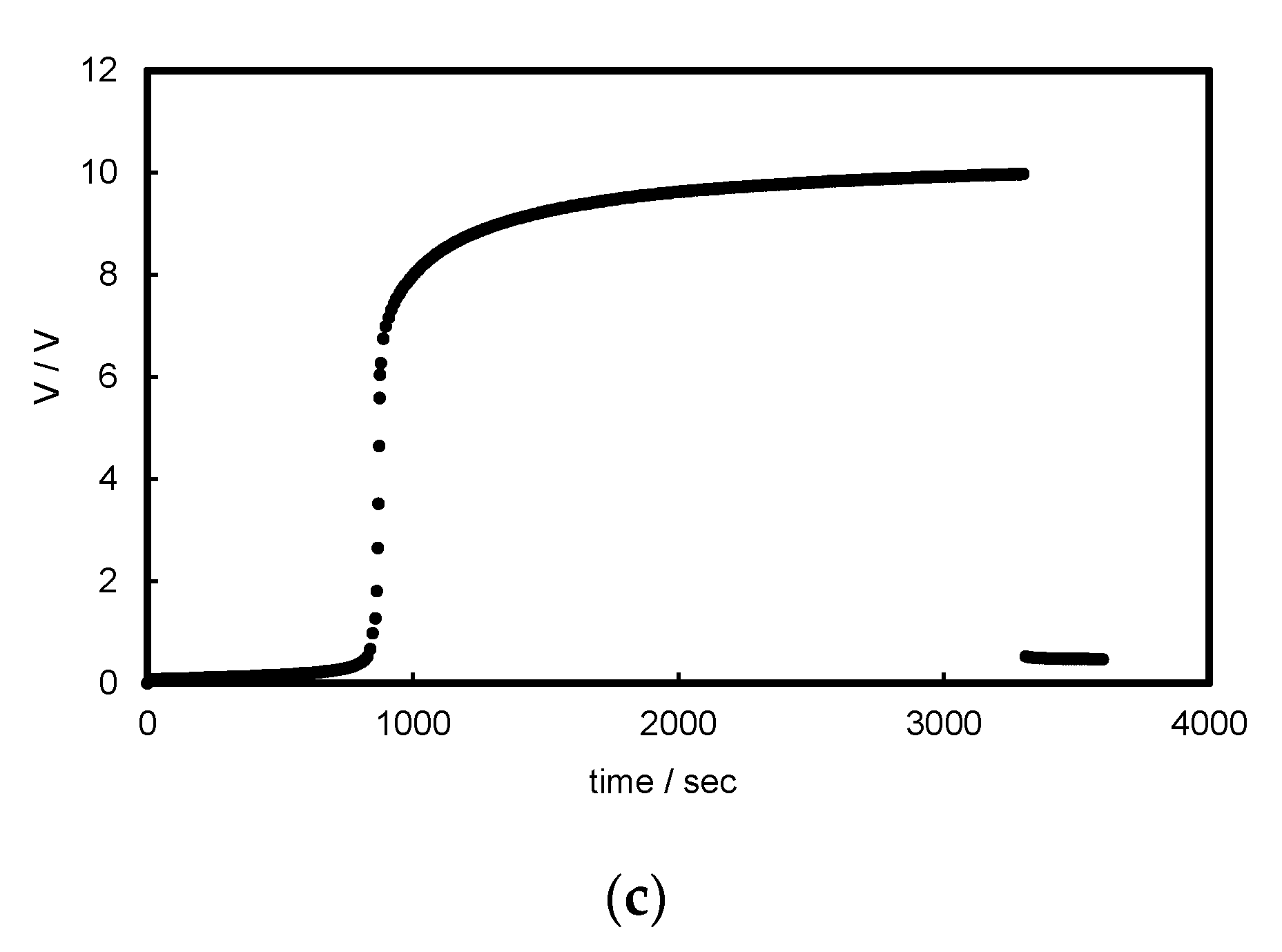
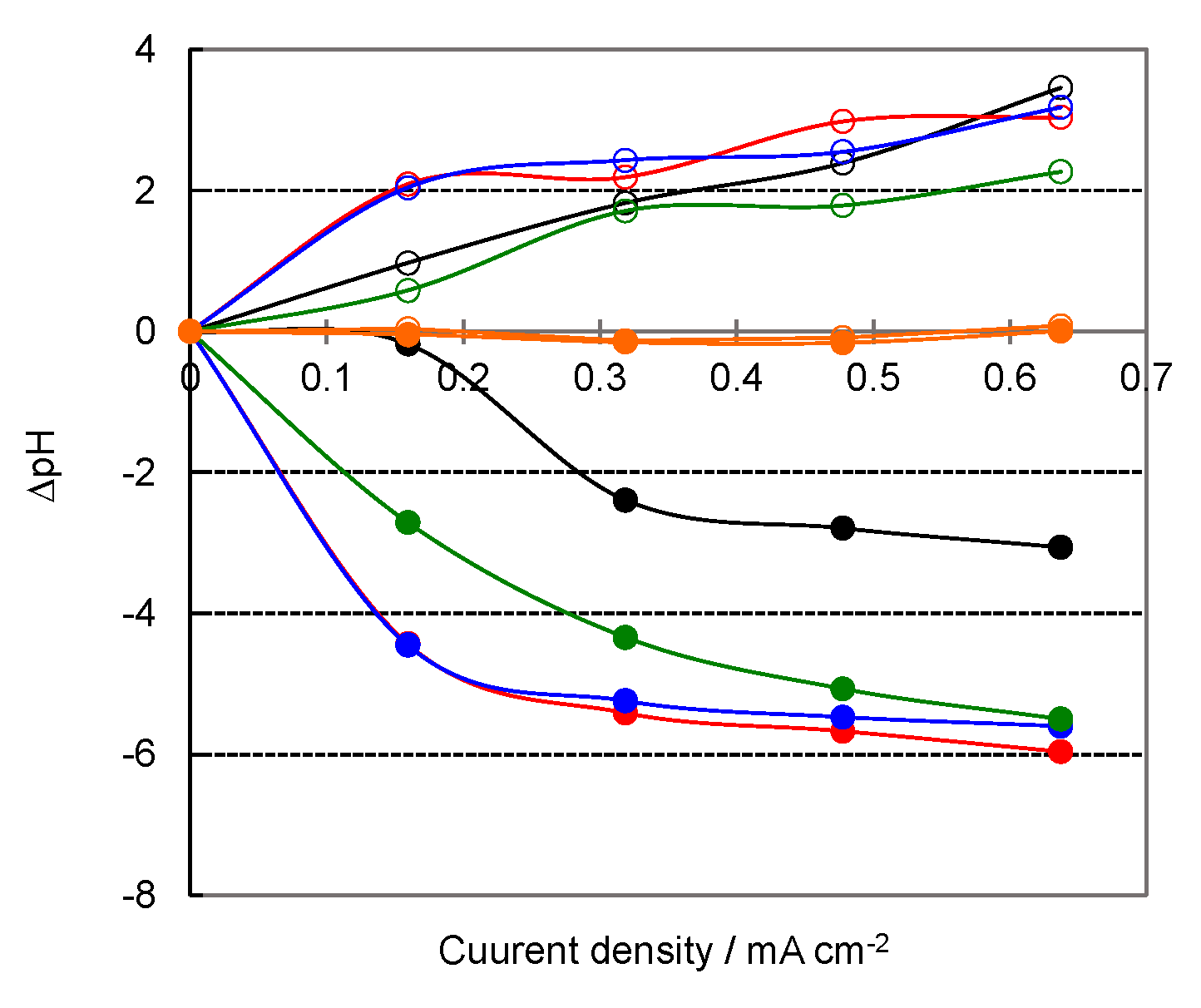
3.1. Chronopotentiograms and pH Changes in BPM/Organic Solvent Systems
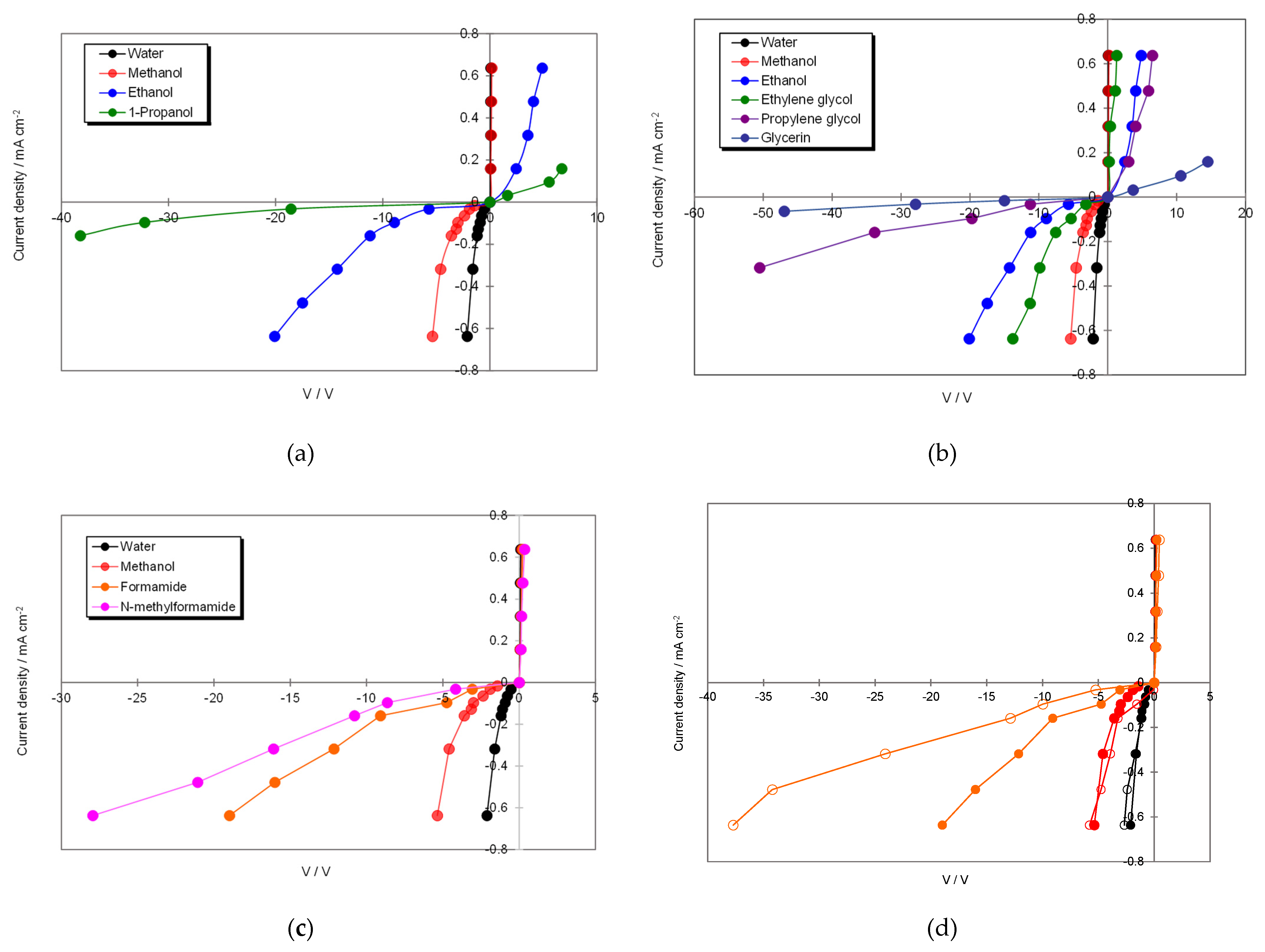
3.2. Current–Voltage Characteristics in BPM/Organic Solvent Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frilette, V.J. Preparation and characterization of bipolar ion exchange membranes. J. Phys. Chem. 1956, 60, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemperman, A.J.B. (Ed.) Handbook on Bipolar Membrane Technology; Twente Univ. Press: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2000; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sata, T. Ion Exchange Membranes: Preparation, Characterization, Modification and Application; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2004; Chapters 3 and 6. [Google Scholar]
- Giesbrecht, P.K.; Freund, M.S. Recent advances in bipolar membrane design and applications. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8060–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärnamäe, R.; Mareev, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Melnikov, S.; Sheldeshov, N.; Zabolotskii, V.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Tedesco, M. Bipolar membranes: A review on principles, latest developments, and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 617, 118538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.; Mondal, A.N.; Yang, Z.; Wycisk, R.; Kreidler, E.; Pintauro, P.N. Freestanding bipolar membranes with an electrospun junction for high current density water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 36092–36104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Feldmann, C. Electrodialysis in a non-aqueous medium: A clean process for the production of acetoacetic ester. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 124, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, N.; Osaki, T.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A. Alcohol splitting in a bipolar membrane and analysis of the product. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 506, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, C.; Xu, T. Ethanol splitting in bipolar membranes: Evidence from NMR analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, C.; Xu, T. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis in an organic medium: Production of methyl methoxyacetate. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xu, T. Electrodialysis with bipolar membranes for sustainable development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddick, J.A.; Bunger, W.B.; Sakano, T.K. Organic Solvents, Physical Properties and Methods of Purification, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, C. Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry, 4th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Tanioka, A. Membrane potential across low-water-content charged membranes: Effect of ion pairing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 14130–14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, T.; Tanioka, A. Dielectric relaxation on the intermediate layer in a bipolar membrane under the water splitting phenomenon: I. Shift of the dielectric properties by means of time-dependent impedance measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 253, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A. Effect of ion-exchange nanofiber fabrics on water splitting in bipolar membrane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondinini, S. pH measurements in non-aqueous and aqueous-organic solvents-definition of standard procedures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 374, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussini, T.; Covington, A.K.; Longhi, P.; Rondinini, S. Criteria for standardization of pH measurements in organic solvents and water + organic solvent mixtures of moderate to high permittivities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M. Acid-base equilibria in dipolar aprotic solvents. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 1992–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R.; Khanarian, G. Water dissociation in bipolar membranes: Experiments and theory. J. Membr. Biol. 1978, 38, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R. The origin and elimination of water splitting in ion exchange membranes during water demineralisation by electrodialysis. Desalination 1979, 28, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R. Strong electric field effects on proton transfer between membrane-bound amines and water. Nature 1979, 280, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafé, S.; Ramírez, P.; Alcaraz, A. Electric field-assisted proton transfer and water dissociation at the junction of a fixed-charge bipolar membrane. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 294, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. I. Dielektrizitätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 24, 636–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Solvent | Chemical Formula | εra [-] | pKSH b [-] | Viscosity [mPas] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | 78.4 | 14.00 | 1.00 |
| Methanol (MeOH) | CH3OH | 32.7 | 16.71 | 0.611 |
| Ethanol (EtOH) | CH3CH2OH | 24.6 | 18.90 | 1.19 |
| 1-propanol (PrOH) | CH3CH2CH2OH | 20.5 | 19.43 | 2.20 |
| ethylene glycol (Et(OH)2) | HOCH2CH2OH | 37.7 | 15.84 | 19.9 |
| propylene glycol (Pr(OH)2) | CH3CH(OH)CH2OH | 32.0 | 17.21 | 56.0 |
| Glycerin (Pr(OH)3) | HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH | 42.5 | - | 1412 |
| Formamide (FA) | HCONH2 | 111.0 | 16.80 | 3.75 |
| N-methylformamide (NMF) | HCONHCH3 | 182.4 | 10.74 | - |
| Membrane | Matrix a | Reinforcement b | Ion-Exchange Groups | Ion-Exchange Capacity [mmol/g-dry membr.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K501 (CEM) | poly(St-co-DVB) | PVC woven fabric | sulfonic acid | 2.0 |
| A501 (AEM) | poly(St-co-DVB-co-CMS) | PVC woven fabric | quaternary alkyl ammonium | 1.8 |
| A201 (AEM) | Poly(St + DVB + VI) | PP woven fabric | quaternary imidazole | 1.4 |
| Solvent | ΔpHCEL | ΔpHAEL |
|---|---|---|
| FA | −0.21 | 0.46 |
| NMF | −0.56 | 0.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onishi, N.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A.; Matsumoto, H. Current–Voltage Characteristics and Solvent Dissociation of Bipolar Membranes in Organic Solvents. Membranes 2022, 12, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121236
Onishi N, Minagawa M, Tanioka A, Matsumoto H. Current–Voltage Characteristics and Solvent Dissociation of Bipolar Membranes in Organic Solvents. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121236
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnishi, Nobuyuki, Mie Minagawa, Akihiko Tanioka, and Hidetoshi Matsumoto. 2022. "Current–Voltage Characteristics and Solvent Dissociation of Bipolar Membranes in Organic Solvents" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121236
APA StyleOnishi, N., Minagawa, M., Tanioka, A., & Matsumoto, H. (2022). Current–Voltage Characteristics and Solvent Dissociation of Bipolar Membranes in Organic Solvents. Membranes, 12(12), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121236






