Polymer Membranes as Innovative Means of Quality Restoring for Wastewater Bearing Heavy Metals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
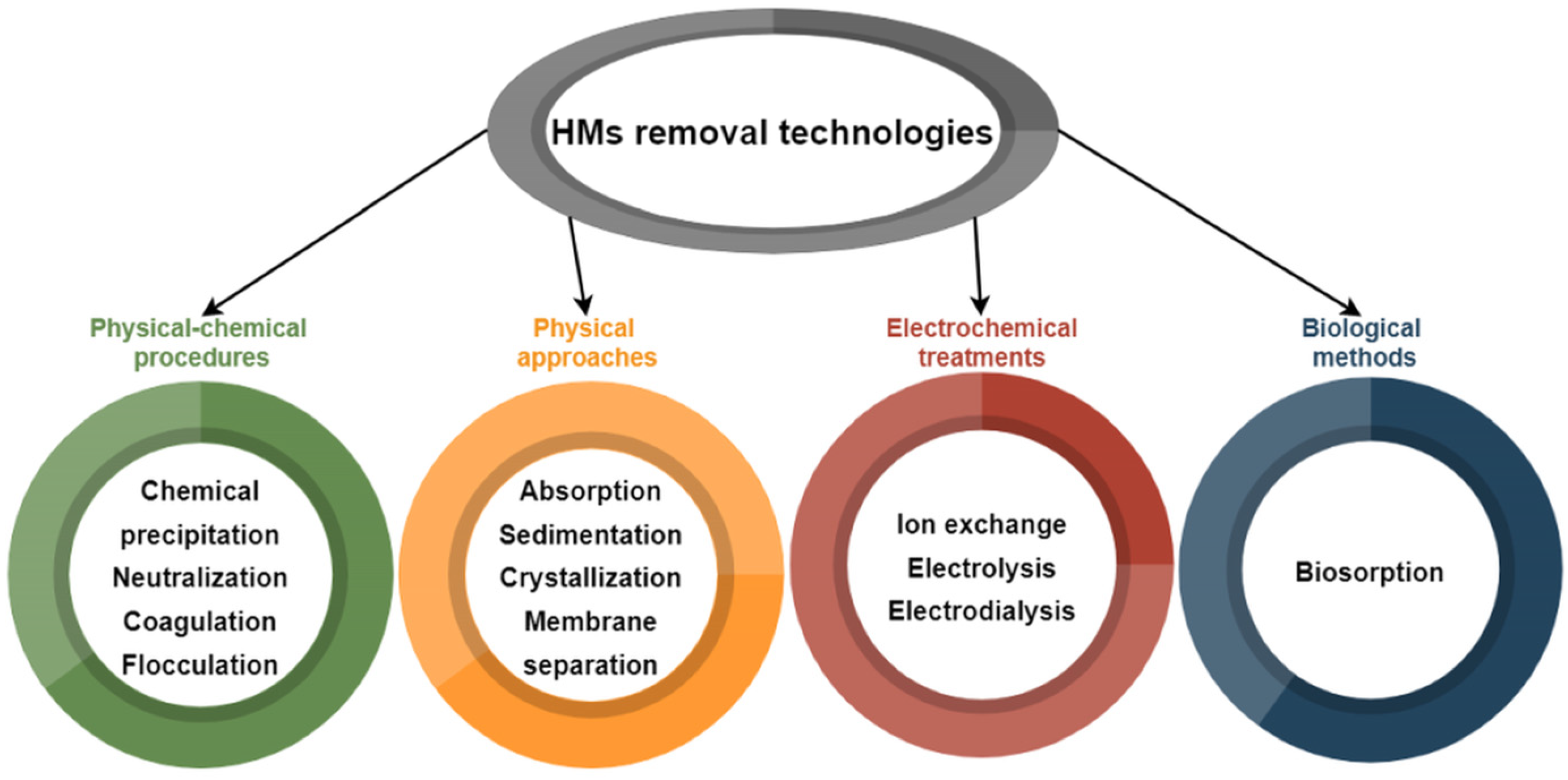
2. Conventional Technologies for Heavy Metals (HMs) Removal from Wastewaters
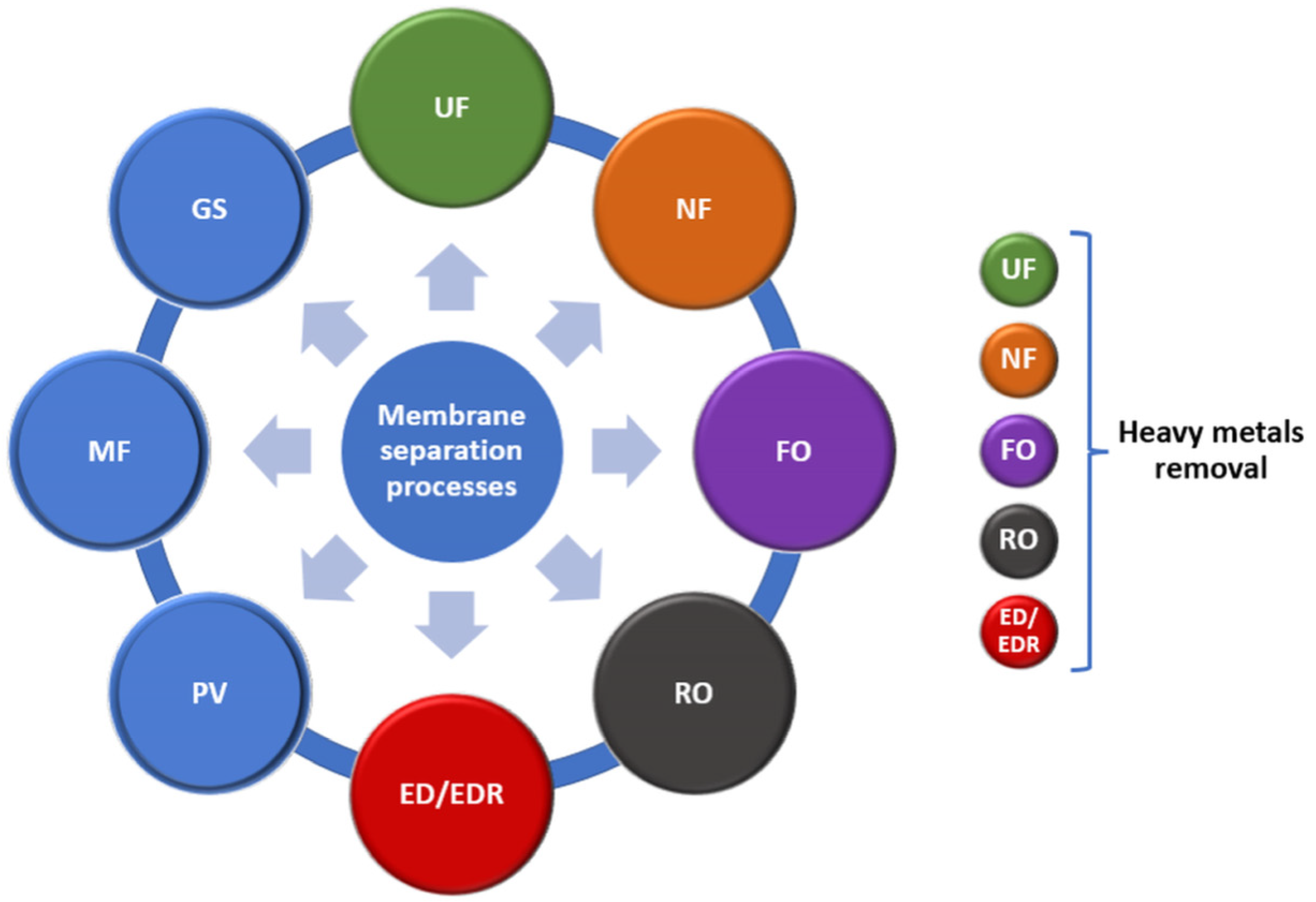
3. Types of Membranes for Water Quality Restoration
3.1. Membranes Based on Different Types of Precursors
3.2. Membranes Based on Porosity Feature
4. Membrane Approaches for Water Decontamination
4.1. Ultrafiltration (UF)
4.2. Nanofiltration (NF)
4.3. Microfiltration (MF)
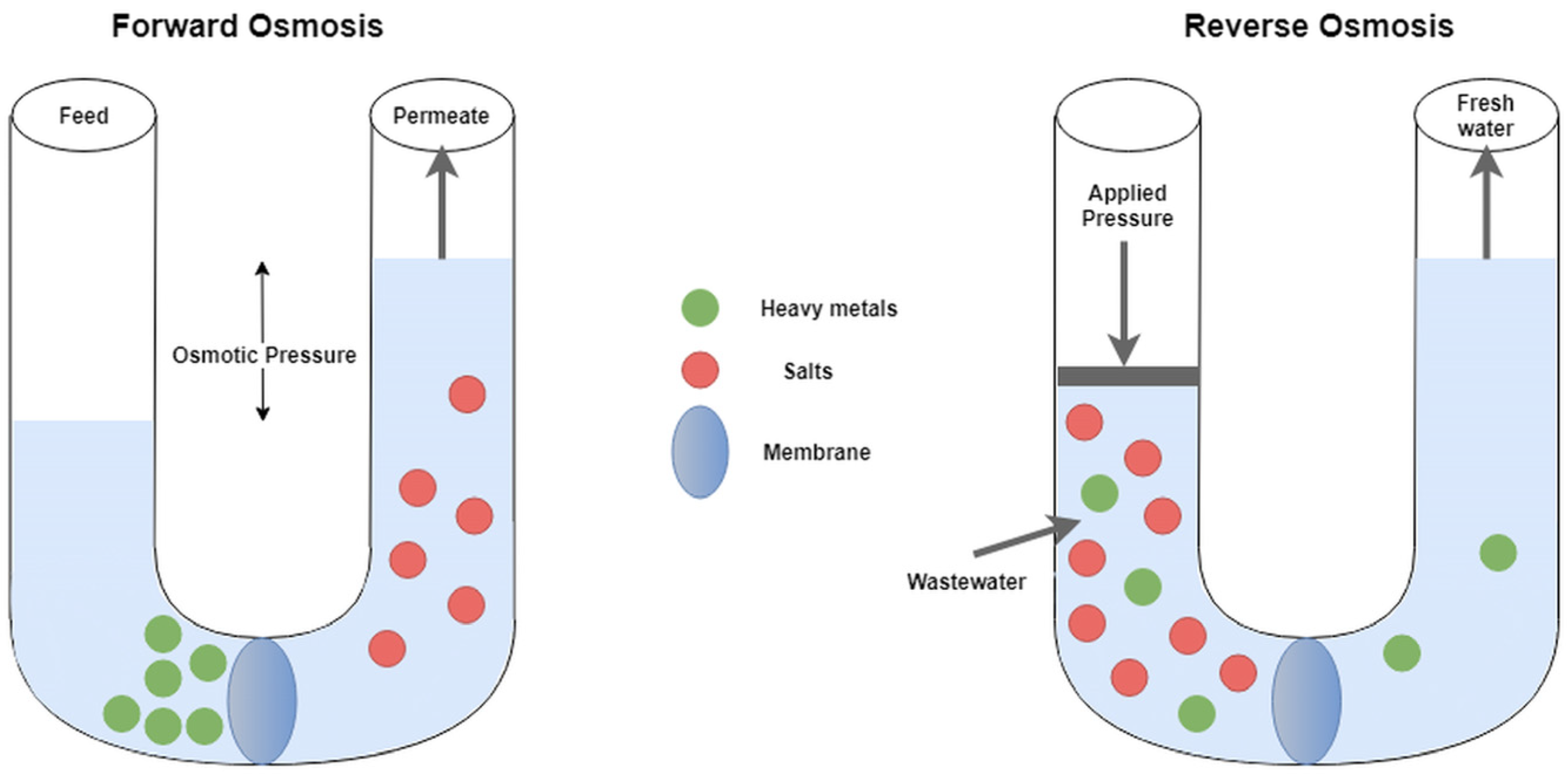
4.4. Forward Osmosis (FO)
4.5. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
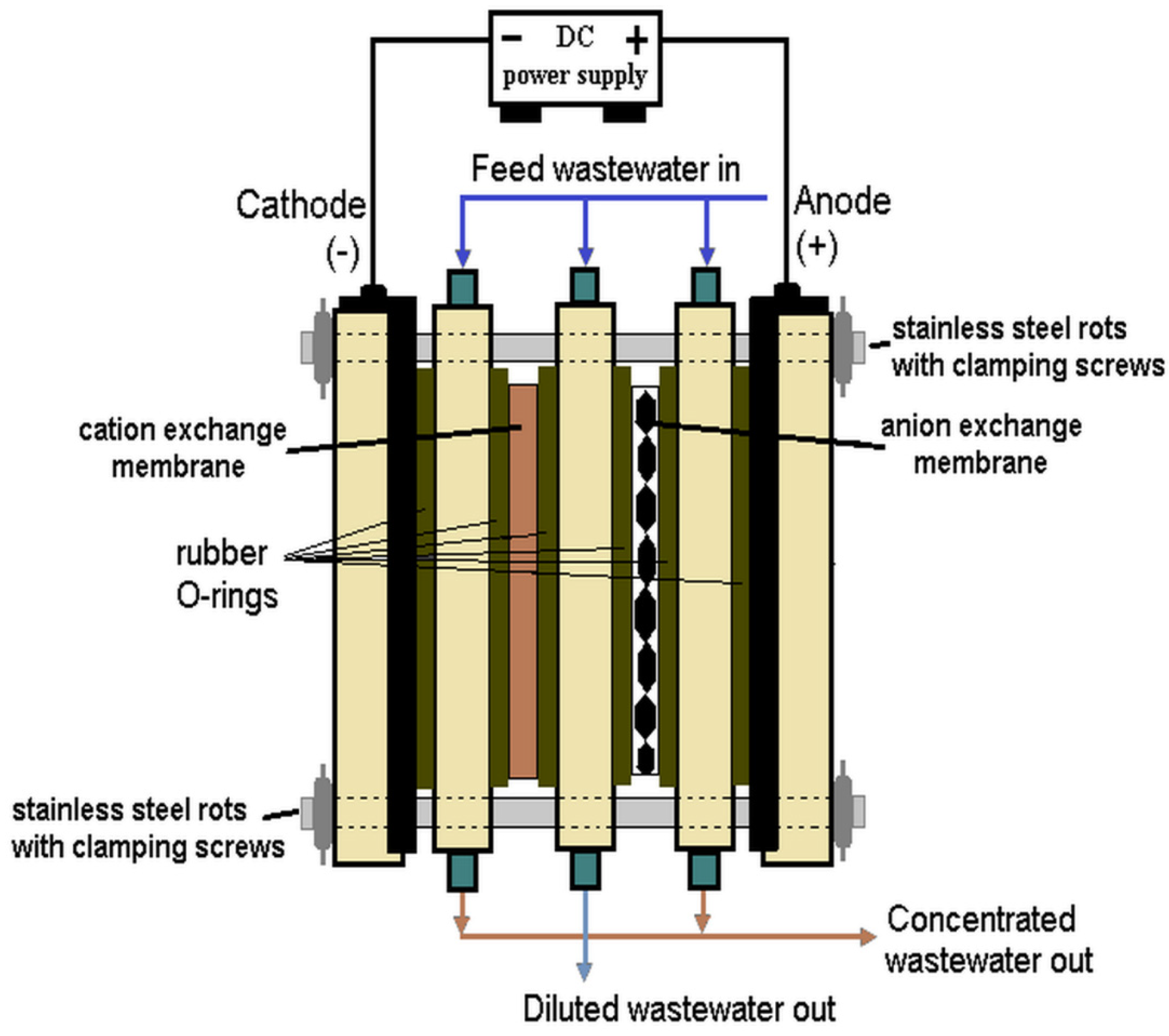
4.6. Electrodialysis (ED)
4.7. Chemical Modification with the Aim of Attaining Improved Properties
| Metallic Ion | Type of Membrane | Optimal Operational Conditions | Maximum Percentage Extraction (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | adsorbents/ion exchange resins-PVA membranes | voltage of 5 V, 1.5 h | 80.11 | [132] |
| Zn | organically modified montmorillonite polyethersulfone membranes | voltage of 5 V, 1 h | ~95 | [133] |
| Mg | ion exchange membranes | current density of 1.65 mA cm−2, 930 h | 84 | [135] |
| Cu | styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer membrane | voltage of 5 V, 1.5 h | 70.31 | [136] |
| Zn, Cu, Ni Al | Nafion 450 and Selemion membranes | current density of 10 mA cm−2, 6 h voltage of 5 V, 6 h | 68.5, 23.5, 46.0 77.4 | [137] |
| Zn | ion exchange membranes | voltage of 13 V, 25 min, flow velocity of 8 cm s−1 | 99.35 | [138] |
| Cu, As, Sb | ion exchange membranes | current density of 225 A m−2, 3 h | 68, 78, 85 | [139] |
| Pb, Cr Cu, Zn | (AR204SXR412) and (CR67, MK111) anion and cation exchange membranes AMV and CMV anion and cation exchange membranes | voltage of 30 V | 38.68, 39.00 41.52, 43.88 | [140] |
| Zn, Ni | Nafion 417 commercial membranes | current density of 40 mA cm−2, 2 h | 90 | [154] |
| As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mg, Ni, Zn | bipolar membrane | current density of 3.0 mA cm−2, 45 h | 93.4, 90.9, 71.5, 69.5, 98.8, 94.8, 91.5, 75.7, 96.4 | [161] |
| Fe | membrane containing cellulose acetate and chitosan-silver ions | voltage of 15 V, 1 h | 63.7 | [174] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaffei, C.; Pageau, K.; Suzuki, A.; Gouia, H.; Ghorbal, M.H.; Daubresse, C.M. Cadmium toxicity induced changes in nitrogen management in Lycopersicon esculentum leading to a metabolic safeguard through an amino acid storage strategy. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Akesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpor, O.B.; Ohiobor, G.O.; Olaolu, T.D. Heavy metal pollutants in wastewater effluents: Sources, effects and remediation. Adv. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Wang, R.; Lee, J. Emerging materials to prepare mixed matrix membranes for pollutant removal in water. Membranes 2021, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Kapri, A.; Goel, R. Chapter 1. Heavy Metal Pollution: Source, Impact, and Remedies: 1–28. In Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lars, J. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, H.M.; Eweida, E.A.; Farag, A. Heavy metals in drinking water and their environmental impact on human health. In Proceedings of the International Conference for Environmental Hazards Mitigation, Giza, Egypt, 9–12 September 2000; pp. 542–556. [Google Scholar]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy Metals”—A meaningless term. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/processes/heavy/heavy-metals/heavymetals.htm#ixzz5q90pHKIB (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Gimmler, H.; Carandang, J.; Boots, A.; Reisberg, E.; Woitke, M. Heavy metal content and distribution within a woody plant during and after seven years continuous growth on municipal solid waste (MSW) bottom slag rich in heavy metals. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2002, 76, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; McBride, M.B. Phytotoxic Effects of Cu and Zn on soybeans grown in field-aged soils: Their additive and interactive actions. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.P.; Ahmad, P.; Gadgil, K.; Sharma, S. Heavy metal toxicity: Effect on plant growth, biochemical parameters and metal accumulation by Brassica juncea L. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2009, 3, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gendi, A.; Ali, S.; Abdalla, H.; Saied, M. Microfiltration/ultrafiltration polyamide-6 membranes for copper removal from aqueous solutions. Membr. Water Treat. 2016, 7, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Dwayne, J.S. Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Environmental Toxicology; Andreas, L., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Guntilake, S.K. Methods of removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Stud. 2015, 1, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dermont, G.; Bergeron, M.; Mercier, G.; Richer- Laflache, M. Metal-contaminated soils: Remediation practices and treatment and treatment technologies. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2008, 12, 188–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizge, N.; Keskinler, B.; Barlas, H. Sorption of Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution by Lewatit cation-exchange resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, D.S.; Jeon, D.S.; Park, M.S.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Goo, J.W.; Kim, S.B.; Chung, D.Y. Application of Electrocoagulation and Electrolysis on the Precipitation of Heavy Metals and Particulate Solids in Washwater from the Soil Washing. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniedanesh, M.; Alwi, S.R.; Manan, Z. Potential of Heavy Metal Recovery from Wastewater and Sewage Sludge. In Proceedings of the 6th Internetional Conference on Process Systems Engineering, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 25–27 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.P.; Aris, A.Z. A review on economically adsorbents on heavy metals removal in water and wastewater. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials as Sorbents to Remove Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 2, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, L.H.; Aguiar, A.O.; Pires, W.L.; Miranda, G.A.; Teixeira, L.P.T.; Almeida, G.C.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis applied to gold mining effluent treatment and reuse. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.M.; Adrian, D.D. A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Kumar, A.; Charaborty, S.; Ray, M. Removal and recovery of chromium from wastewater using short chain polyaniline synthesized on jute fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 141, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddad, Z.; Gerente, C.; Andres, Y.; LeCloirec, P. Adsorption of several metal ions onto a low-cost biosorbent: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathmann, H.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E. An Introduction to Membrane Science and Technology. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237324166_An_Introduction_to_Membrane_Science_and_Technology (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Algieri, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Candamano, S. A way to membrane- based environmental remediation for heavy metal removal. Environments 2021, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, T.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ramli, S.; Mohd, S.S. Potential of membrane technology for treatment and reuse of water from old mining lakes. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 2887–2897. [Google Scholar]
- Said, K.A.M.; George, G.G.; Alipah, N.A.M.; Ismail, N.Z.; Jama’in, R.L. Effect of activated carbon in PSF-PEI-Ag symmetric membrane. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 87, 03008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlosser, S. Membrane filtration, Research Gate. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258239813 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Qiu, Y.R.; Mao, L.J. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by ultrafiltration assisted with copolymer of maleic acid and acrylic acid. Desalinisation 2013, 329, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căprărescu, S.; Văireanu, D.I.; Cojocaru, A.; Maior, I.; Purcar, V.; Sârbu, A. Removal of copper ions from aqueous solutions using cation- and anion-exchange membranes by electrodialysis process. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Ser. B 2009, 71, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Imdad, S.; Dohare, R.K. A critical review on heavy metals removal using liquid membranes from the industrial wastewater. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 173, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Ruan, H. Sustainable reverse osmosis, electrodialysis and bipolar membrane electrodialysis application for cold-rolling wastewater treatment in the steel industry. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M.H.V. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, E.; Chorka, J.; Mikulasek, P. Characterization of Nanofiltration Membrane and Its Application for the Separation of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Available online: www.researchgate.net/publication/327844860 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Aloulou, W.; Aloulou, H.; Khemakhem, M.; Duplay, J.; Daramola, M.O.; Amar, R.B. Synthesis and Characterization of clay-based ultrafiltration membranes supported on natural zeolite for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnau, I.; Freeman, B. (Eds.) Chapter 1 Membrane Formation and Modification. In ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 744, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Germany, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. (Eds.) Membrane Technology in the Chemical Industry; Wiley–VCH, Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001; p. 299. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strathmann, H. Membrane Separation Processes, 3. Membrane Preparation and Membrane Module Constructions. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; Volume 22, pp. 483–512. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Colombi Ciacchi, L.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in Nanoporous Membranes for Water Purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. A review on membrane fabrication: Structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination 2013, 326, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.A.; Hillmyer, N.A. Nanoporous membranes derived from block copolymers: From drug delivery to water filtration. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3548–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; He, G.W.; Wang, S.F.; Yu, S.N.; Pan, F.S.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.Y. Recent advances in the fabrication of advanced composite membranes. J. Mater Chem. A 2013, 1, 10058–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetty, S.; Arcari, M.; Adamcik, J.; Mezzenga, R. Hybrid amyloid membranes for continuous flwflow catalysis. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13867–13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFriend, K.A.; Wiesner, M.R.; Barron, A.R. Alumina and aluminate ultrafiltration membranes derived from alumina nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 224, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmood, I.; Lopes, C.B.; Lopes, I.; Ahmad, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Nanoscale materials and their use in water contaminants removal—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1239–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ahlawat, W.; Bhanjana, G.; Heydarifard, S.; Nazhad, M.M.; Dilbaghi, N. Nanotechnology-based water treatment strategies. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 1838–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.P.; Li, D.; Jing, W.H.; Xing, W.H.; Fan, Y.Q. Synthesis of visible-light responsive C, N and Ce co-doped TiO2 mesoporous membranes via weak alkaline sol-gel process. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 15309–15315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciotti, M.; Boffa, V.; Magnacca, G.; Jorgensen, L.B.; Kristensen, P.K.; Farsi, A.; Konig, K.; Christensen, M.L.; Yue, Y.Z. Deposition of thin ultrafiltration membranes on commercial SiC microfiltration tubes. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemoller, M. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Wang, H.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wei, G.; Su, Z.Q. Graphene film doped with silver nanoparticles: Self-assembly formation, structural characterizations, antibacterial ability, and biocompatibility. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Vecitis, C.D.; Elimelech, M. Electrochemical carbon-nanotube filter performance toward virus removal and inactivation in the presence of natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, M.S.; Kandaswamy, A.; Vijayalakshmi, A. Preparation and characterisation of flat sheet micro/nanoporous membranes using polysulfone blend with PVP/PEG and chitosan/chitosan nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Optoelectron. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 8, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Iannace, S.; Di Maio, E.; Nicolais, L. Preparation and Characterization of Polyurethane Porous Membranes by Particulate-leaching Method. Cell. Polym. 2001, 20, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-González, Y.; Aimar, P.; Lahitte, J.F.; Remigy, J.-C. Towards green membranes: Preparation of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes using methyl lactate as a biosolvent. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2011, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koromilas, N.D.; Anastasopoulos, C.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Kallitsis, J.K. Preparation of Porous Polymeric Membranes Based on a Pyridine Containing Aromatic Polyether Sulfone. Polymers 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, T.; Kitaura, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Nakatsuka, S.; Watabe, T.; Matsuyama, H. Membrane fouling properties of hollow fiber membranes prepared from cellulose acetate derivatives. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 376, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.G.; Deng, C.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Highly permeable cellulose acetate nanofibrous composite membranes by freeze-extraction. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughi, E.; Mousavi, S.M. Preparation and characterization of novel polysulfone nanofiltration membranes for removal of cadmium from contaminated water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 90, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Abdulkarim, A.A.; Ooi, B.S.; Ismail, S. Recent development in additives modifications of polyethersulfone membrane for flux enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliwati, E.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Kassim, M.A.; Abdullah, M.S. Effect of modified PVDF hollow fiber submerged ultrafiltration membrane for refinery wastewater treatment. Desalination 2011, 283, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.T.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekierka, A.; Yalcinkaya, F. Selective cobalt-exchange membranes for electrodialysis dedicated for cobalt recovery from lithium, cobalt and nickel solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Majumder, S.K. Fabrication of the polysulfone- based composite ultrafiltration membranes for the adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from their contaminated aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.P.; Bordado, J.C. Smart Composite Reverse-Osmosis Membranes for Energy Generation and Water Desalination Processes A2-. In Smart Composite Coatings and Membranes; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.; Elam, J.W.; Darling, S.B. Membrane materials for water purification: Design, development, and application. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Goh, P.; Lau, W.; Misdan, N.; Ismail, A. Nanomaterials for biofouling and scaling mitigation of thin film composite membrane: A review. Desalination 2016, 393, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N.; Hashaikeh, R. Electrically conductive polymeric membrane for fouling prevention and detection: A review. Desalination 2016, 391, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, L.; García-Payo, M.C.; Khayet, M. Effects of mixed solvents on the structural morphology and membrane distillation performance of PVDF-HFP hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaydevsinh, M.; Gohil; Rikarani, R. Choudhury Chapter 2–Introduction to Nanostructured and Nano-Enhanced Polymeric Membranes: Preparation, Function, and Application for Water Purification. In Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification, Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, R.O.; Scamehorn, J.F.; Christian, S.D. Use of micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration to remove dissolved organics from aqueous streams. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1985, 20, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Garcia, V.; Pongracz, E.; Keiski, R.L. The removal of zinc from synthetic wastewaters by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration: Statistical design of experiments. Desalination 2009, 240, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y.Y.; Qu, Y.H.; Luo, F.; Lin, D.; Liu, H.L. Recovery and reuse of surfactant SDS from a MEUF retentate containing Cd2+ or Zn2+ by ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessbousse, H.; Verchère, J.F.; Lebrun, L. Characterisation of metal-complexing membranes prepared by the semi-interpenetrating polymer networks technique. Application to the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; El Hashani, A.; Tieke, B. Ion-selective membranes prepared upon layer-by-layer assembly of azamacrocycles and polyelectrolytes. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 287, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Friedrich, T.; Tieke, B. Layer-by-layer assembled polyelectrolyte blend membranes and their use for ion separation and rejection. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yaroshchuk, A.; Bruening, M.L. Fundamentals of selective ion transport through multilayer polyelectrolyte membranes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi, G.; Sachan, S.; Kishore, N.; Kumar, A. Separation of chromium (VI) using modified ultrafiltration charged carbon membrane and its mathematical modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Sheng, L.G.; Wei, Y.W.; Jun, W.Y. Preparation and adsorption ability of poly-sulfone microcapsules containing modified chitosan gel. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2005, 10, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffaj, N.; Loukil, H.; Younssi, S.A.; Albizane, A.; Bouhria, M.; Persin, M.; Larbot, A. Filtration of solution containing heavy metals and dyes by means of ultrafiltration membranes deposited on support made of Morrocan clay. Desalination 2004, 168, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Lo, W.H.; Babel, S. Physicochemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Q.; Xu, Z.K.; Liu, Z.M.; Xu, Y.Y. Ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes of sulfonated polyetherimide/polyetherimide blends: Preparation, morphologies and anti-fouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 218, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R.; Malaisamy, R.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Mohan, D. Cellulose acetate-poly(ether sulfone) blend ultrafiltration membranes. II: Application studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Mohan, D.; Rangarajan, R. Studies on cellulose acetate polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes II. Effect of additive concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 268, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, R.M.; Wienk, I.M.; Van den Boomgaard, T.H.; Smolders, C.A. Microstructures in phase inversion membranes. Part 2. The role of a polymeric additive. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, H.T.; Lee, S.T.; Han, M.J. Role of polymer additive in casting solution in preparation of phase inversion polysulfone membranes. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2000, 33, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, N.A.; Pradanos, P.; Palacio, L.; Pagliero, C.; Marchese, J.; Hernandez, A. Pore size distributions based on AFM imaging and retention of multidisperse polymer solutes: Characterisation of polyethersulfone UF membranes with dopes containing different PVP. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 187, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafreniere, L.Y.; Talbot, F.D.F.; Matsuura, T.; Sourirajan, S. Effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone additive on the performance of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1987, 26, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Zain, N.M.; Noordin, M.Y. Synthesis, characterization and performance of asymmetric polyetehrsulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membranes with polyethylene glycol of different molecular weights as additives. Desalination 2007, 207, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicz, J. Removal of chromium ions (VI) from underground water in the hybrid complexation-ultrafiltration process. Desalination 2000, 129, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Sun, S.P.; Zhu, W.P.; Chung, T.S. Chelating polymer modified P84 nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for high efficient heavy metal removal. Water Res. 2014, 63, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Interfacially polymerized composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for low-pressure water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 430, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Z. Novel polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiltration membrane blended with functionalized halloysite nanotubes for dye and heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Chung, T.S. Layer-by-layer construction of graphene oxide (GO) framework composite membranes for highly efficient heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, V.; Jyothi, M.S.; Balakrishna, R.G.; Padaki, M.; Deon, S. Novel modified poly vinyl chloride blend membranes for removal of heavy metals from mixed ion feed sample. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.P.; Gao, J.; Sun, S.P.; Zhang, S.; Chung, T.S. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer (PAMAM) grafted on thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, M.; Guha, B.K. Effect of pH on rejection of Cr(VI) by Nanofiltration. Desalination 2008, 219, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Qdaisa, H.; Moussab, H. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: A comparative study. Desalination 2004, 164, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.S. Investigation of amphoteric polybenzimidazole (PBI) nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for both cation and anions removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.G. Membrane methods in tailoring simpler, more efficient, and cost-effective wastewater treatment alternatives. Desalination 2008, 222, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. A study on acid reclamation and copper recovery using low pressure nanofiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 56, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.V.P.; Chaudhari, L.B. Application of nanofiltration for the rejection of nickel ions from aqueous solutions and estimation of membrane transport parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figoli, A.; Cassano, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Mozumder, M.S.I.; Uddin, M.T.; Islam, M.A.; Drioli, E. Influence of operating parameters on the arsenic removal by nanofiltration. Water Res. 2010, 44, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.V.P.; Chaudhari, L.B. Separation of binary heavy metals from aqueous solutions by nanofiltration and characterization of the membrane using Spiegler- Kedem model. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Ultrathin graphene nanofiltration membrane for water purification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3693–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shen, X.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Polythyleneimine-modified original positive charged nanofiltration membrane: Removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, M.W.; Alkhudhiri, A.; Al-Batty, S.; Zaacharof, M.P.; Maddy, J.; Hilal, N. Ceramic microfiltration membranes in wastewater treatment: Filtration behavior, fouling and prevention. Membranes 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Lin, H.; Chhuon, K. Application of Microfiltration membrane technology in water treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 571, 012158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawther Hussein, T. Forward Osmosis Process for Removal of Cd2+ Ions from Simulated Wastewater by Using Cellulose Acetate (CA) Membrane. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Ma, T.; Goh, K.; Pei, Z.; Chong, J.Y.; Wang, Y.N. Forward Osmosis Membranes: The significant roles of selective layer. Membranes 2022, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawther Hussein, T. Comparative Study for Removal of Zn2+ ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption and Forward Osmosis. Iraqi J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2017, 18, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, R.R.; Eisenberg, T.N.; Middlebrooks, E.J. Reverse Osmosis in the Treatment of Drinking Water. Reports. Paper 505. 1982. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/water_rep/505 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Bakalar, T.; Bugel, M.; Gajdosova, L. Heavy metal removal using reverse osmosis. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2009, 14, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin. Reverse osmosis applications: Prospects and challenges. Desalination 2016, 391, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makisha, N. Membrane bioreactors for treatment of galvanic wastewater. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 97, 05047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, L.; Kumar Gupta, P.; Kumar, N.; Kumar Srivastava, A.; Naryan, A.V.; Rajendran, S.; Ravi, K.M.; Narasanagi, M.; Sukanya, P. Functionalized cellulose nanofiber-composite membranes for wastewater treatment—A review. J. Nanotechnol. Mater. Sci. 2018, 5, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines on Water Purification by Reverse Osmosis (RO), Reports no RDSO/WKS/8215/2. Available online: https://rdso.indianrailways.gov.in/works/uploads/File/WKS-G-8.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Baptista Ventura, L.M.; Gaya de Figueiredo, M.A.; Sena, M.E. Membranes Selection for Effluent Treatment with Cadmium Sulfate. Am. J. Chem. Appl. 2017, 4, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ates, N.; Uzal, N. Removal of heavy metals from aluminum anodic oxidation wastewaters by membrane filtration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22259–22272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaci, B.S.; Gashi, S.T. Reverse Osmosis Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater Effluents Using Biowaste Materials Pretreatment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimi, T.; Sadiku, M.; Berisha, A.; Berisha, V. Separation of Heavy Metals Salts from Aqueous Solutions by Reverse Osmosis Membranes (317K-2). Int. J. Sci. Res. Rev. 2016, 40, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaruzaman, S.; Fikrah Aris, N.I.; Yahaya, N.; Hong, L.S.; Raznisyafiq Razak, M. Removal of Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Environmental Water Samples by Using Cellulose Acetate Membrane. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al–Alawy, A.F.; Salih, M.H. Comparative Study between Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Membranes for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater. Eng. J. 2017, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Y.M.; Liang, T.M. A feasibility study of industrial wastewater recovery using electrodialysis reversal. Desalination 2008, 221, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H. Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 177, 876–880. [Google Scholar]
- Căprărescu, S.; Radu, A.L.; Purcar, V.; Ianchiș, R.; Sârbu, A.; Ghiurea, M.; Nicolae, C.; Modrogan, C.; Văireanu, D.I.; Périchaud, A.; et al. Adsorbents/ion exchangers-PVA blend membranes: Preparation, characterization and performance for the removal of Zn2+ by electrodialysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căprărescu, S.; Ianchiş, R.; Radu, A.L.; Sârbu, A.; Şomoghi, R.; Trică, B.; Alexandrescu, E.; Spătaru, C.I.; Fierăscu, R.C.; Ion-Ebraşu, D.; et al. Donescu, Synthesis, characterization and efficiency of new organically modified montmorillonite polyethersulfone membranes for removal of zinc ions from wastewasters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 137, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Mao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, F.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Xu, C. Systematic research on the bipolar membrane reverse electrodialysis performance and its application in electrodialysis desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Gally, C.; Benvenuti, T.; de Moraes da Trindade, C.; Siqueira Rodrigues, M.A.; Zoppas- Ferreira, J.; Perrez- Herranz, V.; Moura Bernardes, A. Electrodialysis for tertiary treatmentof municipal wastewater: Efficiency of ion removal and ageing of ion exchange membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căprărescu, S.; Corobea, M.C.; Purcar, V.; Spătaru, C.I.; Ianchiş, R.; Vasilievici, G.; Vuluga, Z. San copolymer membranes with ion exchangers for Cu (II) removal from synthetic wastewater by electrodialysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Costa, R.F.; Klein, W.C.; Bernardes, A.M.; Ferreira, J.Z. Evaluation of the electrodialysis process for the treatment of metal finishing wastewater. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2002, 13, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho Choi, K.; Jeoung, T.K. Removal of zinc ions in wastewater by electrodialysis. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, J.P.; Cifuentes, L. On the kinetics of Cu, As and Sb transport through cation and anion exchange membranes in acidic electrolytes. Can. Metall. Q. 2004, 43, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Moheb, A.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Razmi, A. Modeling of metal ion removal from wastewater by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Peng, C.; Almeria, O.J.; Xu, H. Effect of pH on separation of Pb (II) and NO3−from aqueous solutions using electrodialysis. Desalination 2012, 285, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ghander, N.S.; Rahman, S.U.; Zaidi, S.M.J. A modified electrodialytic cell to recover heavy metals from wastewater. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 24, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.; Habib, G. Application of electrodialysis in waste water treatment and impact of fouling on process performance. J. Med. Case Rep. Rev. 2018, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căprărescu, S.; Miron, A.R.; Purcar, V.; Radu, A.L.; Sârbu, A.; Nicolae, C.A.; Pascu, M.N.; Ion-Ebraşu, D.; Radiţoiu, V. Treatment of Crystal violet from synthetic solution using membranes doped with natural fruit extract. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Rakib, M.; Durand, G.; Avila-Rodríguez, M. Treatment of solutions containing trivalent chromium by electrodialysis. Desalination 2006, 191, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.M.; Sotoca, J.A.; Exposito, E.; Gallud, F.; García-García, V.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Brackish water desalination by electrodialysis: Batch recirculation operation modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Kaviani, A. Water shortage and seawater desalination by electrodialysis. Desalination 2003, 158, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, R. Chapter 2 Preparation of Polymeric Membranes. In Handbook of Environmental Engineering; Wang, L.K., Ed.; Membrane and Desalination Technologies; Springer Science þBusiness Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.J.; Donaldson, J.D.; Grimes, S.M.; Yasri, N.G. Separation of nickel from cobalt using electrodialysis in the presence of EDTA. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2000, 30, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, S.; Lignot, B.; Bourseau, P.; Jaouen, P.; Prost, C. Desalination of mussel cooking juices by electrodialysis: Effect on the aroma profile. J. Food Eng. 2005, 69, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căprărescu, S.; Miron, A.R.; Purcar, V.; Radu, A.L.; Sârbu, A.; Ion-Ebraşu, D.; Atanase, L.I.; Ghiurea, M. Efficient removal of Indigo Carmine dye by a separation process. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapotot, A.; Pourcelly, G.; Gavach, C. Transport competition between monovalent and divalent cations through cation-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 96, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, L.; Crisostomo, G.; Ibanez, J.P.; Casas, J.M.; Alvarez, F.; Cifuentes, G. On the electrodialysis of aqueous CuSO4–H2SO4 electrolytes with metallic impurities. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 207, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarosa, V.E.; Peretti, F.; Caldart, V.; Zoppasb, J.; Zeni, M. Study of ion-selective membranes from electrodialysis removal of industrial effluent metals II: Zn and Ni. Desalination 2002, 149, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Moheb, A.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Razmi, A. Separation of copper ions by electrodialysis using Taguchi experimental design. Desalination 2004, 169, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Razmi, A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Effect of operating parameters on Pb2+ separation from wastewater using electrodialysis. Desalination 2004, 167, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğütveren, Ü.B.; Koparal, S.; Özel, E. Electrodialysis for the removal of copper ions from wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1997, 32, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, L.; Goncharuk, V. Electrodialysis of solutions containing Mn (II) ions. Desalination 2009, 241, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiewicz, K.; Pietrzak, R. Metal ions removal by polymer membranes of different porosity. Sci. World. J. 2013, 2013, 957202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, N.; Atassi, Y. Enhancement of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions by polyaniline deposition on electrospun polyacrylonitrile membranes. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Ke, X.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, R.; Ding, R.; Van der Bruggen, B. Arsenic and cation metal removal from copper slag using a bipolar membrane electrodialysis system. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Malik, M.; Azimi, G. Separation of lithium, nickel, manganese, and cobalt from waste lithium-ion batteries using electrodialysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 178, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Xie, X.; Sun, L.; Lei, W.; Wang, F. An efficient two-chamber electrodeposition- electrodialysis combination craft for nickel recovery and phosphorous removal from spent electroless nickel plating bath. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Volodine, A.; Vand der Bruggen, B. Facile fabrication of a positively charged nanofiltration membrane for heavy metal and dye removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Deon, S.; Morin- Crini, N.; Crini, G.; Fievet, P. Polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration for heavy metal removal: Influence of chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose on filtration performances. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Saini, R.; Singh, D. Review paper on removal of heavy metal ions from industrial waste water effluent. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1168, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletski, Z. Chapter 1 Advances in Membrane Materials and Process for Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Multidisciplinary Advances in Efficient Separation Processes; Chernyshova, I., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Xi, C.; Zhang, F. A review: Adsorption and removal of heavy metals based polyamide- amines composites. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 814643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, H.T.N. Heavy metal sequestration from contaminated water: A review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar]
- Sandu, T.; Chiriac, A.L.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Stoycheva, I.; Căprărescu, S.; Damian, C.M.; Iordache, T.V.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Sârbu, A. Advanced hybrid membranes for efficient nickel retention from simulated wastewater. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Cheng, Z.F. Recent advances in adsorptive membranes for removal of harmful cations. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, T.S.; Hossain, M.M.; Jeong, H.M.; Kim, K. Heavy metal removal applications. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunita, M.; Irawanti, R.; Koesmawati, T.A.; Lugito, G.; Wenten, I.G. Graphene Oxide (GO) Membrane in Removing Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Review. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2020, 82, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Căprărescu, S.; Zgârian, R.G.; Tihan, G.T.; Purcar, V.; Eftimie Totu, E.; Modrogan, C.; Chiriac, A.L.; Nicolae, C.A. Biopolymeric membrane enriched with chitosan and silver for metallic ions removal. Polymers 2020, 12, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Nikouzad, S.K. A positively charged composite loose nanofiltration membrane for water purification from heavy metals. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.; Zhang, H.Z.; Sun, J.Y.; Xu, Z.L. Three-channel capillary nanofiltration membranewith quaternary ammonium inccorporated for heavy metals removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ai, P.; Chen, G. Positively charged PVC ultrafiltration membrane via micellar enhanced ultrafiltrationfor removing trace heavy metal cations. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 46, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, G.; Zinadini, S.; Rajabi, L.; Derakhshan, A.A. Removal of heavy metal ions using a new a high performance nanofiltration membrane modified with curcumin boehmite nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, S.; Shahbazi, A. High-performance nanofiltration membrane blended by Fe3O4@SiO2-CS bionanocomposite for efficient simultaneous rejection of salts/heavy metals ions/dyes with high permeability, retention increase and fouling decline. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 127930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekhar Nayak, M.; Islur, A.M.; Inamuddin; Lakshmi, B.; Marwani, H.M.; Khan, I. Polyphenylsulfone/multiwalled carbon nanotubes mixed ultrafiltration membranes: Fabrication, characterization and removal of heavy metals Pb2+, Hg2+, and Cd2+ from aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4661–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Investigated Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Concentration of draw solution | 10–150 g/L |
| Concentration of feed solution | 10–200 mg/L |
| Flow rate of draw solution | 30–100 L/hr |
| Flow rate of feed solution | 30–100 L/hr |
| Temperature of draw solution | 10–40 °C |
| Temperature of feed solution | 10–40 °C |
| No. | Water That Needs to Be Treated | Removed Heavy Metal | Rejection Percentage (%) | Membrane Used | Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Drinking water supplies | Ni, Cu, Zn | - | PA—TW-30-1812-50 | [118] |
| 2. | Industrial processes in metal mechanics | Cd | >95 >95 >97 >90 | HRP98PP-CA SW 30-PA BW30 LE-PA NF-90-PA | [124] |
| 3. | Aluminium oxidation wastewater | WW from the aluminium industry (Al, Cr, Ni) | 87 90 | PTUF NF270 SW 30 | [125] |
| 4. | Mining flotation process effluents | Pb, Cd, Ni, Zn, Mn, Co | >95% | Biowastes for pre-treatment + cellulose acetate—coal asymmetric RO membrane | [126] |
| 5. | Synthetic wastewaters; mining flotation process | Hg, Mn, Cr, Cu | - | Coal modified cellulose acetate: 317K-2 316K-2 | [127] |
| 6. | Steel manufacturing plant | Cu, Cd | 79.89; 76.62 | Cellulose Acetate Membrane (CAM) | [128] |
| 7. | Steel manufacturing plant | Zn, Ni, Cu, Cr | 99.49; 99.49; 99.33; 99.93 | Polyamide membranes | [129] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandu, T.; Sârbu, A.; Căprărescu, S.; Stoica, E.-B.; Iordache, T.-V.; Chiriac, A.-L. Polymer Membranes as Innovative Means of Quality Restoring for Wastewater Bearing Heavy Metals. Membranes 2022, 12, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121179
Sandu T, Sârbu A, Căprărescu S, Stoica E-B, Iordache T-V, Chiriac A-L. Polymer Membranes as Innovative Means of Quality Restoring for Wastewater Bearing Heavy Metals. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121179
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandu, Teodor, Andrei Sârbu, Simona Căprărescu, Elena-Bianca Stoica, Tanța-Verona Iordache, and Anita-Laura Chiriac. 2022. "Polymer Membranes as Innovative Means of Quality Restoring for Wastewater Bearing Heavy Metals" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121179
APA StyleSandu, T., Sârbu, A., Căprărescu, S., Stoica, E.-B., Iordache, T.-V., & Chiriac, A.-L. (2022). Polymer Membranes as Innovative Means of Quality Restoring for Wastewater Bearing Heavy Metals. Membranes, 12(12), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121179












