Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability of Nb-Ni-Ti-Zr-Co High Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Hydrogen Permeation Tests
2.4. Ab Initio Calculations
3. Results
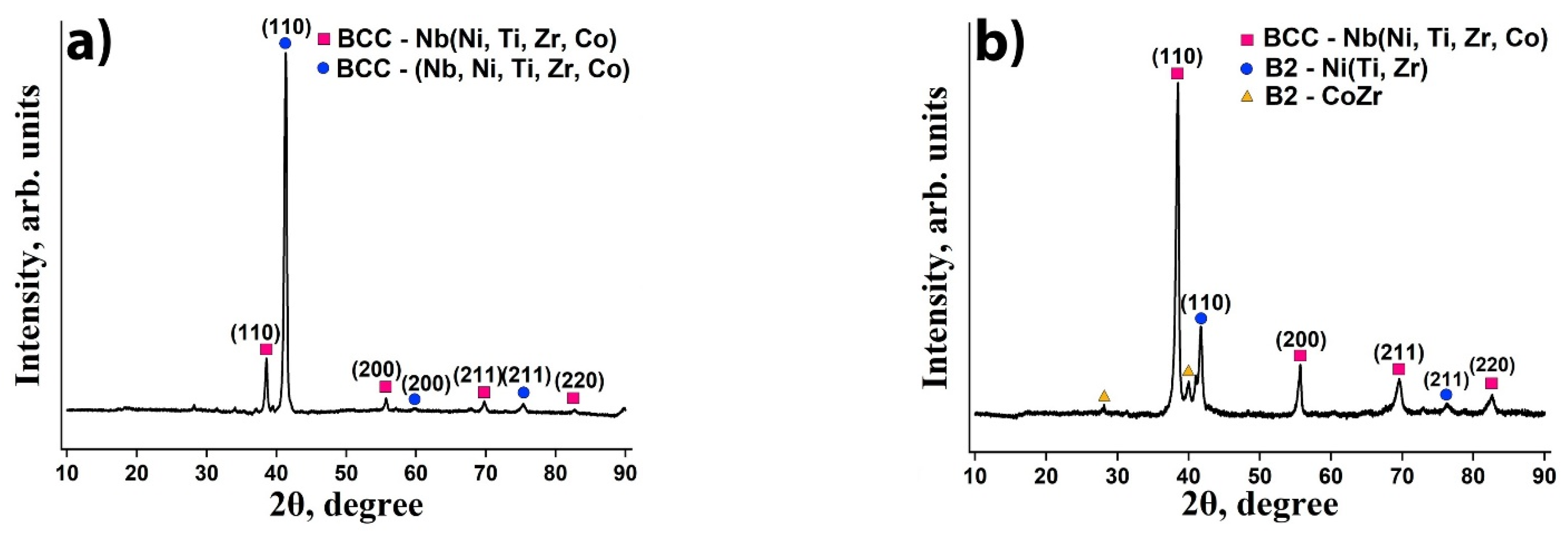
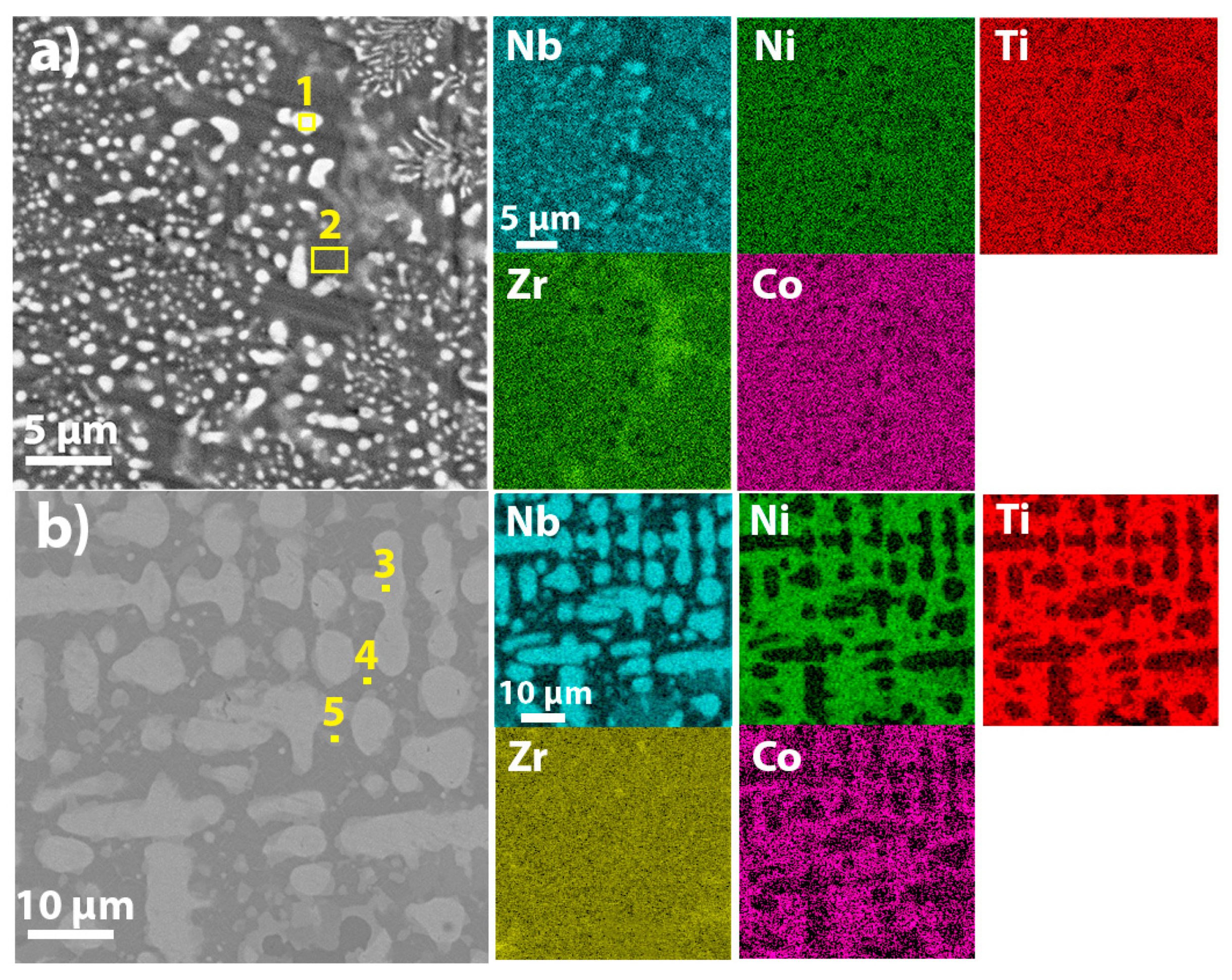
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Composition
3.2. Hydrogen Permeability
3.3. Lattice Constants and Hydrogen Binding Energy in HEAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- A fine-grained microstructure with BCC-(Nb, Ni, Ti, Zr, Co) and BCC-Nb(Ni, Ti, Zr, Co) lattices is formed in the equimolar Nb20Ni20Ti20Zr20Co20 alloy, while coarser dendritic microstructure with Nb-enriched BCC-Nb(Ni, Ti, Co), B2-Ni(Ti, Zr) and B2-CoZr phases is presented in the Nb40Ni25Ti18Zr12Co5 alloy.
- The lattice parameter and hydrogen binding energy in the interstitial sites are higher for the Nb-enriched BCC lattice than that for the BCC lattice with near equimolar composition, which indicates higher hydrogen solubility in the Nb-enriched phase. The hydrogen binding energy decreases in both tetrahedral and octahedral sites in the BCC-(Nb, Ni, Ti, Zr, Co) lattice, which apparently causes higher diffusivity of hydrogen.
- The Nb20Ni20Ti20Zr20Co20 alloy shows lower activation energy and higher permeability at temperatures of 300–350 °C as well as higher resistance to hydrogen embrittlement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ockwig, N.W.; Nenoff, T.M. Membranes for Hydrogen Separation. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4078–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.D. Non-Pd BCC Alloy Membranes for Industrial Hydrogen Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.J.; Maroño, M.; Sánchez-Hervás, J.M. Pd-Based Membranes for Hydrogen Separation: Review of Alloying Elements and Their Influence on Membrane Properties. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Q.; Diniz da Costa, J.C.; Duke, M.; Giessler, S.; Socolow, R.; Williams, R.H.; Kreutz, T. Inorganic Membranes for Hydrogen Production and Purification: A Critical Review and Perspective. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhong, B.; Xiao, H.; Ye, X.; Lu, L.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. Effect of Degassing Treatment on the Deuterium Permeability of Pd-Nb-Pd Composite Membranes during Deuterium Permeation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.W.; Donelson, R. Developments and Design of Novel (Non-Palladium-Based) Metal Membranes for Hydrogen Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5657–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Min, R.N.; Zhao, P.; Misra, R.D.K.; Huang, P.R.; Zou, Y.J.; Chu, H.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.X. Design of Nb-Based Multi-Phase Alloy Membranes for High Hydrogen Permeability and Suppressed Hydrogen Embrittlement. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, T.; Shimizu, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Rong, R.; Watanabe, N.; Yukawa, H.; Morinaga, M.; Yasuda, I. Enhanced Hydrogen Embrittlement of Pd-Coated Niobium Metal Membrane Detected by in Situ Small Punch Test under Hydrogen Permeation. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446–447, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnone, E.; Jeon, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Fleury, E. Relationship between Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeation Properties in the Multiphase Ni21Ti23Nb56 Alloy Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Liu, Y. Microstructure of Nb-Ta-V Based Hydrogen Permeation High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 849, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Inui, H.; Tokui, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Aoki, K. Microstructures and Hydrogen Permeability of Directionally Solidified Nb–Ni–Ti Alloys with the Nb–NiTi Eutectic Microstructure. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Huang, H.; Sun, B.; Song, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Hydrogen Permeability of Multiphase V-Ti-Ni Alloy Membranes. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakova, R.M.; Kurbanova, E.D.; Sidorov, N.I.; Polukhin, V.A. Nb–Ni- and V–Ni-Based Membranes for High-Purity Hydrogen Production. Russ. Metall. Met. 2022, 2022, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpo, Y.; Yamaura, S.-I.; Nishida, M.; Kimura, H.; Inoue, A. Development of Melt-Spun Ni–Nb–Zr–Co Amorphous Alloy for High-Performance Hydrogen Separating Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.X.; Ishikawa, K.; Aoki, K. Effect of Elements Addition on Hydrogen Permeability and Ductility of Nb40Ti18Zr12Ni30 Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divinski, S.V.; Lukianova, O.A.; Wilde, G.; Dash, A.; Esakkiraja, N.; Paul, A. High-Entropy Alloys: Diffusion. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Metals and Alloys; Caballero, F.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 402–416. ISBN 978-0-12-819733-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Zhong, Y.-Z.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Hsu, T.; Yeh, J.-W. Physical Metallurgy of Concentrated Solid Solutions from Low-Entropy to High-Entropy Alloys. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, K. Microstructure, Phase Stability and Mechanical Properties of Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr and Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr–Hf High Entropy Alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2015, 25, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H. A Review for Consistent Analysis of Hydrogen Permeability through Dense Metallic Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, D.R. Optimized Norm-Conserving Vanderbilt Pseudopotentials. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 085117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonze, X.; Amadon, B.; Antonius, G.; Arnardi, F.; Baguet, L.; Beuken, J.-M.; Bieder, J.; Bottin, F.; Bouchet, J.; Bousquet, E. The ABINIT Project: Impact, Environment and Recent Developments. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 248, 107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.H.; Allan, D.C.; Amadon, B.; Antonius, G.; Applencourt, T.; Baguet, L.; Bieder, J.; Bottin, F.; Bouchet, J.; Bousquet, E. ABINIT: Overview and Focus on Selected Capabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaiche, L.; Vanderbilt, D. The Virtual Crystal Approximation Revisited: Application to Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Perovskites. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 7877–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosez, P.; Desquesnes, D.; Gonze, X.; Rabe, K.M. First-Principles Study of Lattice Instabilities in BaxSr1−xTiO3. AIP Conference Proceedings 2000, 535, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashi, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Matsuda, T.; Aoki, K. Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability in Nb–Ti–Co Multiphase Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 425, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Li, X.; Rettenmayr, M.; Liu, D.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.; Xu, D.; Fu, H. Design of Hydrogen Permeable Nb–Ni–Ti Alloys by Correlating the Microstructures, Solidification Paths and Hydrogen Permeability. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 3505–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Tokui, S.; Aoki, K. Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeation of Cold Rolled and Annealed Nb40Ti30Ni30 Alloy. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, A.; Tosti, S.; Basile, A. 4—Alternatives to Palladium in Membranes for Hydrogen Separation: Nickel, Niobium and Vanadium Alloys, Ceramic Supports for Metal Alloys and Porous Glass Membranes. In Handbook of Membrane Reactors; Basile, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 183–217. ISBN 978-0-85709-414-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Zhang, G.; Morinaga, M. Alloy Design of Nb-Based Hydrogen Permeable Membrane with Strong Resistance to Hydrogen Embrittlement. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Zhuang, H.; Lackner, K.S. Probing the Interactions between Interstitial Hydrogen Atoms in Niobium through Density Functional Theory Calculations. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Region | Concentration, at. % | Possible Phases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Ni | Ti | Zr | Co | |||
| Nb20Ni20Ti20Zr20Co20 | 1 | 74 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 6 | BCC-Nb(Ni, Ti, Zr, Co) |
| 2 | 15 | 20 | 16 | 29 | 19 | BCC-(Nb, Ni, Ti, Zr, Co) | |
| Nb40Ni25Ti18Zr12Co5 | 3 | 88.8 | 3.7 | 6.5 | - | 0.9 | BCC-Nb(Ni, Ti, Co) |
| 4 | 7.7 | 41.6 | 26.3 | 16.6 | 7.6 | B2-Ni(Ti, Zr), B2-CoZr | |
| 5 | 31 | 36 | 17.7 | 8.5 | 6.5 | BCC-Nb(Ni, Ti, Zr, Co), B2-Ni(Ti, Zr) | |
| Alloy | Phase | Lattice Constant, Å | Eb, eV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp | a, Calc | b, Calc | c, Calc | |||
| Nb74Ni6Ti9Zr5Co6 | pure | 3.306 | 3.192 | 3.192 | 3.192 | - |
| H in T sites | 3.275 | 3.293 | 3.293 | 0.760 | ||
| H in O sites | 3.137 | 3.137 | 3.586 | 0.441 | ||
| Nb15Ni20Ti16Zr29Co19 | pure | 3.090 | 2.979 | 2.979 | 2.979 | - |
| H in O sites | 2.727 | 2.727 | 3.863 | 0.248 | ||
| Nb88.8Ni3.7Ti6.5Co0.9 | pure | 3.306 | 3.251 | 3.251 | 3.251 | - |
| H in T sites | 3.331 | 3.354 | 3.354 | 1.037 | ||
| H in O sites | 3.196 | 3.196 | 3.641 | 0.777 | ||
| Nb7.7Ni41.6Ti26.32Zr16.6Co7.59 | pure | 3.060 | 2.855 | 2.855 | 2.855 | - |
| H in O sites | 2.609 | 2.609 | 3.717 | 0.686 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashkarov, E.; Krotkevich, D.; Koptsev, M.; Ognev, S.; Svyatkin, L.; Travitzky, N.; Lider, A. Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability of Nb-Ni-Ti-Zr-Co High Entropy Alloys. Membranes 2022, 12, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111157
Kashkarov E, Krotkevich D, Koptsev M, Ognev S, Svyatkin L, Travitzky N, Lider A. Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability of Nb-Ni-Ti-Zr-Co High Entropy Alloys. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111157
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashkarov, Egor, Dmitriy Krotkevich, Maxim Koptsev, Sergei Ognev, Leonid Svyatkin, Nahum Travitzky, and Andrey Lider. 2022. "Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability of Nb-Ni-Ti-Zr-Co High Entropy Alloys" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111157
APA StyleKashkarov, E., Krotkevich, D., Koptsev, M., Ognev, S., Svyatkin, L., Travitzky, N., & Lider, A. (2022). Microstructure and Hydrogen Permeability of Nb-Ni-Ti-Zr-Co High Entropy Alloys. Membranes, 12(11), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111157







