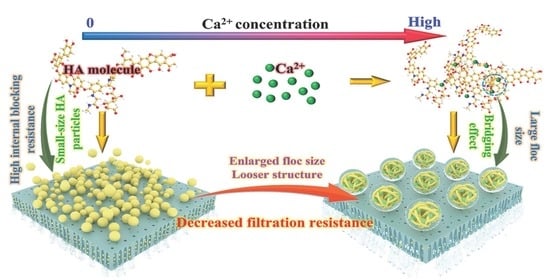
Impacts of Calcium Addition on Humic Acid Fouling and the Related Mechanism in Ultrafiltration Process for Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
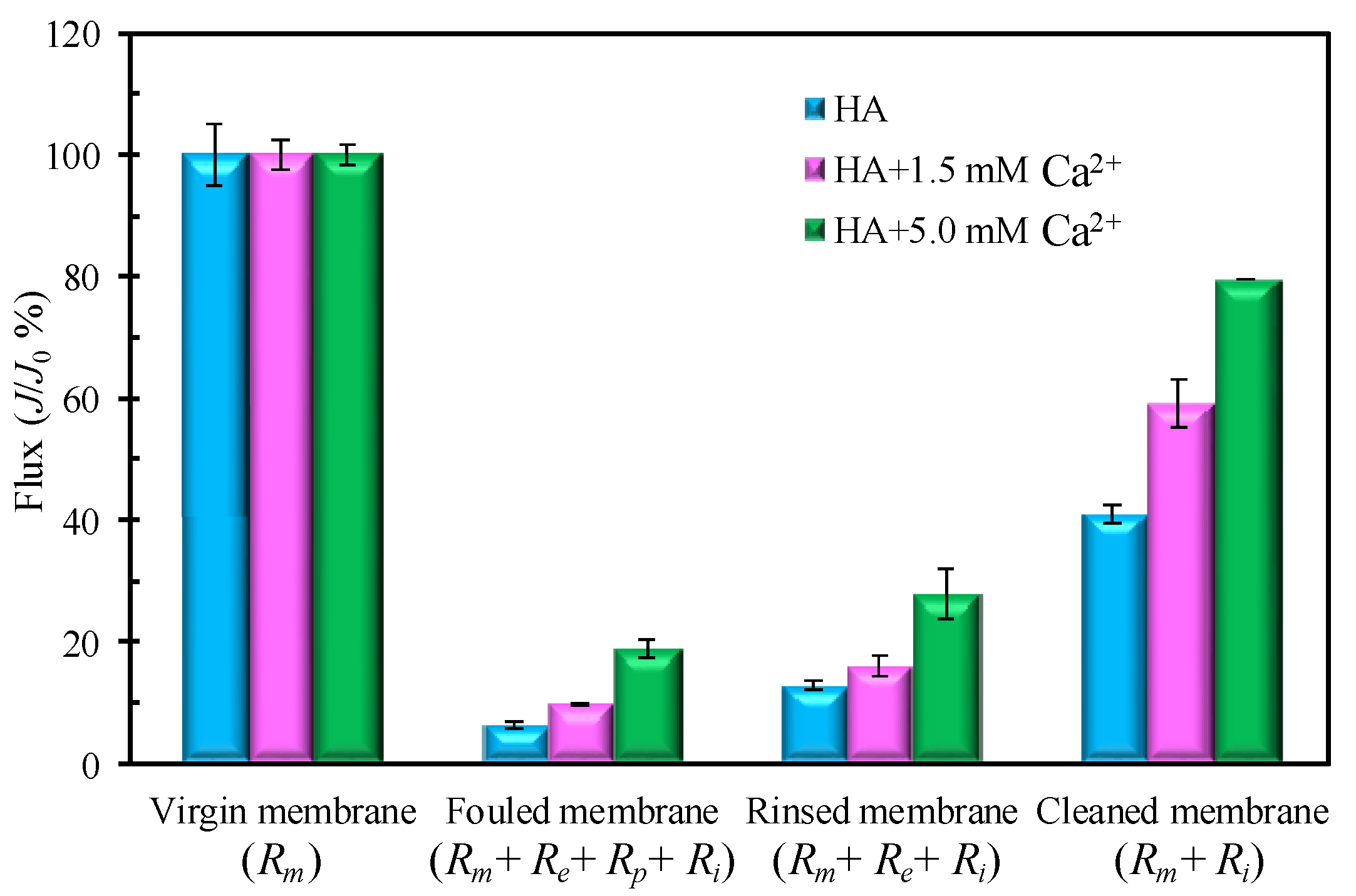
2.2. Filtration Resistance Tests
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Extended Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (XDLVO) Theory
3. Results
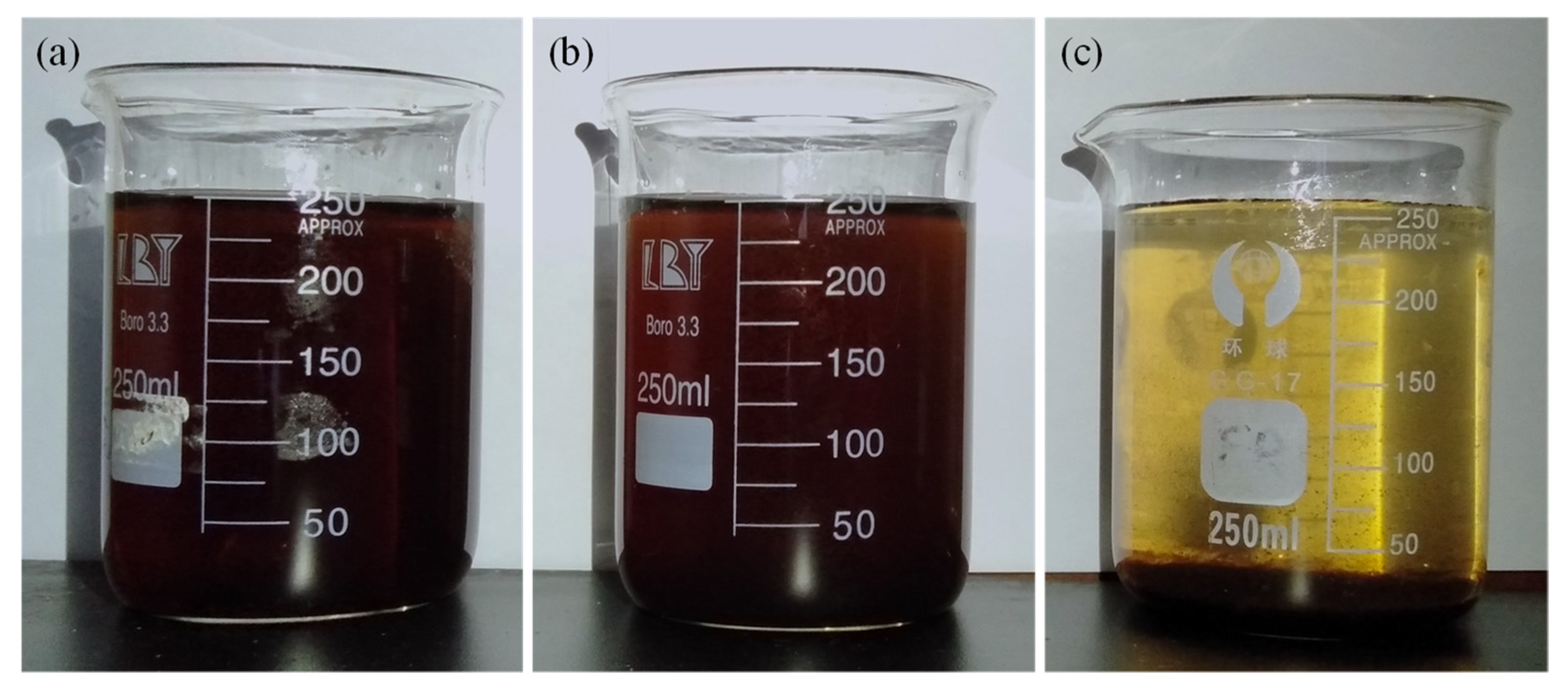
3.1. Impacts of Ca2+ Concentration on Filtration Behaviors of HA
3.2. Characterization of HA under Different Ca2+ Concentrations
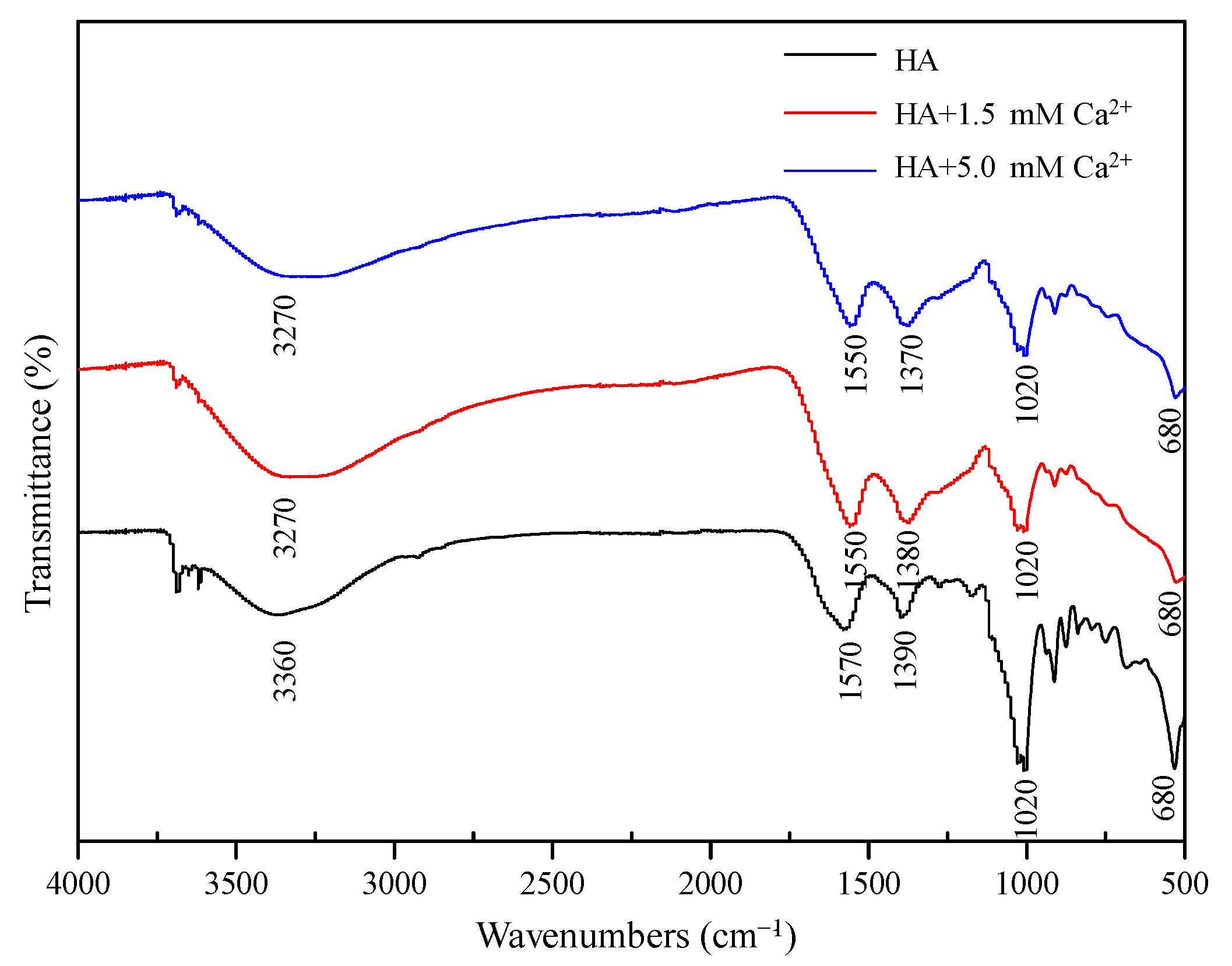
3.2.1. FT-IR Spectra Analysis
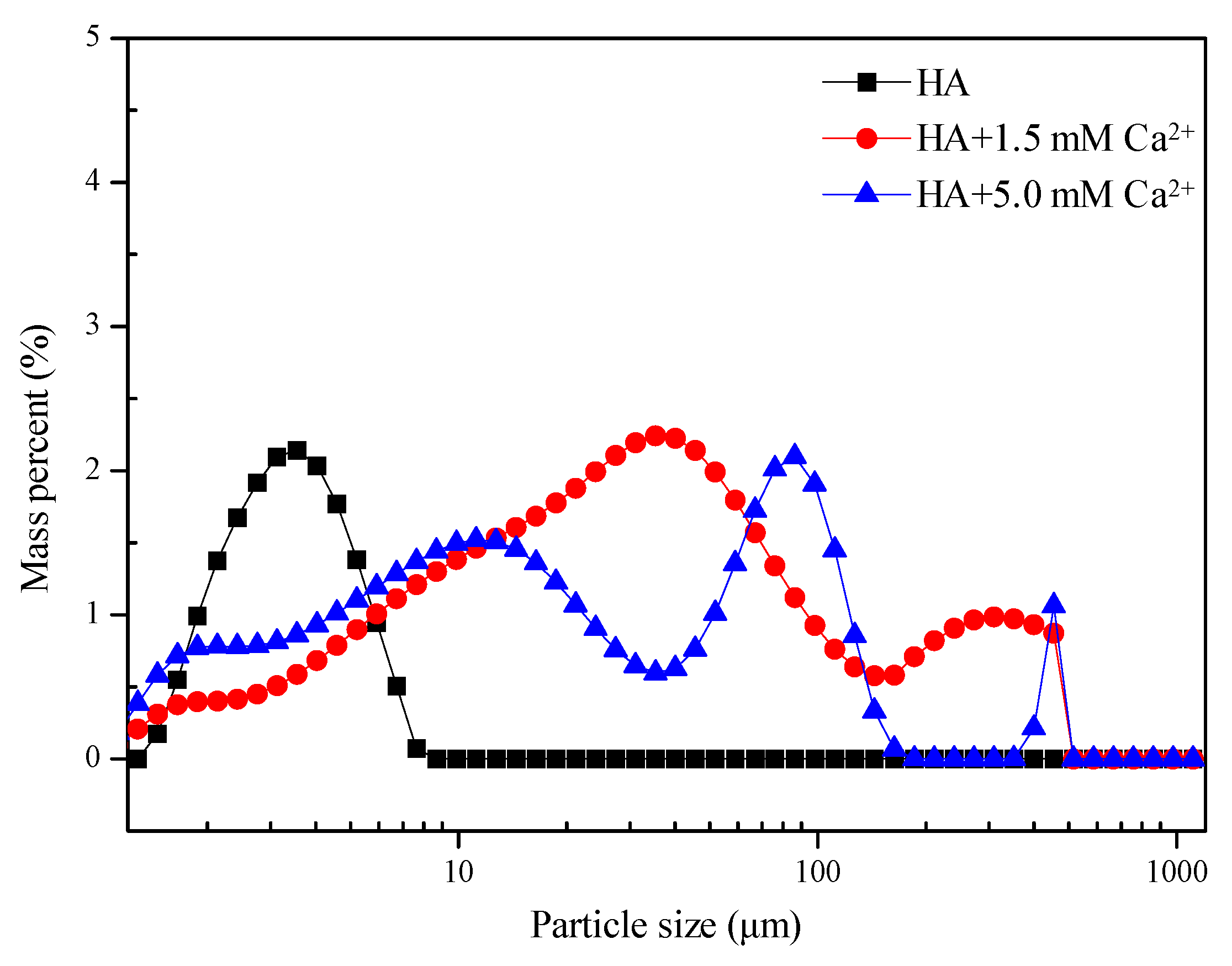
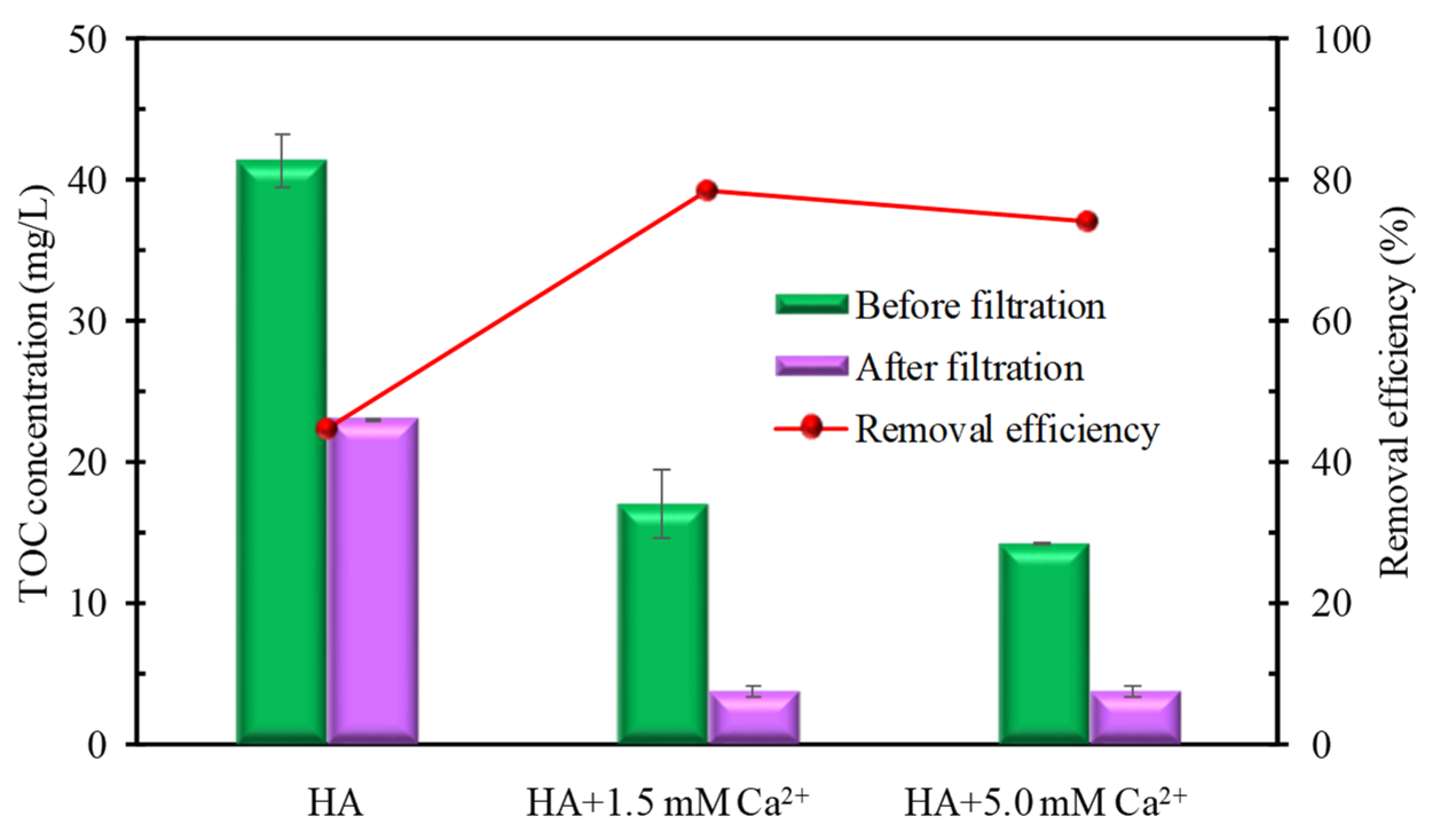
3.2.2. Particle Size Distribution (PSD) and TOC Removal Measurements
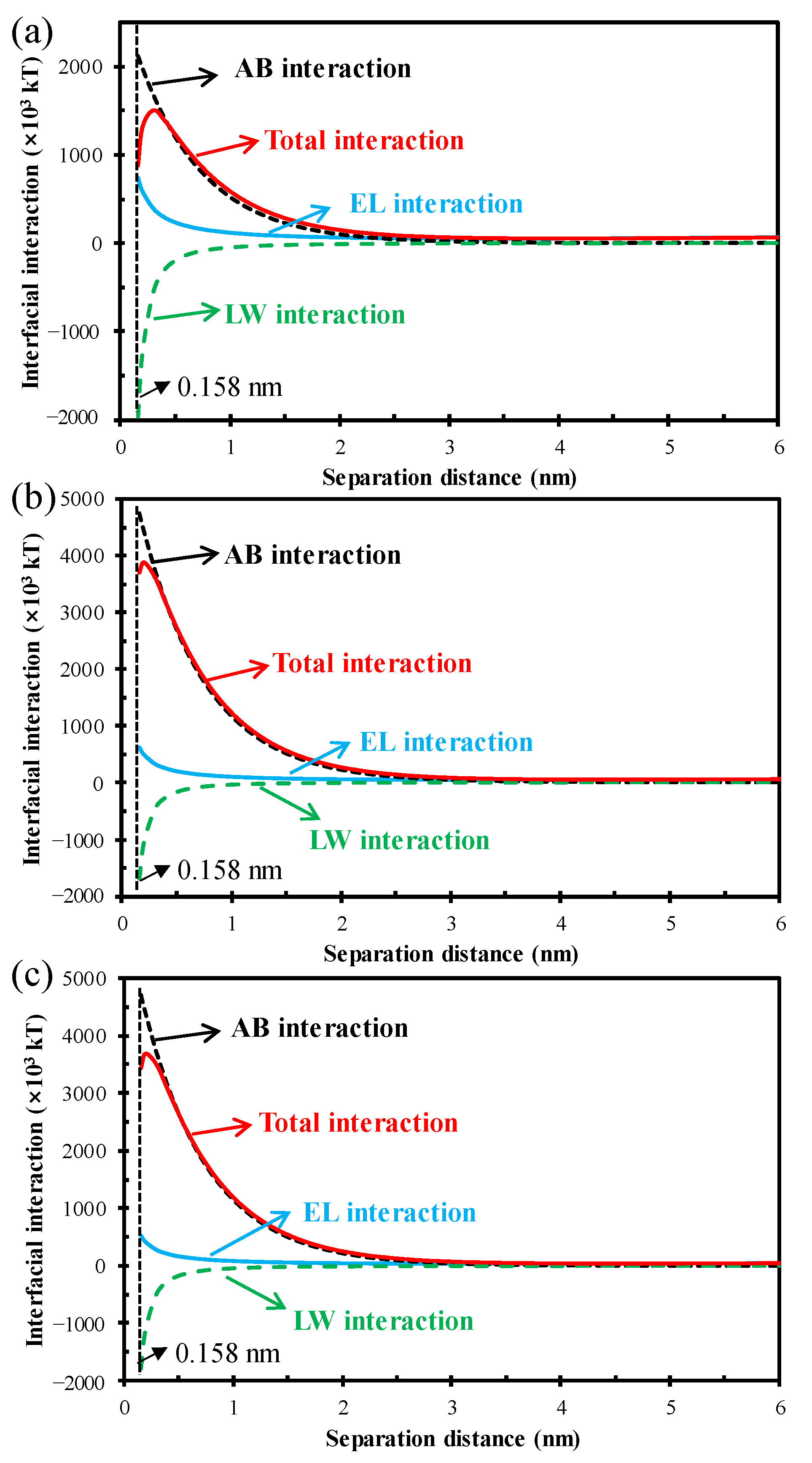
3.3. Thermodynamic Mechanism of HA Fouling Behavior
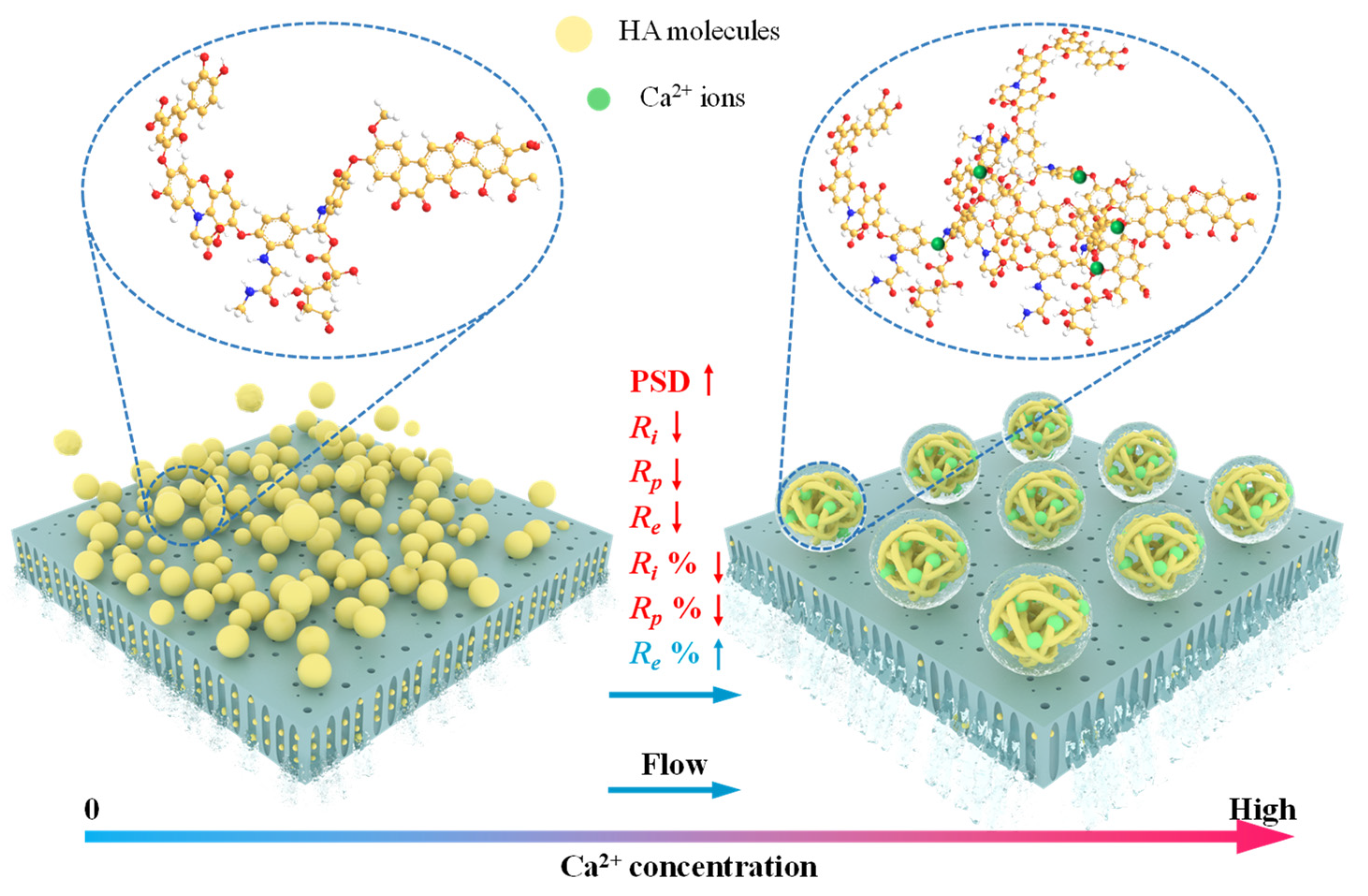
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamura, H.; Okimoto, K.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Hydrophilic fraction of natural organic matter causing irreversible fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2014, 54, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Dong, L.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Deng, Y.; You, X.; Yang, L.; Liao, B.-Q. Synergistic fouling behaviors and mechanisms of calcium ions and polyaluminum chloride associated with alginate solution in coagulation-ultrafiltration (UF) process. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, G.; Xu, D.; Yan, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhao, J.; Tang, X. A solar photo-thermochemical hybrid system using peroxydisulfate for organic matters removal and improving ultrafiltration membrane performance in surface water treatment. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Elimelech, M. Combined influence of natural organic matter (NOM) and colloidal particles on nanofiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Soltani, A.; Zheng, X.; Ernst, M. Effect of inorganic colloidal water constituents on combined low-pressure membrane fouling with natural organic matter (NOM). J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Quantification of interfacial energies associated with membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor by using BP and GRNN artificial neural networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Teng, J.; Chen, Y.; Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. New insights into membrane fouling by alginate: Impacts of ionic strength in presence of calcium ions. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Crawshaw, J.; Liu, T.; Graham, N. Ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter: Mechanisms and mitigation by pre-ozonation and pH. Water Res. 2018, 139, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zeng, B.; Lin, H.; Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Hong, H.; Zhang, M. Fundamental thermodynamic mechanisms of membrane fouling caused by transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Gao, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Yue, Q. Alleviating membrane fouling of modified polysulfone membrane via coagulation pretreatment/ultrafiltration hybrid process. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hong, H.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Lin, H. Thermodynamic mechanisms of membrane fouling during filtration of alginate solution in coagulation-ultrafiltration (UF) process in presence of different ionic strength and iron(III) ion concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi, S.; Benjamin, M.M. Using adsorbent mixtures to mitigate membrane fouling and remove NOM with microgranular adsorptive filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Song, B.; Li, D.; Cao, P.; Peng, X.; Liu, S. Advanced oxidation processes and selection of industrial water source: A new sight from natural organic matter. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Pan, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhao, D.; Teng, J.; Hong, H.; Lin, H. Effects of polysaccharides’ molecular structure on membrane fouling and the related mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Leung, K.-T.; Lin, H.; Liao, B. Evaluation of membrane fouling in a microalgal-bacterial membrane photobioreactor: Effects of SRT. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, N.A.; Choppin, G.R. Humic acids coagulation: Influence of divalent cations. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, H.; Gao, S.; Li, G.; Cui, F.; Qu, F. Applying ultraviolet/persulfate (UV/PS) pre-oxidation for controlling ultrafiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) in surface water. Water Res. 2018, 132, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wu, G.; Li, W.; Miao, R.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Roles of membrane–foulant and inter/intrafoulant species interaction forces in combined fouling of an ultrafiltration membrane. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hua, X.; Miao, R.; Ma, B.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Influence of floc charge and related distribution mechanisms of humic substances on ultrafiltration membrane behavior. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 609, 118260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lin, W.; Shao, R.; Shen, Y.-X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, X. Interaction between humic acid and silica in reverse osmosis membrane fouling process: A spectroscopic and molecular dynamics insight. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Song, T.; Yu, Y.; Qu, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Tang, W. Insight into the influence of humic acid and sodium alginate fractions on membrane fouling in coagulation-ultrafiltration combined system. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Kim, H.; Jung, J.; Jo, S.; Choi, H. Influence of extreme concentrations of hydrophilic pore-former on reinforced polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes for reduction of humic acid fouling. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Z. A new ultrasonic cleaning model for predicting the flux recovery of the UF membrane fouled with humic acid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, M.M.M.; Anioke, G.; Nakagoe, O.; Tanabe, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Fujioka, T. Membrane fouling, chemical cleaning and separation performance assessment of a chlorine-resistant nanofiltration membrane for water recycling applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Wang, L.-L.; Ye, X.-D.; Li, W.-W.; Ren, X.-M.; Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Wang, X.-K. Coagulation Kinetics of Humic Aggregates in Mono- and Di-Valent Electrolyte Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5042–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, S.; Nakhla, G. Impact of calcium on the membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Khan, I.A.; Siyal, M.I.; Lee, C.-K.; Kim, J.-O. Optimization of membrane modification using SiO2 for robust anti-fouling performance with calcium-humic acid feed in membrane distillation. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Ding, M.; Xie, Z. Mechanistic insights into the removal of PFOA by 2D MXene/CNT membrane with the influence of Ca2+ and humic acid. Desalination 2022, 529, 115643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Elimelech, M. Impact of humic acid fouling on membrane performance and transport of pharmaceutically active compounds in forward osmosis. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.E.; Chang, Y.-C.; Liang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-P.; Chiang, P.-C. Identifying the rejection mechanism for nanofiltration membranes fouled by humic acid and calcium ions exemplified by acetaminophen, sulfamethoxazole, and triclosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; He, D.-Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.-Q. Probing the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in humic acids-induced ultrafiltration membrane fouling using an integrated approach. Water Res. 2015, 81, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansima, M.A.C.K.; Ketharani, J.; Samarajeewa, D.R.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Herath, A.C.; Makehelwala, M.; Indika, S.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Weragoda, S.K.; Wei, Y.; et al. Probing fouling mechanism of anion exchange membranes used in electrodialysis self-reversible treatment by humic acid and calcium ions. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 8, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listiarini, K.; Sun, D.D.; Leckie, J.O. Organic fouling of nanofiltration membranes: Evaluating the effects of humic acid, calcium, alum coagulant and their combinations on the specific cake resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 332, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Interaction mechanisms of humic acid combined with calcium ions on membrane fouling at different conditions in an ultrafiltration system. Desalination 2015, 357, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, W.; Ma, J. Opposite impacts of K+ and Ca2+ on membrane fouling by humic acid and cleaning process: Evaluation and mechanism investigation. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Qu, F.; Liu, B.; Yu, H.; Li, K.; Shao, S.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Hydraulic irreversibility of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acid: Effects of membrane properties and backwash water composition. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, T. A comparison of the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on membrane fouling with humic acid: Are there any differences or similarities? J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, O.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, K. Membrane Bioreactor in China: A Critical Review. Int. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Lee, E.; Vonghia, E.; Hong, Y.; Liao, B. 1—Introduction to aerobic membrane bioreactors: Current status and recent developments. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Ng, H.Y., Ng, T.C.A., Ngo, H.H., Mannina, G., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Xiao, T.; Tan, Y.Z.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Contaminant rejection in the presence of humic acid by membrane distillation for surface water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Lu, Q.; Mao, X.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Hu, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H. Probing the intermolecular interaction mechanisms between humic acid and different substrates with implications for its adsorption and removal in water treatment. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousman, M.; Bennasar, M. Determination of various hydraulic resistances during cross-flow filtration of a starch grain suspension through inorganic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 105, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, J.; Rao, L.; Lin, H.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liao, B.-Q. Inkjet printing of dopamine followed by UV light irradiation to modify mussel-inspired PVDF membrane for efficient oil-water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 619, 118790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhao, L.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Hong, H.; He, Y. Membrane fouling caused by biological foams in a submerged membrane bioreactor: Mechanism insights. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tao, M.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, Y.; Hong, H.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H. In-situ growth of UiO-66-NH2 in porous polymeric substrates at room temperature for fabrication of mixed matrix membranes with fast molecular separation performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hong, H.; Lin, H. Novel catalytic self-cleaning membrane with peroxymonosulfate activation for dual-function wastewater purification: Performance and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Lin, H. Preparation of nickel@polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) conductive membranes to couple a novel electrocoagulation-membrane separation system for efficient oil-water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H. A new strategy to accelerate co-deposition of plant polyphenol and amine for fabrication of antibacterial nanofiltration membranes by in-situ grown Ag nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J. Acid—Base interfacial interactions in aqueous media. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 78, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Hong, H.; Lin, H. A novel in-situ micro-aeration functional membrane with excellent decoloration efficiency and antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Hong, H.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. Facile synthesis of 2D TiO2@MXene composite membrane with enhanced separation and antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Agarwal, G.K. Extended DLVO interactions between spherical particles and rough surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z.; Hong, H.; Chen, C. Preparation of Ni@UiO-66 incorporated polyethersulfone (PES) membrane by magnetic field assisted strategy to improve permeability and photocatalytic self-cleaning ability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 618, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brant, J.A.; Childress, A.E. Colloidal adhesion to hydrophilic membrane surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, D.; Xu, C.; Zhong, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, M.; Ma, J. Synergistic oxidation-filtration process analysis of catalytic CuFe2O4 - Tailored ceramic membrane filtration via peroxymonosulfate activation for humic acid treatment. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararajan, M.; Rajaraman, G.; Ghosh, S.K. Speciation of uranyl ions in fulvic acid and humic acid: A DFT exploration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 18038–18046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, J.; Chen, Y.; Bollag, J.M. Characterization of Humic Acids, Composts, and Peat by Diffuse Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guan, J.; Santiwong, S.R.; Waite, T.D. Characterization of floc size and structure under different monomer and polymer coagulants on microfiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 321, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-G.; Lei, Q.; Chen, J.-R.; Hong, H.-C.; He, Y.-M.; Lin, H.-J. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor: Impacts of floc size. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Leung, K.-T.; Lin, H.; Liao, B. Membrane fouling in a microalgal-bacterial membrane photobioreactor: Effects of P-availability controlled by N:P ratio. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; He, Y. Different fouling propensities of loosely and tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) and the related fouling mechanisms in a membrane bioreactor. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Contact Angle (°) | Zeta Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Glycerol | Diiodomethane | ||
| PVDF membrane | 62.16 ± 0.10 | 57.22 ± 1.47 | 23.15 ± 0.82 | −25.21 ± 2.46 |
| HA | 48.93 ± 0.28 | 70.99 ± 0.99 | 34.36 ± 0.51 | −26.67 ± 0.50 |
| HA + 1.5 mM Ca2+ | 42.36 ± 0.47 | 74.25 ± 0.18 | 41.36 ± 0.10 | −22.87 ± 0.50 |
| HA + 5.0 mM Ca2+ | 41.75 ± 0.12 | 73.64 ± 0.31 | 38.61 ± 0.08 | −19.03 ± 0.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, H.; Long, Y.; Shen, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H. Impacts of Calcium Addition on Humic Acid Fouling and the Related Mechanism in Ultrafiltration Process for Water Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111033
Zou H, Long Y, Shen L, He Y, Zhang M, Lin H. Impacts of Calcium Addition on Humic Acid Fouling and the Related Mechanism in Ultrafiltration Process for Water Treatment. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111033
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Hui, Ying Long, Liguo Shen, Yiming He, Meijia Zhang, and Hongjun Lin. 2022. "Impacts of Calcium Addition on Humic Acid Fouling and the Related Mechanism in Ultrafiltration Process for Water Treatment" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111033
APA StyleZou, H., Long, Y., Shen, L., He, Y., Zhang, M., & Lin, H. (2022). Impacts of Calcium Addition on Humic Acid Fouling and the Related Mechanism in Ultrafiltration Process for Water Treatment. Membranes, 12(11), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111033