Polyphenylene Sulfide-Based Membranes: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PPS Resin Synthesis
2.1. Phillips Method
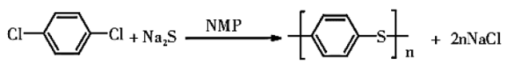
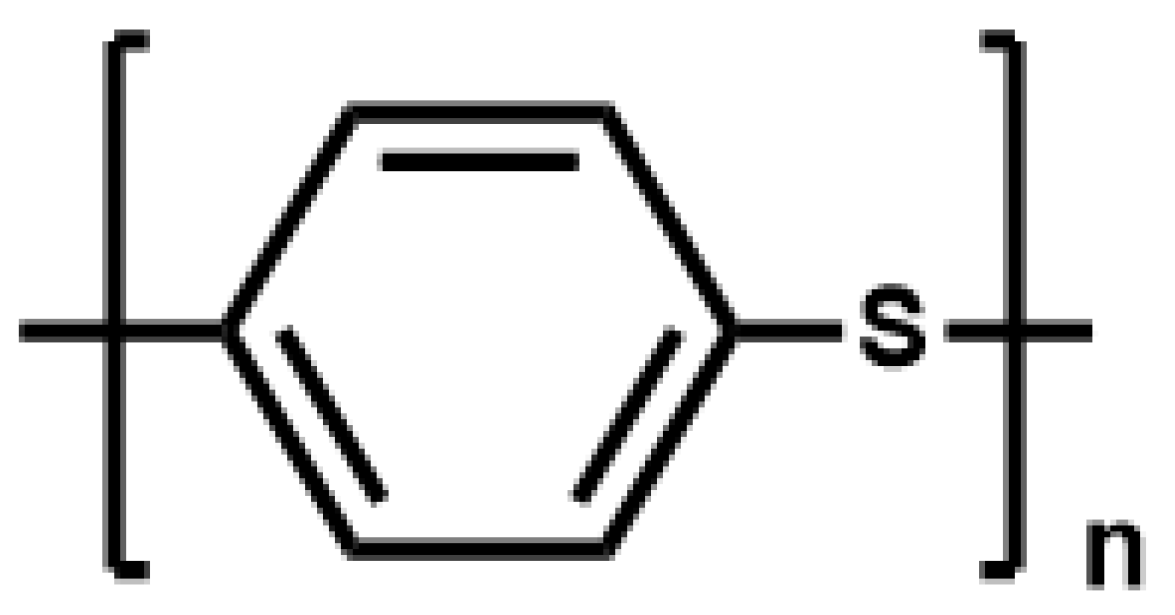
2.2. Sulfur Method

2.3. Other Methods
2.4. Synthesis Methods of Resins with Special Structure
2.4.1. Linear High-Molecular Weight Resin
2.4.2. Branched High Molecular Weight Resin

2.4.3. Resin with Low Melting Temperature
3. PPS Flat Membrane
3.1. PPS Flat Membrane Preparation Process
3.2. PPS Flat Membrane Modification Process
3.3. Development Prospects of PPS Flat Membrane
4. PPS Hollow Fiber Membrane
5. PPS Ultrafine Fiber Membrane
5.1. PPS Ultrafine Fiber Membrane Preparation Process
5.2. Application and Modification of PPS Ultrafine Fiber Membrane
5.2.1. Separation Field
5.2.2. Adsorption Field
5.2.3. Lithium Ion Battery and Electrolytic Cell Separator Field
5.2.4. Catalytic Field
5.3. Development Prospects of PPS Ultrafine Fiber Membrane
6. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.B.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic PVDF Membranes for Effective Separation of Water-in-Oil Emulsions with High Flux. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Aguayo, A.T.; Bilbao, J.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Membrane Reactors for in Situ Water Removal: A Review of Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10342–10354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y. Preparation and properties of high toughness RBAO macroporous membrane support. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Jung, J.T.; Wang, H.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Moore, T.; Sanguineti, A.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) and stretching methods. J. Membrane Sci. 2016, 509, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaji, A.D.; Kutubkhanah, I.K.; Wie, J.M. Advances in seawater desalination technologies. Desalination 2008, 221, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Li, L. Nafion membranes as electrolyte and separator for sodium-ion battery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16110–16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attias, R.; Salama, M.; Hirsch, B.; Goffer, Y.; Aurbach, D. Anode-Electrolyte Interfaces in Secondary Magnesium Batteries. Joule 2019, 3, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsik, C.; Jungrok, L.; Seongwoo, R.; Bon-Cheol, K. Fabrication and Applications of Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) Composites: A Short Review. Compos. Res. 2020, 33, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Mai, Y.W.; Li, R.K.Y.; Ye, L. Impact strength and crystallization behavior of nano-SiOx/poly(phenylene sulfide) (PPS) composites with heat-treated PPS. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.; Benevides, R.C.; Laribi, M.A.; Fitoussi, J.; Shirinbayan, M.; Bakir, F.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Multi-scale analysis of the effect of loading conditions on monotonic and fatigue behavior of a glass fiber reinforced polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 145, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanthapanichakoon, W.; Hata, M.; Nitta, K.; Furuuchi, M.; Otani, Y. Mechanical degradation of filter polymer materials: Polyphenylene sulfide. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Du, J.; Dang, J.; Geng, W.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Q. Thermal conductivities, mechanical and thermal properties of graphite nanoplatelets/polyphenylene sulfide composites. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 22101–22105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.M.; Lee, C.L.; Tai, N.H. Chemical resistance of carbon fiber-reinforced poly (ether ether ketone) and poly (phenylene sulfide) composites. Polym. Composite. 1992, 13, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Pascual, A.M.; Naffakh, M. Synthesis and characterization of nitrated and aminated poly(phenylene sulfide) derivatives for advanced applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 131, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, C.J.; Liu, F.T.; Jiang, M.J.; Wang, H.Y. Bristle worm inspired ultra-durable superhydrophobic coating with repairable microstructures and anti-corrosion/scaling properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Huang, H.; Zhao, L.; Nie, K.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Fabrication and application of poly (phenylene sulfide) ultrafine fiber. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 150, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.; Cabrera, N.O.; Barkoula, N.M.; Peijs, T. Low velocity impact performance of recyclable all-polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wei, J.; Liao, R.; Tang, C.Y. Zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes: Towards enhanced performance for forward osmosis. J. Membrane Sci. 2012, 405, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Hay, A.S. A facile synthesis and the polymerization of macrocyclic 1, 4-phenylene sulfide (PPS) oligomers. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 5050–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahate, A.S.; Nemade, K.R.; Waghuley, S.A. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS): State of the art and applications. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2013, 29, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.J.T.; Hill, J.H.W. Production of Polymers from Aromatic Compounds. United State Patent No. 3354129, 21 November 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.R.; Wu, Q.X.; Yang, J.; Hou, C.S.; Zhu, J.M. A Study on the structure of Poly (p-phenylene sulfide) prepared by sulfur solution method. J. Sichuan Univ. Nat. Sci. Edit. 1988, 25, 101–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, J.; Seferis, J.; Sheppard, C. Dual-mechanism kinetics of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) melt-crystallization. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1994, 42, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.P. Application and production methods of polyphenylene sulfide. Chem. Eng. Eq. 2009, 10, 142–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Macallum, A.D. A dry synthesis of aromatic sulfides; phenylene sulfide resins. J. Org. Chem. 1948, 13, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, E.; Yamamoto, K.; Jikei, M.; Nishide, H. New synthesis of poly (phenylene sulfides) through oxygen oxidative polymerization of diphenyl disulfide with vanadium oxide catalyst. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4138–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, R.W.; Handlovits, C.E.; Smith, H.A. Phenylene sulfide polymers. III. The synthesis of linear polyphenylene sulfide. J. Polym. Sci. 1962, 58, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.T.; Lacey, L.E. Arylene sulfide polymer prepared from aminoalkanoat. United State Patent No. 4324886, 13 April 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.X.; Yang, Y.S. The synthesis of Poly (p-phenylene sulfide) resin with linear high mdecular weight. J. Sichuan Univ. Nat. Sci. Edit. 1998, 35, 488–490. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.J.; Yan, Y.G. Study on synthesis of linear and high molecular weight poly (pheneylene sulfide) at atmospheric pressure. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 15, 170–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, D.F.; Jiang, W.W.; Li, J.J.; Yang, Q. Study on synthesis of linear and high molecular poly (p-phenylene sulfide) with lithium sulfide. New Chem. Mater. 2013, 41, 50–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, R.W. p-Phenylene sulfide polymers. United State Patent No. 3919177, 11 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Edmends, J.T.; Hill, H.W. Synthesis of High Molecular Weight Branched Polyphenylene Sulfide. United State Patent No. 3354129, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Luo, M.M. Study of branch-reactive-high-molecular-weight Poly(phenylene sulfide) synthesized by sulfur solution routh. Chem. Res. Appl. 1995, 7, 271–276. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jikei, M.; Hu, Z.; Kakimoto, M.-A.; Imai, Y. Synthesis of Hyperbranched Poly (phenylene sulfide) via a Poly (sulfonium cation) Precursor. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.X.; Chen, Y.R.; Xiong, Y.X.; Luo, J.X. Synthesis and curing of low melting-point poly-(p-phenylene sulfide). Adv. Eng. Sci. 1982, 2, 71–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.P.; Wang, M.M.; Jiang, Y.N.; Qi, C.Y.; An, H.Y. Preparation of Low Melting Point Linear High Molecular Weight Polyphenylene Sulfide. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2016, 10, 2277–2279. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, B. A Preparation Method of Polyphenylene Sulfide Resin for Melt Blowing. Chinese Patent No. CN 107722274a, 23 February 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Zeng, Y.; Meng, X.; Tian, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, S. Porous polyphenylene sulfide membrane with high durability against solvents by the thermally induced phase-separation method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B. Structure control of polyphenylene sulfide membrane prepared by thermally induced phase separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 3280–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B. Effect of Diluent Mixture on Porous Structure of Polyphenylene Sulfide via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2009, 46, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Xiao, C. Effects of nucleating agents on the porous structure of polyphenylene sulfide via thermally induced phase separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, S.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Comparison of Various Solvents for Poly(Phenylene Sulfide) Microporous Membrane Preparation via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2014, 53, 1477–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Tian, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Preparation of microporous PVDF membrane via tips method using binary diluent of DPK and PG. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 3518–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, C.; Huang, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, K. Effect of additive and coagulation bath temperature on structure and properties of HDPE membranes via thermally induced phase separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 4834–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Han, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, P. Preparation of a hydrophobically enhanced antifouling isotactic polypropylene/silicone dioxide flat-sheet membrane via thermally induced phase separation for vacuum membrane distillation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fan, T.; Cheng, B. Preparation of a polyphenylene sulfide membrane from a ternary polymer/solvent/non-solvent system by thermally induced phase separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10503–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Li, J. Preparation, characterization of PPS micro-porous membranes and their excellent performance in vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membrane Sci. 2018, 556, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgard, R.A. Method for preparing poly(phenylene sulfide) membranes. United State Patent No. 5507984, 16 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, C.L.; Peng, Y.J.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.Y. Bipolar membrane prepared by grafting and plasma polymerization. J. Membrane Sci. 2003, 219, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Su, K. Superhydrophilic poly(p-phenylene sulfide) membrane preparation with acid/alkali solution resistance and its usage in oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. Ultrafiltration membranes from PVDF/PMMA blends. J. Membrane Sci. 1992, 73, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Fang, H.; Wang, J.W.; Hao, L.Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.S. Preparation and characterization of silicon nitride hollow fiber membranes for seawater desalination. J. Membrane Sci. 2014, 450, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; DesLauriers, P.; Fahey, D.R.; Wood, F.; Cornforth, F. Photodegradation and photostabilization of poly (p-phenylene sulfide). Part 2. UV induced physicochemical changes. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1995, 48, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, B.; Meng, S.; Chen, L.; Zhu, M. Effect of TiO2@SiO2 nanoparticles on the mechanical and UV-resistance properties of polyphenylene sulfide fibers. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2015, 25, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, M.; Su, K. Higher UV-shielding ability and lower photocatalytic activity of TiO2@SiO2/APTES and its excellent performance in enhancing the photostability of poly(p-phenylene sulfide). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21758–21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Spray-coating process in preparing PTFE-PPS composite super-hydrophobic coating. Aip Adv. 2014, 4, 031327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Qin, S.; Wu, J.; Cong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, Q. Bio-Inspired Superhydrophobic Polyphenylene Sulfide/Polytetrafluoroethylene Coatings with High Performance. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7222–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.T.; Miao, J.L.; Li, Z.H.; Cheng, B.W. Bio-inspired robust superhydrophobic-superoleophilic polyphenylene sulfide membrane for efficient oil/water separation under highly acidic or alkaline conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Y.; Su, K.M.; Fan, T.T.; Li, Z.H. Study on the structure and properties of PPS/PCNF hybrid membranes and their applications in wastewater treatment. Polymer 2019, 176, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Khataee, A. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/TiO2 blended PES nanofiltration membrane with improved antifouling and separation performance. Desalination 2016, 393, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Li, Z.H. Research progress of polyphenylene sulfide separation membrane materials. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.H.; Cao, L.; Cheng, B. A Superhydrophilic and Anti-Biofouling Polyphenylene Sulfide Microporous Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.; Ho, C.M. Surface molecular property modifications for poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) based microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 2009, 7, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ou, Y.; Lei, W.X.; Wan, L.S.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.K. CuSO4/H2O2-Induced Rapid Deposition of Polydopamine Coatings with High Uniformity and Enhanced Stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3054–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Luo, J.; Lv, Y.; Shen, P.; Xu, Z.K. Surface engineering of polymer membranes via mussel-inspired chemistry. J. Membrane Sci. 2015, 483, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, B.D.; Park, H.B.; Ju, H.; Rowe, B.W.; Miller, D.J.; Chun, B.J.; Kin, K.; Freeman, B.D. Influence of polydopamine deposition conditions on pure water flux and foulant adhesion resistance of reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and microfiltration membranes. Polymer 2010, 51, 3472–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, K.; Fan, T.; Cao, L. Mussel-inspired modification of PPS membrane to separate and remove the dyes from the wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Han, C.; Cui, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Electrostatic Assembly of a Titanium Dioxide@Hydrophilic Poly(phenylene sulfide) Porous Membrane with Enhanced Wetting Selectivity for Separation of Strongly Corrosive Oil-Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 35479–35487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Han, N.; Han, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Design of a Janus F-TiO2@PPS Porous Membrane with Asymmetric Wettability for Switchable Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 22408–22418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.K. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Mao, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Underwater superoleophobic-underoil superhydrophobic Janus ceramic membrane with its switchable separation in oil/water emulsions. J. Membrane Sci. 2018, 565, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Han, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Xia, B.; Han, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X. Adhesive-free in situ synthesis of a coral-like titanium dioxide@poly(phenylene sulfide) microporous membrane for visible-light photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffaj, N.; Persin, M.; Younsi, S.A.; Albizane, A.; Cretin, M.; Larbot, A. Elaboration and characterization of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes deposited on raw support prepared from natural Moroccan clay: Application to filtration of solution containing dyes and salts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoon, K.; Zhang, X.; Elyassi, B.; Brewer, D.D.; Gettel, M.; Kumar, S.; Lee, J.A.; Maheshwari, S.; Mittal, A.; Sung, C.-Y.; et al. Dispersible Exfoliated Zeolite Nanosheets and Their Application as a Selective Membrane. Science 2011, 334, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lin, X.; Ou, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Simon, G.P.; Easton, C.D.; Wang, H. Highly crosslinked, chlorine tolerant polymer network entwined graphene oxide membrane for water desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.; Kim, D.; Jung, H.-T. Enhanced water permeation based on nanoporous multilayer graphene membranes: The role of pore size and density. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17773–17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Su, K.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B. Graphene oxide hybrid poly(p-phenylene sulfide) nanofiltration membrane intercalated by bis(triethoxysilyl) ethane. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Su, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. A metal-nano GO frameworks/PPS membrane with super water flux and high dyes interception. J. Membrane Sci. 2019, 574, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Su, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Jia, K. NGO/PA layer with disordered arrangement hybrid PPS composite membrane for desalination. Desalination 2020, 479, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylton, K.; Mitra, S. A microfluidic hollow fiber membrane extractor for arsenic(V) detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylton, K.; Mitra, S. Automated, on-line membrane extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Saridara, C.; Mitra, S. Microfluidic supported liquid membrane extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 543, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Sheng, J.; Zhao, J.S. Study on hollow fiber microfiltration membrane of polyphenylene sulfide-Spinning of hollow fiber. J. Tex. Res. 2003, 24, 73–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.J.; Lim, D.Y.; Jeon, H.Y. Determining the absorption properties of split-type microfiber fabrics by measuring the change in color depth. Text. Res. J. 2004, 74, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Lebdeh, T.M.; Fini, E.; Lumpkin, M. Flexural and tensile characteristics of microfiber-reinforced very high strength concrete thin panels. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 5, 184–197. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Recent Progress in the Preparation, Characterization, and Applications of Nanofibers and Nanofiber Membranes via Electrospinning/Interfacial Polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 756–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Lv, Z.; Cai, X.; Hou, S. Macro/microfiber-shaped electronic devices. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, G.; Ma, W.; Meng, L.; Yin, H.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, R. Fabrication and Properties of Poly(L-lactide) Nanofibers via Blend Sea-Island Melt Spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Shivananju, B.N.; Lakshmi, K.P.; Asokan, S. Dual functional performance of fiber Bragg gratings coated with metals using flash evaporation technique. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2012, 18, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Bubakir, M.M.; Li, H. Melt-electrospinning of Polyphenylene Sulfide. Fiber Polym. 2018, 19, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Tan, J.; Yu, S.Y.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Lyu, T.T.; Jiao, Z.W.; Li, H.Y.; Ramakrishna, S. High-efficiency preparation of polypropylene nanofiber by melt differential centrifugal electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B. Application and Prospect of melt blown nonwovens. Fujian Qing Fang 2011, 4, 46–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, C.F.; Vasserman, I.; Gsell, T.C. Polyarylene Sulfide Melt Blown Fibers and Products. United State Patent No. 6110589, 29 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, A.B.; Harmon, W.S. Melt-Blown Polyarylene Sulfide Microfibers and Method of Making the Same. United State Patent No. 5695869, 9 December 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.W.; Luo, D.; Yan, J.B.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.X. Effect of hot rolling pressure and temperature on properties of polyphenylene sulfide melt blown nonwovens. Tech. Tex. 2017, 35, 16–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, N. Aerosol Indirect Effect on Biogeochemical Cycles and Climate. Science 2011, 334, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, E.P.; Jack, D.W.; Volavka-Close, N.H.; Kinney, P.L. Particulate matter pollution in African cities. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ou, G.; Wang, N.; We, H. Graphene-based Recyclable Photo-Absorbers for High-Efficiency Seawater Desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 9194–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, P. Hydrophobic Light-to-Heat Conversion Membranes with Self-Healing Ability for Interfacial Solar Heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4889–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.; Kang, G.; Cho, S.K.; Park, W.; Kim, K.; Padilla, W.J. Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Q.; Lin, P.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Flexible and Highly Efficient Bilayer Photothermal Paper for Water Desalination and Purification: Self-Floating, Rapid Water Transport, and Localized Heat. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 11204–11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.W.; Yan, J.B.; Zhao, Z.H.; Yin, X.Z.; Yue, H.S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.X. Oil absorption of melt blown polyphenylene sulfide nonwovens. Tech. Tex. 2017, 35, 20–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Polyphenylene sulfide microfiber membrane with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13243–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Su, Y.; Fan, Q.; Li, Z.; Cui, W.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Robust Graphene@ PPS Fibrous Membrane for Harsh Environmental Oil/Water Separation and All-Weather Cleanup of Crude Oil Spill by Joule Heat and Photothermal Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 19377–19386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Han, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of polyphenylene sulfide nanofibrous membrane via sacrificial templated-electrospinning for fast gravity-driven water-in-oil emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-W.; Liang, H.-W.; Yu, S.-H. Macroscopic-Scale Assembled Nanowire Thin Films and Their Functionalities. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4770–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkin, R.T.; McNeil, M.S. Laboratory evaluation of zero-valent iron to treat water impacted by acid mine drainage. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Mallouk, T.E. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2564–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.C.; Yin, X.Z.; Peng, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.X.; Chen, S.H. Removal of Chromium(VI) by Zero-Valent Iron Supported on Polyphenylene Sulfide Superfine Fiber. Synth. Fiber China 2017, 46, 31–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.R.; Sculley, J.; Zhou, H.C. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Separations. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 869–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachfule, P.; Das, R.; Poddar, P.; Banerjee, R. Structural, Magnetic, and Gas Adsorption Study of a Series of Partially Fluorinated Metal-Organic Frameworks (HF-MOFs). Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 3855–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.W.; Rossin, J.A.; DeCoste, J.B.; Killops, K.L.; Browe, M.; Valdes, E.; Jones, P. Zirconium Hydroxide-Metal-Organic Framework Composites for Toxic Chemical Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5462–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ren, L.; Liu, M.; Huang, S.; Xiao, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. Polyphenylene Sulfide Ultrafine Fibrous Membrane Modified by Nanoscale ZIF-8 for Highly Effective Adsorption, Interception, and Recycling of Iodine Vapor. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 31291–31301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.S.; Hitt, J. Lithium ion battery separators: Development and performance characterization of a composite membrane. J. Membrane Sci. 2013, 425, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Luo, D.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Yin, X.Z.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, H. Preparation and Performance of Polyphenylene Sulfide Nonwoven-Based Heat resistant Composite Separator for Lithium Ion Battery. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 34, 152–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Chen, M.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Polyphenylene sulfide nonwoven-based composite separator with superior heat-resistance and flame retardancy for high power lithium ion battery. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 157, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Choi, E.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H. Evaporation-induced, close-packed silica nanoparticle-embedded nonwoven composite separator membranes for high-voltage/high-rate lithium-ion batteries: Advantageous effect of highly percolated, electrolyte-philic microporous architecture. J. Membrane Sci. 2012, 415, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.Z.; Yin, X.Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.X. Preparation and performance of polysiloxane/polyphenelene sulfide nonwoven composite separator. Fuhe Cailiao Xuebao 2019, 36, 1995–2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Yin, X.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.C. Enhanced mechanical behavior and electrochemical performance of composite separator by constructing crosslinked polymer electrolyte networks on polyphenylene sulfide nonwoven surface. J. Membrane Sci. 2020, 597, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoadley, J.; Ginter, J. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) as a Membrane in Electrolysis Cells; SAE Technical Paper 961438; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes de Oliveira, M.C.; Sayeg, I.J.; Ett, G.; Altobelli Antunes, R. Corrosion behavior of polyphenylene sulfide-carbon black-graphite composites for bipolar plates of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 16405–16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; He, C.; Hu, L.; Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Load of Ag3PO4 Particles on Sulfonated Polyphenylene Sulfide Superfine Fibre with High Visible-light Photocatalytic Activity. Fiber Polym. 2018, 19, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Ferrous-oxalate-decorated polyphenylene sulfide fenton catalytic microfiber for methylene blue degradation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; He, B.; Song, Y.; Ji, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, J.; Younas, M. Biodiesel production through heterogeneous catalysis using a novel poly (phenylene sulfide) catalytic membrane. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7422–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Lyu, L.; Li, Z. Polyphenylene Sulfide-Based Membranes: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Membranes 2022, 12, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100924
Gao Y, Zhou X, Zhang M, Lyu L, Li Z. Polyphenylene Sulfide-Based Membranes: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Membranes. 2022; 12(10):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100924
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuan, Xinghai Zhou, Maliang Zhang, Lihua Lyu, and Zhenhuan Li. 2022. "Polyphenylene Sulfide-Based Membranes: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives" Membranes 12, no. 10: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100924
APA StyleGao, Y., Zhou, X., Zhang, M., Lyu, L., & Li, Z. (2022). Polyphenylene Sulfide-Based Membranes: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Membranes, 12(10), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100924




