Application and Visualization of Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants in Electrodialysis Processing of Aqueous Solutions Prone to Gypsum Scale Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
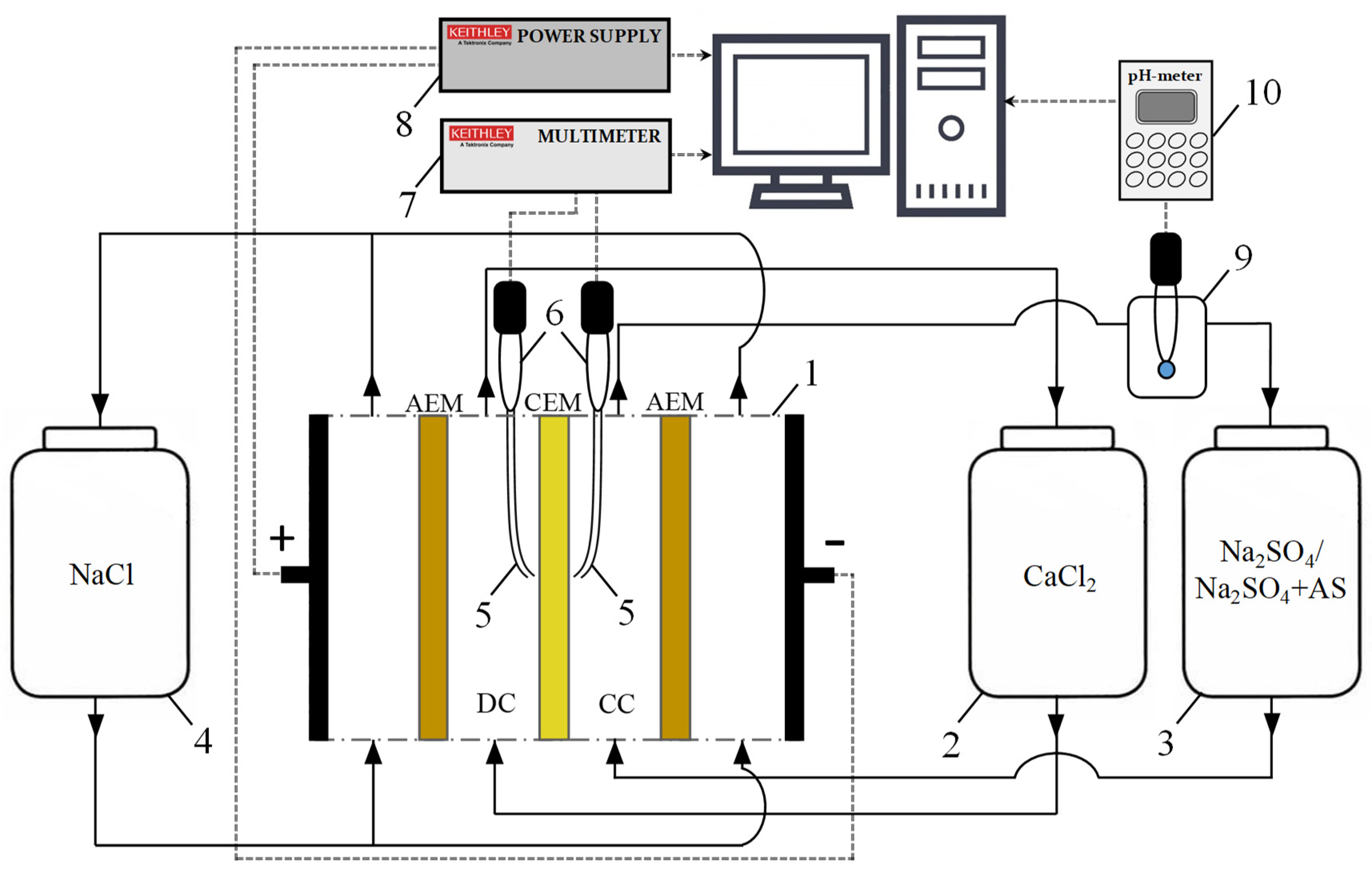
2.2. Electrodialysis Experimental Setup
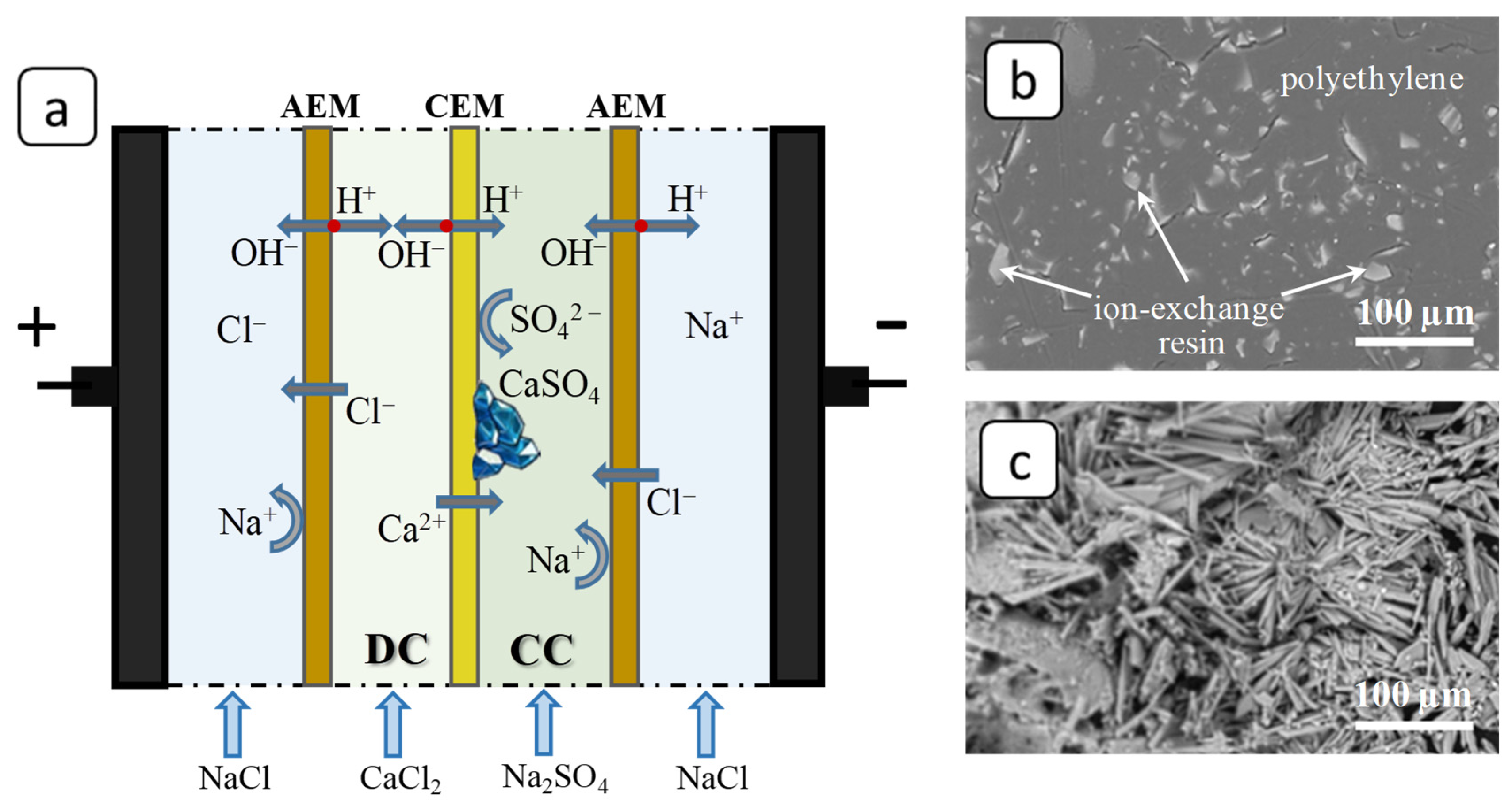
2.3. Membrane Scaling Characterization
3. Results
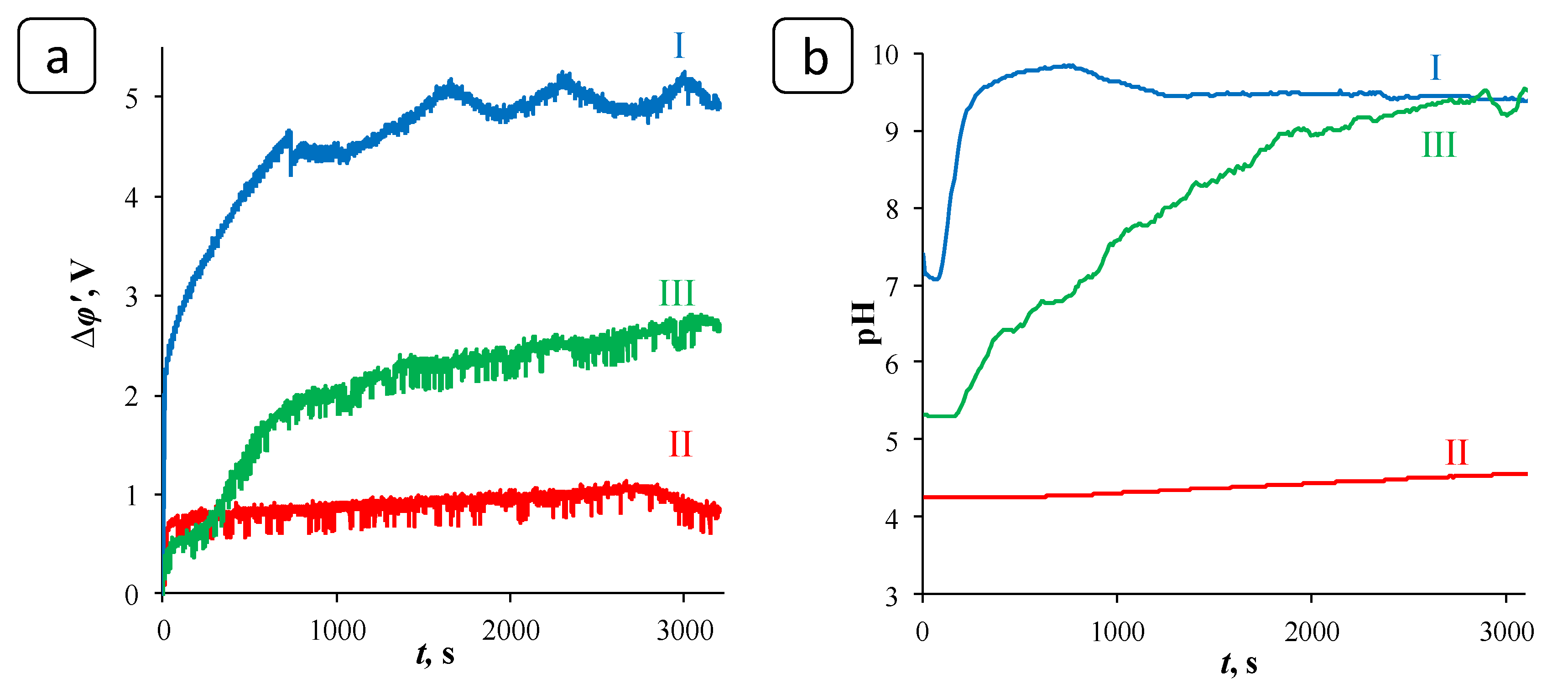
3.1. Chronopotentiometry
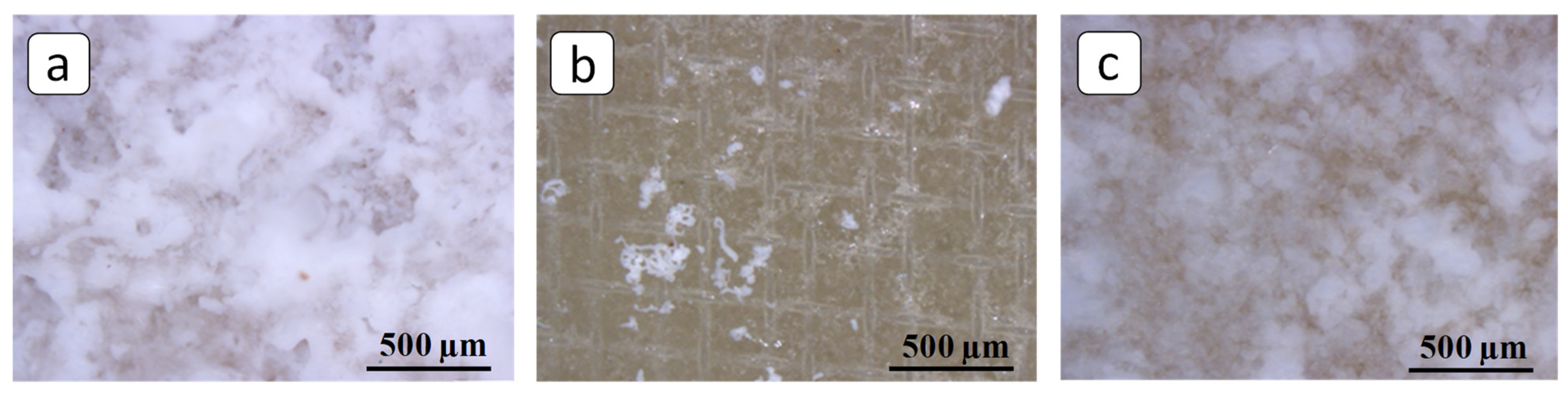
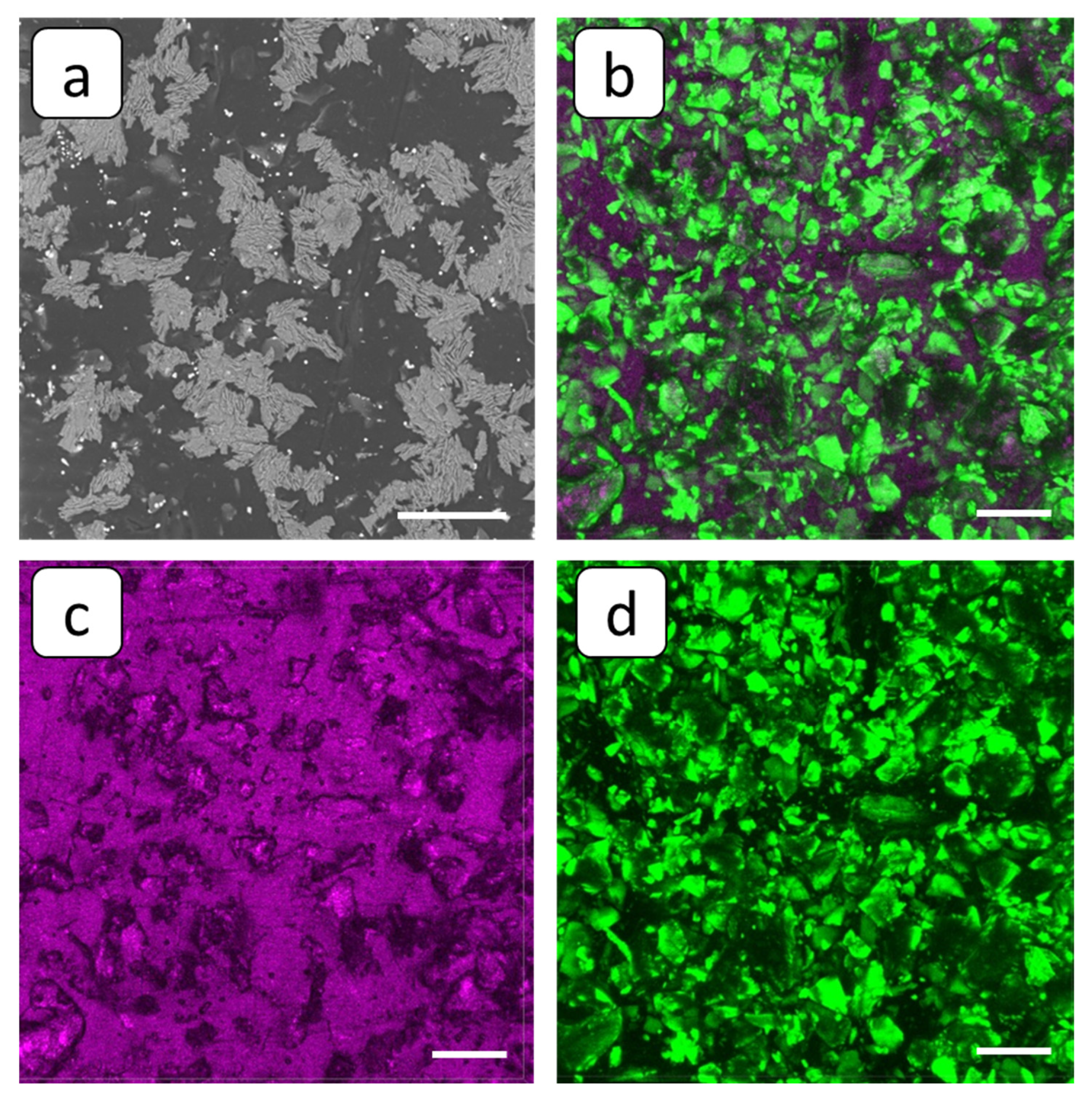
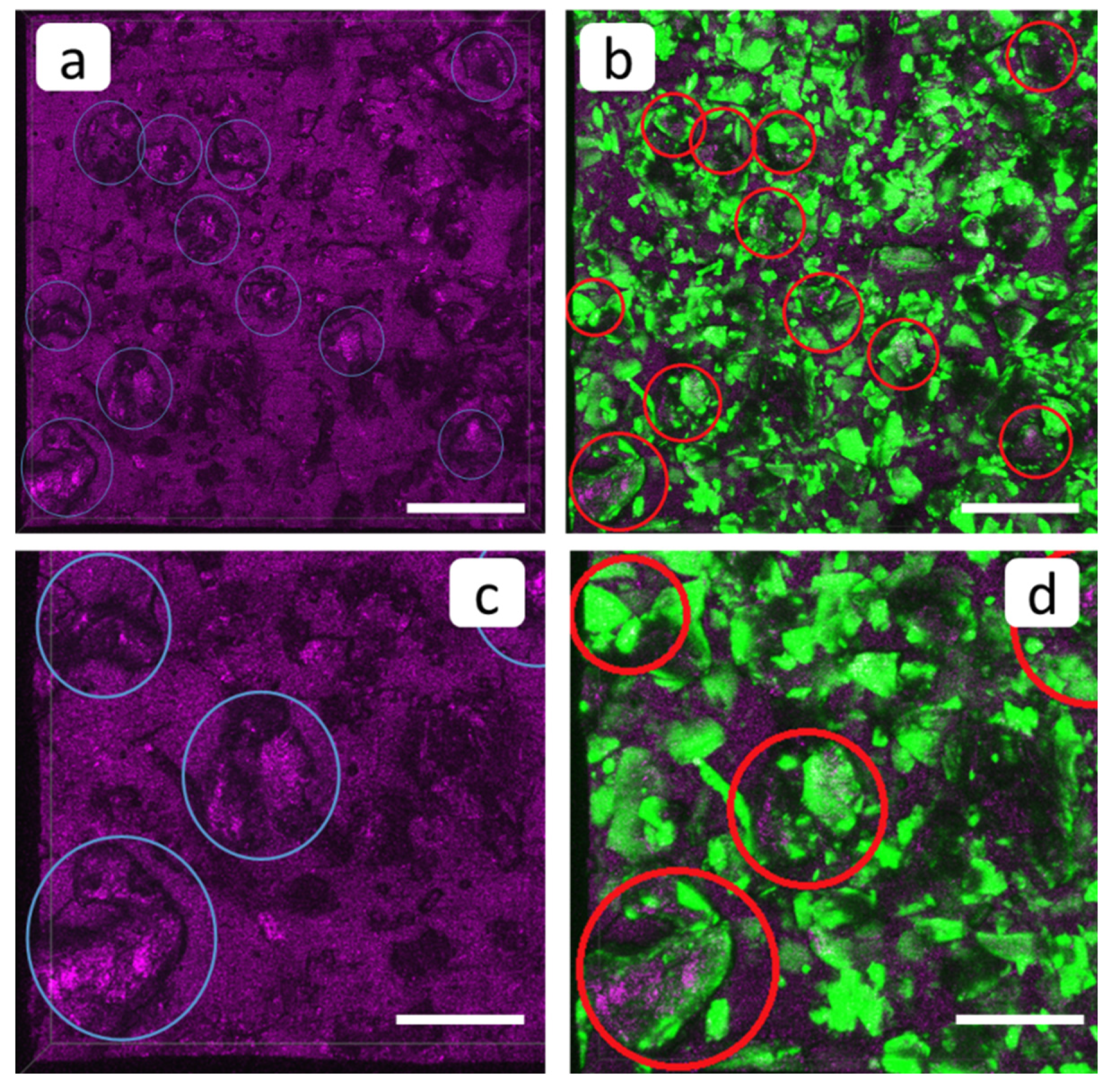
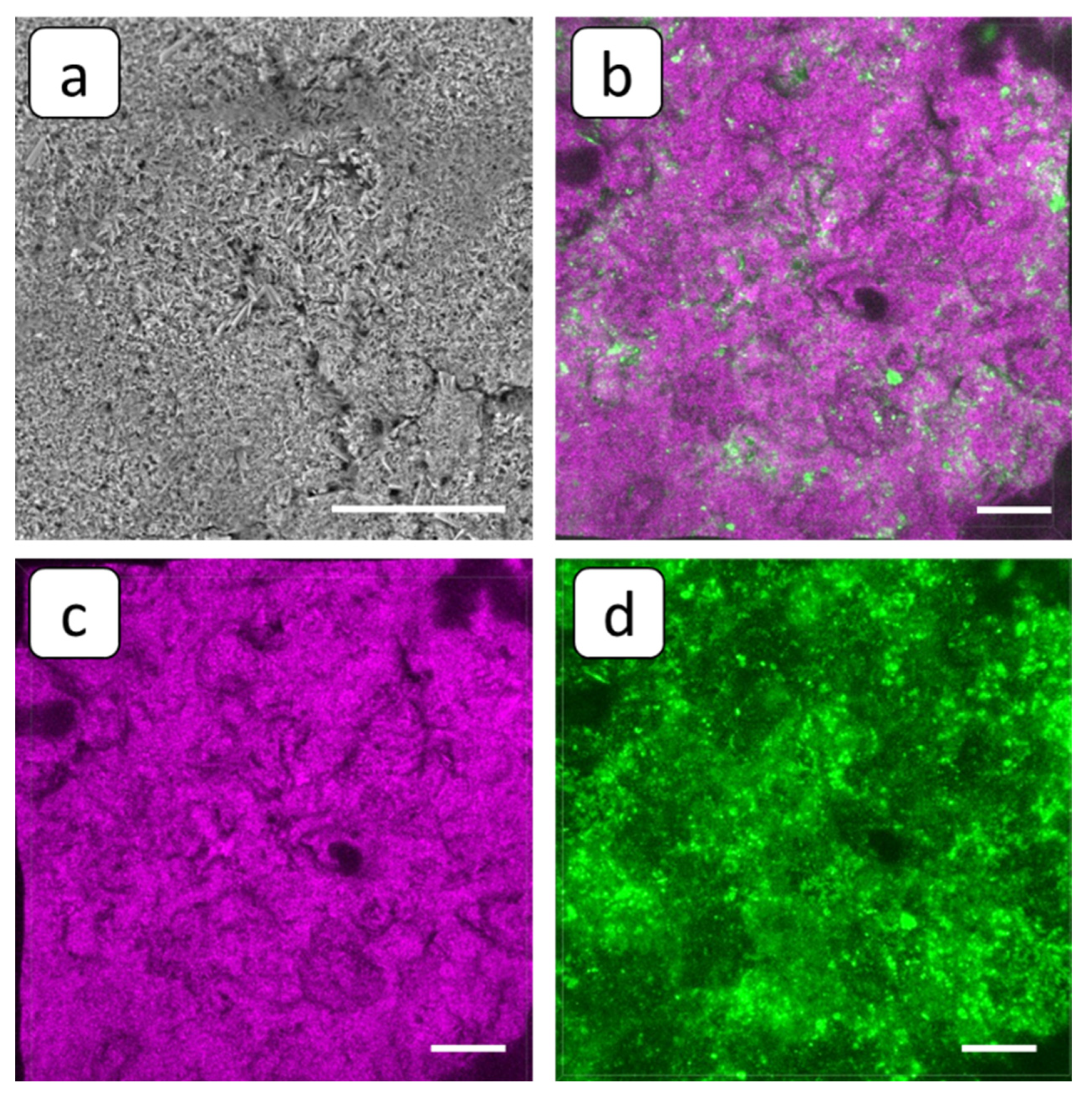
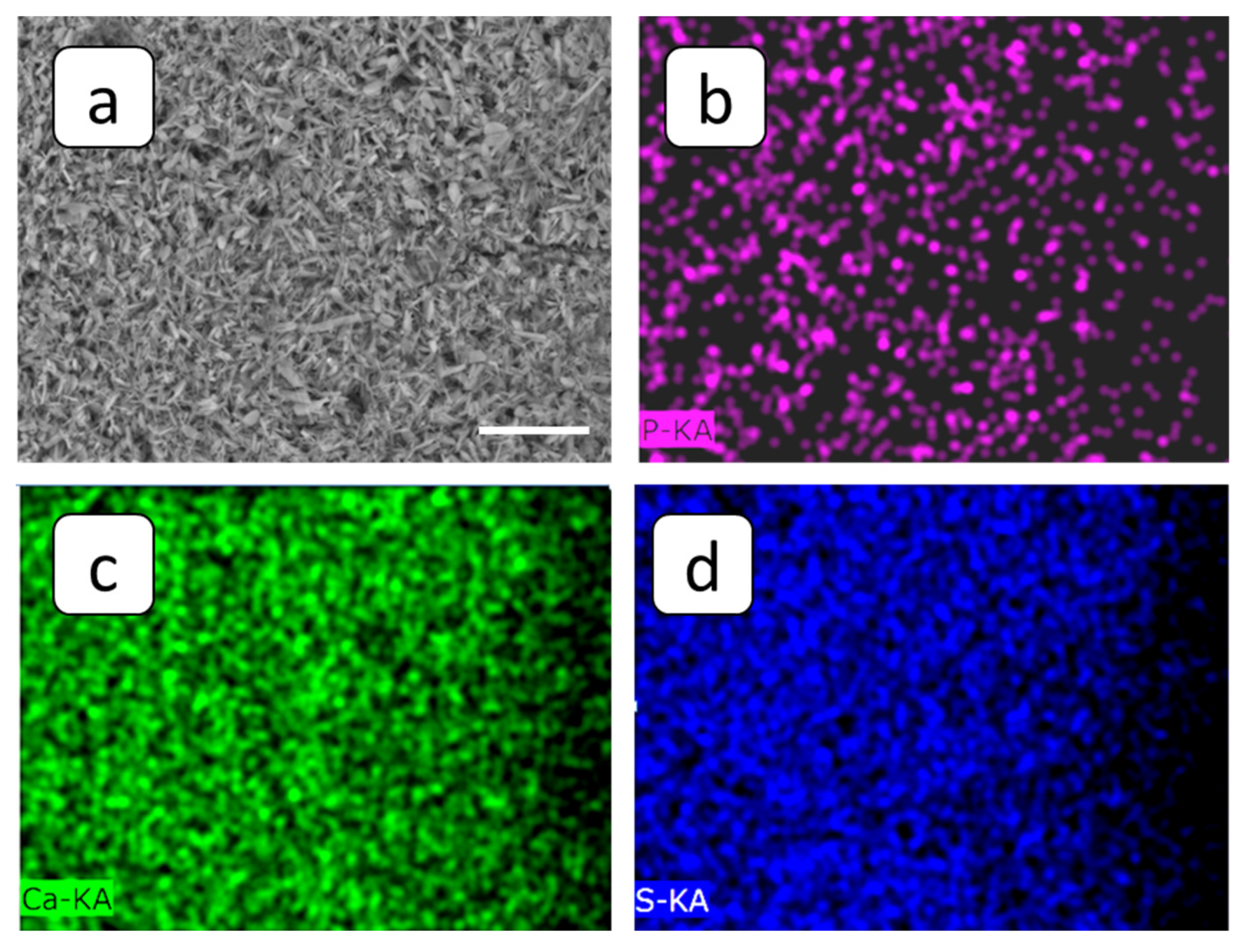
3.2. SEM and FM Analysis of Membranes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoang, T.A. Mechanisms of scale formation and inhibition, In Water-Formed Deposits; Amjad, Z., Demadis, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Chapter 2; p. 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R. Review of the State of the Art of Antiscalant Selection. In Mineral Scales in Biological and Industrial Systems; Amjad, Z., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Chapter 13; p. 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, V.V.; Porozhnyy, M.V.; Rybalkina, O.A.; Sabbatovskiy, K.G.; Nikonenko, V.V. Modification of a heterogeneous cation-exchange membrane by Ti-Si based particles to enhance electroconvection and mitigate scaling during electrodialysis. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 391, 138913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L. A review on ion-exchange membranes fouling and antifouling during electrodialysis used in food industry: Cleanings and strategies of prevention. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asraf-Snir, M.; Gilron, J.; Oren, Y. Scaling of cation exchange membranes by gypsum during donnan exchange and electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 567, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butylskii, D.Y.; Troitskiy, V.A.; Skudarnova, A.S.; Sharafan, M.V. Scaling on the Surface of an MA-41P Anion-Exchange Membrane in the Concentration Chamber of an Electrodialyzer during Processing of Dilute Stratal Water Imitates. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, J. Reverse osmosis: Fundamental causes of membrane deposition and approaches to mitigation. In Water-Formed Deposits; Amjad, Z., Demadis, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Chapter 10; p. 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Rahman, F.; Shafi, H.Z.; Zubair, S.M. Scaling of reverse osmosis membranes used in water desalination: Phenomena, impact, and control; future directions. Desalination 2019, 455, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, G.-R.; Das, R. Inorganic scaling in reverse osmosis (RO) desalination: Mechanisms, monitoring, and inhibition strategies. Desalination 2019, 468, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semblante, G.U.; Lee, J.Z.; Lee, L.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Brine pre-treatment technologies for zero liquid discharge systems. Desalination 2018, 441, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xue, L. Development of lower cost seawater desalination processes using nanofiltration technologies–A review. Desalination 2015, 376, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, J.; Usero, J.; Rosado, D.; El Bakouri, H.; Riaza, A.; Bernaola, F.-J. Comparative study of brine management technologies for desalination plants. Desalination 2014, 336, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Shen, P.; Uytterhoeven, C.; Mamrol, N.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Composite anti-scaling membrane made of interpenetrating networks of nanofibers for selective separation of lithium. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Ren, L.; Wang, J. Fabrication of hydrophilic cation exchange membrane with improved stability for electrodialysis: An excellent anti-scaling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 617, 118618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booster, J.; Van Sandwijk, A.; Reutr, M. Opposing scaling and fouling during electrodialysis of sodium fluoride solution in a membrane cell reactor. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X. Membrane-based electrochemical precipitation for water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, L.; Du, J.; Fu, R.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Zhang, Y. Fracsis: Ion fractionation and metathesis by a NF-ED integrated system to improve water recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, W.E. Desalination by ED and EDR-state-of-art in 1981. Desalination 1982, 42, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xie, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G.; Morrison, L.; Croot, P.; Zhang, X. Nutrient recovery from pig manure digistate using electrodialysis reversal: Membrane fouling and feasibility of long-time operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Intensification of demineralization process and decrease in scaling by application of pulsed electric field with short pulse/pause conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. Positive Impact of Pulsed Electric Field on Lactic Acid Removal, Demineralization and Membrane Scaling during Acid Whey Electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Z.; Lei, C.; Fu, R.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. Application of Pulsed Electric Field in Antifouling Treatment of Sodium Gluconate Mother Liquor by Electrodialysis. Materials 2020, 13, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Bazinet, L.; Barbeau, B. Eco-efficient treatment of ion exchange spent brine via electrodialysis to recover NaCl and minimize waste disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, A.; Low, J.H.; Gray, S.; Childress, A.E.; Le-Clech, P.; Leslie, G. Scale formation and control in high pressure membrane water treatment systems: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanenko, I.; Kryvoruchko, A.; Yurlova, L. Study of the scaling process on membranes. Desalination 2004, 167, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, M.; Mitko, K.; Piotrowsky, K.; Dydo, P.; Laskowska, E.; Jakobik-Kolon, A. Prospects for high water recovery membrane desalination. Desalination 2017, 401, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, L.A. Removal of Mn(II) compounds from water in electrodialysis desalination. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2015, 37, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, C.; Karimi, L.; Ghassemi, A.; Sharbat, A. High-recovery electrodialysis reversal for the desalination of inland brackish waters. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 5, 11029–11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lin, L.; Ma, G.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; He, Q.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Xu, P. Study of polyethyleneimine coating on membrane permselectivity and desalination performance during pilot-scale electrodialysis of reverse osmosis concentrate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-J.; Park, J.-S. Understanding membrane fouling in electrically driven energy conversion devices. Energies 2021, 14, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.; Golovesov, V.; Ryabova, A.; Tkachenko, S.; Redchuk, A.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Rudakova, G.; Pervov, A.; Popov, K. Visualization of a novel fluorescent-tagged bisphosphonate behavior during reverse osmosis desalination of water with high sulfate content. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, S.; Ryabova, A.; Oshchepkov, M.; Popov, K. Fluorescent-tagged Antiscalants: A New Look at the Scale Inhibition Mechanism and Antiscalant Selection. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, B. Fluorescent-tagged hyper-branched polyester for inhibition of CaSO4 scale and the scale inhibition mechanism. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, A.; Gurreri, L.; Ciofalo, M.; Micale, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A. Electrodialysis for water desalination: A critical assessment of recent developments on process fundamentals, models and applications. Desalination 2018, 434, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korngold, E.; Aronov, L.; Belayev, N.; Kock, K. Electrodialysis with brine solutions oversaturated with calcium sulfate. Desalination 2005, 172, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, M.; Mitko, K.; Laskowska, E.; Chorążewska, M.; Piotrowski, K.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Dydo, P. Energy consumption and gypsum scaling assessment in a hybrid nanofiltration-reverse osmosis-electrodialysis system. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Oshchepkov, M.; Kamagurov, S.; Tkachenko, S.; Dikareva, J.; Rudakova, G. Synthesis and properties of novel fluorescent-tagged polyacrylate-based scale inhibitors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.; Kamagurov, S.; Tkachenko, S.; Ryabova, A.; Popov, K. Insight into the Mechanisms of Scale Inhibition: A Case Study of a Task-Specific Fluorescent-Tagged Scale Inhibitor Location on Gypsum Crystals. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedova, G.Z.; Klimova, Z.G.; Sapoznikova, G.S. Ion-Exchange Membranes, Granular Materials, and Powders: Catalogue; NIITEKhim: Moscow, Russia, 1977. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rösler, H.-W.; Maletzki, F.; Staude, E. Ion transfer across electrodialysis membranes in the overlimiting current range: Chronopotentiometric studies. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Buzzi, D.C.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Mass Transfer Phenomena during Electrodialysis of Multivalent Ions: Chemical Equilibria and Overlimiting Currents. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akberova, E.M.; Yatsev, A.M.; Goleva, E.A.; Vasil’eva, V.I. Кoнденсирoванные среды и межфазные границы. Kondens. Sredy Mezhfaz. Gran. 2017, 19, 452–463. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, R. Strong electric field effects on proton transfer between membrane-bound amines and water. Nature 1979, 280, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabolotskii, V.I.; Shel’deshov, N.V.; Gnusin, N.P. Dissociation of water molecules in systems with ion-exchange membranes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1988, 57, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Rudakova, G.; Larchenko, V.; Tusheva, M.; Kamagurov, S.; Dikareva, J.; Kovaleva, N.A. Comparative Performance Evaluation of Some Novel «Green» and Traditional Antiscalants in Calcium Sulfate Scaling. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7635329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.S.; Popov, K.I. Mechanisms of scale inhibition derived from a fluorescent-tagged antiscalant visualization. In Water-Formed Deposits; Amjad, Z., Demadis, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Rolf, J.; Wang, Z.; Violet, C.; Elimelech, M. Distinct impacts of natural organic matter and colloidal particles on gypsum crystallization. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyumentsev, V.A.; Fazlitdinova, A.G.; Dozhdikova, D.V.; Krivtsov, I.V. Effect of nanoadditives on the kinetics of CaSO4·2H2O formation and the mosaic structure of crystals. Inorg. Mater. 2015, 51, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhina, M.; Popov, K.; Oshchepkov, M.; Tkachenko, S.; Vorob’eva, A.; Rudakova, G. Impact of colloidal iron hydroxide and colloidal silicon dioxide on calcium sulfate crystallization in the presence of antiscalants. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2022, 11, 1147–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.; Popov, K.; Kovalenko, A.; Redchuk, A.; Dikareva, J.; Pochitalkina, I. Initial Stages of Gypsum Nucleation: The Role of “Nano/Microdust”. Minerals 2020, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
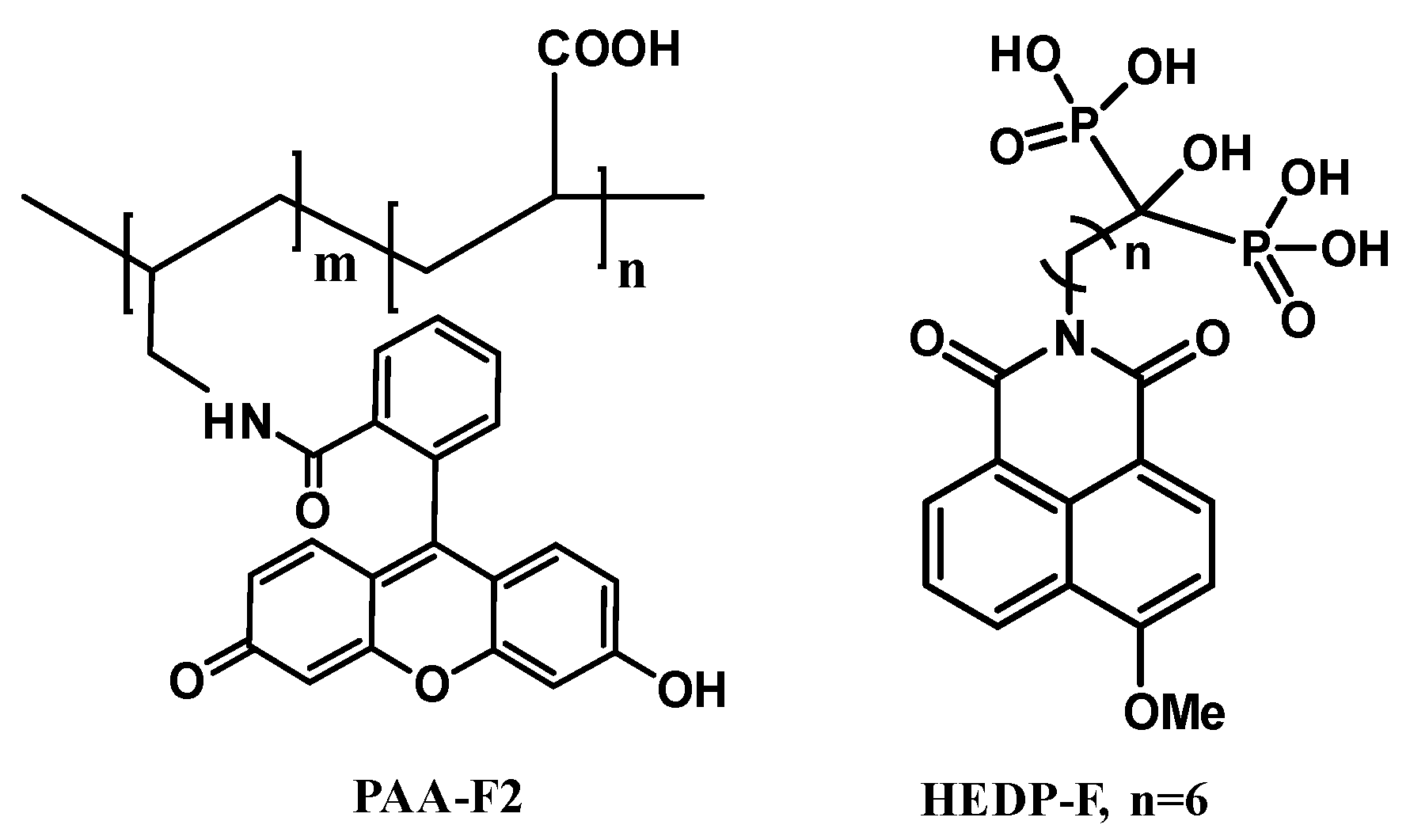


| Measurement Time, h | pH | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | In the Presence of PAA-F2 | In the Presence of HEDP-F | |
| 0, Initial pH | 7.40 | 4.25 | 5.31 |
| 3, Final pH | 8.85 | 5.38 | 9.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil, V.; Oshchepkov, M.; Ryabova, A.; Trukhina, M.; Porozhnyy, M.; Tkachenko, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Popov, K. Application and Visualization of Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants in Electrodialysis Processing of Aqueous Solutions Prone to Gypsum Scale Deposition. Membranes 2022, 12, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101002
Gil V, Oshchepkov M, Ryabova A, Trukhina M, Porozhnyy M, Tkachenko S, Pismenskaya N, Popov K. Application and Visualization of Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants in Electrodialysis Processing of Aqueous Solutions Prone to Gypsum Scale Deposition. Membranes. 2022; 12(10):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil, Violetta, Maxim Oshchepkov, Anastasia Ryabova, Maria Trukhina, Mikhail Porozhnyy, Sergey Tkachenko, Natalia Pismenskaya, and Konstantin Popov. 2022. "Application and Visualization of Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants in Electrodialysis Processing of Aqueous Solutions Prone to Gypsum Scale Deposition" Membranes 12, no. 10: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101002
APA StyleGil, V., Oshchepkov, M., Ryabova, A., Trukhina, M., Porozhnyy, M., Tkachenko, S., Pismenskaya, N., & Popov, K. (2022). Application and Visualization of Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants in Electrodialysis Processing of Aqueous Solutions Prone to Gypsum Scale Deposition. Membranes, 12(10), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101002










