Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by ClO2 Pre-Oxidation: Fouling Mechanism and Interface Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Sewage
2.2. Experimental Setup
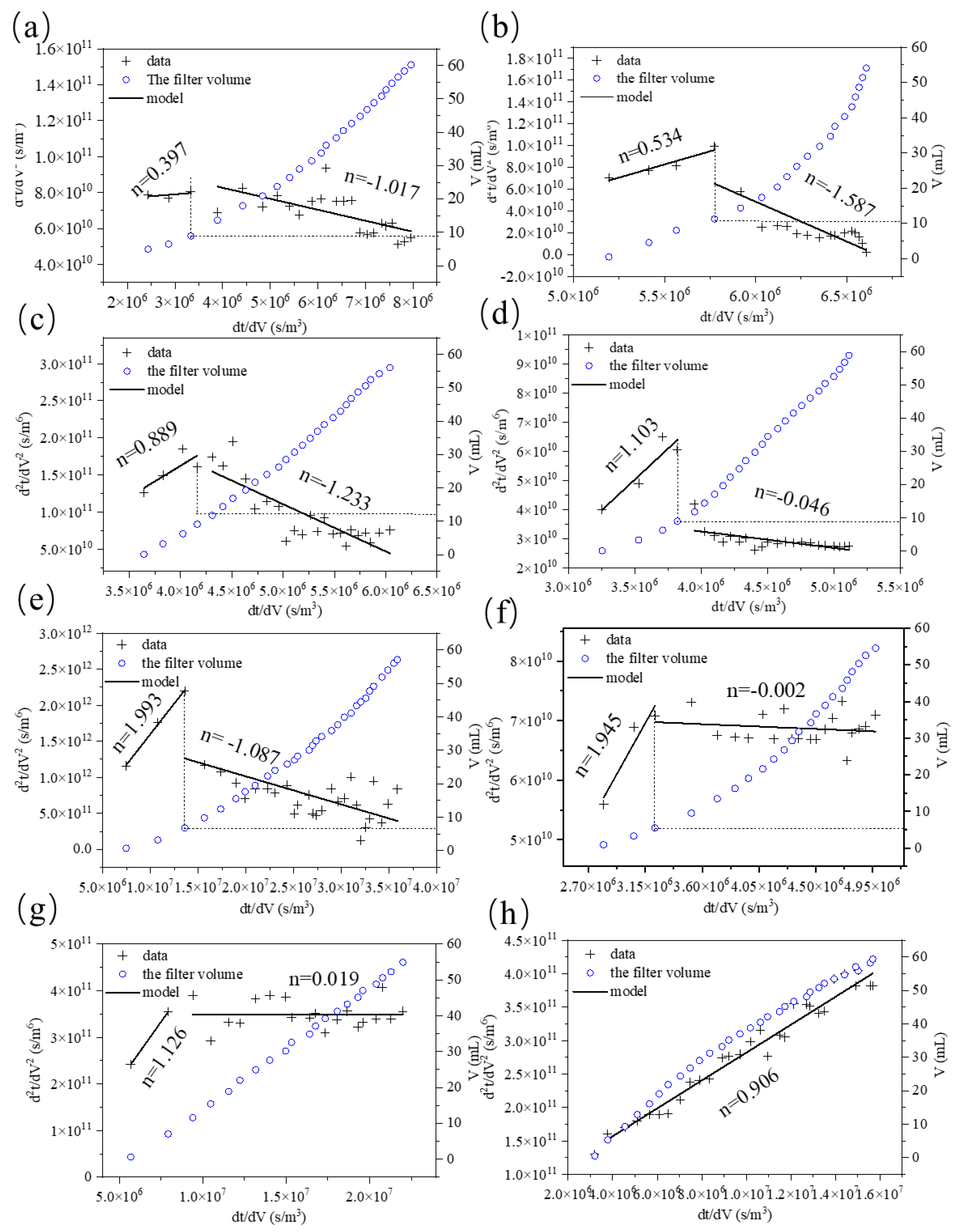
2.3. Membrane Fouling Assessment and Mechanism Analysis
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Effect of ClO2 Pre-Oxidation on UF Membrane Fouling Alleviation
3.1.1. ClO2 Pre-Oxidation for HA Fouling
3.1.2. ClO2 Pre-Oxidation for SA Fouling
3.1.3. ClO2 Pre-Oxidation for BSA Fouling
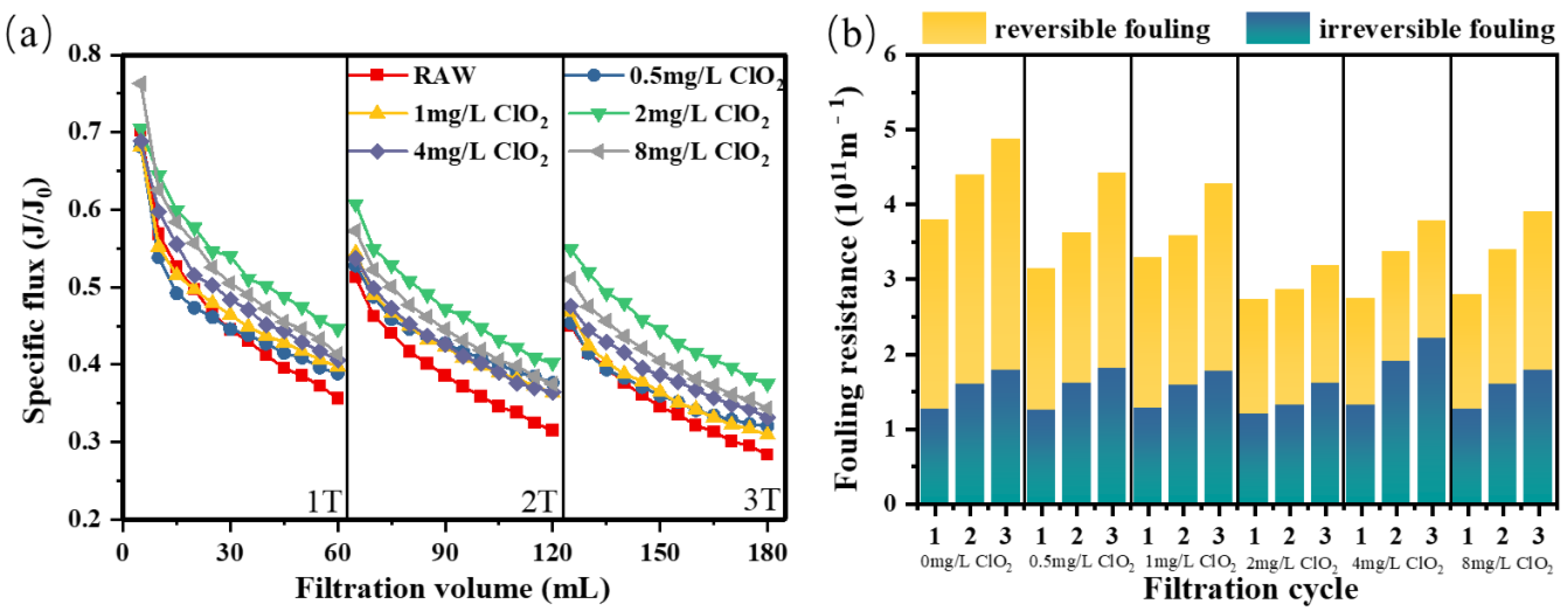
3.1.4. ClO2 Pre-Oxidation for NOM Fouling
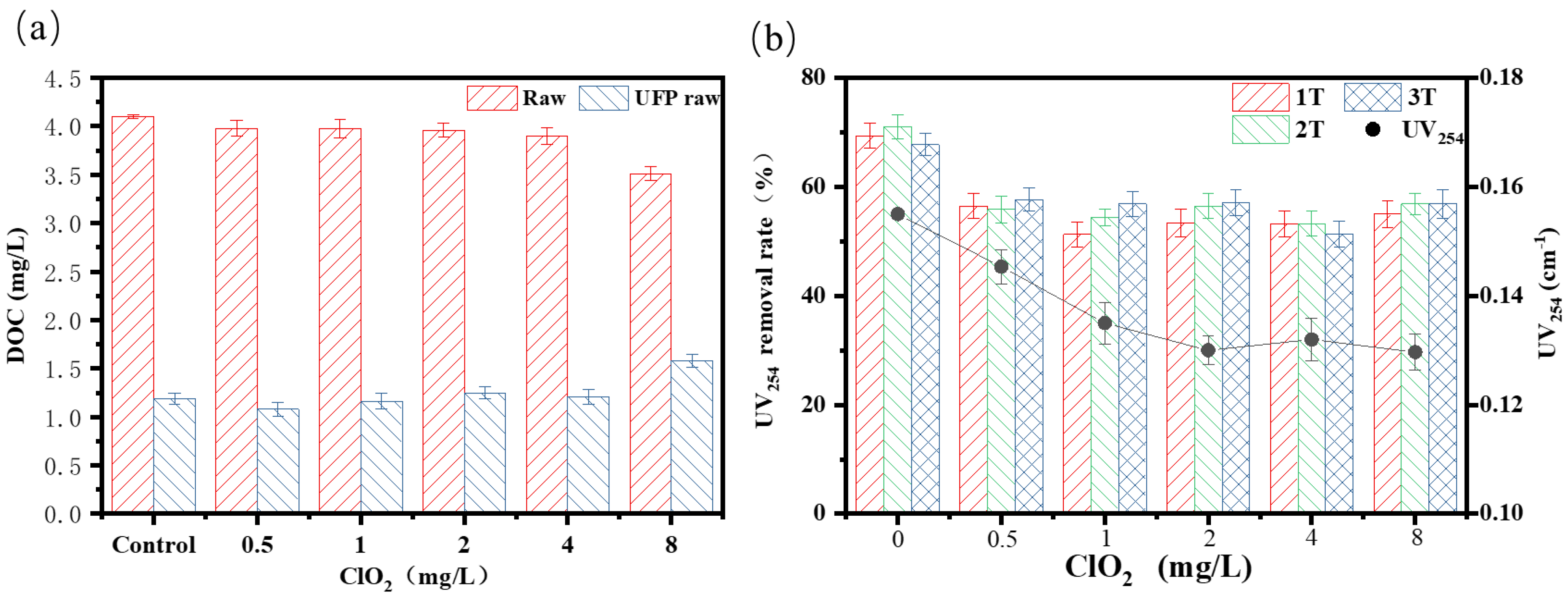
3.2. Effect of ClO2 Pre-Oxidation on Purification Performance
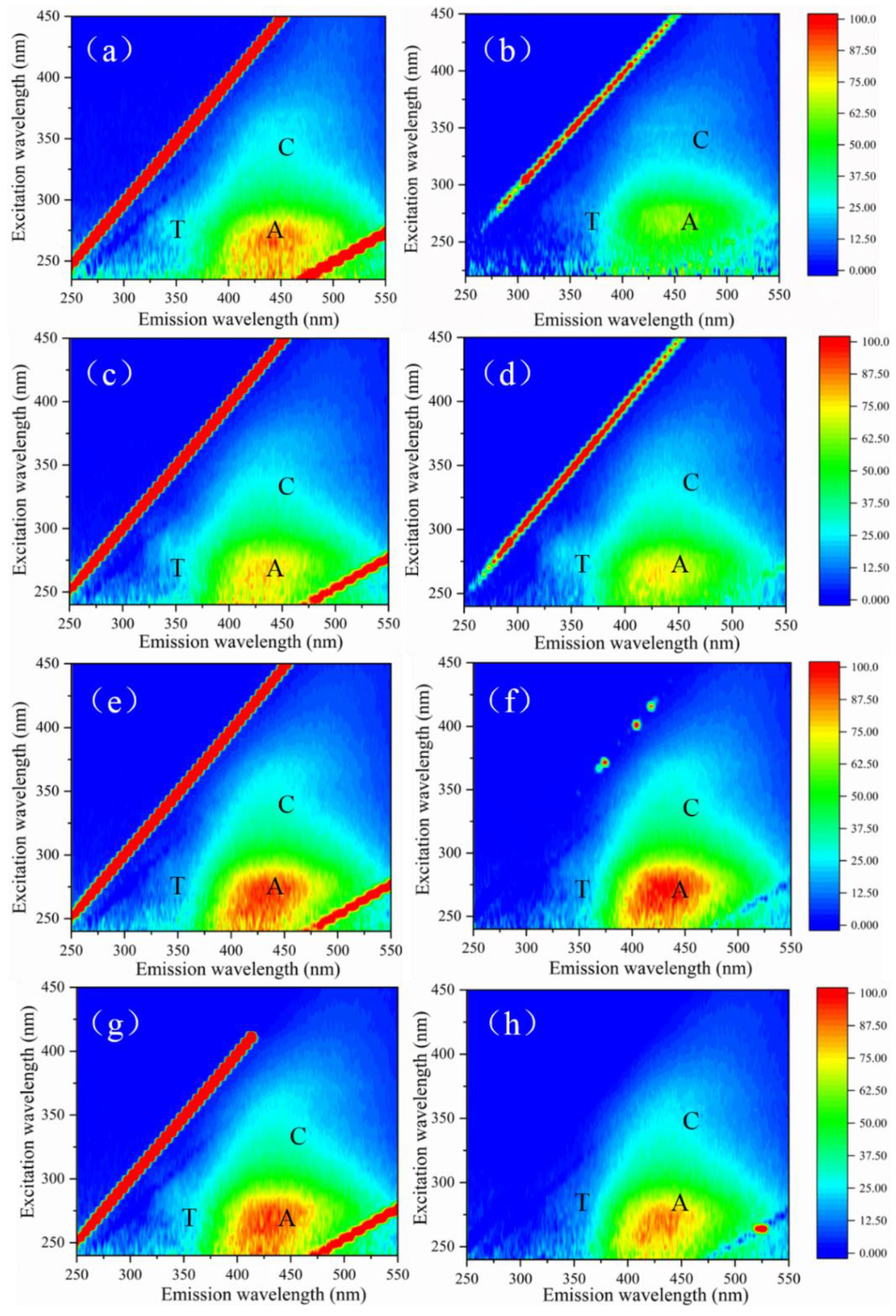
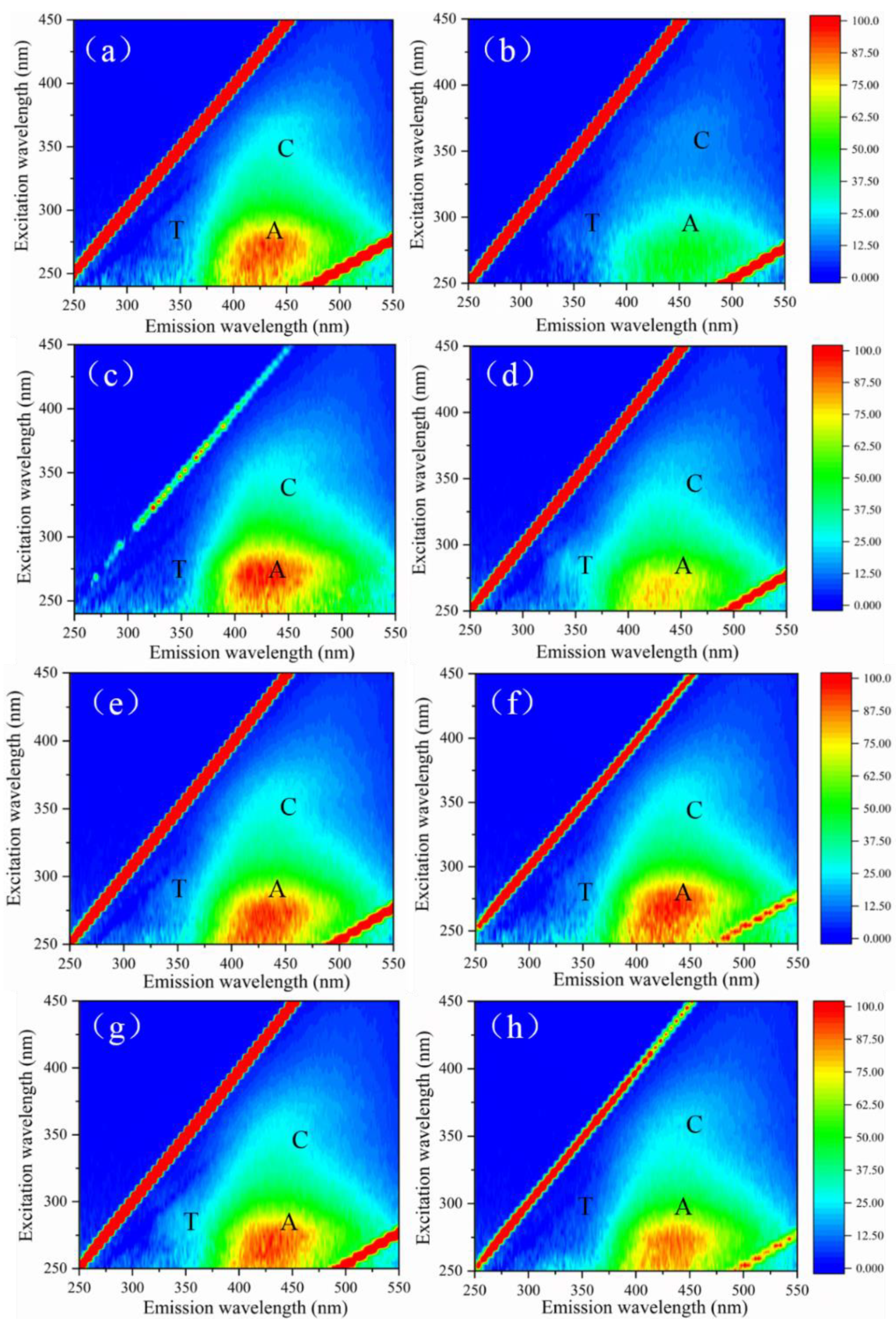
3.3. Effect of ClO2 Pre-Oxidation on Interface Characteristics and Fouling Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santschi, P.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.; Schwehr, K.A.; Lin, P.; Yeager, C.; Kaplan, D. Recent advances in the detection of specific natural organic compounds as carriers for radionuclides in soil and water environments, with examples of radioiodine and plutonium. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 171, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Madronich, S.; Lal, A.; Zepp, R.G.; Lucas, R.M.; Overholt, E.P.; Rose, K.C.; Schladow, S.G.; Lee-Taylor, J. Climate change-induced increases in precipitation are reducing the potential for solar ultraviolet radiation to inactivate pathogens in surface waters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.; Goslan, E.; Parsons, S.; Jefferson, B. Treatment of disinfection by-product precursors. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, R.E. Organic Matter, Humus, Humate, Humic Acid, Fulvic Acid. 2008. Available online: http://www.harvestgrow.com/.pdf%20web%20site/Humates%20General%20Info.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.-W.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, J.-L.; Liang, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B. Impact of humic/fulvic acid on the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using nanomaterials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468-469, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Qu, F.; Liu, B.; Liang, H. The influence of environmental factor on the coagulation enhanced ultrafiltration of algae-laden water: Role of two anionic surfactants to the separation performance. Chemosphere 2021, 132745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genz, A.; Baumgarten, B.; Goernitz, M.; Jekel, M. NOM removal by adsorption onto granular ferric hydroxide: Equilibrium, kinetics, filter and regeneration studies. Water Res. 2008, 42, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter from drinking water by advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämuuronen, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Mänttäri, M. Natural Organic Matter Removal from Drinking Water by Membrane Technology. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Qu, F.; Liu, B.; Van der Bruggen, B. Separation performance of ultrafiltration during the treatment of algae-laden water in the presence of an anionic surfactant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 281, 119894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, B.; Bai, L.; Shi, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Improving the performance of loose nanofiltration membranes by poly-dopamine/zwitterionic polymer coating with hydroxyl radical activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 238, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Cao, A.; Yang, Y.; Mahmud, S.; Su, P.; Yang, J.; He, Z.; Lai, Q.; Zhu, L.; Tu, Z.; et al. Hierarchically superhydrophilic poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane with self-cleaning fabricated by surface mineralization for stable separation of oily wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Niazi, M.; Sher, F.; Jahan, Z.; Noor, T.; Azhar, O.; Rashid, T.; Iqbal, N. Metal Organic Frameworks Derived Sustainable Polyvinyl Alcohol/Starch Nanocomposite Films as Robust Materials for Packaging Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Jahan, Z.; Sher, F.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Kakar, S.J.; Gul, S. Nano architectured cues as sustainable membranes for ultrafiltration in blood hemodialysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, O.; Jahan, Z.; Sher, F.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Kakar, S.J.; Shahid, M. Cellulose acetate-polyvinyl alcohol blend hemodialysis membranes integrated with dialysis performance and high biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 126, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Fu, W.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, T.; Li, X. Membrane fouling by the aggregations formed from oppositely charged organic foulants. Water Res. 2019, 159, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Tian, J.; Chen, W.; Liang, H.; Li, G.; Van der Bruggen, B. Membrane Fouling and Rejection of Organics during Algae-Laden Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration: A Comparison between in Situ Pretreatment with Fe(II)/Persulfate and Ozone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Shen, J.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Kang, J. Catalytic ozonation of iohexol with α-Fe0.9Mn0.1OOH in water: Efficiency, degradation mechanism and toxicity evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 402, 123574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Xie, Z.; Tang, M.; Fu, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; et al. Insights into the simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal process for in situ sludge reduction and potential phosphorus recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Xie, Z.; Fu, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, P.; Yu, J.; Ma, J.; Gao, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Interaction and removal of oxytetracycline with aerobic granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 320, 124358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, H.; Huang, H.; Yang, X. ClO2 pre-oxidation changes the yields and formation pathways of chloroform and chloral hydrate from phenolic precursors during chlorination. Water Res. 2018, 148, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, F.; Wang, Y. Characterization of enoxacin (ENO) during ClO2 disinfection in water distribution system: Kinetics, byproducts, toxicity evaluation and halogenated disinfection byproducts (DBPs) formation potential. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Gan, W.; Du, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Shang, C.; Yang, X. Disinfection byproducts and their toxicity in wastewater effluents treated by the mixing oxidant of ClO2/Cl2. Water Res. 2019, 162, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.-L.; Ye, Z.-X.; Huang, H.; Yang, X. ClO2 pre-oxidation impacts the formation and nitrogen origins of dichloroacetonitrile and dichloroacetamide during subsequent chloramination. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, X. The reactions of chlorine dioxide with inorganic and organic compounds in water treatment: Kinetics and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2287–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Q. Algal fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes and control strategies: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 203, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-Y.; Ernst, M.; Cui, F.; Jekel, M. Effect of particle size and concentration on the synergistic UF membrane fouling by particles and NOM fractions. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.; Amy, G.; Foss, D.; Cho, J. Variations of Molecular Weight Estimation by HP-Size Exclusion Chromatography with UVA versus Online DOC Detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3393–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.C.; Zydney, A.L. A Combined Pore Blockage and Cake Filtration Model for Protein Fouling during Microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Young, T.A.; Jacangelo, J.G. Unified Membrane Fouling Index for Low Pressure Membrane Filtration of Natural Waters: Principles and Methodology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Gan, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Van der Bruggen, B. Algae-laden water treatment using ultrafiltration: Individual and combined fouling effects of cells, debris, extracellular and intracellular organic matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, F.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Ahmad, T.; Akram, M.A.; Safdar, A.; Butt, M.S.; Noor, T.; Sher, F. Synthesis and Characterization of PVA/Starch Hydrogel Membranes Incorporating Essential Oils Aimed to be Used in Wound Dressing Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 29, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubeen, F.; Liaqat, A.; Sultan, M.; Iqbal, S.Z.; Sajid, I.; Sher, F. Green synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 5-fluorouracil derivatives as potent anticancer agents. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liang, H.; Ding, A.; Tang, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Gan, Z.; Wu, D.; Li, G. Ferrous iron/peroxymonosulfate oxidation as a pretreatment for ceramic ultrafiltration membrane: Control of natural organic matter fouling and degradation of atrazine. Water Res. 2017, 113, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, W.; Huang, S.; Ge, Y.; Bond, T.; Westerhoff, P.; Zhai, J.; Yang, X. Chlorite formation during ClO2 oxidation of model compounds having various functional groups and humic substances. Water Res. 2019, 159, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Shao, S.; Yu, H.; Han, Z.-S.; Du, X.; Li, G. Control of natural organic matter fouling of ultrafiltration membrane by adsorption pretreatment: Comparison of mesoporous adsorbent resin and powdered activated carbon. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liang, H.; Ding, A.; Qu, F.; Shao, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; Li, G. Effects of pre-ozonation on the ultrafiltration of different natural organic matter (NOM) fractions: Membrane fouling mitigation, prediction and mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xie, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Dewil, R.; Van der Bruggen, B. Application of UV/chlorine pretreatment for controlling ultrafiltration (UF) membrane fouling caused by different natural organic fractions. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 127993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Chen, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, T.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Van der Bruggen, B. Microcystis aeruginosa-laden water treatment using enhanced coagulation by persulfate/Fe(II), ozone and permanganate: Comparison of the simultaneous and successive oxidant dosing strategy. Water Res. 2017, 125, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation−Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Tang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Application of low-dosage UV/chlorine pre-oxidation for mitigating ultrafiltration (UF) membrane fouling in natural surface water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, J.; Hoek, E.M.V. Natural organic matter fouling due to foulant–membrane physicochemical interactions. Desalination 2007, 202, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Taurozzi, J.S.; Alpatova, A.L.; Wang, F.; Tarabara, V.V. Performance of polymeric membranes treating ozonated surface water: Effect of ozone dosage. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dosage (mg/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −3.75 | −1.63 | 0.12 | −5.36 | −4.23 | −4.02 | −0.03 | −8.28 |
| 2 | −4.25 | 9.22 | 0.08 | 5.05 | −4.50 | 14.07 | −0.01 | 9.96 |
| 4 | −4.76 | 13.24 | 0.05 | 8.53 | −4.76 | 11.07 | 0.02 | 8.23 |
| 8 | −5.28 | 14.10 | 0.02 | 8.90 | −5.01 | 13.89 | 0.03 | 8.91 |
| Dosage (mg/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −2.37 | −6.03 | 0.11 | −8.29 | −3.36 | 1.30 | −0.02 | −2.04 |
| 1 | −5.28 | 10.63 | 0.06 | 5.41 | −5.01 | 14.85 | 0.02 | 9.89 |
| 4 | −5.54 | 8.43 | 0.02 | 2.91 | −5.14 | 13.19 | 0.03 | 8.11 |
| 8 | −5.80 | −7.35 | −0.01 | −13.16 | −5.46 | 5.29 | 0.10 | −0.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, K.; Li, G.; Shi, Z. Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by ClO2 Pre-Oxidation: Fouling Mechanism and Interface Characteristics. Membranes 2022, 12, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010078
Liu B, Wang M, Yang K, Li G, Shi Z. Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by ClO2 Pre-Oxidation: Fouling Mechanism and Interface Characteristics. Membranes. 2022; 12(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bin, Meng Wang, Kaihan Yang, Guangchao Li, and Zhou Shi. 2022. "Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by ClO2 Pre-Oxidation: Fouling Mechanism and Interface Characteristics" Membranes 12, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010078
APA StyleLiu, B., Wang, M., Yang, K., Li, G., & Shi, Z. (2022). Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by ClO2 Pre-Oxidation: Fouling Mechanism and Interface Characteristics. Membranes, 12(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010078







