Investigating the Proton and Ion Transfer Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Prepared for Bioelectrochemical Applications Using Hydrophobic Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Supported Ionic Liquid Membrane Preparation
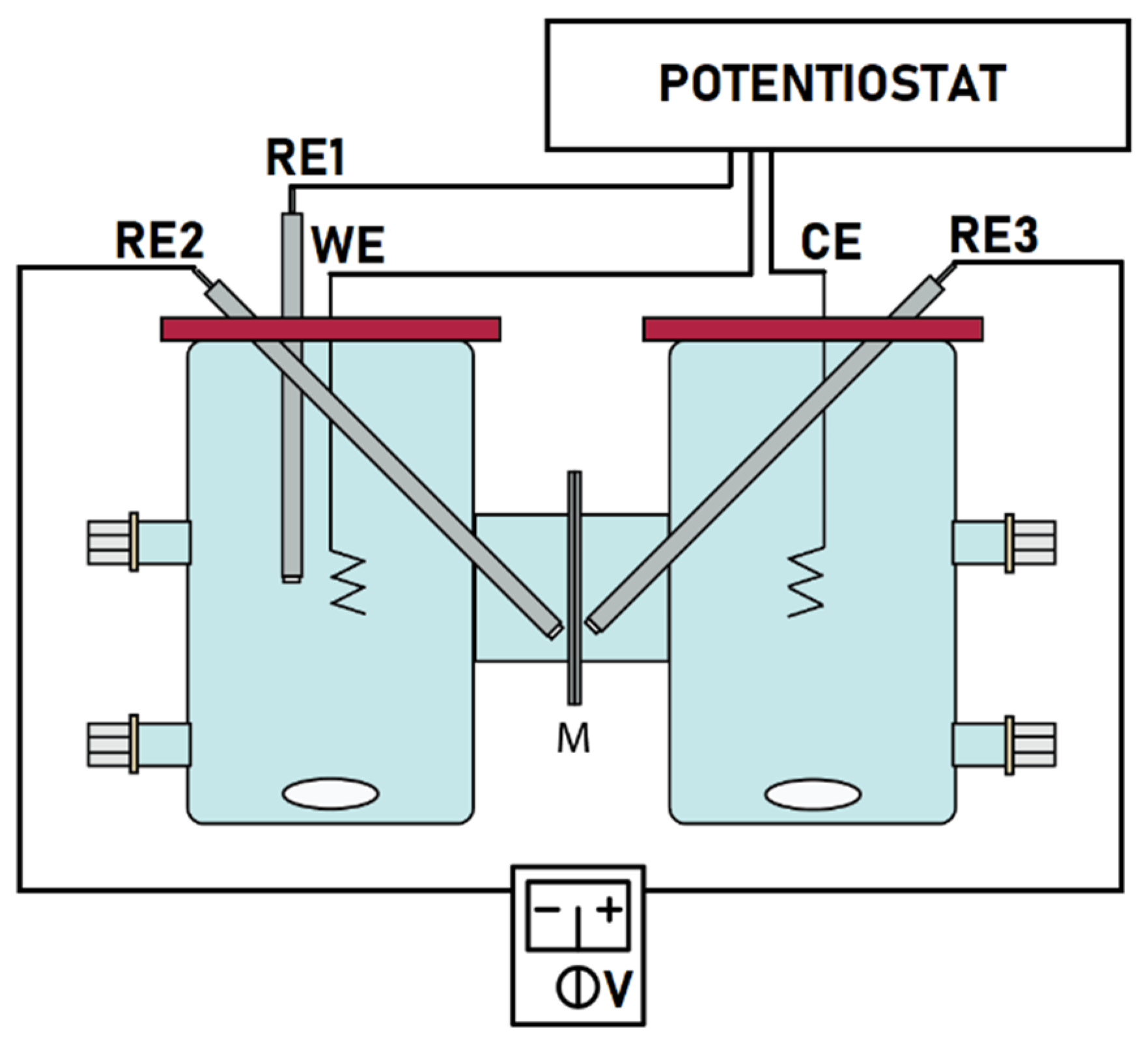
2.2. Proton Transfer Characteristics
2.3. Transport Numbers and Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
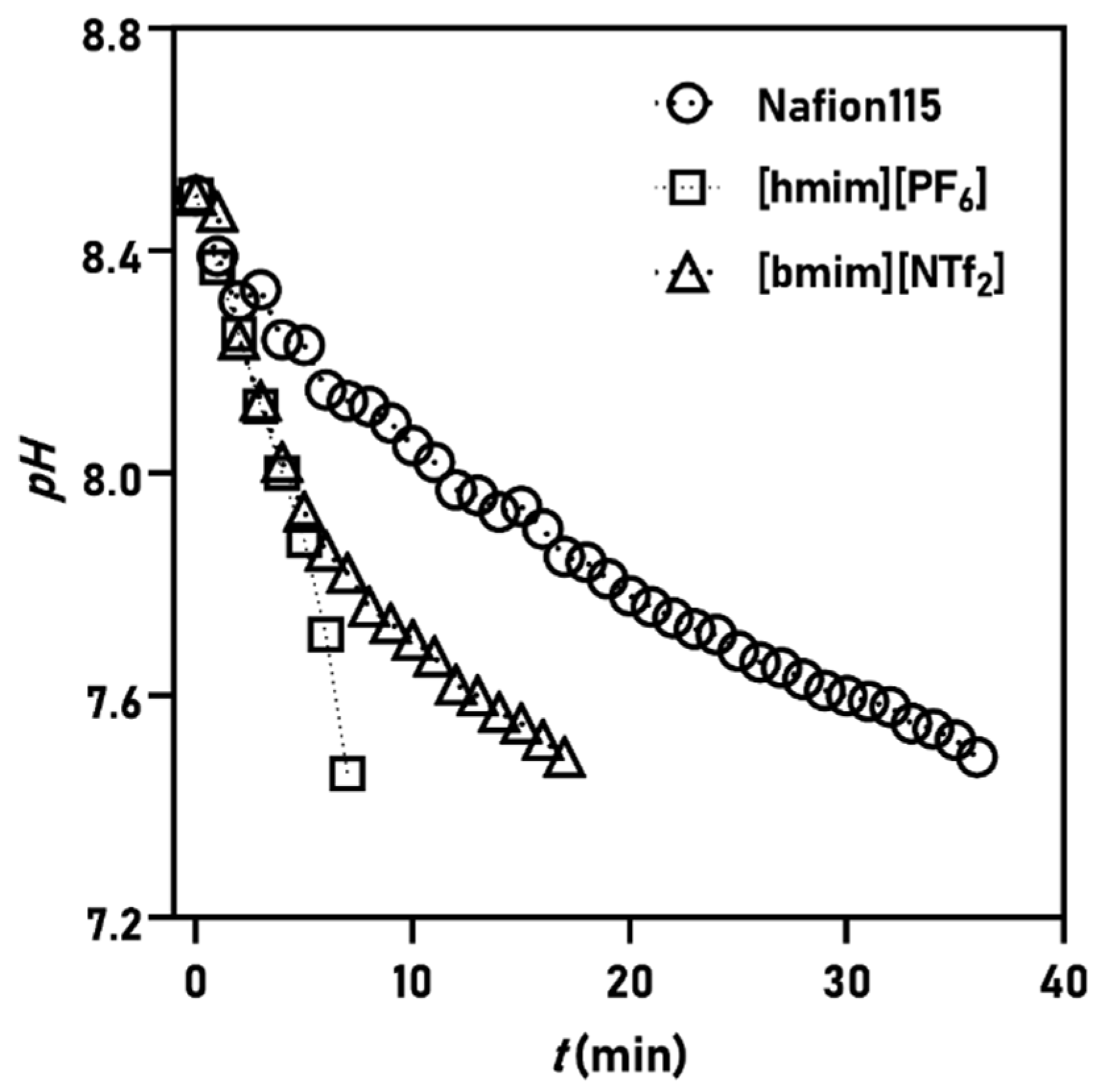
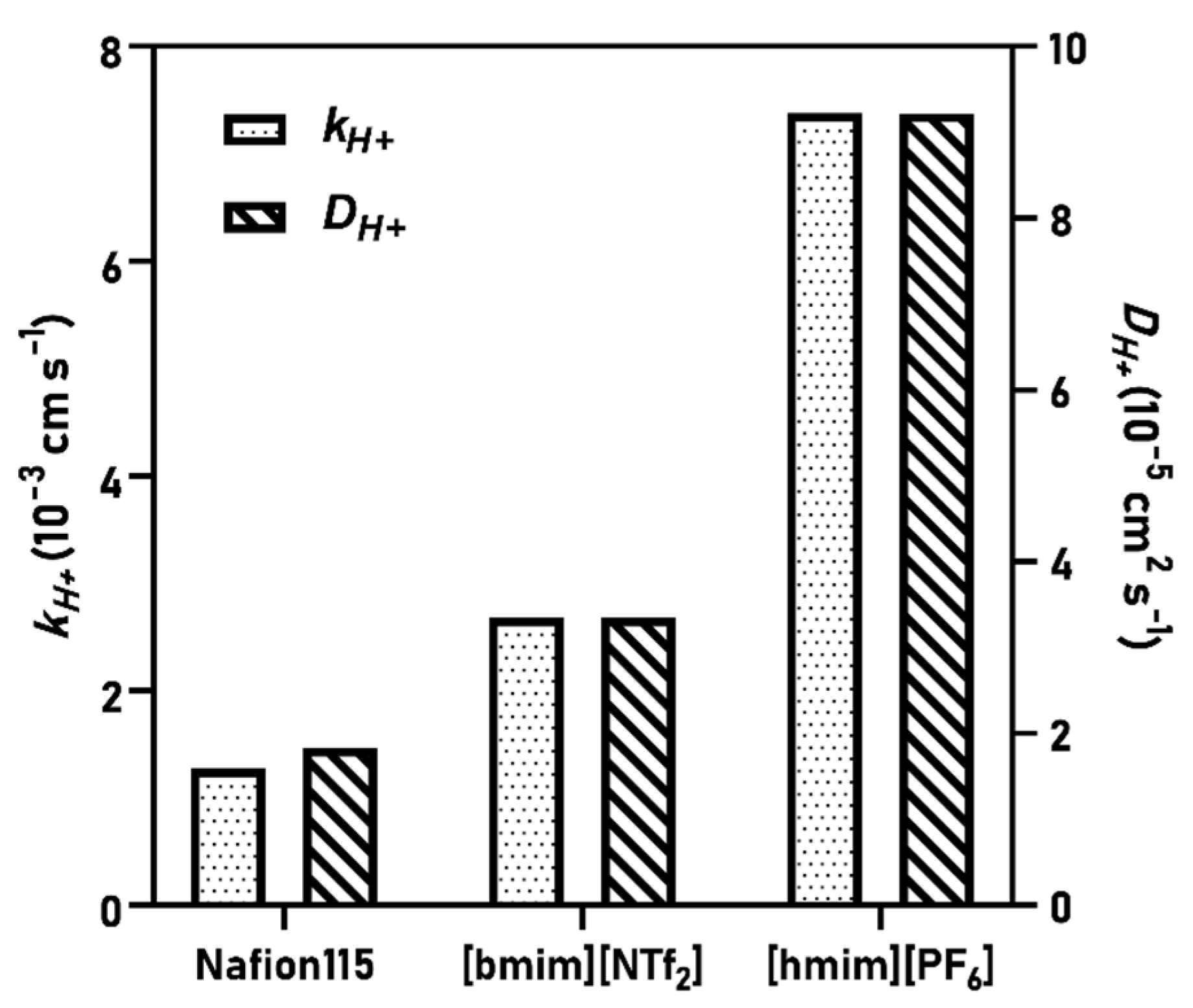
3.1. Proton Mass Transfer Characteristics
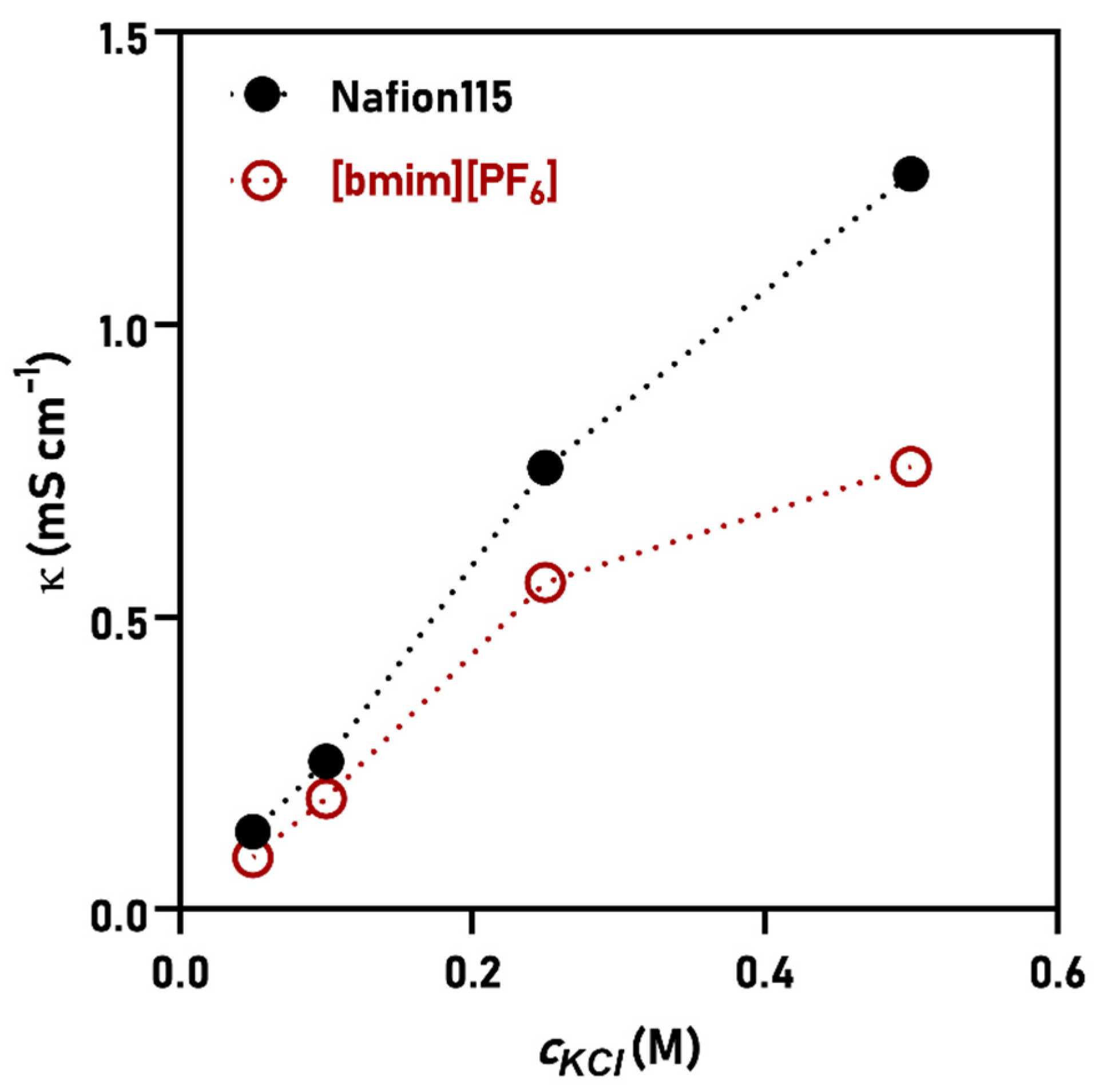
3.2. Cation Transport Numbers and Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E. Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliot, M.; Galier, S.; Roux de Balmann, H.; Bergel, A. Ion transport in microbial fuel cells: Key roles, theory and critical review. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 1682–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids: A brief history. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.H.; Chen, C.C. Flammability estimation of 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 66, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrenberg, M.; Beck, M.; Neise, C.; Keßler, O.; Kragl, U.; Verevkin, S.P.; Schick, C. Vapor pressure of ionic liquids at low temperatures from AC-chip-calorimetry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 21381–21390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Clarke, C.J.; Bui-Le, L.; Hallett, J.P.; Licence, P. Thermally-stable imidazolium dicationic ionic liquids with pyridine functional groups. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8762–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetta, A.; Becherini, S.; Pretti, C.; Monni, G.; Casu, V.; Chiappe, C.; Guazzelli, L. Insights into the levulinate-based ionic liquid class: Synthesis, cellulose dissolution evaluation and ecotoxicity assessment. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13010–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keaveney, S.T.; Haines, R.S.; Harper, J.B. Ionic liquid solvents: The importance of microscopic interactions in predicting organic reaction outcomes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Claus, J.; Sommer, F.O.; Kragl, U. Ionic liquids in biotechnology and beyond. Solid State Ion. 2018, 314, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmero, L.; Mezzetta, A.; Pomelli, C.S.; Chiappe, C.; Guazzelli, L. Evaluation of the effect of the dicationic ionic liquid structure on the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Ionic liquids in surface electrochemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yu, H. Ionic liquids for electrochemical energy storage devices applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Anguille, S.; Bendahan, M.; Moulin, P. Ionic liquids combined with membrane separation processes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Feng, S.; Li, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X. Recent development of ionic liquid membranes. Green Energy Environ. 2016, 1, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, B.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A.F. Recent progress in ionic liquid membranes for gas separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; De Los Ríos, A.P.; Mateo-Ramírez, F.; Juarez, M.D.; Lozano-Blanco, L.J.; Godínez, C. New application of polymer inclusion membrane based on ionic liquids as proton exchange membrane in microbial fuel cell. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Pérez de los Ríos, A.; Mateo-Ramírez, F.; Godínez, C.; Lozano-Blanco, L.J.; Moreno, J.I.; Tomás-Alonso, F. New application of supported ionic liquids membranes as proton exchange membranes in microbial fuel cell for waste water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bakonyi, P.; Zhen, G.; Kumar, G.; Lu, X.; Su, L.; Saratale, G.D.; Kim, S.H.; Gubicza, L. Performance evaluation of microbial electrochemical systems operated with Nafion and supported ionic liquid membranes. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bakonyi, P.; Göllei, A.; Rózsenberszki, T.; Takács, P.; Salekovics, A.; Kumar, G.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. On the efficiency of dual-chamber biocatalytic electrochemical cells applying membrane separators prepared with imidazolium-type ionic liquids containing [NTf2]− and [PF6]− anions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Kaufer, B.; Bakonyi, P.; Rózsenberszki, T.; Rivera, I.; Buitrón, G.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Supported ionic liquid membrane based on [bmim][PF6] can be a promising separator to replace Nafion in microbial fuel cells and improve energy recovery: A comparative process evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gilmore, B.F. The antimicrobial potential of ionic liquids: A source of chemical diversity for infection and biofilm control. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Kong, L.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Antibacterial activities of N-alkyl imidazolium-based poly (ionic liquid) nanoparticles. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserjési, P.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. Gas separation properties of supported liquid membranes prepared with unconventional ionic liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.R.; Woolf, L.A.; Kanakubo, M. Temperature and pressure dependence of the viscosity of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.R.; Kanakubo, M.; Woolf, L.A. Temperature and pressure dependence of the viscosity of the ionic liquids 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium BiS (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Wan Daud, W.R.; Ismail, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Leong, J.X.; Miskan, M.; Ben Liew, K. Effect of pre-treatment and biofouling of proton exchange membrane on microbial fuel cell performance. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 5480–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Logan, B.E. Separator characteristics for increasing performance of microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8456–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suransh, J.; Tiwari, A.K.; Mungray, A.K. Modification of clayware ceramic membrane for enhancing the performance of microbial fuel cell. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, e13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoni, S.E.; Aldao, C.M. On diffusion, drift and the Einstein relation. Eur. J. Phys. 2002, 23, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Moon, S.H. Structural change of ion-exchange membrane surfaces under high electric fields and its effects on membrane properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 265, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisch, F.; Schröder, U.; Scholz, F. The suitability of monopolar and bipolar ion exchange membranes as separators for biological fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koryta, J. Diffusion. Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1985, 194, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmon, N. The Grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 244, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukierman, S. Proton mobilities in water and in different stereoisomers of covalently linked gramicidin A channels. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, R.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Reis, M.A.M.; Crespo, J.G. Supported liquid membranes using ionic liquids: Study of stability and transport mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, P.; Koók, L.; Rózsenberszki, T.; Tóth, G.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Development and application of supported ionic liquid membranes in microbial fuel cell technology: A concise overview. Membranes 2020, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashin, A.S.; Galkin, K.I.; Khokhlova, E.A.; Ananikov, V.P. Direct observation of self-organized water-containing structures in the liquid phase and their influence on 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural formation in ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Rȩkawek, A.; Marciniak, A. Solubility of 1-alkyl-3-ethylimidazolium-based ionic liquids in water and 1-octanol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, B.R.; Lee, H.S. Membranes for bioelectrochemical systems: Challenges and research advances. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranke, J.; Othman, A.; Fan, P.; Müller, A. Explaining ionic liquid water solubility in terms of cation and anion hydrophobicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Koga, Y. Relative hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of some “ionic liquid” anions determined by the 1-propanol probing methodology: A differential thermodynamic approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Insight into the behavior at the hygroscopicity and interface of the hydrophobic imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 31, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Santos, L.M.; Fernandes, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.; Marrucho, I.M. An overview of the mutual solubilities of water-imidazolium-based ionic liquids systems. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2007, 261, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Bynre, N. Utilizing water activity as a simple measure to understand hydrophobicity in ionic liquids. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Swatloski, R.P.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids: Alternatives to Volatile Organic Compounds for Liquid-Liquid Separations. ACS Symp. Ser. 2002, 818, 289–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura, A.; Shiramatsu, Y.; Murata, K.; Kawamoto, T. Solubility-switchable ionic liquids: A control of hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity using a protective group. Chem. Lett. 2018, 47, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollet, A.L.; Porion, P.; Vaultier, M.; Billard, I.; Deschamps, M.; Bessada, C.; Jouvensal, L. Anomalous diffusion of water in [BMIM][TFSI] room-temperature ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11888–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, S.T.; Okello, M. The 2-position of imidazolium ionic liquids: Substitution and exchange. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaoui, A.; Mahendra, V.; Mitchell, G.; Cherifi, Z.; Harrane, A.; Belbachir, M. Design, Synthesis and Thermo-chemical Properties of Rosin Vinyl Imidazolium Based Compounds as Potential Advanced Biocompatible Materials. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020, 11, 3723–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Eulate, E.A.; Silvester, D.S.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Void-assisted ion-paired proton transfer at water-ionic liquid interfaces. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 14903–14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghini, N.; Gómez-González, V.; Varela, L.M.; Martinelli, A. Structural origin of proton mobility in a protic ionic liquid/imidazole mixture: Insights from computational and experimental results. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 23195–23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, A.; Maréchal, M.; Östlund, Å.; Cambedouzou, J. Insights into the interplay between molecular structure and diffusional motion in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids: A combined PFG NMR and X-ray scattering study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 5510–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koók, L.; Zitka, J.; Szakács, S.; Rózsenberszki, T.; Otmar, M.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Bakonyi, P. Efficiency, operational stability and biofouling of novel sulfomethylated polystyrene-block-poly (ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene cation exchange membrane in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Property | [bmim][PF6] | [hmim][PF6] | [bmim][NTf2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molar mass (g mol−1) | 284.18 | 312.24 | 419.36 |
| Density (g cm−3) | 1.37 * | 1.2932 ** | 1.4366 ** |
| Viscosity (mPa s) | 273 * | 496.4 ** | 50.9 ** |
| Structure of cations | 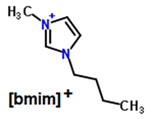  | ||
| 9.29 | |||
| 3.62 | |||
| Structure of anions |  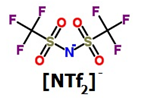 | ||
| Membrane | kH+ (10−3 cm s−1) | DH+ (10−5 cm s−1) | μH+ (10−7 m2 V−1 s−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion115 | 1.27 | 1.83 | 0.713 | This work |
| [bmim][NTf2] | 2.68 | 3.35 | 1.30 | |
| [hmim][PF6] | 7.38 | 9.22 | 3.59 | |
| CMI-7000 | 2.02 | 9.29 | 3.62 | [40] |
| UFM | 2.82 | 9.31 | 3.63 | |
| SPEEK | 4.66 | 9.32 | 3.63 | |
| glass fiber | 0.94 | 9.40 | 3.66 | [28] |
| textile | 30.27 | 9.08 | 3.54 |
| Membrane | tK+ | tNa+ | tH+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion115 | 0.907 | 0.910 | 0.978 |
| [bmim][PF6] | 0.747 | 0.761 | 0.933 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koók, L.; Lajtai-Szabó, P.; Bakonyi, P.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Investigating the Proton and Ion Transfer Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Prepared for Bioelectrochemical Applications Using Hydrophobic Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquids. Membranes 2021, 11, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050359
Koók L, Lajtai-Szabó P, Bakonyi P, Bélafi-Bakó K, Nemestóthy N. Investigating the Proton and Ion Transfer Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Prepared for Bioelectrochemical Applications Using Hydrophobic Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquids. Membranes. 2021; 11(5):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050359
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoók, László, Piroska Lajtai-Szabó, Péter Bakonyi, Katalin Bélafi-Bakó, and Nándor Nemestóthy. 2021. "Investigating the Proton and Ion Transfer Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Prepared for Bioelectrochemical Applications Using Hydrophobic Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquids" Membranes 11, no. 5: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050359
APA StyleKoók, L., Lajtai-Szabó, P., Bakonyi, P., Bélafi-Bakó, K., & Nemestóthy, N. (2021). Investigating the Proton and Ion Transfer Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Prepared for Bioelectrochemical Applications Using Hydrophobic Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquids. Membranes, 11(5), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050359








