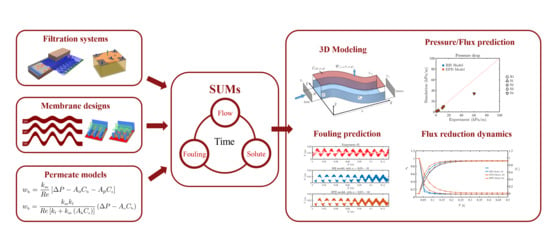
Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
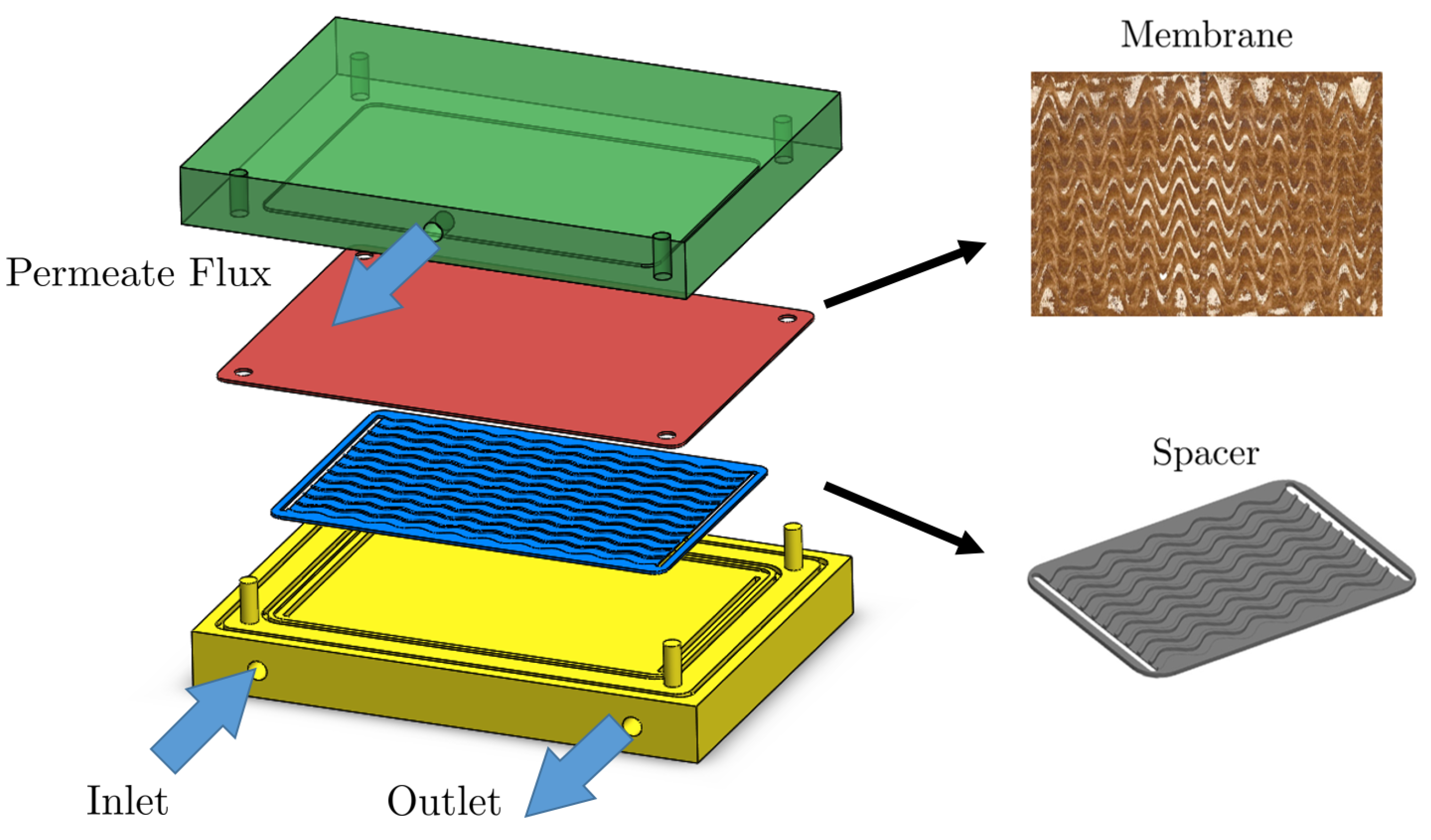
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation
2.2. Resistance-in-Series Model
2.3. Effective Pressure Drop Model
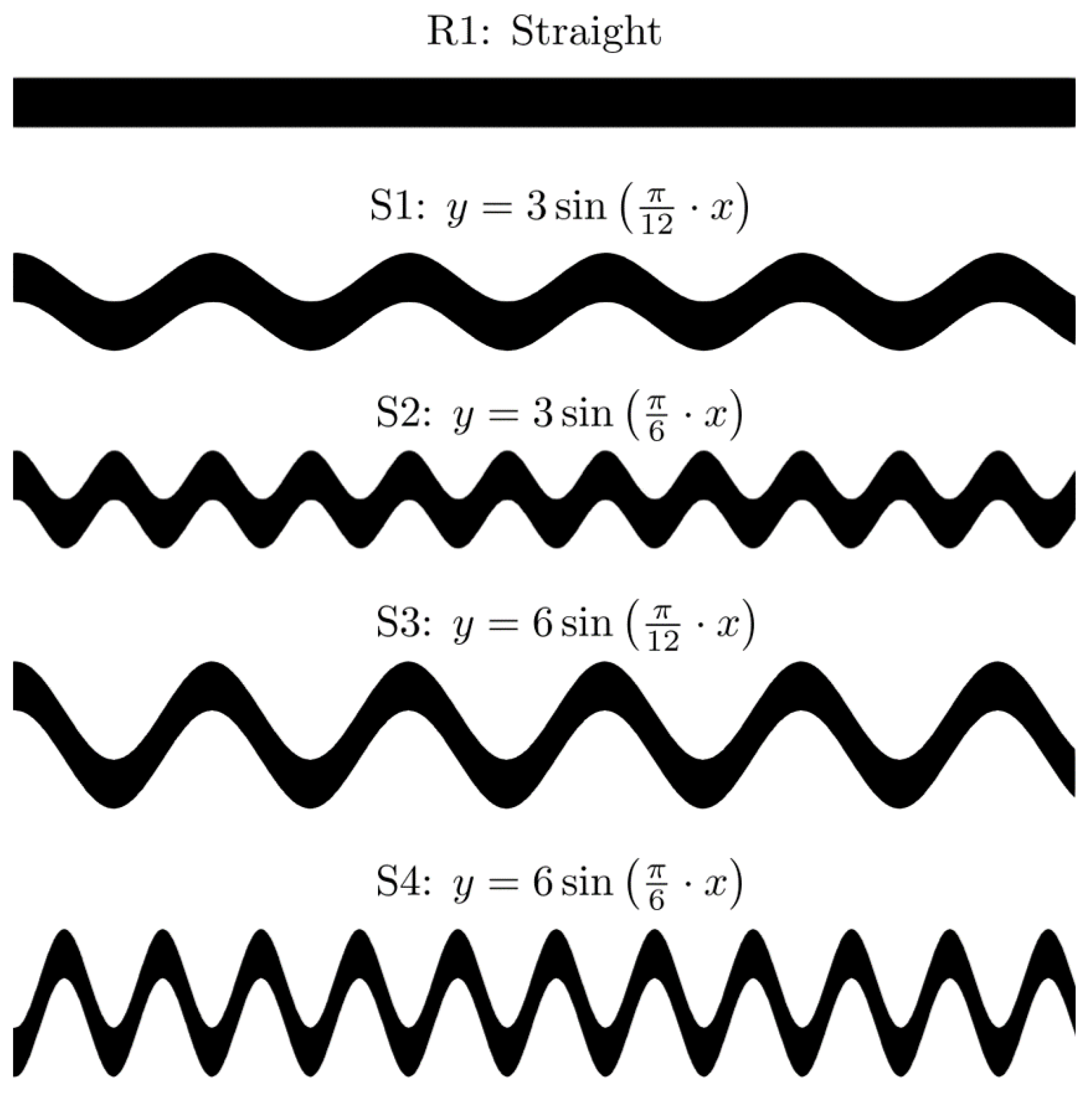
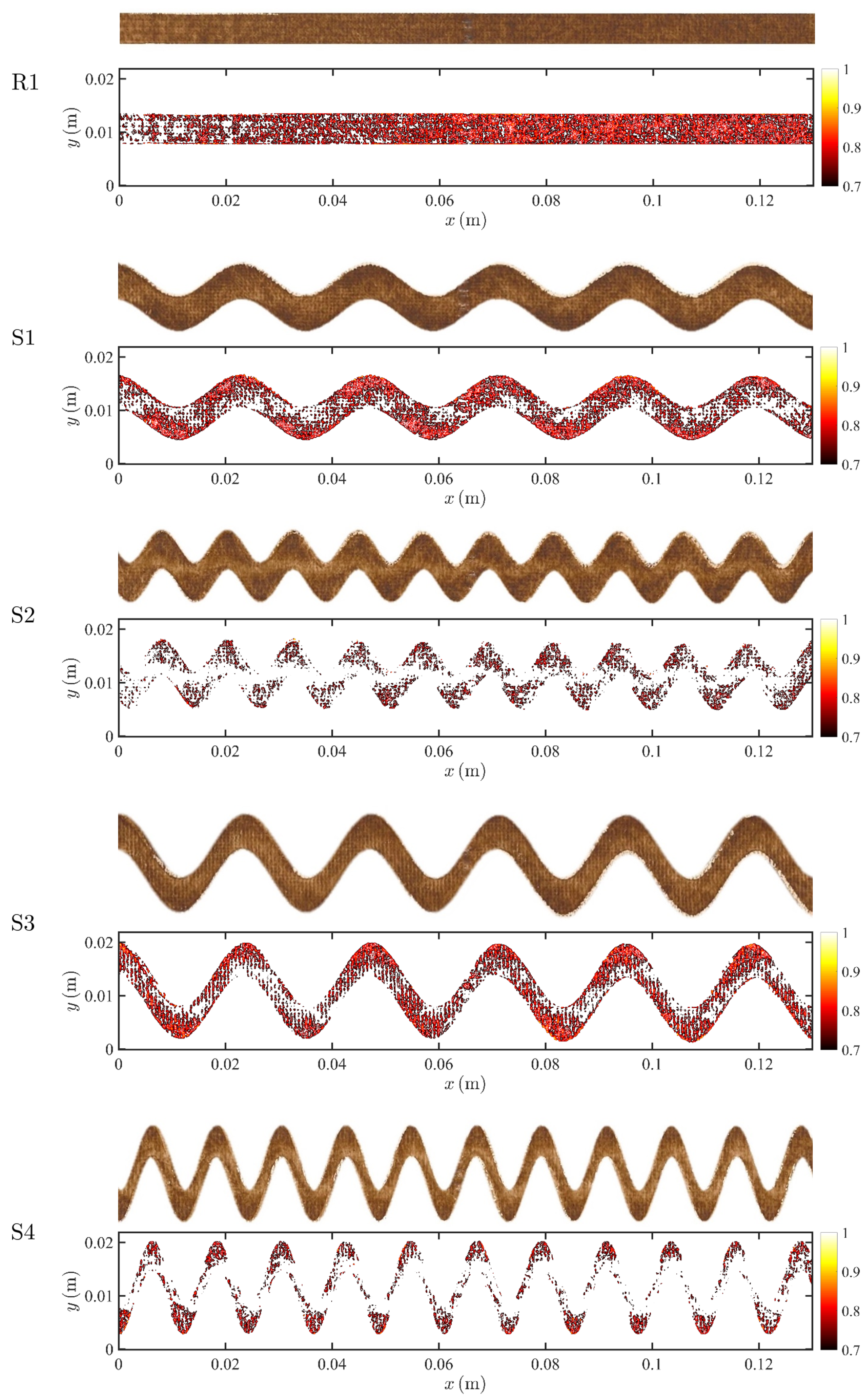
3. Experimental Data and Image Post-Processing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Steady-State Flux and Pressure
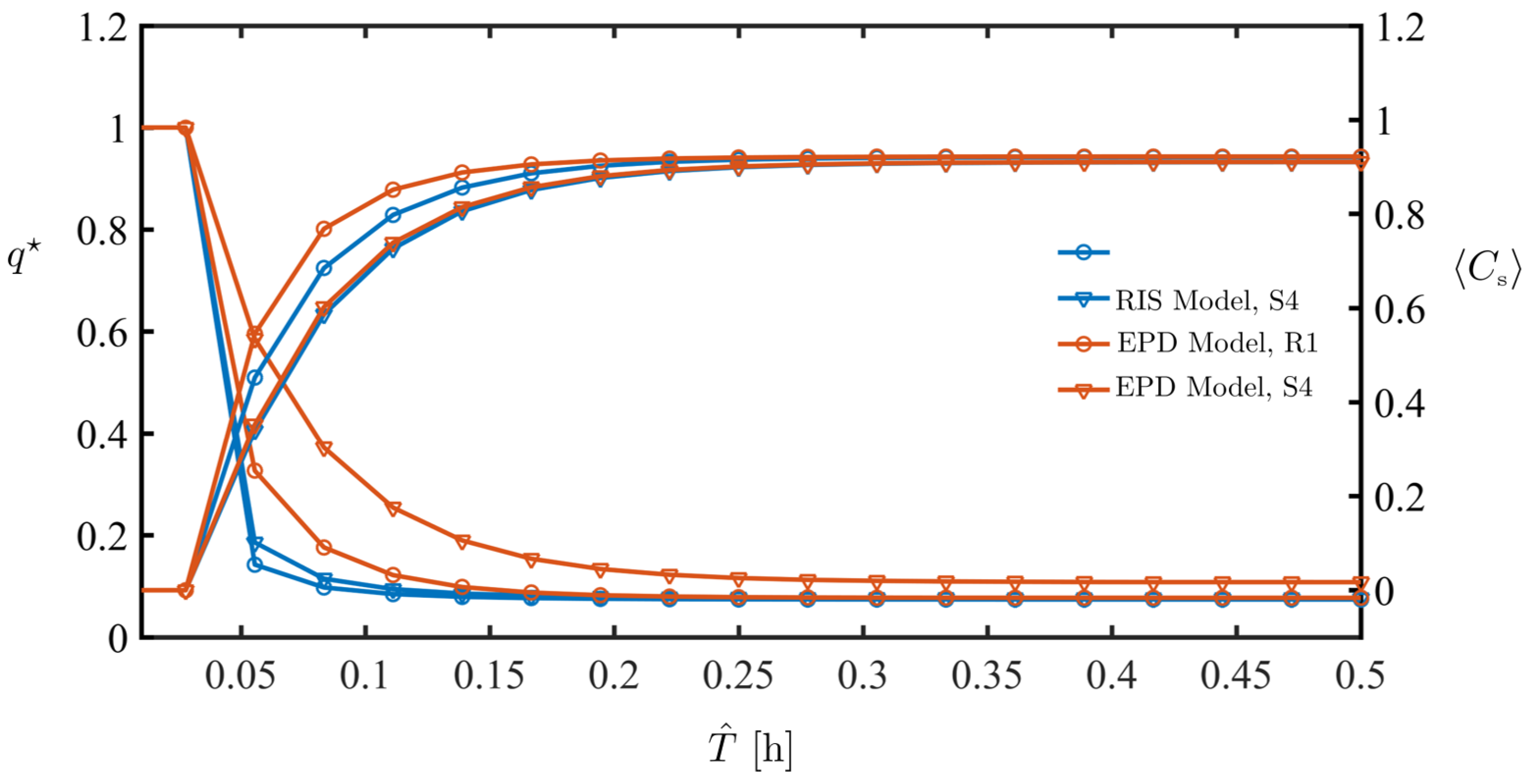
4.2. Dynamics
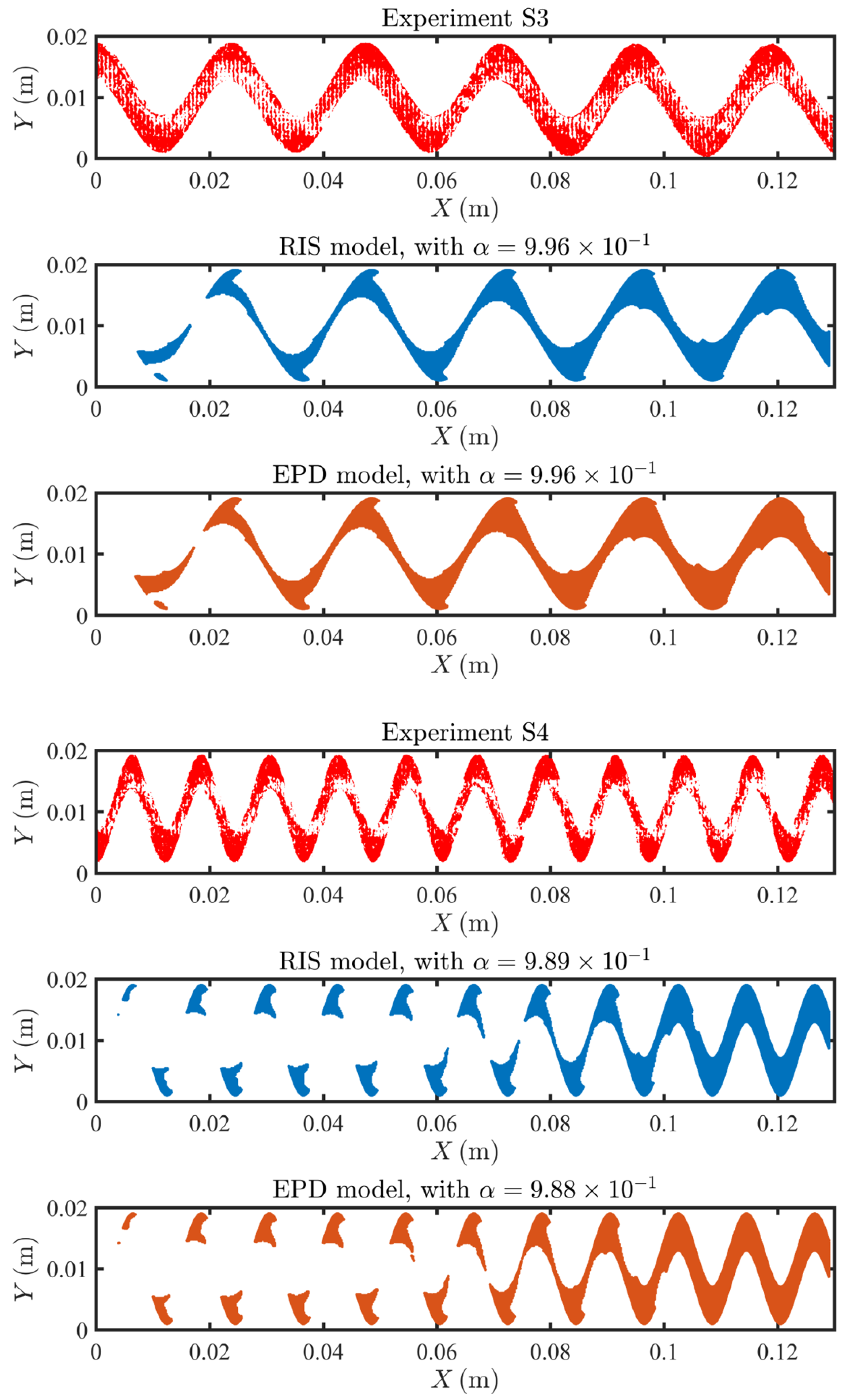
4.3. Fouling Pattern
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviation | |
| RIS | resistance-in-series |
| EPD | effective-pressure-drop |
| SUMs | Stanford University Membrane solver |
| Parameters | |
| time | |
| location vector | |
| location coordinate | |
| B | spacer width |
| H | spacer height |
| L | spacer length |
| velocity | |
| velocity components | |
| pressure | |
| density | |
| kinematic viscosity | |
| bulk concentration | |
| D | molecular diffusion coefficient |
| adsorption coefficient | |
| desorption coefficient | |
| equilibrium foulant concentration | |
| porous media structure parameter | |
| permeate water flux | |
| intrinsic membrane rejection rate | |
| hydraulic membrane water permeability | |
| pressure drop | |
| local pressure | |
| ambient pressure | |
| average inlet pressure | |
| outlet pressure | |
| osmotic coefficient | |
| fouled membrane permeability | |
| clean membrane resistance | |
| is the fouled membrane resistance | |
| foulant coefficient | |
| permeate flow rate | |
| non-fouled region | |
| Reynolds | |
| Péclet | |
| Damköhler number | |
| error of flux | |
| error of pressure |
References
- Honarparvar, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Alborzi, A.; Afroz, K.; Reible, D. Frontiers of Membrane Desalination Processes for Brackish Water Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzmann, C.; Löwenberg, J.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. State-of-the-art of reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 216, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, S.; Boyce, M. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: Phenomena and prevention. Desalination 2011, 281, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, M. Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination. Membranes 2021, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, A.; Ranauro, R.; Verdone, N. Treatment of landfill leachate by reverse osmosis. Water Res. 1999, 33, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A. Purification of landfill leachate with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. Desalination 1998, 119, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, Y.; Ruiz, M. Reverse osmosis applied to metal finishing wastewater. Desalination 2002, 142, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardianto, A.; McCool, B.C.; Cohen, Y. Accelerated desupersaturation of reverse osmosis concentrate by chemically-enhanced seeded precipitation. Desalination 2010, 264, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, B.C.; Rahardianto, A.; Faria, J.; Kovac, K.; Lara, D.; Cohen, Y. Feasibility of reverse osmosis desalination of brackish agricultural drainage water in the San Joaquin Valley. Desalination 2010, 261, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardianto, A.; McCool, B.C.; Cohen, Y. Reverse osmosis desalting of inland brackish water of high gypsum scaling propensity: Kinetics and mitigation of membrane mineral scaling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Gormly, S.; Beaudry, E.G.; Flynn, M.T.; Adams, V.D.; Childress, A.E. Membrane contactor processes for wastewater reclamation in space: Part I. Direct osmotic concentration as pretreatment for reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 257, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, P.L.T. Concentration Polar zation in Reverse Osmosis Desalination with Variable Flux and Incomplete Salt Rejection. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund. 1965, 4, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablani, S.; Goosen, M.; Al-Belushi, R.; Wilf, M. Concentration polarization in ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis: A critical review. Desalination 2001, 141, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hoek, E.M. Modeling concentration polarization in reverse osmosis processes. Desalination 2005, 186, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, G.; Boesen, C. Concentration polarization in a reverse osmosis test cell. Desalination 1977, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardianto, A.; Shih, W.Y.; Lee, R.W.; Cohen, Y. Diagnostic characterization of gypsum scale formation and control in RO membrane desalination of brackish water. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, W.Y.; Rahardianto, A.; Lee, R.W.; Cohen, Y. Morphometric characterization of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) scale on reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucs, S.S.; Linares, R.V.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Picioreanu, C. Biofouling in forward osmosis systems: An experimental and numerical study. Water Res. 2016, 106, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Haavisto, S.; Li, W.; Tang, C.Y.; Salmela, J.; Fane, A.G. Novel approach to characterizing the growth of a fouling layer during membrane filtration via optical coherence tomography. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14273–14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Murdoch, L.C.; Ladner, D.A. Hydrodynamics of sinusoidal spacers for improved reverse osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, K.Y.; Liang, Y.Y.; Lau, W.J.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. A Review of CFD Modelling and Performance Metrics for Osmotic Membrane Processes. Membranes 2020, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillen, G.; Hoek, E.M. Modeling the impacts of feed spacer geometry on reverse osmosis and nanofiltration processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Song, L. Numerical study on permeate flux enhancement by spacers in a crossflow reverse osmosis channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwarno, S.; Chen, X.; Chong, T.; Puspitasari, V.; McDougald, D.; Cohen, Y.; Rice, S.A.; Fane, A.G. The impact of flux and spacers on biofilm development on reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, C.; Ladner, D.A.; Economy, J. Using polyelectrolyte coatings to improve fouling resistance of a positively charged nanofiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 347, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Zhu, X.; Childress, A.E.; Hong, S. Role of membrane surface morphology in colloidal fouling of cellulose acetate and composite aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 127, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijenhoek, E.M.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Liu, M.; Lin, B.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, Q. A novel method of surface modification on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane by grafting poly (ethylene glycol). Polymer 2007, 48, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.R.; Doneva, T.A. Atomic force microscopy studies of membranes: Effect of surface roughness on double-layer interactions and particle adhesion. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2000, 229, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, D.; Steele, M.; Weir, A.; Hristovski, K.; Westerhoff, P. Functionalized nanoparticle interactions with polymeric membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B.; Tartakovsky, A.M.; Battiato, I. Dispersion controlled by permeable surfaces: Surface properties and scaling. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 801, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, P.; Richardson, G.; Witelski, T.; Cummings, L. Flow and fouling in a pleated membrane filter. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 795, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, P.; Cummings, L.J. Flow and fouling in membrane filters: Effects of membrane morphology. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 818, 744–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.D.; Gao, C.J.; Chen, W.D.; Jie, X.M.; Cao, Y.M.; Yuan, Q. Study on hypochlorite degradation of aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, S.H.; Wang, L.; Greenberg, A.R.; Pellegrino, J.; Ding, Y. Use of nanoimprinted surface patterns to mitigate colloidal deposition on ultrafiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 428, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiato, I.; Bandaru, P.; Tartakovsky, D.M. Elastic Response of Carbon Nanotube Forests to Aerodynamic Stresses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 144504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, I.; Howell, P.; Shipley, R. Control and optimization of solute transport in a thin porous tube. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 033101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekutin, J.; Kotowska, U. Model of Hydraulic Resistance When Forecasting Reverse Osmosis in Water Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chougradi, A.; Zaviska, F.; Abed, A.; Harmand, J.; Jellal, J.E.; Heran, M. Batch Reverse Osmosis Desalination Modeling under a Time-Dependent Pressure Profile. Membranes 2021, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Murdoch, L.C.; Ladner, D.A. Mitigating membrane fouling with sinusoidal spacers. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 168, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyster, E.; Cohen, Y. Numerical study of concentration polarization in a rectangular reverse osmosis membrane channel: Permeate flux variation and hydrodynamic end effects. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B.; Battiato, I. Rough or Wiggly? Membrane Topology and Morphology for Fouling Control. arxiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology In addition, Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Protein and humic acid adsorption onto hydrophilic membrane surfaces: Effects of pH and ionic strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchymiak, M.; Lyster, E.; Glater, J.; Cohen, Y. Kinetics of gypsum crystal growth on a reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, G.S.; Joseph, D.D. Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 1967, 30, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
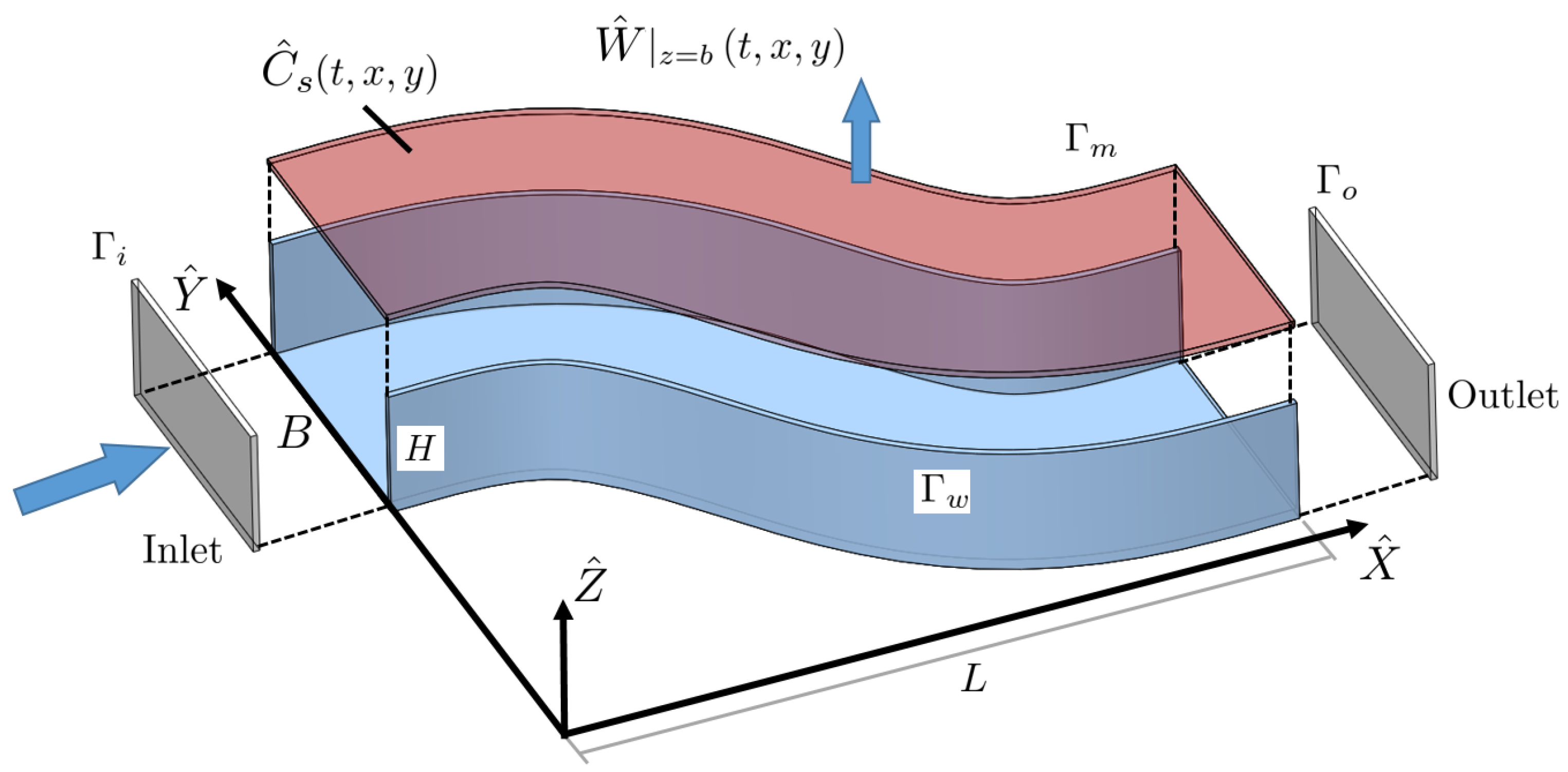



| Boundary | Flow | Bulk Concentration | Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet, | |||
| Outlet, | |||
| Solid Wall, | |||
| Membrane, |
| Parameter | Experimental Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Value | ||
| Width | B | m | |
| Height | H | m | |
| Viscosity | |||
| Diffusion Coeff. | D | ||
| Outlet Pressure | 4137 | Psi | |
| Inlet Velocity | |||
| Concentration | 50 | ||
| Permeability | |||
| Model | Re | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIS EPD | 900 | 2 | 0.07 - | - 3600 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, B.; Xie, P.; Ladner, D.; Battiato, I. Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050349
Ling B, Xie P, Ladner D, Battiato I. Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Membranes. 2021; 11(5):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050349
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Bowen, Peng Xie, David Ladner, and Ilenia Battiato. 2021. "Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes" Membranes 11, no. 5: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050349
APA StyleLing, B., Xie, P., Ladner, D., & Battiato, I. (2021). Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Membranes, 11(5), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050349