Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Iongel Membranes Reinforced with Nanoclays for CO2 Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
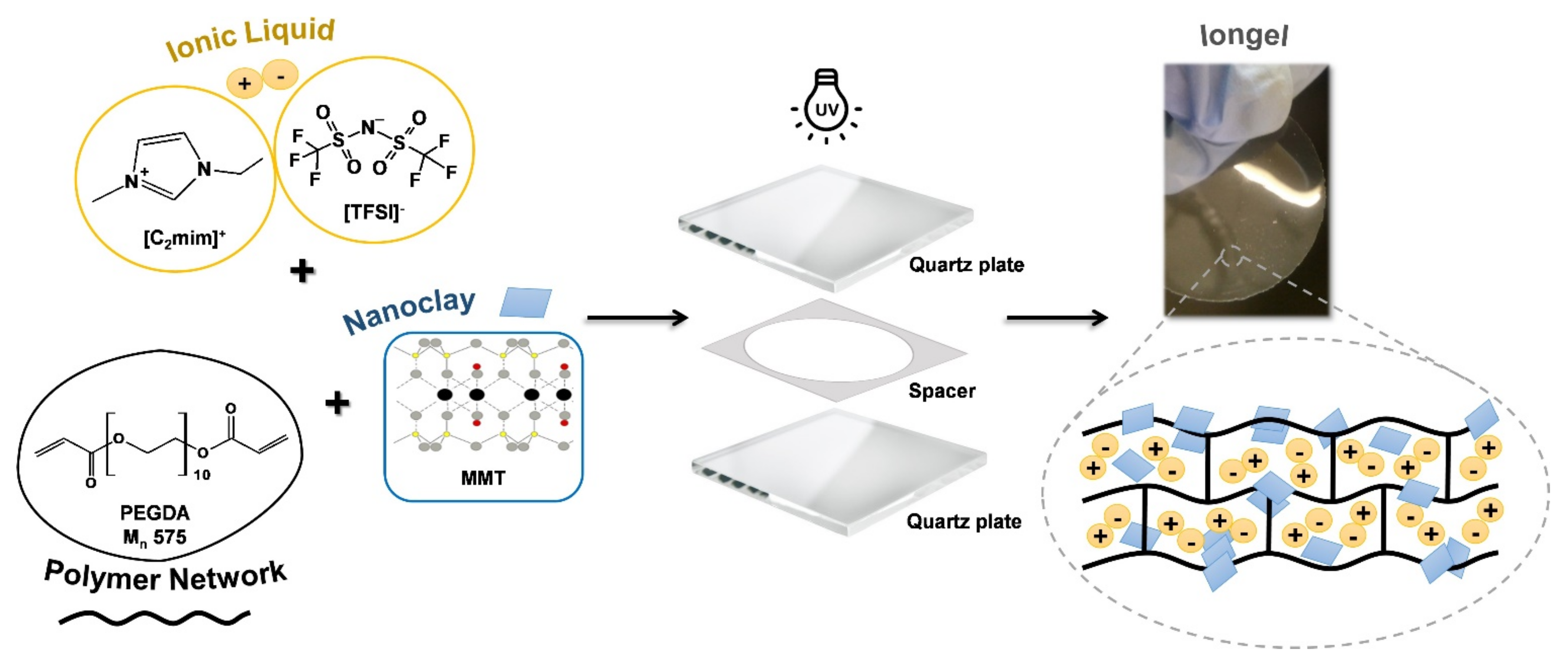
2.2. Preparation of the Iongels
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Gas Permeation Experiments
3. Results
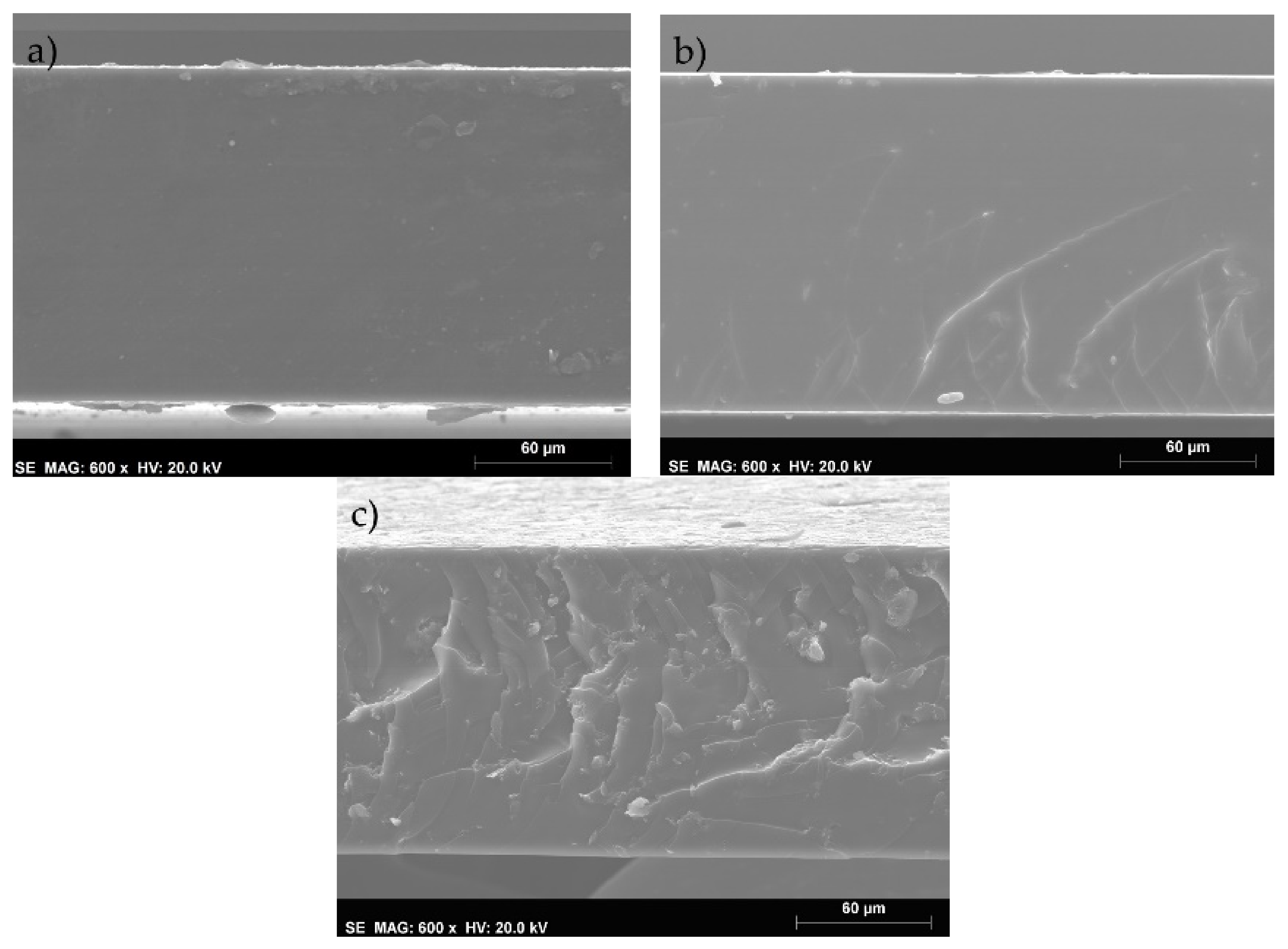
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
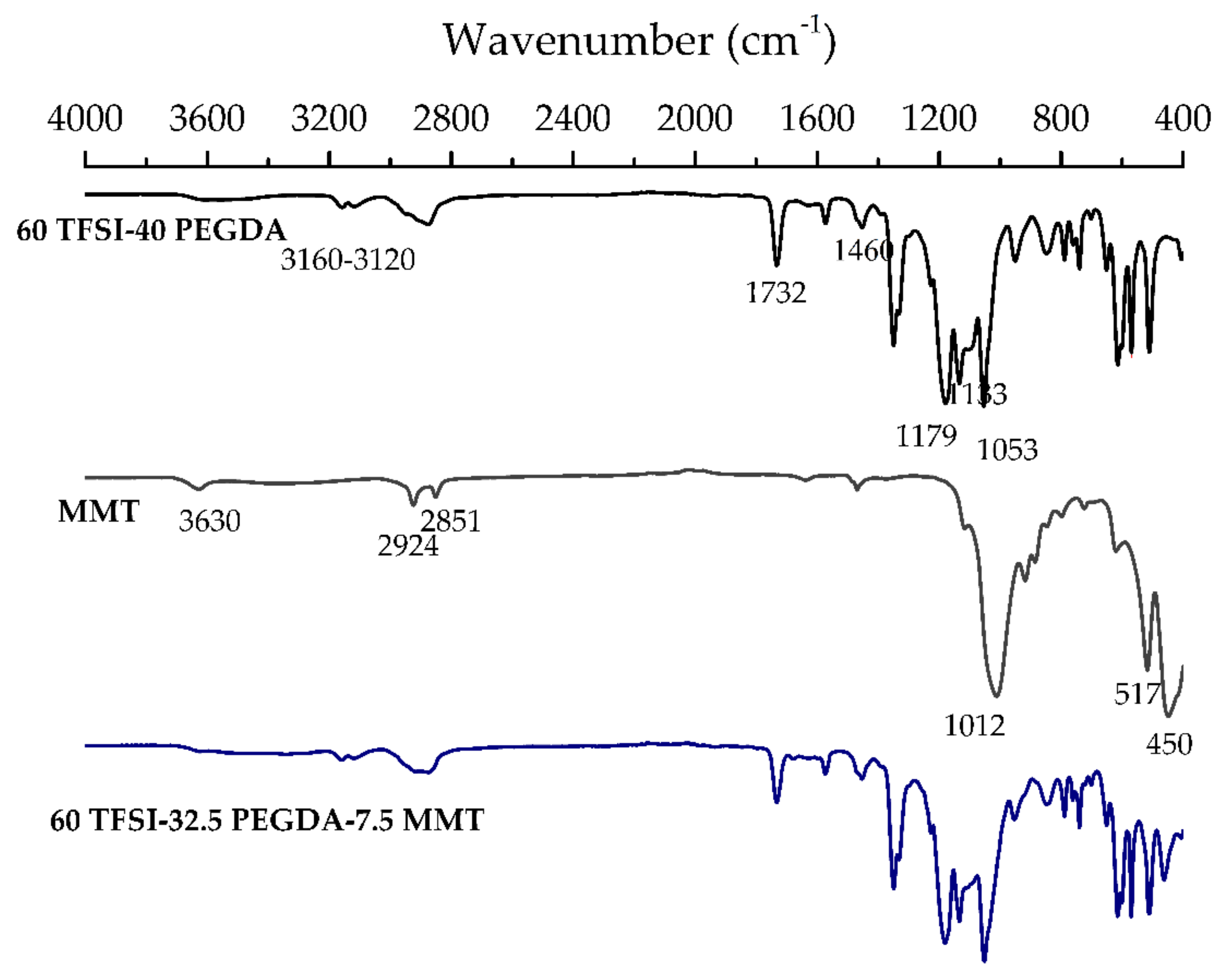
3.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
3.3. Contact Angle Measurements
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.5. Mechanical Properties
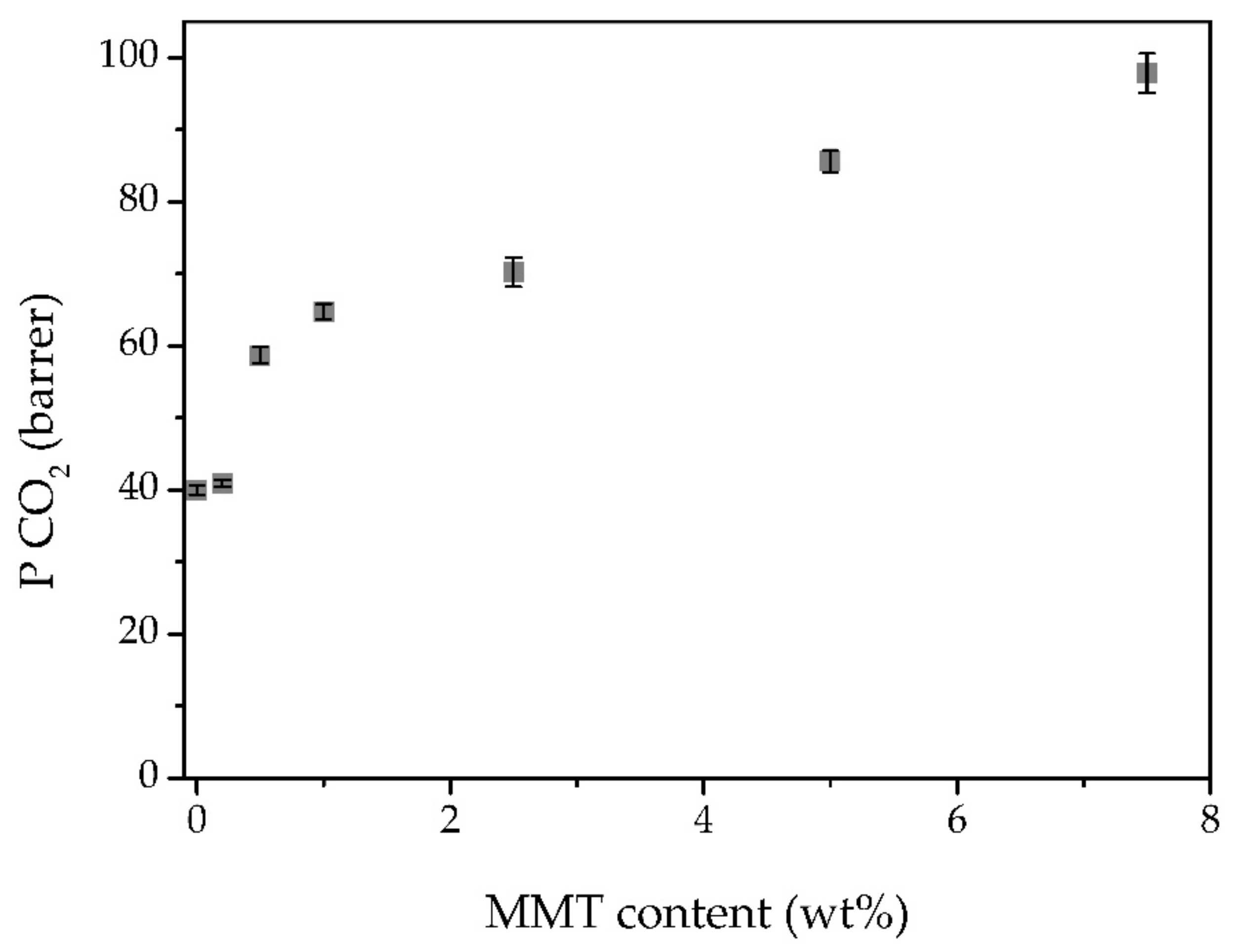
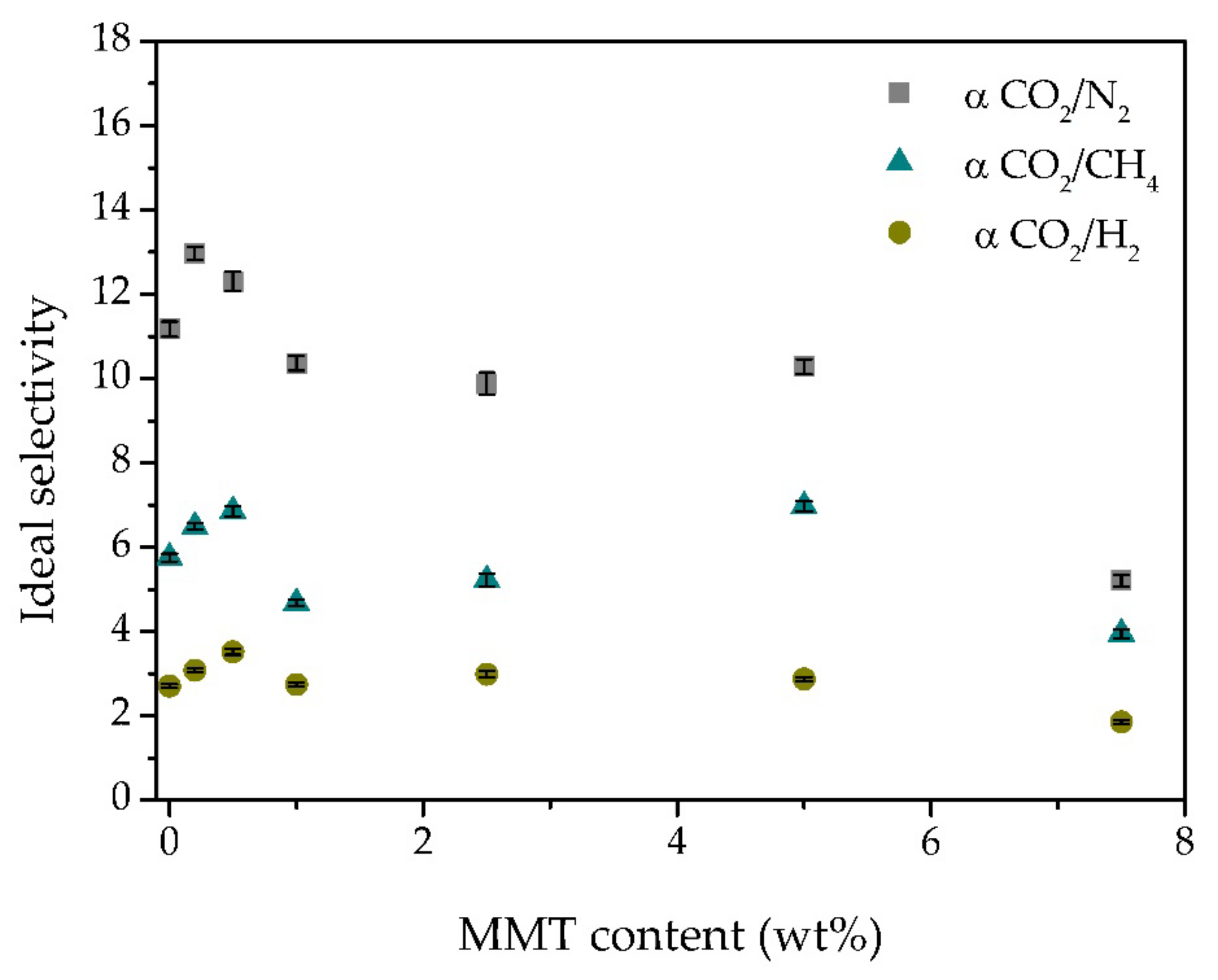
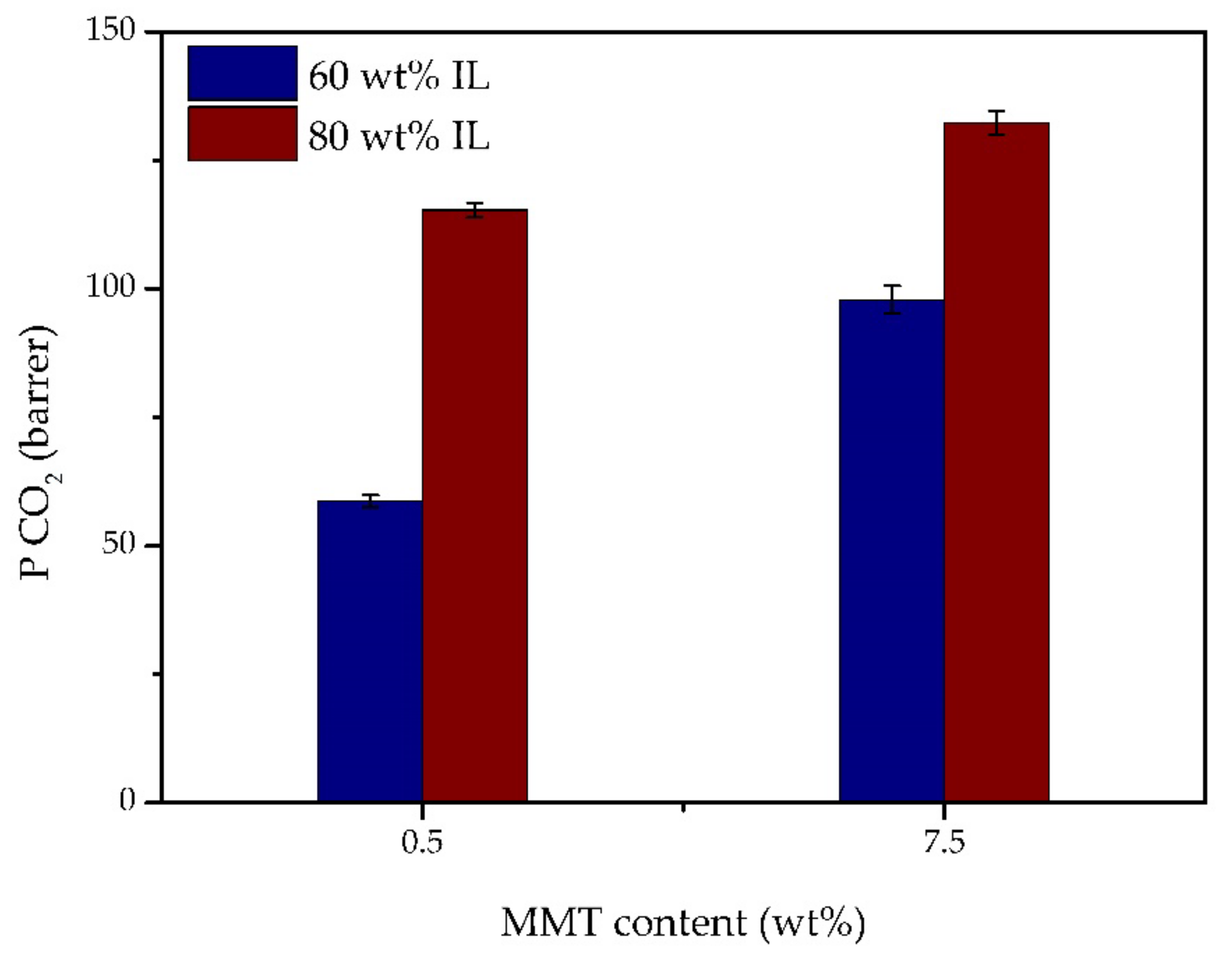
3.6. Gas Permeation Experiments
3.7. Comparison with Other Iongel Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Membrane area |
| ATR-FTIR | Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| d | Distance of the probe from the point of contact to the point of puncture |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| F | Applied force |
| IL | Ionic Liquid |
| l | Iongel thickness |
| MMM | Mixed Matrix Membrane |
| MMT | Montmorillonite |
| MOF | Metal Organic Framework |
| P | Permeability |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PEGDA | Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate |
| PIL | Poly(ionic liquid) |
| PVDF | Poly(vinylidene) fluoride |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SILM | Supported Ionic Liquid Membrane |
| t | Time |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| Tonset | Onset temperature |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| Vfeed | Volume of the feed compartment |
| Vperm | Volume of the permeate compartment |
| Δp | Pressure variation between the feed and the permeate compartments of the cell over time |
| Δp0 | Pressure variation between the feed and the permeate compartments of the cell at the beginning of the experiment |
| α | Ideal selectivity |
| β | Geometric parameter of the cell |
| Cations | |
| [C2mim]+ | 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium |
| Anions | |
| [B(CN)4]− | Tetracyanoborate |
| [C(CN)3]− | Tricyanomethanide |
| [FSI]− | Bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide |
| [TFSI]−- | Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
References
- Smiglak, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Lu, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Mac Farlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids for Energy, Materials, and Medicine. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9228–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Chemical Industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcarelli, L.; Shaplov, A.S.; Salsamendi, M.; Nair, J.R.; Vygodskii, Y.S.; Mecerreyes, D.; Gerbaldi, C. Single-Ion Block Copoly(Ionic Liquid)s as Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10350–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.; Al-Othman, A.; Nancarrow, P.; Elsayed, Y.; Tawalbeh, M. Enhanced Proton Conduction in Zirconium Phosphate/Ionic Liquids Materials for High-Temperature Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 4857–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Fakude, C.T.; Mabuba, N.; Peleyeju, G.M.; Arotiba, O.A. The Determination of 2-Phenylphenol in the Presence of 4-Chlorophenol Using Nano-Fe3O4/Ionic Liquid Paste Electrode as an Electrochemical Sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Bosom, S.; Karam, N.; Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Gurke, J.; Casado, N.; Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G.G. Conducting Polymer-Ionic Liquid Electrode Arrays for High-Density Surface Electromyography. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Renny, M.N.; Tomé, L.C.; Olmedo-Martínez, J.L.; Udabe, E.; Jenkins, E.P.W.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G.G.; McLeod, R.R.; Proctor, C.M. Reducing Passive Drug Diffusion from Electrophoretic Drug Delivery Devices through Co-Ion Engineering. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Ionic Liquid-Based Materials: A Platform to Design Engineered CO2 Separation Membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2785–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of Ionic Liquids with Membrane Technology: A New Approach for CO2 Separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Anguille, S.; Bendahan, M.; Moulin, P. Ionic Liquids Combined with Membrane Separation Processes: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Porcarelli, L.; Bara, J.E.; Forsyth, M.; Mecerreyes, D. Emerging Iongel Materials Towards Applications in Energy and Bioelectronics. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 3239–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.S.; De Añastro, A.F.; Olmedo-Martínez, J.L.; Nabais, A.R.; Neves, L.A.; Mecerreyes, D.; Tomé, L.C. Influence of Anion Structure on Thermal, Mechanical and CO2 Solubility Properties of Uv-Cross-Linked Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate Iongels. Membranes 2020, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Cussler, E.L.; Lodge, T.P. ABA-Triblock Copolymer Ion Gels for CO 2 Separation Applications. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard-Lack, A.; Buchtová, N.; Humbert, B.; Le Bideau, J. Ion Segregation in an Ionic Liquid Confined within Chitosan Based Chemical Ionogels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 23947–23951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gao, X.; Lu, F.; Sun, N.; Zheng, L. Facile Preparation of Supramolecular Ionogels Exhibiting High Temperature Durability as Solid Electrolytes. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.A.M.; Bayley, P.M.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Ionogels Based on Ionic Liquids as Potential Highly Conductive Solid State Electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Hata, K.; Katakabe, T.; Kondoh, M.; Watanabe, M. Nanocomposite Ion Gels Based on Silica Nanoparticles and an Ionic Liquid: Ionic Transport, Viscoelastic Properties, and Microstructure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9013–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Li, P.; Chung, T.S. PVDF/Ionic Liquid Polymer Blends with Superior Separation Performance for Removing CO2 from Hydrogen and Flue Gas. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11796–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, J.H.; Jin, J.; Xu, J.; Peng, T.; Ryu, K.I. Preparation of Iodine-Free Ionic Liquid Gel Electrolyte Using Polyethylene Oxide (PEO)-Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and Its Application in Ti-Foil-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 201, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.G.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Poly(Ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Ion-Gels with High “Free” Ionic Liquid Content: Platform Membrane Materials for CO2/Light Gas Separations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Pyrrolidinium-Based Polymeric Ionic Liquid Materials: New Perspectives for CO2 Separation Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Z.V.; Cowan, M.G.; McDanel, W.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Determination and Optimization of Factors Affecting CO2/CH4 Separation Performance in Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Ionic Liquid-Zeolite Mixed-Matrix Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 509, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabais, A.R.; Martins, A.P.S.; Alves, V.D.; Crespo, J.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Tomé, L.C.; Neves, L.A. Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Based Engineered Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2/H2 Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, T.K.; McDanel, W.M.; Cowan, M.G.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. Vinyl-Functionalized Poly(Imidazolium)s: A Curable Polymer Platform for Cross-Linked Ionic Liquid Gel Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, V.A.; Macala, M.K.; Baker, J.S.; Hopkinson, D. Cross-Linked Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Ion Gels Containing Functionalized Imidazolium Ionic Liquids as Carbon Dioxide Separation Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 11658–11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Tian, Z.; Xin, Q.; He, G.; Peng, D.; Chen, S.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Advances in High Permeability Polymer-Based Membrane Materials for CO2 Separations. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1863–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, B.; Nabais, A.R.; Casimiro, M.H.; Martins, A.P.S.; Francisco, R.O.; Neves, L.A.; Pereira, C.C.L. Impact on CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 Separation Performance Using Cu-BTC with Supported Ionic Liquids-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Guan, K.; Jin, W. Size Effects of Graphene Oxide on Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2 Separation. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Z.; Asghari, M. Preparation and Characterization of Ultra-Thin Poly Ether Block Amide/Nanoclay Nanocomposite Membrane for Gas Separation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Guiver, M.D. A Highly Permeable Aligned Montmorillonite Mixed-Matrix Membrane for CO2Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9321–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, A.; Zulfiqar, M.; Arshad, U.; Mahmood, S.; Iqbal, T.; Rafiq, S.; Iqbal, M.Z. Development and Performance Evaluation of Cellulose Acetate-Bentonite Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2 Separation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 8855577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Ching, O.P.; Shariff, A.B.M. Current Status and Future Prospect of Polymer-Layered Silicate Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, A.V.; Alekseeva, O.V.; Shibaeva, V.D.; Agafonov, A.V. Synthesis, Structure and Thermal Properties of Montmorillonite/Ionic Liquid Ionogels. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34885–34894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha Ray, S. Chapter 1: An Overview of Pure and Organically Modified Clays. In Clay-Containing Polymer Nanocomposites: From Fundamentals to Real Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Ching, O.P.; Shariff, A.B.M. Polymer-Nanoclay Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation: A Review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 625, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Afonso, C.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Integrated CO 2 Capture and Enzymatic Bioconversion in Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defontaine, G.; Barichard, A.; Letaief, S.; Feng, C.; Matsuura, T.; Detellier, C. Nanoporous Polymer—Clay Hybrid Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajó, J.J.; Teijeira, T.; Fernández, J.; Salgado, J.; Villanueva, M. Thermal Stability of Some Imidazolium [NTf2] Ionic Liquids: Isothermal and Dynamic Kinetic Study through Thermogravimetric Procedures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 112, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard, S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Effects of Montmorillonite Nano-Clay Fillers on PEI Mixed Matrix Membrane for CO2 Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Alizadeh, A.; Rajabi, H.; Daraei, P. Preparation, Characterization and Performance of Polyethersulfone/Organically Modified Montmorillonite Nanocomposite Membranes in Removal of Pesticides. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 382, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudian, S.; Wahit, M.U.; Ismail, A.F.; Yussuf, A.A. Preparation of Regenerated Cellulose/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite Films via Ionic Liquids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozi, M.; Pakizeh, M. Study the Effects of Cloisite15A Nanoclay Incorporation on the Morphology and Gas Permeation Properties of Pebax2533 Polymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Oh, P.C.; Shariff, A.M. Polyetherimide-Montmorillonite Mixed Matrix Hollow Fibre Membranes: Effect of Inorganic/Organic Montmorillonite on CO2/CH4 Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The Upper Bound Revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.W.; Robeson, L.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Influence of Temperature on the Upper Bound: Theoretical Considerations and Comparison with Experimental Results. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, W.; Mansouri, J.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Improving CO2 Separation Performance of Thin Film Composite Hollow Fiber with Pebax®1657/Ionic Liquid Gel Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 537, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Aboudzadeh, M.A.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Mecerreyes, D.; Marrucho, I.M. Polymeric Ionic Liquids with Mixtures of Counter-Anions: A New Straightforward Strategy for Designing Pyrrolidinium-Based CO2 Separation Membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10403–10411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, A.S.L.; Ventaja, L.; Tomé, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Towards Biohydrogen Separation Using Poly(Ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Composite Membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friess, K.; Lanč, M.; Pilnáček, K.; Fíla, V.; Vopička, O.; Sedláková, Z.; Cowan, M.G.; McDanel, W.M.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; et al. CO2/CH4 Separation Performance of Ionic-Liquid-Based Epoxy-Amine Ion Gel Membranes under Mixed Feed Conditions Relevant to Biogas Processing. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 528, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, R.M.; Tomé, L.C.; Mantione, D.; Mecerreyes, D.; Marrucho, I.M. Mixing Poly(Ionic Liquid)s and Ionic Liquids with Different Cyano Anions: Membrane Forming Ability and CO2/N2 Separation Properties. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 552, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Yasuda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Yoshida, A.; Li, X.; Hashimoto, K.; Nagai, K.; Shibayama, M.; Watanabe, M. Sulfonated Polyimide/Ionic Liquid Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation: Transport Properties in Relation to Their Nanostructures. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7112–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Yasuda, T.; Ma, X.; Watanabe, M. Sulfonated Polyimide/Ionic Liquid Composite Membranes for Carbon Dioxide Separation. Polym. J. 2017, 49, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Harra, K.E.; Kammakakam, I.; Devriese, E.M.; Noll, D.M.; Bara, J.E.; Jackson, E.M. Synthesis and Performance of 6FDA-Based Polyimide-Ionenes and Composites with Ionic Liquids as Gas Separation Membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uk Hong, S.; Park, D.; Ko, Y.; Baek, I. Polymer-Ionic Liquid Gels for Enhanced Gas Transport. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1, 7227–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Mok, M.M.; Cowan, M.G.; Mcdanel, W.M.; Carlisle, T.K.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. High-Permeance Room-Temperature Ionic-Liquid-Based Membranes for CO2/N2 Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 20064–20067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDanel, W.M.; Cowan, M.G.; Chisholm, N.O.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Fixed-Site-Carrier Facilitated Transport of Carbon Dioxide through Ionic-Liquid-Based Epoxy-Amine Ion Gel Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 492, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Isik, M.; Freire, C.S.R.; Mecerreyes, D.; Marrucho, I.M. Novel Pyrrolidinium-Based Polymeric Ionic Liquids with Cyano Counter-Anions: High Performance Membrane Materials for Post-Combustion CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 483, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Hao, T.; Wang, H.; Ding, X.; Meng, J. Tuning the Microstructure of Crosslinked Poly(Ionic Liquid) Membranes and Gels via a Multicomponent Reaction for Improved CO2 Capture Performance. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 593, 117405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammakakam, I.; Bara, J.E.; Jackson, E.M.; Lertxundi, J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Tomé, L.C. Tailored CO2-Philic Anionic Poly(Ionic Liquid) Composite Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Transport Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5954–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yu, J.; Dai, Z.; Deng, L. Cross-Linked PEG Membranes of Interpenetrating Networks with Ionic Liquids as Additives for Enhanced CO2 Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Bai, L.; Gao, H.; Deng, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S. Pebax-Based Composite Membranes with High Gas Transport Properties Enhanced by Ionic Liquids for CO2 Separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6422–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudiono, Y.C.; Carlisle, T.K.; LaFrate, A.L.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Novel Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Polymerizable Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids and SAPO-34 Particles to Improve CO 2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, R.; Kishida, M.; Sawa, H.; Kidesaki, T.; Sato, S.; Kanehashi, S.; Nagai, K. Characterization and Gas Permeation Properties of Polyimide/ZSM-5 Zeolite Composite Membranes Containing Ionic Liquid. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 454, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbaran, F.; Kamio, E.; Matsuyama, H. Inorganic/Organic Composite Ion Gel Membrane with High Mechanical Strength and High CO2 Separation Performance. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 544, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamio, E.; Yasui, T.; Iida, Y.; Gong, J.P.; Matsuyama, H. Inorganic/Organic Double-Network Gels Containing Ionic Liquids. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamio, E.; Minakata, M.; Iida, Y.; Yasui, T.; Matsuoka, A.; Matsuyama, H. Inorganic/Organic Double-Network Ion Gel Membrane with a High Ionic Liquid Content for CO2 Separation. Polym. J. 2021, 53, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kamio, E.; Kinoshita, M.; Matsuoka, A.; Nakagawa, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Matsuyama, H. Inorganic/Organic Micro-Double-Network Ion Gel-Based Composite Membrane with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and CO2 Permeance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 12698–12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbaran, F.; Kamio, E.; Matsuyama, H. Ion Gel Membrane with Tunable Inorganic/Organic Composite Network for CO2 Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12763–12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi Estahbanati, E.; Omidkhah, M.; Ebadi Amooghin, A. Interfacial Design of Ternary Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Pebax 1657/Silver-Nanopowder/[BMIM][BF4] for Improved CO2 Separation Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10094–10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, R.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. (Cross-Linked Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Ionic Liquid-Zeolite) Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Gas Separations Based on Curable Ionic Liquid Prepolymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 4704–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, H.R.; Azizi, N.; Arzani, M.; Mohammadi, T. Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Using a Nanocomposite Ionic Liquid Gel Membrane. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 46, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.M.; Nabais, A.R.; Tomé, L.C.; Neves, L.A. Impact of MOF-5 on Pyrrolidinium-Based Poly(Ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Membranes for Biogas Upgrading. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Tonset (°C) |
|---|---|
| [C2mim][TFSI] | 412 |
| PEGDA | 369 |
| MMT | 200 |
| 60 TFSI-40 PEGDA | 339 |
| 60 TFSI-39.8 PEGDA-0.2 MMT | 339 |
| 60 TFSI-39.5 PEGDA-0.5 MMT | 340 |
| 60 TFSI-39 PEGDA-1 MMT | 339 |
| 60 TFSI-37.5 PEGDA-2.5 MMT | 340 |
| 60 TFSI-35 PEGDA-5 MMT | 331 |
| 60 TFSI-32.5 PEGDA-7.5 MMT | 326 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nabais, A.R.; Francisco, R.O.; Alves, V.D.; Neves, L.A.; Tomé, L.C. Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Iongel Membranes Reinforced with Nanoclays for CO2 Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120998
Nabais AR, Francisco RO, Alves VD, Neves LA, Tomé LC. Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Iongel Membranes Reinforced with Nanoclays for CO2 Separation. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120998
Chicago/Turabian StyleNabais, Ana R., Rute O. Francisco, Vítor D. Alves, Luísa A. Neves, and Liliana C. Tomé. 2021. "Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Iongel Membranes Reinforced with Nanoclays for CO2 Separation" Membranes 11, no. 12: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120998
APA StyleNabais, A. R., Francisco, R. O., Alves, V. D., Neves, L. A., & Tomé, L. C. (2021). Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Iongel Membranes Reinforced with Nanoclays for CO2 Separation. Membranes, 11(12), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120998









