Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Properties of Cellulose Triacetate Mixed–Matrix Membranes with CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers
2.3. Preparation of CTA-CeO2@GO Mixed-Matrix Membrane and Its Mechanism of Formation
2.4. Materials Characterization
2.5. Gas Sorption and Gas Permeation Measurements
3. Results
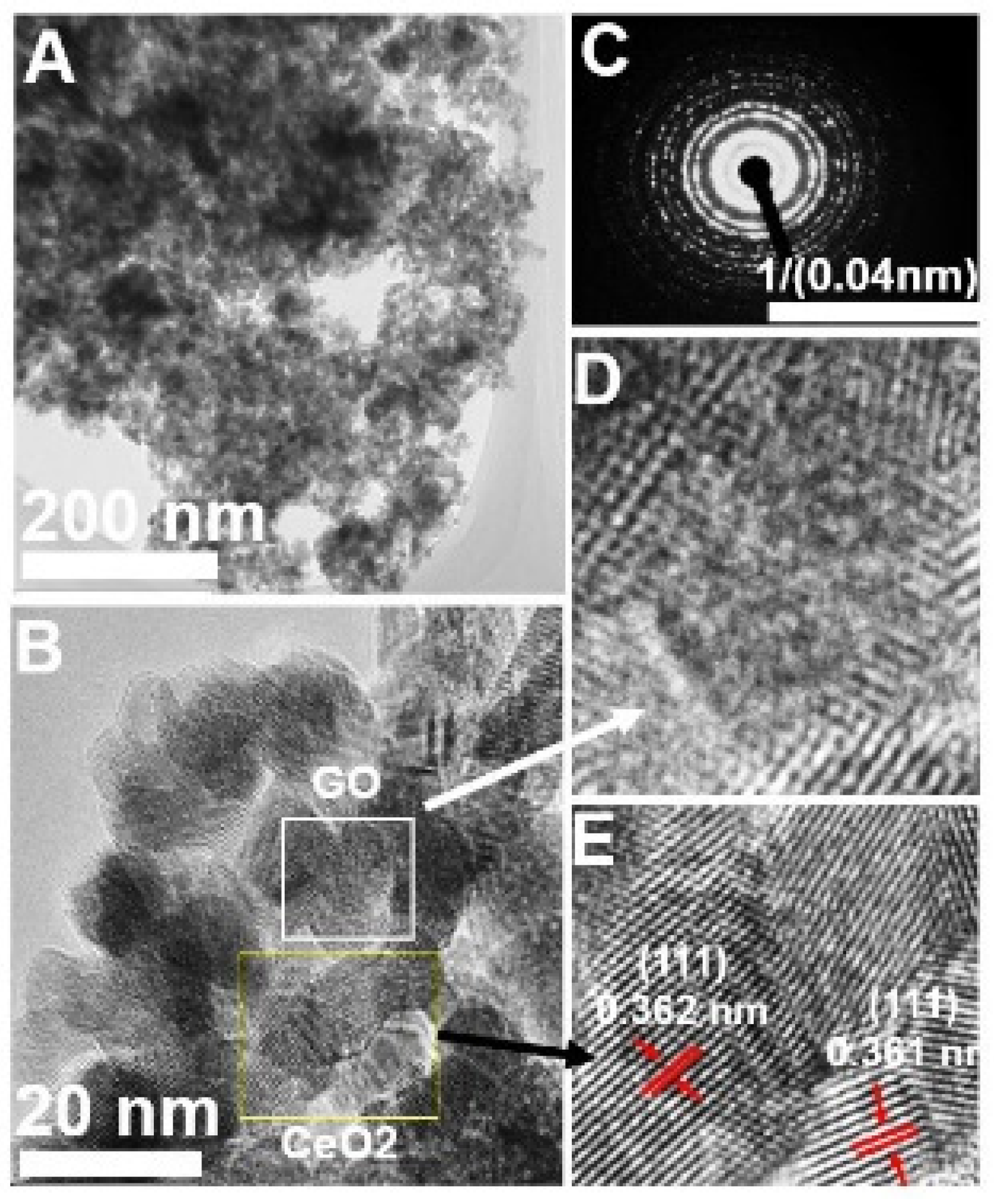
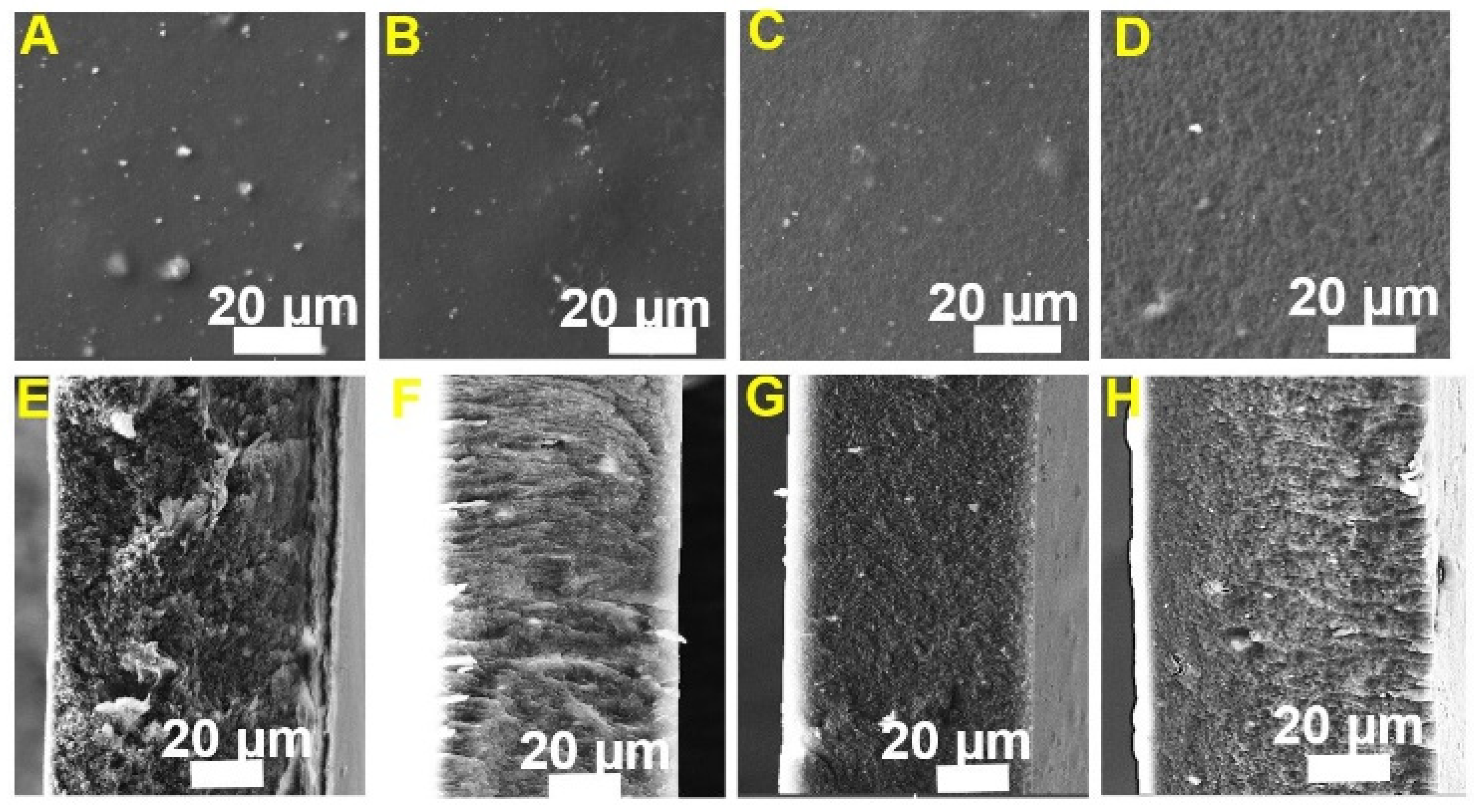
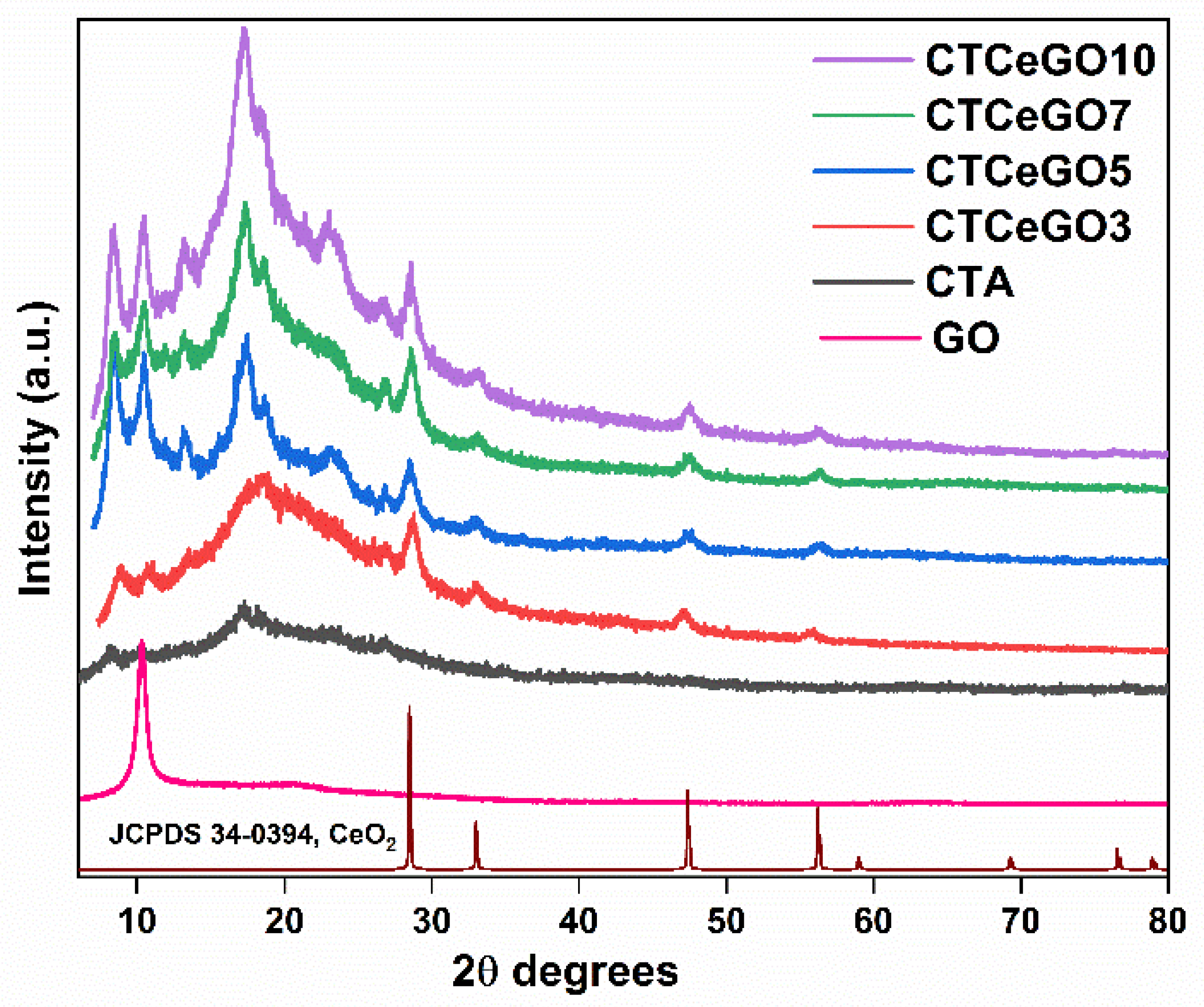
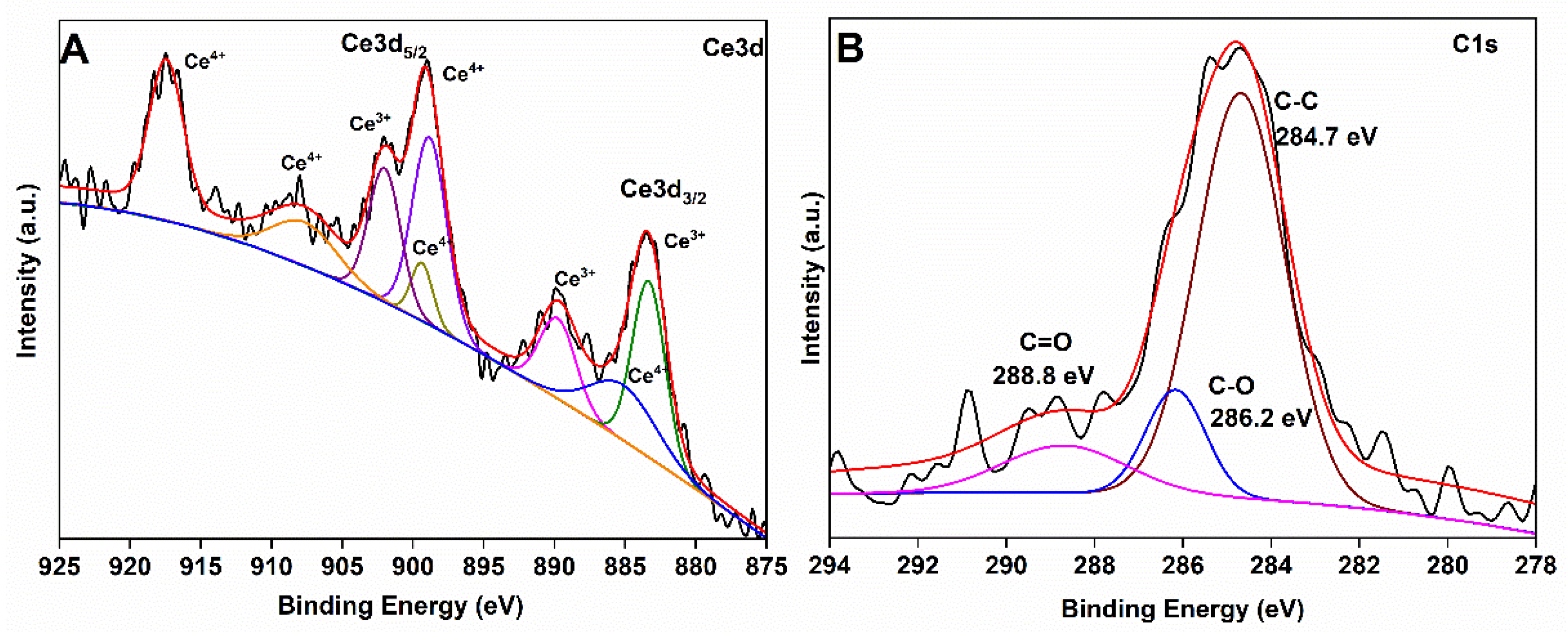
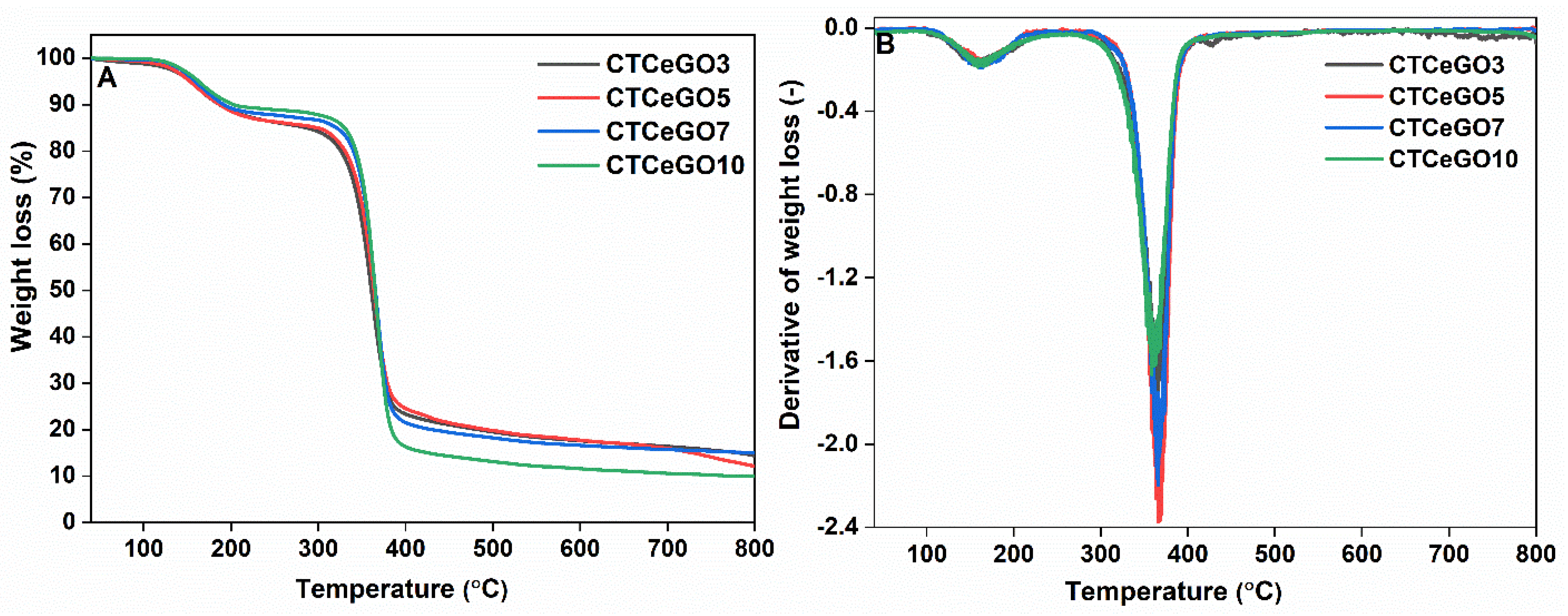
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterizations
3.2. Gas Separation Performances Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugo Moretti, I. Chapter 9—Polymeric membrane-based plants for biogas upgrading. In Membrane Engineering for the Treatment of Gases: Volume 1: Gas-Separation Issues with Membranes, 2nd ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 242–255. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoba, M.; Bhagiyalakshmi, M.; Alqaheem, Y.; Alomair, A.A.; Pérez, A.; Rana, M.S. Recent progress of fillers in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, D.; Yang, Z.; Xin, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ning, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. Liquid-like CNT/SiO2 nanoparticle organic hybrid materials as fillers in mixed matrix composite membranes for enhanced CO2-selective separation. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 11949–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangu, K.K.; Maddila, S.; Mukkamala, S.B.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. A review on contemporary metal–organic framework materials. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 446, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Zhai, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Christopher, M.P.; Long, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Mixed matrix membranes containing MOF@COF hybrid fillers for efficient CO2/CH4 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, S.; Bandaru, P.R. A methodology for quantitatively characterizing the dispersion of nanostructures in polymers and composites. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Wong, D.A.; Yang, J. Recent advances in polymer-inorganic mixed matrix membranes for CO2 Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Sanip, S.M.; Ng, B.C.; Aziz, M. Recent advances of inorganic fillers in mixed matrix membrane for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Seoane, B.; Zamaro, J.M.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Combination of MOFs and zeolites for mixed-matrix membranes. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 2781–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, A.; Sieffert, D.; Staudt, C.; Ferrando, M.; Güell, C.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Combination of ordered mesoporous silica MCM-41 and layered titanosilicate JDF-L1 fillers for 6FDA-based copolyimide mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Mixed matrix membranes for gas separation by combination of silica MCM-41 and MOF NH2-MIL-53(Al) in glassy polymers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 192, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.; Othman, N.H.; Alias, N.H.; Shahruddin, M.Z.; Roslan, R.A.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Mixed matrix membranes incorporated with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and zeolitic imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanofillers for gas separation. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Goh, P.S.; Taniguchi, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Zahri, K. The role of geometrically different carbon-based fillers on the formation and gas separation performance of nanocomposite membranes. Carbon 2019, 149, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Mohd Noh, A.N.; Leo, C.P.; Ahmad, A.L. CO2 removal using membrane gas absorption with PVDF membrane incorporated with POSS and SAPO-34 zeolite. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 118, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Lu, F.; Kong, C.Y.; Cao, L.; Thorne, T.J.; Sun, Y.-P. Graphene oxides for homogeneous dispersion of carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, H.-Y. One-pot synthesis of CdS sensitized TiO2 decorated reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane and the effective removal of organic pollutant from water. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15247–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, W.-Q.; Wang, L.-L.; Huang, G.-F. Interfacial Interactions of Semiconductor with Graphene and Reduced Graphene Oxide: CeO2 as a Case Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20350–20357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.F.; Isawi, H.; Badway, N.A.; Elbayaa, A.A.; Shawky, H. Graphene oxide incorporated cellulose triacetate/cellulose acetate nanocomposite membranes for forward osmosis desalination. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M. Polymer nanocomposites-A comparison between carbon nanotubes, graphene, and clay as nanofillers. Materials 2016, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kundalwal, S.I.; Kumar, S. Gas barrier performance of graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Carbon 2016, 98, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojha, G.P.; Pant, B.; Park, S.-J.; Park, M.; Kim, H.-Y. Synthesis and characterization of reduced graphene oxide decorated with CeO2-doped MnO2 nanorods for supercapacitor applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A. Catalytic properties of ceria and CeO2-containing materials. Catal. Rev. 1996, 38, 439–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, C.; Ashtiani, S.; Sofer, Z.; Hrdlička, Z.; Průša, F.; Vopička, O.; Friess, K. CeO2-blended cellulose triacetate mixed-matrix membranes for selective CO2 separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaie, S.S.; Krantz, W.B.; Greenberg, A.R. Dense polymer film and membrane formation via the dry-cast process part I. Model development. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 94, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchione, M.; Jansen, J.C.; Drioli, E. The dry phase inversion technique as a tool to produce highly efficient asymmetric gas separation membranes of modified PEEK. Influence of temperature and air circulation. Desalination 2006, 192, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, K.; Hynek, V.; Šípek, M.; Kujawski, W.M.; Vopička, O.; Zgažar, M.; Kujawski, M.W. Permeation and sorption properties of poly(ether-block-amide) membranes filled by two types of zeolites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopička, O.; Friess, K.; Hynek, V.; Sysel, P.; Zgažar, M.; Šípek, M.; Pilnáček, K.; Lanč, M.; Jansen, J.C.; Mason, C.R.; et al. Equilibrium and transient sorption of vapours and gases in the polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Friess, K.; Drioli, E. Organic vapour transport in glassy perfluoropolymer membranes: A simple semi-quantitative approach to analyze clustering phenomena by time lag measurements. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, K.; Jansen, J.C.; Bazzarelli, F.; Izák, P.; Jarmarová, V.; Kačírková, M.; Schauer, J.; Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P. High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Correlation of membrane structure with gas and vapour transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, D.; Singh, V.; Park, S.; Schulte, A.; Seal, S.; Khondaker, S.I. Anchoring ceria nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide and their electronic transport properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 24494–24500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, P.; He, D.; Cheng, Y.; Liao, L.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Z.; Li, P. Cerium oxide immobilized reduced graphene oxide hybrids with excellent microwave absorbing performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14155–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Shrestha, L.K.; Minami, K.; Subramanian, M.; Jayavel, R.; Ariga, K. Dimensionally integrated nanoarchitectonics for a novel composite from 0D, 1D, and 2D nanomaterials: RGO/CNT/CeO2 ternary nanocomposites with electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18480–18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, H.; Ahn, B.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.S. Cellulose triacetate-based polymer gel electrolytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; Ragab, S.; El Sikaily, A.; Khaled, A. Synthesis of cellulose triacetate from cotton cellulose by using NIS as a catalyst under mild reaction conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, B.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; Jeyadheepan, K. Synthesis and formation of phase-tuned TiO2-/ioniclLiquid-incorporated polymeric membranes for ammonia sensing at room temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15884–15895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Su, X.; Ye, H.; Li, N. Tröger ’s base mixed matrix membranes for gas separation incorporating NH2-MIL-53(Al) nanocrystals. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plain surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D. Mixed matrix membranes for natural gas upgrading: Current status and opportunities. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4139–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Rahimi, P.; Joseph, Y. Structure-function relationships of nanocarbon/polymer composites for chemiresistive sensing: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, D.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Mixed matrix membranes comprising polymers of intrinsic microporosity and covalent organic framework for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaeva, D.; Azcune, I.; Tanczyk, M.; Warmuzinski, K.; Jaschik, M.; Sandru, M.; Dahl, P.I.; Genua, A.; Loïs, S.; Sheridan, E.; et al. The performance of affordable and stable cellulose-based poly-ionic membranes in CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Číhal, P.; Vopička, O.; Lanč, M.; Kludský, M.; Velas, J.; Hrdlička, Z.; Michalcová, A.; Dendisová, M.; Friess, K. Poly(butylene succinate)-cellulose triacetate blends: Permeation, pervaporation, sorption and physical structure. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.; Khoshnamvand, M.; Regmi, C.; Friess, K. Interfacial Design of Mixed Matrix Membranes via Grafting PVA on UiO-66-NH2 to Enhance the Gas Separation Performance. Membranes 2021, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


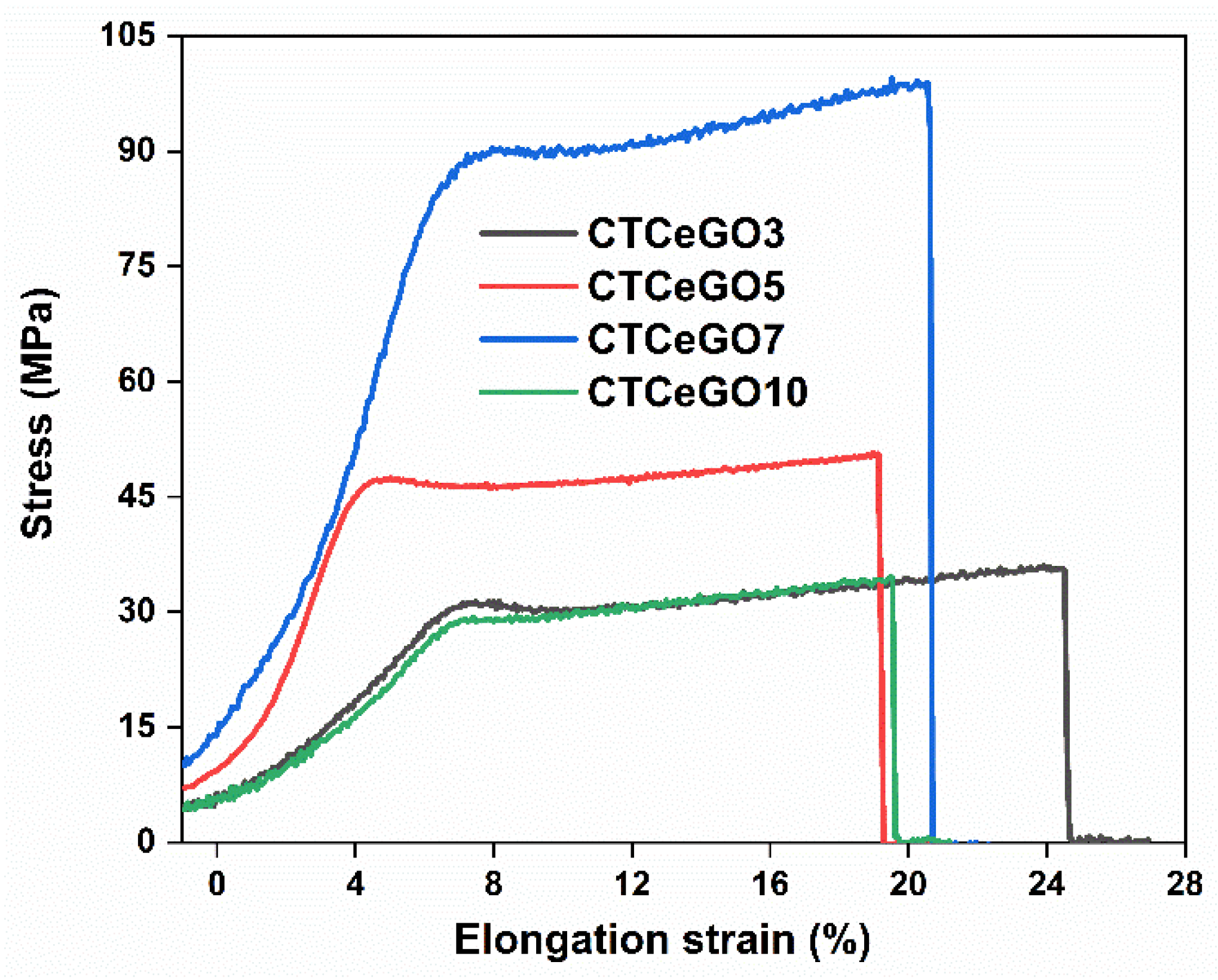
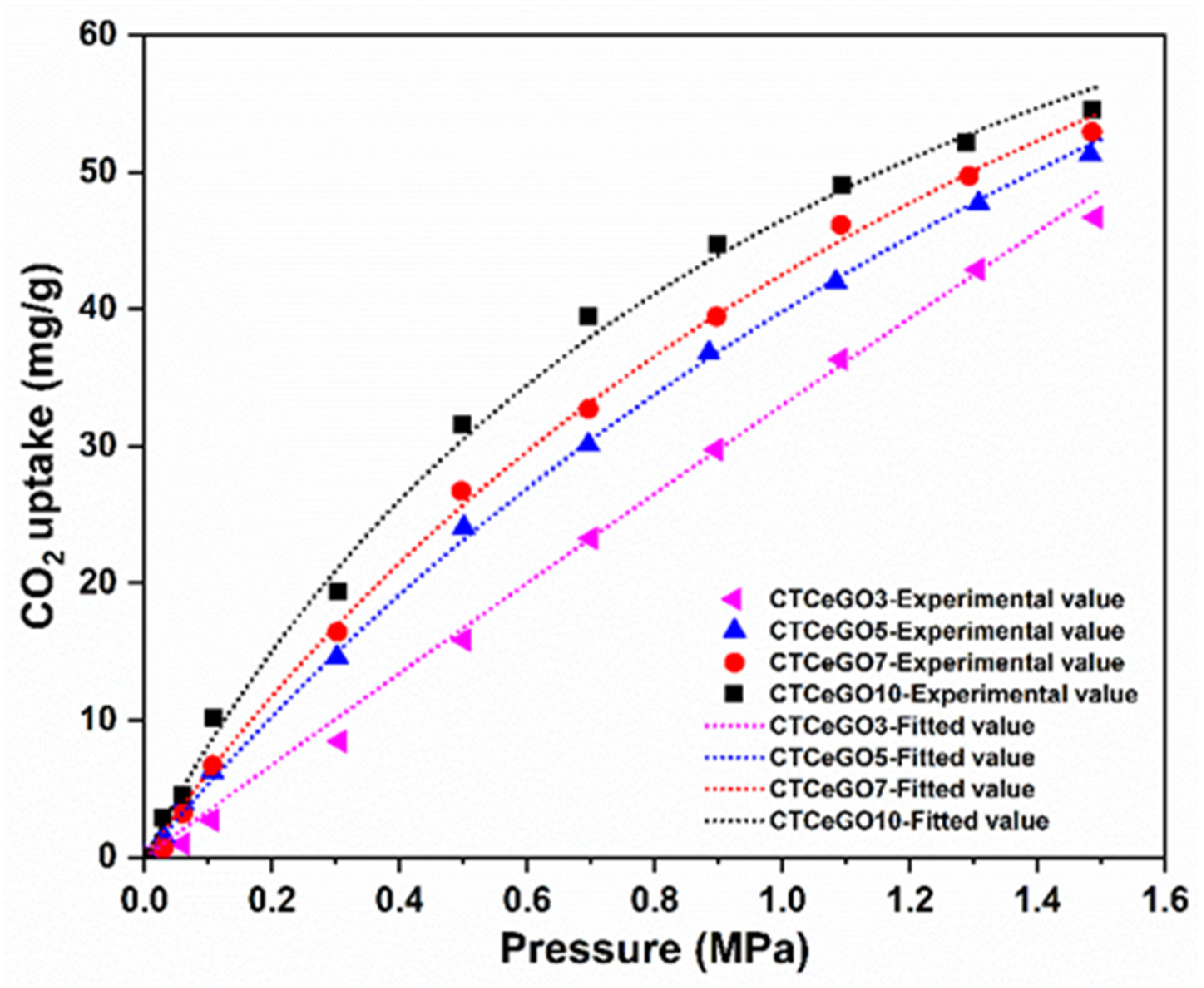
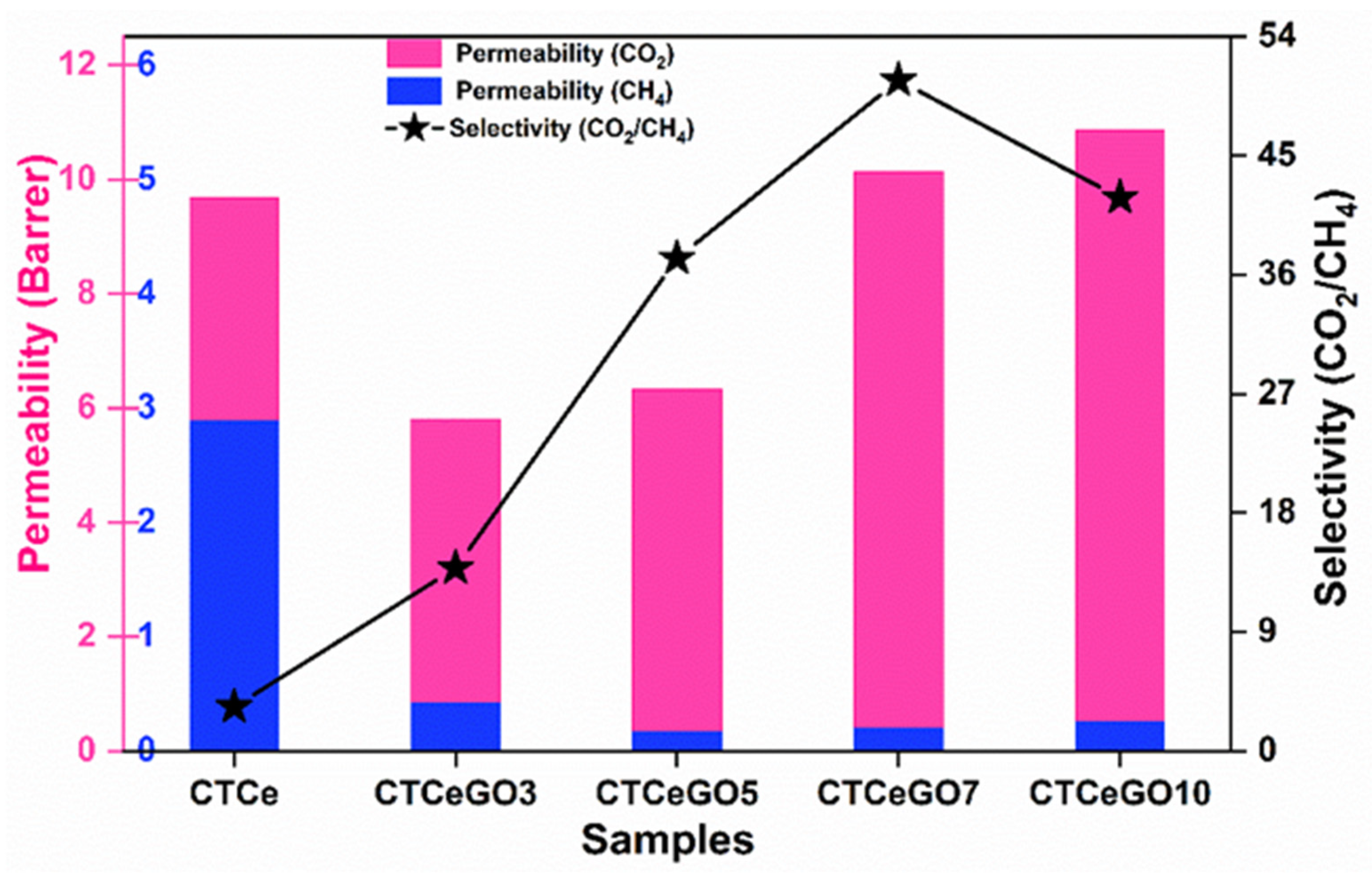
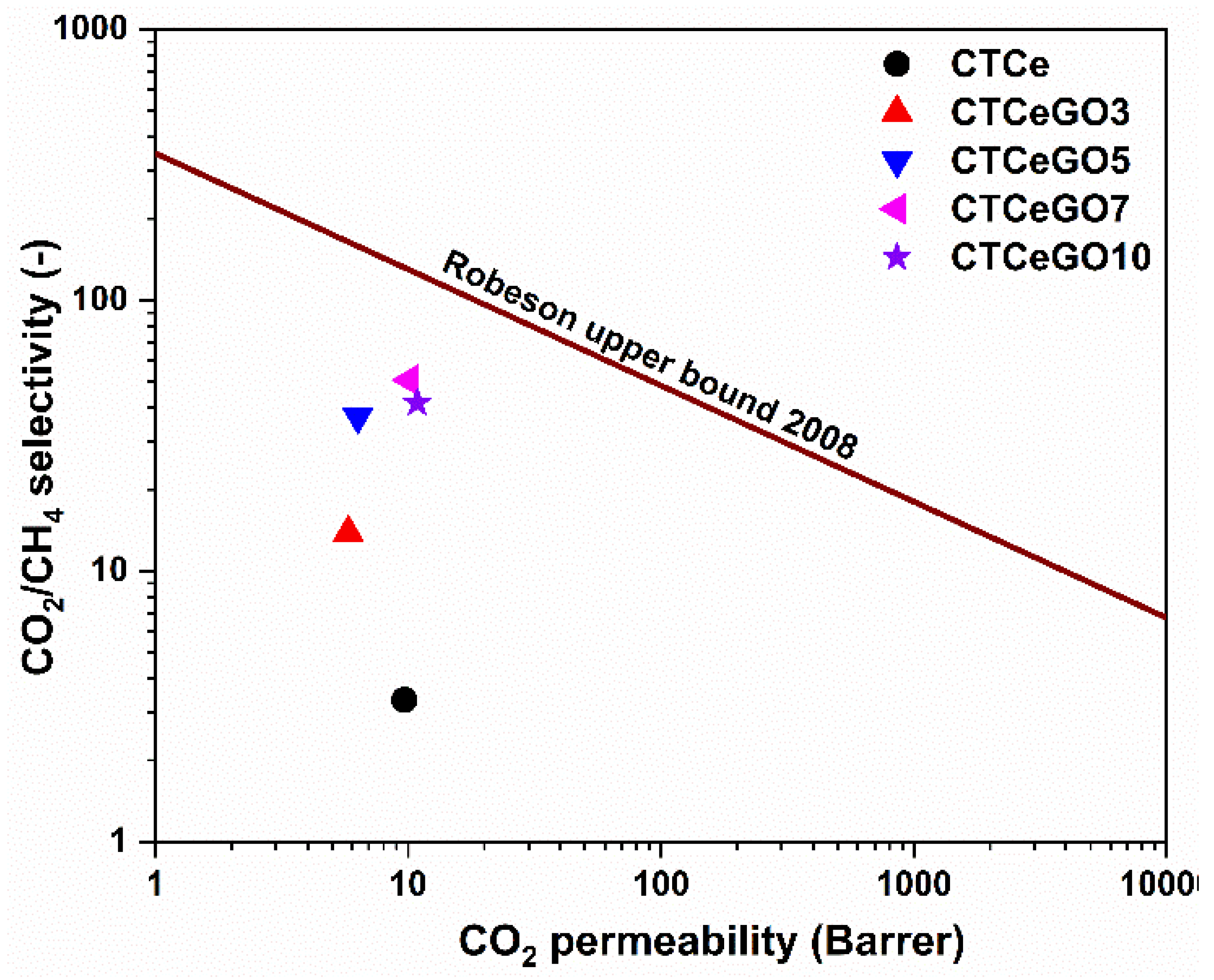
| # | Stress (MPa) | Elongation at Maximum Stress (%) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTCeGO3 | 36.3 ± 4.5 | 26.2 ± 4.5 | 1.02 ± 0.14 |
| CTCeGO5 | 50.7 ± 3.3 | 18.9 ± 3.8 | 1.14 ± 0.15 |
| CTCeGO7 | 99.5 ± 10.2 | 20.2 ± 6.1 | 1.31 ± 0.20 |
| CTCeGO10 | 34.5 ± 7.1 | 19.5 ± 3.0 | 1.52 ± 0.11 |
| # | Permeability (Barrer) | Selectivity (CO2/CH4) | Solubility Coefficient (10−4 mol m−3 Pa−1) | Diffusivity Coefficient (10−12 m2 s−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | CO2 | CH4 | CO2 | CH4 | ||
| CTA-CeO2 | 9.67 | 2.89 | 3.35 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 1.6 | 5.4 |
| CTCeGO3 | 5.81 | 0.42 | 13.83 | 31.71 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 1.57 |
| CTCeGO5 | 6.33 | 0.17 | 37.23 | 42.99 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 1.70 |
| CTCeGO7 | 10.14 | 0.20 | 50.7 | 79.66 | 0.72 | 0.44 | 1.20 |
| CTCeGO10 | 10.87 | 0.26 | 41.81 | 14.85 | 0.47 | 2.29 | 1.42 |
| Membrane Type | Permeability (Barrer) /Selectivity (-) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed porous fillers MOFs and zeolite silicate-1 blended with polysulfone [HUKUST-1/S1C-PSF (16 wt% filler mixture)] | PCO2 = 8.9 CO2/CH4 = 22.4 | Zornoza et al. [11] |
| Ordered mesoporous silica and layered titanosilicate fillers with 6FDA-based copolyimide [MMMs (MCM-41(8Wt.%)+JDF-L1(4 wt.%) with 6FDA-4MPD/6FDA-DABA] | PH2 = 440 H2/CH4 = 32.0 | Galve et al. [12] |
| GO and ZIF-8 blended with Polyethersulfone matrix followed by Pebax coating [2 rGO-ZIF-8-M] | PCO2 = N/A CO2/CH4 = 35.0 | Jamil et al. [14] |
| MOF(UiO-66-NH2)@COF (TpPa-1) hybrid fillers in polysulfone matrix [5 wt% of MOF@COF fillers] | PCO2 = 7.1 CO2/CH4 = 46.7 | Cheng et.al. [7] |
| CNT/SiO2 composite core incorporated into Pebax-1657 matrix | PCO2 = 148.3 CO2/N2 = 66.5 | Wang et al. [5] |
| Ordered mesoporous silica(MCM-41) and MOF (NH2-MIL-53(AL) blended with polysulfones [8/8 wt.% of each MCM-41 and MOF] | PH2 =19.5 H2/CH4 = 67.3 | Valero et.al. [13] |
| Cellulose-based poly-ionic liquid membranes P[CA][Tf2N] | PCO2 = 8.9 CO2/CH4 = 22.3 | Nikolaeva et.al. [43] |
| Poly(butylene succinate)-cellulose triacetate blends [CTA + 10 wt% PBS] | PCO2 = 3.5 CO2/CH4 = 35.0 | Cihal et al. [44] |
| PVA grafted on UiO-66-NH2 incorporated into polyvinyl amine matrix [24 wt% MOF] | PCO2 = 76.13 CO2/N2 = 45.6 | Ashtiani et.al. [45] |
| CeO2@GO blended CTA membrane [7 wt.% GO with respect to CeO2 concentration] | PCO2 = 10.14 CO2/CH4 = 50.7 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Regmi, C.; Ashtiani, S.; Sofer, Z.; Friess, K. Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Properties of Cellulose Triacetate Mixed–Matrix Membranes with CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers. Membranes 2021, 11, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100777
Regmi C, Ashtiani S, Sofer Z, Friess K. Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Properties of Cellulose Triacetate Mixed–Matrix Membranes with CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers. Membranes. 2021; 11(10):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100777
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegmi, Chhabilal, Saeed Ashtiani, Zdeněk Sofer, and Karel Friess. 2021. "Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Properties of Cellulose Triacetate Mixed–Matrix Membranes with CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers" Membranes 11, no. 10: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100777
APA StyleRegmi, C., Ashtiani, S., Sofer, Z., & Friess, K. (2021). Improved CO2/CH4 Separation Properties of Cellulose Triacetate Mixed–Matrix Membranes with CeO2@GO Hybrid Fillers. Membranes, 11(10), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100777








