Performance of a Micro-Scale Membrane Reactor for Greywater Treatment at Household Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Greywater
2.2. Frequency and Duration of Water Use at Student Residences
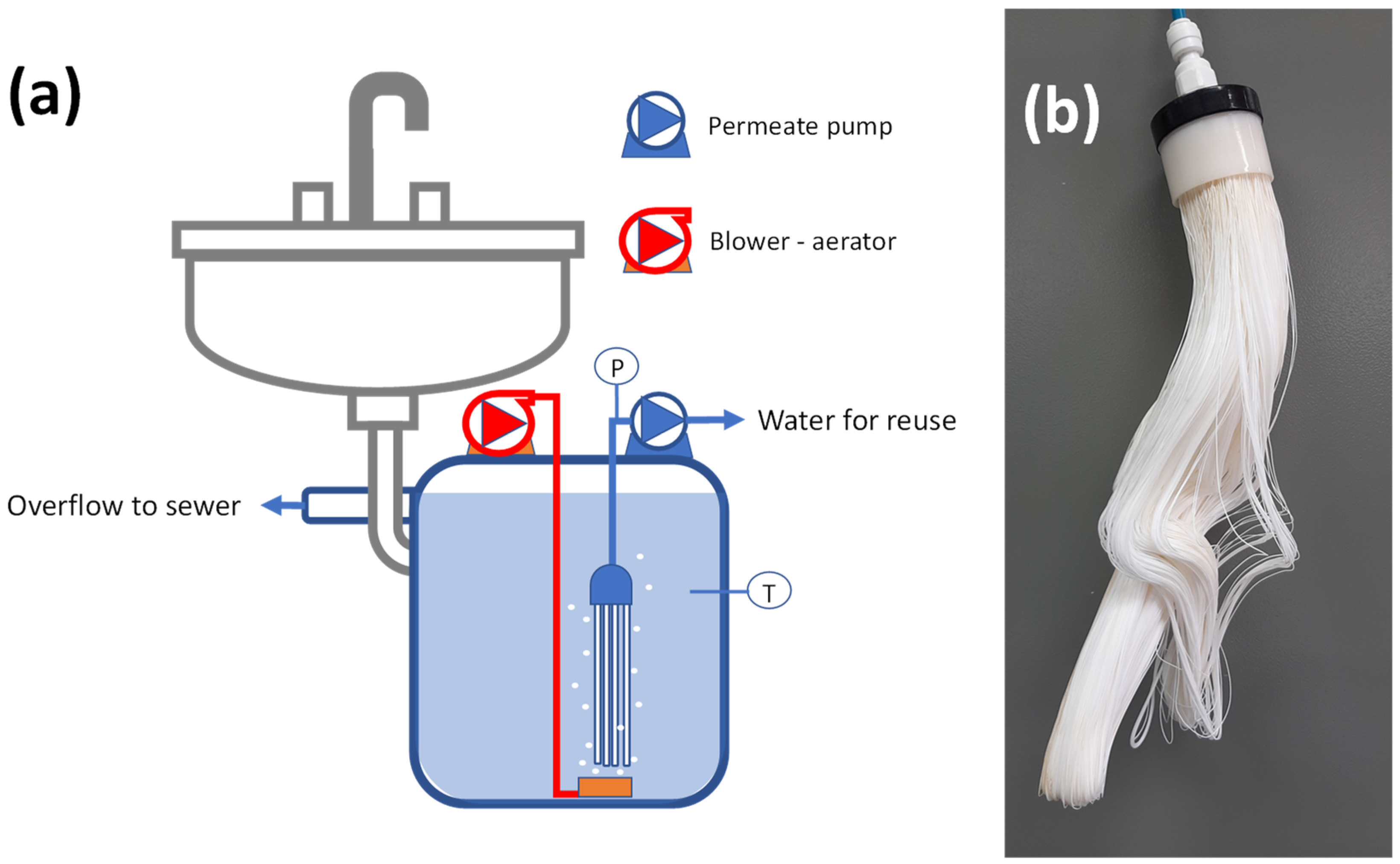
2.3. Membrane Reactor Design
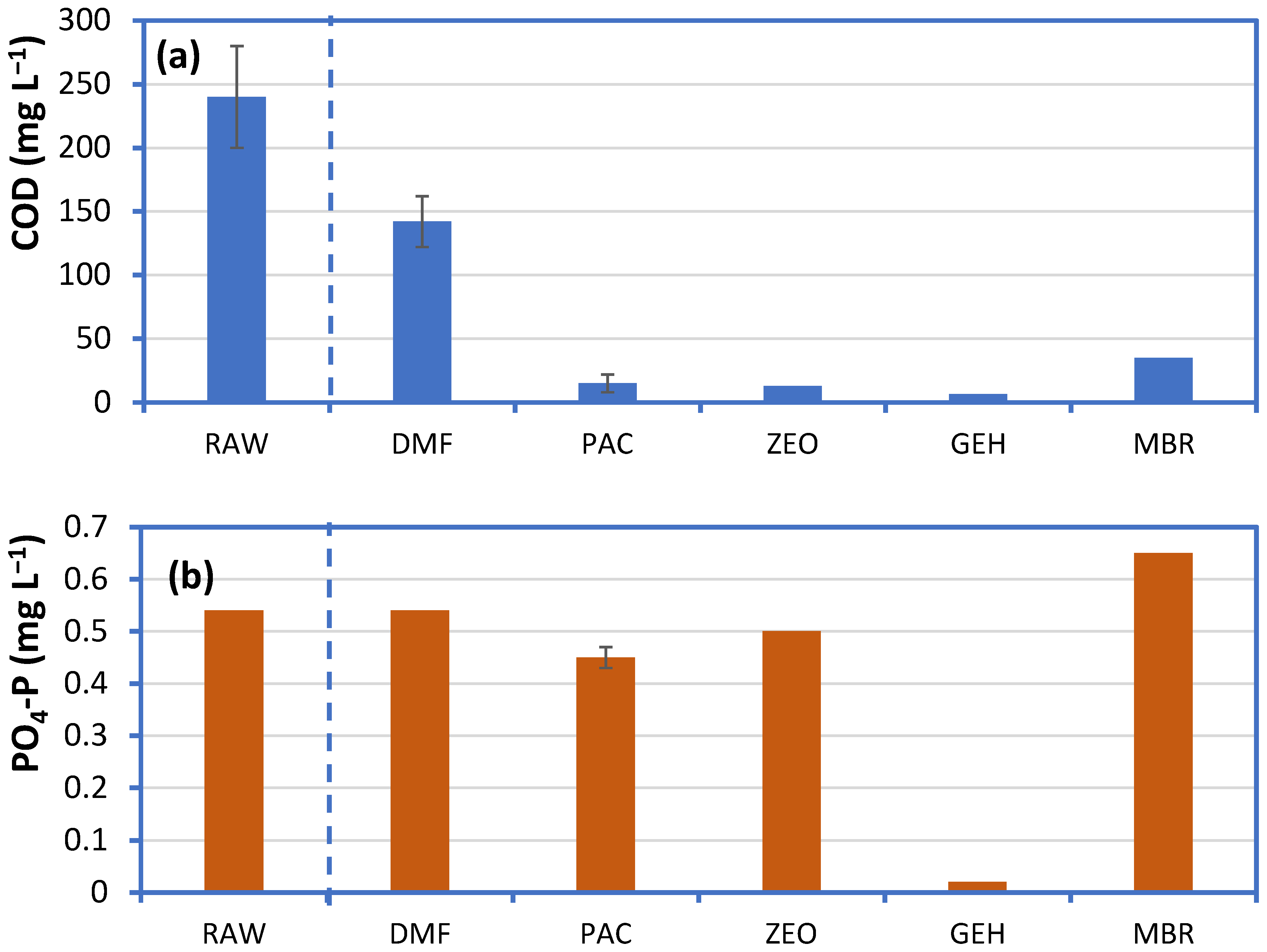
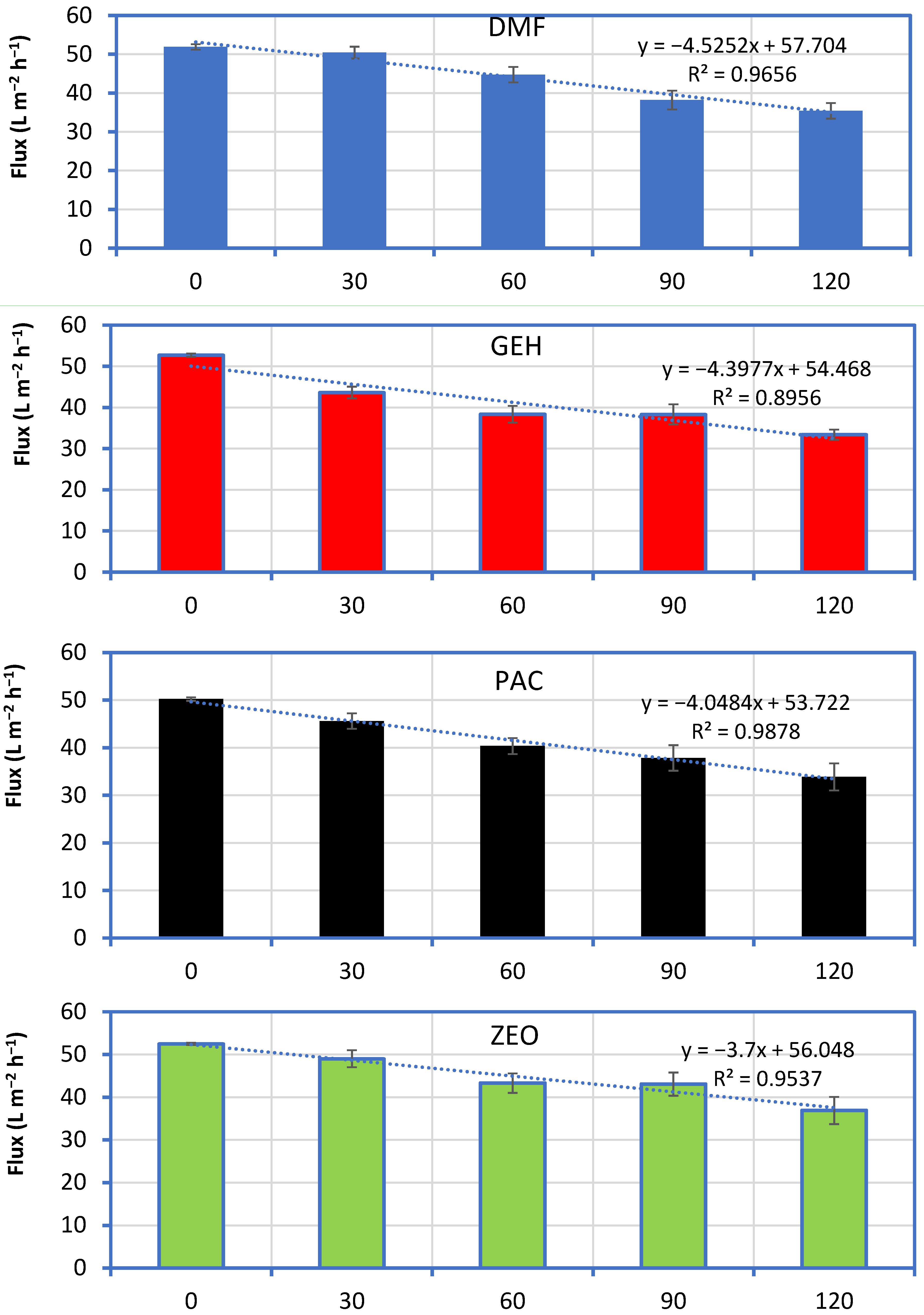
2.4. Effect of Additives on Membrane Reactor Performance
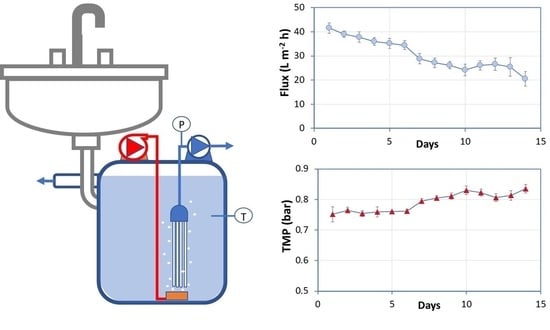
2.5. Medium-Term Operation of the Membrane Reactor Using Activated Sludge
2.6. Calculations
- T = operational temperature (°C)
- JT = permeate flux at operational temperature Τ (L m−2 h−1)
- QP = permeate flowrate at operational temperature Τ (L h−1)
- Am = membrane filtration area (m2)
3. Results
3.1. Frequency and Duration of Water Use at Student Residences
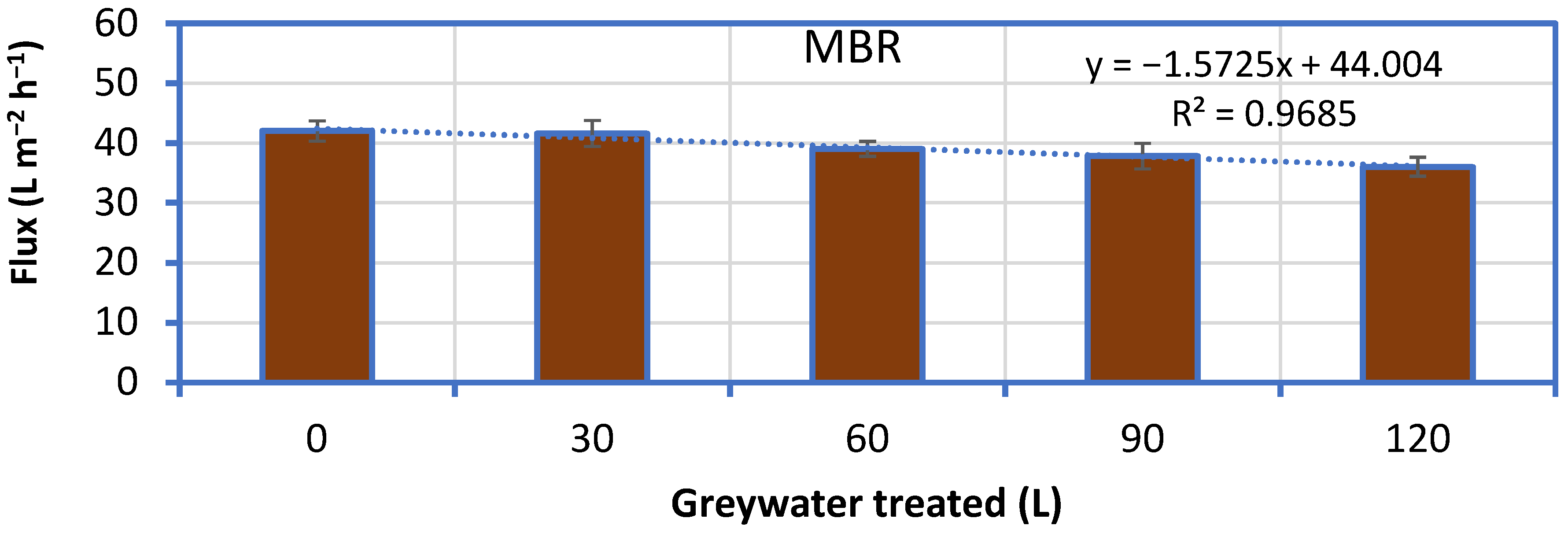
3.2. Effect of Additives on Membrane Reactor Performance
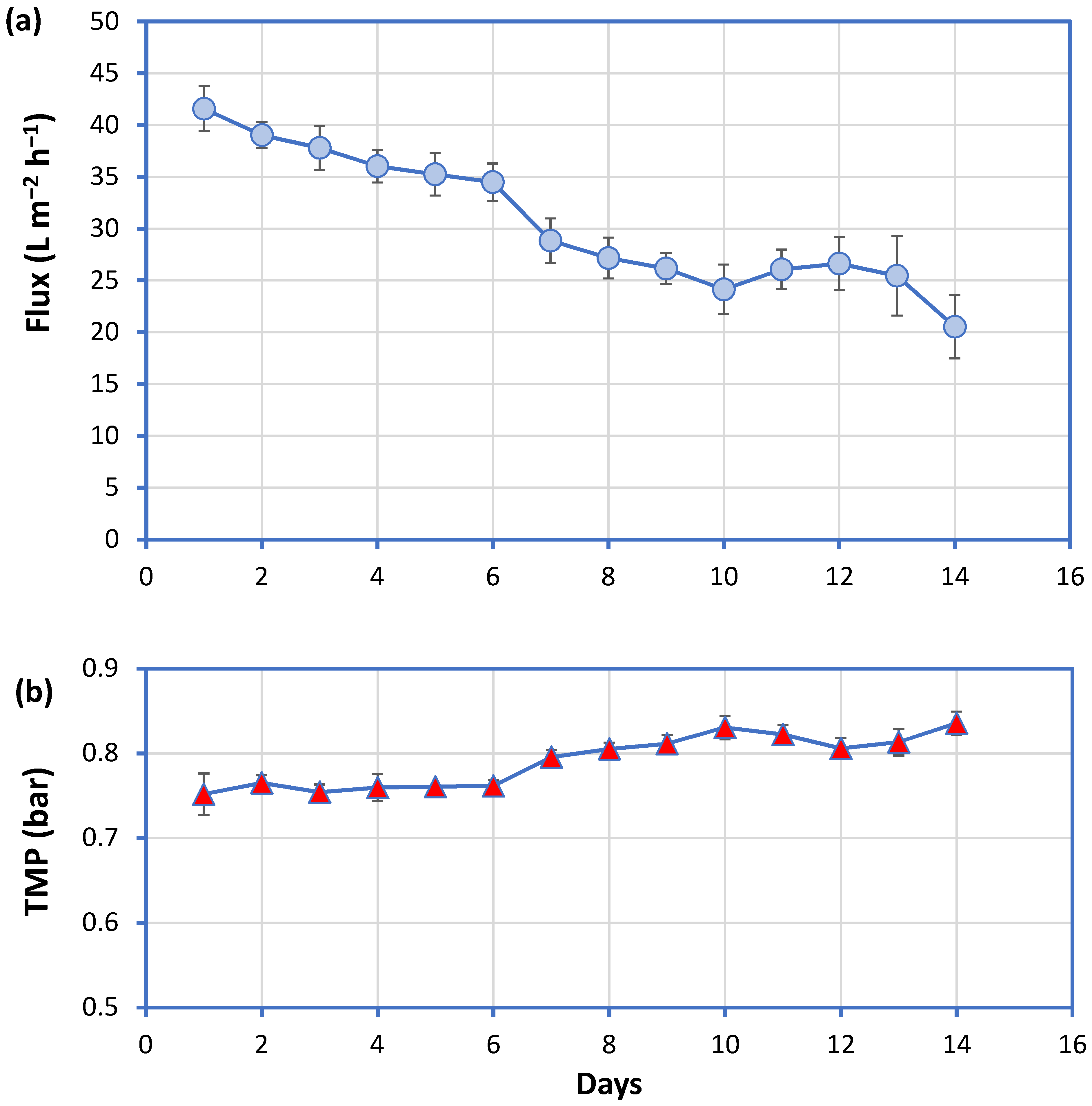
3.3. Medium-Term Operation of a Micro-Scale MBR System
4. Discussion
4.1. Design Considerations for Household Greywater Treatment
4.2. The Role of Additives for Direct Membrane Filtration of Greywater
4.3. Economic Feasibility and Comparison with Previous Studies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spyridi, D.; Vlachokostas, C.; Michailidou, A.V.; Sioutas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N. Strategic planning for climate change mitiga-tion and adaptation: The case of Greece. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 7, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Callegari, A.; Hlavínek, P.; Capodaglio, A.G. Membrane bioreactors for sustainable, fit-for-purpose greywater treatment: A critical review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, P.; Hourlier, F.; Bulteau, G.; Masse, A.; Jaouen, P.; Gerente, C.; Faur, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Estimated costs of imple-mentation of membrane processes for on-site greywater recycling. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Merayo, N.; Prinsen, P.; Luque, R.; Blanco, Á.; Zhao, M. A review on greywater reuse: Quality, risks, barriers and global scenarios. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2018, 18, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, P.; Tchobanoglous, G. Sustainable use of water in the Aegean Islands. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.F.; Hadari, M. Economic feasibility of on-site greywater reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination 2006, 190, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, W.; Van de Caveye, P.; Diamantis, V. Maximum use of resource present in domestic “used water”. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5537–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, V.; Verstraete, W.; Eftaxias, A.; Bundervoet, B.; Siegfried, V.; Melidis, P.; Aivasidis, A. Sewage pre-concentration for maximum recovery and reuse at decentralized level. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, G.; Green, M.; Semiat, R.; Dosoretz, C. Low strength graywater characterization and treatment by direct membrane filtration. Desalination 2004, 170, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabornig, S.; Favero, E. Single household greywater treatment with a moving bed biofilm membrane reactor (MBBMR). J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Jaber, F.H.; Karthikeyan, R. Evaluation of a portable in-house greywater treatment system for potential water-reuse in urban areas. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.J.; Bahrami, M.; Badkouby, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Greywater Treatment Using Single and Combined Adsorbents for Landscape Irrigation. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, N.; Wu, H.; Ang, M.; Zhang, D.-K. The potential application of natural zeolite for greywater treatment. Desalination 2008, 218, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Membrane-based technology in greywater reclamation: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Oschmann, N.; Schäfer, A. Fouling in greywater recycling by direct ultrafiltration. Desalination 2006, 187, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, I.N.; Ahammed, M.M. Quantity and quality characteristics of greywater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyas, H.; Reich, M.; Otterpohl, R. Organic micropollutants in raw and treated greywater: A preliminary investigation. Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsis, P.; Banti, D.C.; Peleka, E.N.; Zouboulis, A.; Samaras, P. Fouling Issues in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) for Wastewater Treatment: Major Mechanisms, Prevention and Control Strategies. Processes 2014, 2, 795–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shi, Y.; Jegatheesan, J.; Haq, I.U. A Review on the Mechanism, Impacts and Control Methods of Membrane Fouling in MBR System. Membranes 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Tay, J.-H. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Technology for Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation: Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ghunmi, L.A.; Zeeman, G.; Fayyad, M.; van Lier, J.B. Grey water treatment systems: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 657–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutsopoulos, C.; Andreadakis, A.; Kouris, N.; Charchousi, D.; Mendrinou, P.; Galani, A.; Mantziaras, I.; Koumaki, E. Greywater characterization and loadings – Physicochemical treatment to promote onsite reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantis, V.; Anagnostopoulos, K.; Melidis, P.; Ntougias, S.; Aivasidis, A. Intermittent operation of low pressure UF mem-branes for sewage reuse at household level. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, D.; Mitrakas, M.; Fytianos, G.; Tsali, A.; Samaras, P. Combined effect of colloids and SMP an membrane fouling in MBRs. Membranes 2020, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkotsis, P.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers. Membranes 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.H.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C.J.N. Grey water treatment concept integrating water and carbon recovery and removal of micropollutants. Water Pract. Technol. 2011, 6, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Y.-K.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.-M. Greywater Reuse System Design and Economic Analysis for Residential Buildings in Taiwan. Water 2016, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Shmueli, O.; Ronen, Z.; Raveh, E. Recycled vertical flow constructed wetland (RVFCW)—A novel method of recycling greywater for irrigation in small communities and households. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, B.; Laine, A.; Parsons, S.; Stephenson, T.; Judd, S. Technologies for domestic wastewater recycling. Urban Water 2000, 1, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Min | Max | Average | Stdev | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of water use (s) per use | ||||
| Wash basin | 20 | 210 | 92 | 48 |
| Kitchen sink | 35 | 240 | 133 | 56 |
| Shower | 280 | 613 | 438 | 108 |
| Frequency of water use per day | ||||
| Wash basin | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Kitchen sink | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Toilet | 2 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Shower | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Quantity of water use (L) per use | ||||
| Wash basin | 2 | 21 | 9 | 5 |
| Kitchen sink | 4 | 24 | 13 | 6 |
| Toilet | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| Shower | 28 | 61 | 44 | 11 |
| Quantity of water use (L) per day | ||||
| Wash basin | 18 | 43 | 28 | 8 |
| Kitchen sink | 13 | 42 | 25 | 9 |
| Toilet | 12 | 30 | 22 | 5 |
| Shower | 28 | 61 | 44 | 11 |
| Technology | Foot-Print | CAPEX (€) | OPEX (€/year) | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-scale MBR | 25 L | 300 | 60 20 | Membrane replacement Electricity consumption | This study |
| Cartridge filtration (polypropylene, activated carbon) | Not reported | 450 | 130 35 | Filter replacement Electricity consumption | [28] |
| Vertical flow constructed wetland | 1000 L | 500 | 80 | Maintenance and labor | [29] |
| Cartridge filtration (microfiltration, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, UV) | 250 L | 880 | Not calculated | [11] | |
| Coarse filtration and disinfection | Not reported | 550–1100 | Not reported | [30] | |
| MBR | Not reported (2 m3/d or 25 PE) | 6000 | 120 100 80 | Disinfectant Electricity consumption Labor (per hour) | [6] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diamantis, V. Performance of a Micro-Scale Membrane Reactor for Greywater Treatment at Household Level. Membranes 2021, 11, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010063
Diamantis V. Performance of a Micro-Scale Membrane Reactor for Greywater Treatment at Household Level. Membranes. 2021; 11(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiamantis, Vasileios. 2021. "Performance of a Micro-Scale Membrane Reactor for Greywater Treatment at Household Level" Membranes 11, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010063
APA StyleDiamantis, V. (2021). Performance of a Micro-Scale Membrane Reactor for Greywater Treatment at Household Level. Membranes, 11(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010063