Electrically Polarized Graphene-Blended Spacers for Organic Fouling Reduction in Forward Osmosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
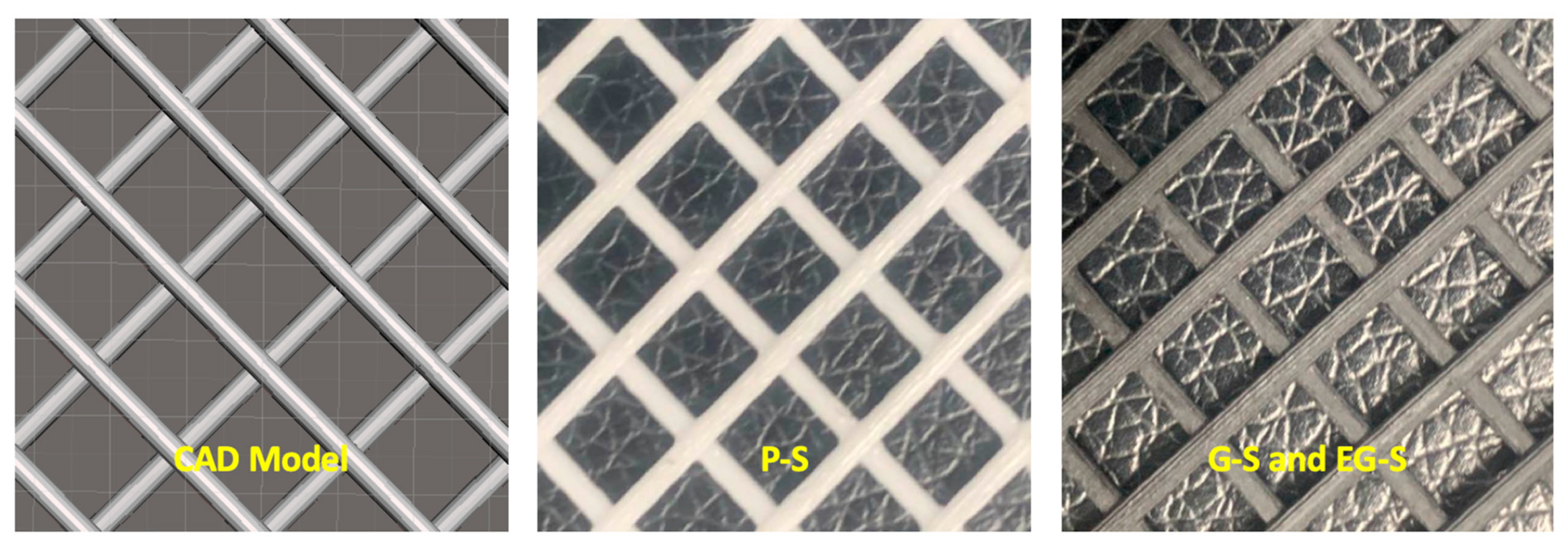
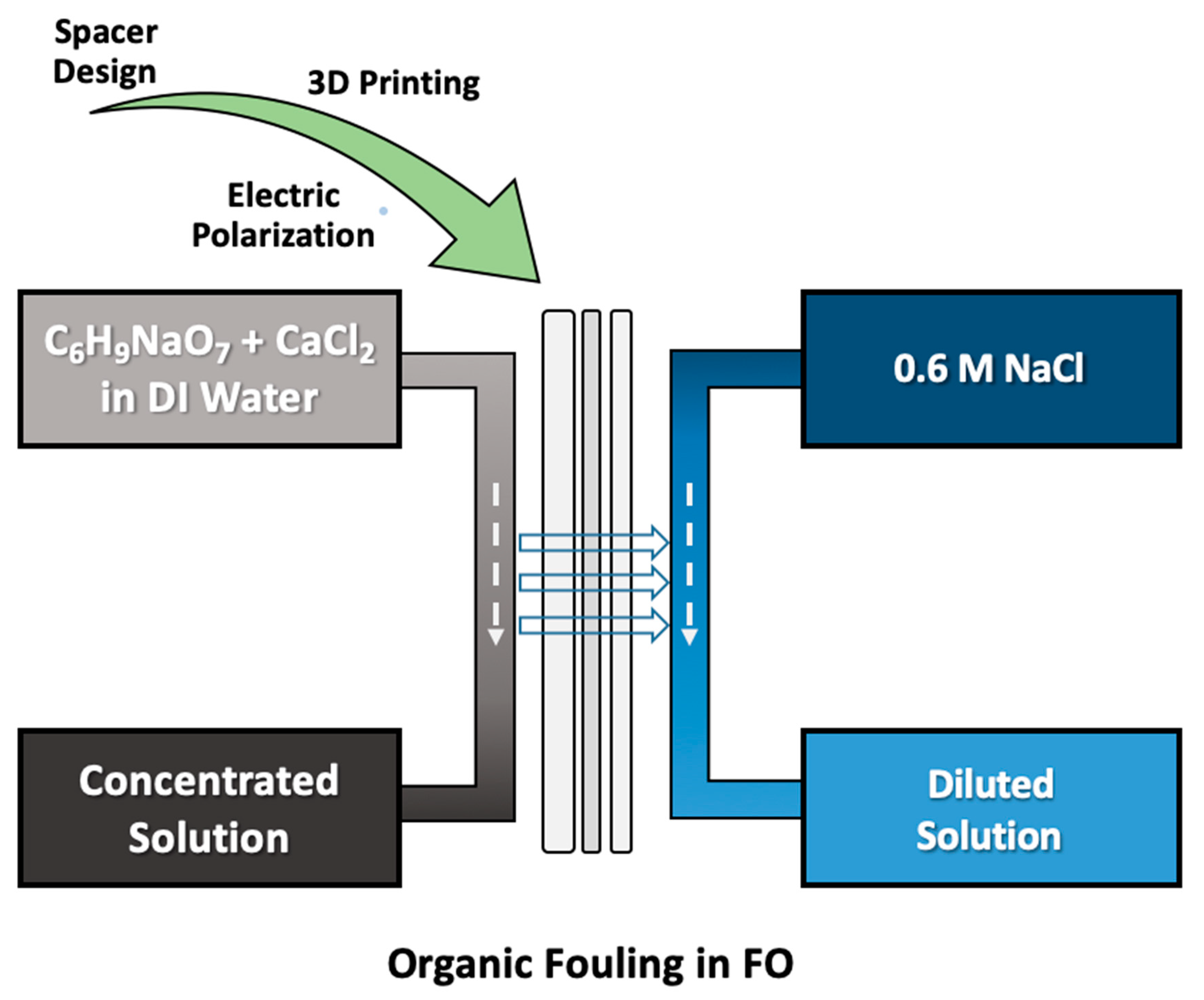
2. Materials and Methods
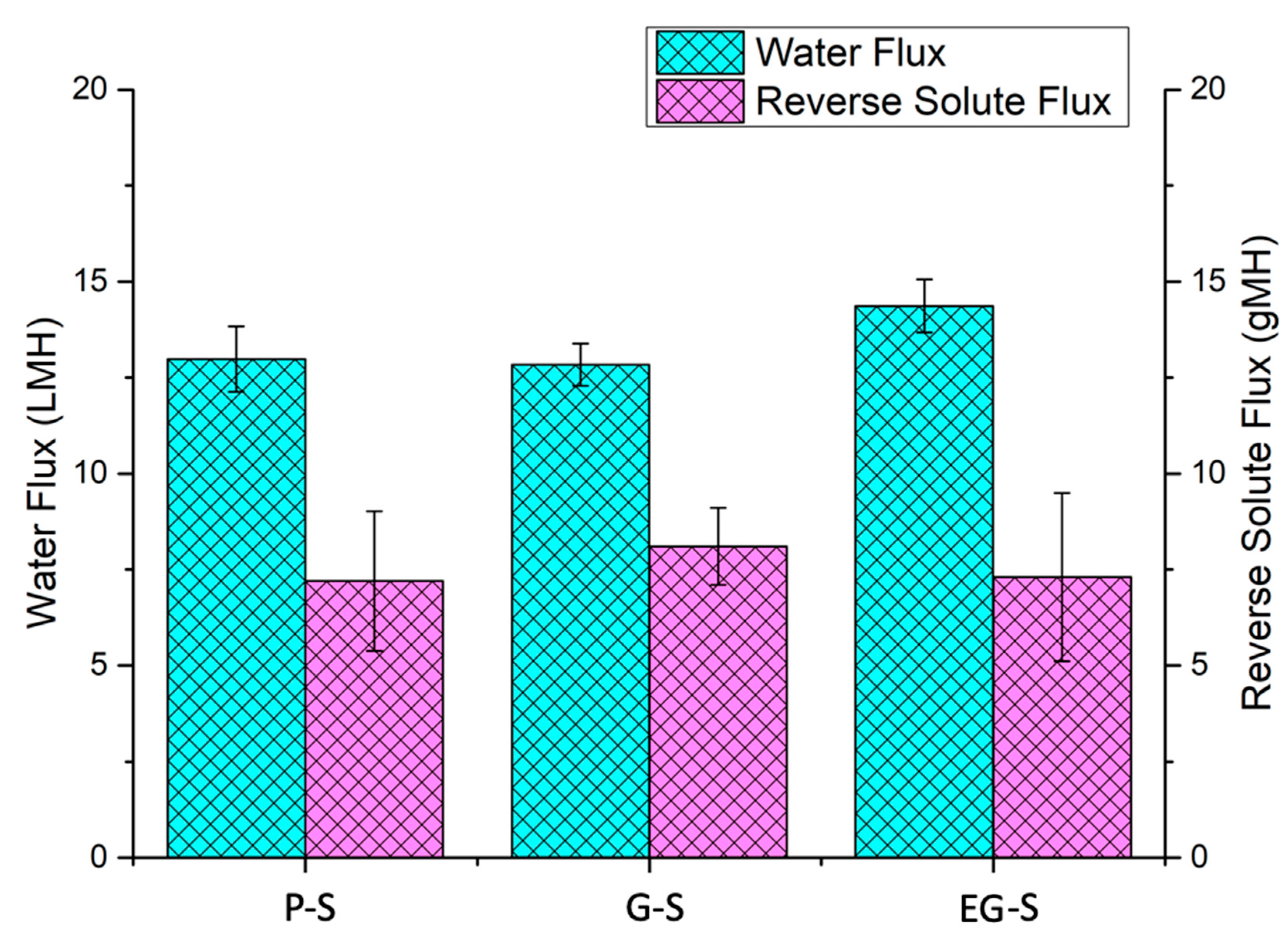
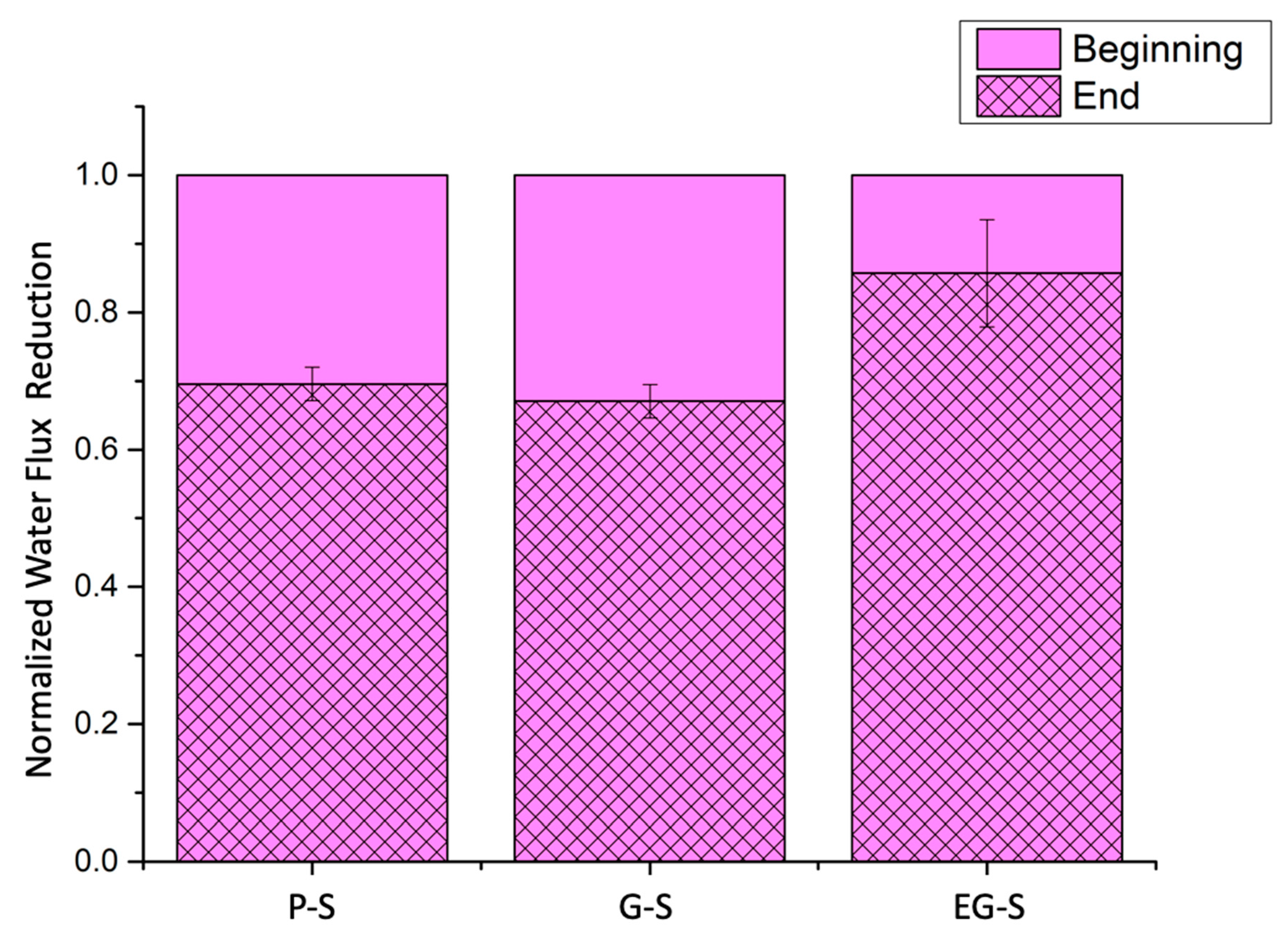
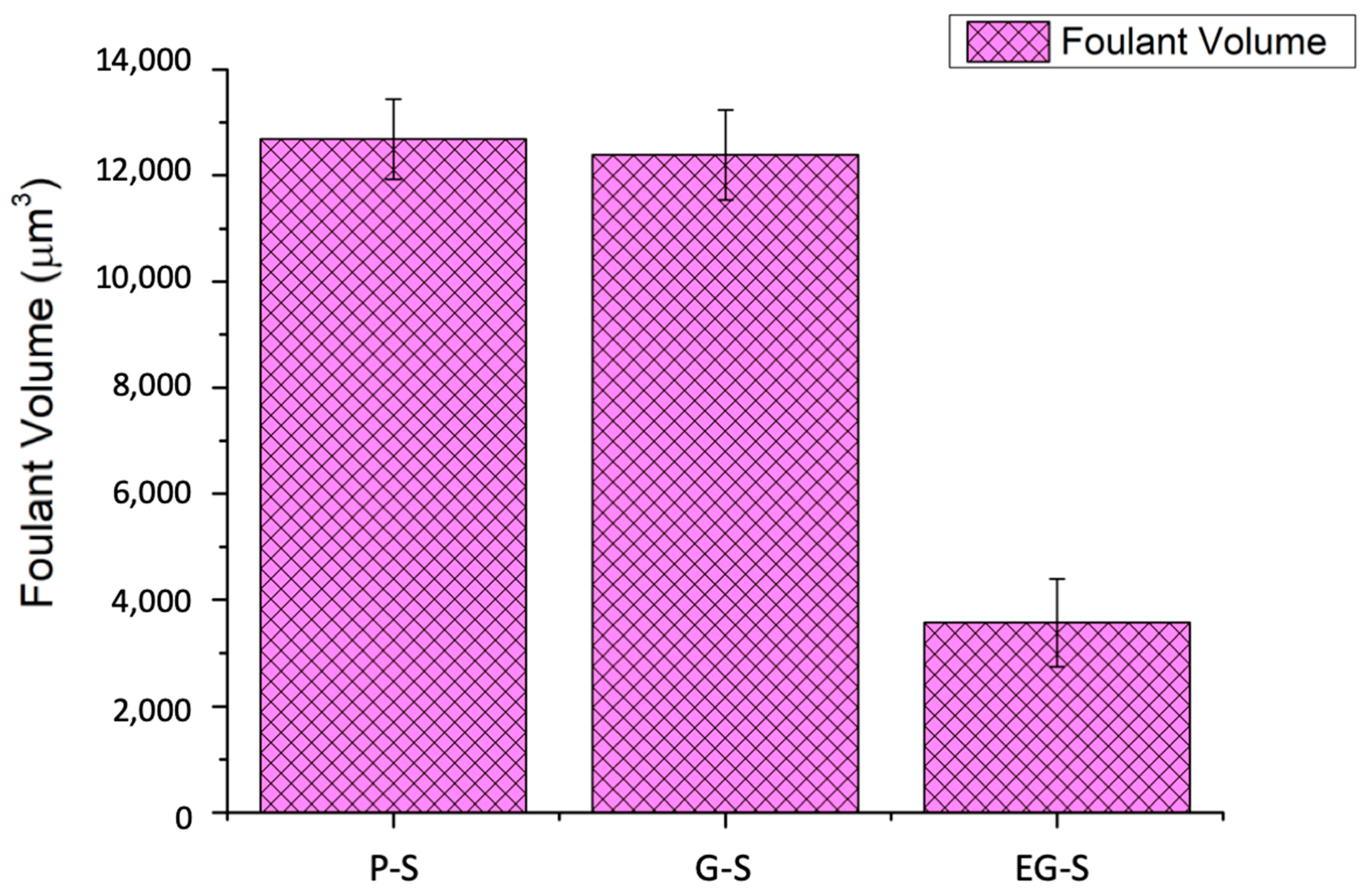
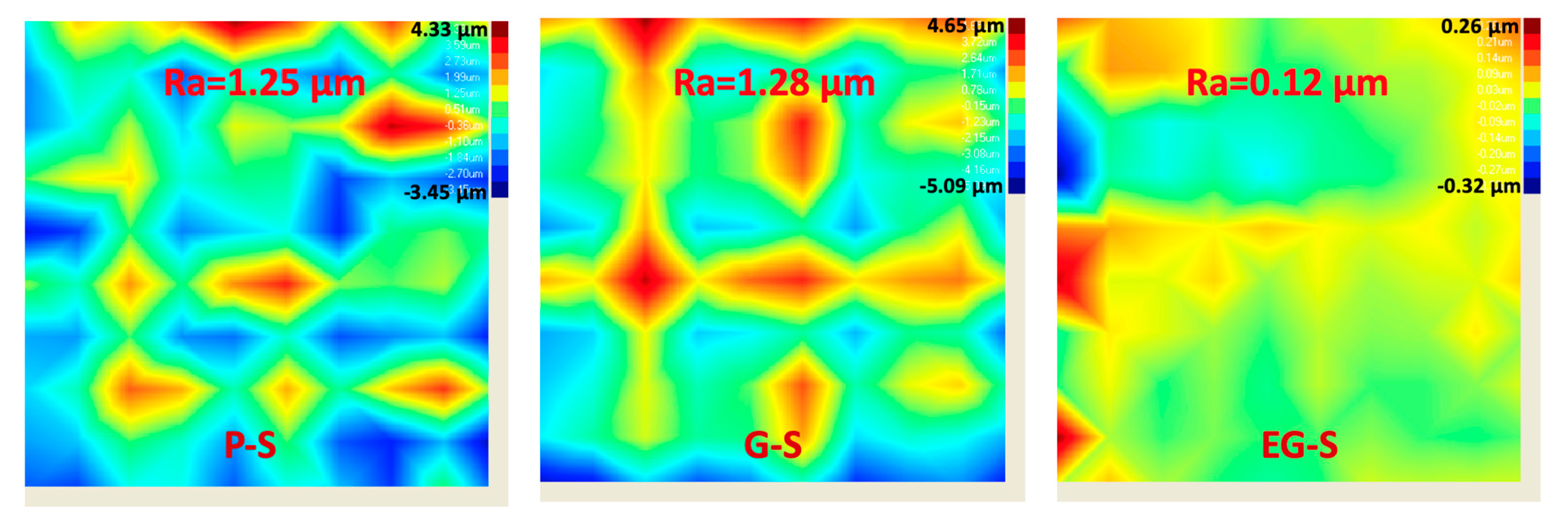
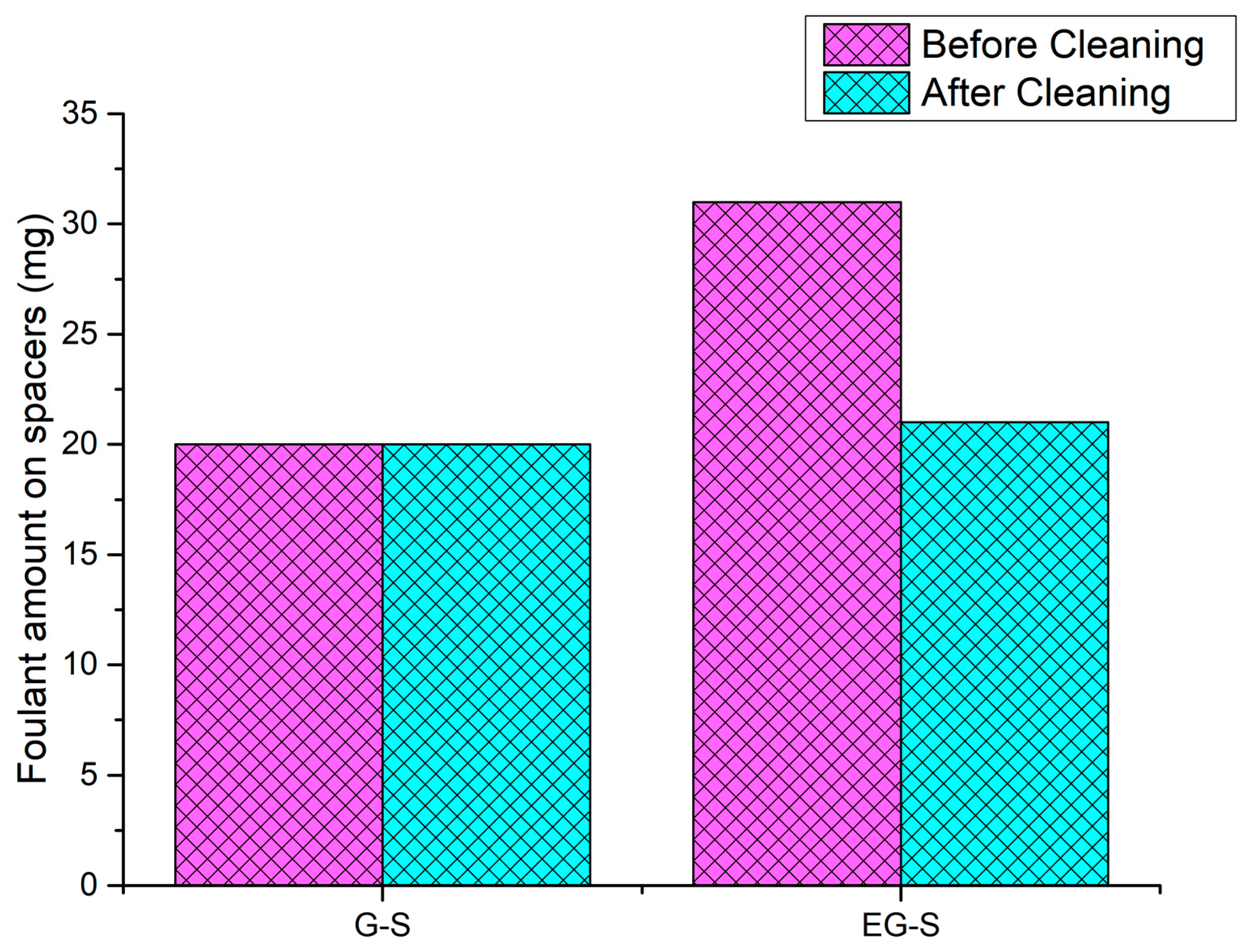
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciardelli, G.; Corsi, L.; Marcucci, M. Membrane separation for wastewater reuse in the textile industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2001, 31, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yanar, N.; Choi, H. Urban Water Management and Quality-Based Water Use. Iglus Q. 2019, 5, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Dashti, A.; Harami, H.R.; Hajilari, N. Fouling-resistant membranes for water reuse. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 715–763. [Google Scholar]
- Panchal, C.B.; Knudsen, J.G. Mitigation of water fouling: Technology status and challenges. Adv. Heat Transf. 1998, 31, 431–474. [Google Scholar]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, K.M.; Gekas, V.; Trägårdh, G. Study of membrane compaction and its influence on ultrafiltration water permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Buehler, M.J. Mechanics and molecular filtration performance of graphyne nanoweb membranes for selective water purification. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11801–11807. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Elimelech, M. Cake-enhanced concentration polarization: A new fouling mechanism for salt-rejecting membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5581–5588. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, K.; Hane, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Amy, G.; Ohkuma, N. Irreversible membrane fouling during ultrafiltration of surface water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, H.C.; Schaule, G.; McDonogh, R. Biofouling on Membranes—A Short Review. In Biofilms—Science and Technology; Melo, L.F., Bott, T.R., Fletcher, M., Capdeville, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik Madenli, E.; Yanar, N.; Choi, H. Enhanced antibacterial properties and suppressed biofilm growth on multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) blended polyethersulfone (PES) membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G. Fundamental understanding of organic matter fouling of membranes. Desalination 2008, 231, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, B.; Ok, Y.S.; Cho, J.; Hur, J. Targeted removal of organic foulants in landfill leachate in forward osmosis system integrated with biochar/activated carbon treatment. Water Res. 2019, 160, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Bakly, S.; Khanafer, D.; Altaee, A.; Padmanaban, V.C.; Samal, A.K.; Hawari, A.H. Organic Fouling in Forward Osmosis: A Comprehensive Review. Water 2020, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.; Ng, H.Y. Forward osmosis organic fouling: Effects of organic loading, calcium and membrane orientation. Desalination 2013, 312, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Mulcahy, D. Effects of membrane orientation on process performance in forward osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Elimelech, M. Chemical and physical aspects of organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Tang, C.Y.; Gray, S.R. Spacer-induced forward osmosis membrane integrity loss during gypsum scaling. Desalination 2016, 392, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, H.S.; Johnson, D.J.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. A review of efforts to reduce membrane fouling by control of feed spacer characteristics. Desalination 2017, 420, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Ho, J.S.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chua, C.K.; Chong, T.H. A review on spacers and membranes: Conventional or hybrid additive manufacturing? Water Res. 2021, 188, 116497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Adjiman, C.S.; Xu, X.Y. The effect of feed spacer geometry on membrane performance and concentration polarisation based on 3D CFD simulations. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taamneh, Y.; Bataineh, K. Improving the performance of direct contact membrane distillation utilizing spacer-filled channel. Desalination 2017, 408, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, K.K.; Wang, Y.-N.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. A conceptual design of spacers with hairy structures for membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, F. Saw-tooth spacer for membrane filtration: Hydrodynamic investigation by PIV and filtration experiment validation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 91, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinge, J.; Wiley, D.E.; Fane, A.G.; Guenther, R. Characterization of a zigzag spacer for ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 172, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balster, J.; Pünt, I.; Stamatialis, D.F.; Wessling, M. Multi-layer spacer geometries with improved mass transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Murdoch, L.C.; Ladner, D.A. Hydrodynamics of sinusoidal spacers for improved reverse osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Kallem, P.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Kang, S.; Choi, H. A New era of water treatment technologies: 3D printing for membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Toward greener membranes with 3D printing technology. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 26, 200027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Qamar, A.; Kerdi, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ghaffour, N.; Shon, H.K. Energy efficient 3D printed column type feed spacer for membrane filtration. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, N.; Thomas, N.; Al-Ketan, O.; Rowshan, R.; Hernandez, H.; Al-Rub, R.K.A.; Arafat, H.A. 3D printed feed spacers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for flux enhancement and biofouling mitigation in RO and UF. Desalination 2018, 425, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdi, S.; Qamar, A.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ghaffour, N. Fouling resilient perforated feed spacers for membrane filtration. Water Res. 2018, 140, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Bio-mimetically inspired 3D-printed honeycombed support (spacer) for the reduction of reverse solute flux and fouling of osmotic energy driven membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 83, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Yang, E.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Nam, S.-E.; Choi, H. Investigation of the performance behavior of a forward osmosis membrane system using various feed spacer materials fabricated by 3D printing technique. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanar, N.; Park, H.; Son, M.; Choi, H. Efficacy of Electrically-Polarized 3D Printed Graphene-blended Spacers on the Flux Enhancement and Scaling Resistance of Water Filtration Membranes. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07210. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, J.C.; Machado, Á.R.; Almeida, E.C.; Silva, E.F.M.S. Mechanical properties of PLA-graphene filament for FDM 3D printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 2423–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; Rastgar, M.; Shakeri, A. Anti-fouling and high water permeable forward osmosis membrane fabricated via layer by layer assembly of chitosan/graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, N.C.; Chen, S.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Hsu, H.-T.; Wu, S.-Y. Innovation in Draw Solute for Practical Zero Salt Reverse in Forward Osmosis Desalination. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6067–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Choi, H.; Liu, L.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Optimized Synthesis Conditions of Polyethersulfone Support Layer for Enhanced Water Flux for Thin Film Composite Membrane. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 19, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, P.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Smith, G.; Temmink, H.; van Loosdrecht, M. Effect of free calcium concentration and ionic strength on alginate fouling in cross-flow membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Choi, H.-g.; Liu, L.; Celik, E.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Efficacy of carbon nanotube positioning in the polyethersulfone support layer on the performance of thin-film composite membrane for desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta Potential Measurement. In Characterization of Nanoparticles Intended for Drug Delivery; McNeil, S.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Sosnowska, K.; Czajkowska-Kośnik, A.; Winnicka, K. Calcium chloride modified alginate microparticles formulated by the spray drying process: A strategy to prolong the release of freely soluble drugs. Materials 2018, 11, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Elimelech, M. Relating Organic Fouling of Reverse Osmosis Membranes to Intermolecular Adhesion Forces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. Febs Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Bernstein, N.J.; Lin, J.; Jordens, J.; Zhao, S.; Tang, C.Y.; van der Bruggen, B. Theoretical and experimental study of organic fouling of loose nanofiltration membrane. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 93, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanar, N.; Liang, Y.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Son, M.; Choi, H. Electrically Polarized Graphene-Blended Spacers for Organic Fouling Reduction in Forward Osmosis. Membranes 2021, 11, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010036
Yanar N, Liang Y, Yang E, Park H, Son M, Choi H. Electrically Polarized Graphene-Blended Spacers for Organic Fouling Reduction in Forward Osmosis. Membranes. 2021; 11(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanar, Numan, Yejin Liang, Eunmok Yang, Hosik Park, Moon Son, and Heechul Choi. 2021. "Electrically Polarized Graphene-Blended Spacers for Organic Fouling Reduction in Forward Osmosis" Membranes 11, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010036
APA StyleYanar, N., Liang, Y., Yang, E., Park, H., Son, M., & Choi, H. (2021). Electrically Polarized Graphene-Blended Spacers for Organic Fouling Reduction in Forward Osmosis. Membranes, 11(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010036




