Preparation of an Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane with Narrow and Uniform Pore Size Distribution via Etching of SiO2 Nano-Particles in a Membrane Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PVDF/PMMA/CA Blend Membranes
2.2.1. Design of Coagulation Bath for Etched Membranes
2.2.2. Basic Chemical Reaction
2.3. Characterization of Etched UF Membranes
2.4. The Performance of Etched UF Membranes
2.5. Antifouling Performance Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. The Pore Size Distribution
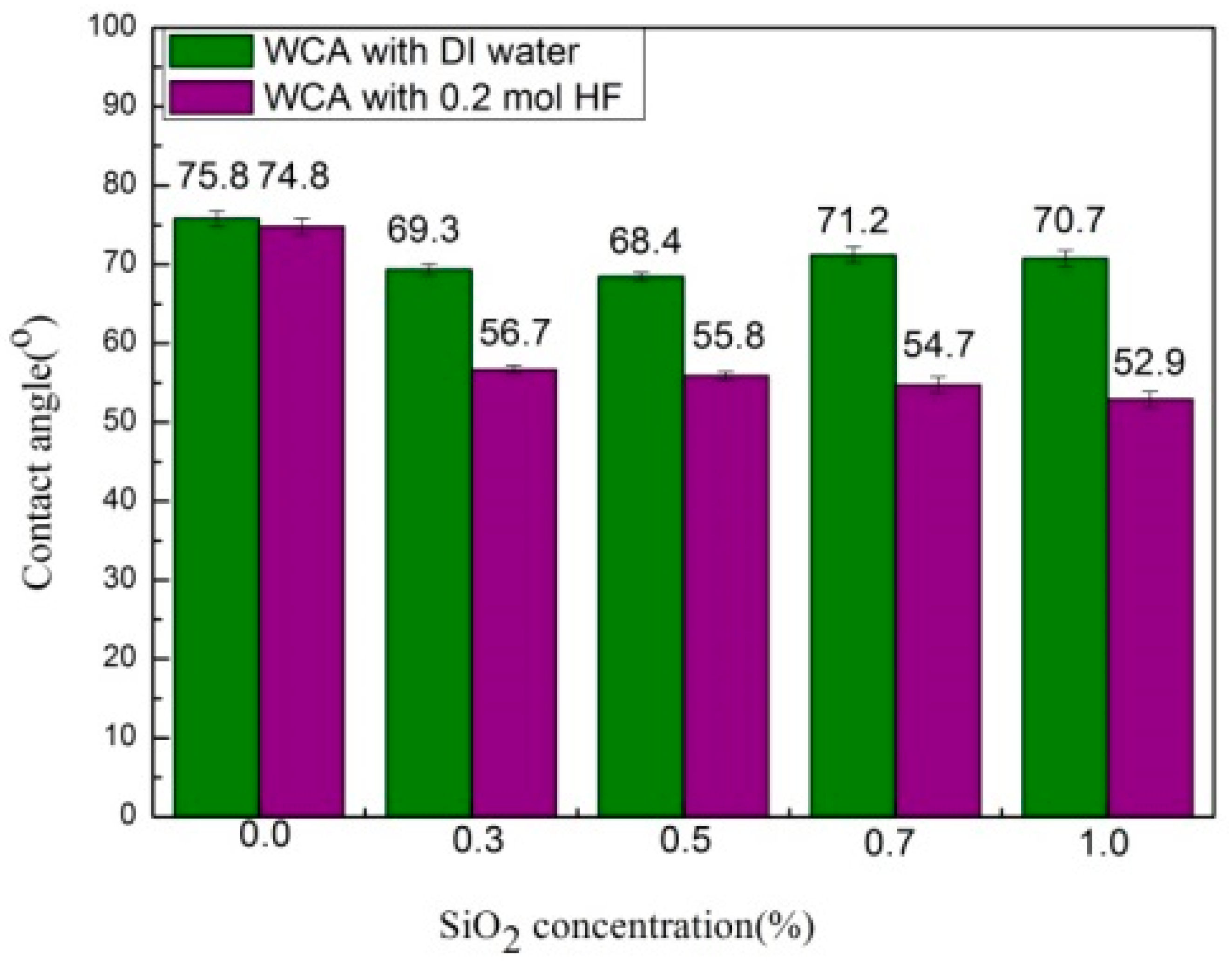
3.2. Surface Hydrophilicity
3.3. Morphological Investigation
3.4. Performance of Blend UF Membranes
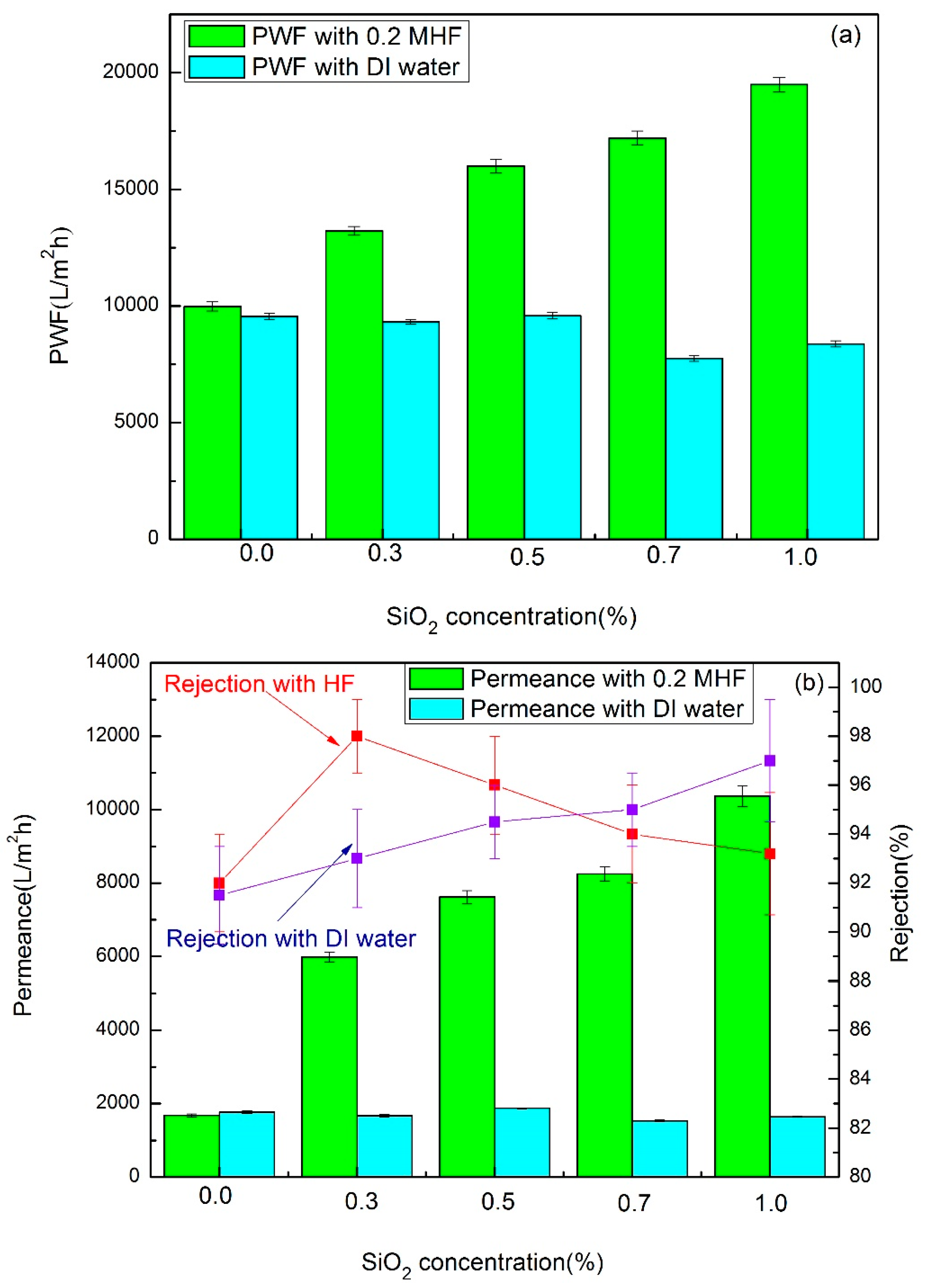
3.4.1. Membrane Permeation Flux
3.4.2. BSA Rejection Performance
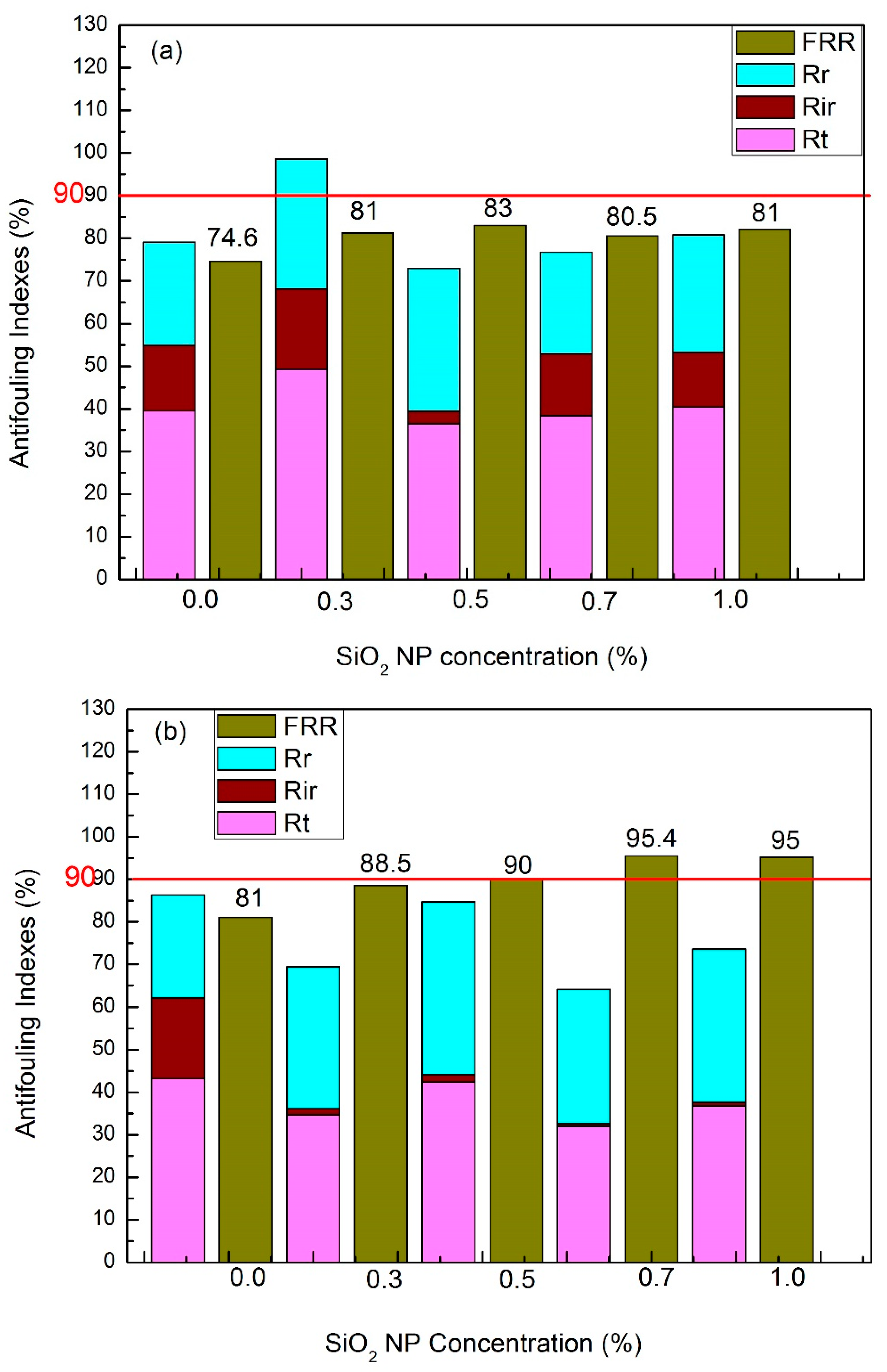
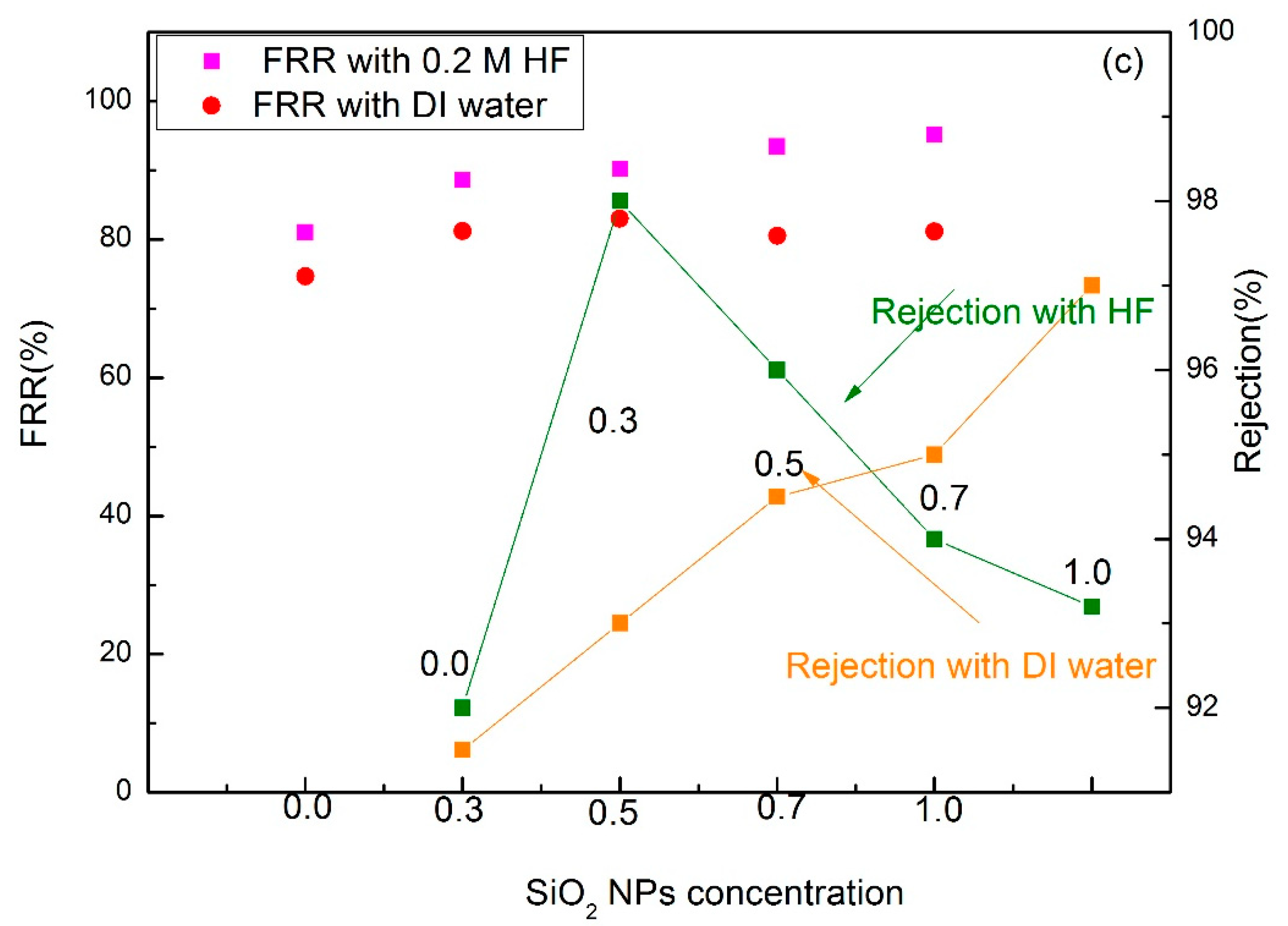
3.5. Antifouling Performance
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | effective area of the membrane (m2) | t | filtration time (h) |
| Cf | concentrations of the feed solution (g/L) | FRR | rejection ratio (%) |
| Cp | concentrations of the permeate solution (g/L) | R | rejection ratio (%) |
| J | permeate flux (L/m2·h) | Rt | total fouling ratio (%) |
| Jp | flux of BSA (L/m2.h) | Rir | irreversible fouling ratio (%) |
| JR | flux of fouled membrane washed with DI-water (L/m2h) | Rr | reversible fouling ratio (%) |
References
- Yang, S.; Zou, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Effects of GO and MOF@GO on the permeation and antifouling properties of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 569, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Mai, W.; Min, C.; Zhou, B.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Qian, X. Improved hydrophilicity, permeability, antifouling and mechanical performance of PVDF composite ultrafiltration membranes tailored by oxidized low-dimensional carbon nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Su, J.; Fu, F.-J.; Mi, B.; Chung, T.-S. Gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) scaling on polybenzimidazole and cellulose acetate hollow fiber membranes under forward osmosis. Membranes 2013, 3, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, C. Foundation of Membrane Separation Technology, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.C. Handbook of Industrial Membrane Technology; Noyes Publications: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Pomalaza-Ráez, C.; Xiao, R. A self-cleaning piezoelectric PVDF membrane system for filtration of kaolin suspension. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Z. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H. A gas-liquid chemical reaction treatment and phase inversion technique for formation of high permeability PAN UF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Gao, C. The influence of phase inversion process modified by chemical reaction on membrane properties and morphology. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X. Experimental study of the control of pore sizes of porous membranes applying chemicals methods. Desalination 2005, 177, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, F. Enhancing membrane performance by blending ATRP grafted PMMA-TiO2 or PMMA-PSBMA-TiO2 in PVDF. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Shao, X.-S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.-Z.; Zhang, Q. The double effects of silver nanoparticles on the PVDF membrane: Surface hydrophilicity and antifouling performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yao, J. Study on the control of pore sizes of membranes using chemicalmethods Part II. Optimization factors for preparation of membranes. Desalination 2008, 225, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Kang, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Giannelis, E.P.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Highly hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membranes via post fabrication grafting of surface-tailored silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6694–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Qi, G.; Xiao, K.; Sun, J.; Giannelis, E.P.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling behavior of superhydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membranes functionalized with surface-tailored nanoparticles: Implications for organic fouling in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, N.; Liu, S.; Qian, Y. Study on the preparation and characteristics of PVDF/CA blend ultrafiltration membrane. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2002, 22, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Ren, J. Preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/acetalyzed poly (vinyl alcohol) ultrafiltration membrane with the enhanced hydrophilicity and the anti-fouling property. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 121, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Shaikh, A.R.; Kakihana, Y.; Sun, Y.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of type of poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) based amphiphilic copolymer on antifouling properties of copolymer/poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Li, L. Preparation of PU modified PVDF antifouling membrane and its hydrophilic performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankappan, H.; Bousquet, G.; Semsarilar, M.; Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Bouyer, D.; Quémener, D. Development of PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane with Zwitterionic Block Copolymer Micelles as a Selective Layer. Membranes 2019, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacob, N.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.; Nazri, N.A.M.; Ng, B.C.; Abidin, M.N.Z.; Yogarathinam, L.T. ZrO2-TiO2 Incorporated PVDF Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment: Effect of Air Gap. Membranes 2020, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Guo, X.; Ying, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. Composite ultrafiltration membrane tailored by MOF@ GO with highly improved water purification performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Bamaga, O.A.; Gzara, L.; Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Soliman, M.; Drioli, E.; Albeirutty, M.H. Assessment of Blend PVDF Membranes, and the Effect of Polymer Concentration and Blend Composition. Membranes 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bey, S.; Semghouni, H.; Criscuoli, A.; Benamor, M.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, F.G.A.A. Extraction Kinetics of As(V) by Aliquat-336 Using Asymmetric PVDF Hollow-Fiber Membrane Contactors. Membranes 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Das, P.; Simon, F.; Stamm, M. Ultralow fouling membranes by surface modification with functional polydopamine. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Yegani, R.; Pourabbas, B. Synthesis of poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) grafted silica nanoparticles with aminimum adhesion of proteins via one-pot one-step method. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2015, 484, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, Y.; Yegani, R. Analysis of fouling mechanismsin TiO2 embedded high density polyethylene membranes forcollagen separation. Chemi. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of a novel PVDF ultrafiltration membrane by blending with TiO2-HNTs nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Ping, Z. Hydrophilic modification of poly (vinylidene fluoride) microporous membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.R.; Patel, H.R. Chemically treated polyethersulfone/polyacrylonitrile blend ultrafiltration membranes for better fouling resistance. Desalination 2008, 221, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.; Bérubé, P.R.; Andrews, R.C. The Effect of Concentration Factor on Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, K.; Teo, W. Preparation and characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Li, K.; Teo, W.K. Porous PVDF asymmetric hollow fiber membranes prepared with the use of smallmolecular additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 178, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Chang, C.; Huang, F. Effect of salt additive on the formation of microporous poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes by phase inversion from LiClO4/Water/DMF/PVDF system. Polymer 2003, 44, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Fan, X.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling, High-Flux Nanofiltration Membranes Enabled by Dual Functional Polydopamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5548–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hang, M.A.; Cui, Z.; Yang, G. Interaction energy and competitive adsorption evaluation of different NOM fractions on aged membrane surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.C.; Liu, T.-Y. The permeation performance of polyacrylonitrile/polyvinylidine fluoride blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, L. Preparation of hydrophilic polysulfone porous membrane by use of amphiphilic cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 132, 41644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Fierro, D.; Buhr, K.; Wind, J.; Du, B.; Boschetti-De-Fierro, A.; Abetz, V. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) mixed polyacrylonitrile (PAN) ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Hao, S.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, P. An easy way for preparing high performance porous silicon powder by acid etching Al-Si alloy powder for lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibrom, A.G.; Das, C. Effects of solubility parameter differences among PEG, PVP and CA on the preparation of ultrafiltration membranes: Impacts of solvents and additives on morphology, permeability and fouling performances. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhetha, T.; Moutloali, R. Antifouling properties of Cu(tpa)@GO/PES composite membranes and selective dye rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z. Preparation of PVDF/GO-SiO2 hybrid microfiltration membrane towards enhanced perm-selectivity and anti-fouling property. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Deng, C.; Fei, P.; Zhong, M.; Su, B. Preparation of ZnO/GO composite material with highly photocatalytic performance via an improved two-step method. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Shan, M.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Synergetic effects of oxidized carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide on fouling control and antifouling mechanism of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; McGlade, D.; Ulbricht, M.; Lawler, J. Quaternized polysulfone and graphene oxide nanosheet derived low fouling novel positively charged hybrid ultrafiltration membranes for protein separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51208–51219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, M.; Khataee, A.; Vatanpour, V. Effect of reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 nanocomposite with different molar ratios on the performance of PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purifi. Technol. 2015, 140, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.R.; Park, C.H.; Tijing, L.D.; Amarjargal, A.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.S. Bimodal fiber diameter distributed grapheme oxide/nylon-6 composite nanofibrous mats via electrospinning. Colloid Surf. A 2012, 407, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, X.; Shi, L.; Cheng, L.; Chen, N.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Study on the control of pore sizes of membranes using chemical methods Part IV. The role of organic acids. Desalination 2013, 324, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Membrane Materials and Preparation of Membrane; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F. Exploration of permeability and antifouling performance on modified cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membrane with cellulose nanocrystals Carbohyd. Polymer 2017, 174, 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, S.; Jayalakshmi, A.; Senthilkumar, S.; Sankar, H.S.H.; Mohan, D.R. Performance Evaluation of Poly (amide-imide) Incorporated Cellulose Acetate Ultrafiltration Membranes in the Separation of Proteins and Its Fouling Propensity by AFM Imaging. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 14016–14029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Prádanos, P.; Hernandez, A. The effect of protein-protein and protein-membrane interactions on membrane fouling in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Harris, J.L.; Roddick, F.A.; Booker, N.A. Influence of the characteristics of natural organic matter on the fouling of microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H. Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
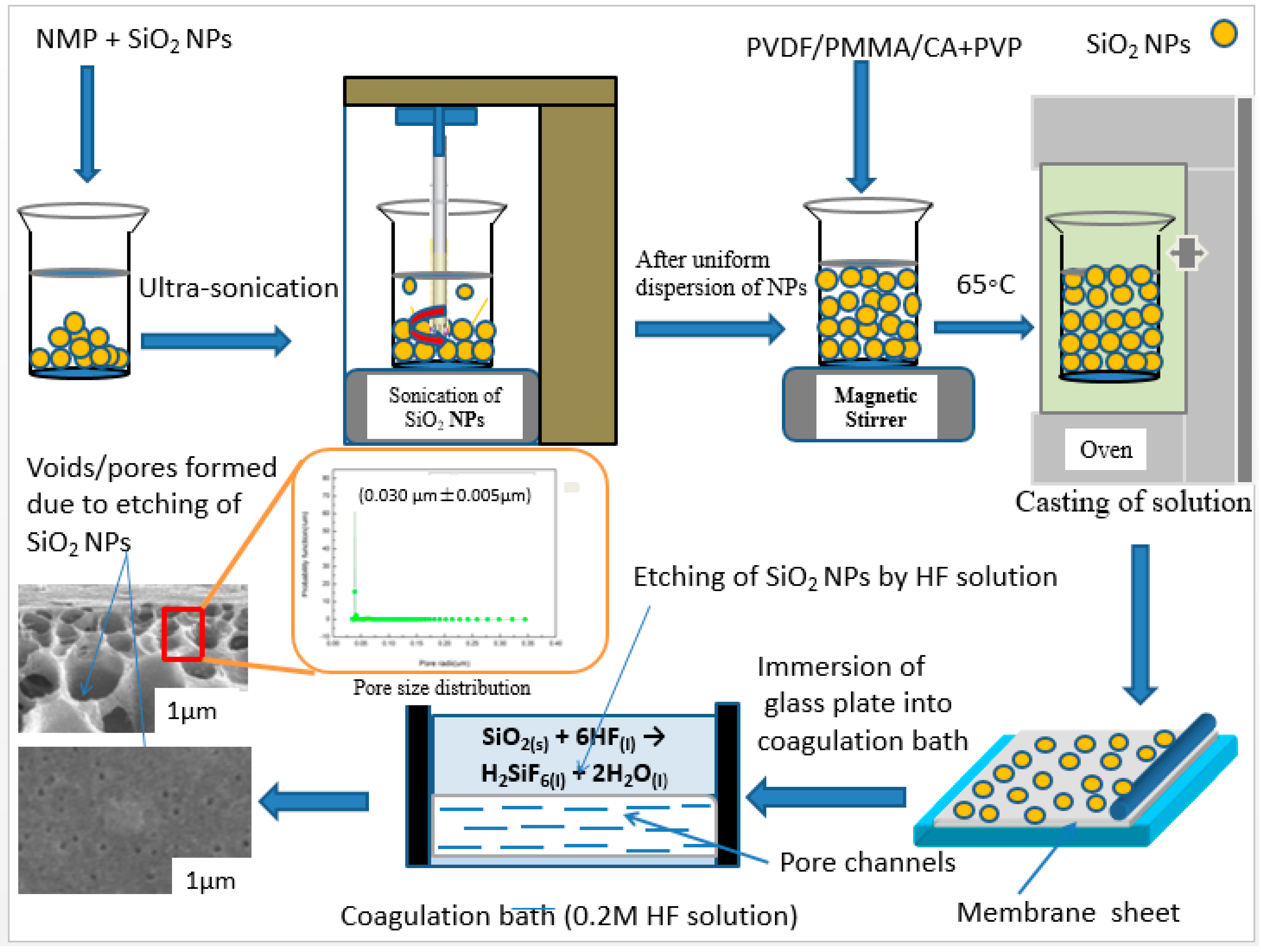
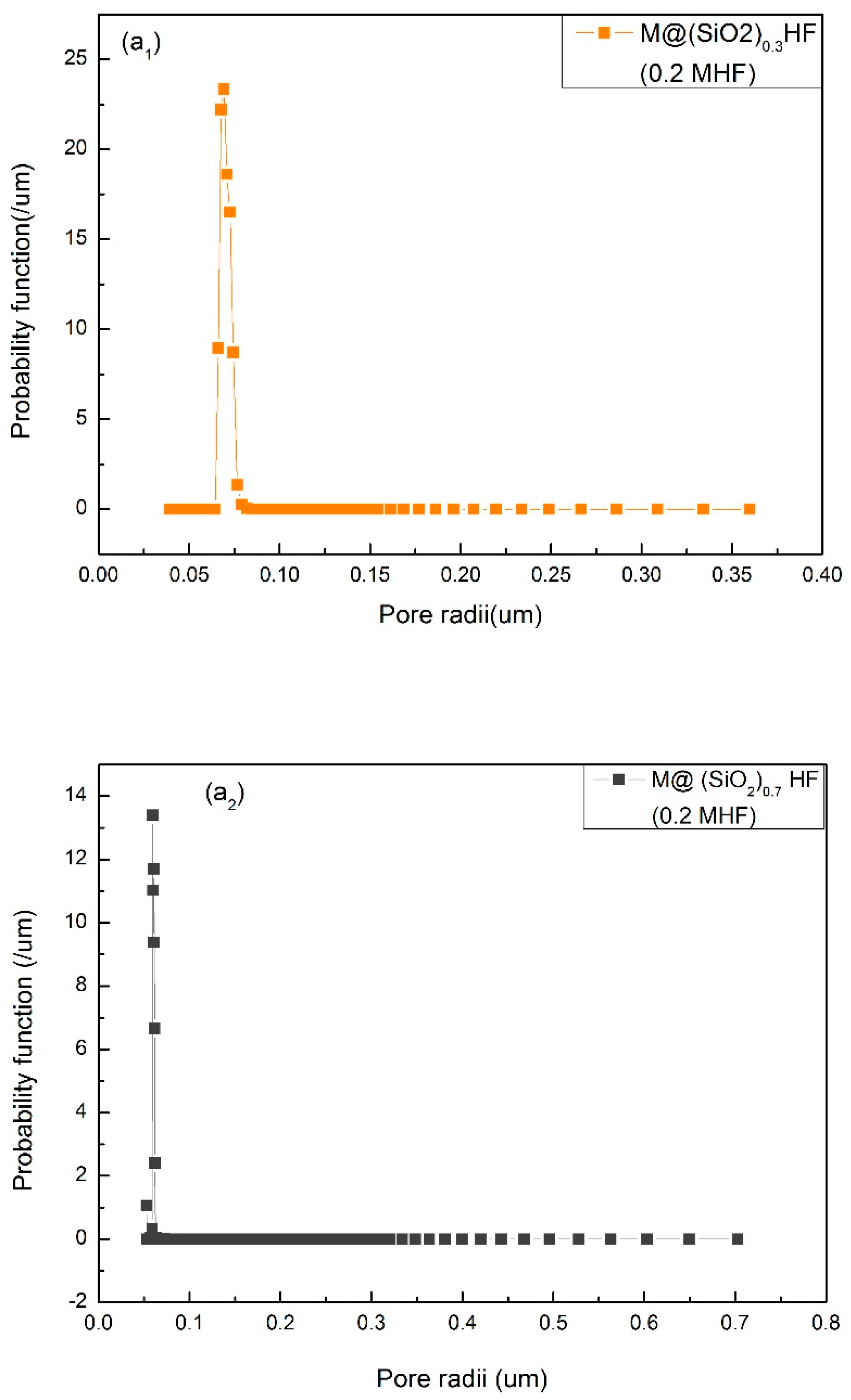
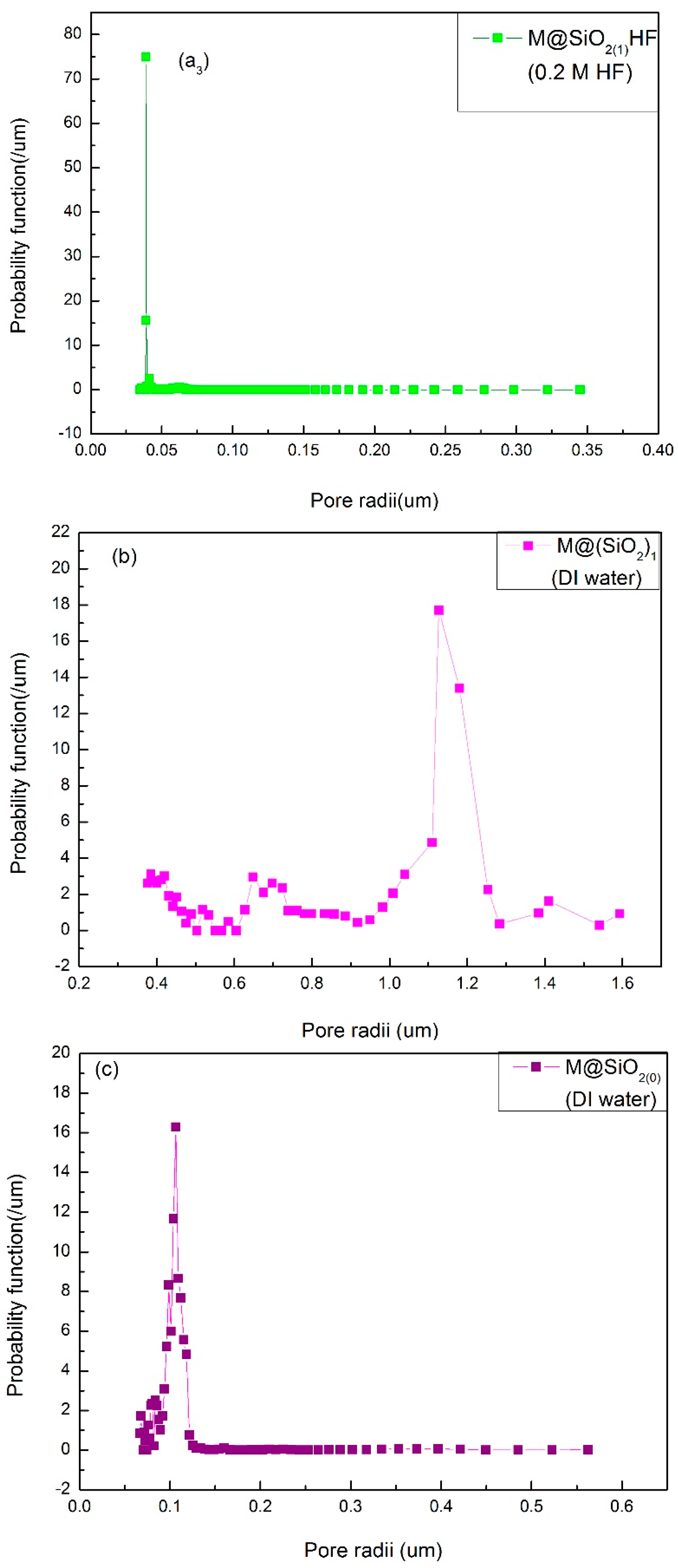

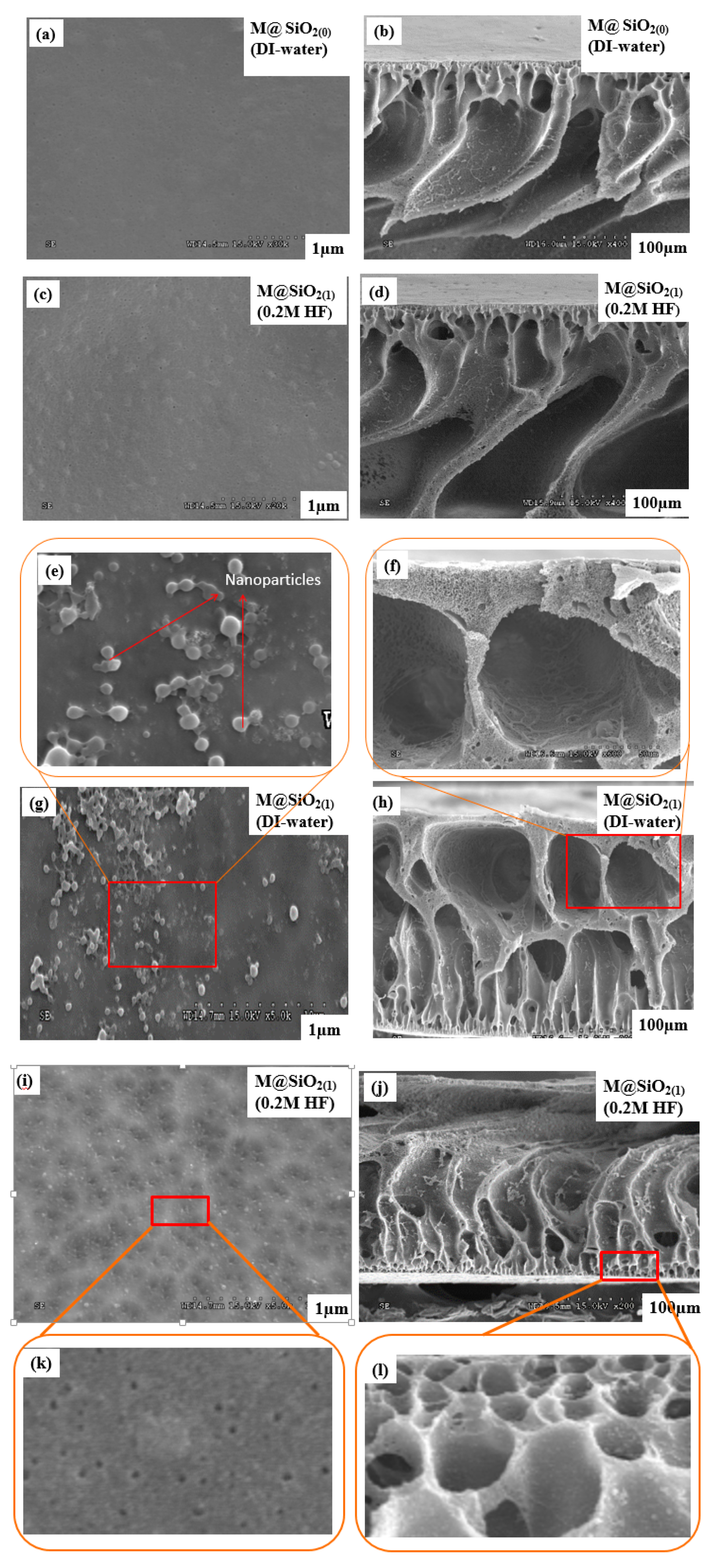
| Sample (16%) | SiO2 NPs (wt%) | Coagulation Bath | Porosity (%) | Mean Pore Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M@SiO2(0) | 0 | DI-water | 77 | 0.10 ± 0.070 |
| M@SiO2(0) HF | 0 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 75 | 0.09 ± 0.010 |
| M@SiO2(1) | 1 | DI-water | 78 | 1.16 ± 0.060 |
| M@SiO2(1) HF | 1 | 0. 2M HF(aq) | 89 | 0.03 ± 0.005 |
| PVDF/PMMA/CA (%) 8.2/2.4/2.4 | Solvent | SiO2NPs (wt%) | PVP | Coagulation Bath | PWF (L·m−2·h−1) | Permeance (L·m−2·h−1) | Rejection BSA (%) | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M@SiO2(0) | NMP | 0 | 3 | DI-water | 9555.0 ± 195 | 1766 ± 35 | 91.5 ± 1.5 | 75.81 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(0) HF | NMP | 0 | 3 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 9555.0 ± 195 | 1681 ± 40 | 92.0 ± 1.0 | 74.82 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(0.3) | NMP | 0.3 | 3 | DI-water | 9323.0 ± 190 | 1670 ± 30 | 93.0 ± 0.6 | 69.36 ± 0.7 |
| M@SiO2(0.3)HF | NMP | 0.3 | 3 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 13,216.0 ± 109 | 5985 ± 134 | 98.0 ± 1.0 | 56.70 ± 0.5 |
| M@SiO2(0.5) | NMP | 0.5 | 3 | DI-water | 9586.0 ± 278 | 1872 ± 15 | 94.5 ± 1.5 | 68.46 ± 0.5 |
| M@SiO2(0.5)HF | NMP | 0.5 | 3 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 15,995.0 ± 145 | 76206 ± 176 | 96.0 ± 1.0 | 55.88 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(0.7) | NMP | 0.7 | 3 | DI-water | 7748.0 ± 298 | 1533 ± 23 | 95.0 ± 0.7 | 71.22 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(0.7) HF | NMP | 0.7 | 3 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 17,197.0 ± 120 | 8246 ± 200 | 94.0 ± 0.5 | 74.74 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(1) | NMP | 1.0 | 3 | DI-water | 8374.0 ±134 | 1640 ± 17 | 97.0 ± 0.3 | 70.78 ± 1.0 |
| M@SiO2(1)HF | NMP | 1.0 | 3 | 0.2 M HF(aq) | 19,494.0 ± 300 | 10,368 ± 89 | 93.5 ± 1.0 | 52.91 ± 1.0 |
| Membrane | Water Flux (L/(m2.h)) | Rejection (%) | Contact Angle (°) | FRR (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF/GO–SiO2(0.5 wt%)(MF) | 850 | 92.0 | 68.0 | 62 | [46] |
| CA/MOF@GO0.12 | 183.51 | 93.3 | 49.5 | 88 | [1] |
| PVDF/GO (1 wt%) (UF) | 505 | 87.0 | 68.0 | 74 | [47] |
| PVDF/GO/MWCNTs (1 wt%) (UF) | 406 | - | 52.0 | 98 | [48] |
| PVDF/GO (2 wt%) (UF) | 25 | - | 64.0 | 80 | [49] |
| PVDF/rGO/TiO 2 (0.05 wt%) (UF) | 221 | 99.0 | 69.0 | 95 | [50] |
| PVDF/GO (3 wt. %) (MF) | 505 | 93.0 | 61.0 | - | [51] |
| CA/PVP(3 wt. %) | 978 | 77.9 | 47.3 | 85.2 | [43] |
| CA/GA/ Na2CO3 (aq). (2 wt.%) | 2836 | 90.8 | - | - | [52] |
| PVDF/PMMA/CA/SiO2(1wt %) | 10,368 | 93.5 | 52.9 | 99 | Present Study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, B.; Haider, S.; Khurram, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Preparation of an Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane with Narrow and Uniform Pore Size Distribution via Etching of SiO2 Nano-Particles in a Membrane Matrix. Membranes 2020, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070150
Khan B, Haider S, Khurram R, Wang Z, Wang X. Preparation of an Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane with Narrow and Uniform Pore Size Distribution via Etching of SiO2 Nano-Particles in a Membrane Matrix. Membranes. 2020; 10(7):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070150
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Bushra, Sajjad Haider, Rooha Khurram, Zhan Wang, and Xi Wang. 2020. "Preparation of an Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane with Narrow and Uniform Pore Size Distribution via Etching of SiO2 Nano-Particles in a Membrane Matrix" Membranes 10, no. 7: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070150
APA StyleKhan, B., Haider, S., Khurram, R., Wang, Z., & Wang, X. (2020). Preparation of an Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane with Narrow and Uniform Pore Size Distribution via Etching of SiO2 Nano-Particles in a Membrane Matrix. Membranes, 10(7), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070150





