Impacts of Sulfuric Acid on the Stability and Separation Performance of Polymeric PVDF-Based Membranes at Mild and High Concentrations: An Experimental Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Conditions
2.1. Materials
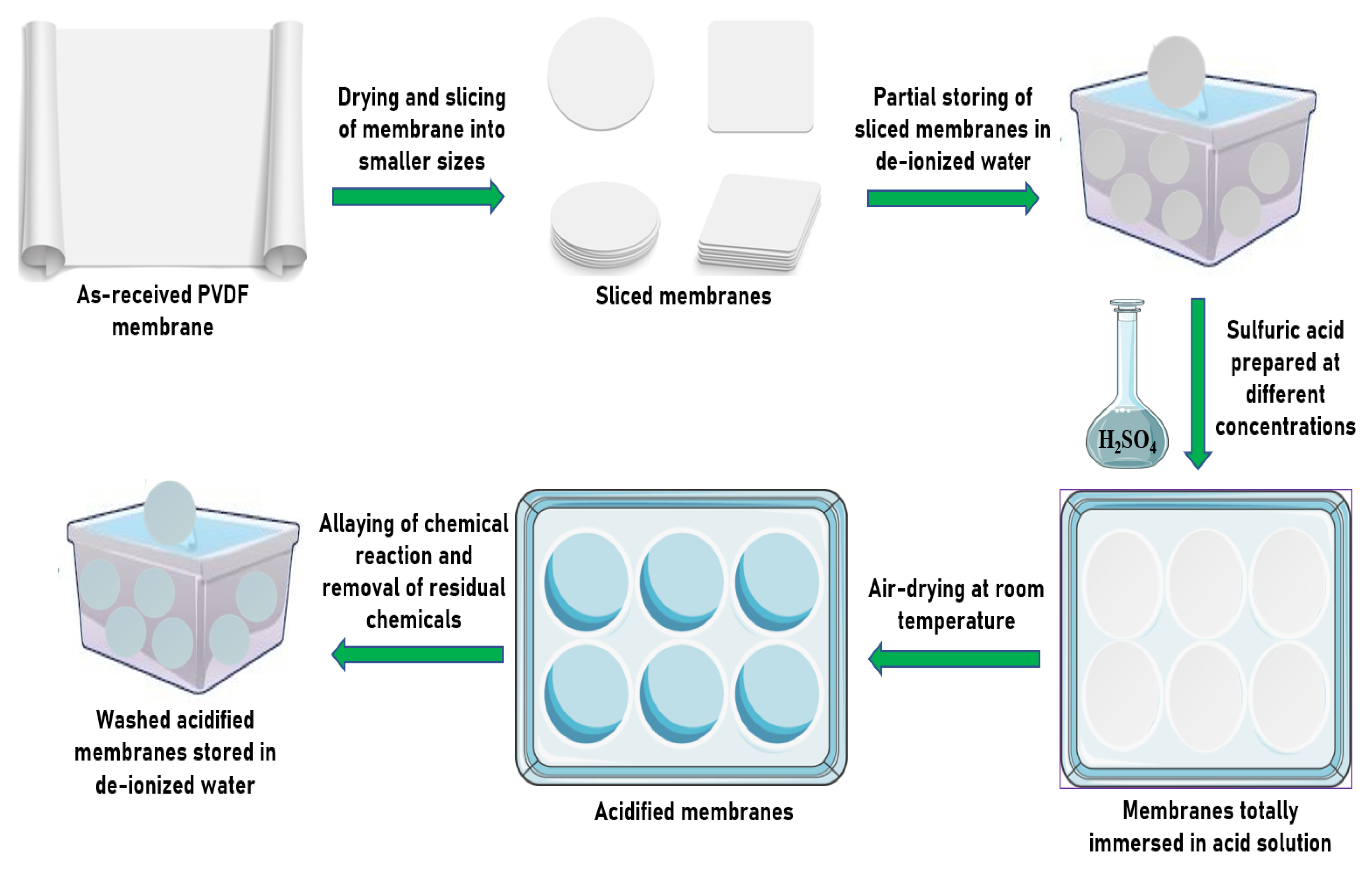
2.2. Membrane Preparation and Embedding
2.3. Membrane Characterization
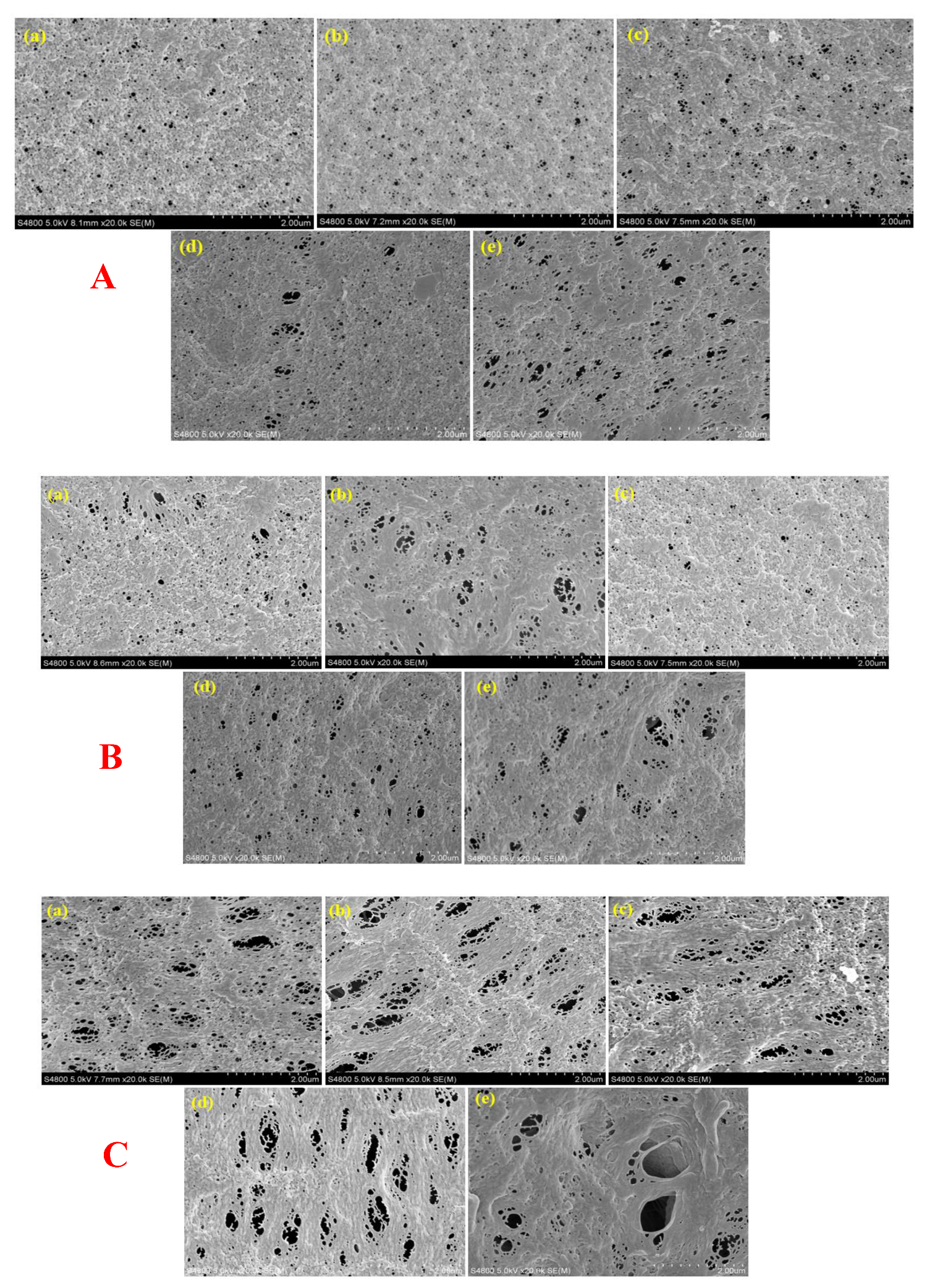
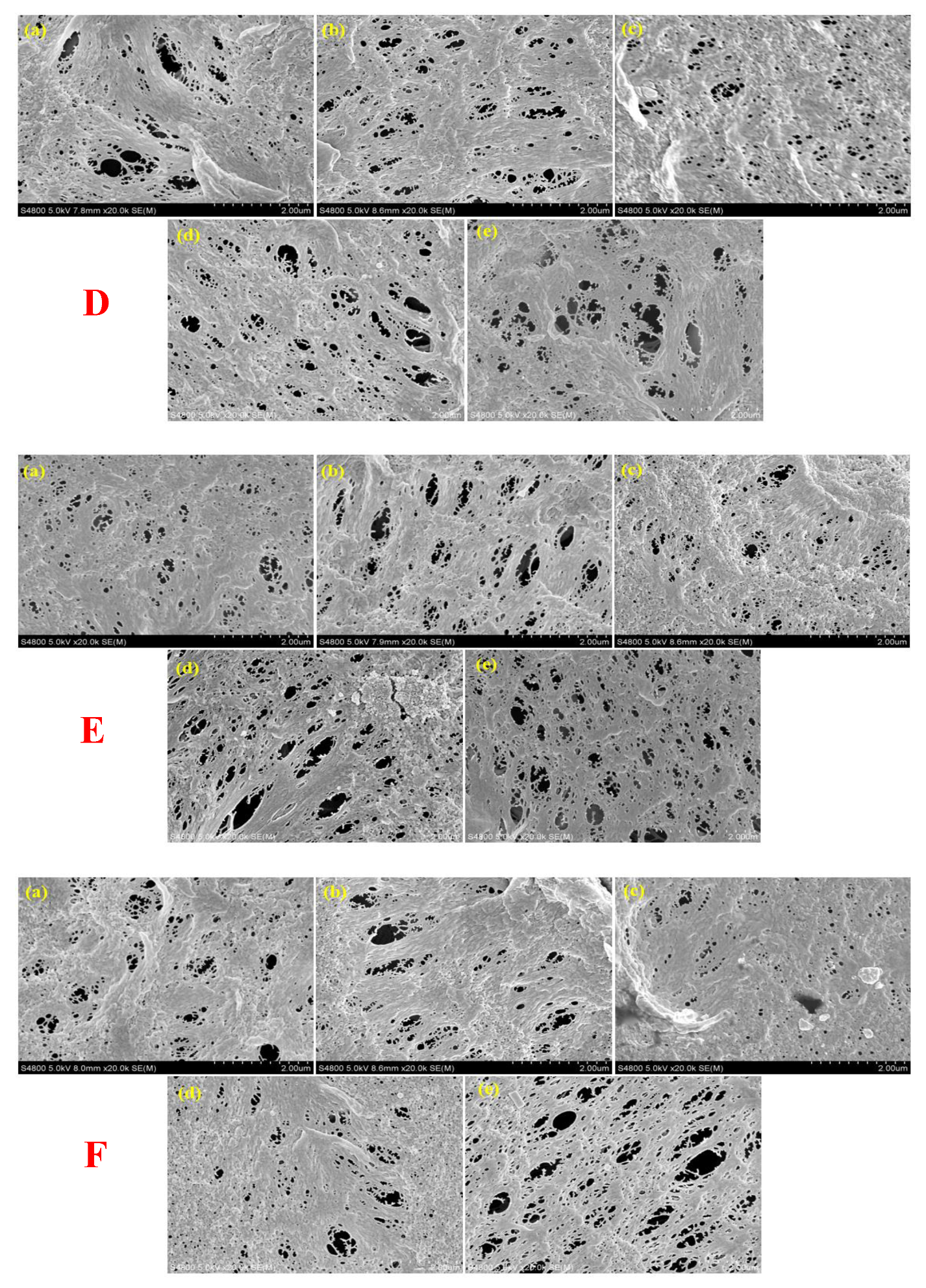
2.3.1. Morphology
2.3.2. X-ray Diffractogram Analysis
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3.4. Thickness, Porosity and Tortuosity
2.3.5. Static Contact Angle Measurement
2.3.6. Zeta Potential
2.3.7. Mechanical Strength
2.3.8. Physical Observation and Examination
2.4. Permeation and Rejection Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Morphology and Elemental Composition
3.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.4. Membrane Thickness and Porosity
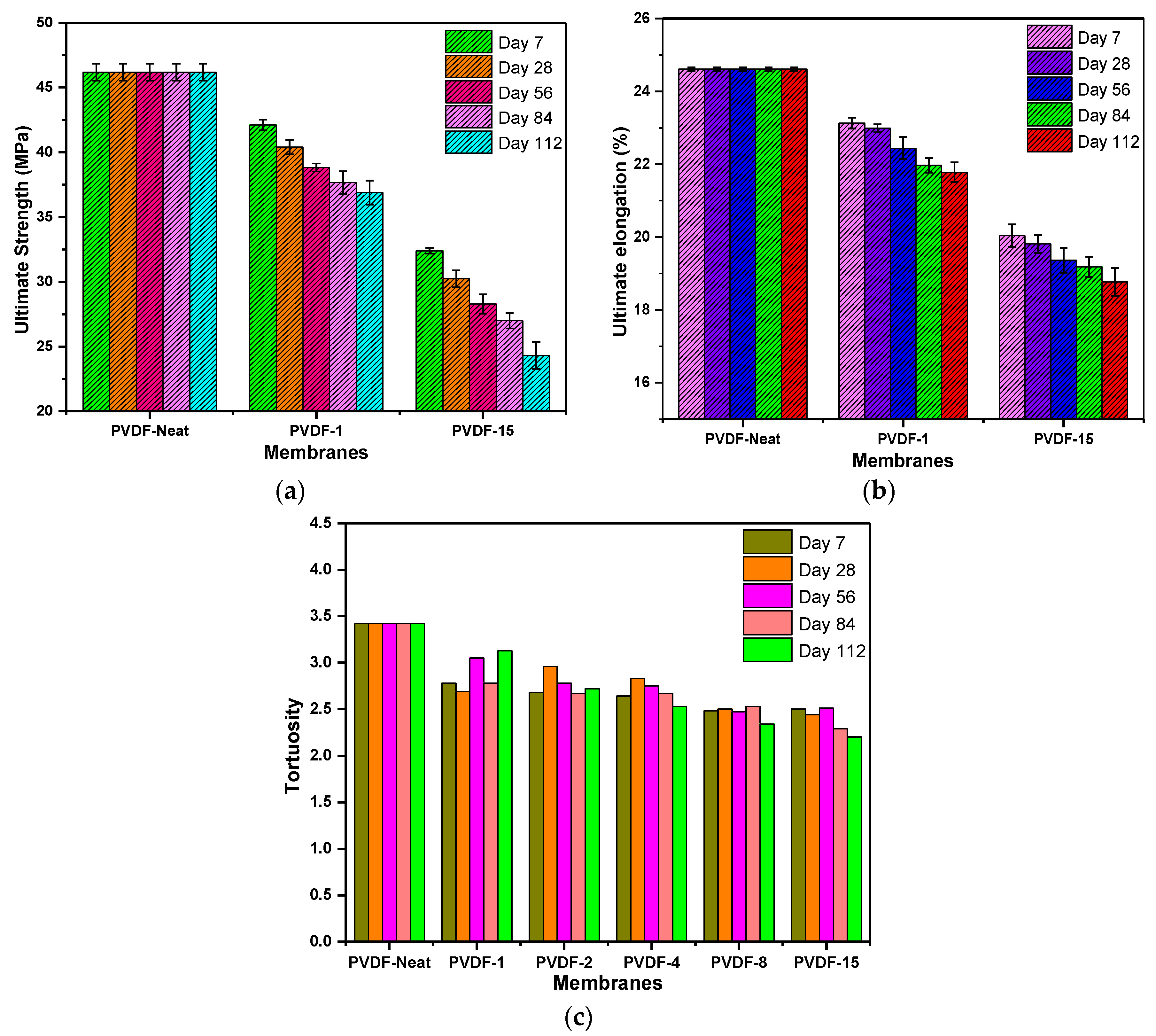
3.5. Membranes’ Mechanical Strength and Tortuosity
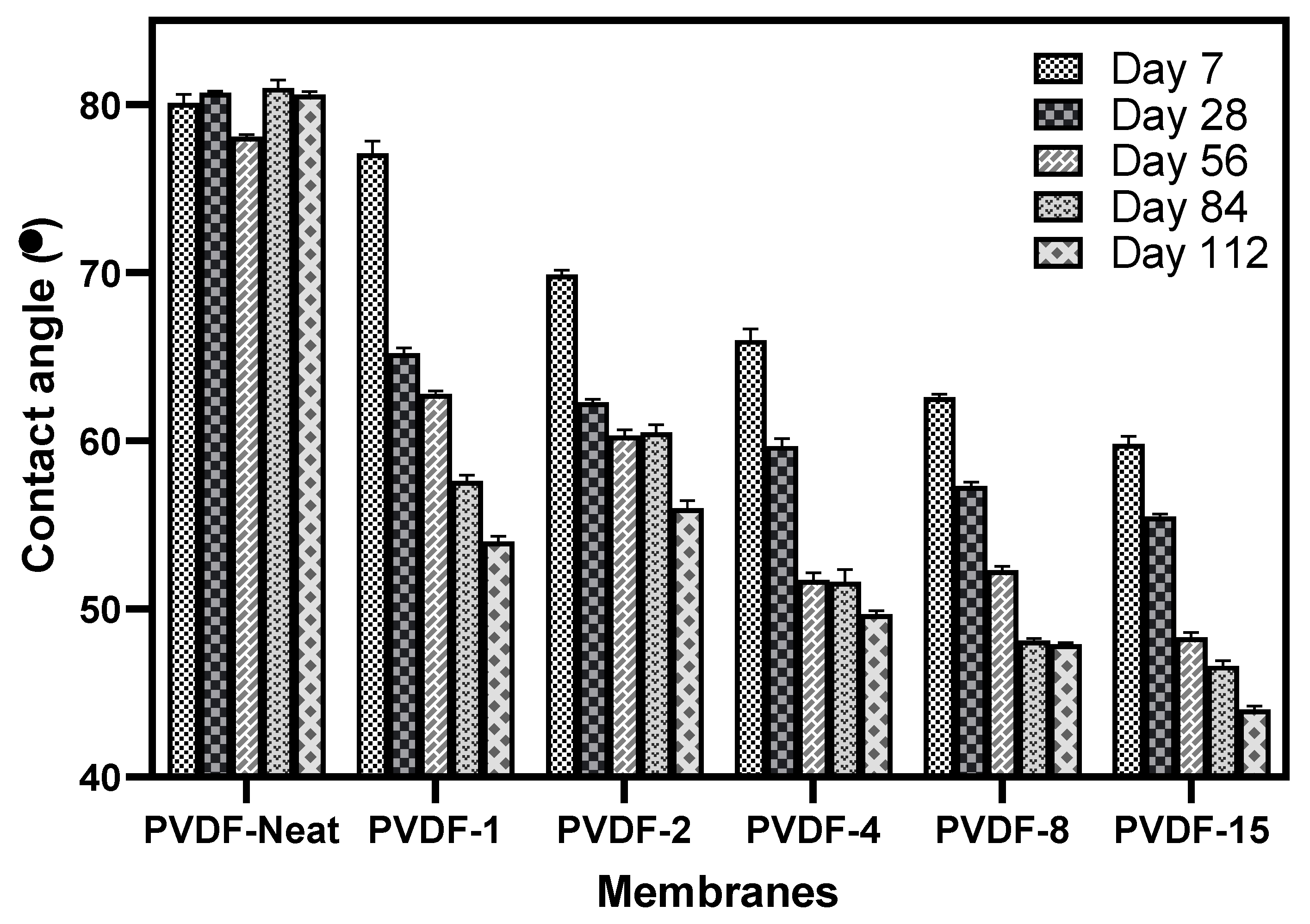
3.6. Membrane Hydrophilicity
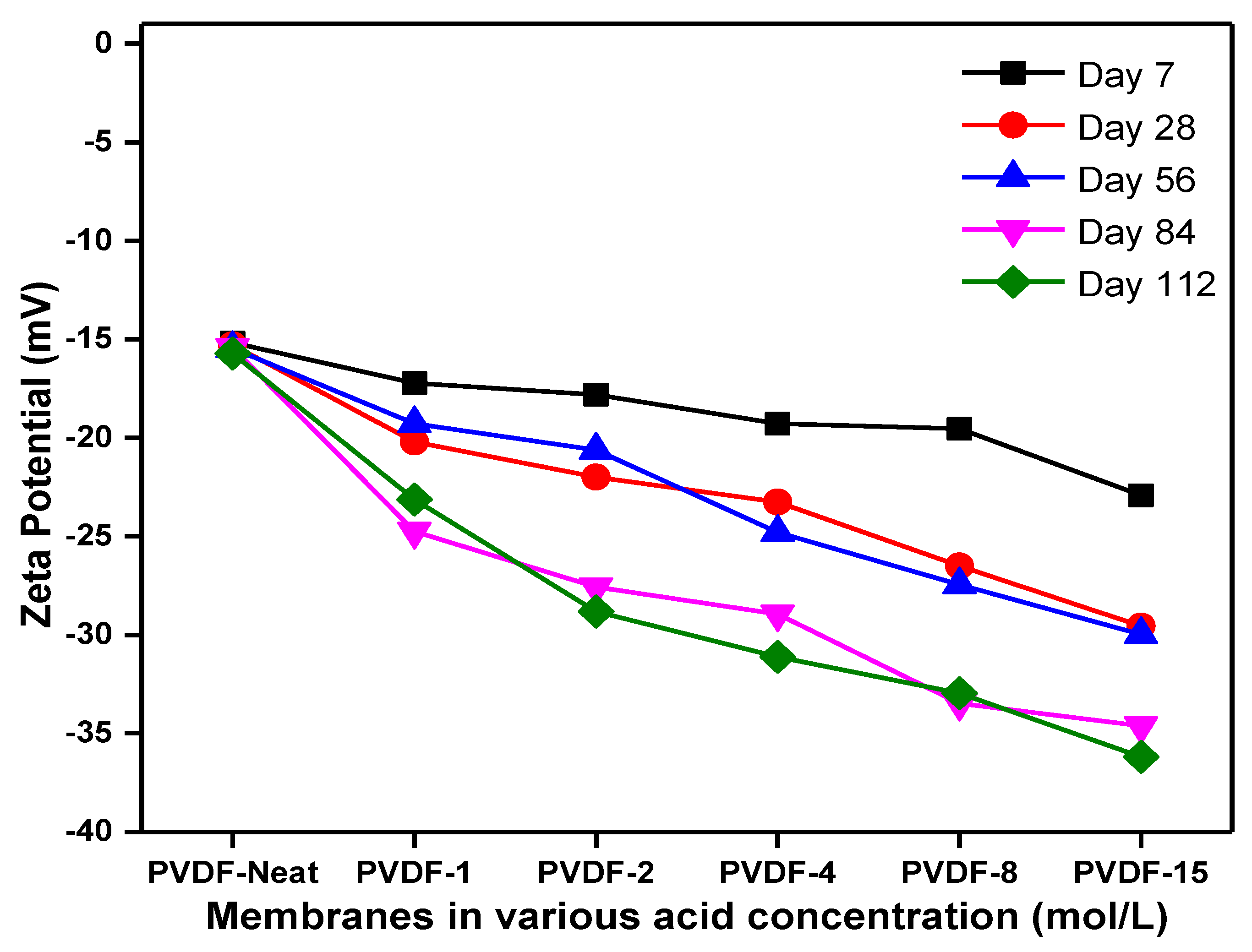
3.7. Membrane Surface Charge
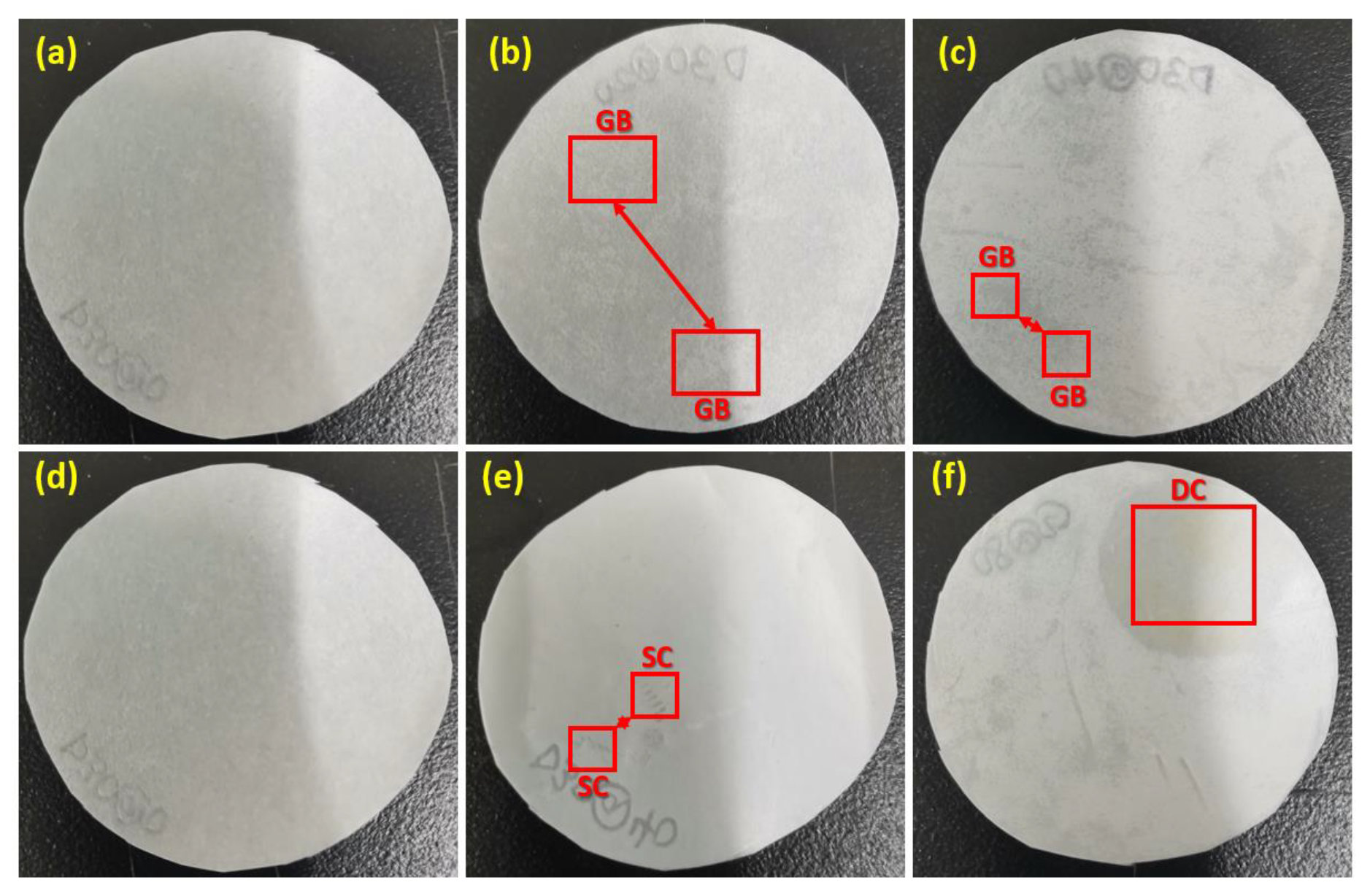
3.8. Physical/Visual Examination
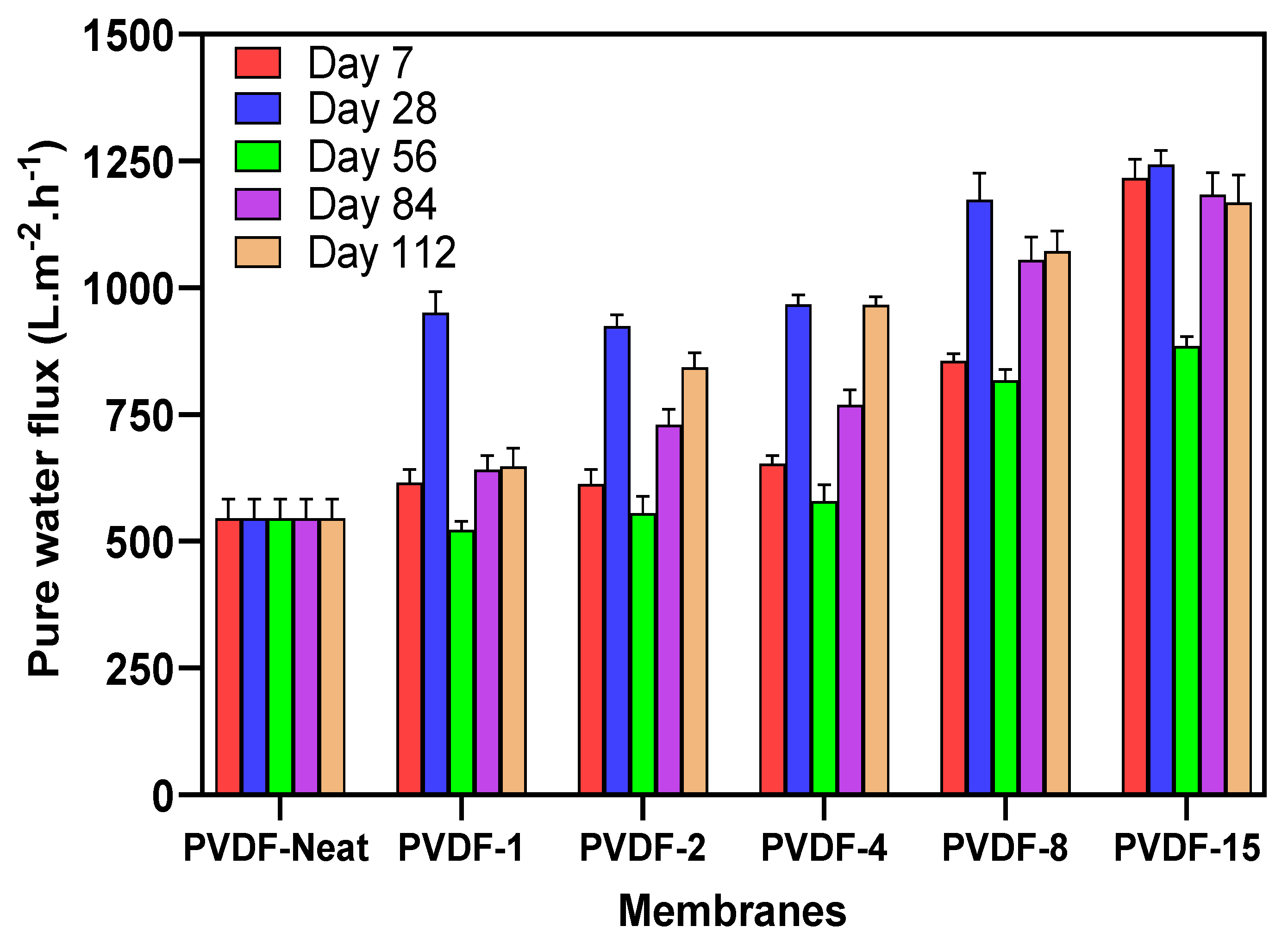
3.9. Membrane Water Permeability and BSA Rejection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Z.; Mahmud, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, S. Polyvinylidene fluoride membrane functionalized with zero valent iron for highly efficient degradation of organic contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, S.; He, G. Application of Mg(OH)2 nanoplatelets as pore former to prepare PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Li, L. Treatment of oily waste water by PVP grafted PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshk, N.; Rana, D.; Narbaitz, R.M.; Matsuura, T. Novel modified PVDF ultrafiltration flat-sheet membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Chu, H.P. Membrane bioreactor for the drinking water treatment of polluted surface water supplies. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4781–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Gestel, T.; Doyen, W.; Leysen, R. A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, X.Y.; Shih, K. In situ embedment and growth of anhydrous and hydrated aluminum oxide particles on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 368, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.A.; Liu, F.; Li, K. A simplified method for preparation of hydrophilic PVDF membranes from an amphiphilic graft copolymer. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awanis Hashim, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Stability of PVDF hollow fibre membranes in sodium hydroxide aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.Z.; Bérubé, P.R. Assessing the effects of sodium hypochlorite exposure on the characteristics of PVDF based membranes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5392–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendergast, M.M.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ramli, W.K.W. Hydrophobic PVDF membrane via two-stage soft coagulation bath system for Membrane Gas Absorption of CO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, S.; Yoshimoto, S.; Teramoto, M.; Al-Marzouqi, M.; Matsuyama, H. CO2 absorption by using PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactors with various membrane structures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 69, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, P.; Liu, H.; Yao, H.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L. Preparation and Characterization of a PVDF Membrane Modified by an Ionic Liquid. Aust. J. Chem. 2019, 72, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhikh, V.; Tsarev, D.; Alentiev, A.; Yampolskii, Y. A novel method for predictions of the gas permeation parameters of polymers on the basis of their chemical structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Hydrophilic modification of P(VDF-co-CTFE) porous membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-d.; Cao, Y.-m. Application and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Hussain, A.; Farrukh, S.; Ahmad, T. Development of Anti-bacterial PVA/Starch Based Hydrogel Membrane for Wound Dressing. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Bamaga, O.A.; Gzara, L.; Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Soliman, M.F.; Drioli, E.; Albeirutty, M. Assessment of blend PVDF membranes, and the effect of polymer concentration and blend composition. Membranes 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alyarnezhad, S.; Marino, T.; Parsa, J.B.; Galiano, F.; Ursino, C.; Garcìa, H.; Puche, M.; Figoli, A. Polyvinylidene fluoride-graphene oxide membranes for dye removal under visible light irradiation. Polymers 2020, 12, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Ji, Z.; Luan, Z. Preparation and properties of PVDF composite hollow fiber membranes for desalination through direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudaib, B.; Gomes, V.; Shi, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Z. Poly (vinylidene fluoride)/polyaniline/MWCNT nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for natural organic matter removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuni, M.F.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M.; Awanis Hashim, N. A systematic assessment method for the investigation of the PVDF membrane stability. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitskaya, A.A. Separation characteristics of charged ultrafiltration membranes modified with the anionic surfactant. Desalination 2005, 184, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, A.F.; Nie, F.Q.; Huang, X.D.; Xu, Z.K.; Yao, K. Acrylonitrile-based copolymer membranes containing reactive groups: Surface modification by the immobilization of biomacromolecules. Polymer 2005, 46, 11060–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.K. A facile method of surface modification for hydrophobic polymer membranes based on the adhesive behavior of poly(DOPA) and poly(dopamine). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Feng, X. Enhancing the performance of PVDF membranes by hydrophilic surface modification via amine treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 185, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Functional surface modification of PVDF membrane for chemical pulse cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatekin, A.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M.; Mayes, A.M. Anti-fouling ultrafiltration membranes containing polyacrylonitrile-graft-poly(ethylene oxide) comb copolymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.F.; Banerjee, P.; Mayes, A.M. Preparation of Protein-Resistant Surfaces on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Membranes via Surface Segregation. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.F.; Mayes, A.M. Design and performance of foul-resistant poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes prepared in a single-step by surface segregation. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, K.R.; Steen, M.L.; Fisher, E.R. Surface modification with nitrogen-containing plasmas to produce hydrophilic, low-fouling membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, M.L.; Jordan, A.C.; Fisher, E.R. Hydrophilic modification of polymeric membranes by low temperature H2O plasma treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 204, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tan, K.L.; Kang, E.T.; Neoh, K.G. Plasma-induced immobilization of poly (ethylene glycol) onto poly (vinylidene fluoride) microporous membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 195, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, H.; Kilduff, J.E.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G.; Belfort, G. High-throughput membrane surface modification to control NOM fouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xiao, K.; Dong, H.; Liao, W.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S. Preparation of Al2O3/PU/PVDF composite membrane and performance comparison with PVDF membrane, PU/PVDF blending membrane, and Al2O3/PVDF hybrid membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of a novel PVDF ultrafiltration membrane by blending with TiO 2 -HNTs nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, J.; Sun, T.; Shang, W.; Dong, W.; Li, M.; Sun, F. Hydrophilic modification and anti-fouling properties of PVDF membrane via in situ nano-particle blending. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25227–25242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuni, M.F.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M.; Aroua, M.K.; Hashim, N.A. Effects of alkaline environments at mild conditions on the stability of PVDF membrane: An experimental study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 15874–15882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuni, M.F.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M.; Aroua, M.K.; Yern Chee, C.; Awanis Hashim, N. Impact of in situ physical and chemical cleaning on PVDF membrane properties and performances. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Gharabli, S.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Kujawa, J.; Nunes, S.P.; Arafat, H.A. Activation of PVDF membranes through facile hydroxylation of the polymeric dope. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 4219–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, K.; Jacob Kaleekkal, N.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Srivastava, S.; Bajaj, H. Tuning the morphology of PVDF membranes using inorganic clusters for oil/water separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z. Effects of solvent compositions on physicochemical properties and anti-fouling ability of PVDF microfiltration membranes for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2012, 297, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsure, N.A.; Hashim, N.A.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M.; Chee, C.Y. Alkaline etching treatment of PVDF membrane for water filtration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22153–22160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.J.; Watts, J.F.; Hill, M.P.; Morrissey, P. Surface modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) by alkaline treatment: 1. The degradation mechanism. Polymer 2000, 41, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, V.; Granville, A.; Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V. Cleaning and ageing effect of sodium hypochlorite on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Preparation of PVDF hollow fiber membranes using SiO2particles: The effect of acid and alkali treatment on the membrane performances. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Z.; Cao, J. Impact of sodium hypochlorite cleaning on the surface properties and performance of PVDF membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanninen, J.; Platt, S.; Weis, A.; Nyström, M. Long-term acid resistance and selectivity of NF membranes in very acidic conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, S.; Nyström, M.; Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G. Stability of NF membranes under extreme acidic conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 239, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, T.; Chen, C.; Li, J. A study on membrane morphology by digital image processing. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 305, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, A.; Favoni, O. Particle size, size distribution and morphological evaluation of airborne dust particles of diverse woods by Scanning Electron Microscopy and image processing program. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L. Simple Expression for the Tortuosity of Porous Media. Transp. Porous Media 2011, 88, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Cai, X.; Lu, J. Fabrication and characterization of novel asymmetric polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes by the nonsolvent thermally induced phase separation (NTIPS) method for membrane distillation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzinun, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Puteh, M.H.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Stability study of PVDF/TiO2 dual layer hollow fibre membranes under long-term UV irradiation exposure. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 15, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, P.; Liu, H.; Yao, H.; Hu, A.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/CaCO3 composite membranes etched by hydrochloric acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33607–33620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, K.T.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane preparation with an environmental diluent via thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Effect of PMMA on crystallization behavior and hydrophilicity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blend prepared in semi-dilute solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 8377–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Magnuson, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, W.; Vardhan, H.; Han, X.; He, G.; Ma, S. PEG@ZIF-8/PVDF Nanocomposite Membrane for Efficient Pervaporation Desulfurization via a Layer-by-Layer Technology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20664–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Chang, L.K.; Yang, C.D.; Lin, D.J.; Cheng, L.P. Effect of polar rotation on the formation of porous poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes by immersion precipitation in an alcohol bath. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.m.; Liu, F.; Ma, B.r.; Xue, L.x. Effect of solvent power on PVDF membrane polymorphism during phase inversion. Desalination 2013, 316, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R. Determination of the α, β, and γ crystalline phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films prepared at different conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón, E.; Álvarez, J.R.; Palacio, L.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Luque, S. Ageing of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes under long-term exposures to alkaline and acidic cleaning solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Fan, X.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Vardhan, H. Improved desulfurization performance of polyethyleneglycol membrane by incorporating metal organic framework CuBTC. Polymers 2020, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkhangelsky, E.; Kuzmenko, D.; Gitis, N.V.; Vinogradov, M.; Kuiry, S.; Gitis, V. Hypochlorite cleaning causes degradation of polymer membranes. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elele, E.; Shen, Y.; Tang, J.; Lei, Q.; Khusid, B.; Tkacik, G.; Carbrello, C. Mechanical properties of polymeric microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Saito, T.; Hickner, M.A. Zeta potential of ion-conductive membranes by streaming current measurements. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4721–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, I.C.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Microfiltration and ultrafiltration membrane science and technology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y. How Pore Hydrophilicity Influences Water Permeability? Research 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Membrane ID | Porosity (%) | Thickness (µm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Days | 28 Days | 56 Days | 84 Days | 112 Days | Before | After | |
| PVDF-neat | 58.6 ± 0.42 | 58.6 ± 0.42 | 58.6 ± 0.42 | 58.6 ± 0.42 | 58.6 ± 0.42 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 196.4 ± 7.07 |
| PVDF-1 | 65.3 ± 0.47 | 66.3 ± 0.46 | 62.3 ± 0.40 | 65.3 ± 0.47 | 61.4 ± 0.46 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 195.2 ± 4.85 |
| PVDF-2 | 66.5 ± 0.56 | 63.2 ± 0.28 | 65.3 ± 0.27 | 66.6 ± 0.24 | 65.9 ± 0.25 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 195.7 ± 5.19 |
| PVDF-4 | 67.0 ± 0.13 | 64.7 ± 0.16 | 65.7 ± 0.52 | 66.6 ± 0.29 | 68.5 ± 0.43 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 193.4 ± 2.55 |
| PVDF-8 | 69.1 ± 0.20 | 68.9 ± 0.10 | 69.3 ± 0.18 | 68.4 ± 0.19 | 71.0 ± 0.16 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 192.9 ± 3.42 |
| PVDF-15 | 68.8 ± 0.30 | 69.7 ± 0.28 | 68.7 ± 0.42 | 71.8 ± 0.33 | 73.2 ± 0.51 | 196.4 ± 7.07 | 192.4 ± 3.95 |
| Membrane ID | BSA Rejection (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Days | 28 Days | 56 Days | 84 Days | 112 Days | |
| PVDF-Neat | 93.2 ± 0.78 | 93.2 ± 0.78 | 93.2 ± 0.78 | 93.2 ± 0.78 | 93.2 ± 0.78 |
| PVDF-1 | 70.7 ± 1.63 | 65.95 ± 3.04 | 76.8 ± 1.98 | 55.7 ± 1.34 | 49.9 ± 1.77 |
| PVDF-15 | 57.0 ± 1.60 | 55.9 ± 1.35 | 56.9 ± 1.84 | 45.8 ± 1.27 | 31.4 ± 2.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lasisi, K.H.; Yao, W.; Ajibade, T.F.; Tian, H.; Fang, F.; Zhang, K. Impacts of Sulfuric Acid on the Stability and Separation Performance of Polymeric PVDF-Based Membranes at Mild and High Concentrations: An Experimental Study. Membranes 2020, 10, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120375
Lasisi KH, Yao W, Ajibade TF, Tian H, Fang F, Zhang K. Impacts of Sulfuric Acid on the Stability and Separation Performance of Polymeric PVDF-Based Membranes at Mild and High Concentrations: An Experimental Study. Membranes. 2020; 10(12):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLasisi, Kayode H., Weihao Yao, Temitope F. Ajibade, Huali Tian, Fang Fang, and Kaisong Zhang. 2020. "Impacts of Sulfuric Acid on the Stability and Separation Performance of Polymeric PVDF-Based Membranes at Mild and High Concentrations: An Experimental Study" Membranes 10, no. 12: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120375
APA StyleLasisi, K. H., Yao, W., Ajibade, T. F., Tian, H., Fang, F., & Zhang, K. (2020). Impacts of Sulfuric Acid on the Stability and Separation Performance of Polymeric PVDF-Based Membranes at Mild and High Concentrations: An Experimental Study. Membranes, 10(12), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120375






