Diversity of Acyl Homoserine Lactone Molecules in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors Treating Sewage at Psychrophilic Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
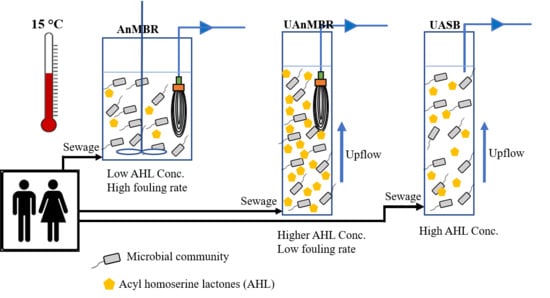
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. AHL Molecules Investigated in the Study
2.3. Sludge and Biofilm Collection and AHL Extraction
2.4. AHL Identification and Quantification
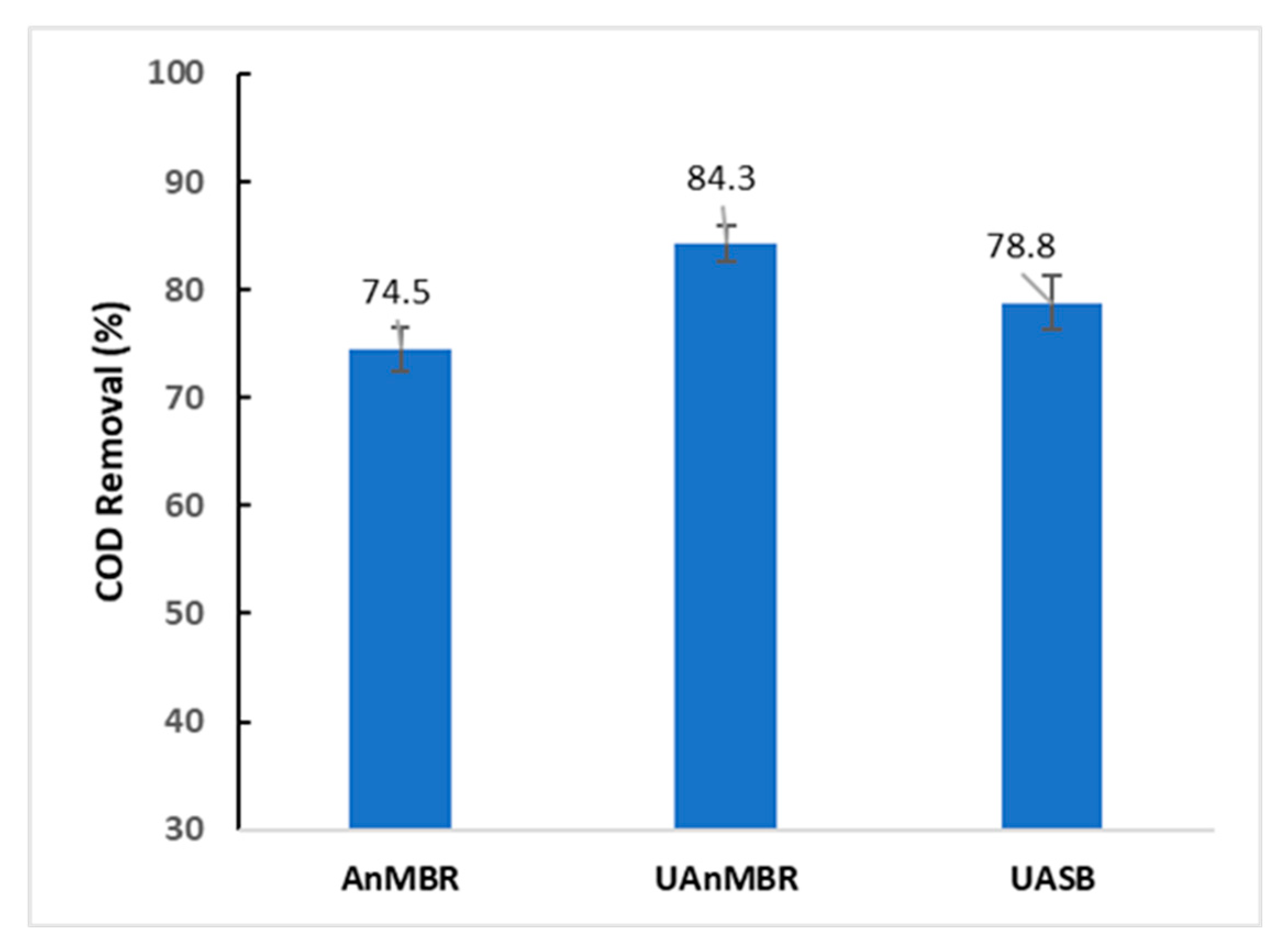
2.5. Influent/Effluent Quality Analysis
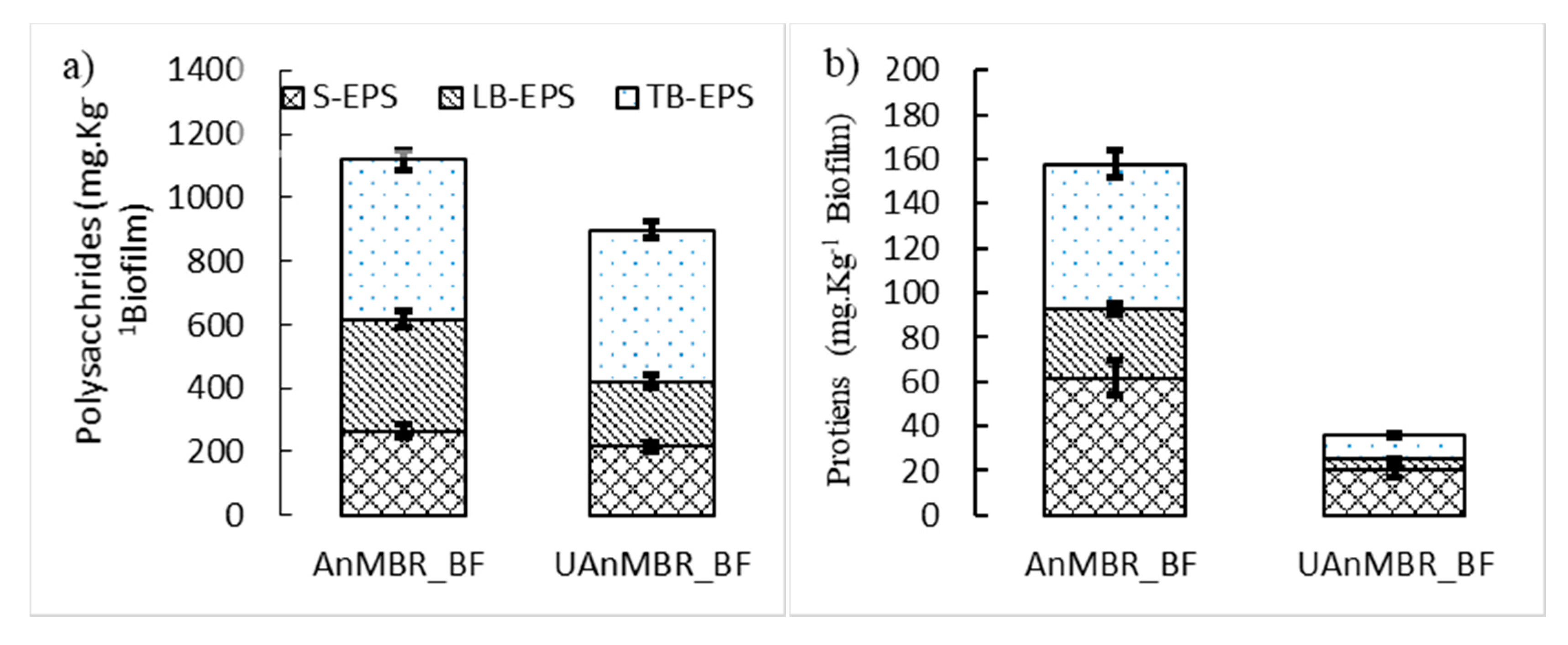
2.6. EPS Extraction, Proteins, and Polysaccharides Measurement
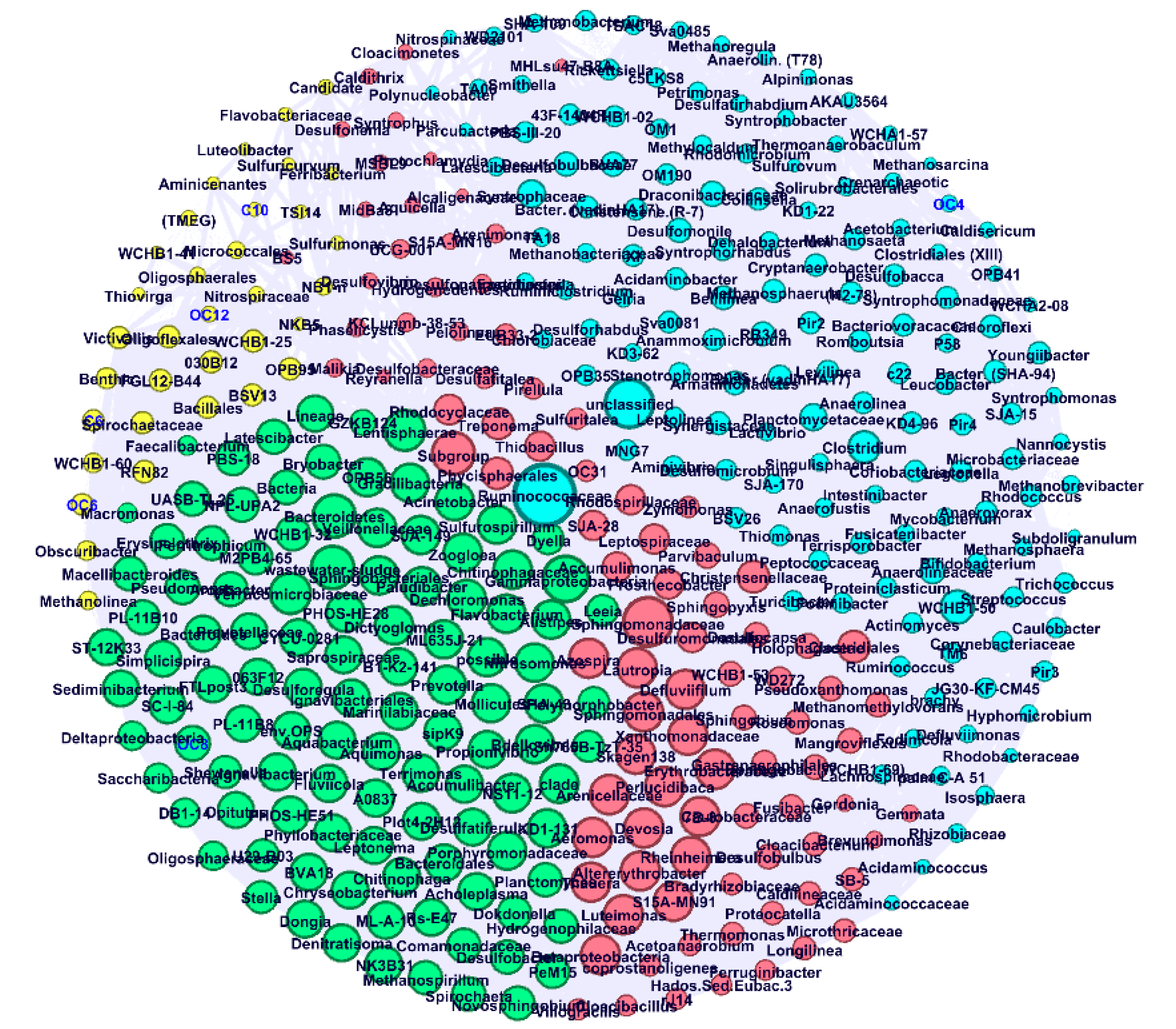
2.7. Molecular Microbial Analysis
2.8. Data Visualization
3. Results
3.1. AHL Types and Concentrations
3.2. Protein and Polysaccharide Correlations with AHL
3.3. Microbial Community in AnMBR, UAnMBR, and UASB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Lier, J.B.; Mahmoud, N.; Zeeman, G. Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008; pp. 415–456. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, C.; Zhang, B. High-concentration food wastewater treatment by an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4110–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkessa, Y.W.; Yan, B.; Li, T.; Tan, M.; She, Z.; Jegatheesan, V.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y. Novel anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) design for wastewater treatment at long HRT and high solid concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, N.M.; Tong, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y. Membrane fouling characteristics of a side-stream tubular anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) treating domestic wastewater. Processes 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, B.; Tarre, S.; Beliavski, M.; Dosoretz, C.G.; Green, M. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for domestic wastewater treatment. Desalination 2009, 243, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B.; Cao, L.; Love, N.G.; Raskin, L.; Skerlos, S.J. Navigating wastewater energy recovery strategies: A life cycle comparison of anaerobic membrane bioreactor and conventional treatment systems with anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5972–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoener, B.D.; Bradley, I.M.; Cusick, R.D.; Guest, J.S. Energy positive domestic wastewater treatment: The roles of anaerobic and phototrophic technologies. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.M.; Moore, J.D.; Blackwell, H.E.; Amador-Noguez, D. Identification of unanticipated and novel N-acyl L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) using a sensitive non-targeted LC-MS/MS method. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, L.; Blanchet, E.; Intertaglia, L.; Baudart-Lenfant, J.; Stien, D.; Suzuki, M.T.; LeBaron, P.; Lami, R. Characterization of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactones in Vibrio tasmaniensis LGP32 by a biosensor-based UHPLC-HRMS/MS method. Sensors 2017, 17, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherji, R.; Prabhune, A. Enzyme purification and kinetic characterization of AHL lactonase from Bacillus sp. RM1 a novel and potent quorum quencher isolated from Fenugreek root nodule rhizosphere. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 909–924. [Google Scholar]
- Doberva, M.; Stien, D.; Sorres, J.; Hue, N.; Sanchez-Ferandin, S.; Eparvier, V.; Ferandin, Y.; LeBaron, P.; Lami, R. Large Diversity and Original Structures of Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in Strain MOLA 401, a Marine Rhodobacteraceae Bacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krick, A.; Kehraus, S.; Eberl, L.; Riedel, K.; Anke, H.; Kaesler, I.; Graeber, I.; Szewzyk, U.; König, G. A marine Mesorhizobium sp. produces structurally novel long-chain N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3587–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, D.L.; Hardman, A.; Camara, M.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Stewart, G.S.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing in Vibrio anguillarum: Characterization of the vanI/vanR locus and identification of the autoinducer N-(3-oxodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, D.L.; Chalker, V.J.; Kirke, D.; Hardman, A.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P. The LuxM Homologue VanM from Vibrio anguillarum Directs the Synthesis of N-(3-Hydroxyhexanoyl) homoserine Lactone and N-Hexanoylhomoserine Lactone. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3537–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.L.; Hanzelka, B.L.; Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Detection, purification, and structural elucidation of the acylhomoserine lactone inducer of Vibrio fischeri luminescence and other related molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 305, 288–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Nahm, C.H.; Kwon, H.; Oh, H.-S.; Won, Y.-J.; Choo, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K. More efficient media design for enhanced biofouling control in a membrane bioreactor: Quorum quenching bacteria entrapping hollow cylinder. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8596–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.M.; Bhangui, P.; Bhat, C. The first report on Listeria monocytogenes producing siderophores and responds positively to N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) molecules by enhanced biofilm formation. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.M.; Naik, S.P.; Dubey, S.K.; Bhat, C.; Charya, L.S. Enhanced exopolysaccharide production and biofilm forming ability in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus sciuri isolated from dairy in response to acyl homoserine lactone (AHL). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-R.; Oh, H.-S.; Jo, S.-J.; Yeon, K.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Lim, D.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, J.-K. Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: Physical and biological effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, K.-M.; Cheong, W.-S.; Oh, H.-S.; Lee, W.-N.; Hwang, B.-K.; Lee, C.-H.; Beyenal, H.; Lewandowski, Z. Quorum sensing: A new biofouling control paradigm in a membrane bioreactor for advanced wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, J.D.; Nerenberg, R. Monitoring bacterial twitter: Does quorum sensing determine the behavior of water and wastewater treatment biofilms? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.F.; Sakinah, M.; Singh, L.; Ab Wahid, Z. Targeting N-acyl-homoserine-lactones to mitigate membrane biofouling based on quorum sensing using a biofouling reducer. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 161, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, H.; Paul, D.; Kweon, J.H. Isolation and molecular characterization of biofouling bacteria and profiling of quorum sensing signal molecules from membrane bioreactor activated sludge. Int. J. Mol. Mciences 2014, 15, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Waheed, H.; Xiao, K.; Hashmi, I.; Zhou, Y. In tandem effects of activated carbon and quorum quenching on fouling control and simultaneous removal of pharmaceutical compounds in membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Xiao, Y.; Hashmi, I.; Stuckey, D.; Zhou, Y. Insights into quorum quenching mechanisms to control membrane biofouling under changing organic loading rates. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-S.; Yeon, K.-M.; Yang, C.-S.; Kim, S.-R.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, S.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.-K. Control of membrane biofouling in MBR for wastewater treatment by quorum quenching bacteria encapsulated in microporous membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4877–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, K.; Zhang, X.; Choo, K.-H. Core-shell structured quorum quenching beads for more sustainable anti-biofouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2019, 150, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Ma, S.; Hu, H.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. The biological role of N-acyl-homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing (QS) in EPS production and microbial community assembly during anaerobic granulation process. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ren, H.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.-L. The diversity, distribution and function of N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) in industrial anaerobic granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Yan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jha, A.K. Specific quorum sensing signal molecules inducing the social behaviors of microbial populations in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Li, W.; Zheng, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, N. Exogenous acyl-homoserine lactones adjust community structures of bacteria and methanogens to ameliorate the performance of anaerobic granular sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, E.; Shamurad, B.; Acharya, K.; Tabraiz, S. Domestic wastewater hydrolysis and lipolysis during start-up in anaerobic digesters and microbial fuel cells at moderate temperatures. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, E.; Yu, Y.; Tabraiz, S.; Yakubu, A.; Curtis, T.P.; Dolfing, J. High rate domestic wastewater treatment at 15 °C using anaerobic reactors inoculated with cold-adapted sediments/soils–shaping robust methanogenic communities. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, E.; Dolfing, J.; Davenport, R.J.; Bowen, E.J.; Curtis, T.P. Developing cold-adapted biomass for the anaerobic treatment of domestic wastewater at low temperatures (4, 8 and 15 C) with inocula from cold environments. Water Res. 2017, 112, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lade, H.; Paul, D.; Kweon, J.H. N-Acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing with special reference to use of quorum quenching bacteria in membrane biofouling control. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, T.; Okutsu, N.; Xie, X.; Ikeda, T. Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. isolated from activated sludge. Sensors 2016, 16, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apha, W. Standart Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Heatth Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F. Mechanism of calcium mitigating membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xia, S.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hermanowicz, S.W. Effect of quorum quenching on the reactor performance, biofouling and biomass characteristics in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2013, 47, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, T.; Khan, S.J.; Waheed, H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hashmi, I.; Iqbal, H. Membrane biofouling retardation and improved sludge characteristics using quorum quenching bacteria in submerged membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 483, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Whiteley, A.S.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Bailey, M.J. Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA-and rRNA-based microbial community composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5488–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo Lahti, S.S. Tools for Microbiome Analysis in R. 2017. Available online: http://microbiome.github.com/microbiome (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Shamurad, B.; Gray, N.; Petropoulos, E.; Tabraiz, S.; Acharya, K.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Sallis, P. Data of metal and microbial analyses from anaerobic co-digestion of organic and mineral wastes. Data Brief 2019, 24, 103934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamurad, B.; Gray, N.; Petropoulos, E.; Tabraiz, S.; Acharya, K.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Sallis, P. Co-digestion of organic and mineral wastes for enhanced biogas production: Reactor performance and evolution of microbial community and function. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodological) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Third International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media; Aalborg Universitet: Aalborg, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.H.; Koh, K.S.; Xie, C.; Tay, M.; Zhou, Y.; Williams, R.; Ng, W.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, R.; Jin, L.; Zhu, W.; Ji, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. The regulation of N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs)-based quorum sensing on EPS secretion via ATP synthetic for the stability of aerobic granular sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Myszka, K.; Czaczyk, K. Characterization of adhesive exopolysaccharide (EPS) produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa under starvation conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.; Vigneswaran, S.; Sathasivan, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Chang, C. Effect of organic loading rate on organic matter and foulant characteristics in membrane bio-reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharghi, E.A.; Shourgashti, A.; Bonakdarpour, B. Considering a membrane bioreactor for the treatment of vegetable oil refinery wastewaters at industrially relevant organic loading rates. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, P.V.D.; Satpradit, O.-A.; Van Bentem, A.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Temmink, H.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C. Effect of temperature shocks on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4491–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Z.; Yang, F.L.; Meng, F.G.; Peng, A.N.; Di, W.A.N.G. Comparison of membrane fouling during short-term filtration of aerobic granular sludge and activated sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Ma, K.; Dong, X. Detection of the quorum sensing signals in methanogenic archaea. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2011, 51, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Ding, G.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, L.; Cai, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Acyl homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing in a methanogenic archaeon. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.; Hornung, B.; Ritari, J.; Paulin, L.; Rijkers, G.T.; Schaap, P.J.; De Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. A comparative and functional genomics analysis of the genus Romboutsia provides insight into adaptation to an intestinal lifestyle. BioRxiv 2019, 845511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, E.; Scott, J.; Minton, N.P.; Winzer, K. An agr quorum sensing system that regulates granulose formation and sporulation in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaen, S.E.; Brackman, G.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Isolation and identification of quorum quenching bacteria from environmental samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 87, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J. Role of N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) based quorum sensing on biofilm formation on packing media in wastewater treatment process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11128–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, A.; Bailey, M.J.; Whiteley, A.S.; Manefield, M. N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) affect microbial community composition and function in activated sludge. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.T.; Terekhova, D.A.; Liou, L.; Hovde, C.J.; Sahl, J.W.; Patankar, A.V.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Edrington, T.S.; Rasko, D.A.; Esperandio, V. Chemical sensing in mammalian host–bacterial commensal associations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9831–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smadja, B.; Latour, X.; Faure, D.; Chevalier, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Orange, N. Involvement of N-acylhomoserine lactones throughout plant infection by Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium atrosepticum). Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





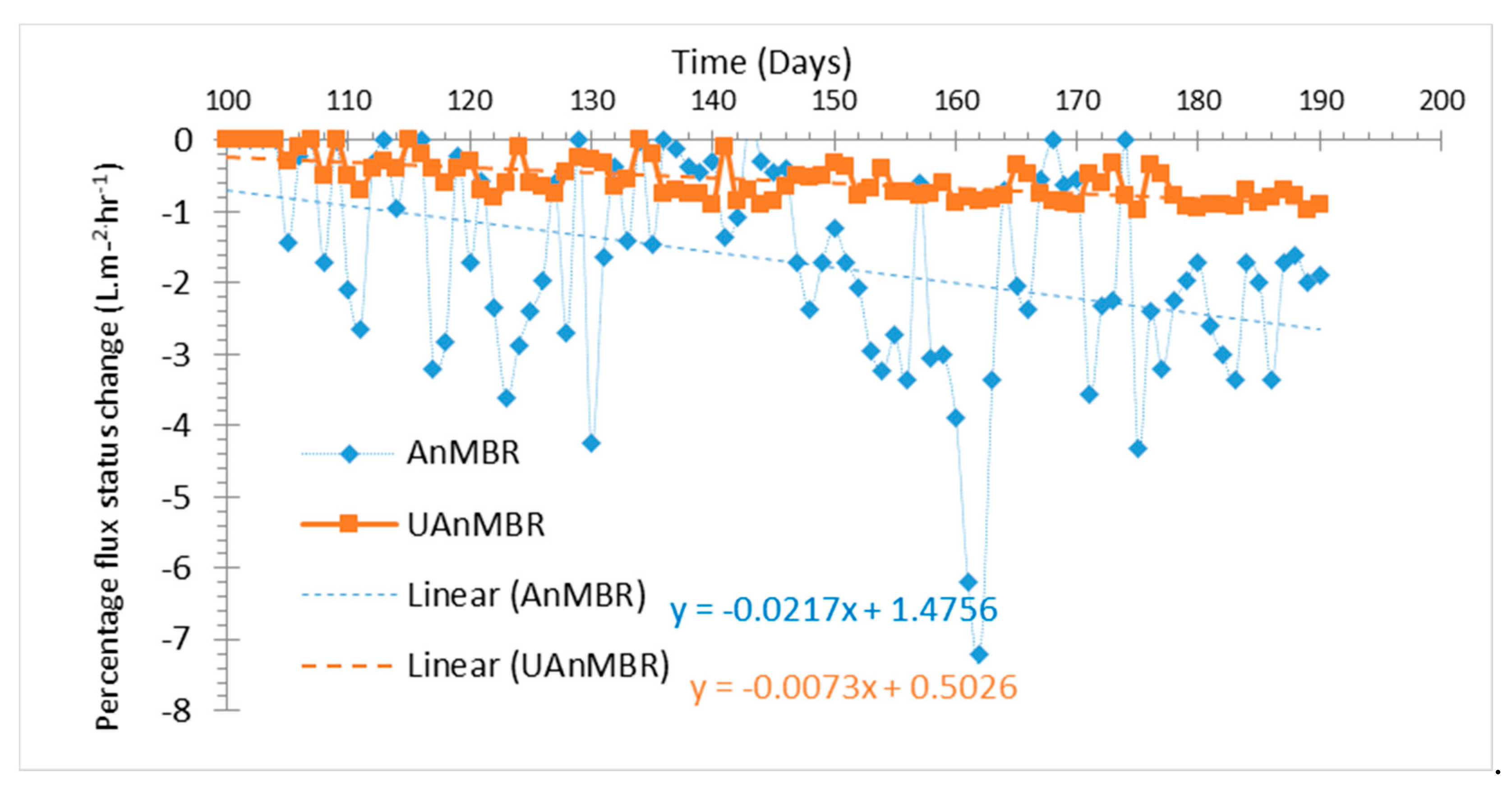
| Reactor Type | AnMBR | UAnMBR | UASB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane type | Hollow fiber, PVDF (0.1 µm) | Hollow fiber, PVDF (0.1 µm) | - |
| Plant scale (volume) | Lab scale (1 L) | Lab scale (1 L) | Lab scale (1 L) |
| Wastewater feed | Domestic sewage | Domestic sewage | Domestic sewage |
| Influent COD (mg L−1) | 269.5 ± 22.7 | 269.5 ± 22.7 | 269.5 ± 22.7 |
| Organic loading rate (kgCOD.m−3 d−1) | 0.108 ± 0.011 | 1.2 ± 0.17 | 1.2 ± 0.17 |
| pH | 6.7–7.2 | 6.7–7.2 | 6.7–7.2 |
| Temperature (°C) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| HRT (Hours) | 60 | 7 | 7 |
| SRT (days) | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Flux (L m−2 hr−1) | 0.75 | 2.18 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabraiz, S.; Shamurad, B.; Petropoulos, E.; Charlton, A.; Mohiudin, O.; Danish Khan, M.; Ekwenna, E.; Sallis, P. Diversity of Acyl Homoserine Lactone Molecules in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors Treating Sewage at Psychrophilic Temperatures. Membranes 2020, 10, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110320
Tabraiz S, Shamurad B, Petropoulos E, Charlton A, Mohiudin O, Danish Khan M, Ekwenna E, Sallis P. Diversity of Acyl Homoserine Lactone Molecules in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors Treating Sewage at Psychrophilic Temperatures. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110320
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabraiz, Shamas, Burhan Shamurad, Evangelos Petropoulos, Alex Charlton, Obaidullah Mohiudin, Mohammad Danish Khan, Emeka Ekwenna, and Paul Sallis. 2020. "Diversity of Acyl Homoserine Lactone Molecules in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors Treating Sewage at Psychrophilic Temperatures" Membranes 10, no. 11: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110320
APA StyleTabraiz, S., Shamurad, B., Petropoulos, E., Charlton, A., Mohiudin, O., Danish Khan, M., Ekwenna, E., & Sallis, P. (2020). Diversity of Acyl Homoserine Lactone Molecules in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors Treating Sewage at Psychrophilic Temperatures. Membranes, 10(11), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110320